Theories of Enzyme Action
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
What does the lock and key hypothesis describe in enzyme activity?
The active site of an enzyme is like a lock that only a complementary substrate molecule can fit into, like a key.
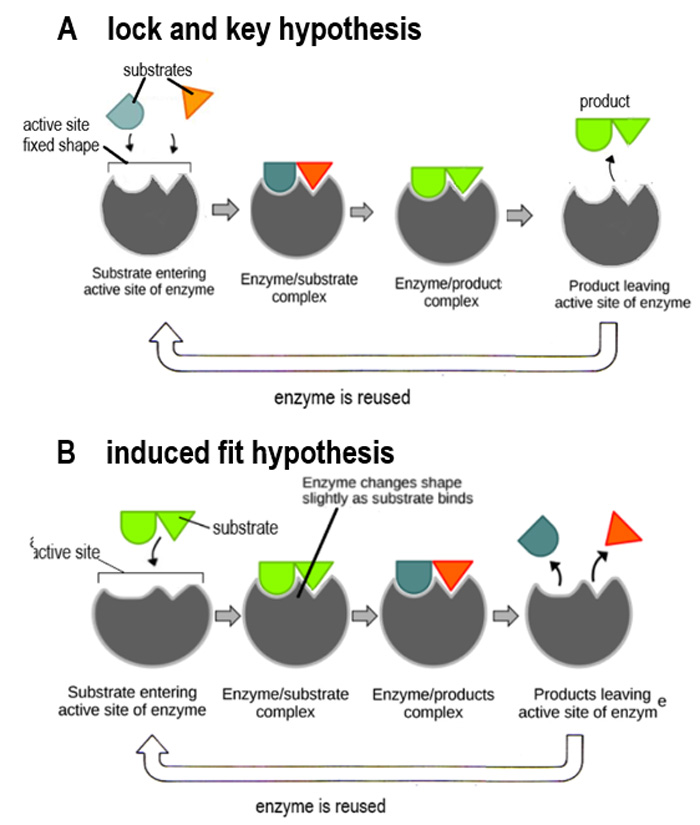
What is the role of the active site in enzyme function? (Lock and Key)
The active site has a fixed shape and must collide correctly with the substrate for bonding to occur.
What is an enzyme-substrate complex?
A temporary complex formed when a substrate binds to an enzyme's active site.
What types of reactions can enzymes facilitate according to the lock and key hypothesis?
Enzymes can either break down substrates (catabolism) or combine substrates to form products (anabolism).
What process is referred to as anabolism in enzymatic reactions?
The process where two substrate molecules are combined to form a single product molecule.
What does catabolism refer to in enzyme reactions?
The process where enzymes break down complex substrate molecules into two or more product molecules.
What is the induced fit hypothesis in enzyme activity?
The theory that describes how the active site changes shape upon substrate binding, enhancing interaction.
How does the induced fit hypothesis affect the activation energy of a reaction?
It lowers the activation energy by straining the bonds in the substrate.
What happens to the active site after products are released in the induced fit hypothesis?
The active site returns to its original shape.
Is the enzyme affected by the reactions it facilitates, after catalysing a reaction?
No, enzymes are not affected by the reactions and can be reused.
What is an example of an enzyme that demonstrates the induced fit hypothesis?
Lysozyme.