Module 2: Foundations in Chemistry
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Electron Relative Mass
1/1836
Relative Isotopic Mass
The mass of the atom of an isotope compared to 1/12th of the mass of a Carbon-12 atom
Relative Atomic Mass
The weighted mean mass of the atom of an element compared to 1/12th of the mass of a Carbon-12 atom
Mole
The amount of any substance that contains as many particles as there are C atoms in exactly 12g of the Carbon-12 isotope
Avogadro Constant
The amount of particles in 1 mole-
6.02×10²³
Molar Mass
The mass of one mole of a substance
Stoichiometry
The ratio of moles of each substance in a chemical equation
Reaction Observation Examples
Effervescence
Solid getting smaller
Colour change
Steam let off
Oxidation Number
A measure of the number of electrons used to bond with the atom of another element
Hydrogen Oxidation Number
+1 (except in metal hydrides where it is -1)
Group 7 Oxidation Number
-1 (except in molecules like chlorates)
Roman Numerals In Elements
The number of electrons in the outer shell, can be used to indicate oxidation number of an atom with variable oxidation states
Nitrate Ions

Carbonate Ions
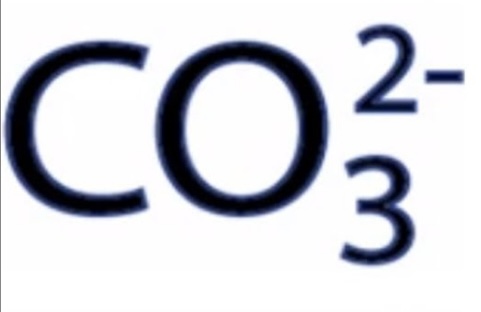
Sulfate Ions
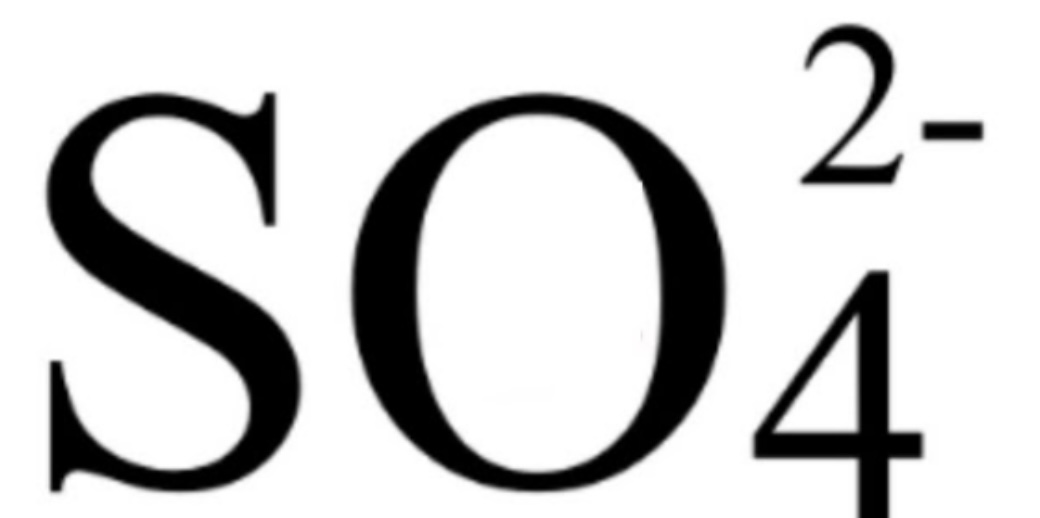
Hydroxide Ions

Ammonium Ions

Zinc Ions
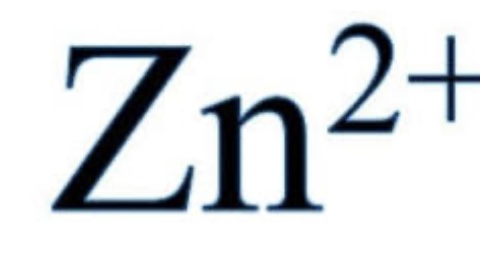
Silver Ions
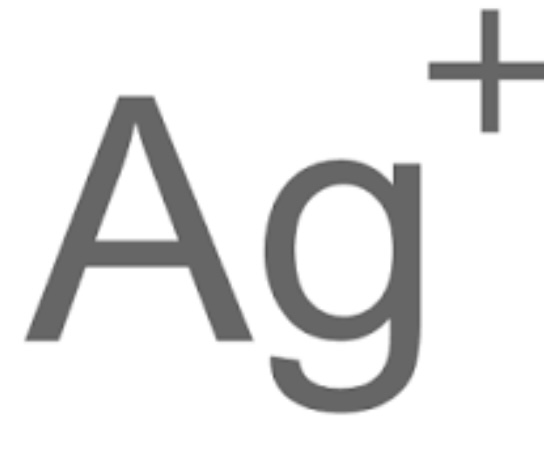
Redox Reaction
A chemical reaction where both oxidation (loss of electrons, increase in oxidation number) and reduction occurs
Disproportionation
When the same element is both oxidised and reduced in a chemical reaction
Shell
A group of atomic orbitals with the same principle quantum number
Formula for amount of electrons in a shell
2n²
Atomic orbital
a region around the nucleus that can hold up to 2 electrons with opposite spins
S orbitals
Spherical
All shells have one
P orbitals
3d dumbbell shaped
Each shell from the second shell has 3 of these at right angles to each other
D orbitals
Has a more complex shape
Each shell from the 3rd shell has 5 of these
Chromium and copper electronic configuration
3d orbital fills fully or halfway before 4s orbital due to the enhanced stability of the full/half full orbital
Giant Lattice
A structure resulting from the attraction of oppositely charged ions in an ionic substance happening in all direction, causing many strong ionic bonds
Factors affecting boiling points of ionic compounds
atom size
ion charge
Solubility rules
ionic lattice must break down
water molecules must be attracted to the ions and surround them
attraction between H2O and individual ions > electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions
Electrical conductivity
requires mobile charge carriers
Covalent bond
the strong electrostatic attraction between a negatively charged shared pair of electrons and the positive nuclei of the bonded atoms that is formed when their orbitals overlap
Octet rule
When the central atom of a covalently bonded molecule has 4 pairs of electrons
Dative bond
When both electrons in a shared pair in a covalently bonded molecule are donated by one atom
Average bond enthalpy
The energy required to break 1 mole of a specified type of bond in a gaseous molecule
Linear molecule shape
180 degrees- has 2 bonding pairs
Trigonal planar
120 degrees- has 3 bonding pairs
Tetrahedral
109.5 degrees- has 4 bonding pairs
Octahedral
90 degrees- has 6 bonding pairs
Trigonal pyramidal
107 degrees- has 3 bonding pairs and 1 lone pair
Non linear
104.5 degrees- has 2 bonding pairs and 2 lone pairs
Molar volume
The volume per mole of gas (24dm³mol^-1)
Gas volume & mole equation
Moles=volume/24
Ideal gas equation
pV=nRT
Converting from degrees Celsius to Kelvin
+273
Assumptions made about the molecules making up a gas in the ideal gas equation
They have random motion,
elastic collisions,
negligible molecule size,
no intermolecular forces between them
Mass Spectrometry
An instrumental method of analysis that can be used to:
Find the abundance and mass of each isotope allowing us to determine its Ar
Find the relative molecular mass of substances made of molecules
Mass spectrometry process
Sample placed in spectrometer
Vaporised & ionised to form + ions which are then accelerated → heavier ions are slower and harder to deflect so the ions of each isotope are separated
Ions are detected on a mass spectrum as a mass to charge ratio (m/z) → the greater the abundance, the larger the signal given off