ACS Biochemistry First Semester
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
Buffer Order and Henderson Hasselbach
Water, Buffer, Salt, Base
pH = pKa + log(A/HA)
pKa decrease as temp increase so pH decrease
Ramachandran plots
Φ = N-R
ψ = C-R
optimal angle to prevent steric hinderance
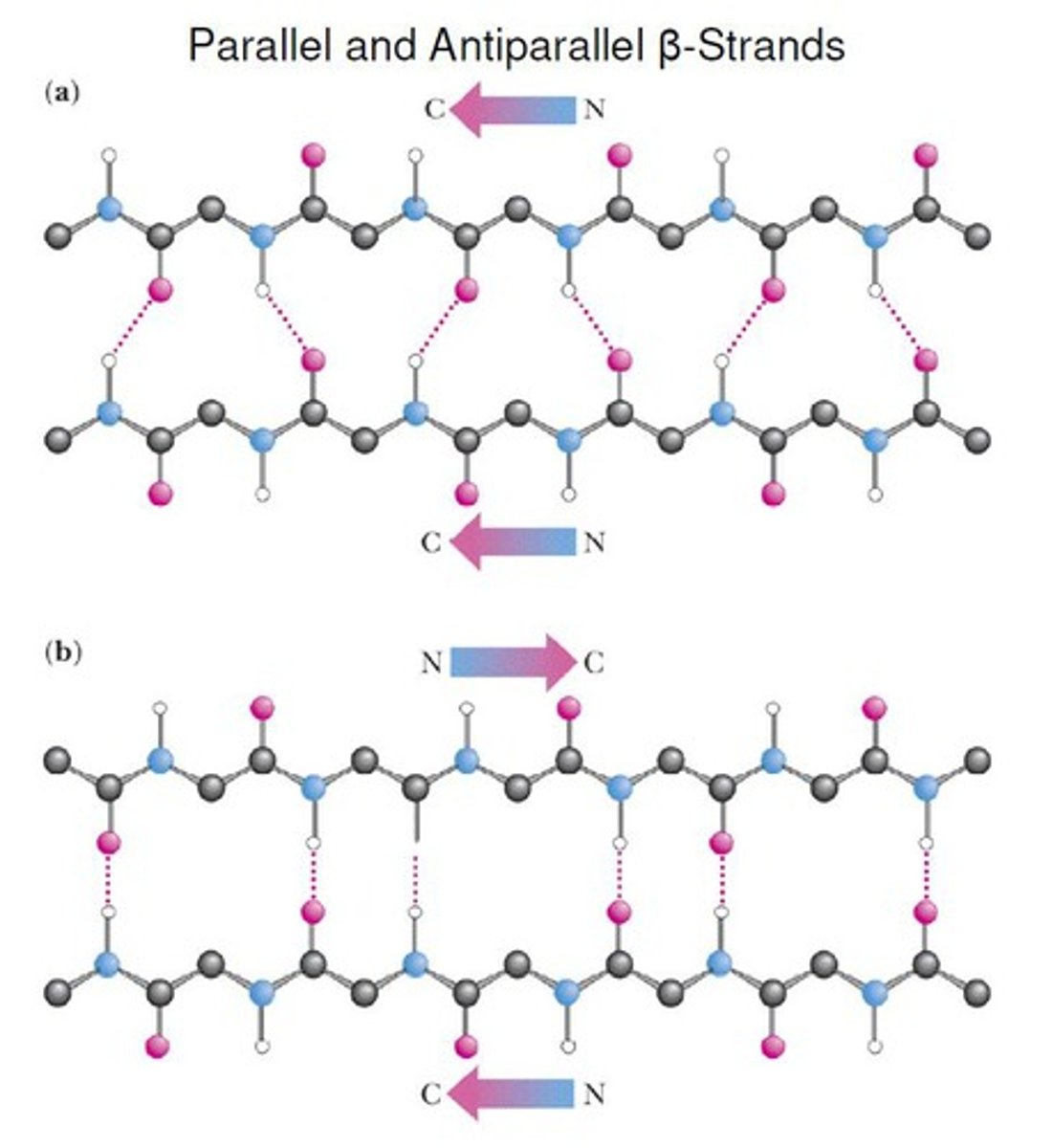
Protein structure of a helix, B sheet, reverse turn
a: LEMARKHQ
B: VICYFTW
RT: PSDNG
how many amino acids in alpha turn helix
3.6
Super secondary structure
helix turn helix
parallel vs. antiparallel
parallel wedges face same way
antiparallel face opposite
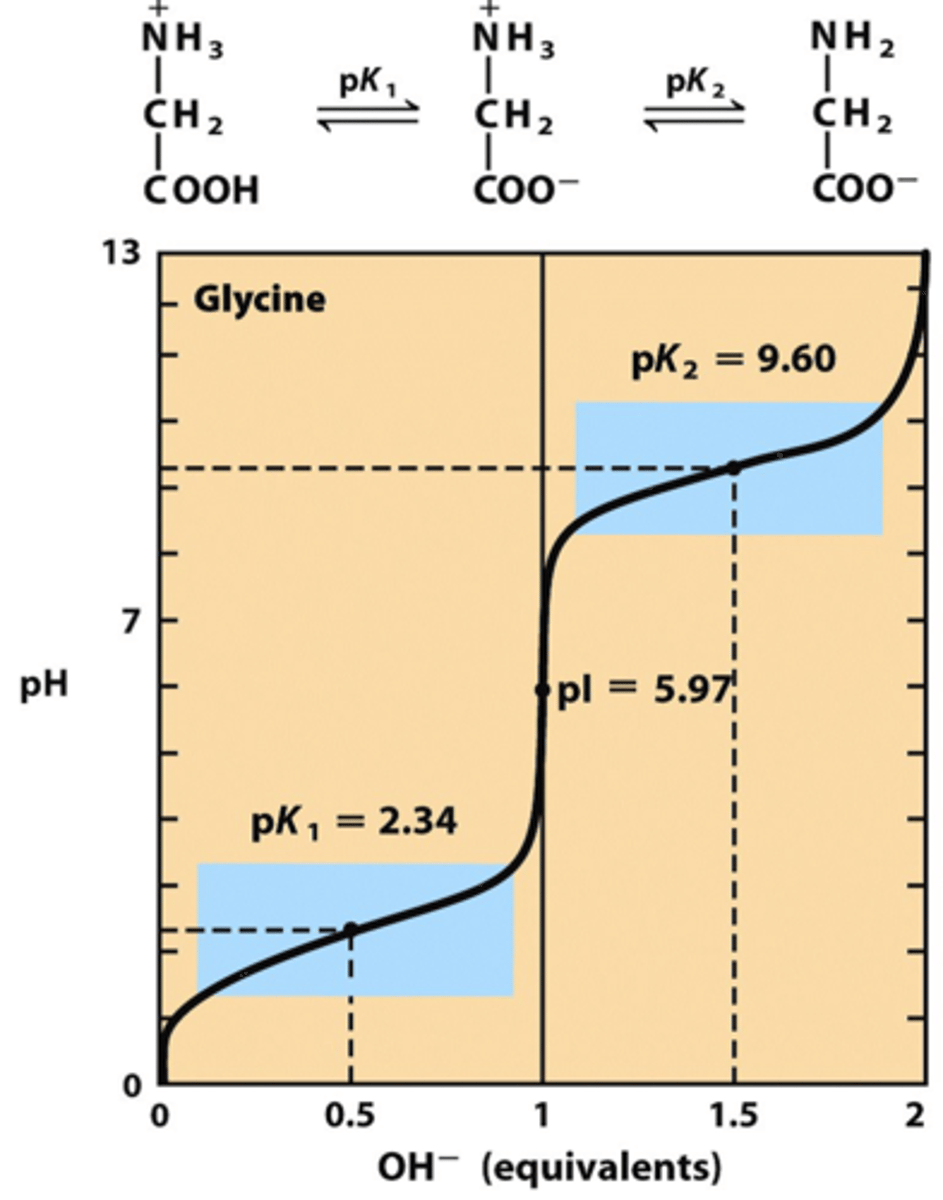
Isoelectric point (pI)
pH at which a particular molecule carries no net electrical charge.
Protein Separation Techniques (ALL)
Homogenization
Salting Out
Affinity Chromatgraphy
Ion Exchange
Size Exclusion/Gel Filtration
H, S, A, I, SG
He said all individuals SinG
Protein Separation Techniques (H)
Homogenization
disrupt cells, sonicator, centrifuge
Protein Separation Techniques (S)
Salting out
different proteins precipitate out at different salt concentrations
Protein Separation Techniques (A)
Affinity chromatography
add a tag; histidine binds; see how well there is an affinity for the group
Protein Separation Techniques (I)
ion exchange
separation based on charge; + proteins stick to - beads
Protein Separation Techniques (SG)
Size Exclusion/Gel Filtration
separation based on size
Cuts (protein separation techniques)
cut out what dont need/isnt protein
(use 40% concen. then keep liquid; if use 60% concen. then keep pellet)
Dialysis
protein separation based on bad with pores
1. Moles in bag + moles in buffer
2. Divide moles by total volume - new concentration
Electrophoresis
gels - move by size with electric current
1. Isoelectric focusing - purely pH
2. SDS page
pH separation is by pI and charge in 2d
Protein sequencing (who cuts after what)
Cyanogen bromide = methionine
trypsin = K, and R
chymotrypsin = F, M, L, W, Y
IP
Immunoprecipitation with proteins
1. add antibodies specific to protein of interest to lysed cells
2. add antibody binding protein on beads
3. centrifuge and protein is on bead with antibodies
4. gel elect
CO-IP
observe protein protein interaction
Messelson Stalh
RATSHIT.
Western Blotting
run gel - transfer to sheet - stained with radioactive antibody - autoradiogram - exposed antibody
ELISA - indirect and sandwich
Enzyme linked immunosorbant assay
1.) indirect - antigen coated well - bind persons antibody - bind antigen with enzyme - bind substrate = rate of color
2.) Sandwich - antibody coated well - bind person antigen - bind 2nd antibody with enzyme - bind substrate = rate of color
Mass spec
identify proteins by size
MALDI
matrix assisted laser desorption ionization (BIG)
ESI
electric spray ionization - charged molecules - time of flight detector
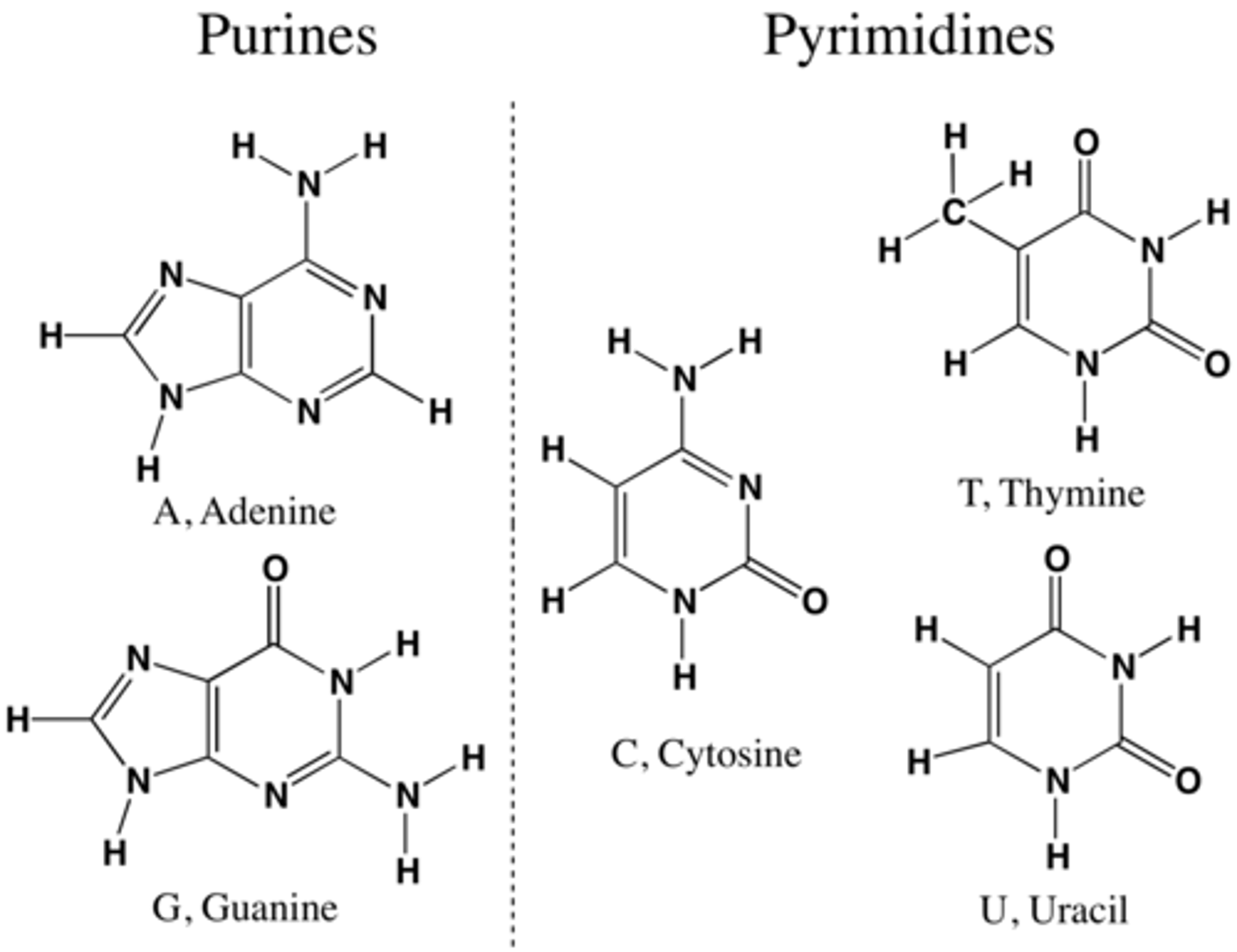
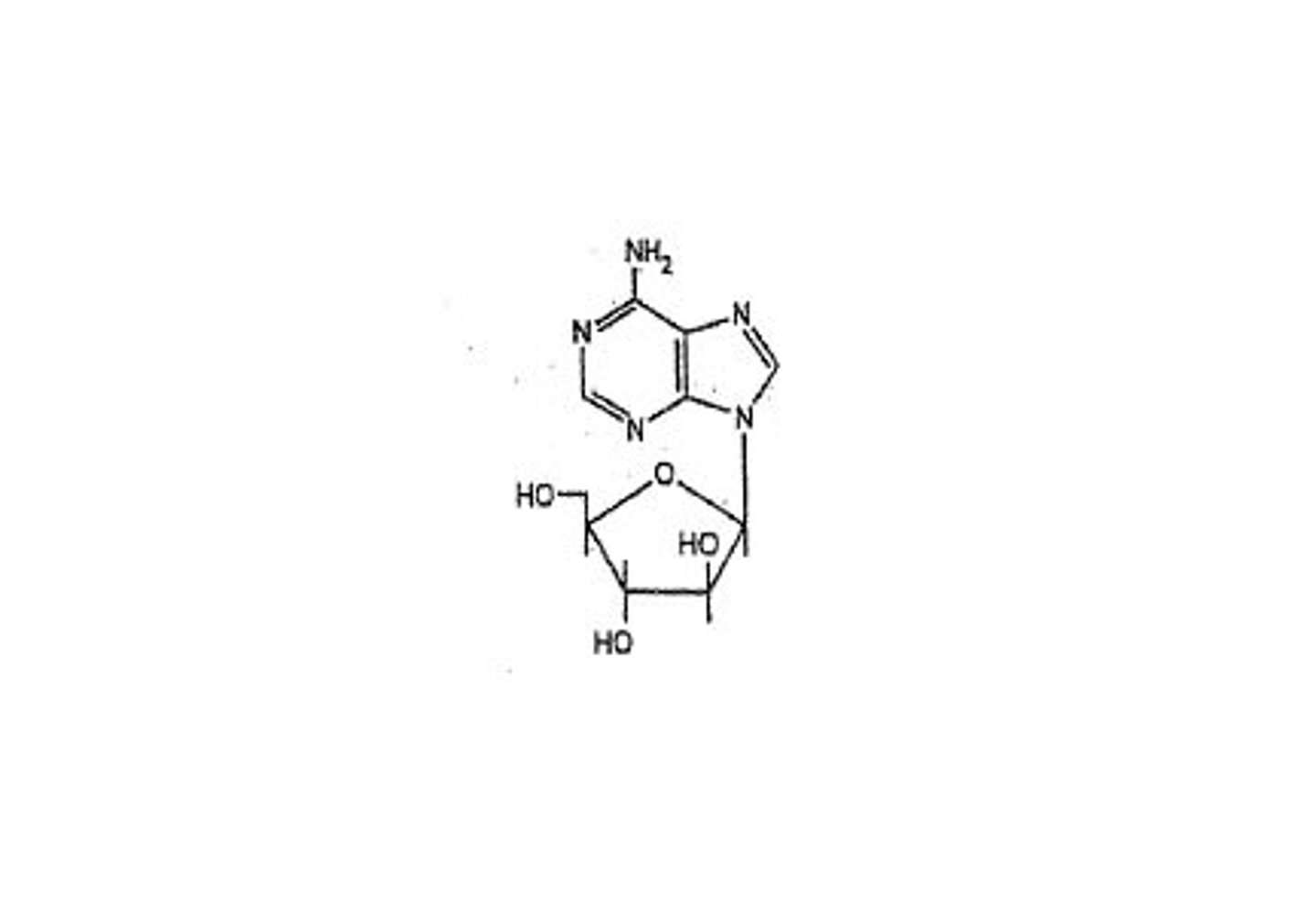
Nucleobase
adenine (2), guanine (3), cytosine (3), thymine/Uracil (2)
nucleoside
adenosine, guanosine, cytidine, thymidine, uridine
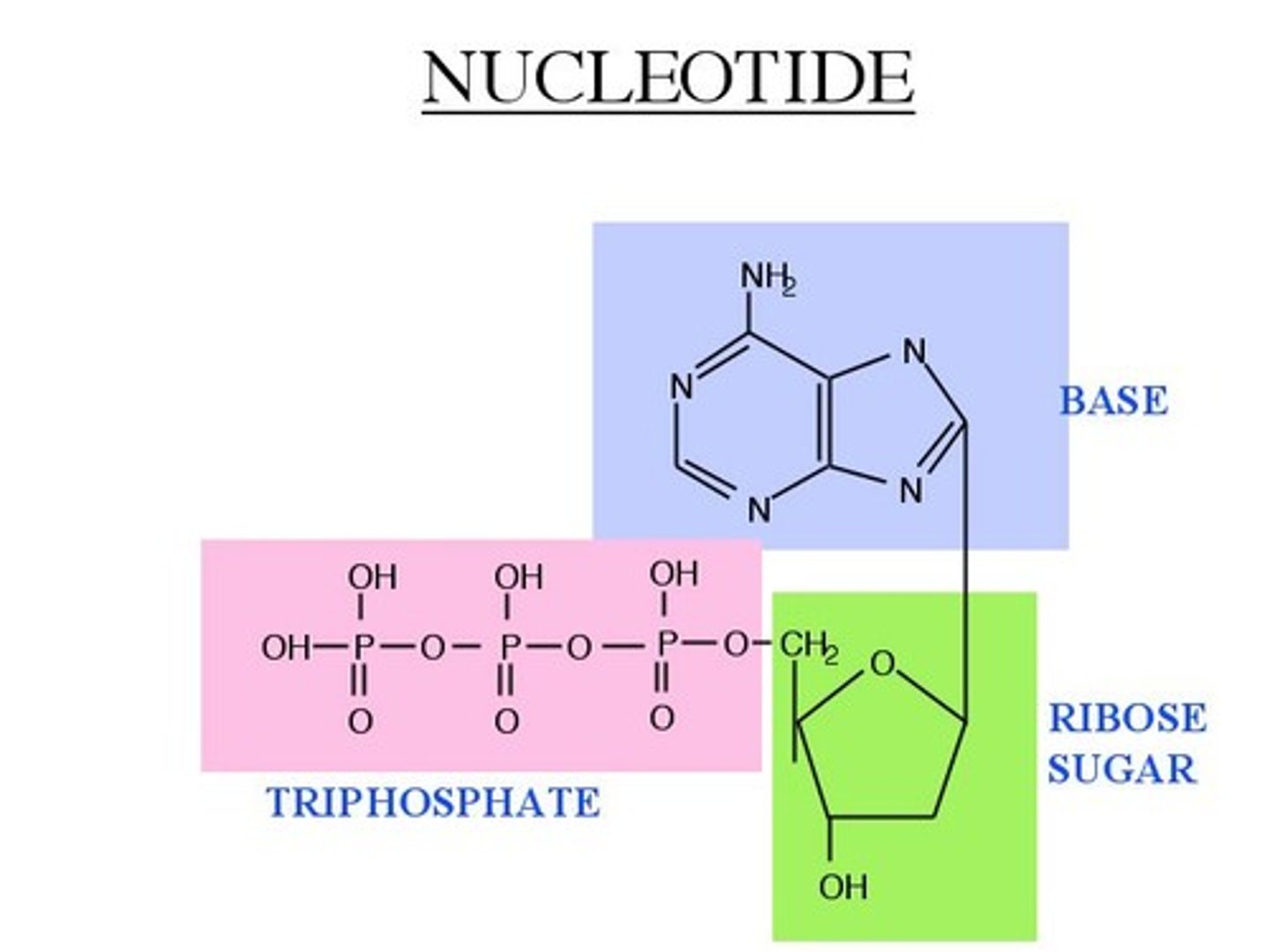
nucleotide
ATP, ADP, AMP
DNA facts
3.4 A separates bases
10 nucleotides in one twist
A form = dehydrated (right); B form = normal (right)
z form = left handed
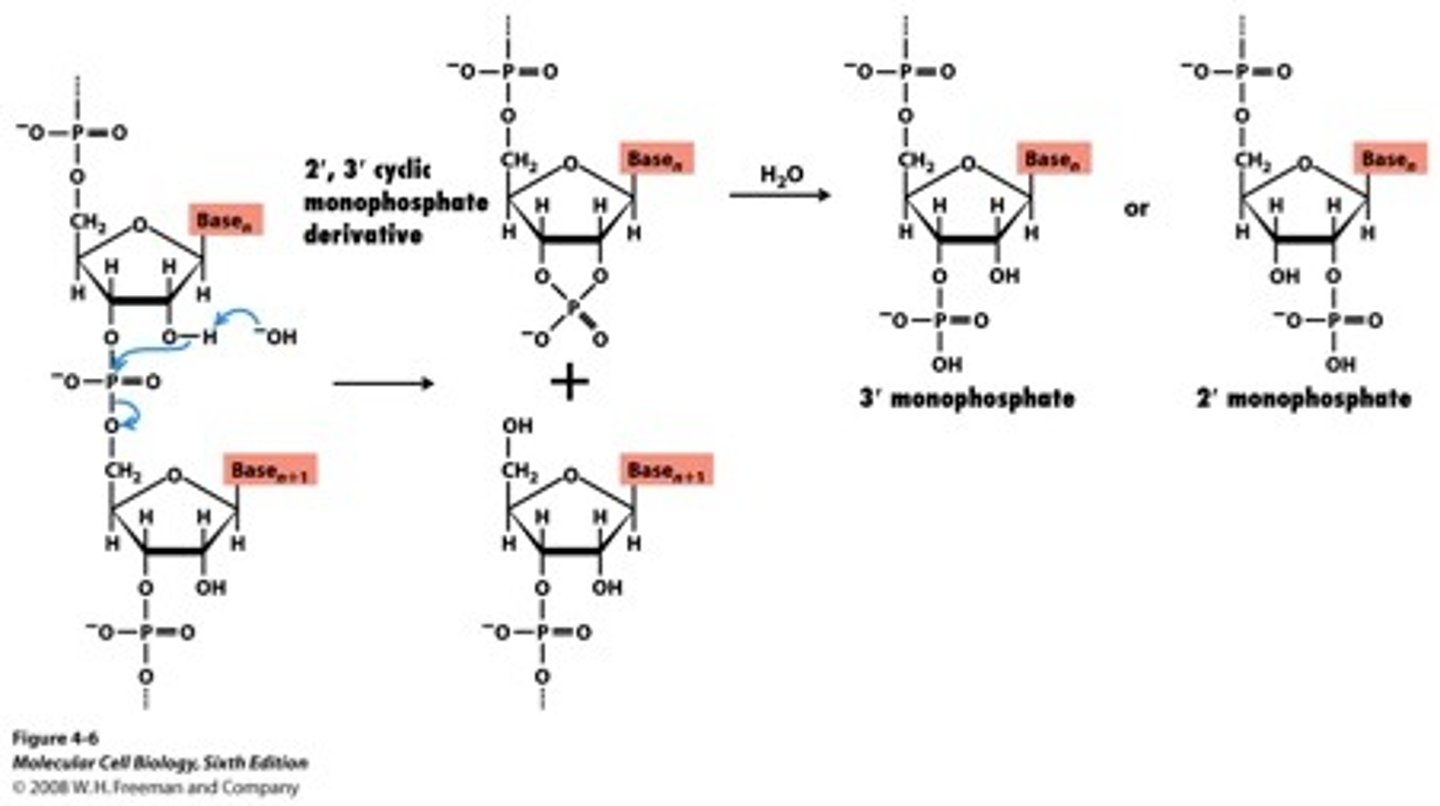
Base hydrolysis RNA
separating nucleosides
DNA Replication mechanism (RNA transcription)
putting two bases together with template present
pyrophosphate leaves
Transcription DNA-->RNA
initiation, elongation, termination
copied 5' --> 3'
template is 3' --> 5'
DNA polymerase vs. RNA Polymerase
High fidelity vs. low fidelity
Endonucleases
bind splice sites
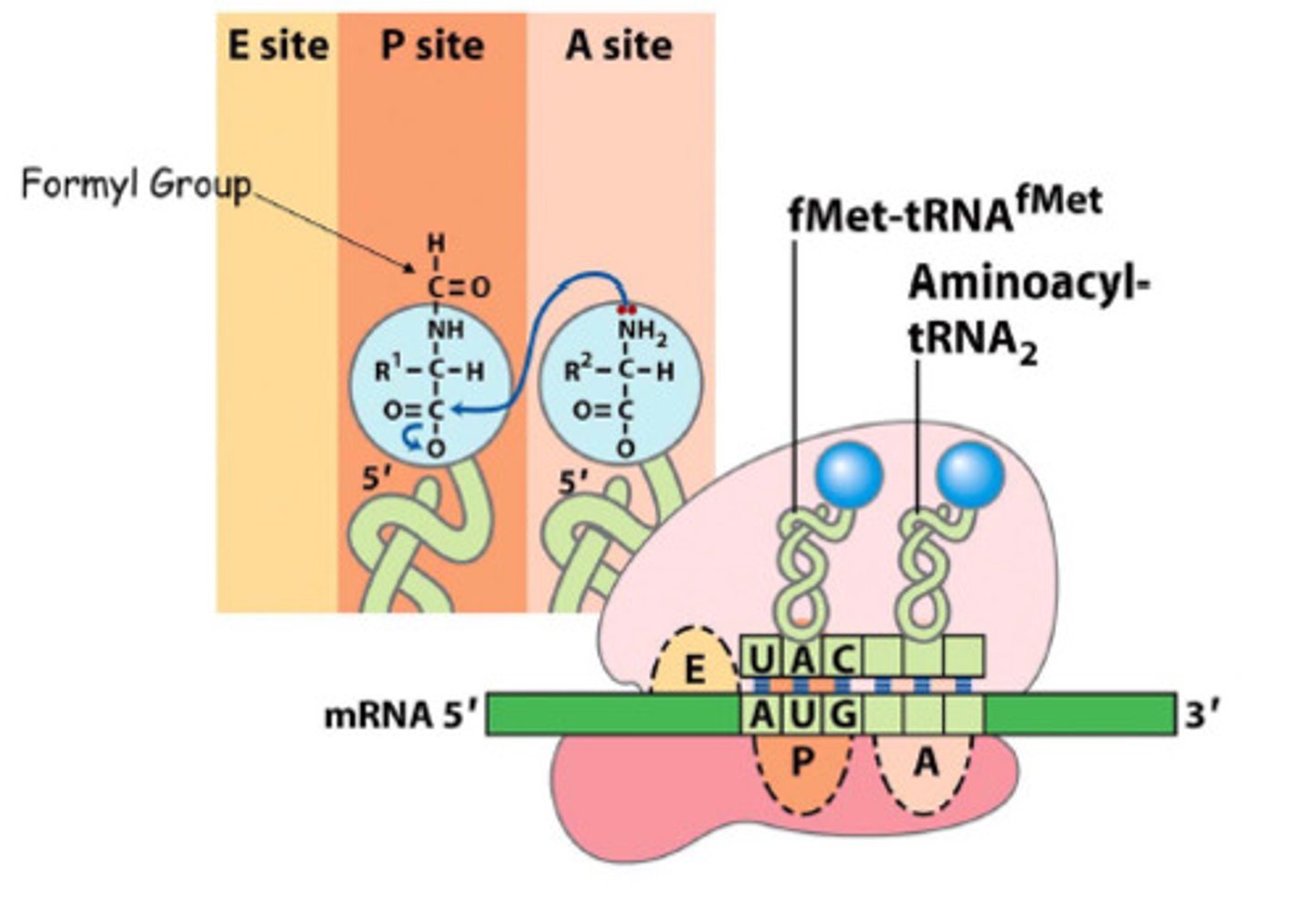
Ribosomal translation
initiation: factors bind 30S/40S -- ribosome binds mRNA -- bring tRNA -- large 50S binds
elongation: peptide bonds form
Peptide bond formation
base first deprotonates the NH2
Restriction enzymes
manipulate DNA, site specific endonucleases, cleaves bases and DNA
recognition sites are a palindrome
Cut into sticky or blunt ends
agarose gels
separate DNA based on base size
more porous than polyacrilamide
southern blotting
uses cDNA from gel -- blot onto sheet -- add p32 labeled probe -- autoradiography --
northern blotting
mRNA version of southern blotting
DNA fingerprinting
tandem repeats
PCR
95. 54. 72.
amplify DNA quickly
separate parent strands
DNA sequencing
similar to PCR - but must know part of sequence
Radioactive -- 4 separate rxns; using ddNTPs because will not make any PO3 group; different fragments; different lengths = where specific nucleotide is located
fluourescence - 1 reaction; fluorescent labeled ddNTPs; separated by capillary electrophoresis; detect flourescence as ejected from capillary
ddNTP
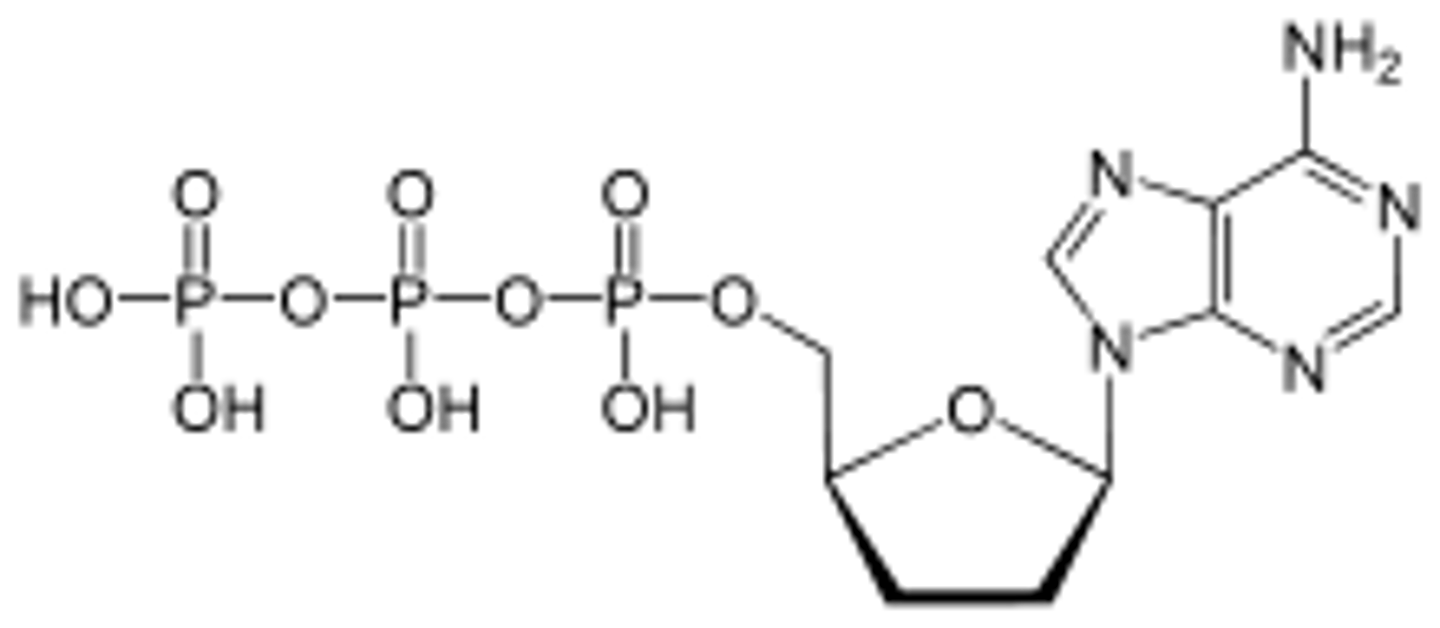
Vectors into plasmids
phage easily infects;
recombinant DNA
Lysogenic - DNA inserts into bacterial genome
Lysic - cells lysed as more phage are made
cDNA
Site directed mutagenesis
create specific targeted changes in DNA
study changes in protein activity - DNA manipulation
need to know gene you want in PCR and non-PCR
(nonPCR) = use whole plasmid; gaps where primer replicated DNA - cant ligate - ligated into host cell = template
(PCR) = use part of plasmid - run through PCr - new sequence = new template = limit is the time of the primers
Homology
Paralog = pair of genes in species
Ortholog = genes in pair of species
identity = % exactly the same
similarity = % similar and exact same
Sequence alignments
what % is similar
Hemoglobin structure
dimer of dimers
O2 binds to Fe on top and use 2nd distal histidine to stabilize the O2 to prevent Superoxide release
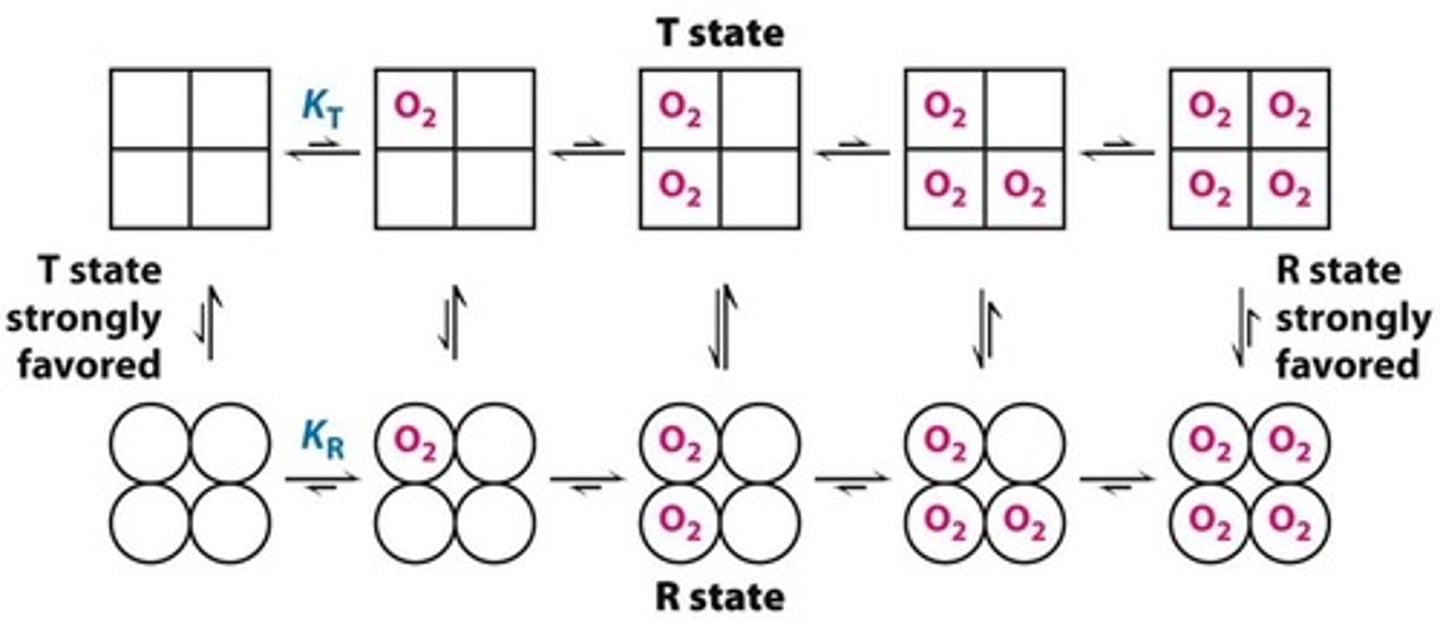
concerted binding
prefer tense state when nothing is bound
prefer relaxed state when stuff if bound
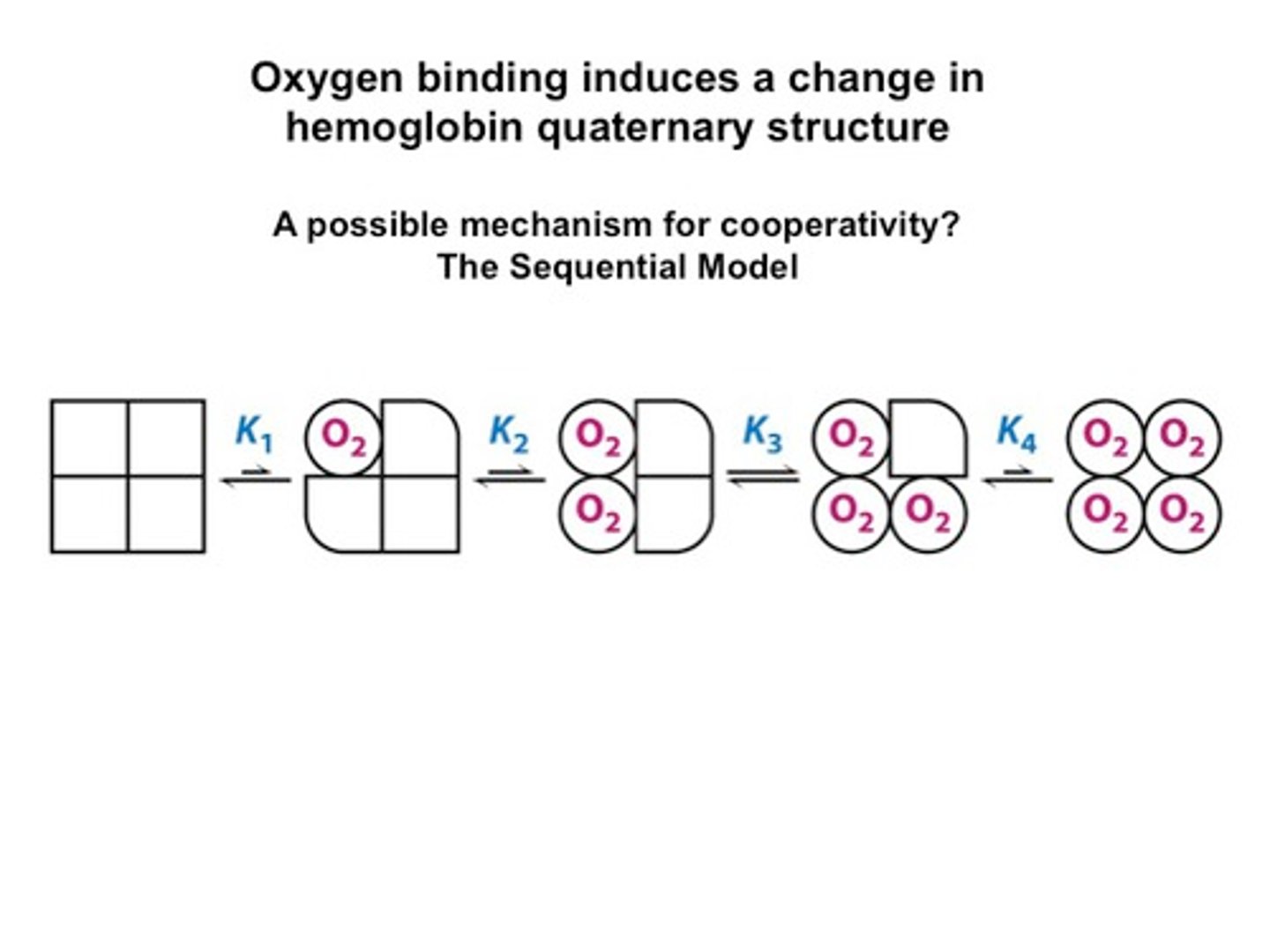
sequential binding
A hypothesis that states that an ion binds to a binding site and progresses through the cell membrane by binding to sequential binding sites that develop a stronger attraction for the ion
Tense state
no O2 bound
wants to release O2
binding affinity is low
relaxed state
O2 is bound
wants to bind O2
binding affinity high
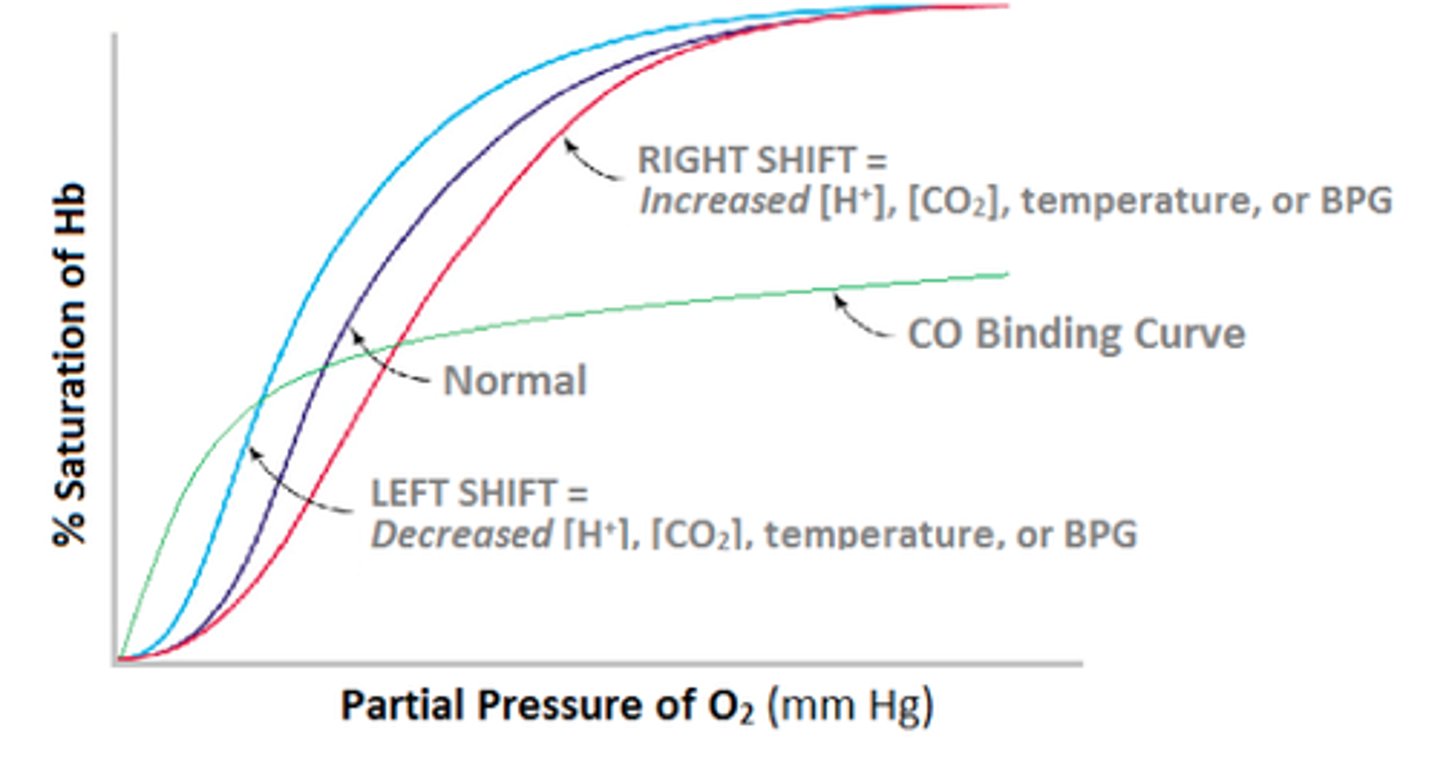
what does a shift to the right from hemoglobin binding oxygen result from?
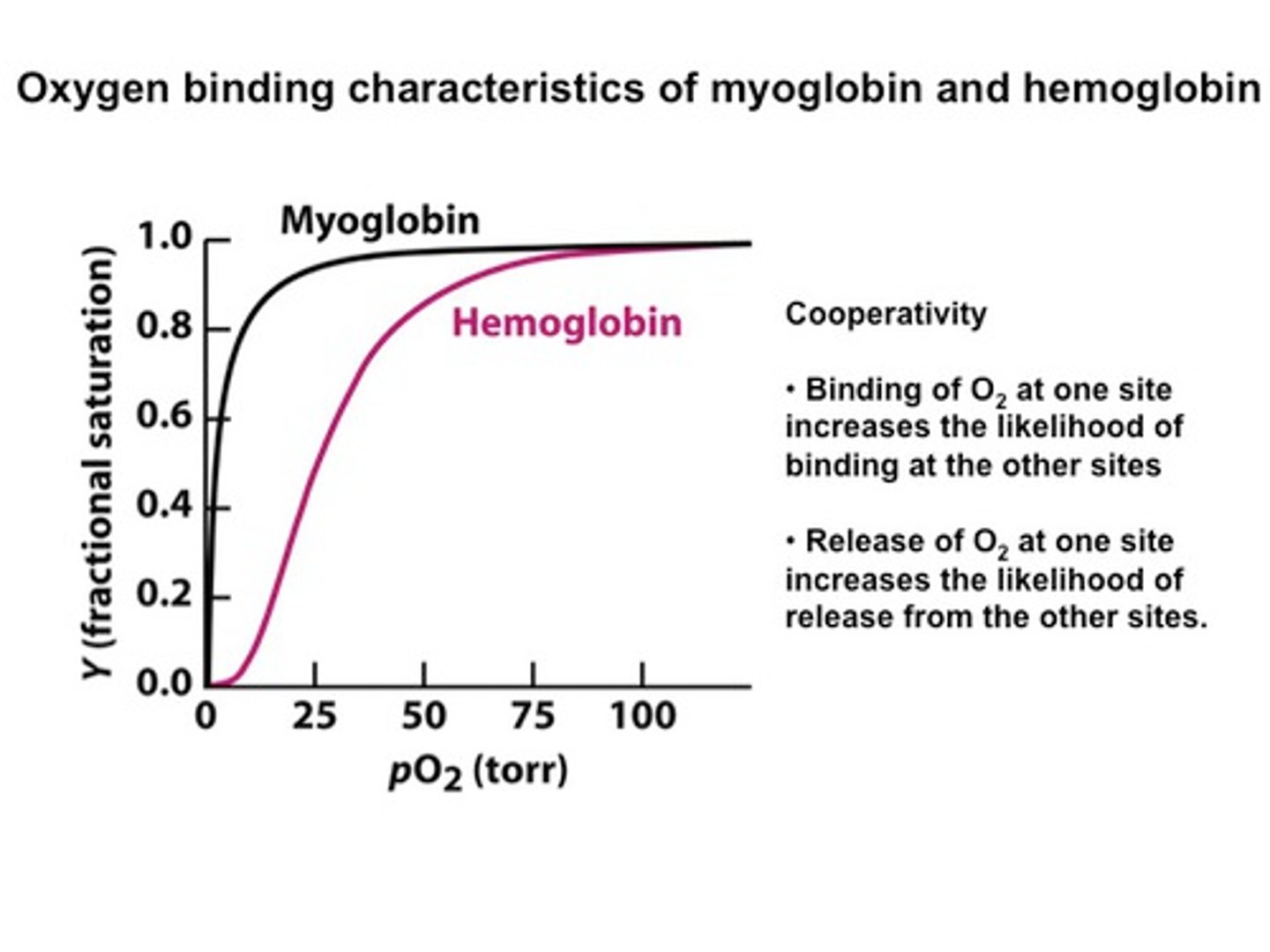
How does the curve of myoglobin binding oxygen compare to that of hemoglobin?
fetal binding is in between
hemoglobin binding oxygen
carbonic anhydrase o2 binding
Myoglobin
high affinity at low pO2 in blood
--> Myoglobin (tertiary structure) has a higher affinity for oxygen than hemoglobin. Tertiary structure---> can bind or release oxygen.
hemoglobin - sigmoidal curve because...?
has cooperativity - easier to bind more O2 after already bound
high pO2 in lungs - bind tightly
low pO2 in muscles - release easily
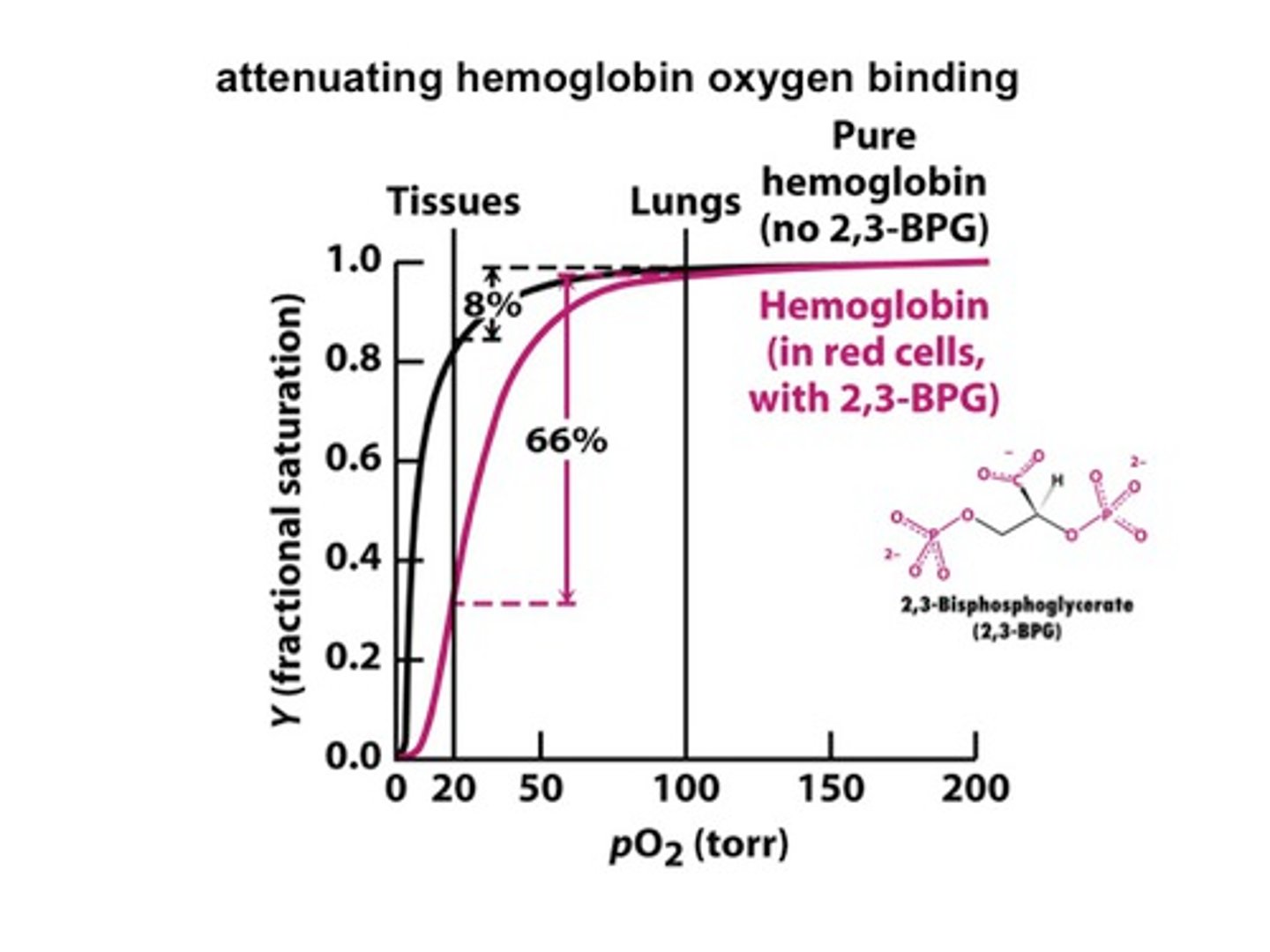
Fetal hemoglobin is special because..?
higher binding affinity - low 2,3 BPG
2,3 BPG
allosteric effector for binding hemoglobin - blocks O2 from binding - keeps in T state
Allosteric Regulation
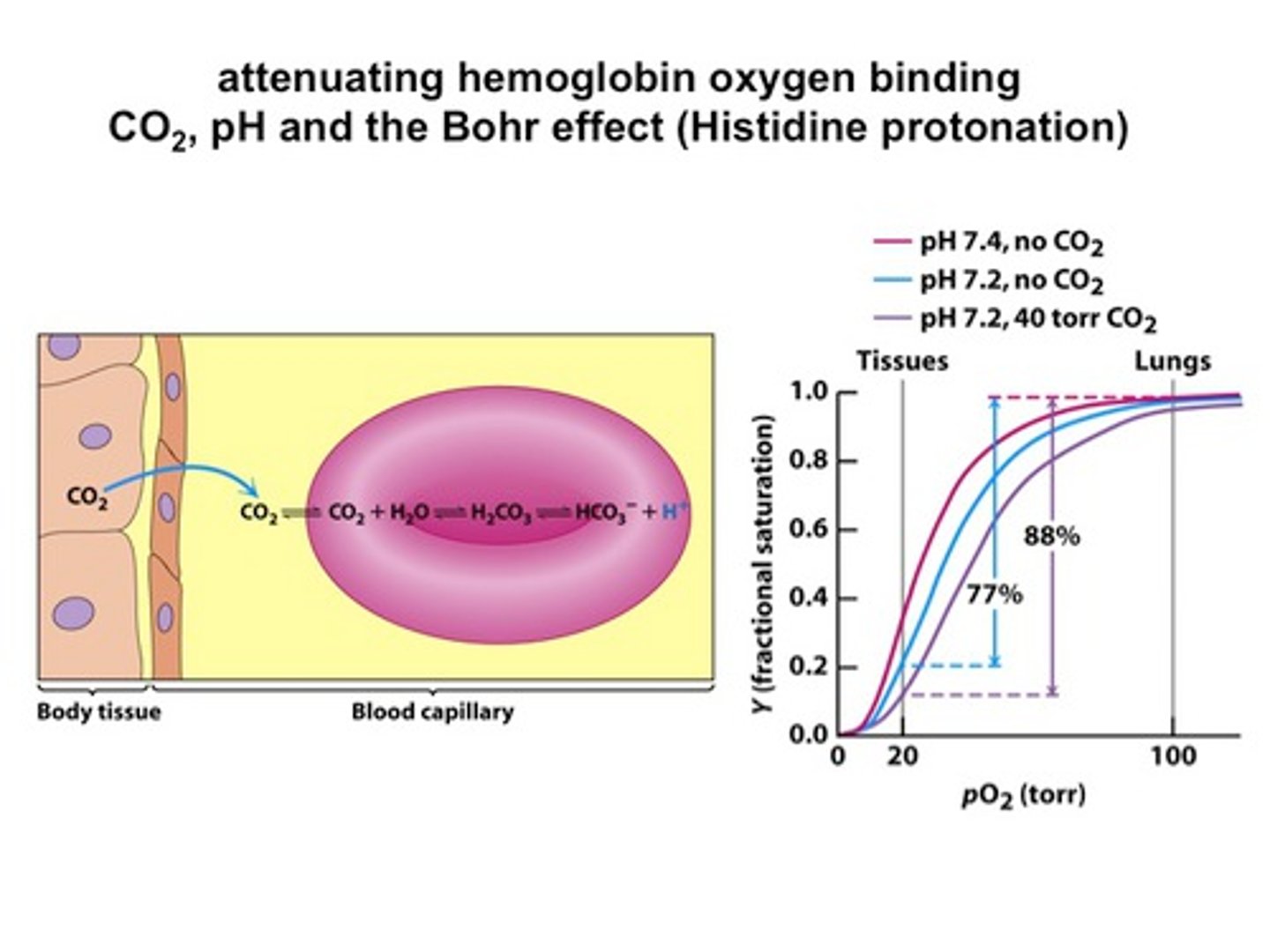
1. Low pH = low O2 affinity
- T state is stabilized by salt bridge (proton added to Histidine)
2. 2, 3 BPG - bound to oxyanion hole
3. CO2 binds to H2O - H2CO3 forms and lowers the pH through HCO3-
4. CO2 binds to NH2 terminus to form carbamate and H+ = lower pH
Sickle Cell Anemia
Glu-->Val (polar --> nonpolar)
disrupts quaternary structure
in deoxy state
stuck in capillaries (stretched back and forth) - firmer
heterozygotes resistant to malaria because RBC are firmer
Thalassemia
a/B - not enough of alpha/beta chain produced
Michaelis Menton german
Die kinetik der invertinwirkung
Briggs-Haldane Equation
Vo = (Vmax*[S])/(Km + [S])
Briggs Equation
Vmax = max rate (usually only up to 80%)
kcat = Vmax/[E] = rate of product formation
Km = Vmax/2 rate of formation at half of the max velocity
kcat/km = 2nd order rate constant
Catalytic Efficiency
catalytically perfect - depend on rate of diffusion

Irreversible inhibition
inhibitor binds so tightly therefore inactivates AKA suicide
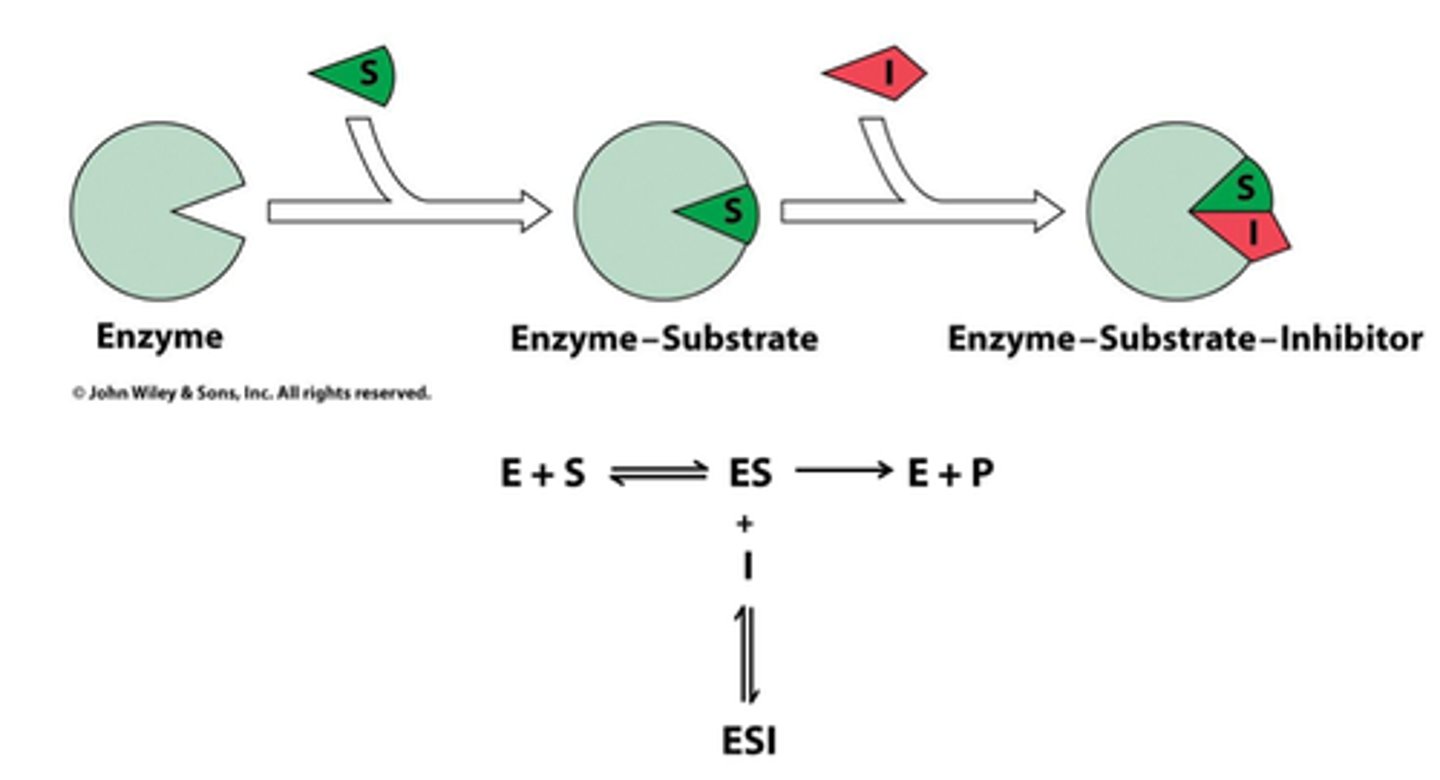
Reversible inhibition (3 types)
depends on dissociation constant
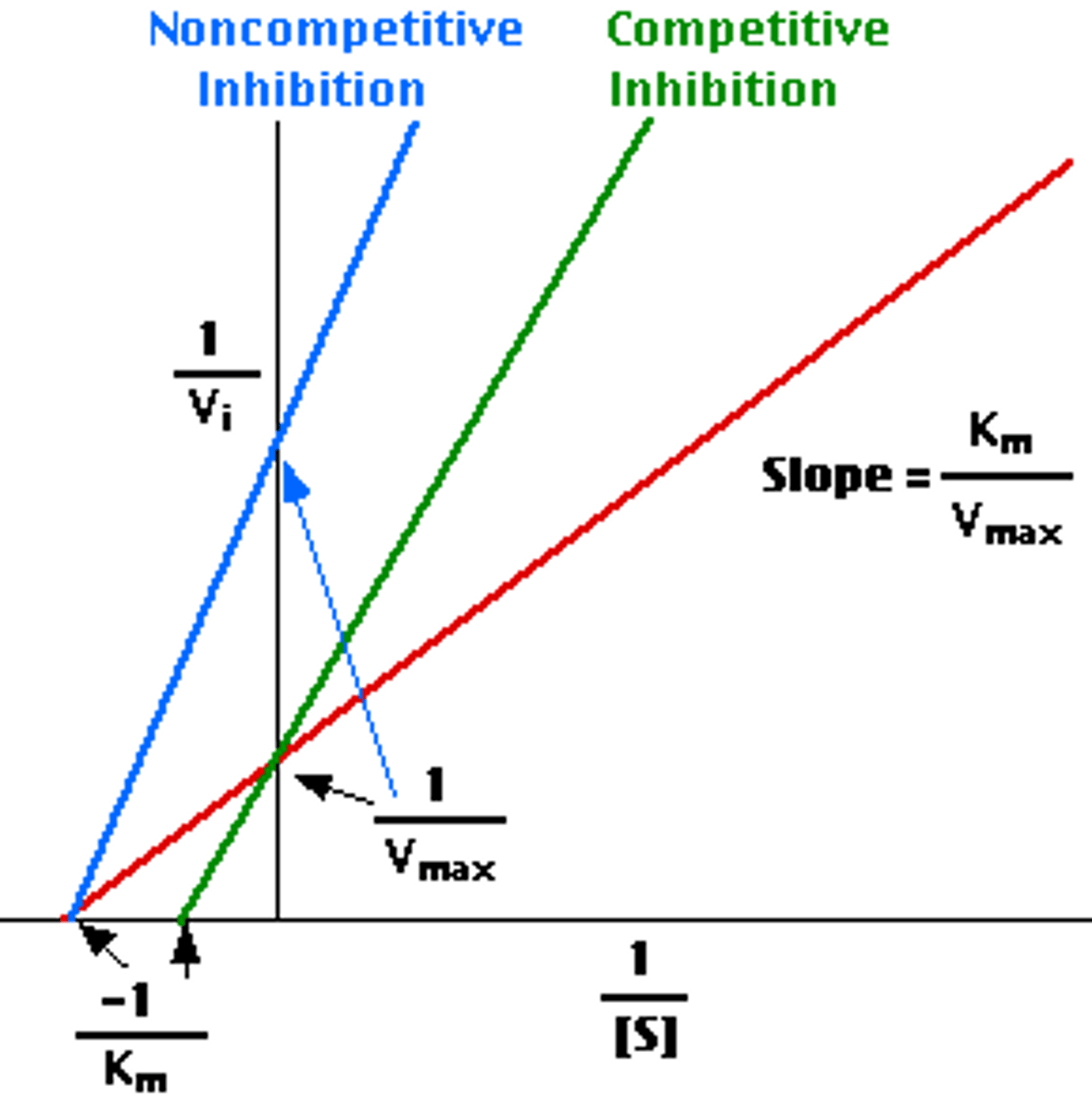
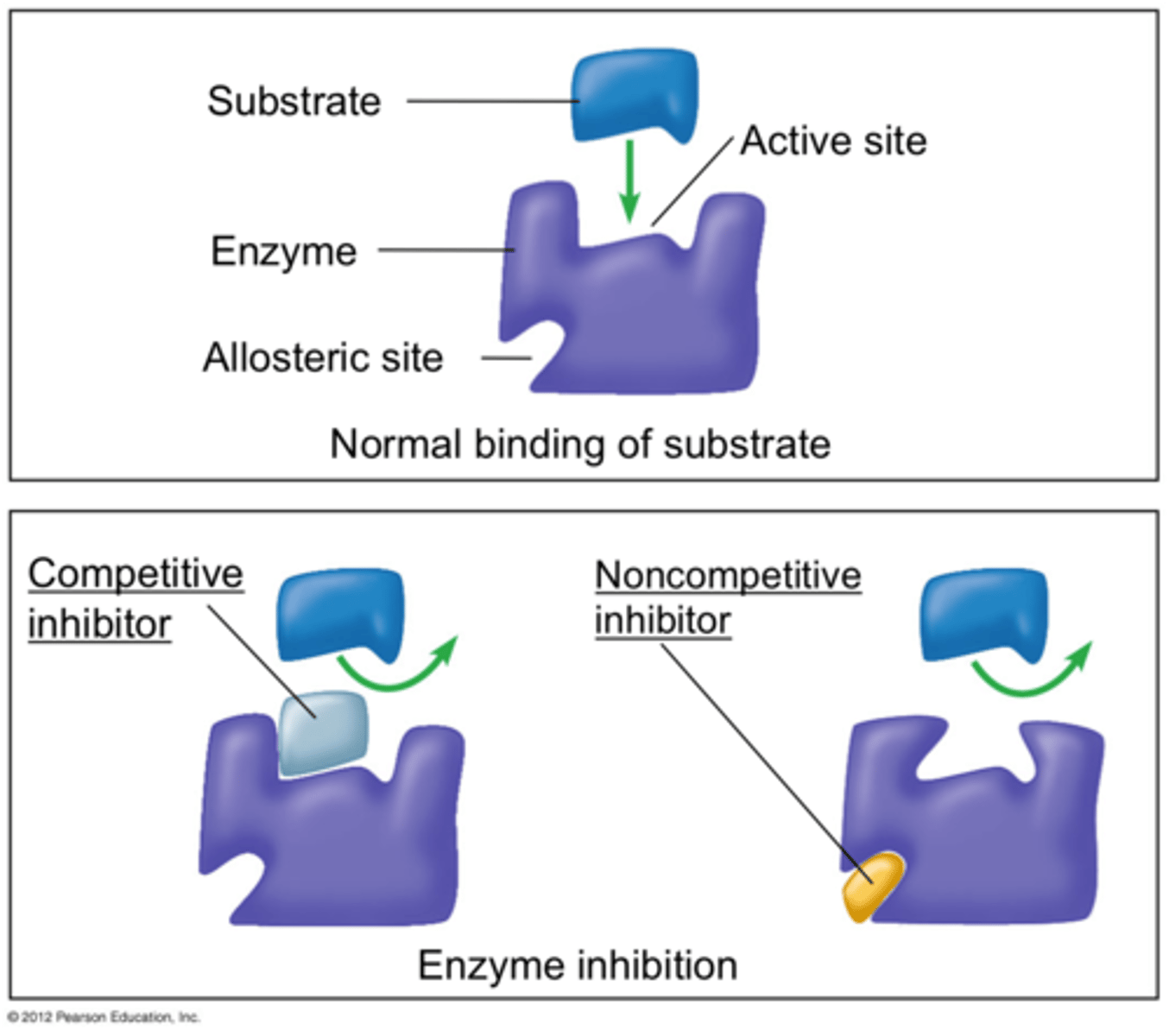
Competitive
Noncompetitive
Uncompetitive
Competitive Inhibition
inhibitor can bind or substrate can bind; since we have infinite substrate then it just takes longer for it to bind more than inhibitor
need increased substrate concentrations
Vmax is not changed
Km increases (Km = substrate concentration when half of active sites are filled)
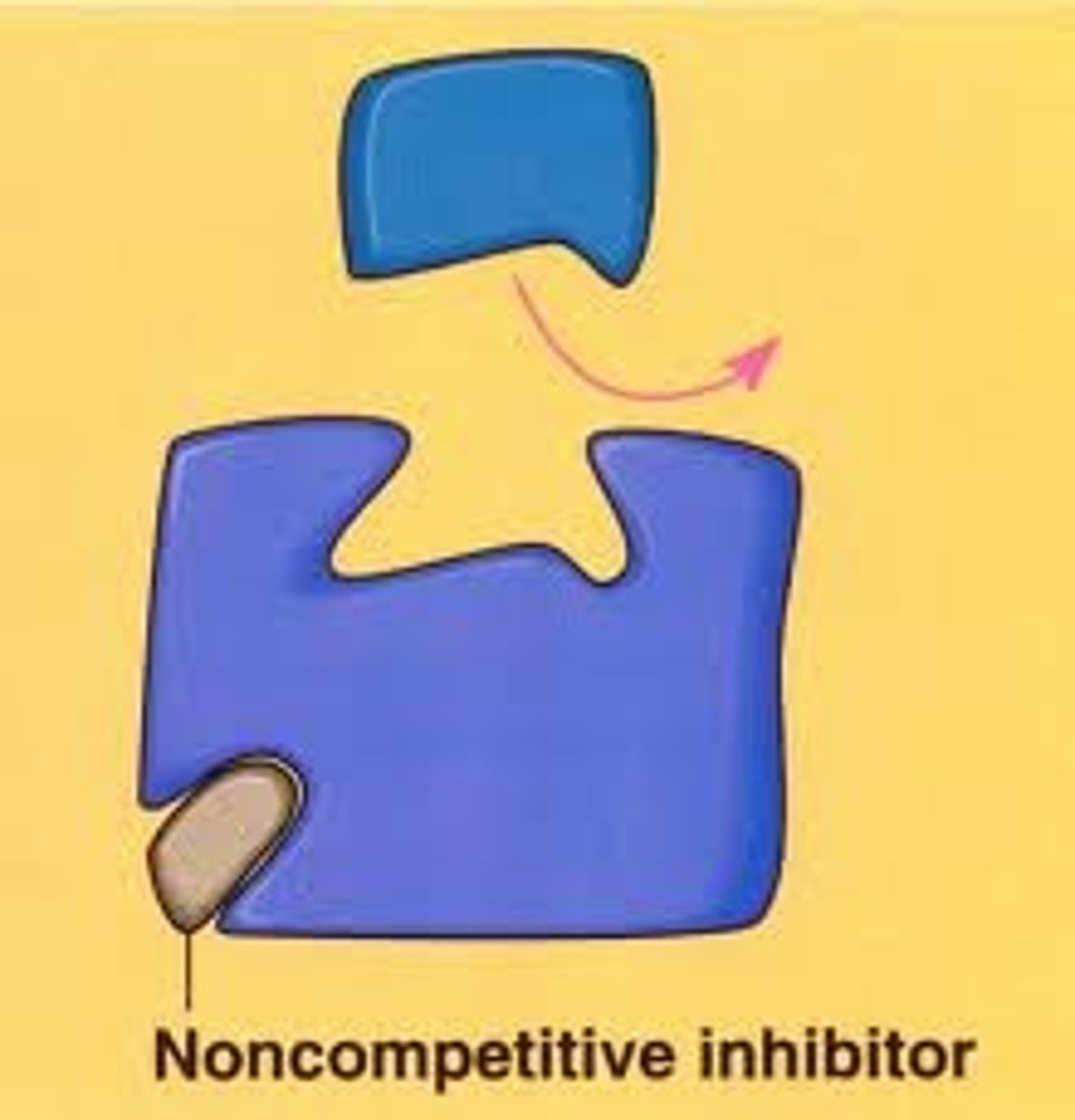
Noncompetitive Inhibition
if inhibitor is bound then the substrate cannot bind
Number of substrates able to bind is decreased because there are fewer possibilities for binding location
Vmax decreases (max velocity is less because it wont take as long to fill all the available spots since inhibitor is decreasing amount)
Km is not changed
Uncompetitive Inhibition
inhibitor keeps substrate bound to enzyme
inhibitor deactivates enzyme
substrate stays bound - therefore not as many spots available
Vmax is decreased
Km is decreased (change number of substrate and ability to bind)
2 Models of substrate binding
induced fit - change
lock and key - fit like a lock and key
Enzyme rates plateau because...
have finished bind all substrate to all available enzymes
pH profile
know pKa's
Sequential binding
ordered: need to bind b/c of substrates
random: random binding
ping pong: 2 reactions - 1st reaction products modifies something in 2nd reaction
Burst/Transient Kinetics
Steady State = after product forms
Burst = initial rate of enzyme
Cysteine Protease
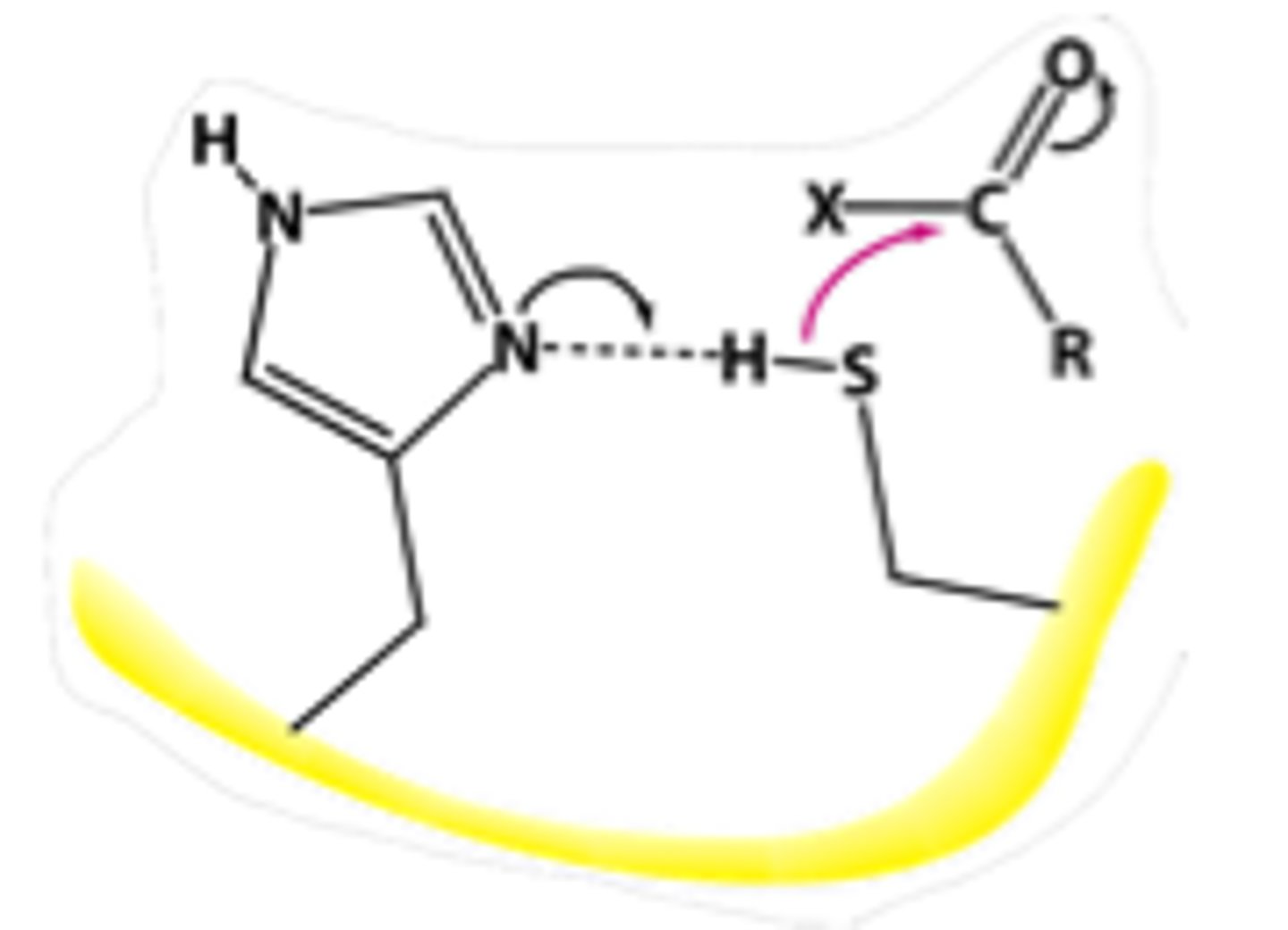
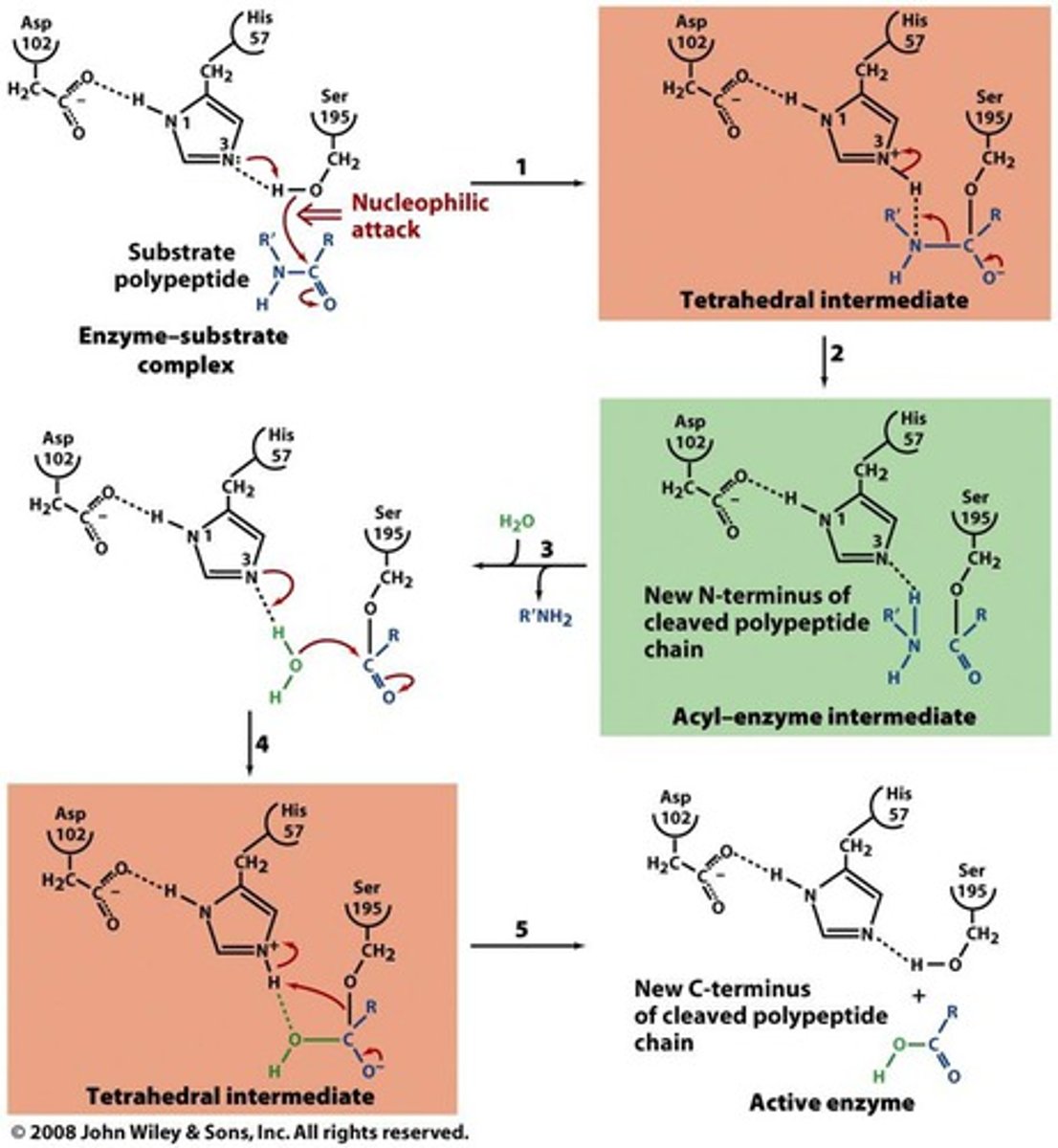
Serine Protease
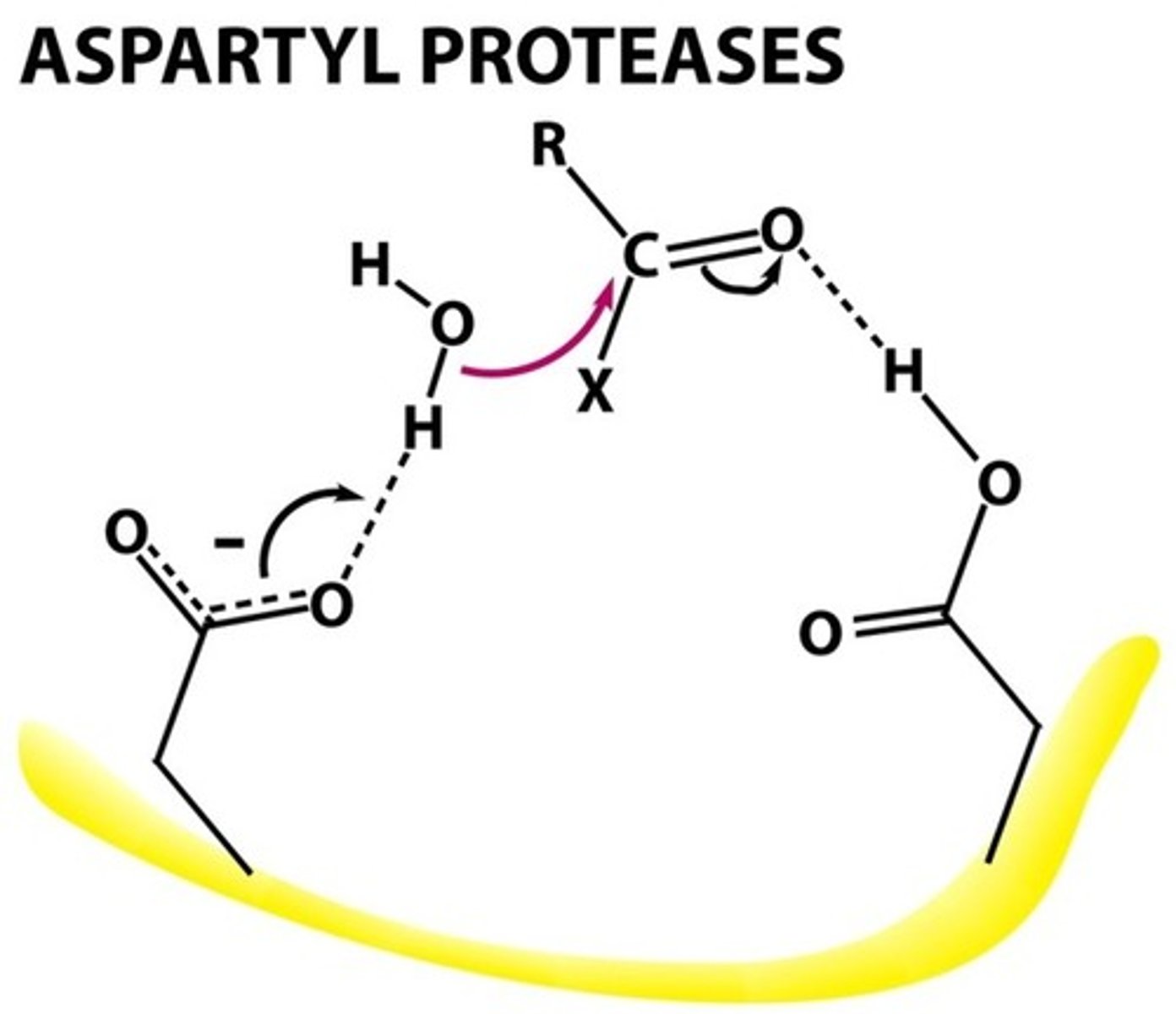
Aspartyl Protease
Metallo Protease
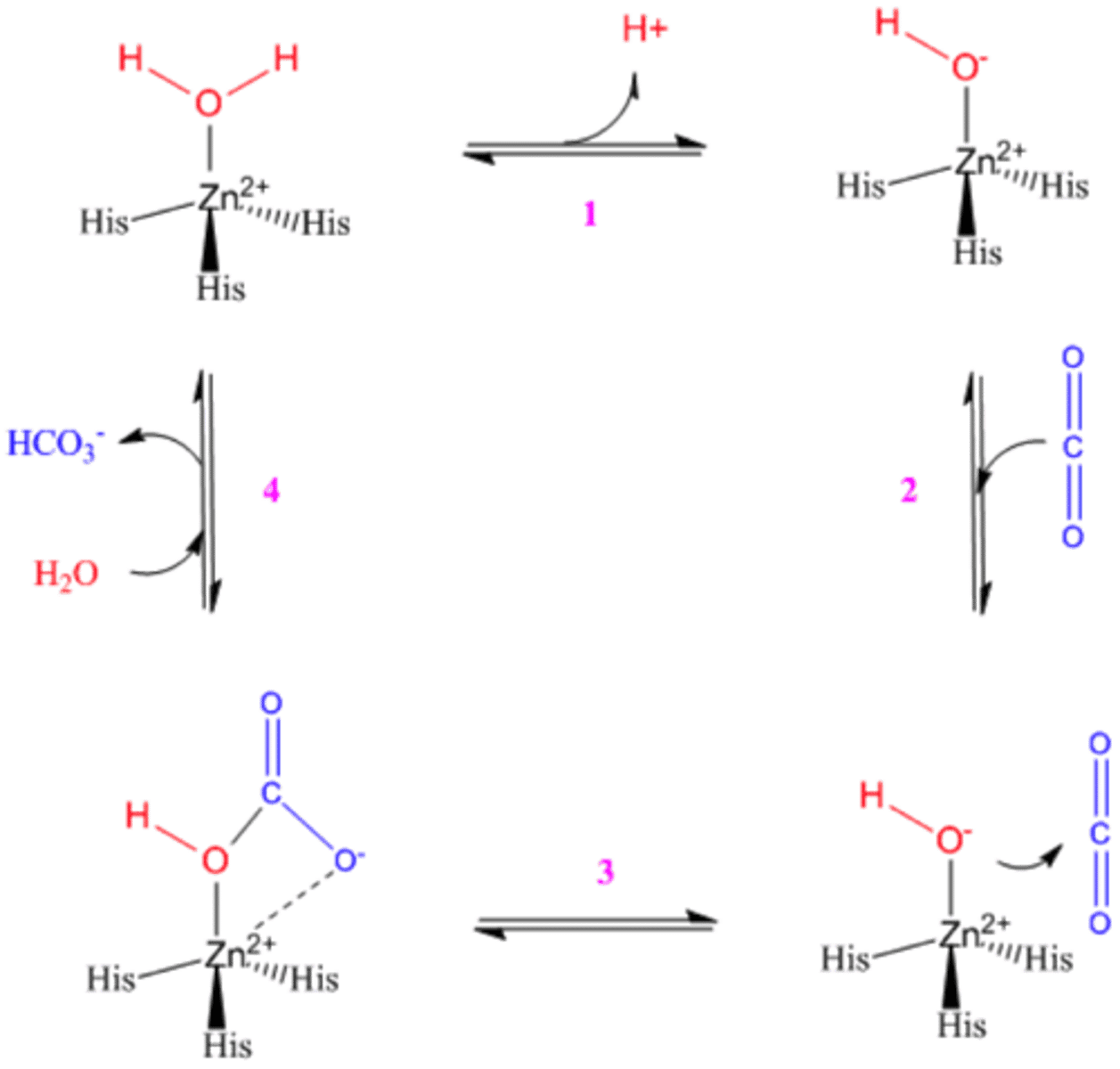
Carbonic Anhydrase Mechanism
Enzyme Regulation (ALL 5)
1. Isozymes
2. Phosphorylation
3. Zymogens
4. Enzyme concentration
5. Allosteric Control
I, P, Z, E, A
Enzyme Regulation (I)
Isozymes = Multiple enzyme forms - different forms of the enzyme can regulate, altered kinetic parameters
Enzyme Regulation (P)
Phosphorylation/kinases - covalent modifications of proteins can activate/deactivate protein function
add/remove groups
Phosphorylation/dephosphorylation
Enzyme Regulation (Z)
zymogens - inactive form of enzyme - activated by cleavage
Enzyme Regulation (E)
Enzyme concentration - concentration of enzyme can control and regulate rate at which reaction is completed
Enzyme Regulation (A)
Allosteric Control - additional binding sites on enzyme that regulate activity - active sites that can inactivate or activate
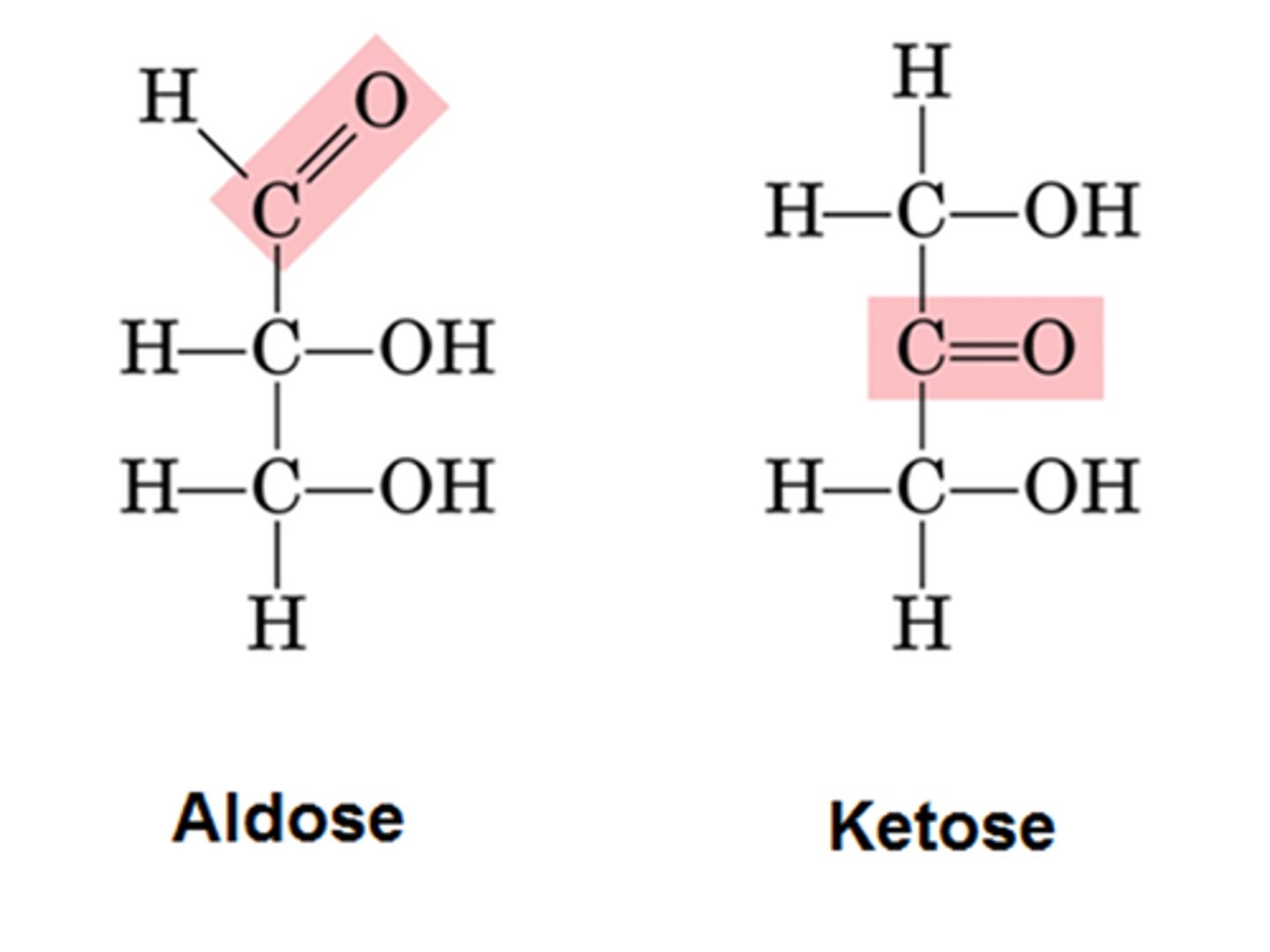
Ketose and aldose
pyranose and furanose
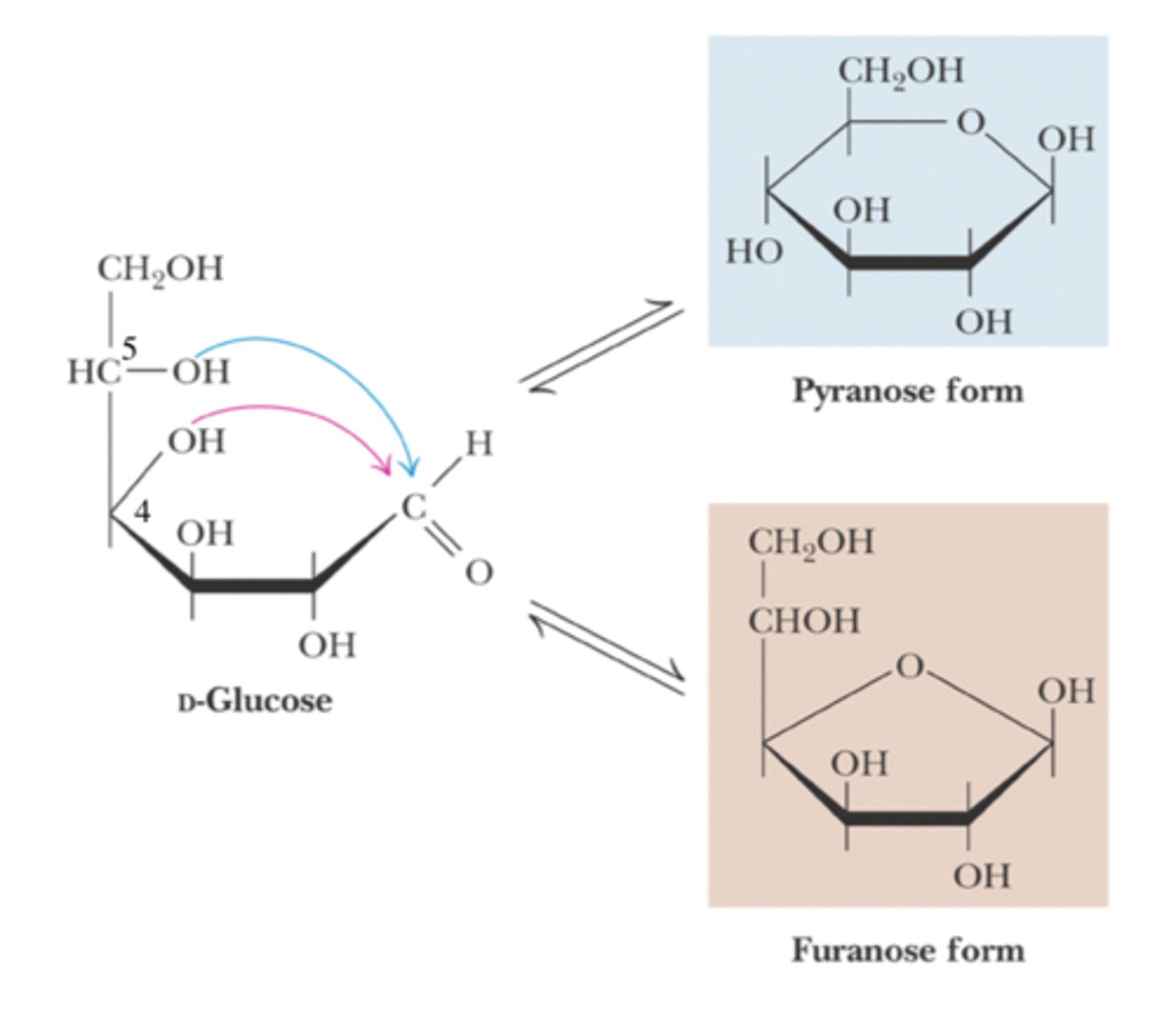
glucose ring structure
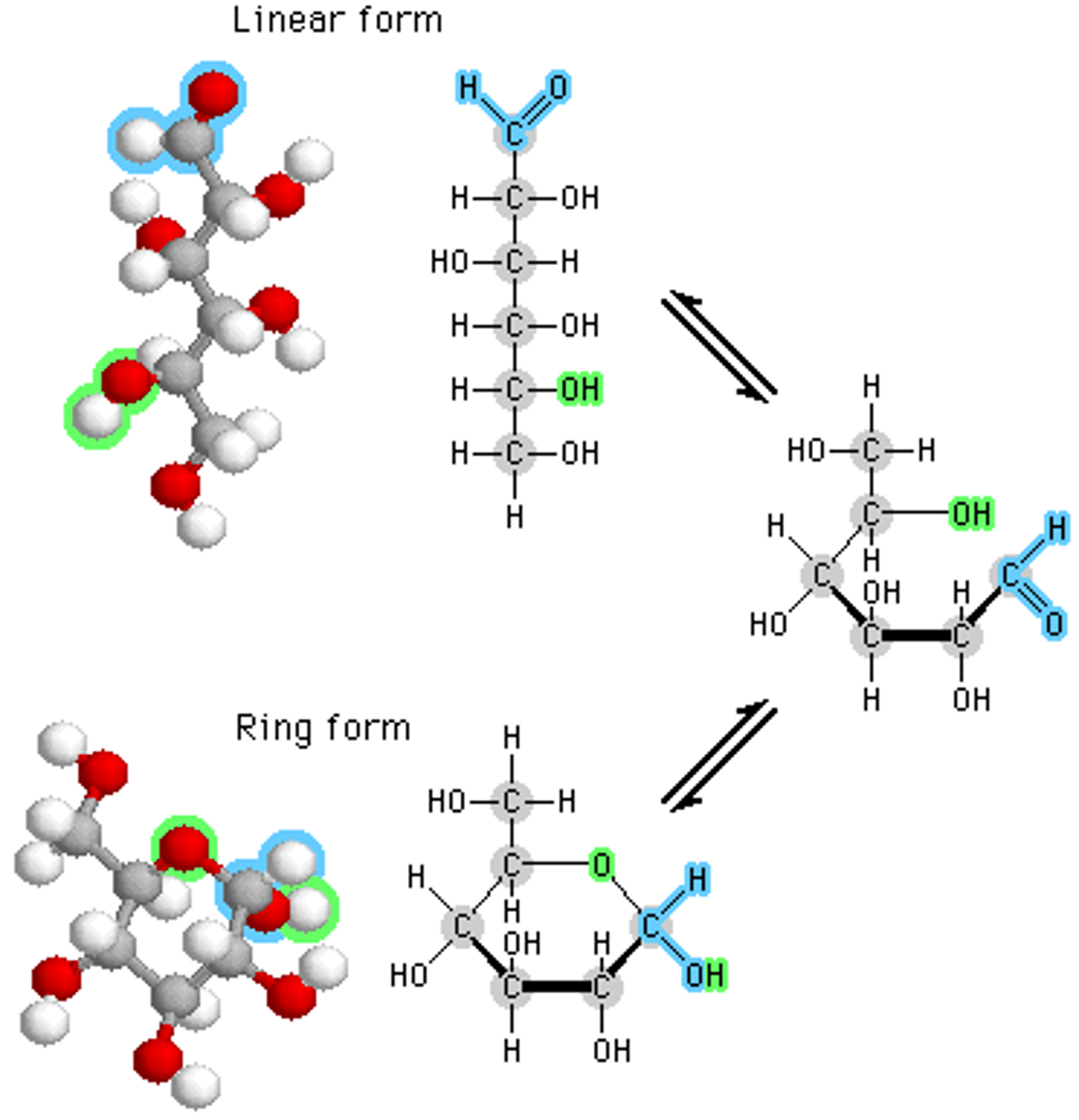
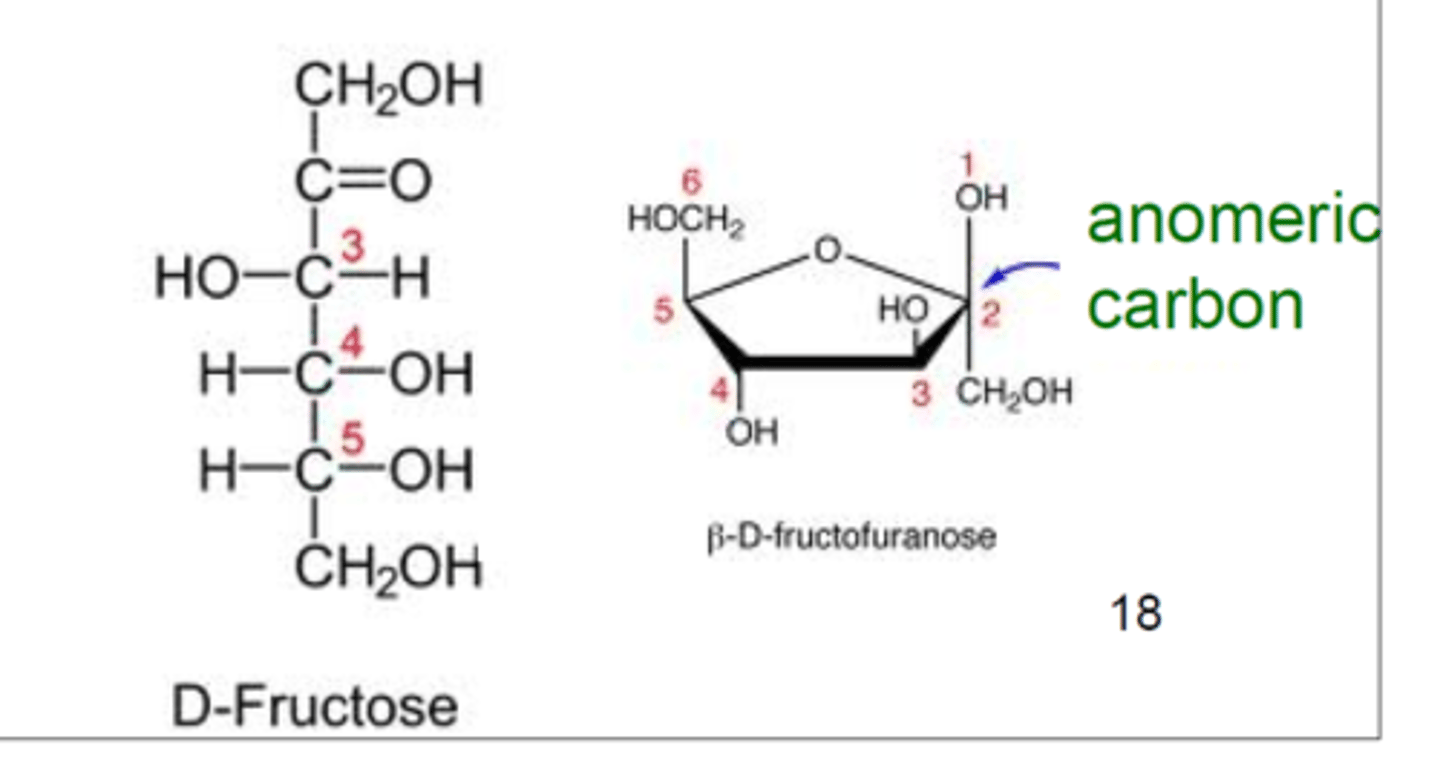
fructose ring structure
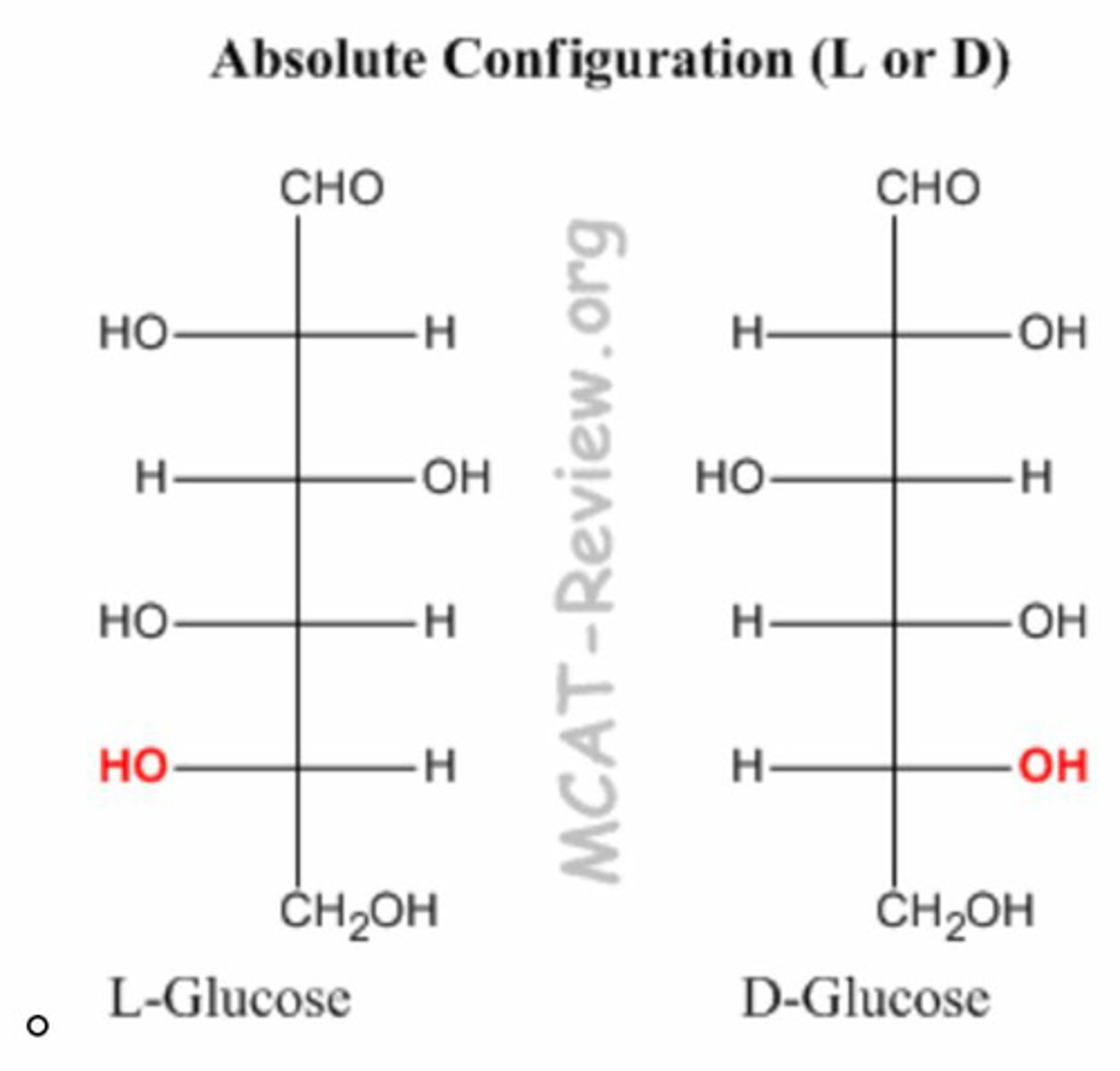
D/L Carbon
1st achiral farthest from anomeric
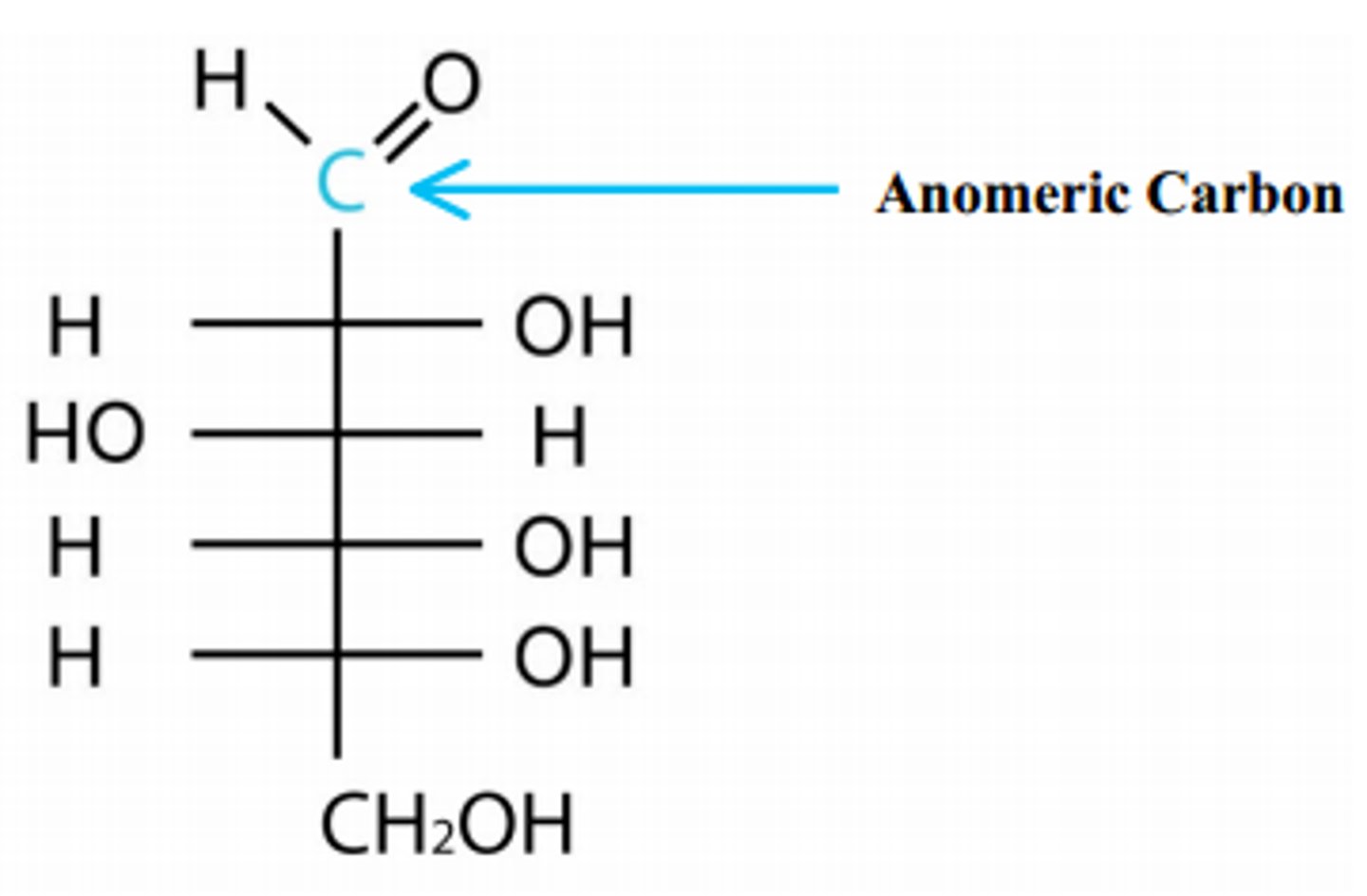
anomeric carbon
determines alpha or beta
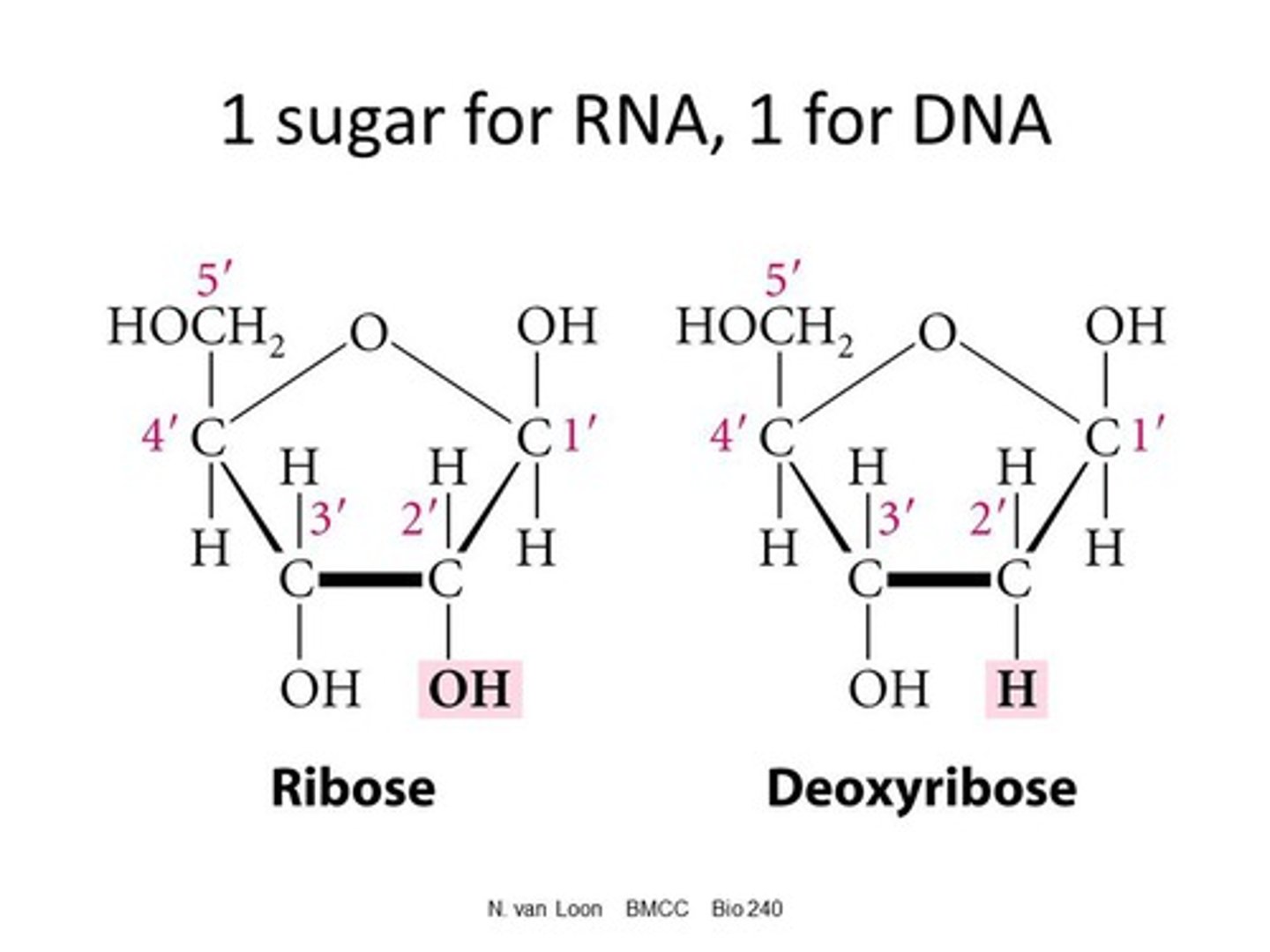
ribose and deoxyribose
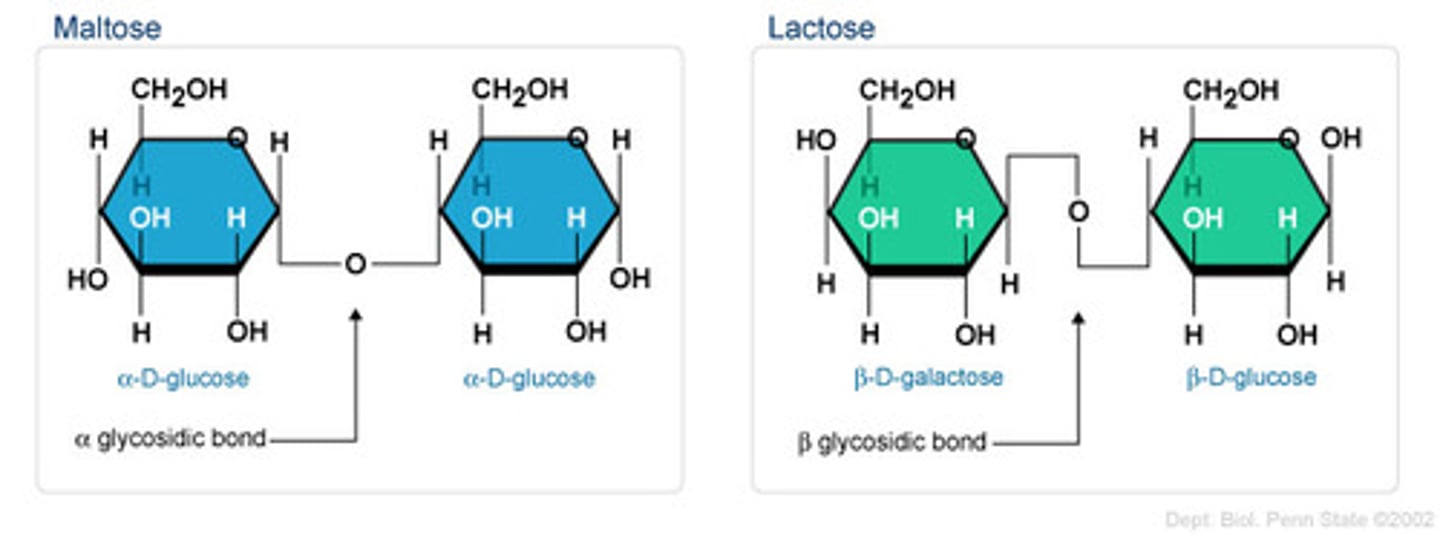
glycosidic bonds
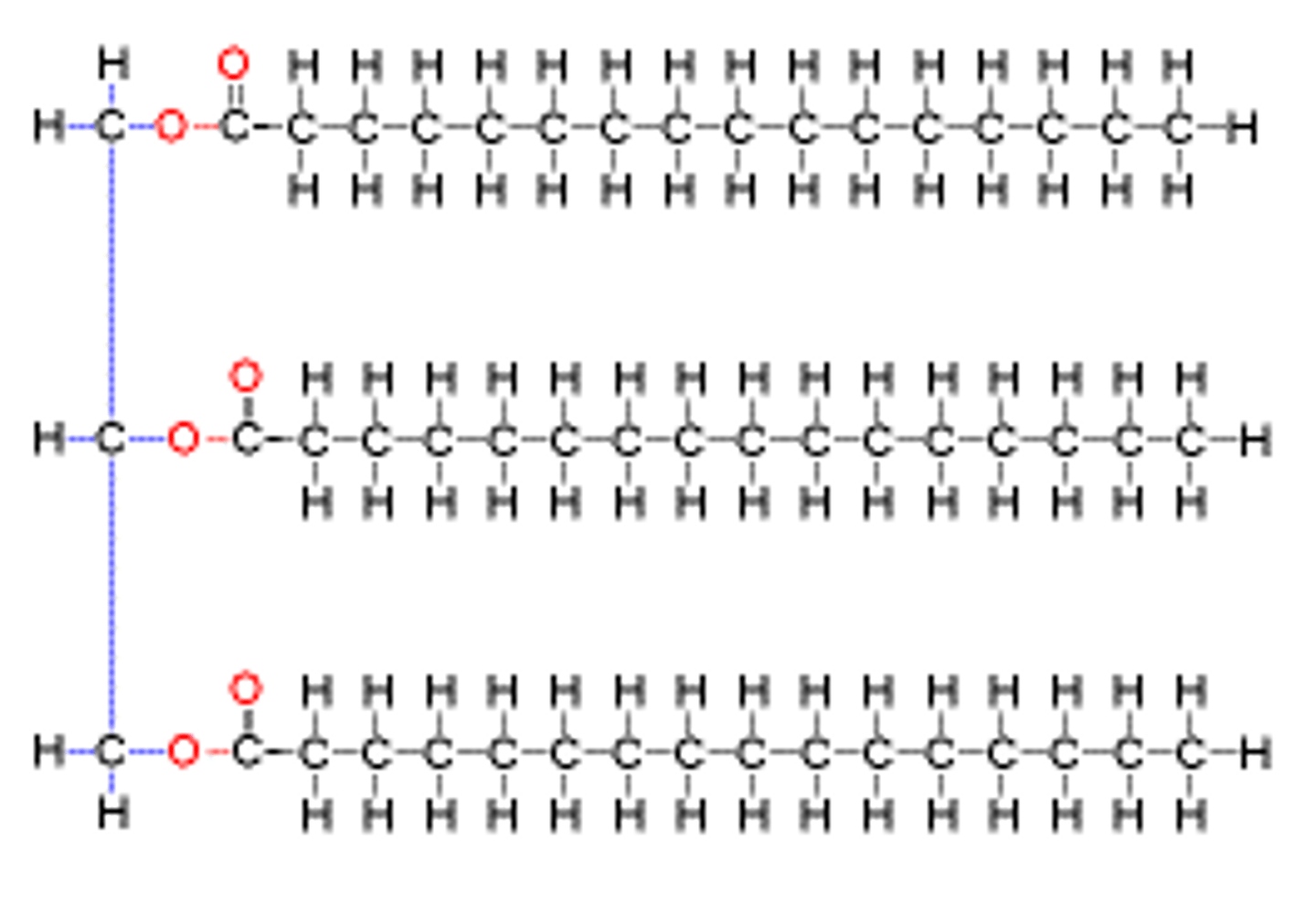
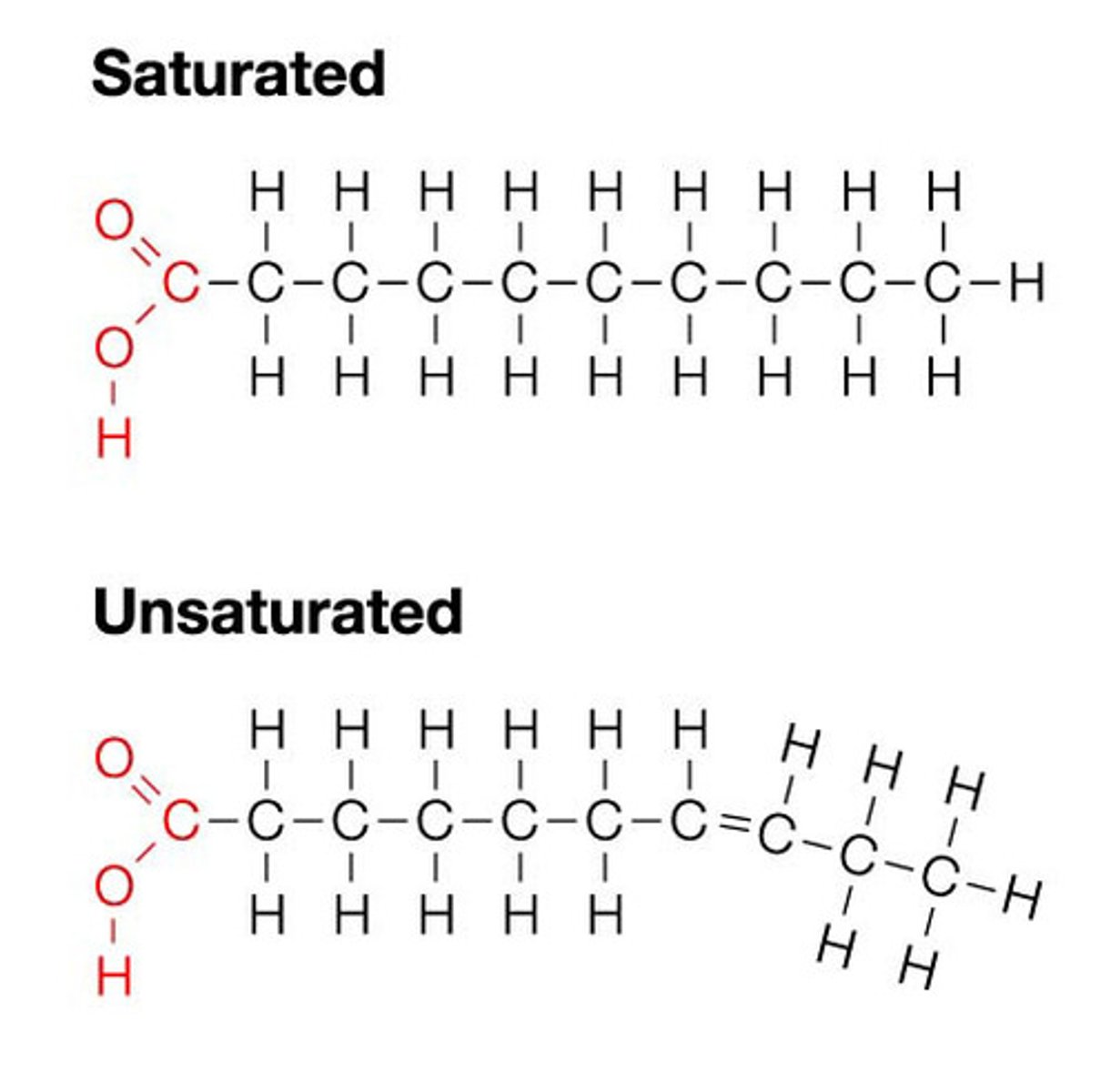
Fatty acid structure
Phospholipid/triglyceride
have no carbs for energy use - use lipids because lipids are easily stored
they serve in the cell membrane as a bi layer - highly impermeable to polar molecules