Anatomy (Biology Review)
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Biology
The study of life
Metabolism
the sum of all chemical processes that occur in an organism
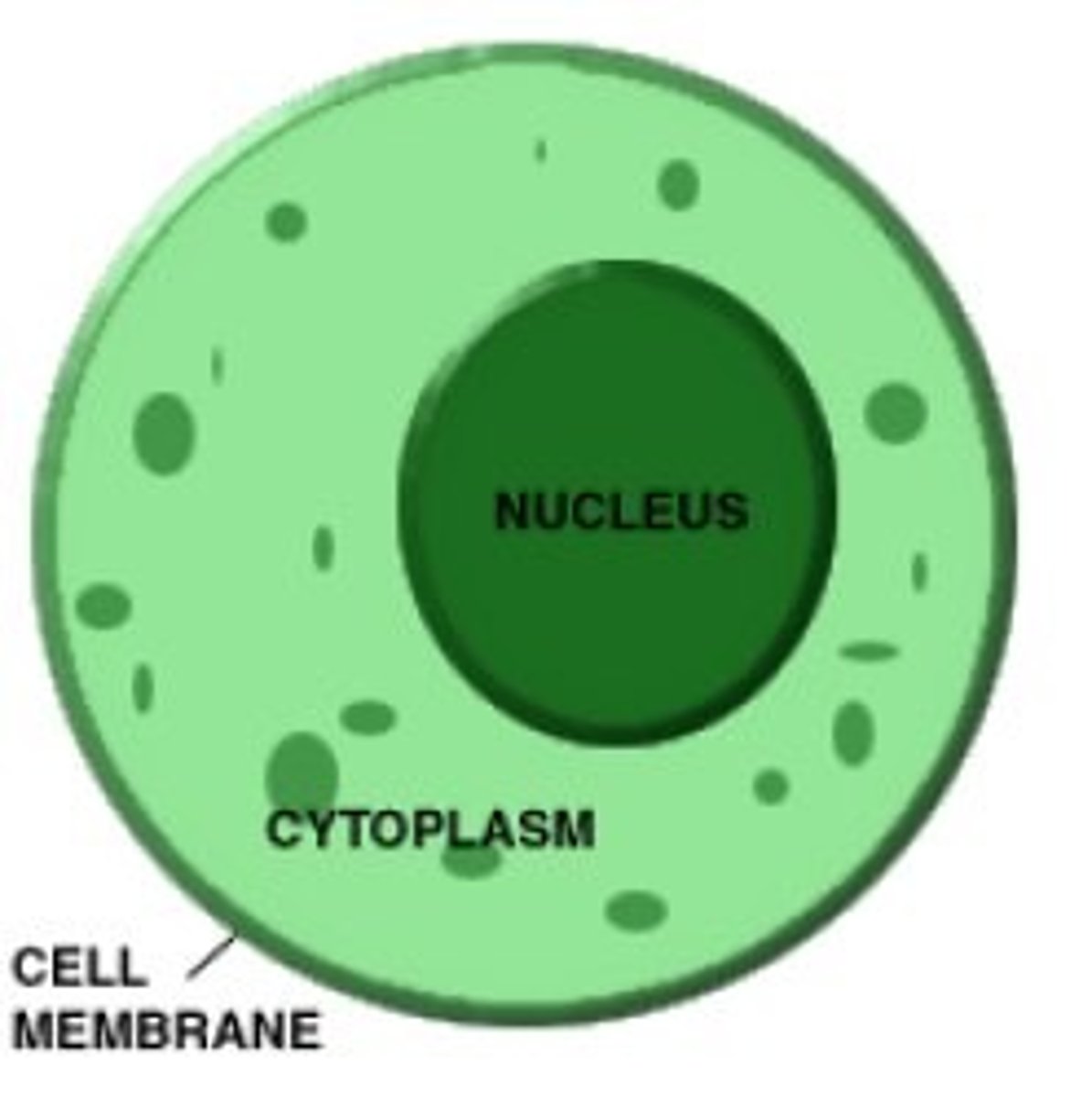
Cells
-Basic unit of life
-Smallest part of organism capable of life
Eukaryote
organism whose cells contain a nucleus
Prokaryote
unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus
Organelle
special structures in cell to help the cell to help the cell function
Cytoplasm
holds everything in place, jelly-like
Hydrophobic
afraid of water
Hydrophilic
water loving
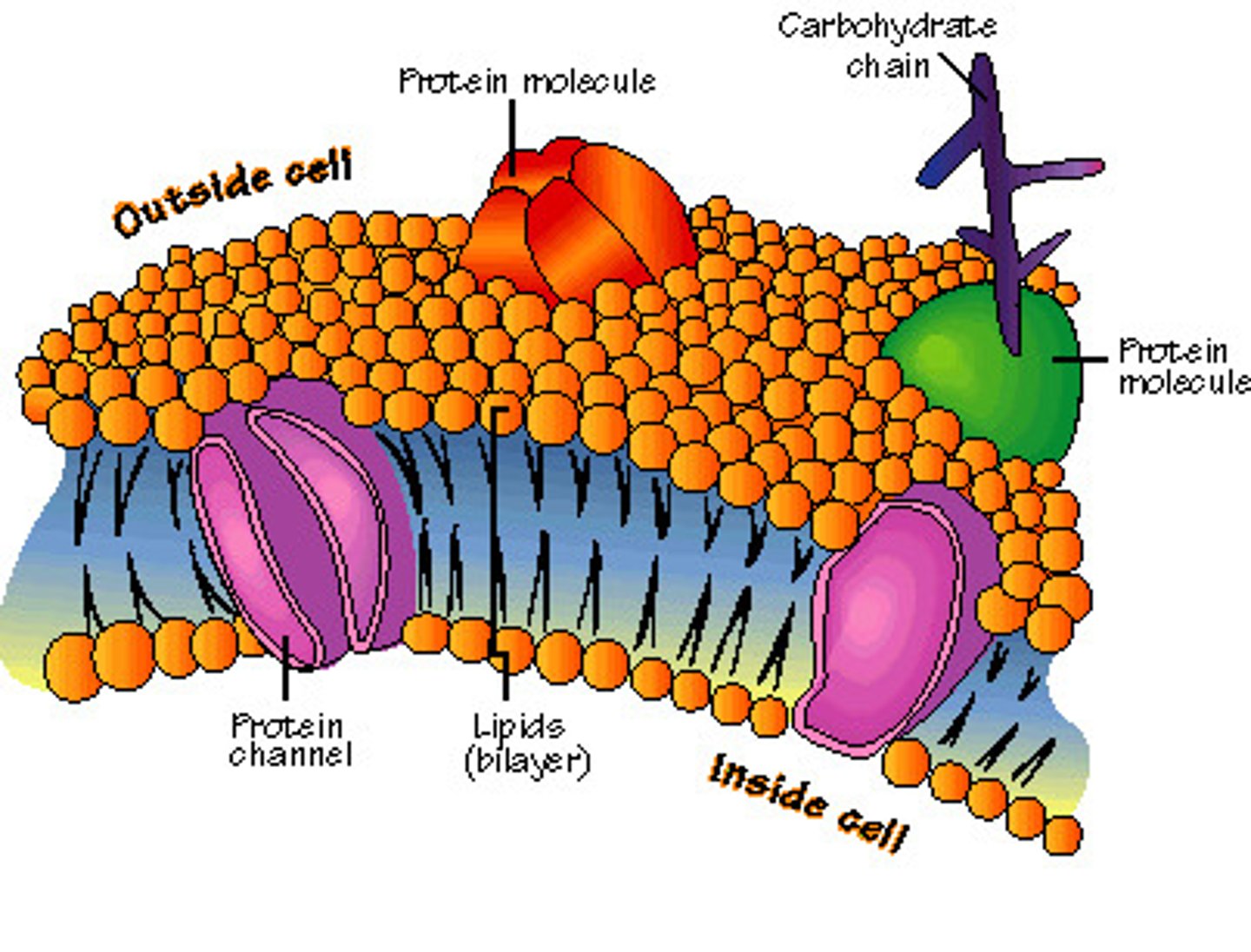
cell membrane
-Controls what goes in and out
-Made of phospholipids
-arranged in bi layer
Homeostasis
a balanced internal state
Cytoskeleton
support, maintain shape, motility, and regulate biochemical activities
Centrioles
Helps with cell division
Flagella
moves fluid through the entire cell (single)
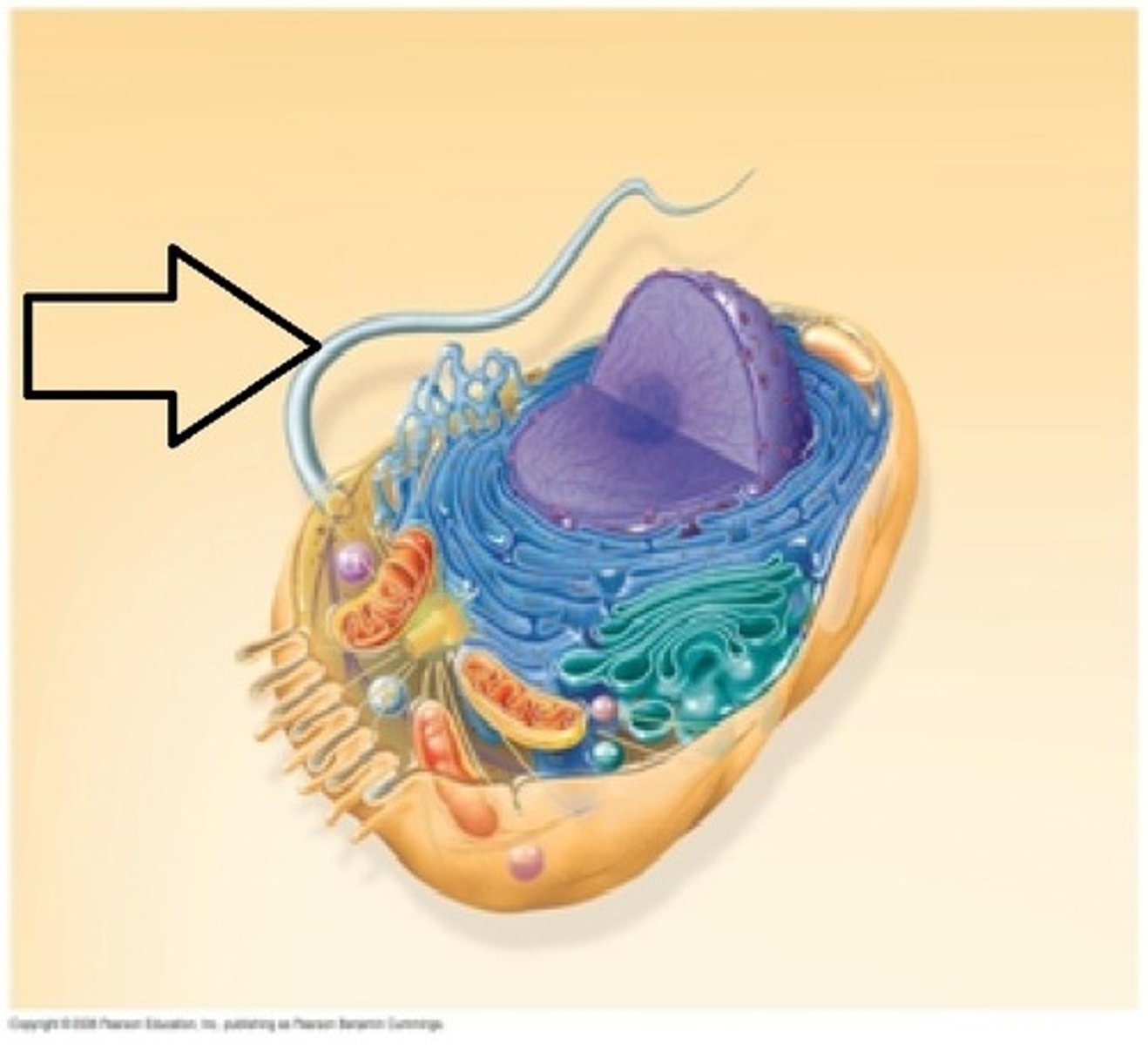
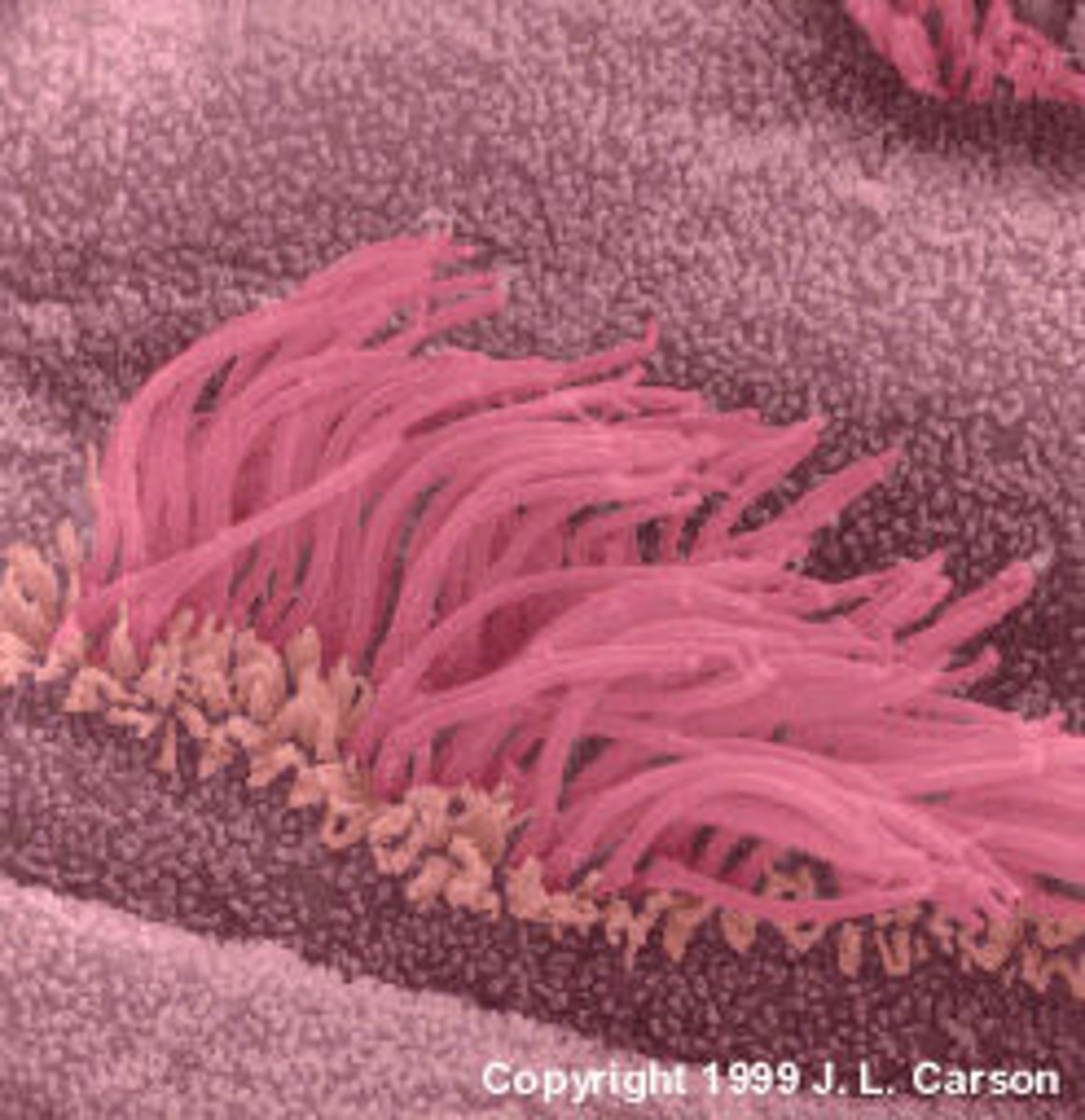
Cilia
moves fluid (many)
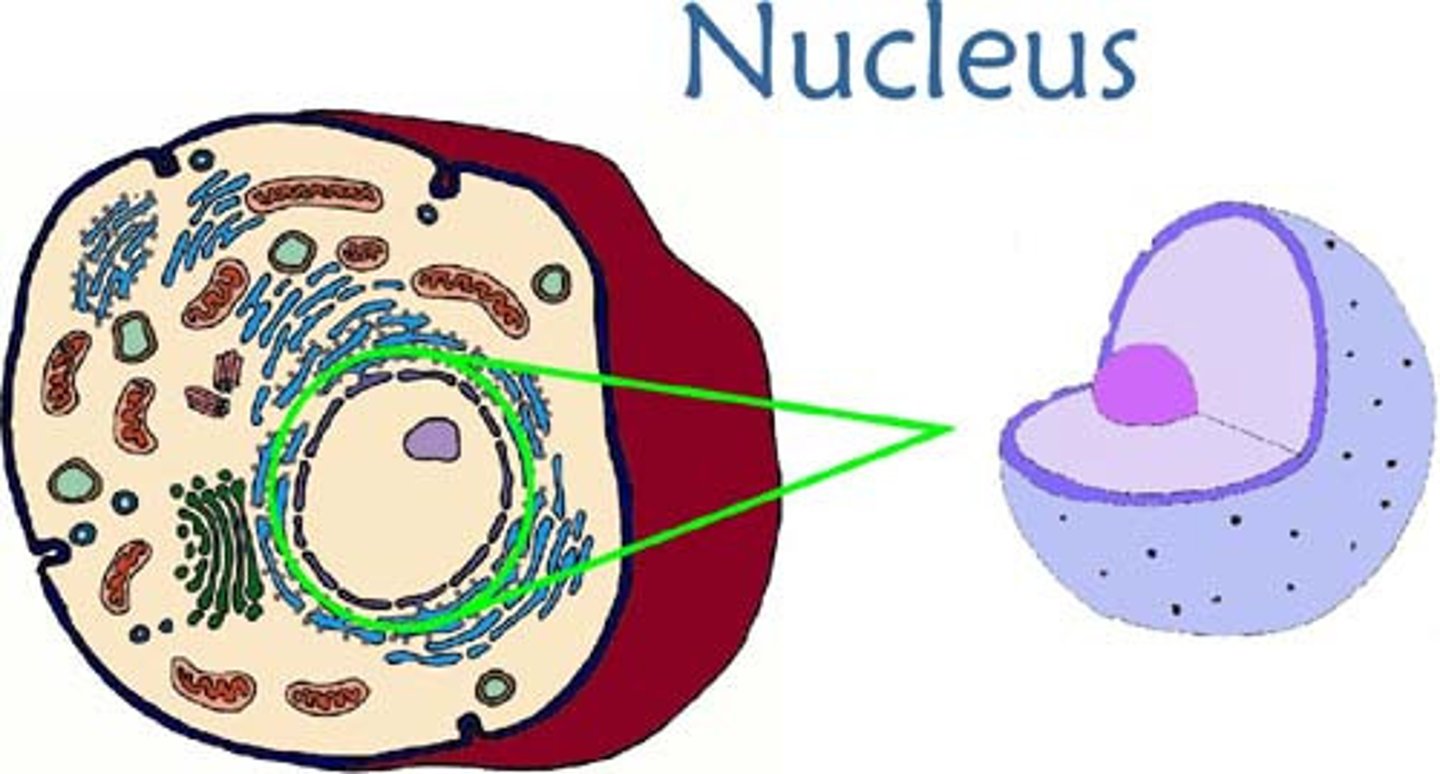
Nucleus
A part of the cell containing DNA and RNA and responsible for growth and reproduction
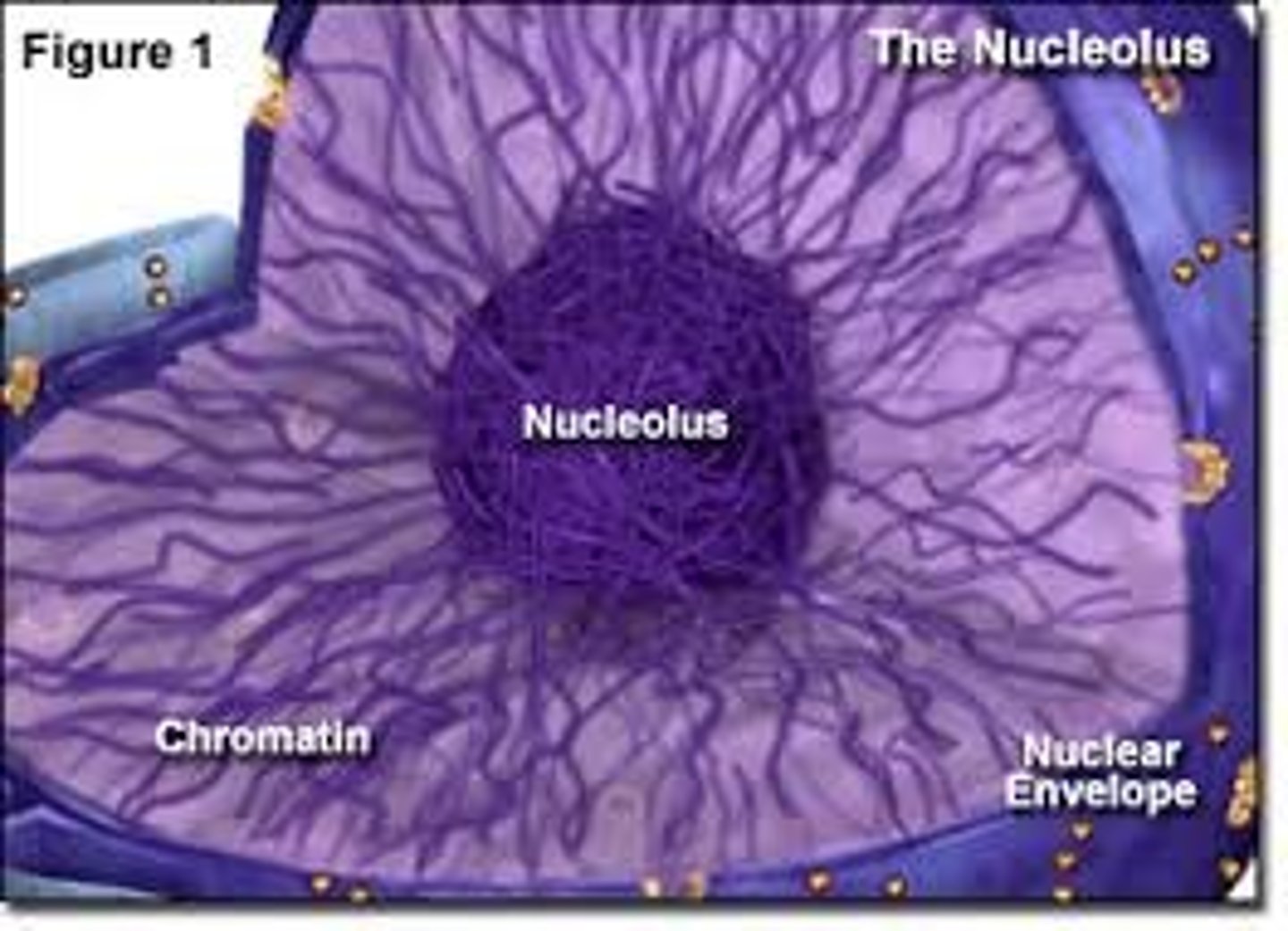
Chromatin
DNA
Nucleolus
Found inside the nucleus and produces ribosomes
Ribosomes
Makes proteins and on Rough ER
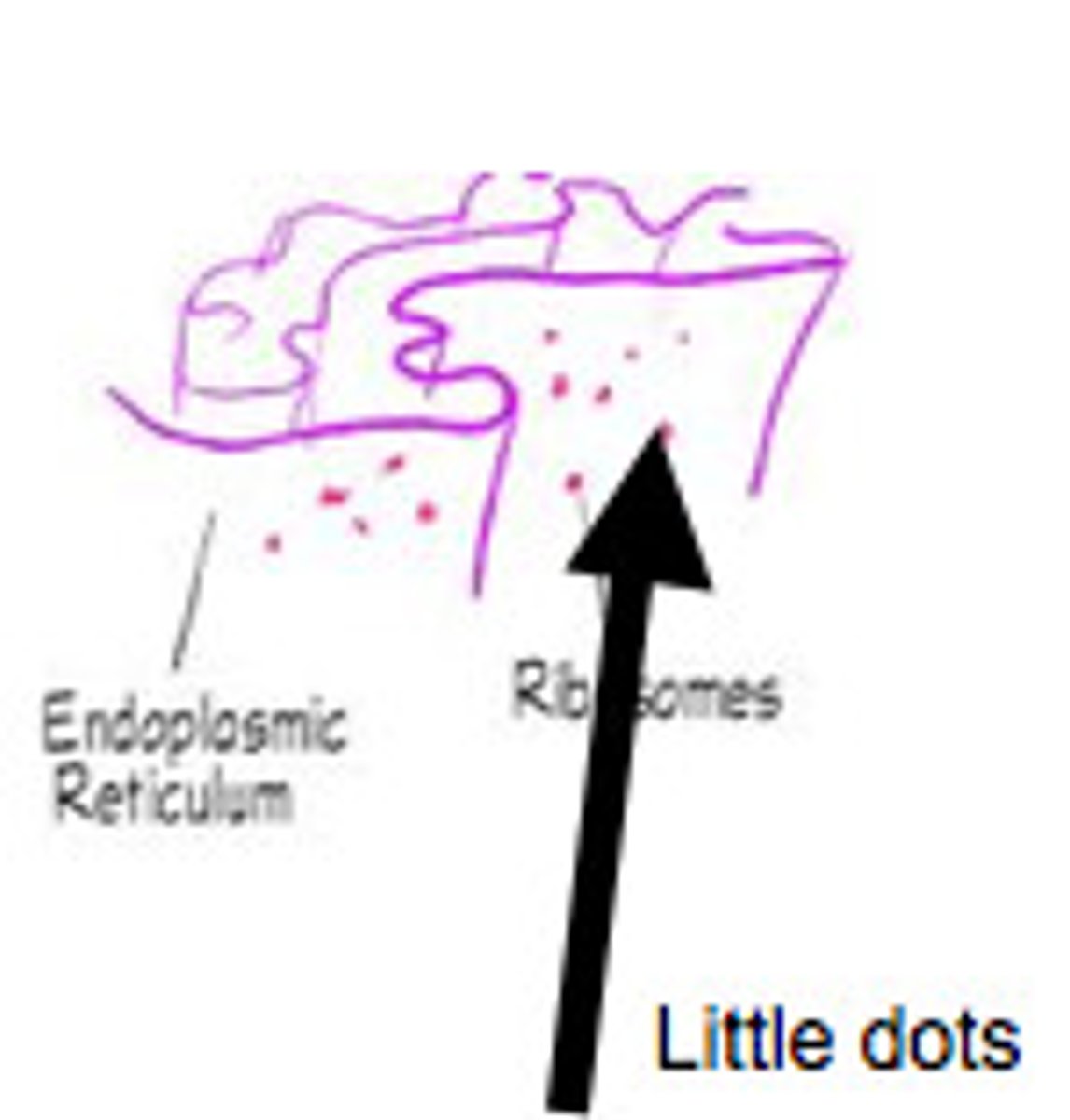
Vesicle
mini-cars that transport proteins around and out the cell
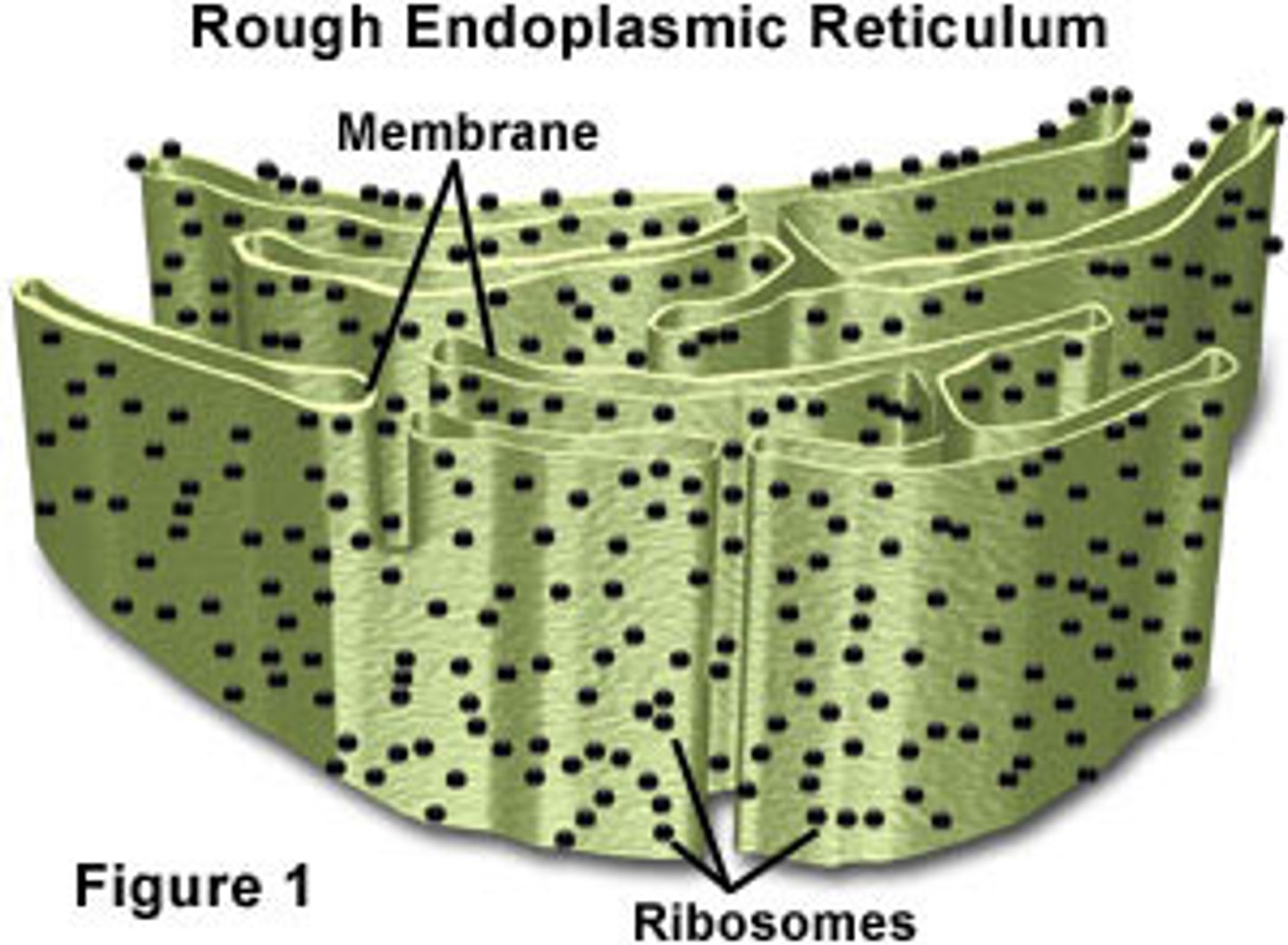
Rough ER
-ER that is dotted with ribosomes
-Makes & packages proteins
Smooth ER
-ER that has no ribosomes
-Makes lipids
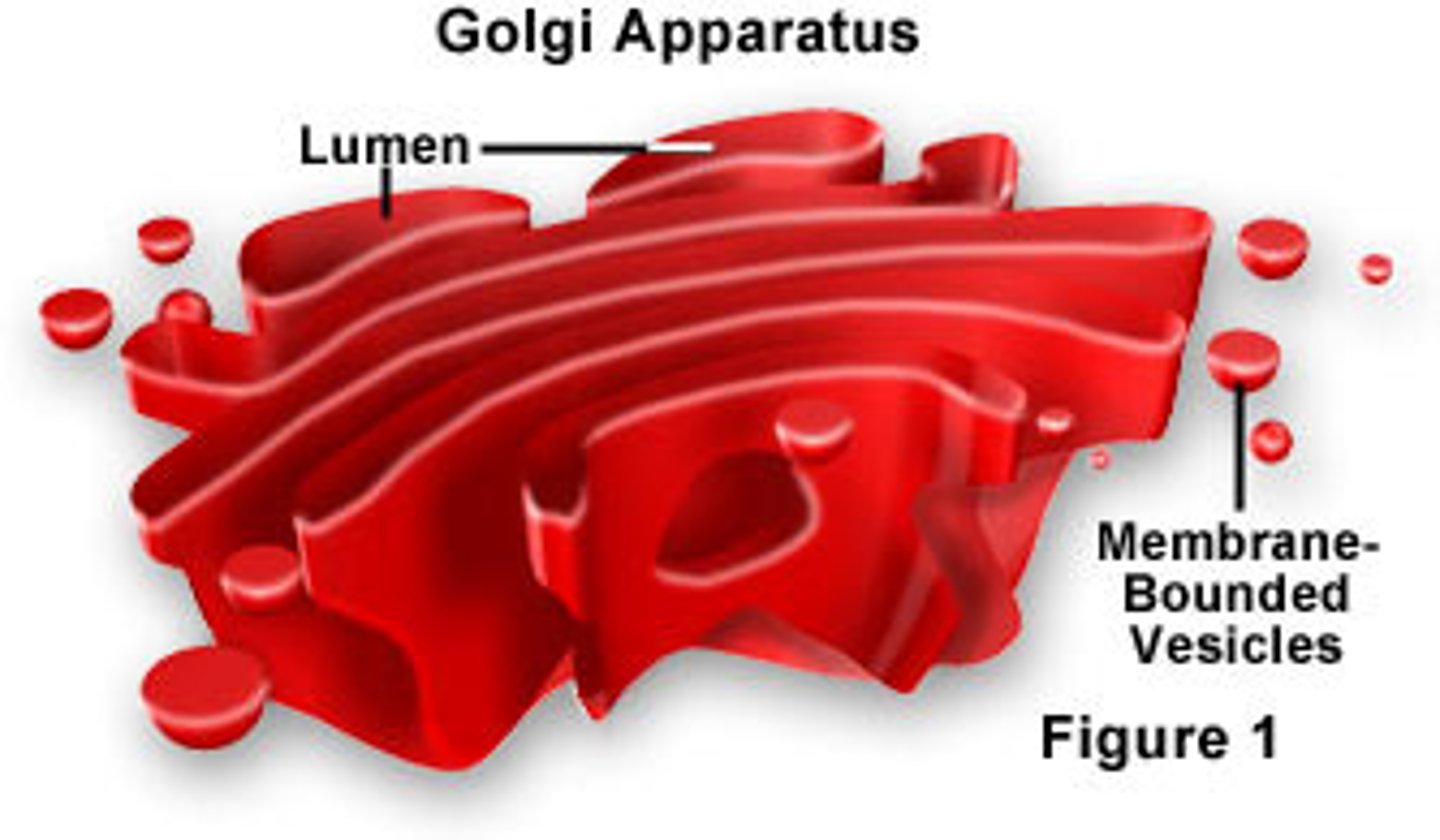
Golgi apparatus
A system of membranes that modifies and packages proteins for export by the cell
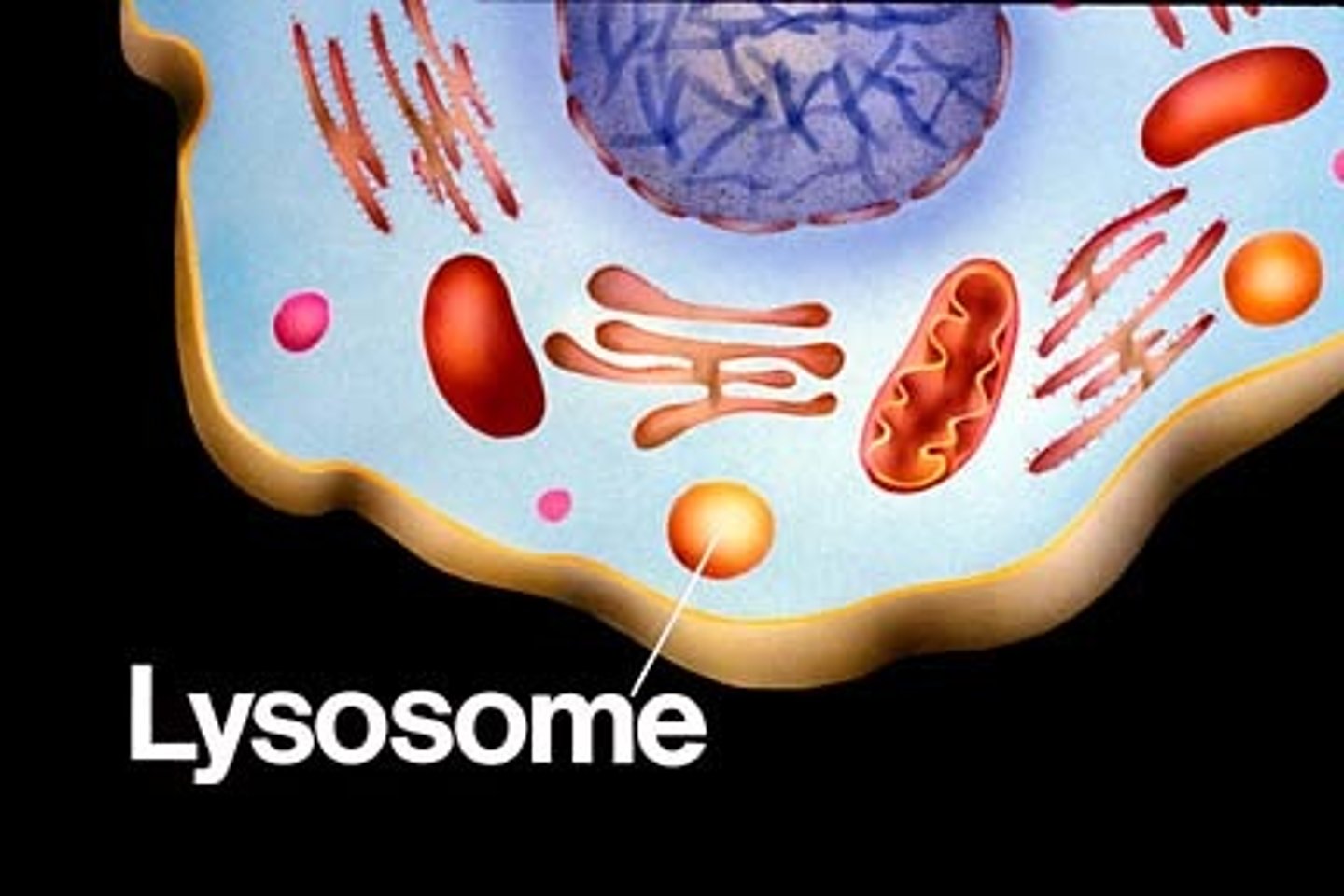
Lysosomes
contain hydrolytic enzymes for digestion
Vacuole
stores food, water, and waste
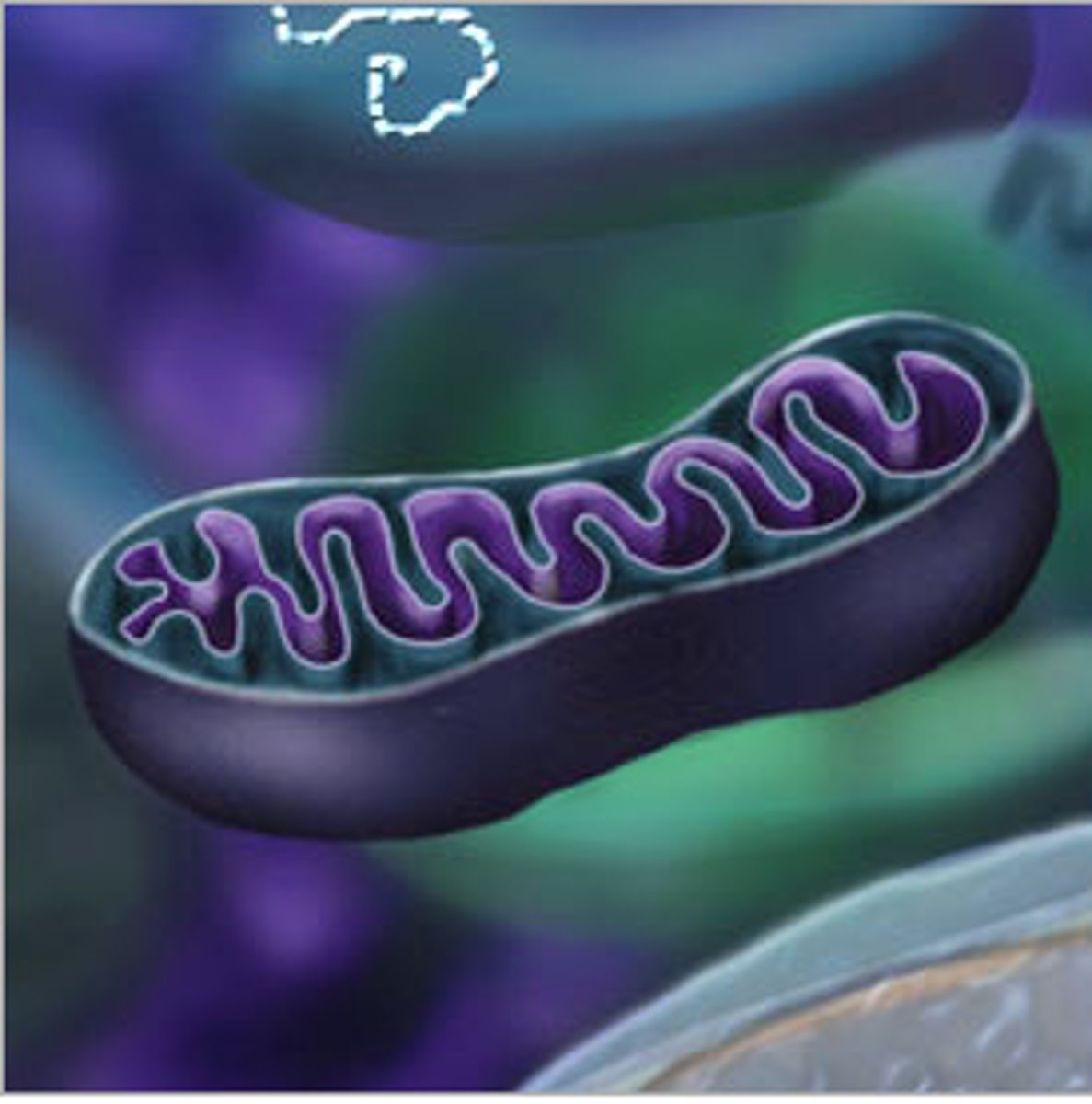
Mitochondria
breaks down energy to release ATP
Living Tissue Composition
cells are organized into tissue
70% water
26% macromolecules
Macromolecules
polymers built from monomers
nucleic acids
DNA and RNA
Lipids
fats, oils
Carbohydrates
monosaccharides
Proteins
amino acids
Enzymes
Catalysts
Interphase
-cell spends most life here
-DNA is doubled
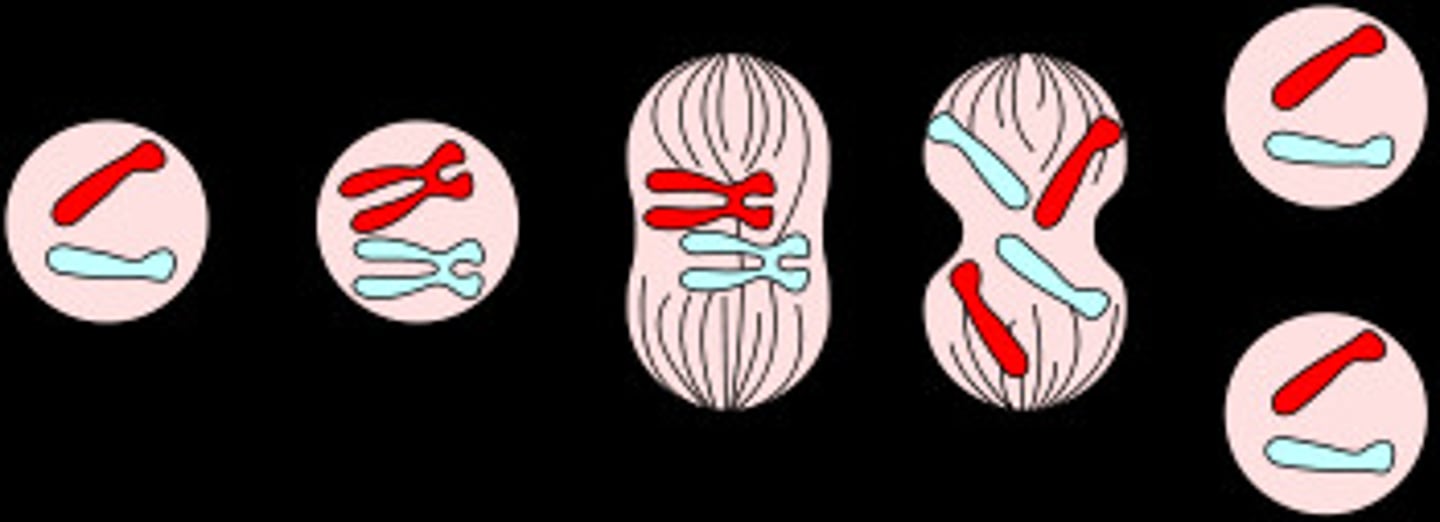
Mitosis
cell division
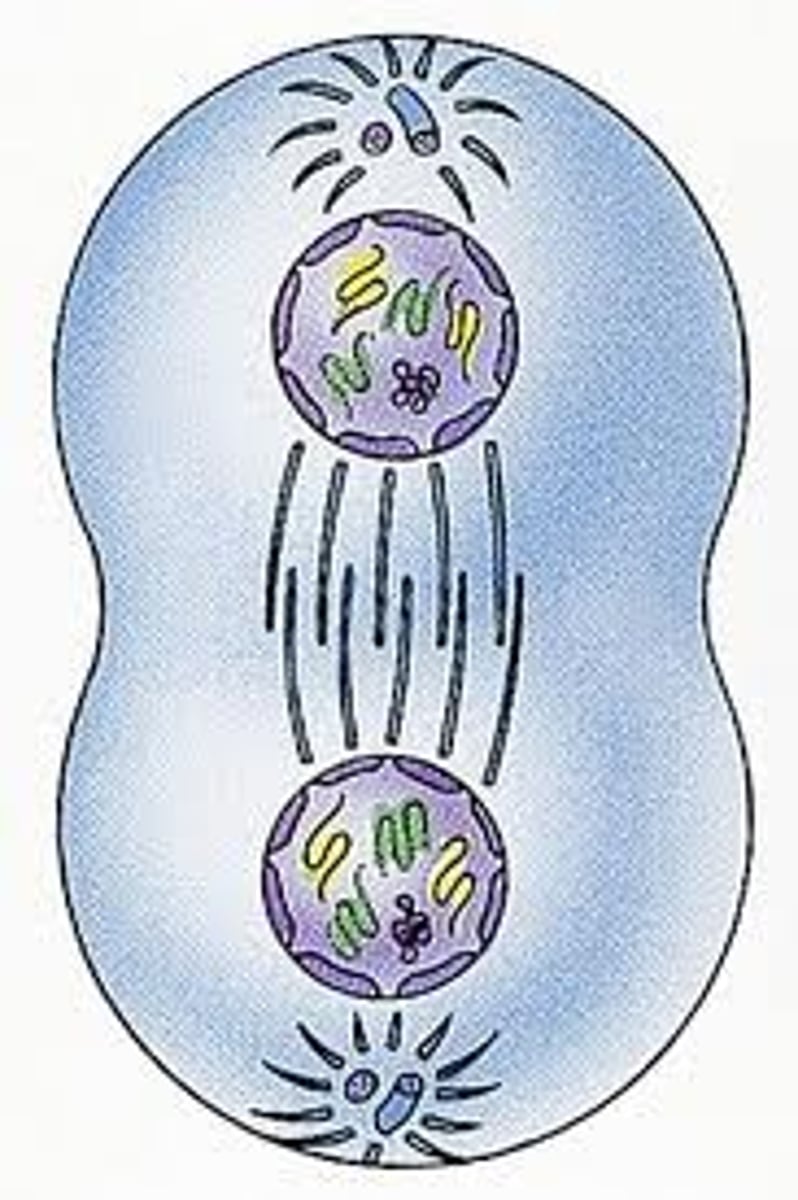
Cytokinesis
division of the cytoplasm
Prophase
first and longest phase of mitosis, during which the chromosomes become visible and the centrioles separate and take up positions on the opposite sides of the nucleus

Metaphase
Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
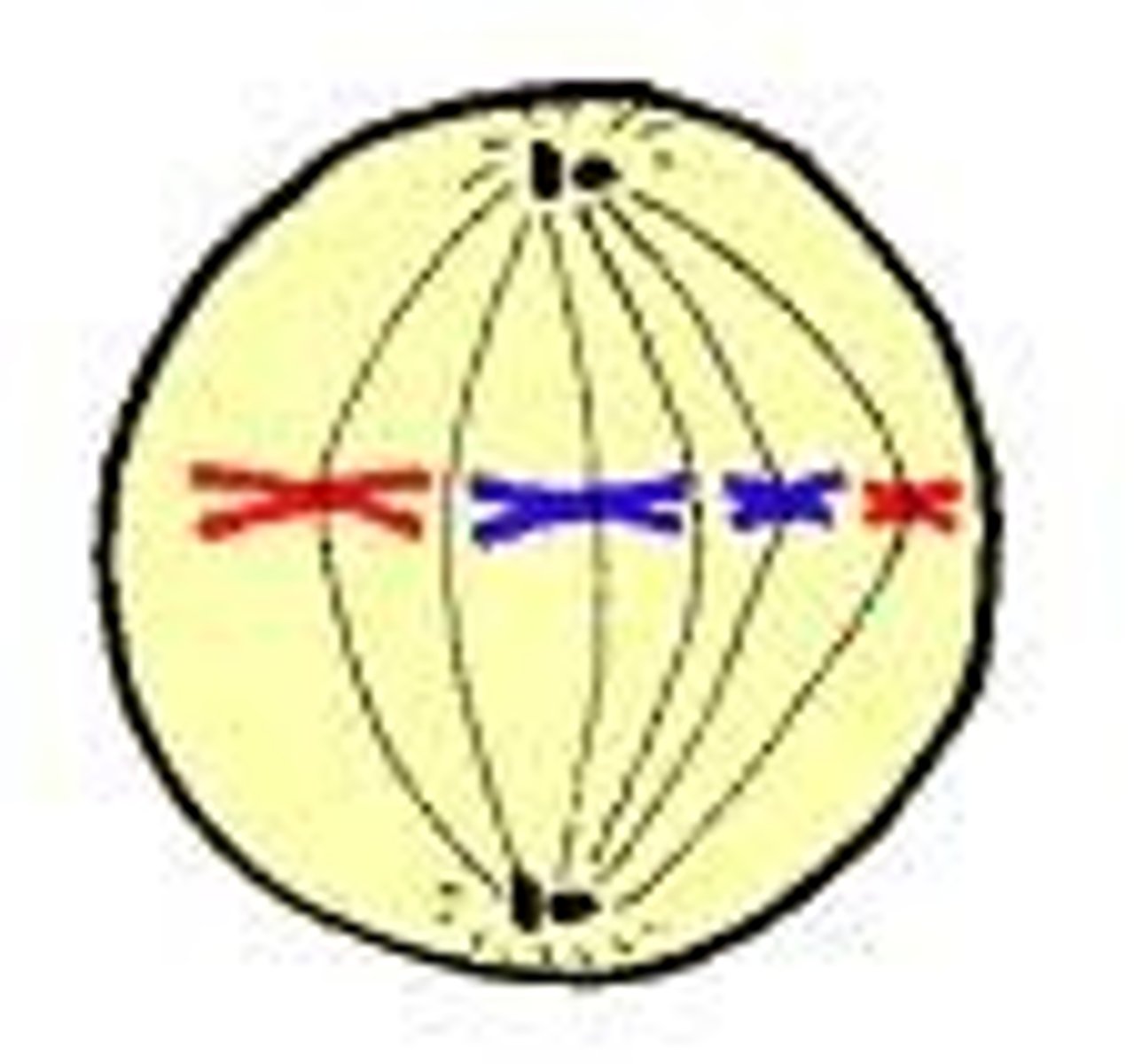
Anaphase
Phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell
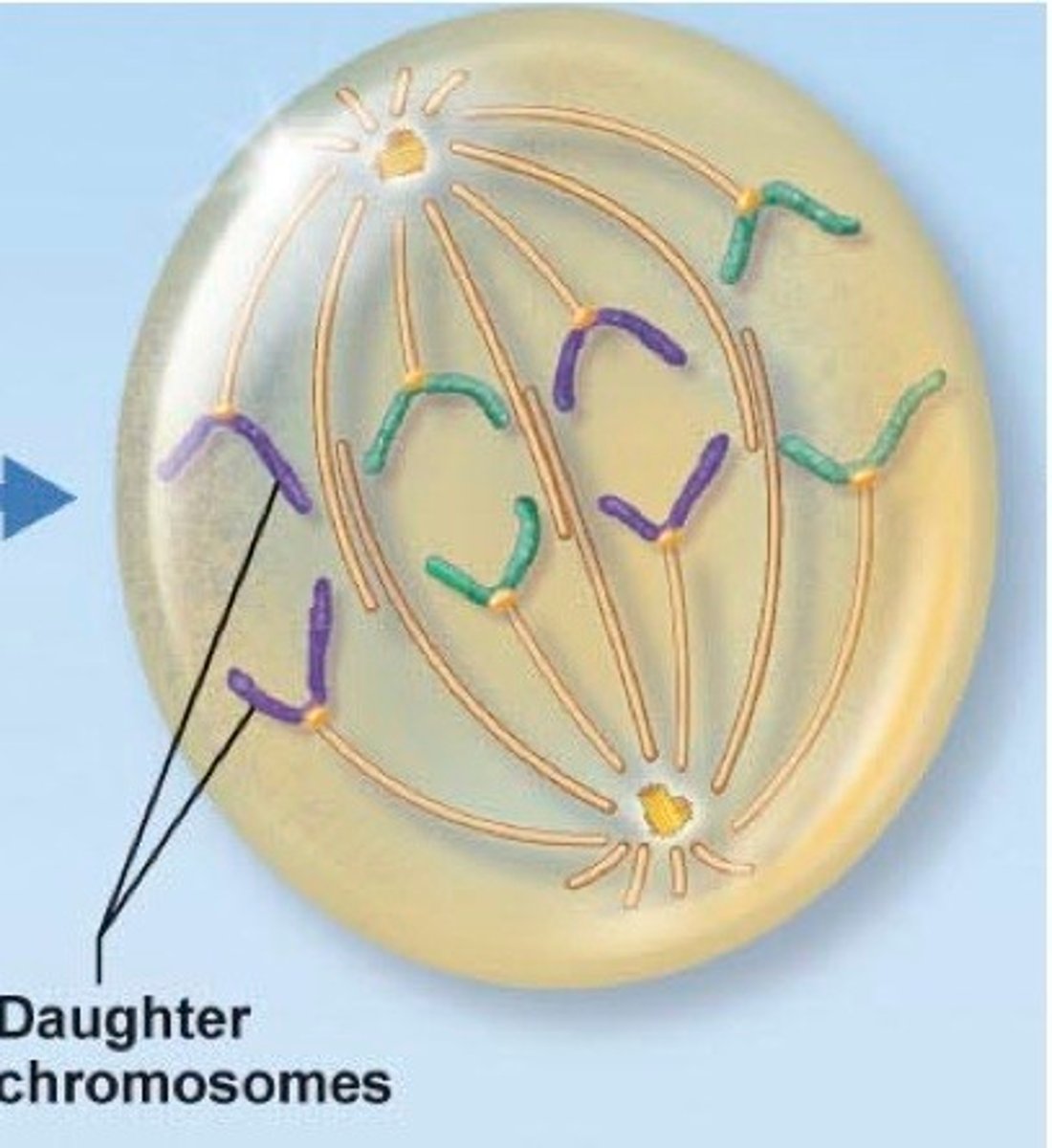
Telophase
After the chromosome seperates, the cell seals off, Final Phase of Mitosis.
Smallest to largest levels of organization
chromosome, macromolecule, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism
Differentiation
process in which cells become specialized in structure and function
gene expression
what a cell becomes
mitochondrial matrix
the fluid that is inside the inner membrane of a mitochondrion
mitochondrial cristae
folds of the mitochondrial inner membrane that provide an increase in the surface area