biol 122 exam 4
1/143
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
144 Terms
ecosystem provide
market and monetary worth and nonmarket values
market values
raw materials, wetlands filter runoff and treat waste, controlling erosion, recreation
nonmarket values
scientific research, cultural value, teaching and learning sources, intrinsic values
organism ecology
how organisms are adapting to environment through physiological and behavior
population ecology
concerned with population size, growth and density
community ecology
focus on interaction among species
ecosystem ecology
concerned with questions of energy flow and chemical cycling
ecology of biosphere
can study the influence of energy and matter on organism across the biosphere
the biosphere includes both
biotic and abiotic factors
biotic factors
living organisms
abiotic factors
nonliving components
water availability, rocks, minerals, temperature, fire, wind, currents (in oceans)
the most important abiotic factor is
energy
most ecosystem on earth are powered by
solar energy via sunlight
some powered by chemicals
inorganic nutrients can impact
plant growth
ex: nitrogen and phosphorous
the field of ecology and evolutionary biology are
intertwined
population response to
biotic factors and abiotic factors
population respond to environmental condition through
physiological, anatomical and behavioral response
physiological responses
functions of body components
sweating in response to heat, increase red cells at high elevation
anatomical responses
adjusting shape or structure of body
many mammals grow seasonal coat when hibernate, plants orient themselves towards light
behavioral responses
altering behavior in responses to environment
taking a bath when its hot
survivorship curve
predict population vary in density dispersion and age structure
population density
number of members of species per unit area or volume of the habitat
dispersion patterns
how members are spaces in habitat
clumped- like school of fish
uniformed- penguins
random-no proper pattern
population age structure can inform future
population size
current human population growth is affected by birth rates
15-30 years ago, since that’s when today child bearer was born
used to predict future population growth
survivorship
chance individual of population will live to certain age
the survivorship curve has __ curves
describe
3
type 1- high risk at old age
type 2- any age likely to die
type 3- high risk at young age
growth models can predict changes in
population size
exponential population growth
each new generation is a multiple of population growth
unlimited resources, no predators or disease
fast population growth
rabbits
most cannot sustain population growth indefinitely
limiting factors
environmental constrains to population growth
carrying capacity
max population size that can survive in environment
logistic growth model
has limiting factors
population grow rapidly until reach carrying capacity them level out (population size stays constant)
birth rate and death rate is the same
density dependent factors
limit population based on density of a population
disease, competition
density independent factors
factors unrelated to density of a population
weather, environmental disturbances
unlike other population, ______ are growing exponentially
humans
niche
how an organism uses resources
interspecific interaction
competition
two or more species rely on similar resources
competitive exclusion principle
if resources required by two species are too similar they cant coexist
mutualism
interaction between species that benefits both species
symbiotic
living in close physical association w one another but not all symbiotic relationships are mutual
predation
interaction which predator species kills and eat another
herbivore
eating of plant parts by another species
parasite
lives on or in a host but does not kill it but obtains nutrients
pathogens
disease causing microorganisms
trophic structure
describes the feeding relationship within community. also describes how energy transferred
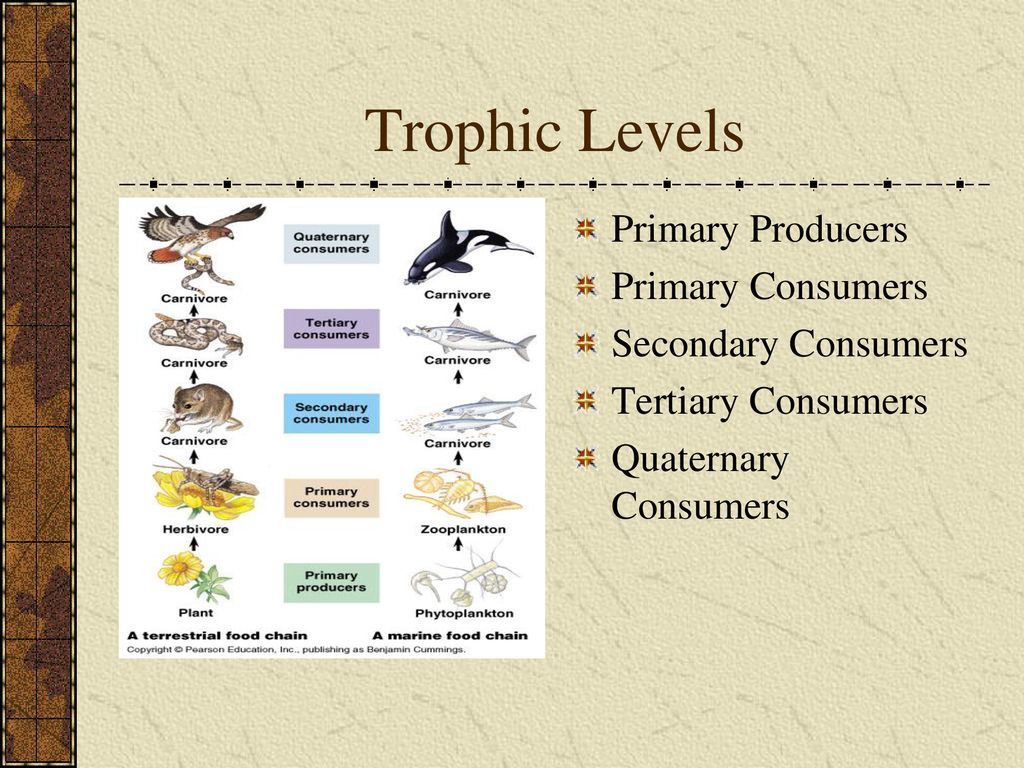
food chains and food webs
describe transfer of organism materials from one tropic level to the next
producers→ primary consumer→ secondary consumer→ tertiary consumer→ quaternary consumer
primary producer
covert solar energy to chemical energy via photosynthesis
primary consumer
herbivores eat primary consumers
secondary consumers
carnivores eat primary consumers
tertiary consumers
top level predators
less energy is available at each transfer
decomposers
organism that breaks down nonliving matter
death at any level sends energy
food web
interconnection of multiple food chains
hypothetical forest community
toxins can accumulate in _____levels
higher
biological magnification
tendency of toxins to become concentrated as they pass through the food chain
species diversity includec
species richness and relative abundance
species richness
same number of species
relative abundance
faction accounted for by each species differs between the two communities
keysone species
species that has disproportionate large effect on environment relative to it abundance
(Yellowstone)
wolves decline→ elk population grow→ eat all food-bevers didn’t have trees→ organism dependent on bearer dames disappeared→ fox population grew bc wolves weren’t hunting them/
reintroducing wolves returned the environment
communities are rarely ____
static
primary succession
area has been rendered virtually lifeless with no soil
secondary succession
disturbance kills most of life bur leaves the soil intact
after disturbance an area reoccupied by series of species this process is called? (takes a long time)
ecological succession
invasive species
organisms introduce in community that is not native. often spread rapidly
invasive species are now a leader cause of __________ of local populations
extinction
Caulerpa taxifolia
invasive species
algae
release into mediterranean
spread through fragmentation
poisonous to many organisms
fast growing
current solution is pumping bleach into species
biological control
intentional release of natural enemy of invasive species
control species must be carefully studied
integrate pest management
uses biological control, pest-resistant crop variety, judicious use of chemicals, release of sterile pest, and other biological and behavioral changes
biodiversity
general term of variety of living things on earth
genetic biodiversity
refers to the collection of genes within a population
severely reducing genetic variation makes population less able to adapt to changing populations
ex: virtually all potatoes in the country were genetically identical, the Irish potato famine causes crop failure
species biodiversity
refer to the number of different species
extinction is the irreversible loss of all populations of a species
estimate that at the current rate half of all living species will be extinct… (unfinished)
extinction debt
delayed species extinctions expected as a consequence of ecosystem perturbation
ecosystem biodiversity
variety of ecosystem found on earth
degradation of ecosystem threatens ecosystems, benefits that ecosystem provides to people such as, waste decomposition, water cycling, nutrients cycling, food production
cause of biodiversity loss
habitat destruction (agriculture, forestry, mining, dam construction)
invasive species (no natural predators)
overharvesting (harvesting species faster than can naturally replenish. ex-hunting)
pollution (air, water, sound)
global climate change
impacts biodiversity at both local and global scales
ex- change in rainfall, disruptions of seasonal pattern, rising temperatures, ocean acidification,
water cycle
perception and evaporation and transpiration
thermohaline circulation
cold water melts from glaciers in north Atlantic
water sinks down and away
make currents throughout oceans
currents carry nutrients and water
biomes
different types of ecological
depends on temperature and rainfall
polar ice
tundares
deserts
low rainfall
both hot and cold