Voice Disorders Final Prep
1/146
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
147 Terms
What two systems and their parts make of the Nervous System?
CNS
cerebral cortex
cerebellum
brainstem
spinal cord
PNS
cranial nerves
spinal nerves
What nerve pathways are in the PNS?
sensory and motor (afferent and efferent)
What areas in the sensory and motor areas contribute to production of voice?
cerebral cortex
cerebellum
basal ganglia
The ___ and left ____ lobes are primarily involved with motor aspects of voice production.
frontal and left temporal
What is normal voice based on?
Ability to hear and process ongoing voice production
What sensory function does CN IX (glossopharyngeal) have?
taste and general sensation back 1/3 tongue
pharynx
larynx
viscera
What sensory function does CN X (vagus) have?
pharynx
larynx
viscera
What motor function does CN IX (glossopharyngeal) have?
constrictors
stylopharyngus
visceral motor (parotid glands)
What motor function does CN X (vagus) have?
palate
pharynx
larynx
esophagus
What motor function does CN XI (spinal accessory) have?
trapezius
sternocleidomastoid
What motor function does CN XII (hypoglossal) have?
tongue (intrinsic+extrinsic)
What are the neurogenic voice conditions?
vocal fold paralysis
spasmodic dysphonia (SD)
essential voice tremor
parkinson disease (PD)
cerebrovascular accident (CVA)
TBI
What is vocal fold paralysis?
damage to Vagus nerve anywhere
What is the SLPs role in vocal fold paralysis?
Collaborate with ENT to confirm diagnosis and rule out mechanical causes
What does the type and extent of dysphonia depend on with vocal fold paralysis?
lesion site
damage is unilateral or bilateral and partial or complete
What are the characteristics of unilateral vocal fold paralysis?
Visual
paralyzed VF is fixed, not fully adducted/abducted
Perceptual
dysphonia, breathy, hoarse vocal quality, reduced phonation time, decreased loudness and monoloudness (diplophonia+pitch breaks)
Why do SLPs wait to treat unilateral vocal fold paralysis? What does therapy look like?
Usually spontaneously recovers within first 9 to 12 months; behavior therapy+voice facilitating approaches
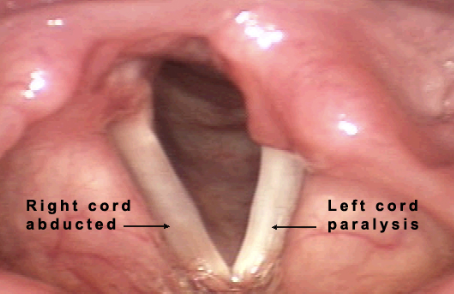
What neurogenic voice disorder is this?
unilateral vocal fold paralysis (UVFP)
If UVFP isn’t resolved within the first 9-12 months, what medical management options are there?
VF medialization
injection laryngoplasty
thyroplasty
VF re-innervation
What is injection laryngoplasty? And what disorder does it help?
provides support to a vocal fold that lacks either the bulk or mobility it had
injects chemicals to increase vocal quality
helps VF paralysis
What is thryoplasty? And what disorder does it help?
free-moving wedge is used to move the VF to midline, rectangular window is cut from thyroid cartilage on paralyzed side
patient is conscious to produce voice to understand where wedge helps best
helps VF paralysis
What is bilateral vocal fold paralysis?
result of lesions high in vagus nerve
can be adductory or abductory
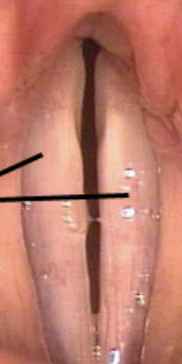
What neurogenic voice disorder is this?
bilateral VF paralysis
What is the gold standard treatment for BVFP?
surgical procedures to open the posterior glottis airway
What is spasmodic dysphonia (SD)?
from laryngeal dystonia (hyperkinetic movement disorder) aka involuntary repetitive movements
What are the types of spasmodic dysphonia and their differences?
Adductor SD
most common
symptoms: strain & intermittent voice stoppages; hoarseness & tremor
hyperadduction VF, tight closure of false VF
Abductor SD
less common
symptoms: fleeting aphonia, VFs abduct suddenly
Mixed SD
least common
features of abductor and adductor
What are the management options for spasmodic dysphonia?
voice therapy
few positive outcomes
best with combo of behavioral and medical
surgical resection of the RLN
injection of BTX-A
surgical modification of VF
What is RLN? What disorder does it treat?
first surgical procedure for SD
injection of lidocaine into RLN to produce temporary unilateral adductor paralysis
if there is improvement in airflow, then RLN may be cut permanently
long-term results = mixed
long-term results of paralyzing thryoarytenoid bilaterally = more promising
What is BTX-A injections? What disorder does it treat?
gold standard for treating SD!!!!
mild symptoms occur up to 2 weeks after
**combined with voice therapy is best
treats SD & essential voice tremor
What is essential voice tremor?
presents in tongue, velar, pharyngeal, laryngeal structure producing tremor in 4-7 second ranges
like a hyperkinetic dysarthria
How is diagnosis of essential voice tremor differentiated?
eliminating contextual speech, asking patient to sustain production of vowels in isolation
normal larynx, alternate tension changes
What is deep brain stimulation? What disorder does it treat?
reduces periodic modulations in fundamental frequency and intensity
helps essential voice tremor
What treatments are used for essential voice tremor?
BTX-injections
deep brain stimulation
pharmacotherapy
voice therapy
reduce voice intensity
elevate voice pitch a half note
attempting to shorten vowel duration
What is Parkinson’s Disease and the symptoms?
hypokinetic dysarthria
symptoms
reduced loudness, breathy voice, monotony of pitch, intermittent and rapid rushes of speech, reduced articulatory contacts
What are the treatment options for Parkinson’s disease?
automatic speech → intentional speech to improve loudness, voice quality, appropriate pitch, rate
LSVT and SPEAKOUT
How is the voice affected by a stroke?
voice and connected speech changes depend on lesion
paralysis is rare as a result of stroke
vocal quality is spastic or flaccid
What is the difference between spastic and flaccid voice quality?
Spastic
slowed artic, strained voice, hypernasality
Flaccid
breathy voice with diminished loudness and air wastage
How do you diagnose voice issues from a stroke?
laryngeal stroboscopy shows laryngeal dysfunction + assess mucosal wave
touching endoscope tip to arytenoids bilaterally to see sensation
pooling of secretions in the hypopharynx
What are the treatment options for vocal issues from stroke?
tracheotomy/airway management
dysphagia/aspiration
secretion management
dysphonia
What vocal issue stems from TBI?
Dysarthria
can be: temporary/chronic, mild/severe, accompanied or not by other language and cognitive disorders
What treatments are effective for TBI? What should intervention focus on?
auditory feedback, counseling, respiratory training
alter pitch upward, reduce vowel duration within words, increasing naturalness of convo
What variables determine a patient’s compliance?
clinician-related barriers; ex. lack of empathy, lack of support
clinic-related factors; ex. commutes, scheduling
How do you increase client compliance?
apply voice facilitating approaches ASAP
capitalize success by making sure client leaves with homework that has audio from session
virtual reality
What is the difference between symptomatic voice therapy and voice facilitating approaches?
Symptomatic
modifies deviant vocal symptoms like breathiness, inappropriate pitch, loudness, hard glottal attack
Voice Facillitating
targets a more optimal vocal response
once elicited → behavior is shaped, stabilized, and habituated using pattern increasing in difficulty
What are the 2 steps to voice facilitating approaches?
1) identify behaviors which need to be eliminated
2) stimulate desired target behavior by using an approach
**stabalize → generalize
How do you determine what voice facilitating approaches to use?
underlying etiology/diagnosis
response to therapeutic probes administered during the diagnostic eval
your comfort teaching a particular approach
patient’s acceptance of using the approach
What screenings are used for voice and what are their aspects?
Quick Screen for Voice
1o min
students in pre-school to high school
responds to checklist of observations during tasks
fails: if 1+ disorders in production in any section
Voice Screening from in the Boone Voice Program for Children
quick+easy
students on all grades
listen to natural sample of voice and speech and rate each scale
fails: if child fails any of the 5 clinical parameters
What do all screening protocols address?
Respiration, phonation, resonance
What is strongly suggested for a voice evaluation?
Case history questionnaire completed in advance
What is included in the physical voice exam?
assessment of general physical condition
ear, nose, throat eval
additional areas depending on age and observed signs
if needed, consult other specialists
What does ASHA define as the SLP and Physician roles in medical evaluation?
A physician who has a discipline in the complaint has to examine all patients in addition to the SLP. It can be before or after the SLPs eval
What is the purpose of voice assessment?
know strengths and deficits
effect of the disorder on individual’s activities and participation
contextual factors that serve as barriers/facilitators of communication
What are the components of the voice evaluation and their order?
case history
patient interview
non-instrumental assessment
instrumental assessment
TF: All components of the voice evaluation are done each time.
False
What is included in the case history?
reason for referral
prelim info that can help hypothesis
medical status, education, occupation/vocations, cultural/linguistic background, auditory/visual status
TF: Older adults with hearing loss are more likely to have dysphonia.
True
What is involved in the patient interview?
Description of the problem/cause
Onset/duration of problem
Variability of problem
Description of voice usage
Psychological screening (stress/anxiety)
Additional info
previous voice therapy/approaches, similar voice problems in family, social history
What are voice disorders commonly confused with?
Common colds
What disorder is associated with lower voice quality in the morning and improved voice quality at night?
LPRD
What disorder is associated with better voice quality in the morning and worse voice quality at night?
Hyperfunction
What is included in the non-instrumental assessment?
behavioral observation
oral mech exam
auditory-perceptual rating
voice-related QOL
What specifically is examined during an oral mech exam?
look for neurologic signs
observe breathing patterns
examine for neck tension (move larynx side to side)
examine oral cavity
listen for oral/nasal resonance balance
What are the auditory-perceptual ratings used?
GRBAS scale
grade, roughness, breathiness, aesthenic, strain
4-point rating scale 0-3 for each parameter
CAPE-V
severity, roughness, breathiness, strain, pitch, loudness
rate 6 aspects by placing a mark on a line
What scale is used to measure voice-related QOL?
Voice Handicap Index (VHI)
tests 3 subscales - functional, physical, emotional
rated 0-4
What is included in the instrumental assessment?
laryngoscopy/phonoscopy
acoustic analysis
aerodynamic analysis
Who can perform a laryngoscopy?
Clinicians with expertise and training in laryngoscopy’s
What are the elements of a phonoscopic exam?
respiratory behavior, vegetative voicing, fundamental frequency range, intensity range at different frequencies, different modal registers, different phonetic contexts, voicing of variable duration
What are the different visual examinations of the larynx?
Indirect laryngoscopy
Direct laryngoscopy
Fiberoptic laryngoscopy
Flexible
Rigid
Stroboscopy
High-speed digital imaging
What can indirect and direct laryngoscopy’s not do?
Cannot see vibrations
What is the difference between flexible fiberoptic laryngoscopy and rigid fiberoptic laryngoscopy?
Flexible = scope is flexible
Rigid = can’t see repetition
What is a laryngostroboscopy? What are it’s limitations?
Synchronizing the flash of stroboscopic light with the F0 of the VF vibration reveals an average pattern of vibration across multiple cycles
Limitations: severely dysphonic patients
What is high-speed digital imaging? What are it’s advantages & limitations?
Captures high quality images of the larynx structures
Advantages
doesn’t need periodic phonation
provides additional info on VF movement including observation of phonatory onset
Limitations
no audio
can’t use flexible endoscopy with it
limited sample of phonation
What can be observed in a laryngoscopic observation?
VF edges
medial edge for smoothness, straightness, presence of mass
Glottic closure
complete, hour-glass, spindle-shaped, incomplete, irregular
Amplitude of vibration
how far VFs move laterally during phonation (one half visible width)
can be affected by F0 and intensity
Mucosal wave
“ripple like motion”
should travel ½ width of VF
Vertical level approximation
VFS must meet on same vertical plane
VF overlap = not on same plane
needs light
Supraglottic activity
look for medio-lateral/antero-posterior involvement
rated during normal pitch & loudness
doesn’t need light
VF mobility
evidence of paralysis of one or both VF
can be normal, limited adduction, limited adduction, fixed (needs position)
Phase closure
observe how long it takes for VF to begin to part from midline until lower lips approximate
Phase symmetry
degree VFs appear to be mirror images of each other in motion
out of phase seen during onset and it moves in the same direction
Non-vibrating portion
immobility of any part of the membranous VF (body or mucosal)
percent of VF non-vibrating
Regularity
consistency of duration of successive cycles of VF vibration
Overall laryngeal function
normal, hypofunctional, hyperfunctional, tremulous, spasmodic
What are the types of glottic closure?
Complete
glottis without evidence of any gapping during max VF adduction
Hour-glass
presence of anterior/posterior gap with mid-membranous VF closure
Spindle-shaped
glottal appearance where both anterior/posterior portions of the VF fold are closed, but a large gap remains in the middle
Incomplete
when the VF fails to touch
Irregular
1 or both VFs approximate in an irregular fashion
How does fundamental frequency and intensity affect amplitude of vibration?
Higher F0 = lower excursion
Greater intensity = increased excursion
How does fundamental frequency and intensity affect the mucosal wave?
Higher F0 = decreased wave
Higher intensity = increased wave
How do you determine vocal hypofunction and hyperfunction based on phase closure?
Hypofunction = open phase predominates
Hyperfunction = closed phase predominates
How do you make acoustic measurements valid?
discriminate normal from dysphonic voice
correlate positively with clinician’s auditory-perceptual judgements
be sufficiently stable to assess change across time
What acoustic analyses can be measured during evaluation and what do they analayze?
sound spectrography
time for loudness and frequency
frequency-related parameters
frequency variability
MPFR
intensity-related parameters
avg intensity (loudness), 65-80dB
intensity variability (range of intensities in connected speech)
dynamic range (softest nonwhisper to loudest shout)
voice range profile (VRP), see patient’s min/max intensity lvls
vocal perturbation-related parameters
short-term cycle to cycle variability in the vocal signal
small amount is normal
jitter + shimmer
vocal noise-related parameter
harmonic + inharmonic
ratios: harmonics → noise (HNR), noise → harmonics (NHR), signal → noise (SNR)
What is fundamental frequency (F0)?
rate of vibration of the VF
What is frequency variability in dysphonic patients?
Frequency can be either more or less variable than expected
What is maximum phonational frequency range? What is a healthy one?
Range of vocal frequencies encompassing lowest register to falsetto register
Healthy = 2.5-3 octaves, smaller in older adults
What does a compressed VRP indicate?
Spastic dysarthria (abnorm freq and intensity range)
What is the difference between sparkle and jitter?
Sparkle = short-term variability in amplitude
Jitter = short-term variability in fundamental freq
What is an important disclaimer with vocal perturbation measures?
Should be interpreted in combo with other instrumental data, auditory-perceptual, observations
What voice noise measures are identified in dysphonic patients?
Low HNR or SNR + high NHR
What is an electroglottographic analysis and how does it determine voice quality?
non-invasive procedure for obtaining an estimate of VF contact patterns during phonation
electrodes are placed on each side of thyroid cartilage
normal = high consistent peaks
breathy = consistent lower peaks
hoarse = inconsistent peaks
What is an aerodynamic analysis measure and what can be done in the clinic?
Patient’s ability to use the larynx to regulate the flow of air for phonation
breathing patterns
clavicular (abnorm)
thoracic (norm)
diaphragmatic-ab (norm)
measures in clinic
lung volumes/capacities
air pressure
airflow
laryngeal resistance
How do you measure phonatory-respiratory efficiency? Describe those methods.
Maximum phonation time (MPT)
longest period during which a patient can sustain phonation of a vowel sound (/a/)
shorter if laryngeal flow is high
longer if laryngeal flow is low
cannot distinguish deficit in breath support
S/Z ratio
indirect index of laryngeal airflow
sustain /s/ and /z/
normal = 1
mass lesions= >1.40
What is an ambulatory phonation monitor used for?
APM is worn to capture voice parameters of an entire day
What are the special populations that we provide voice therapy to?
aging voice
pediatric voice
professional voice
deaf/hard of hearing
transgender patients
What percent of the caseloads for SLPs are elderly clients with communication impairments?
19%
What is presbyphonia?
Age-related weakness of voice in elderly
What is the most common cause of dysphonia in the elderly?
VF atrophy
What are the auditory-perceptual features of the elderly voice?
tremor
hoarseness
breathiness
voice breaks
decreased loudness
slower speaking rate
change in habitual pitch
What are the laryngeal signs of the elderly voice?
mild bowing of the VF margins
spindle-shaped glottis
more anteriorly placed glottal gaps
prominent arytenoid cartilage vocal processes
VF edema
Asymmetry of VF vibration
Predominant open phase
What are the voice-related physiological changes of the elderly voice?
lengthening of vocal tract/oral cavity
reduction in pulmonary function
laryngeal cartilage ossification
increased stiffening of the VF
reduction in VF closure
What are the acoustic features of the elderly voice?
increased F0 in males
decreased F0 in females
decreased SPL
increased noise to harmonics ratio
inconclusive findings on changes in jitter/shimmer
What does increased SPL mean for intensity?
Greater intensity
How do you treat presbyphonia?
Voice therapy
strengthening exercises for respiratory/phonatory control
vocal hygiene
improve respiratory efficiency
increase speech rate
Surgery
laryngoplasty
thyroplasty