✅️⭐️6 - Thoracic Limb Muscles & Joints 2
1/155
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
156 Terms
flexor
The following muscles are part of the [extensor/flexor] group:
-flexor carpi radialis
-superficial digital flexor
-flexor carpi ulnaris
-deep digital flexor
2 multiple choice options
extensor
The arrow on the left is pointing to [extensor/flexor] muscles
2 multiple choice options
![<p>The arrow on the left is pointing to [extensor/flexor] muscles</p><p>2 multiple choice options</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/8f2f955a-8b15-4941-a9fc-89d942250ced.jpg)
flexor
The arrow on the right is pointing to [extensor/flexor] muscles
2 multiple choice options
![<p>The arrow on the right is pointing to [extensor/flexor] muscles</p><p>2 multiple choice options</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/945261cf-132b-4dbf-93b4-f97eb3c5d70a.jpg)
flexor carpi radialis
What muscle is shown?
medial epicondyle of the humerus
Origin of flexor carpi radialis:
palmar base of 2nd and 3rd metacarpal bones
Insertion of flexor carpi radialis:
flex the carpal joints
Action of flexor carpi radialis:
flexor carpi radialis
What muscle are the following associated with?
Origin: medial epicondyle of the humerus
Insertion: palmar base of 2nd and 3rd metacarpal bones
Action: flex the carpal joints
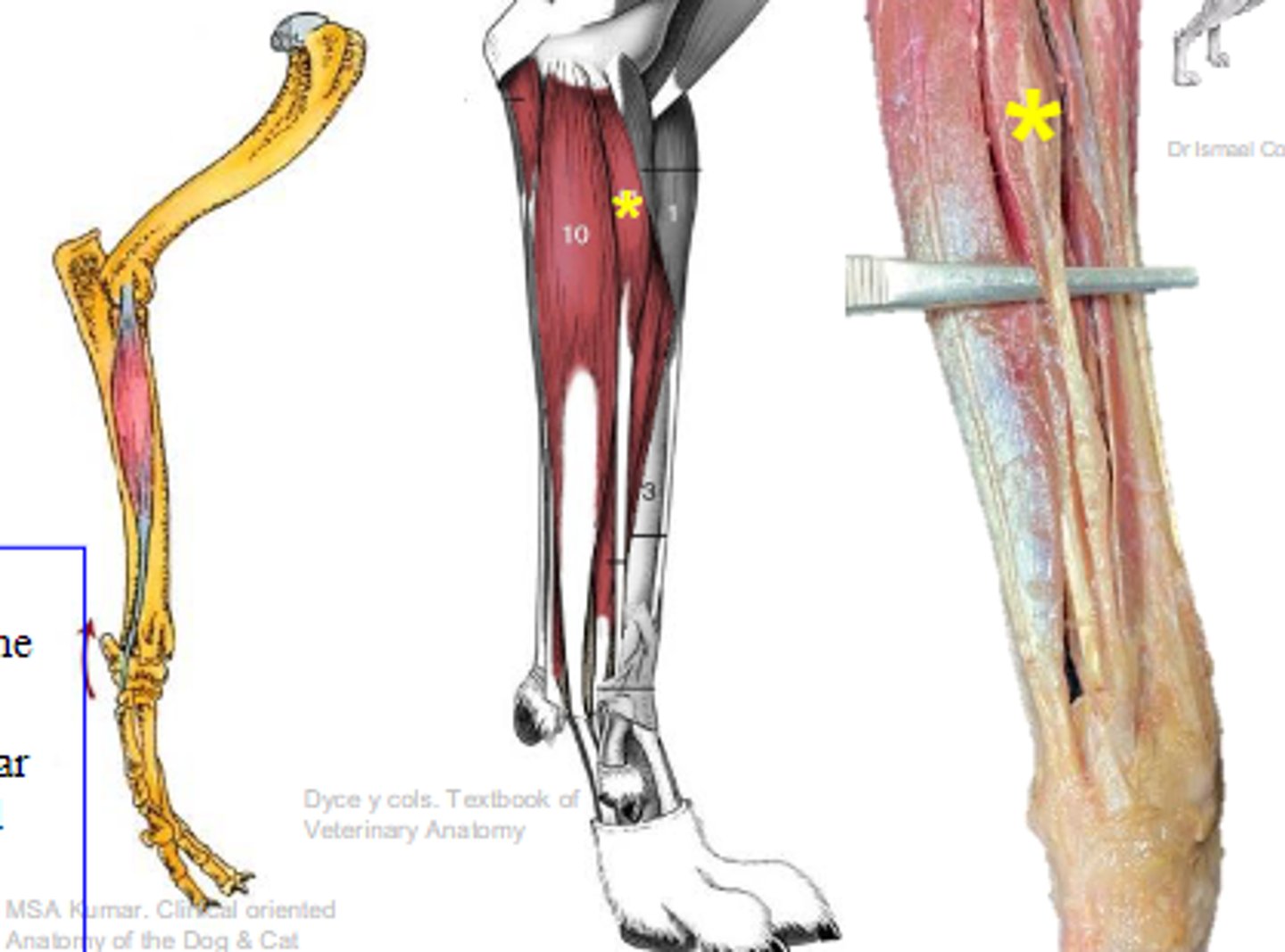
superficial digital flexor
What muscle is shown?
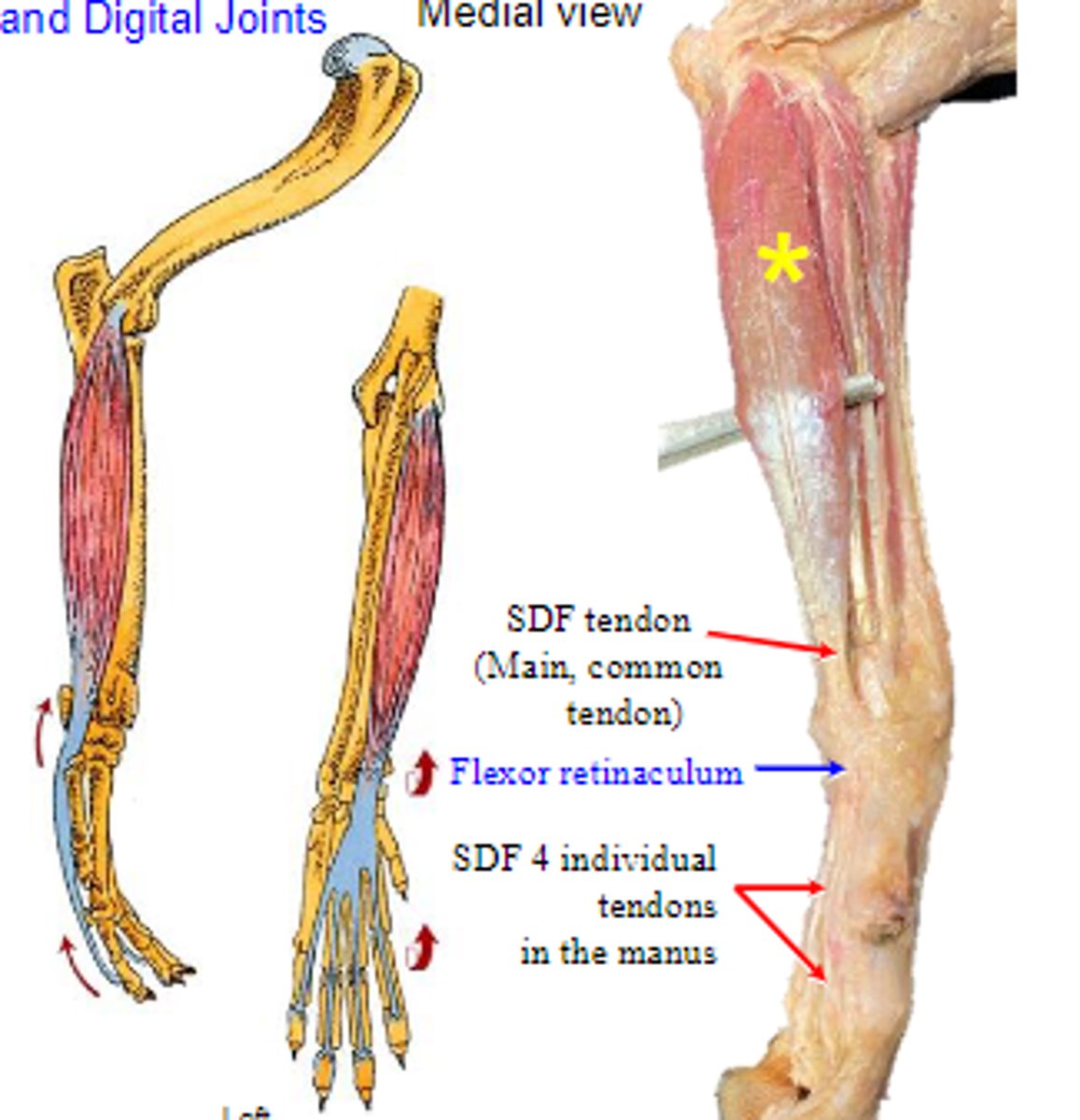
medial epicondyle of humerus
Origin of superficial digital flexor:
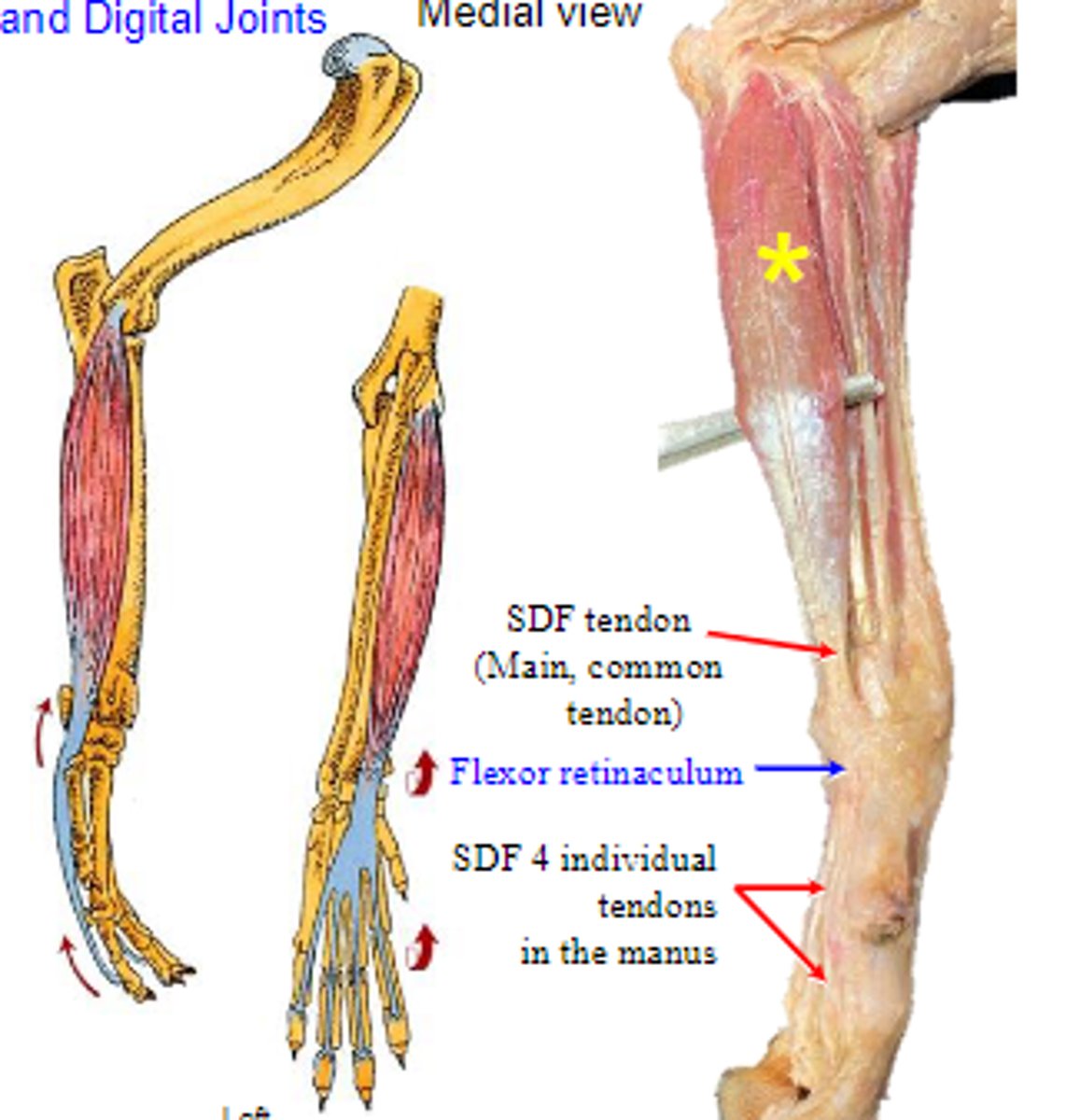
palmar bases of middle phalanges
Insertion of superficial digital flexor:
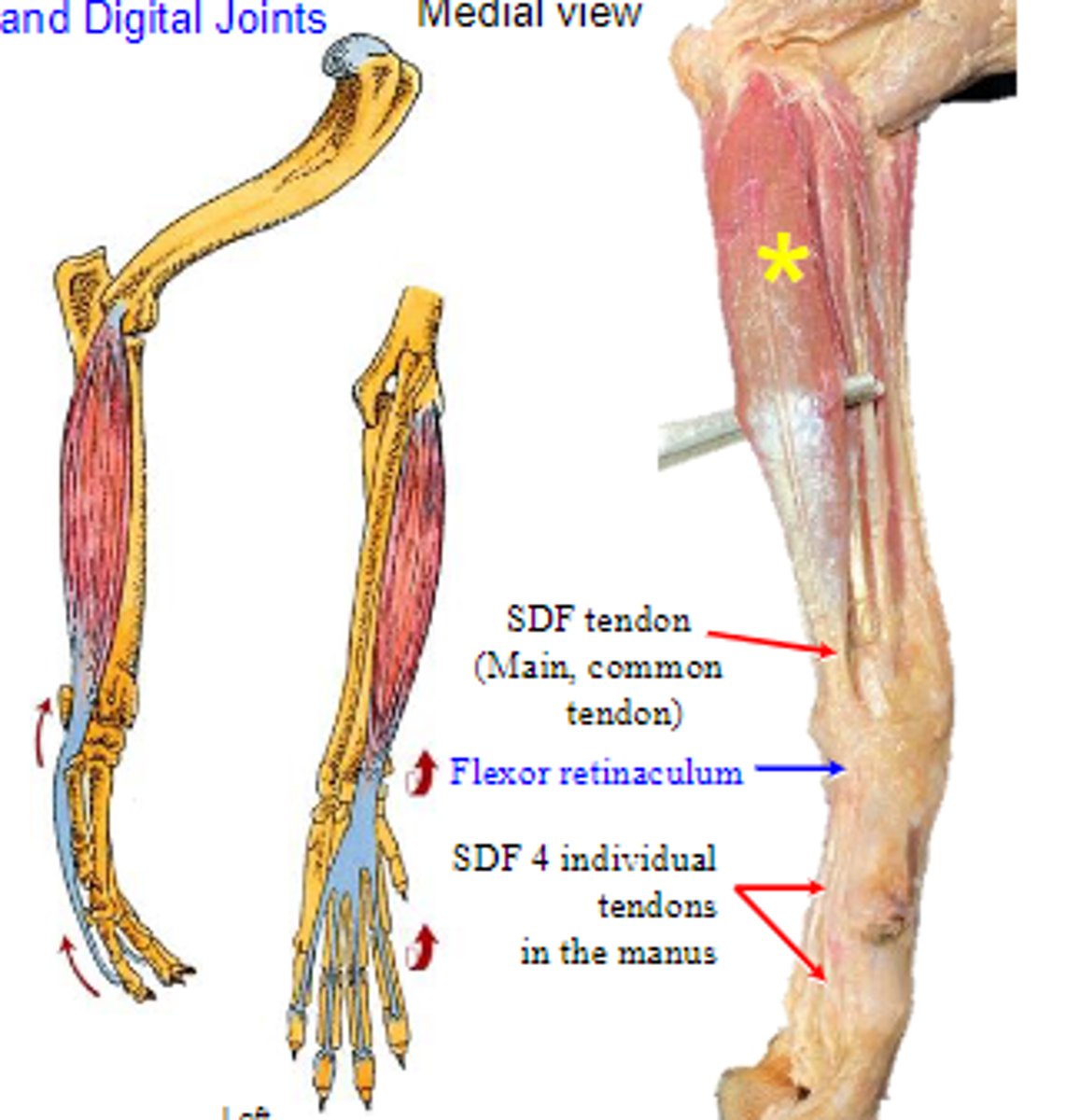
flex the carpal joints; flex the metacarpophalangeal joints; flex the proximal interphalangeal joints
Action of superficial digital flexor:
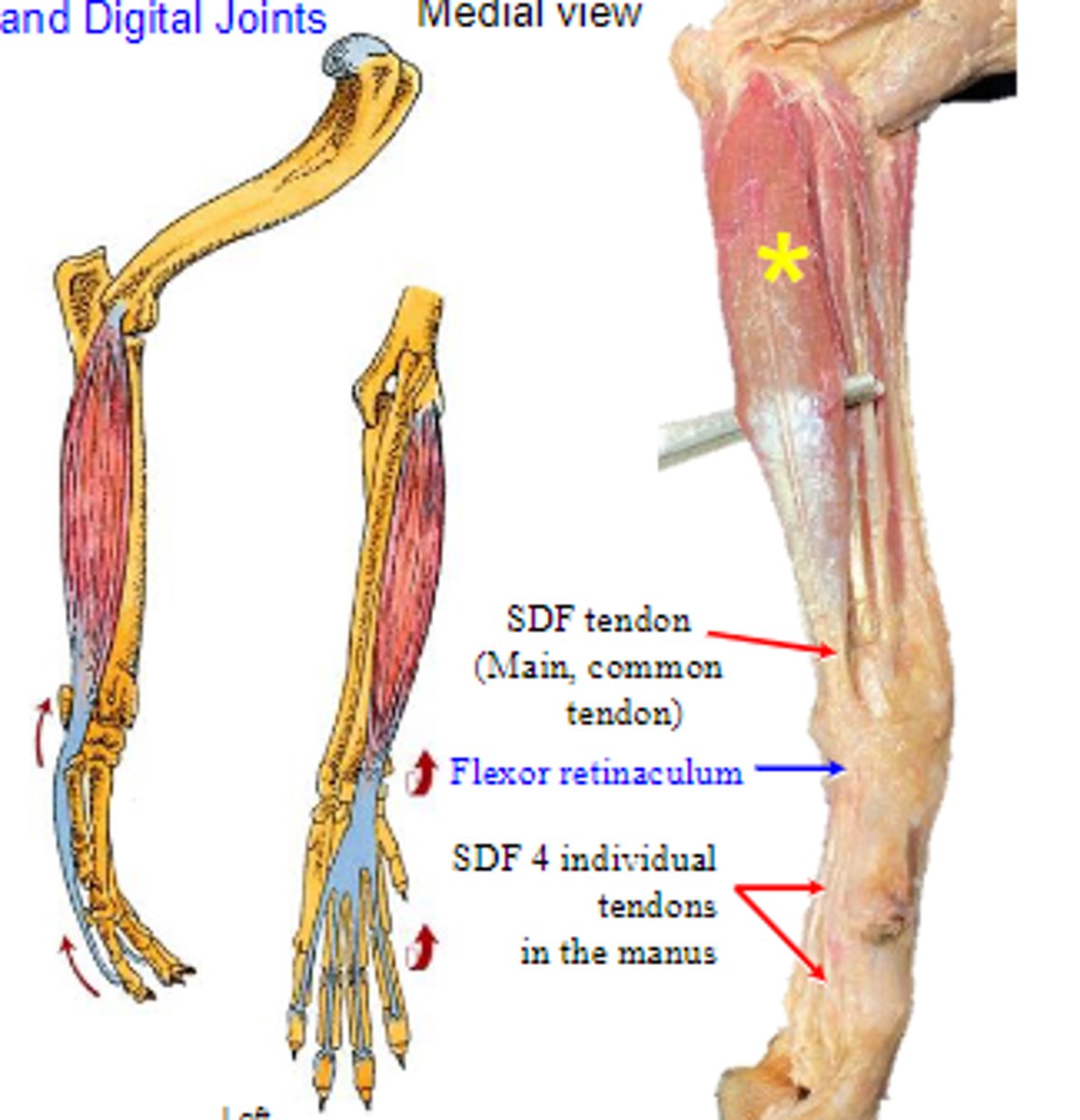
superficial digital flexor
The following are associated with what muscle?
Origin: medial epicondyle of the humerus
Insertion: palmar bases of the middle phalanges
Action: flex the carpal joints; flex the metacarpophalangeal joints; flex the proximal interphalangeal joints
flexor carpi ulnaris
What muscle is shown?
medial epicondyle of the humerus olecranon of the ulna
Origin of flexor carpi ulnaris:
accessory carpal bone
Insertion of flexor carpi ulnaris:
flex the antebrachiocarpal joint
Action of flexor carpi ulnaris:
flexor carpi ulnaris
The following are associated with what muscle?
Origin: medial epicondyle of the humerus olecranon of the ulna
Insertion: accessory carpal bone
Action: flex the antebrachiocarpal joint
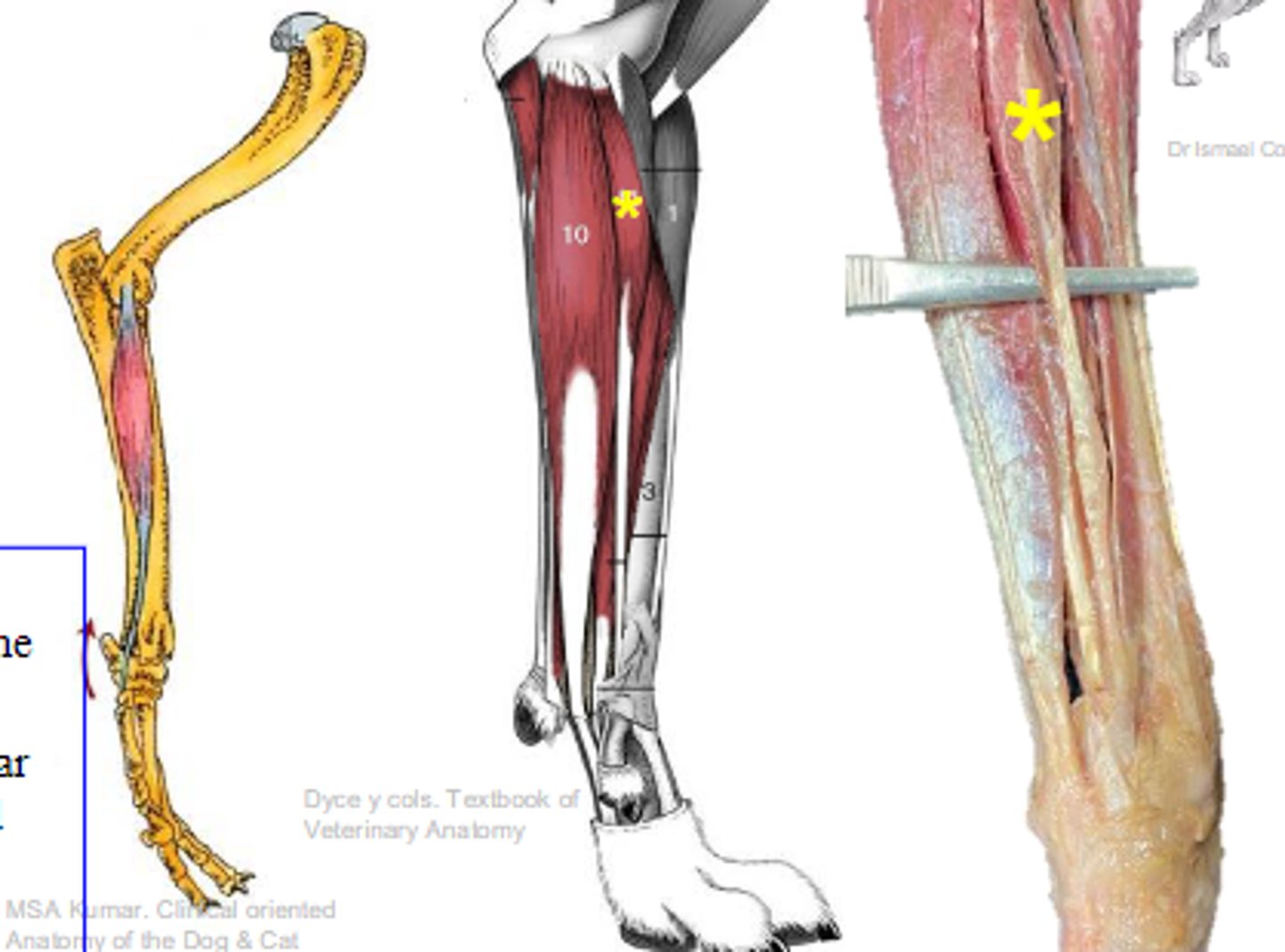
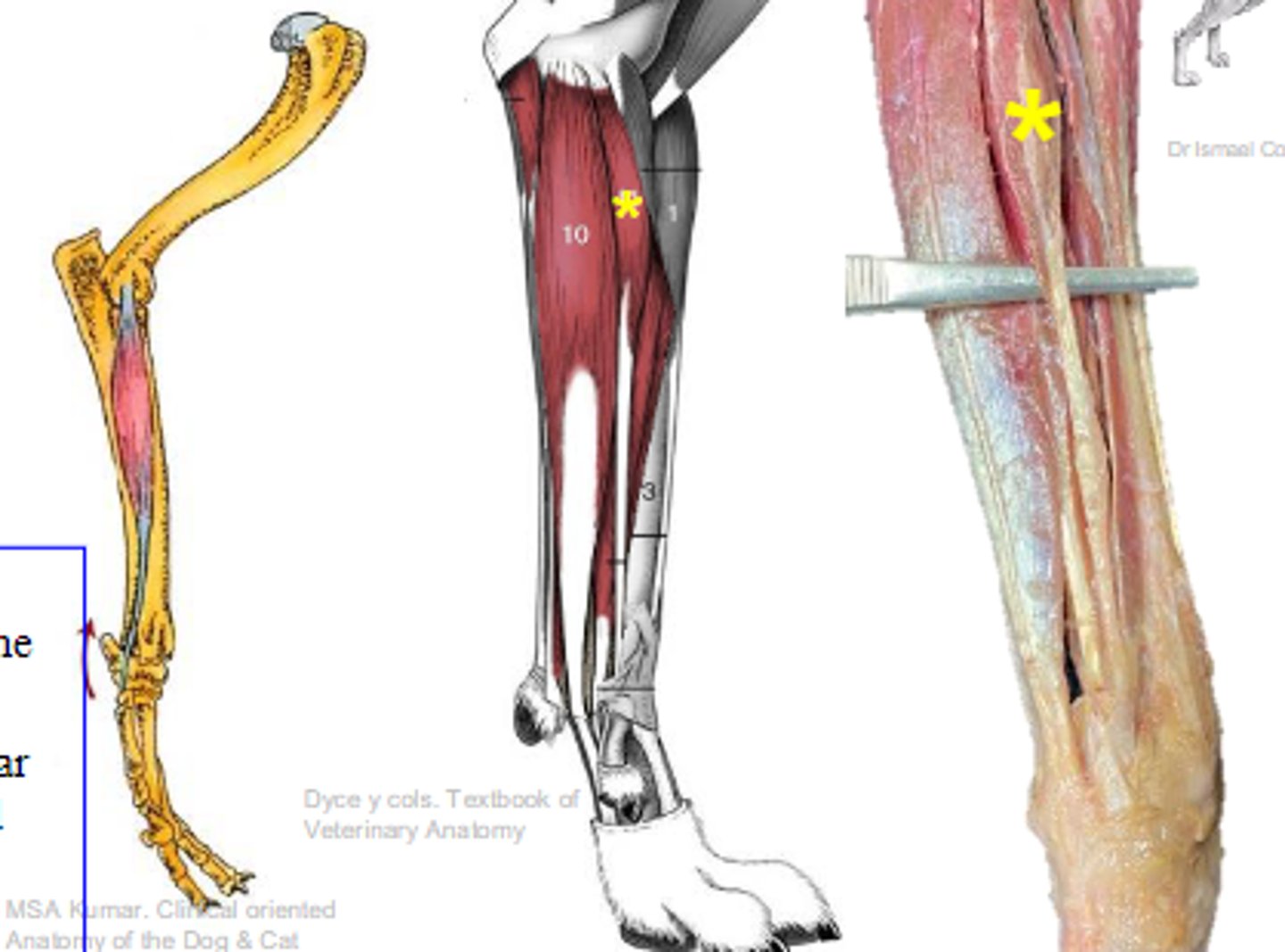
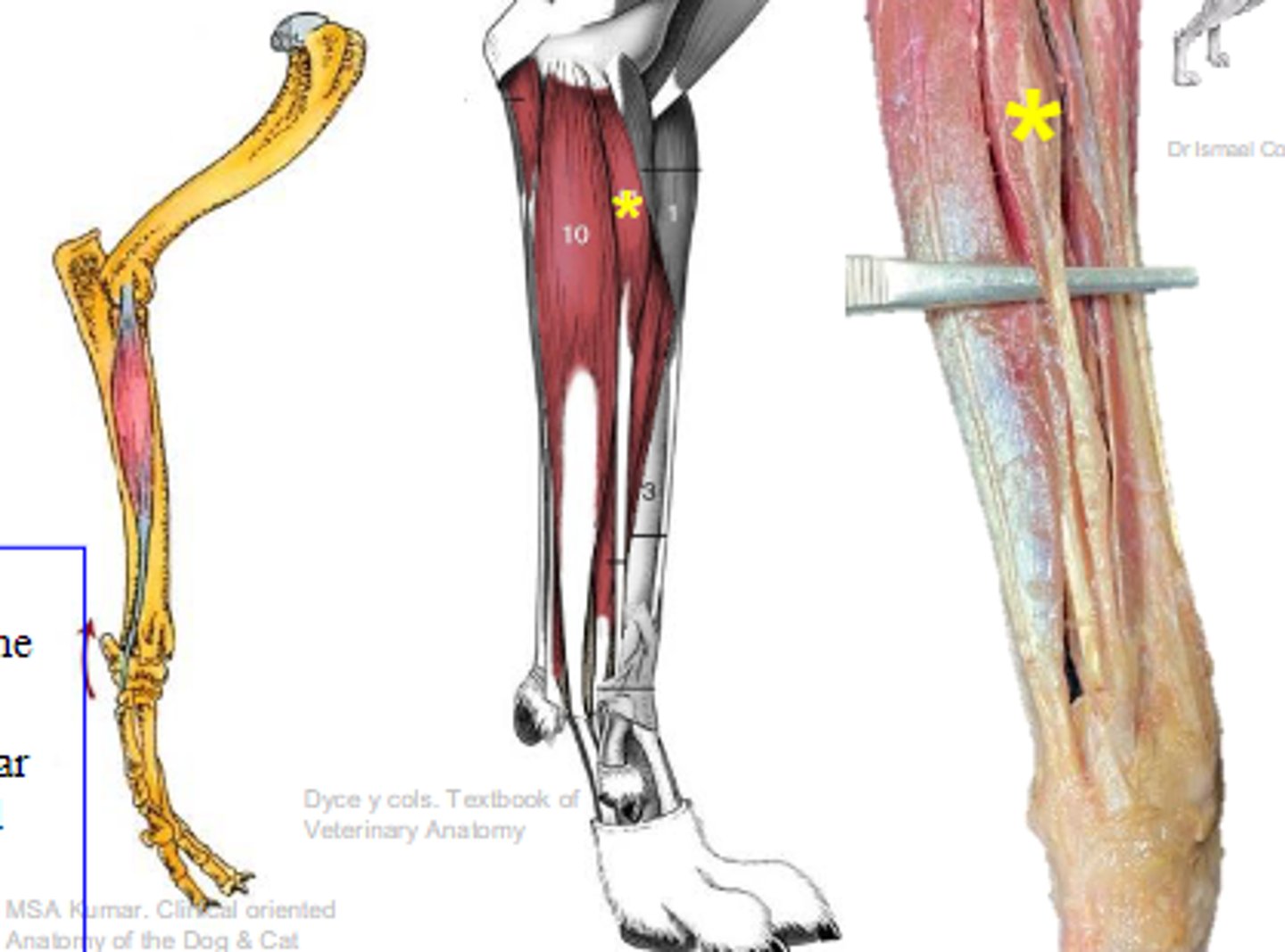
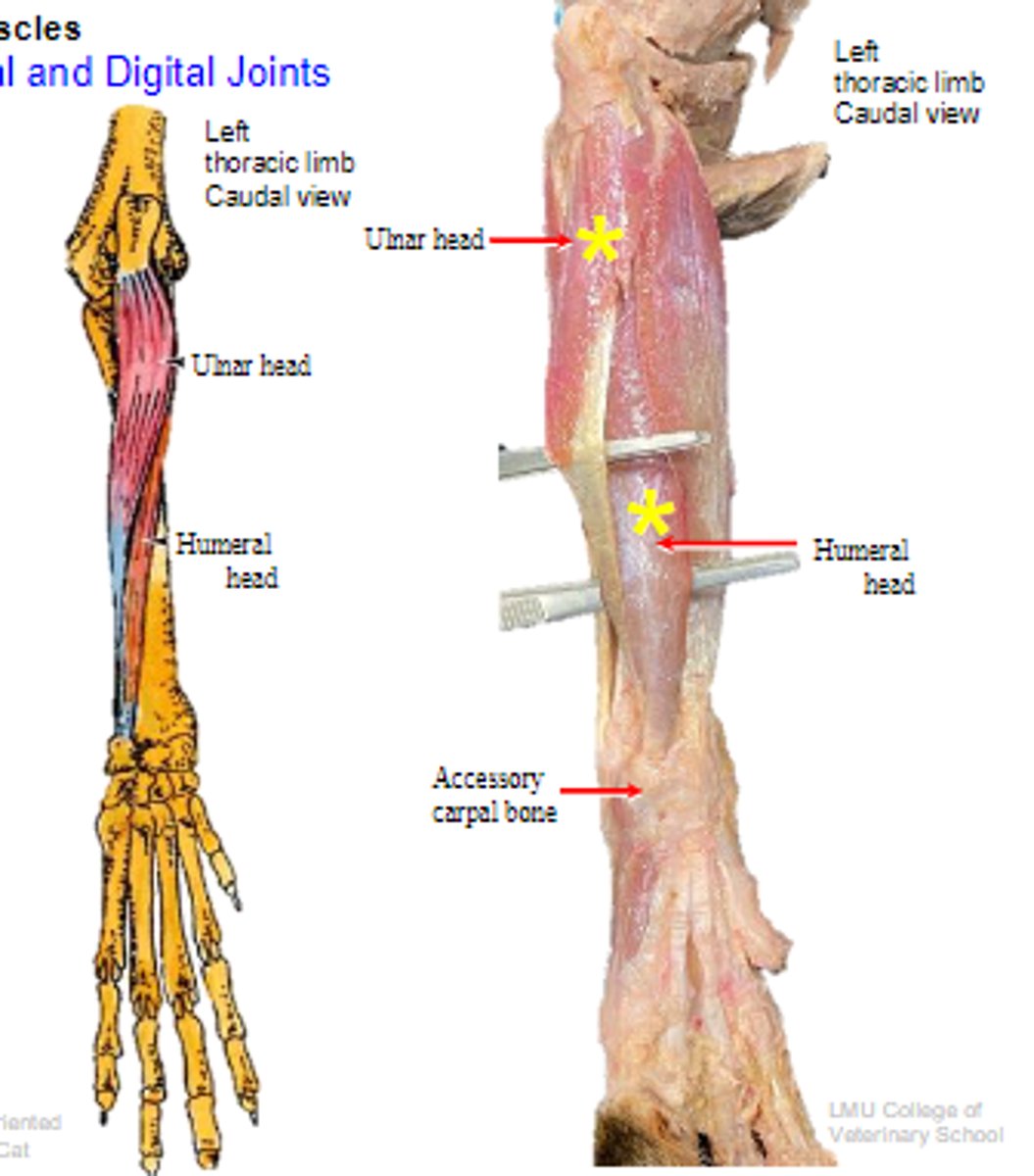
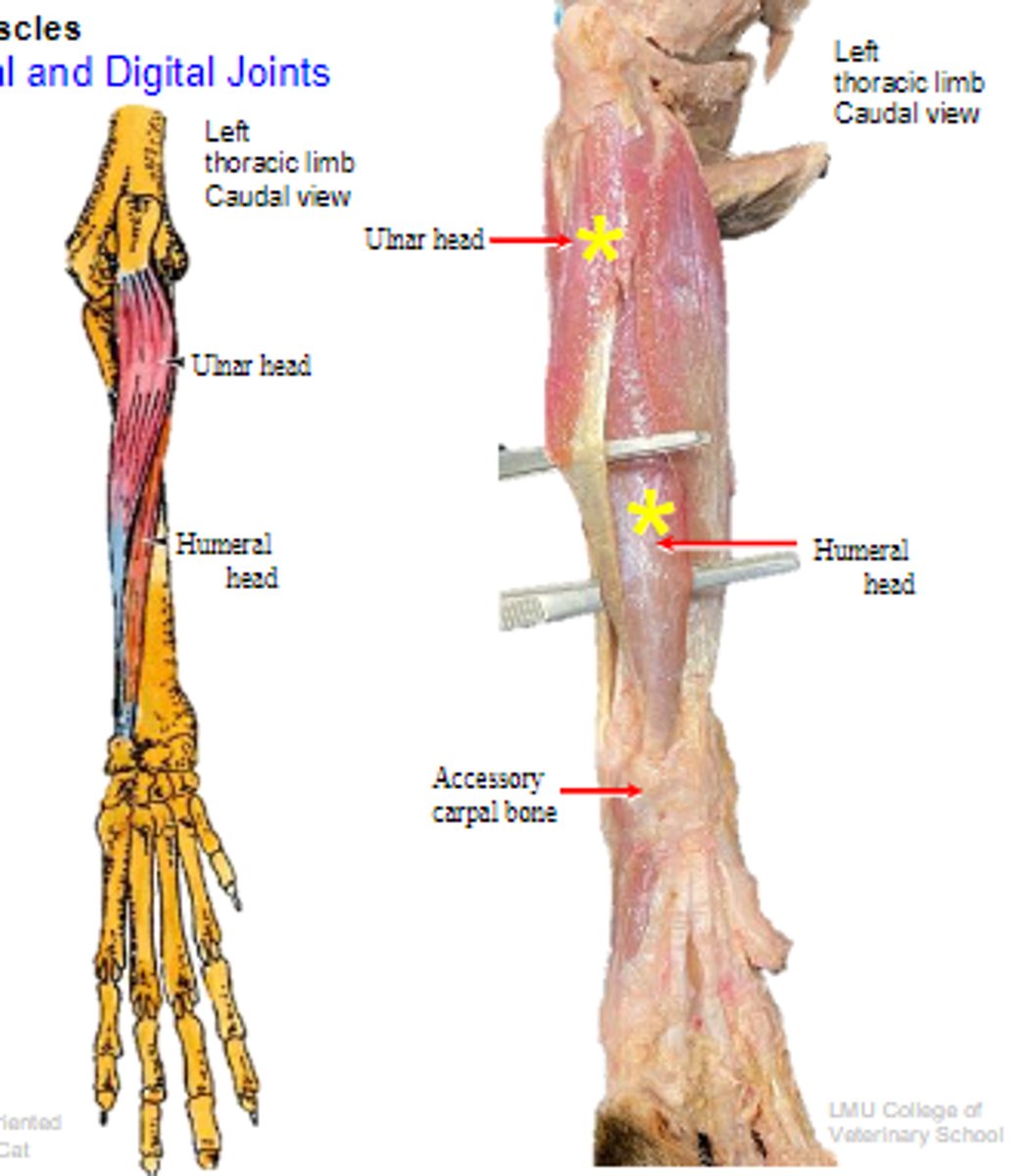
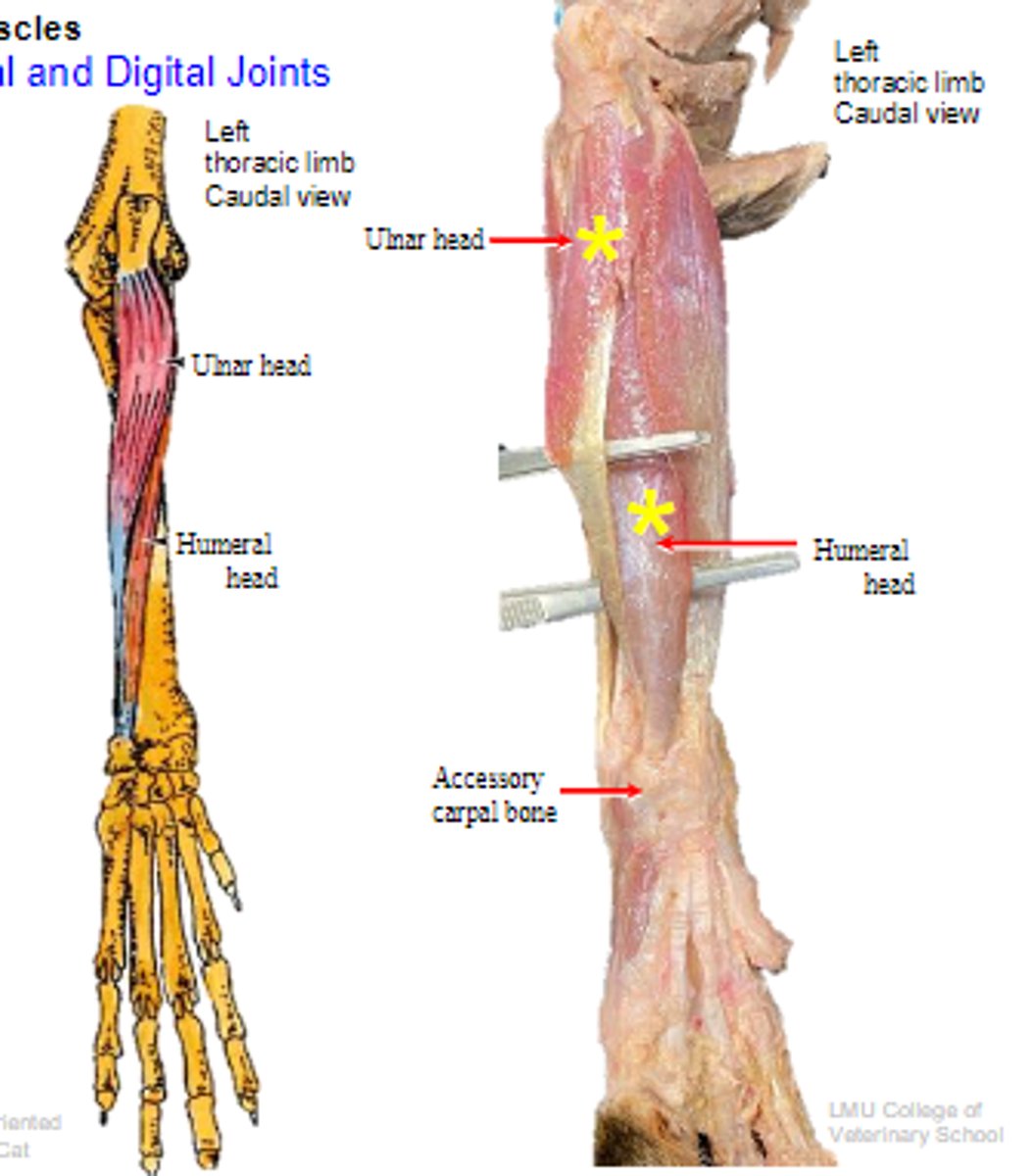
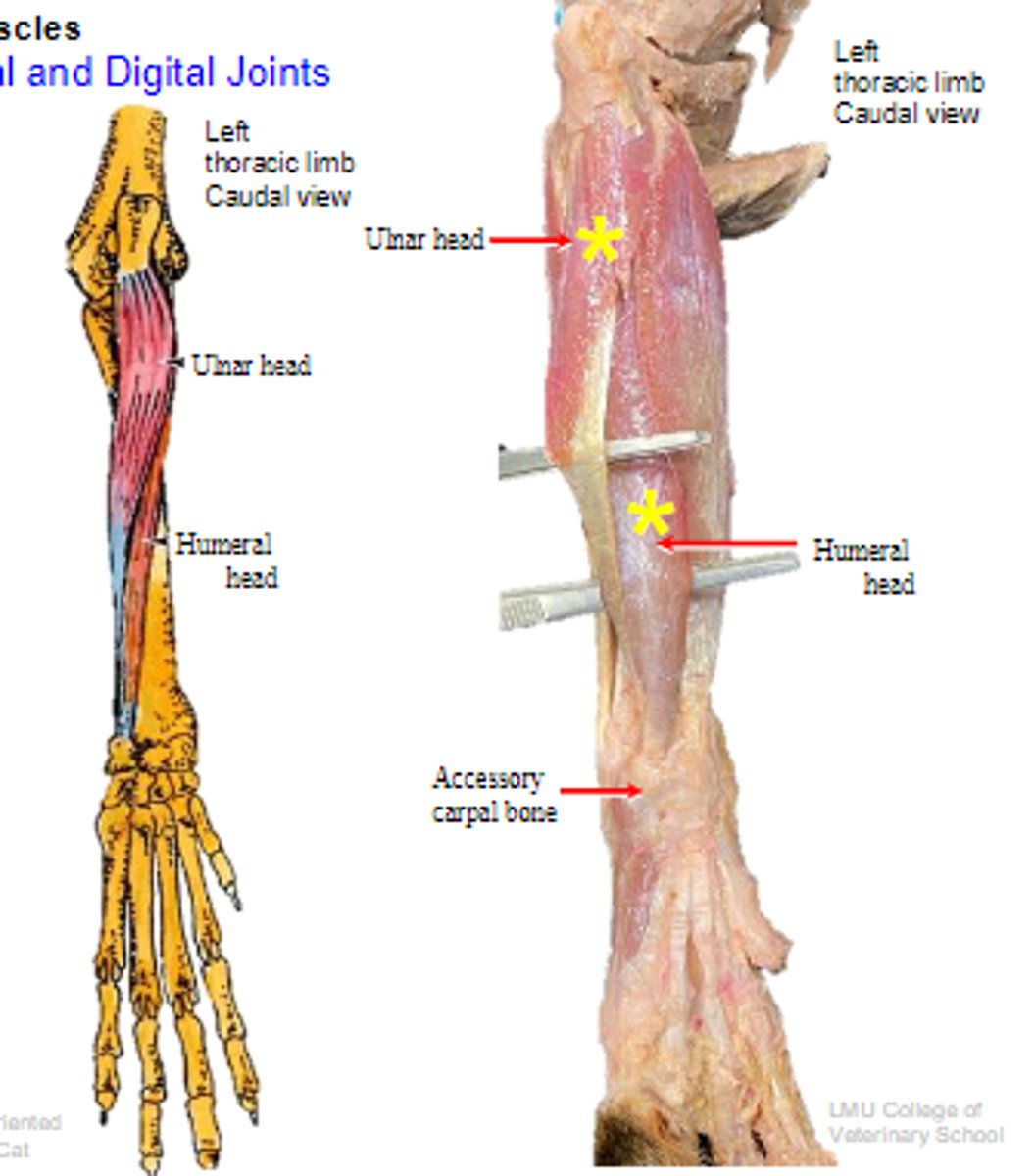
deep digital flexor
What muscle is shown?
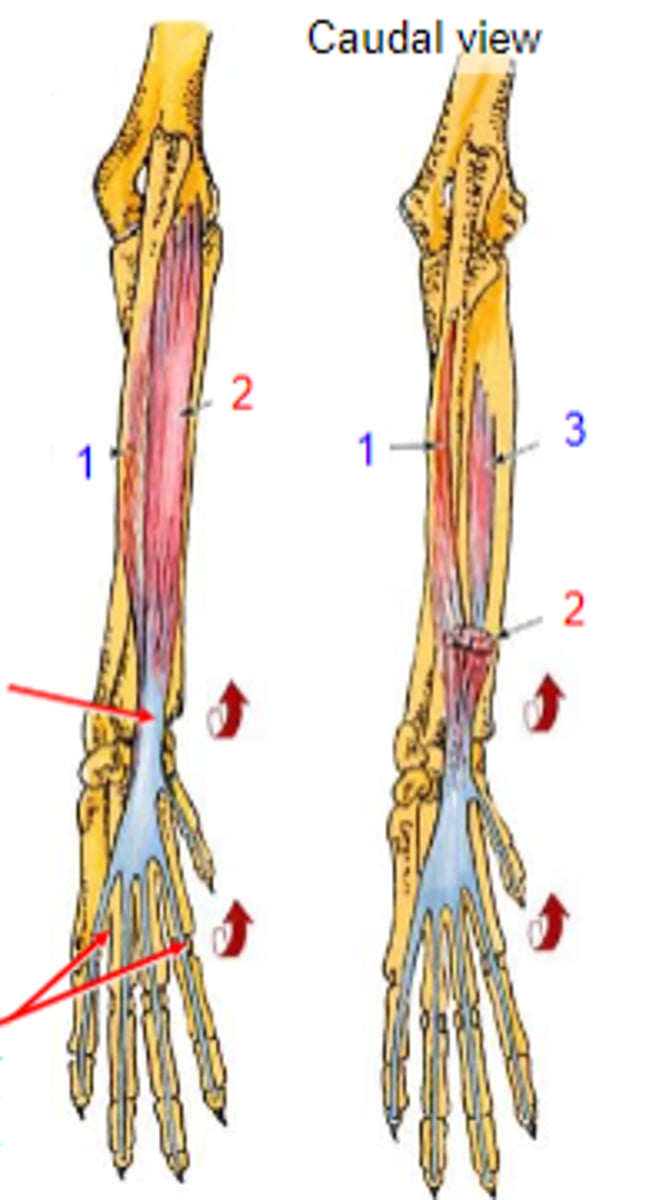
- Ulnar head: (1)body of the ulna
- Humeral head: (2) medial epicondyle of the humerus;
- Radial head: (3) body of the radius
Origin of deep digital flexor:
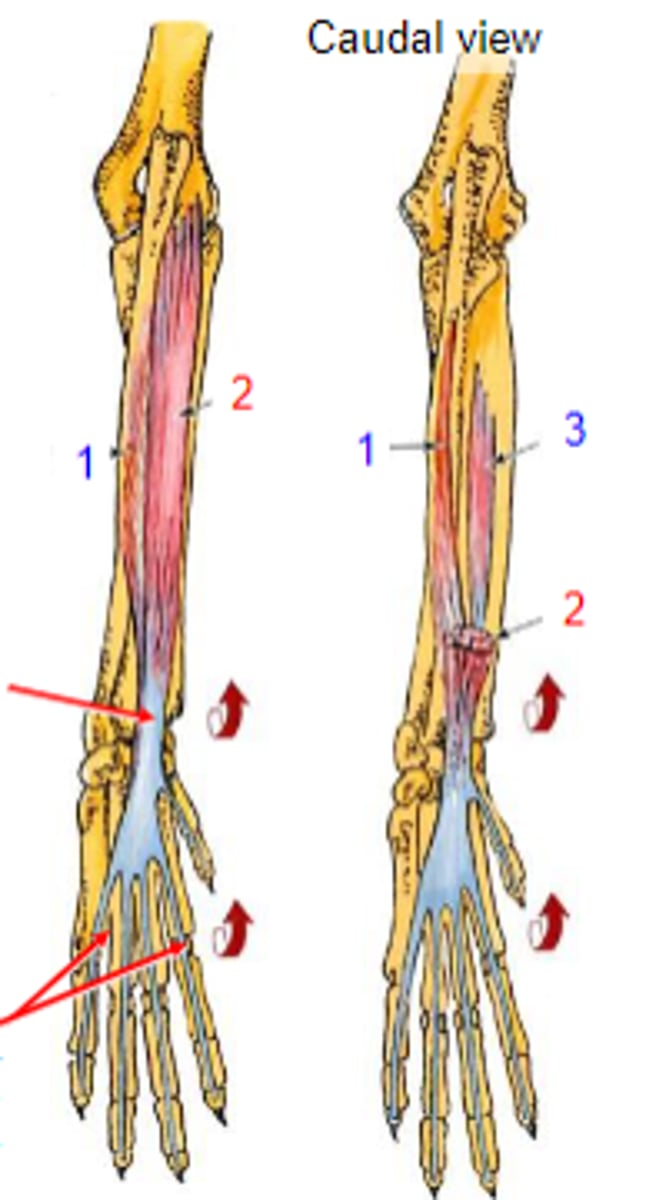
flexor tubercles of the distal phalanges
Insertion of deep digital flexor:
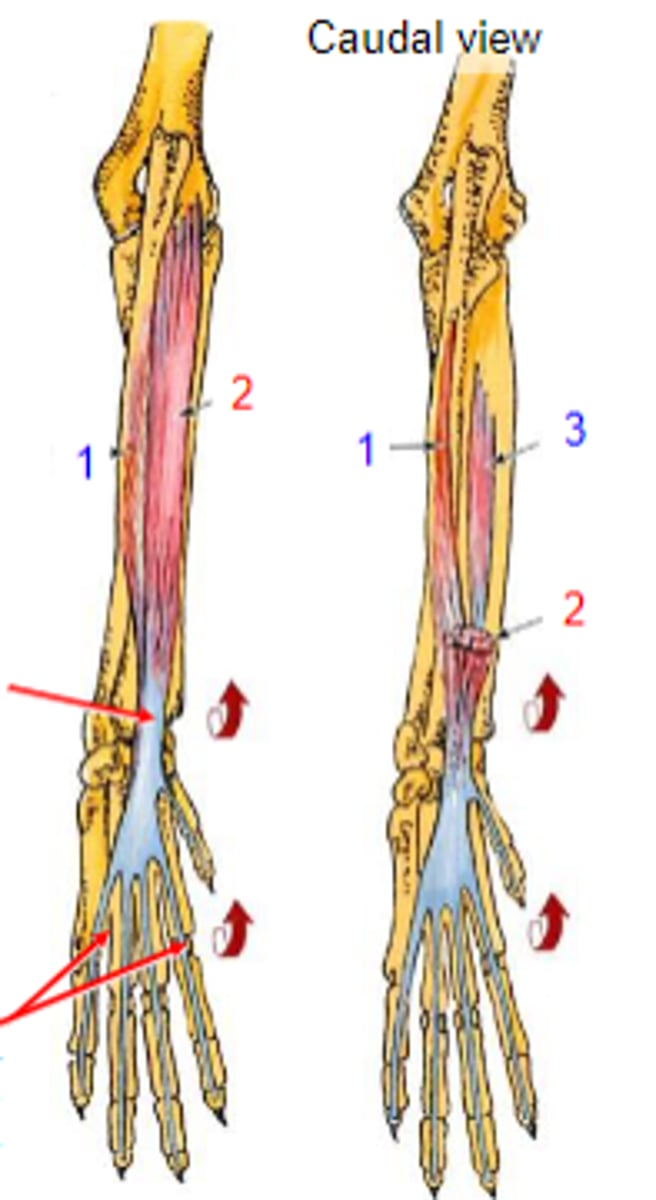
flex the carpal joints; flex the digital joints
Action of deep digital flexor:
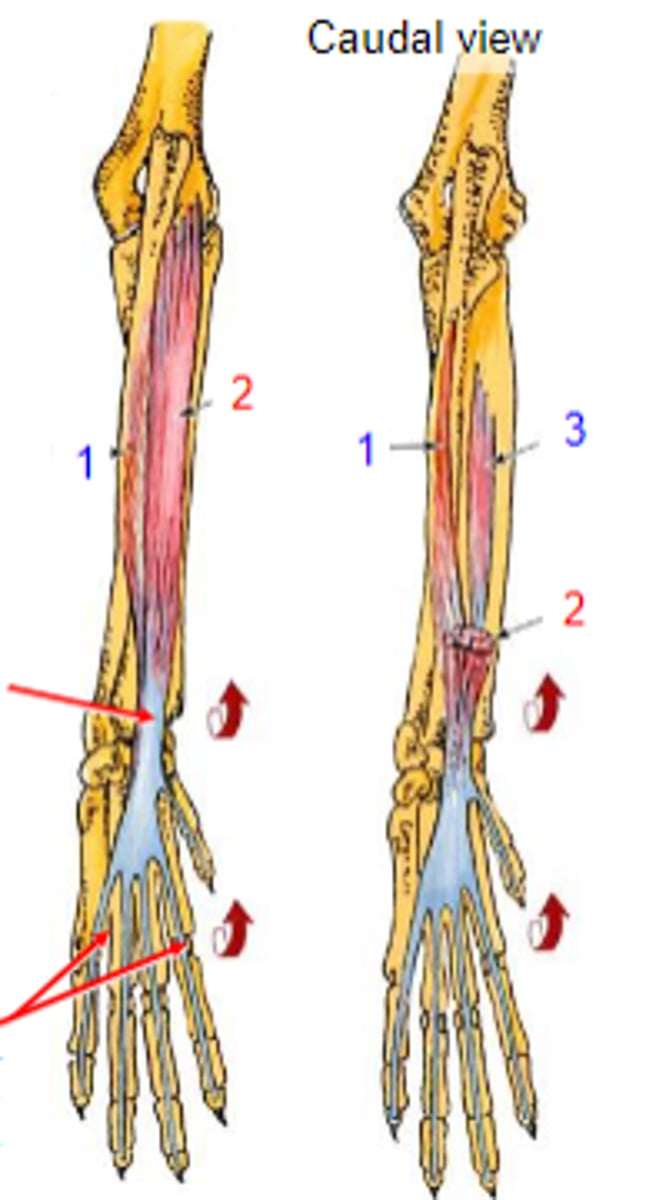
deep digital flexor
The following are associated with what muscle?
Origin:
- Ulnar head: (1)body of the ulna
- Humeral head: (2) medial epicondyle of the humerus;
- Radial head: (3) body of the radius
Insertion: flexor tubercles of the distal phalanges
Action: flex the carpal joints; flex the digital joints
reviewed
Review: deep digital flexor
1. pronator teres
2. pronator quadratus
What are the 2 pronator muscles?
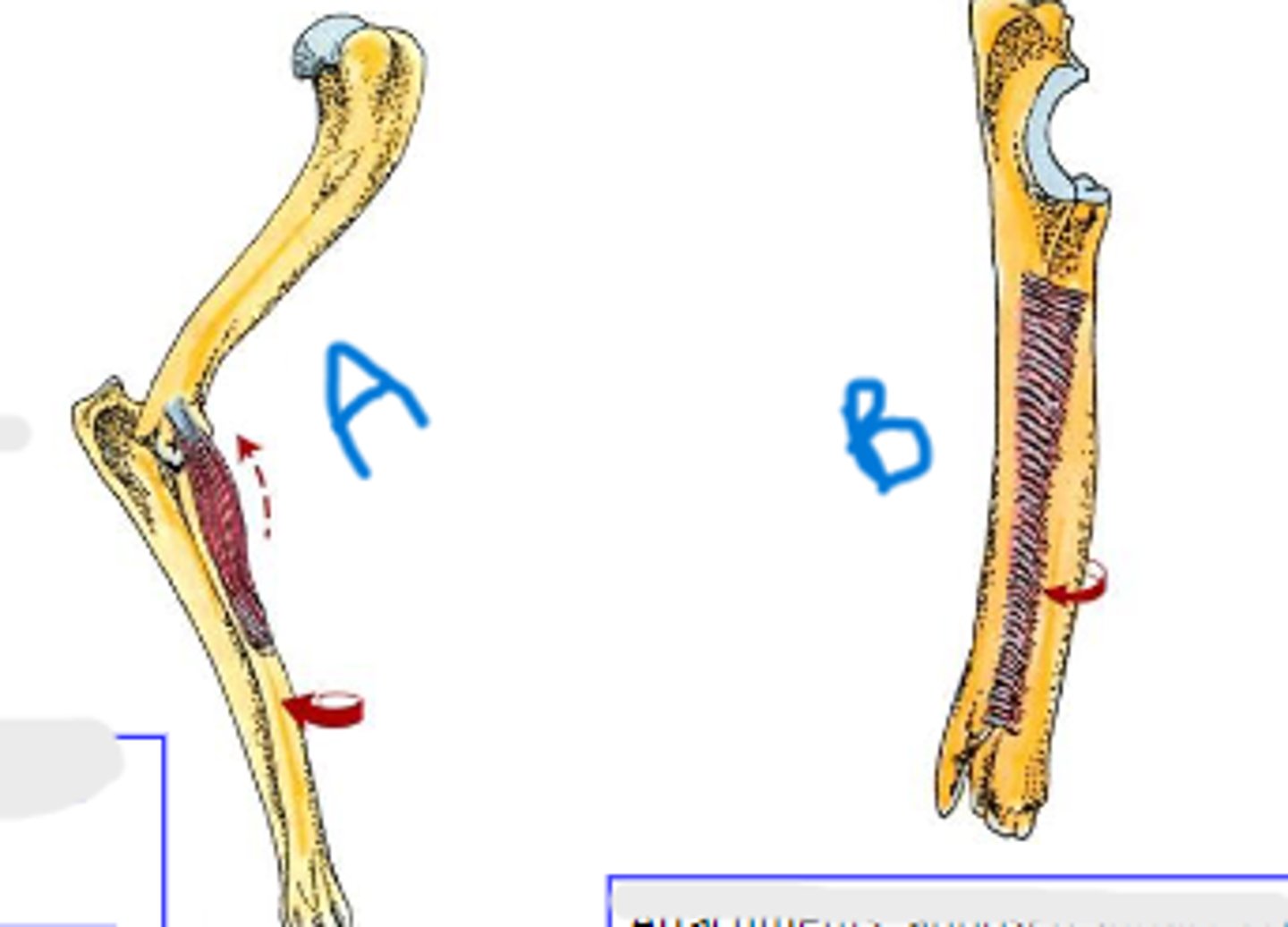
pronator teres
What is muscle A?
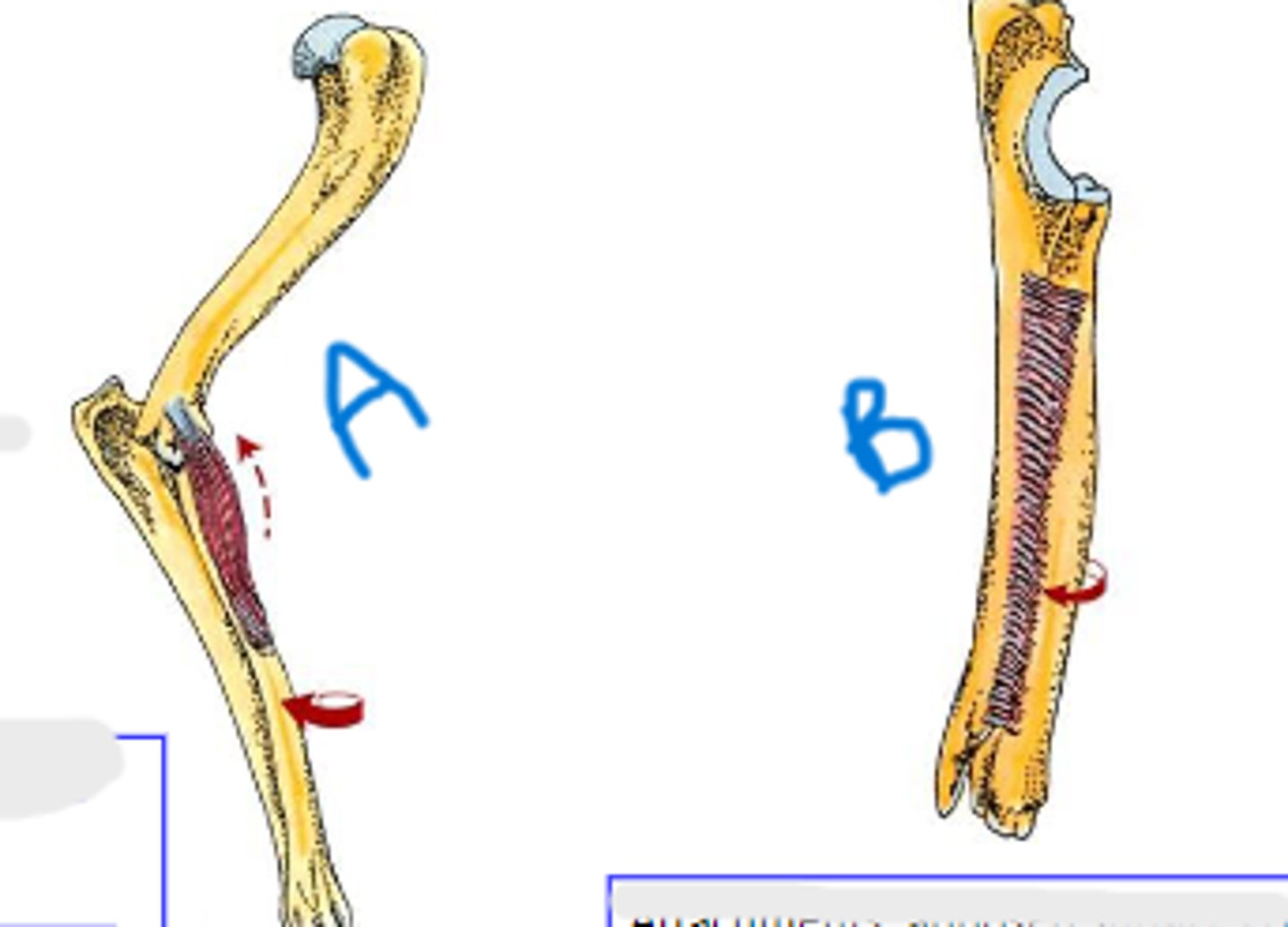
medial epicondyle of humerus
Origin of pronator teres:
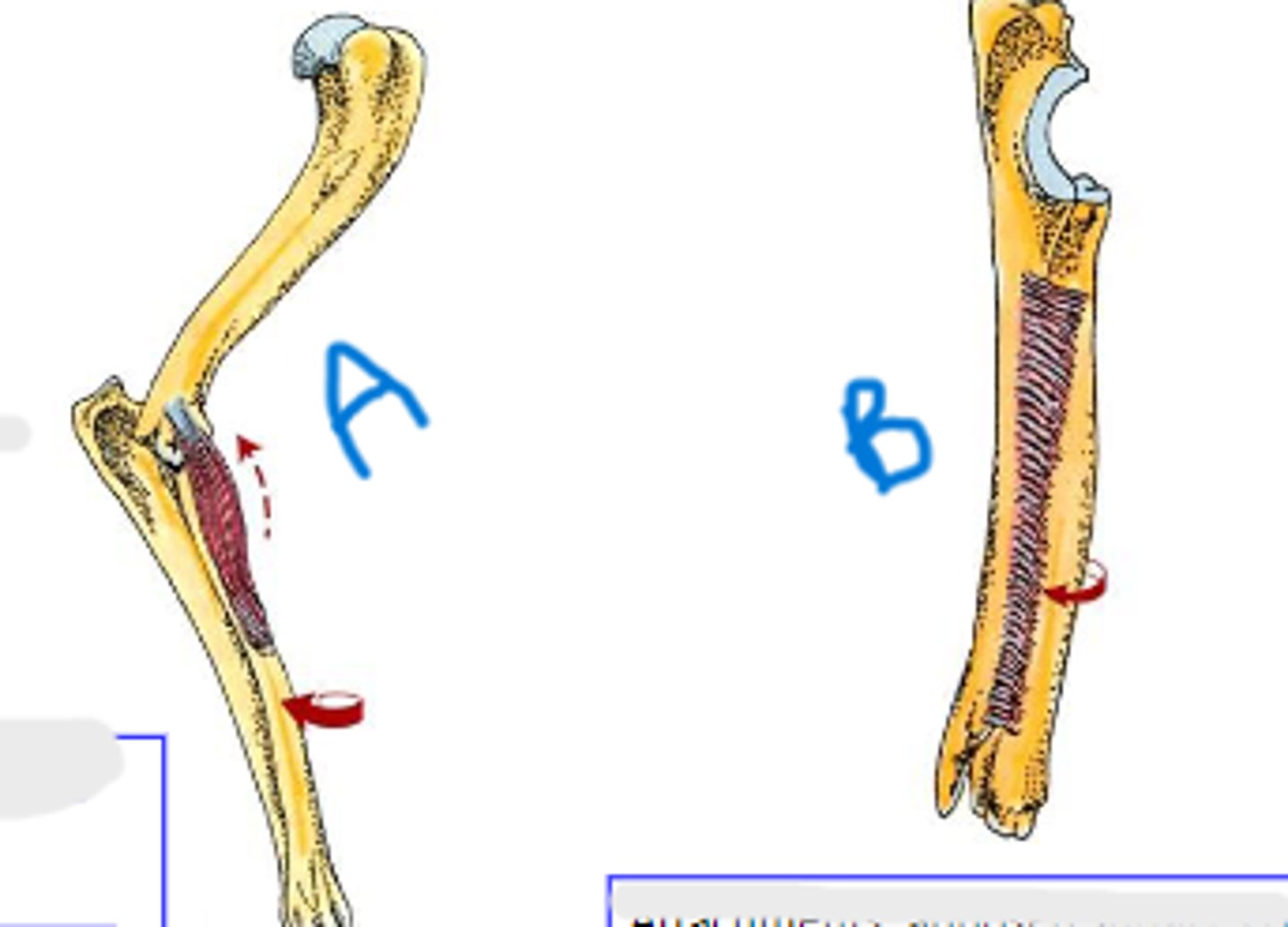
body of radius
Insertion of pronator teres:
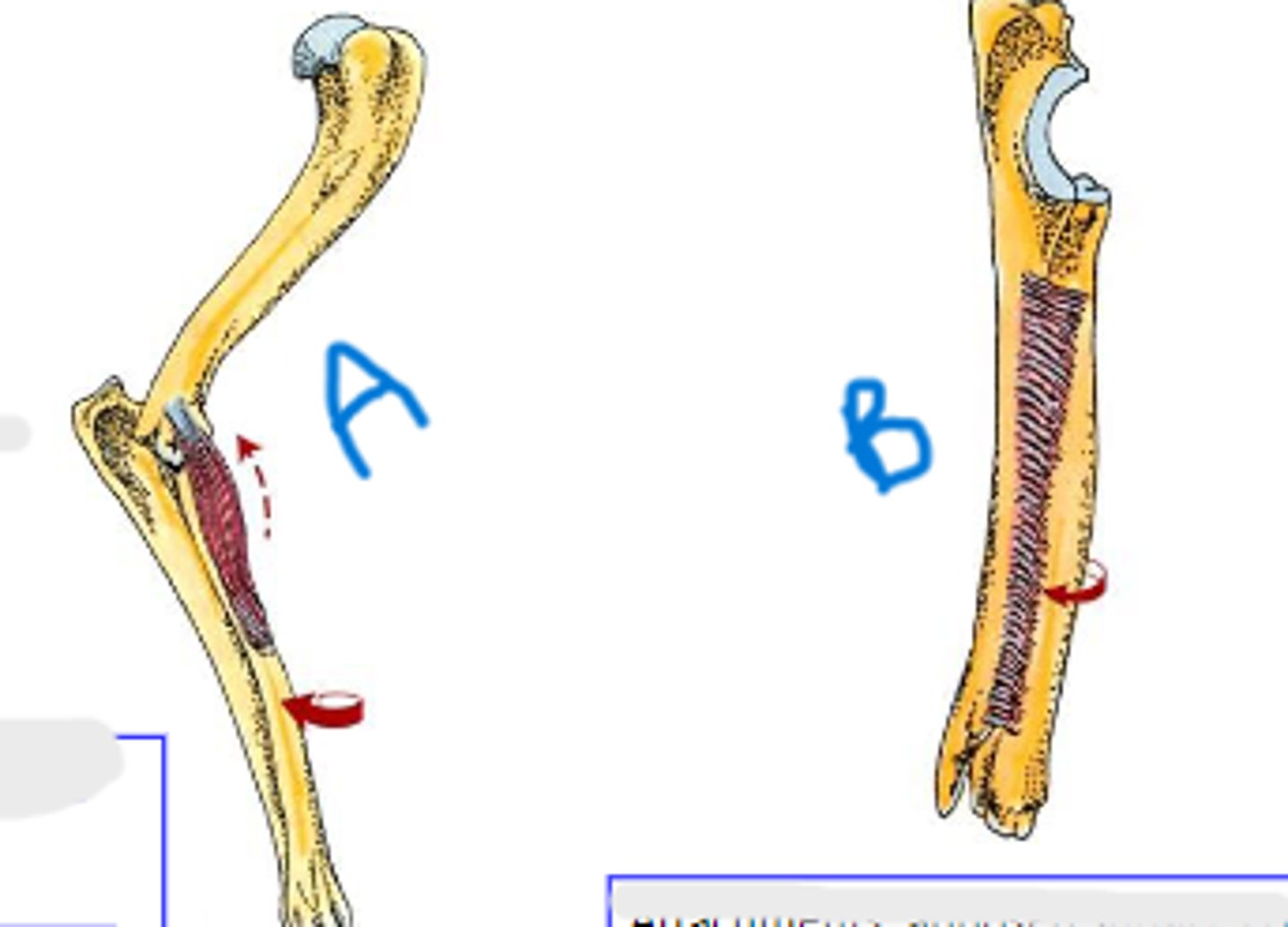
pronation of manus
Action of pronator teres:
pronator teres
The following are associated with what muscle?
Origin: medial epicondyle of the humerus
Insertion: body of radius
Action: pronation of the manus
pronator quadratus
What is muscle B?
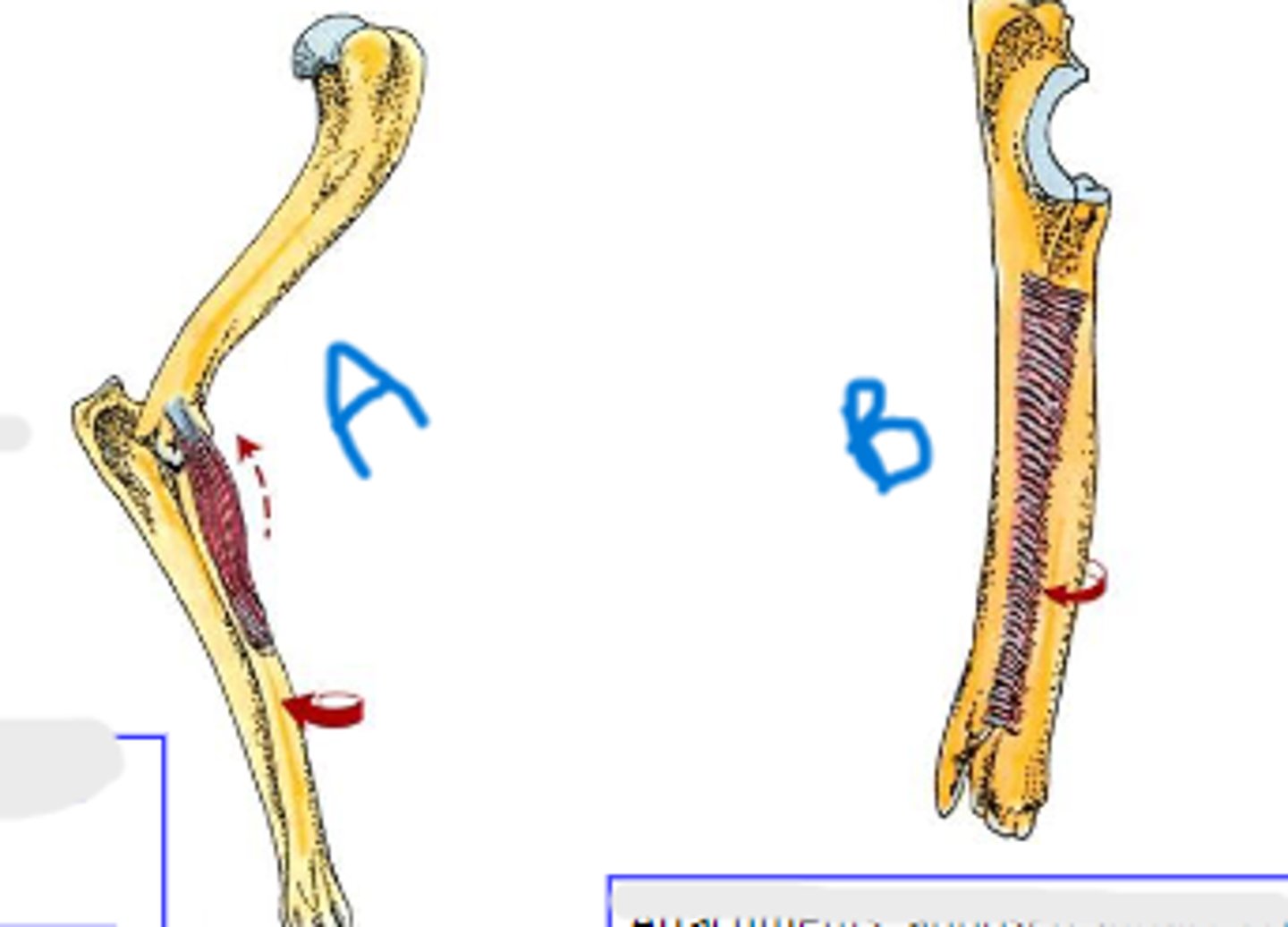
apposed surfaces of radius and ulna
Attachments of pronator quadratus:
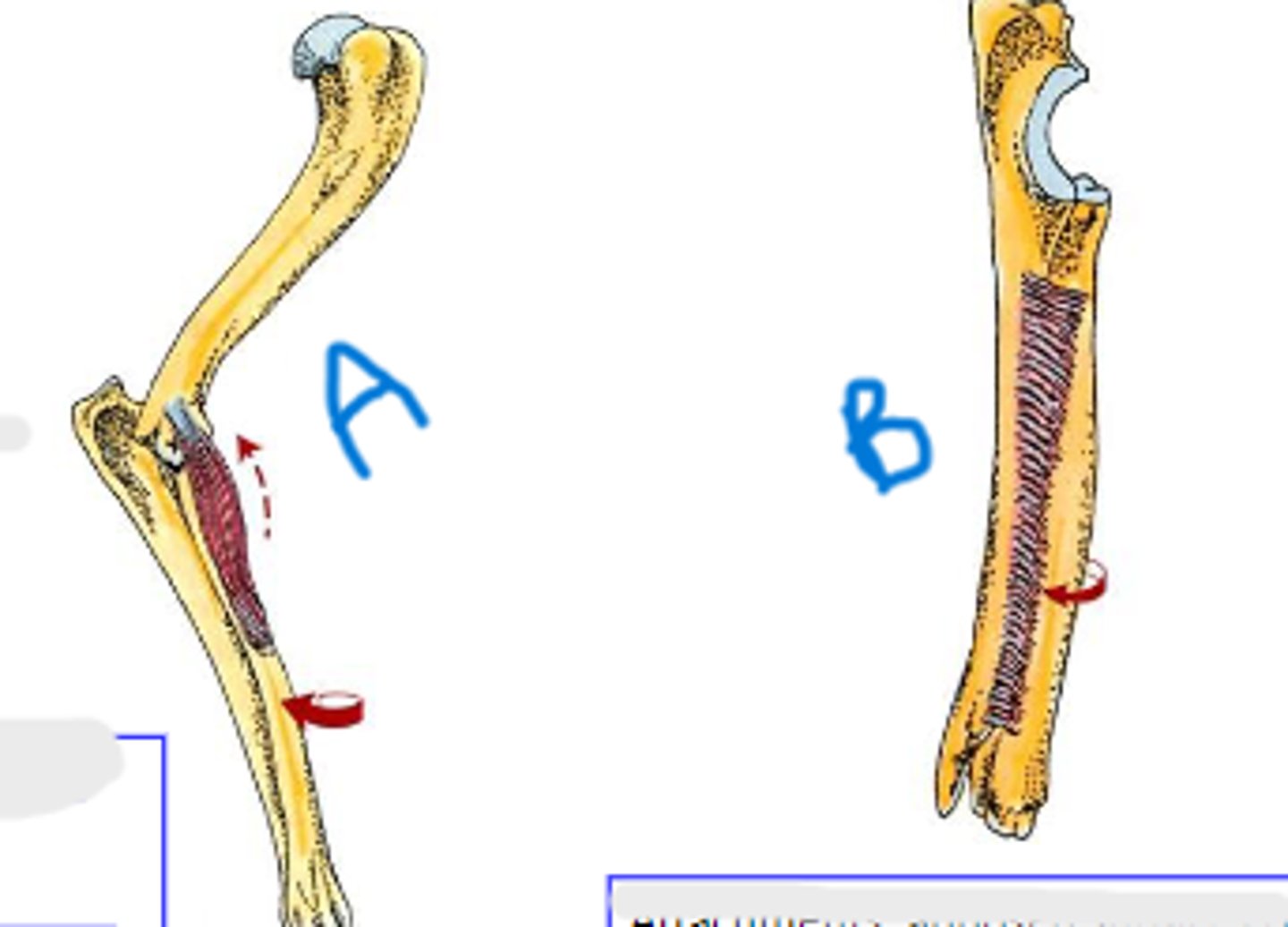
pronation of manus
Action of pronator quadratus:
pronator quadratus
The following are associated with what muscle?
Attachments: apposed surfaces of the radius and the ulna
Action: pronation of the manus
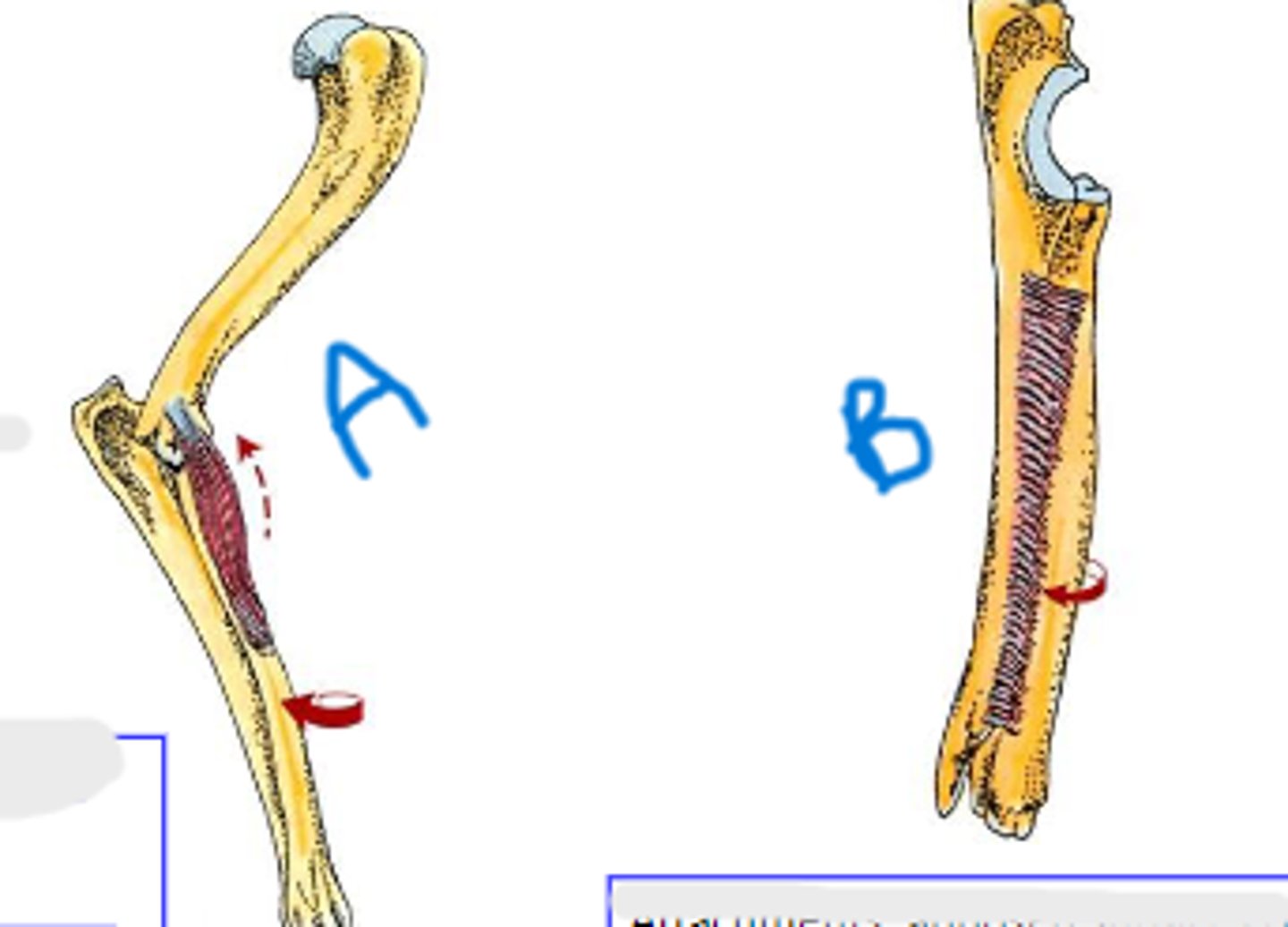
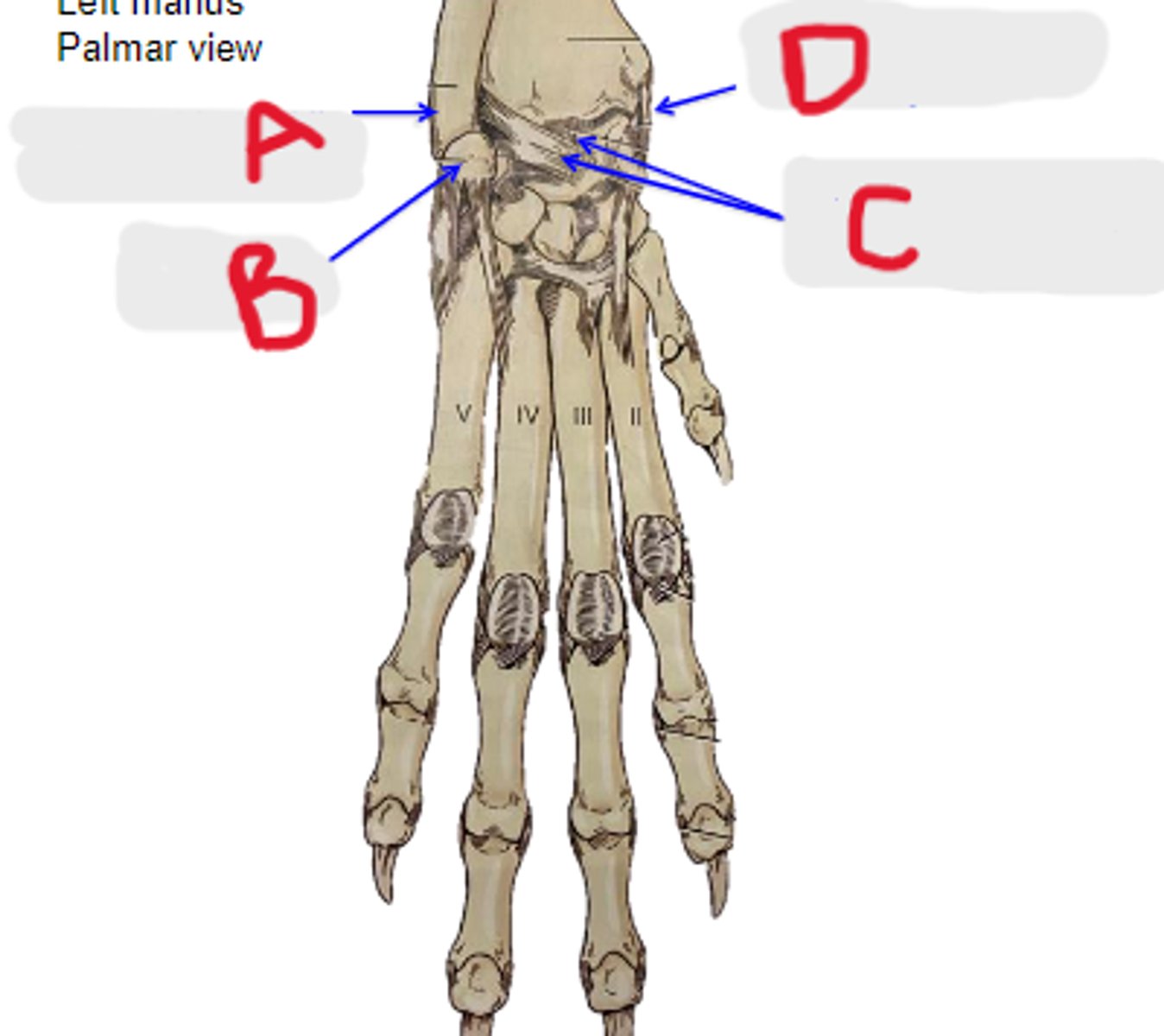
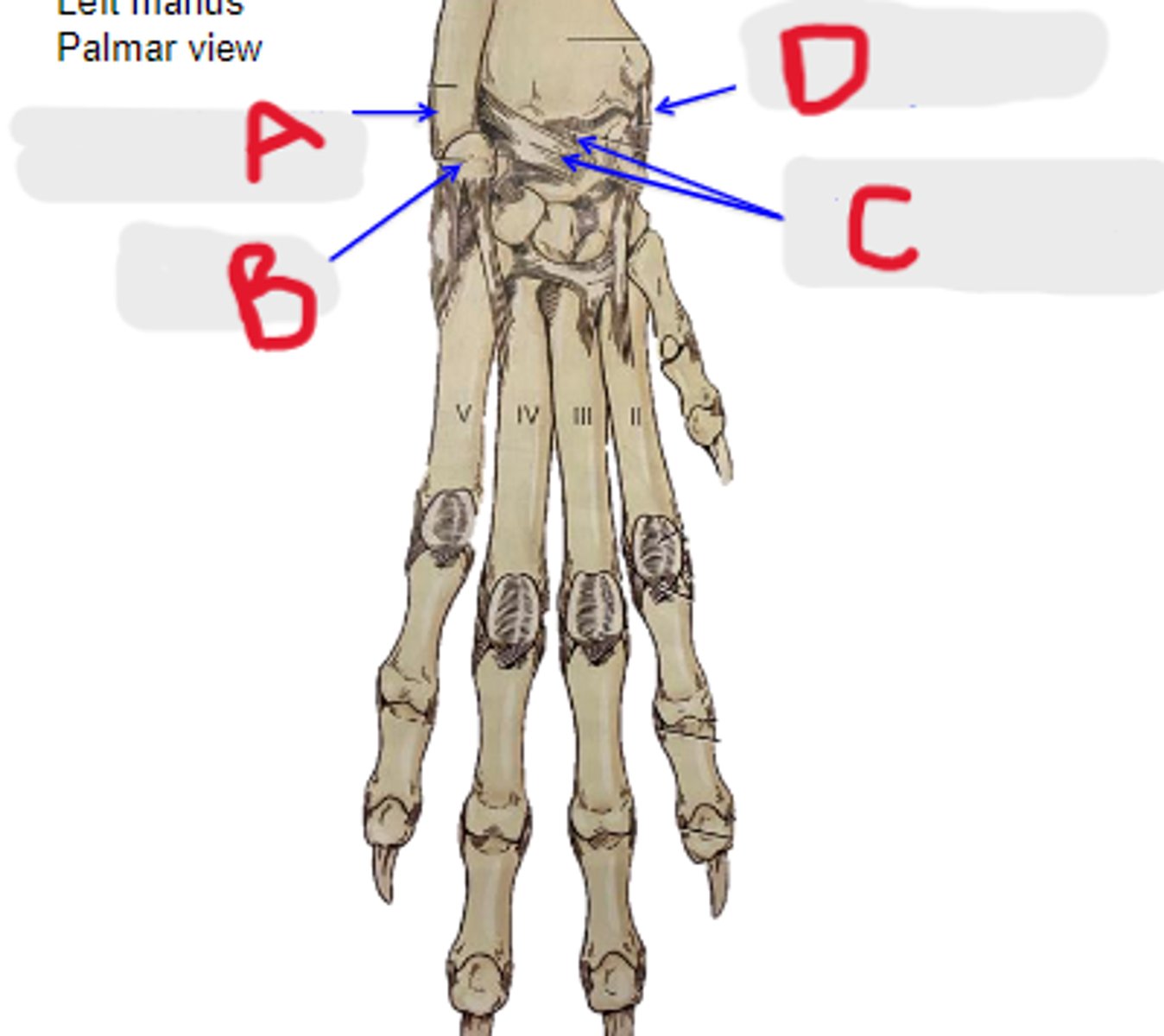
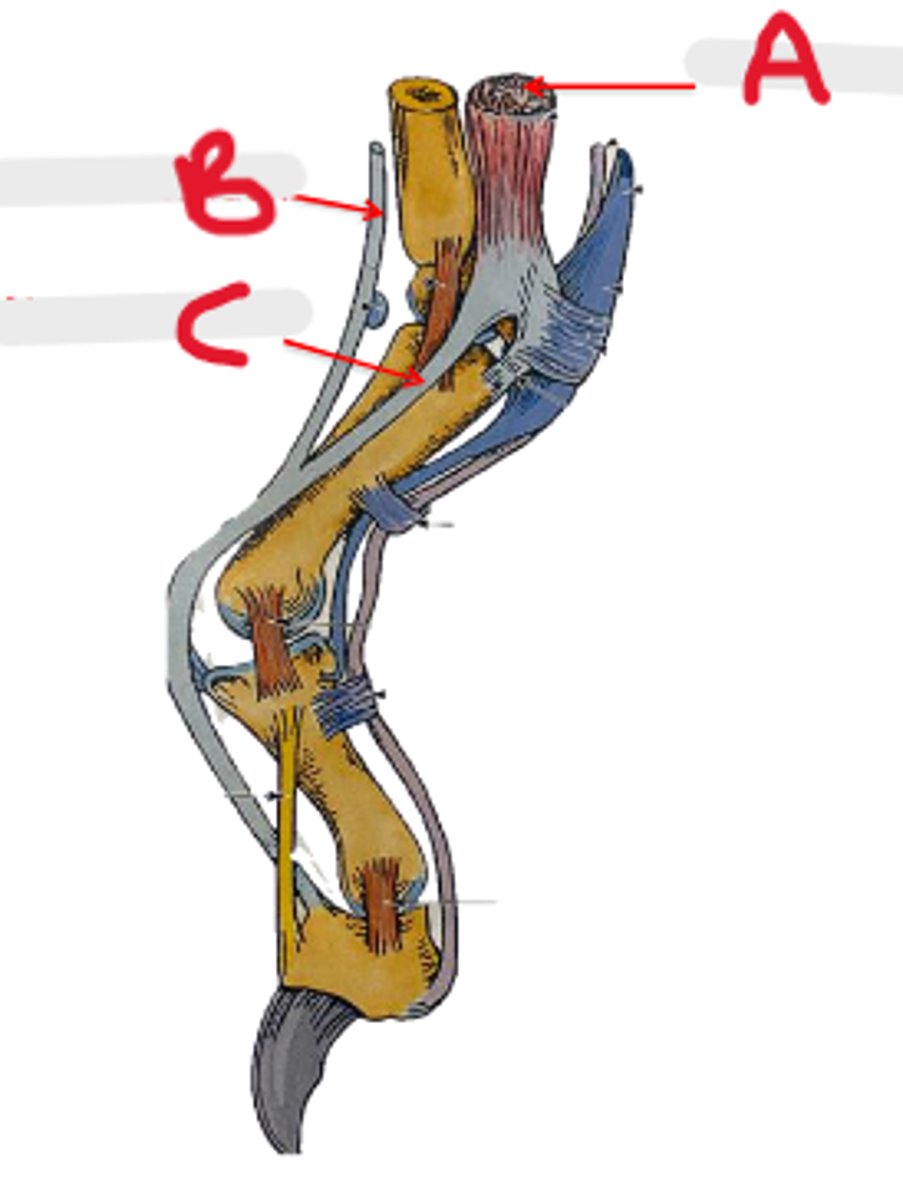
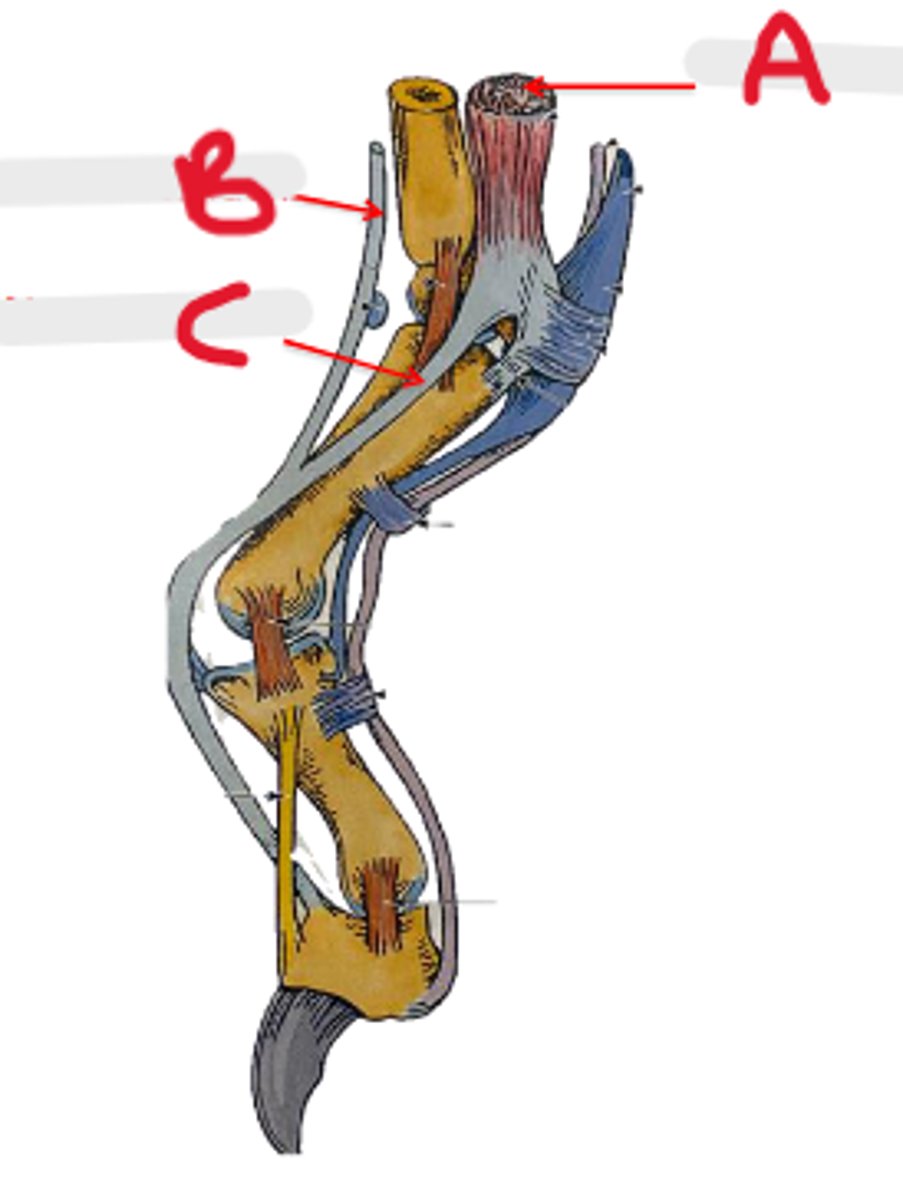
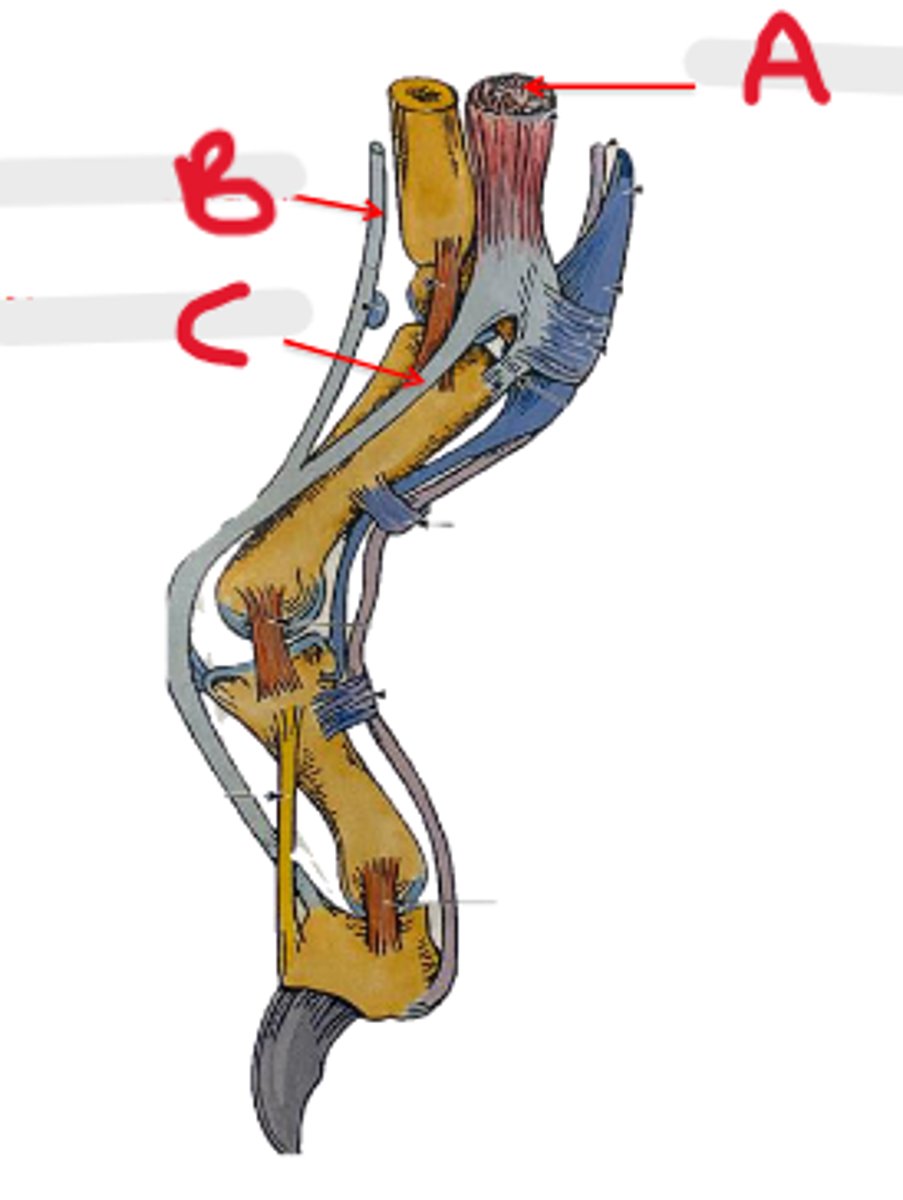
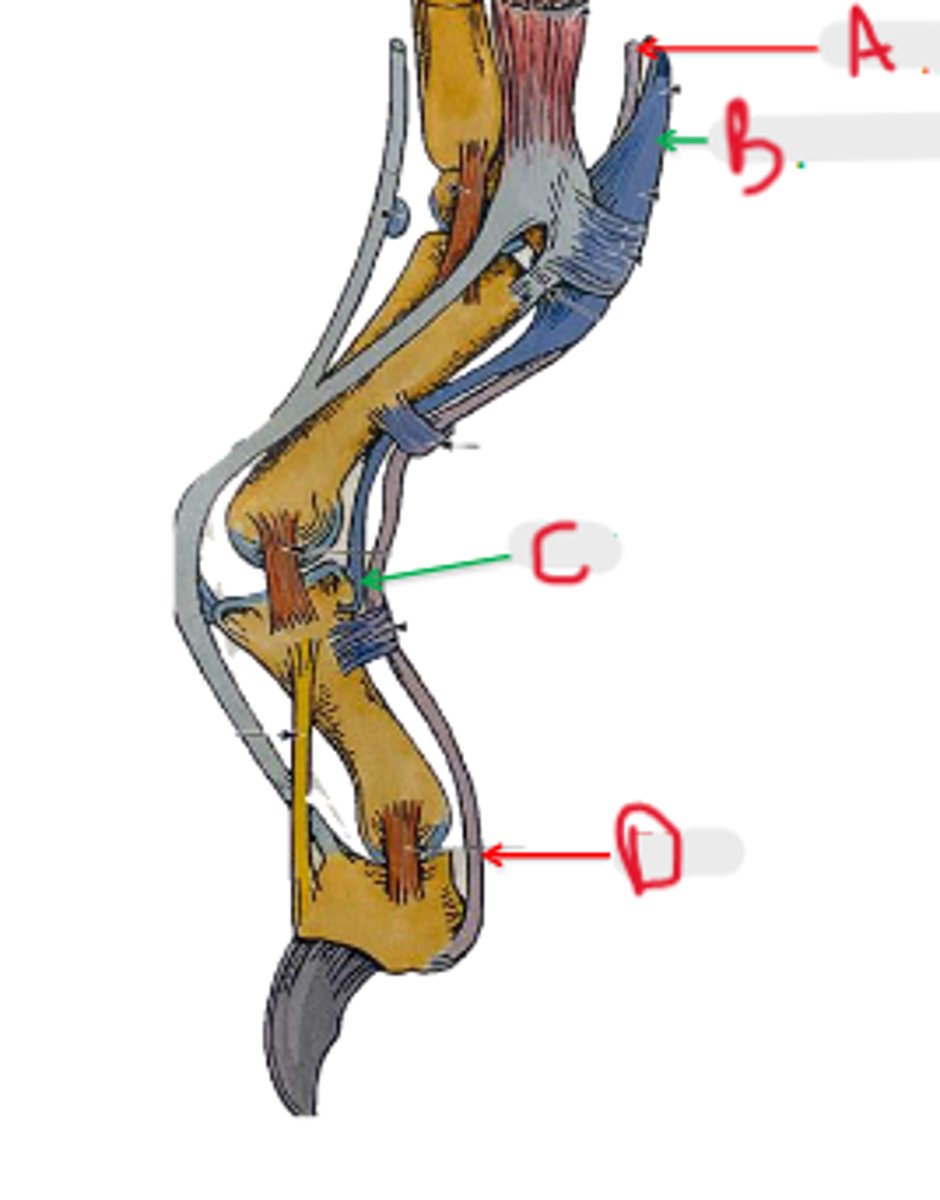
collateral lateral ligament of carpal joints
What is A?
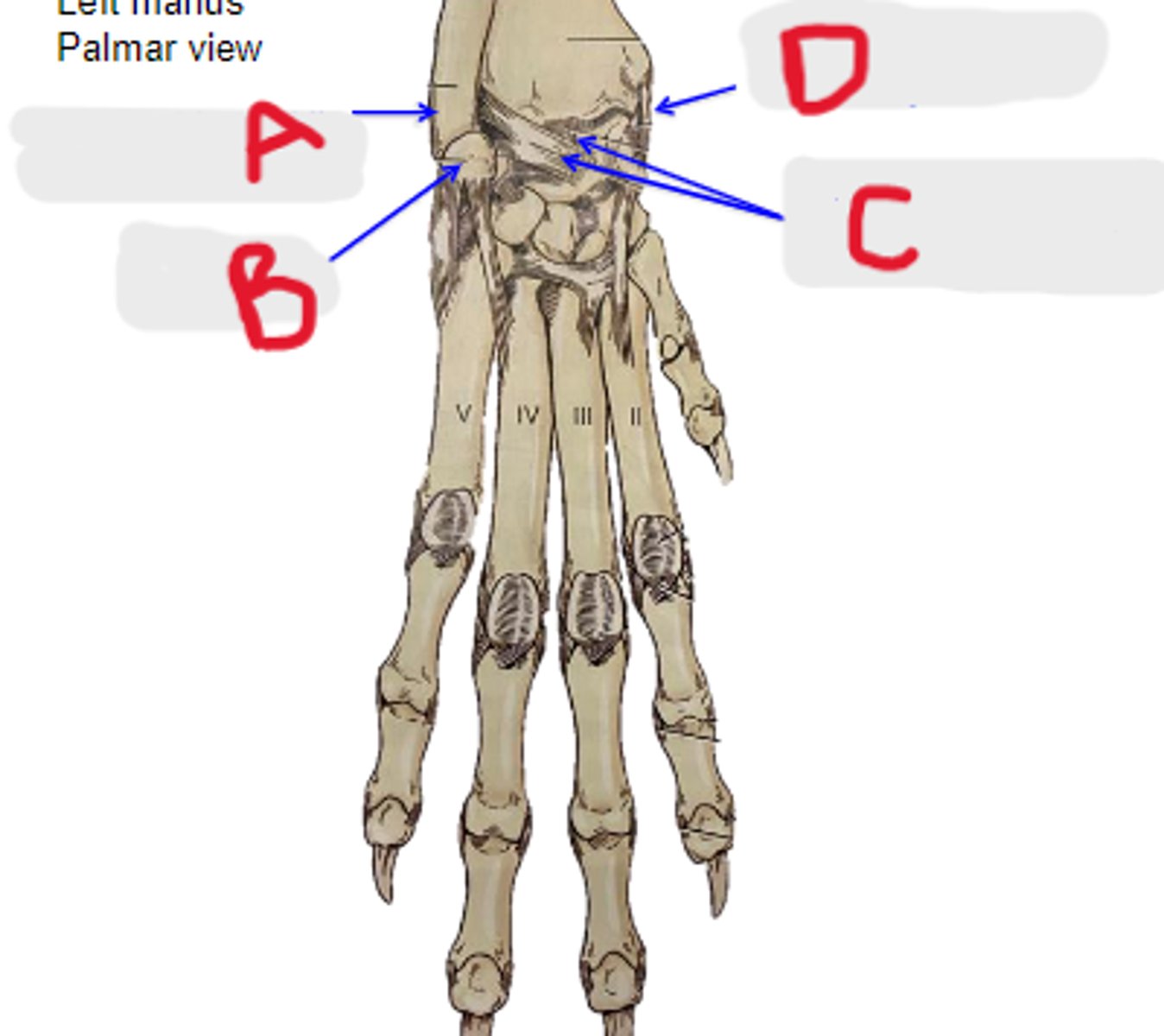
accessory carpal bone
What is B?
palmar radiocarpal & palmar ulnocarpal ligaments
What is C?
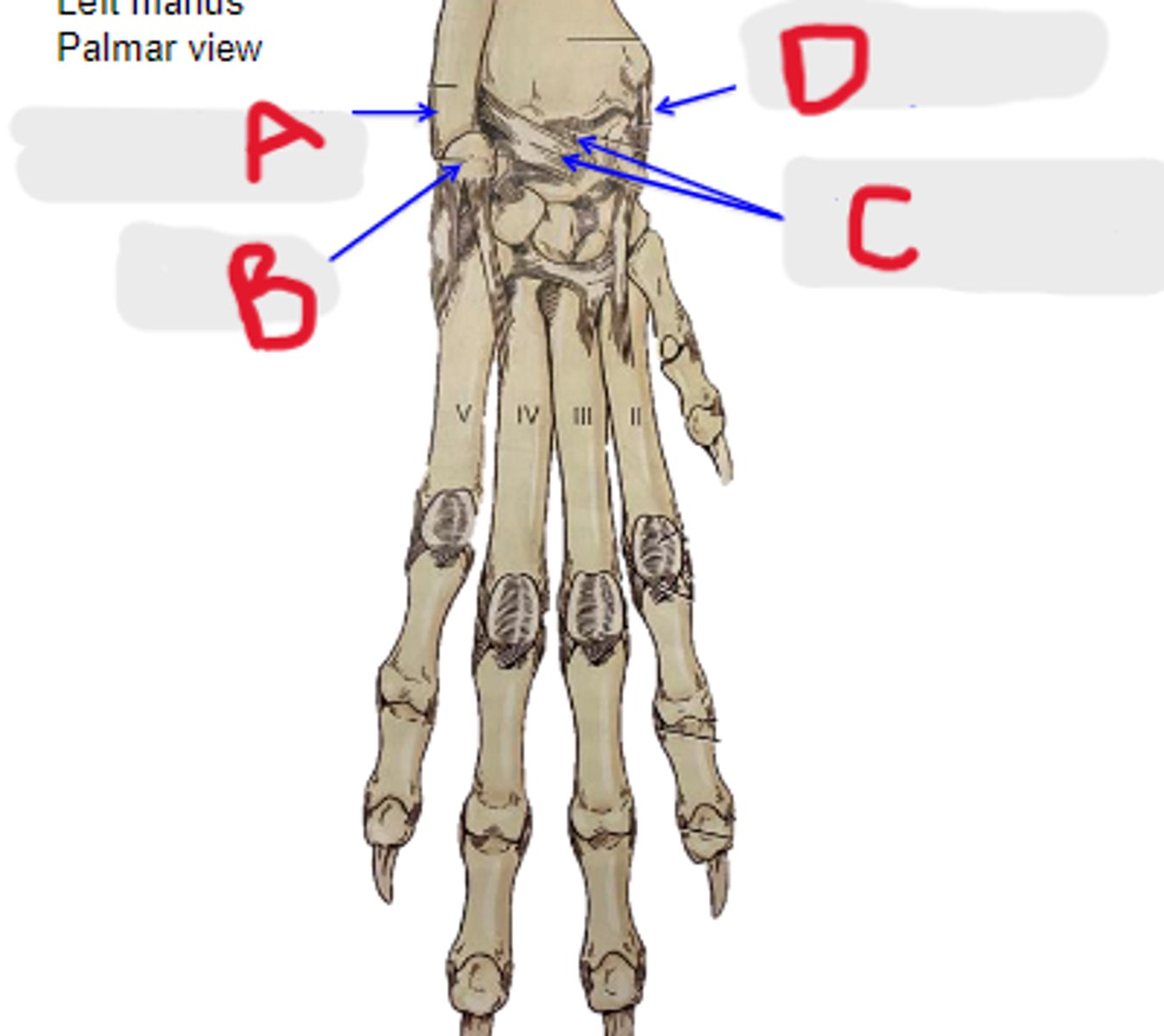
collateral medial ligament of carpal joints
What is D?
intersesamoidean ligament
Connective tissue between the proximal sesamoid bones. Digits II-V
intersesamoidean ligament
What is A?
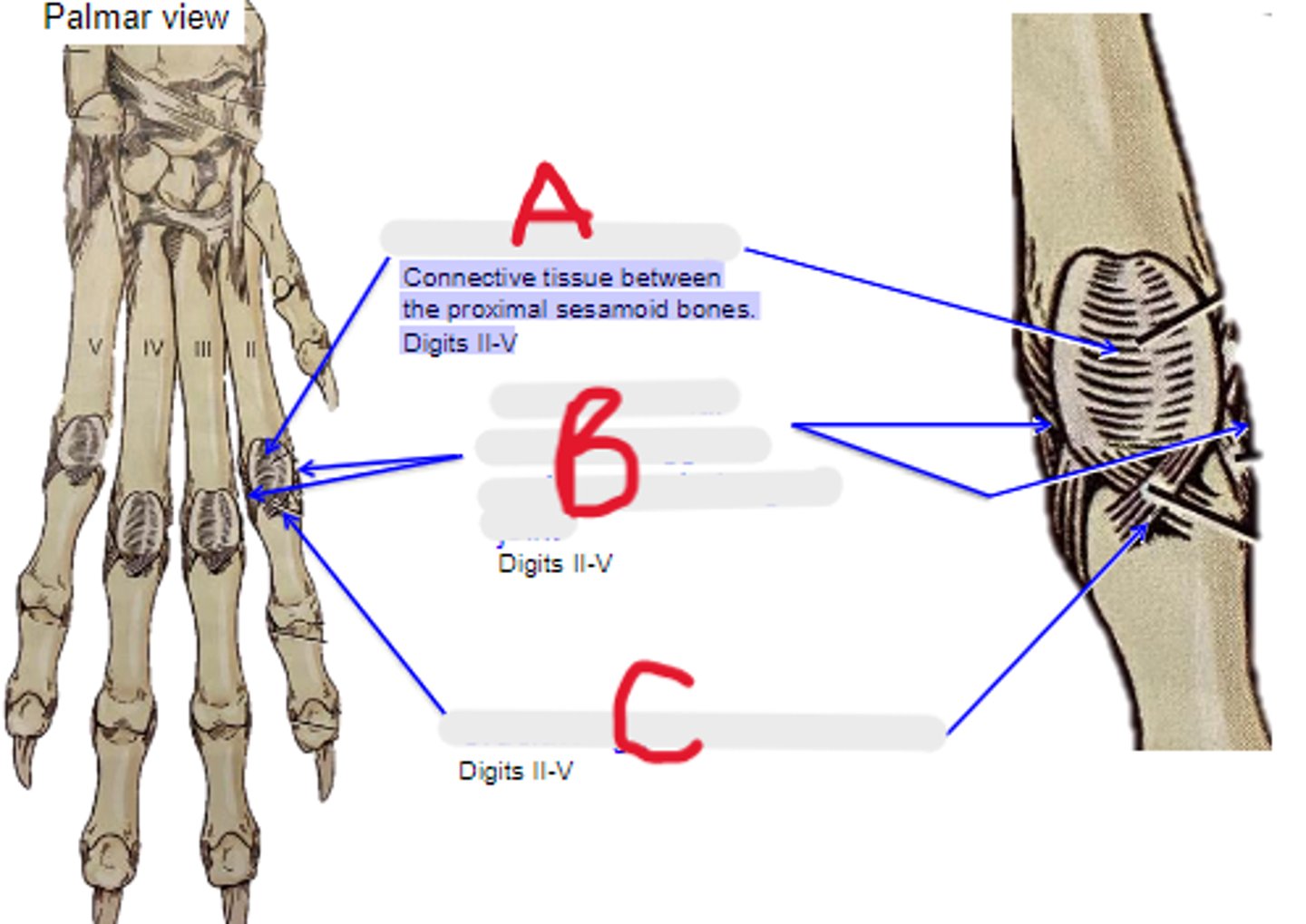
axial & abaxial collateral ligament of metacarpophalangeal joint
What is B?
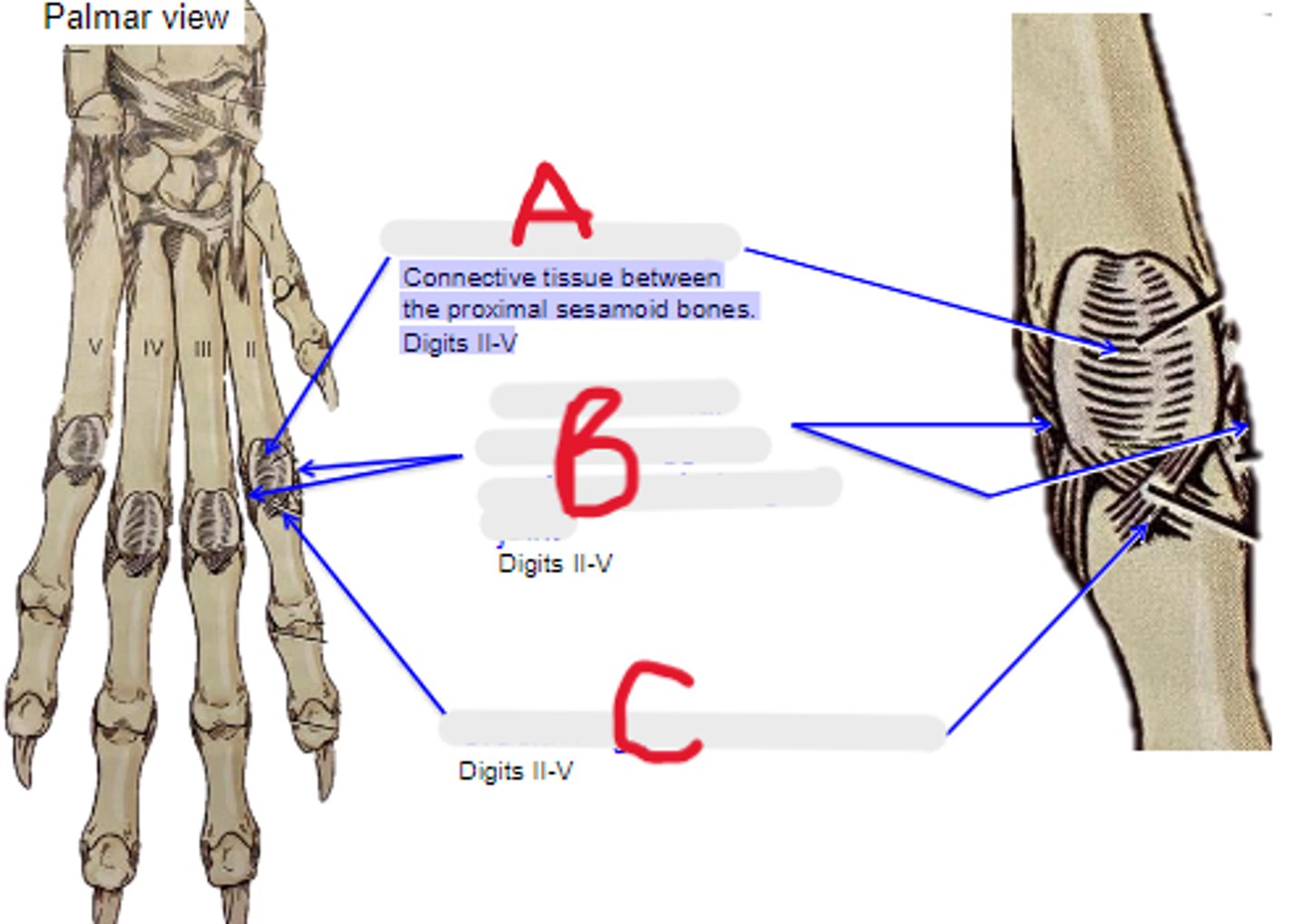
cruciate ligament of sesamoid bone
What is C?
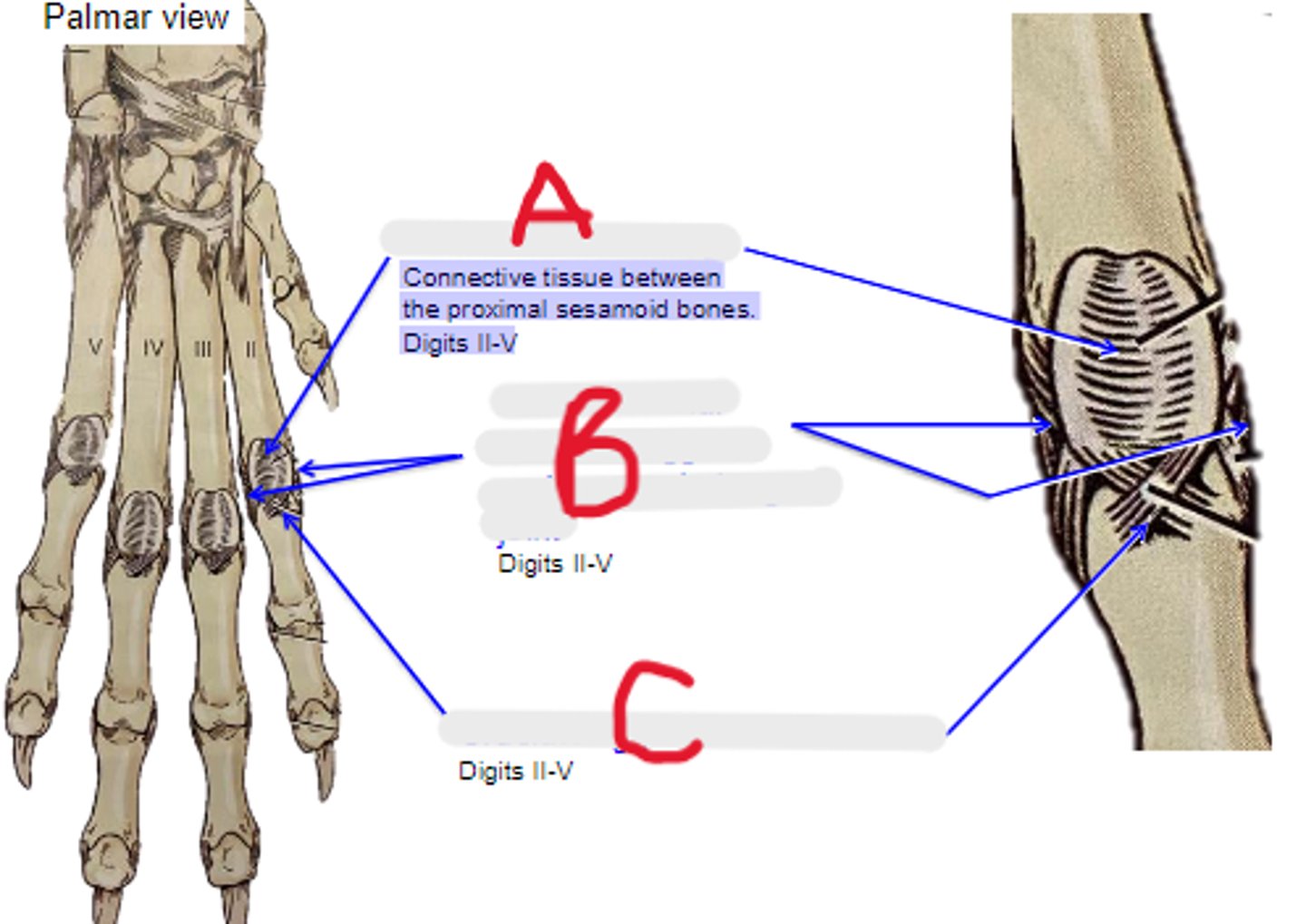
axial & abaxial collateral ligg. of proximal interphalangeal joint
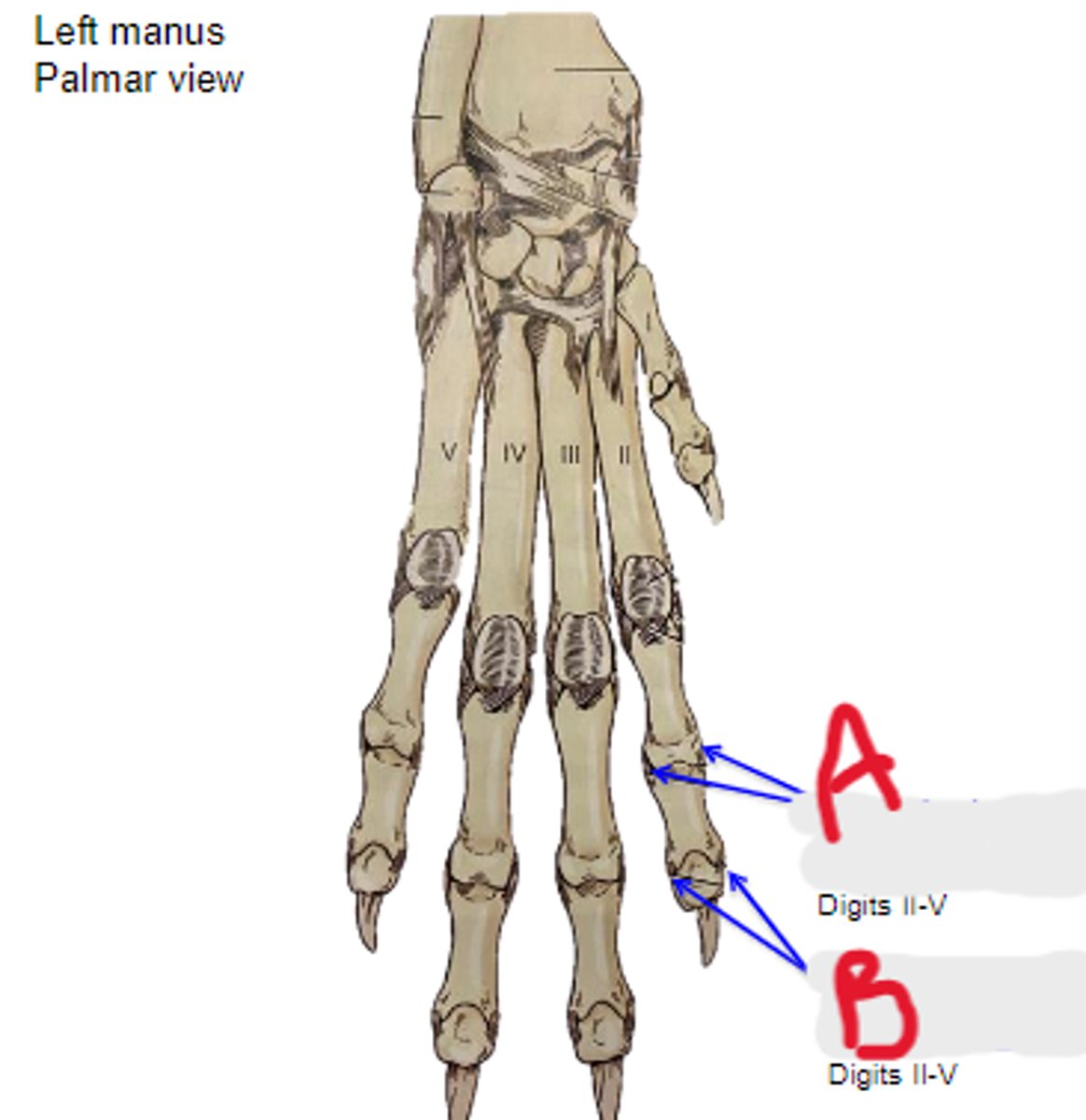
What is A?
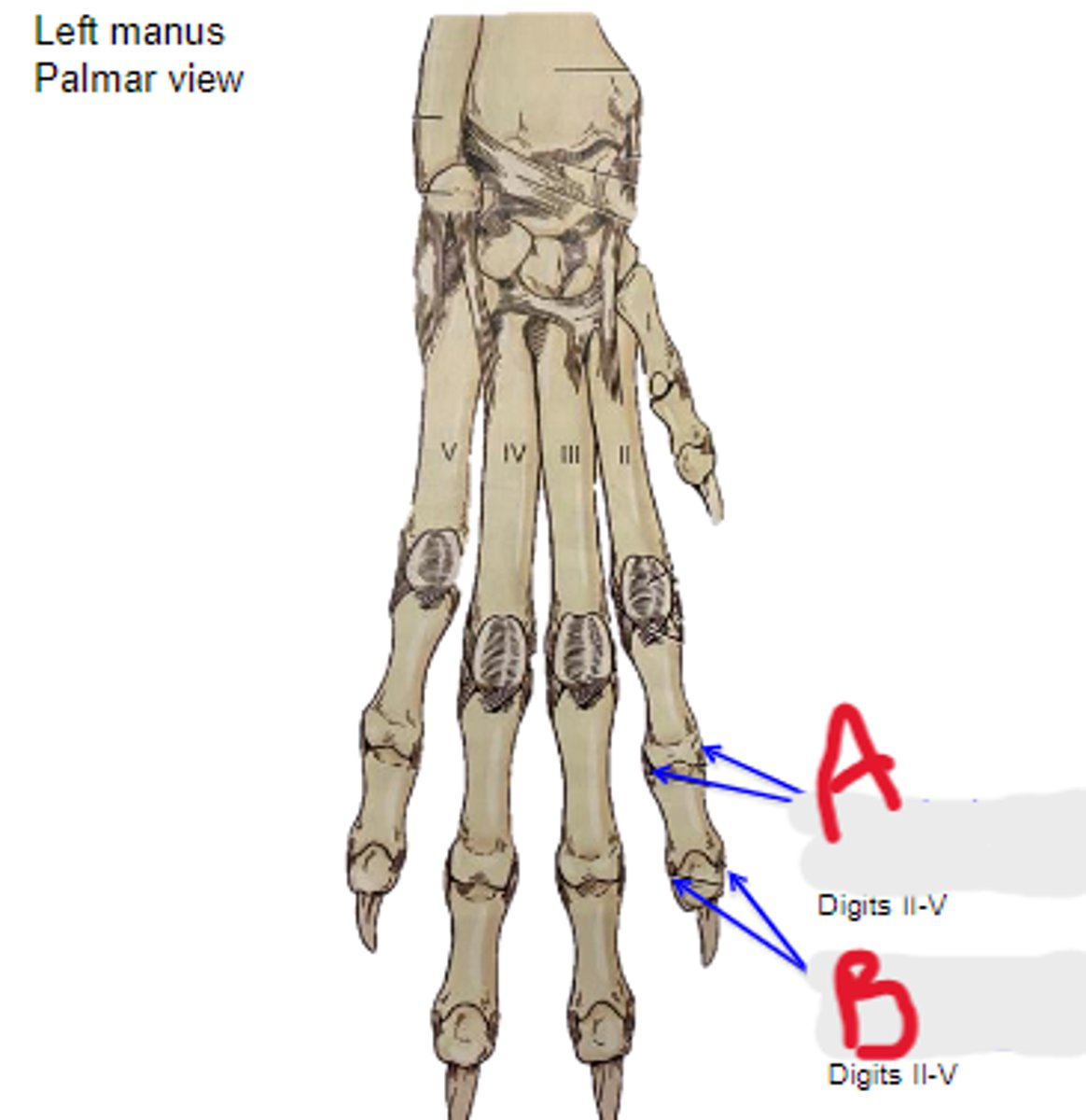
axial & abaxial collateral ligg. of distal interphalangeal joint
What is B?
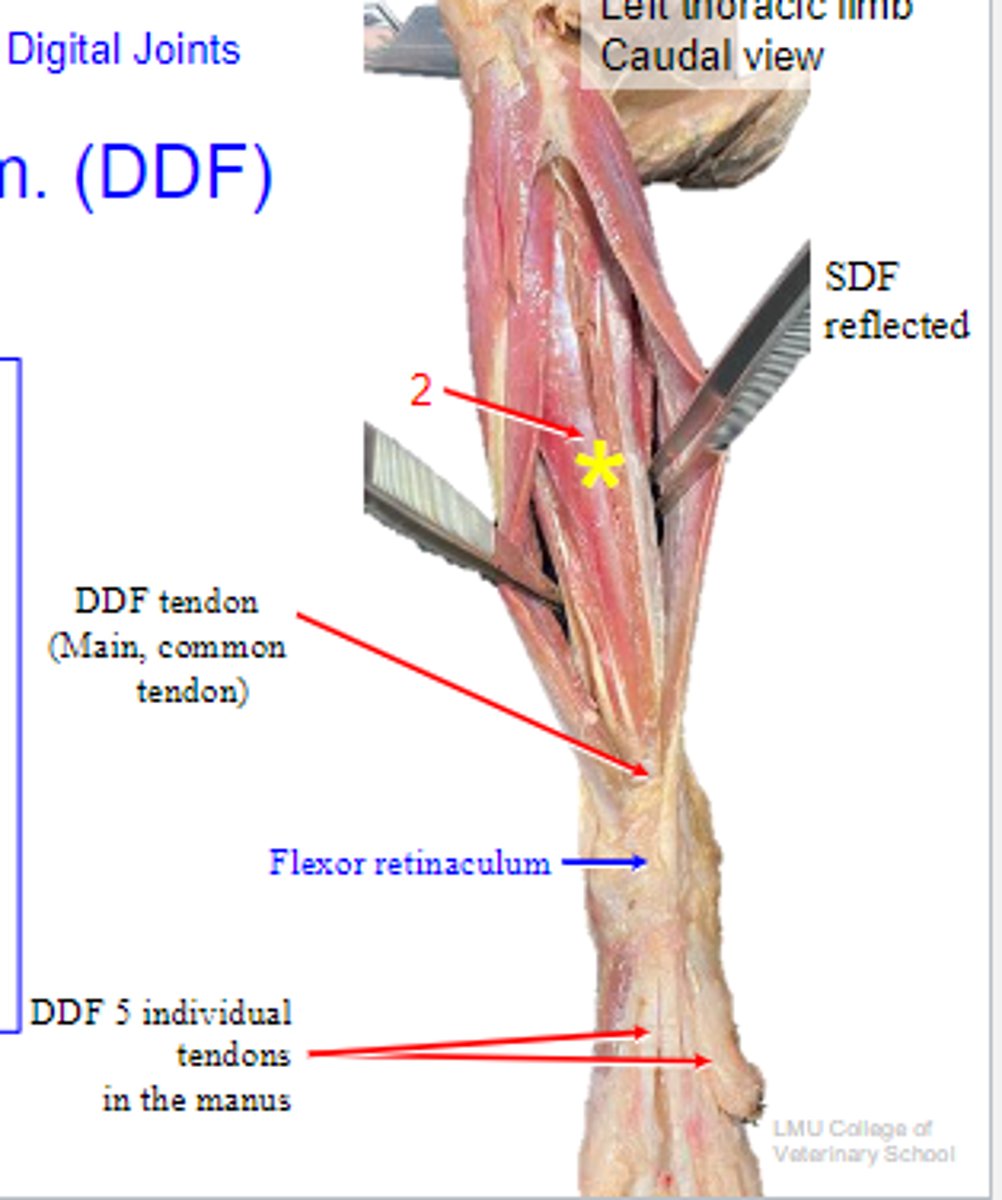
DDF tendon
What is A?
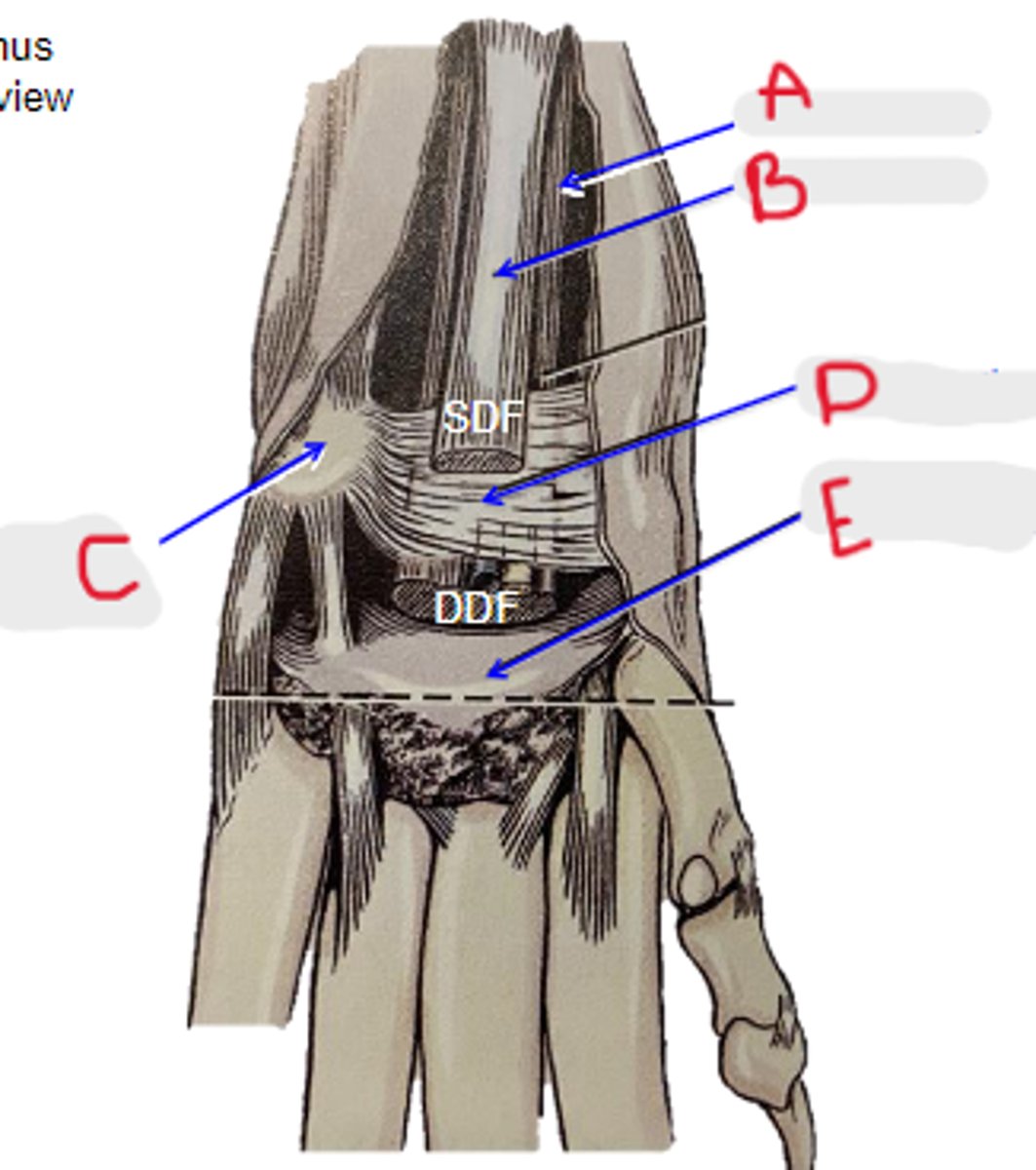
SDF tendon
What is B?
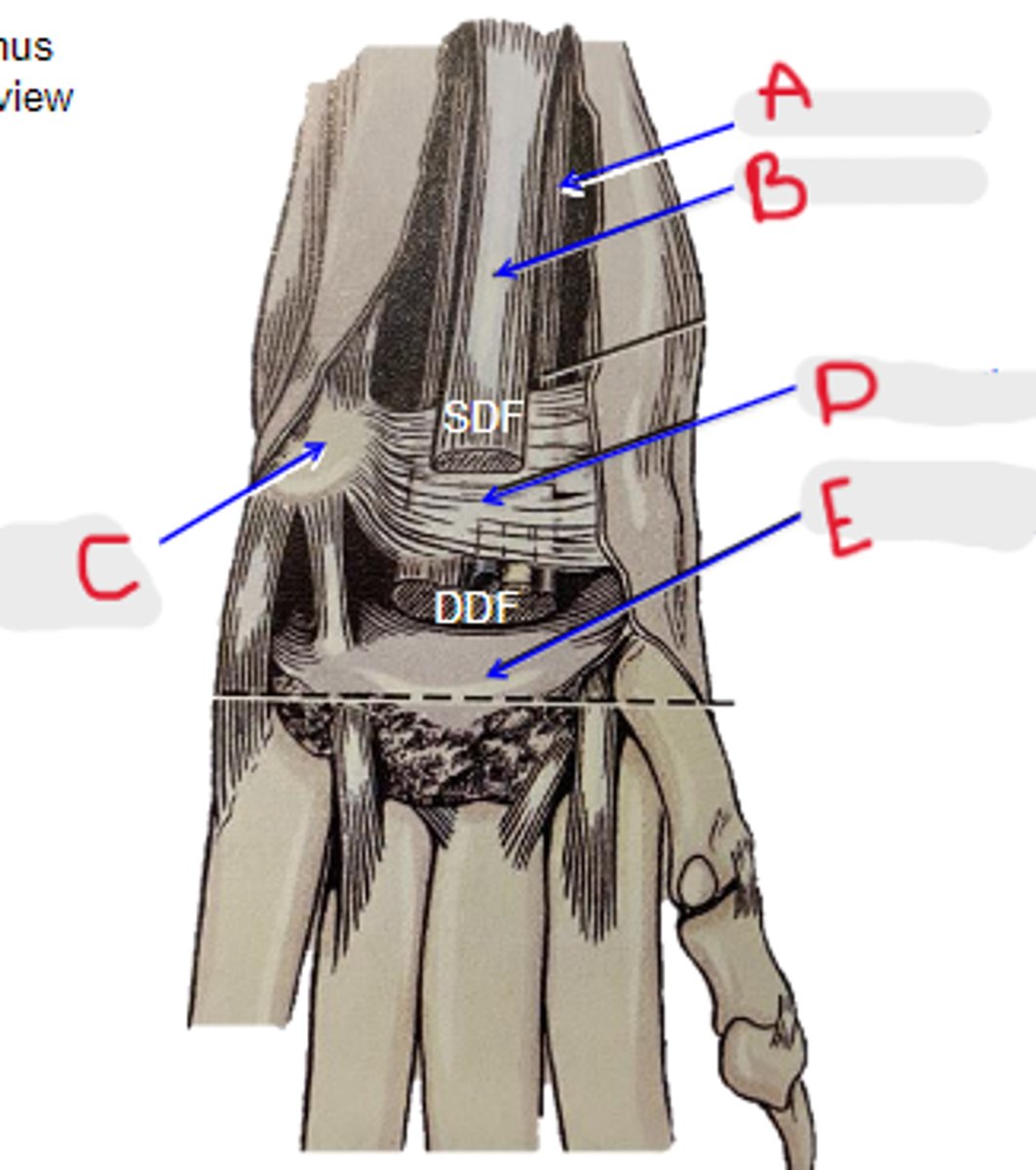
accessory carpal bone
What is C?
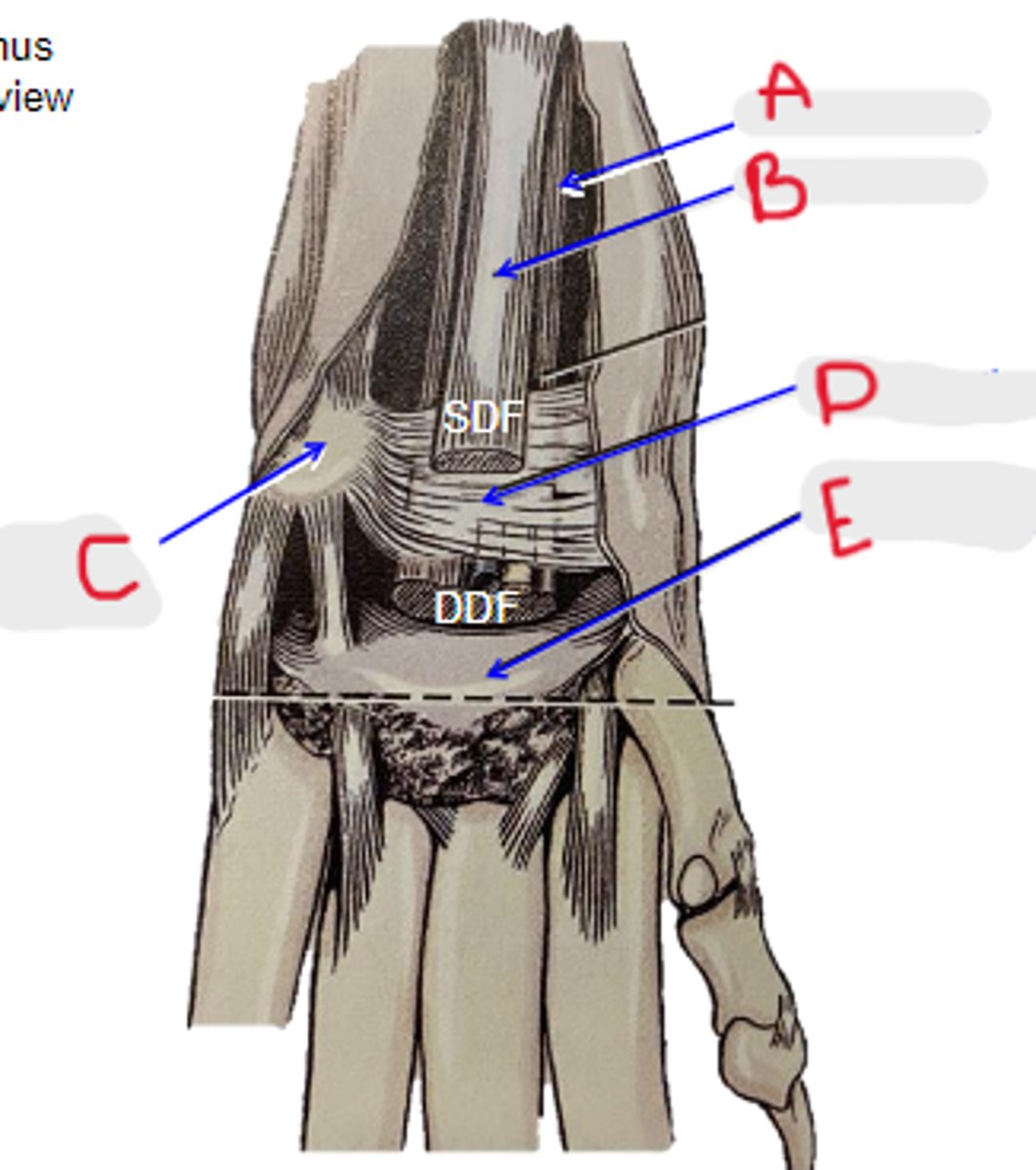
flexor retinaculum
What is D?
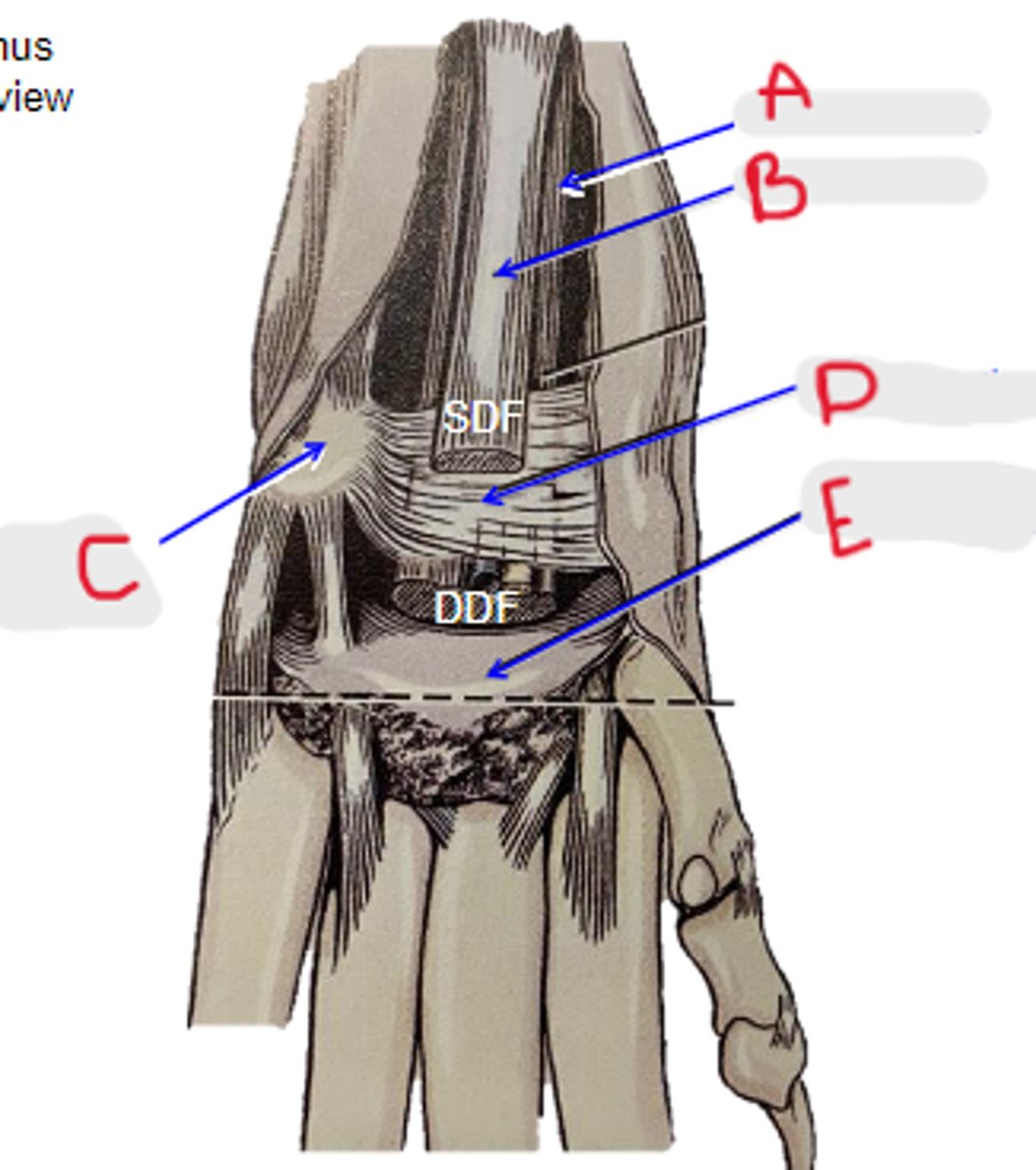
palmar carpal fibrocartilage
What is E?
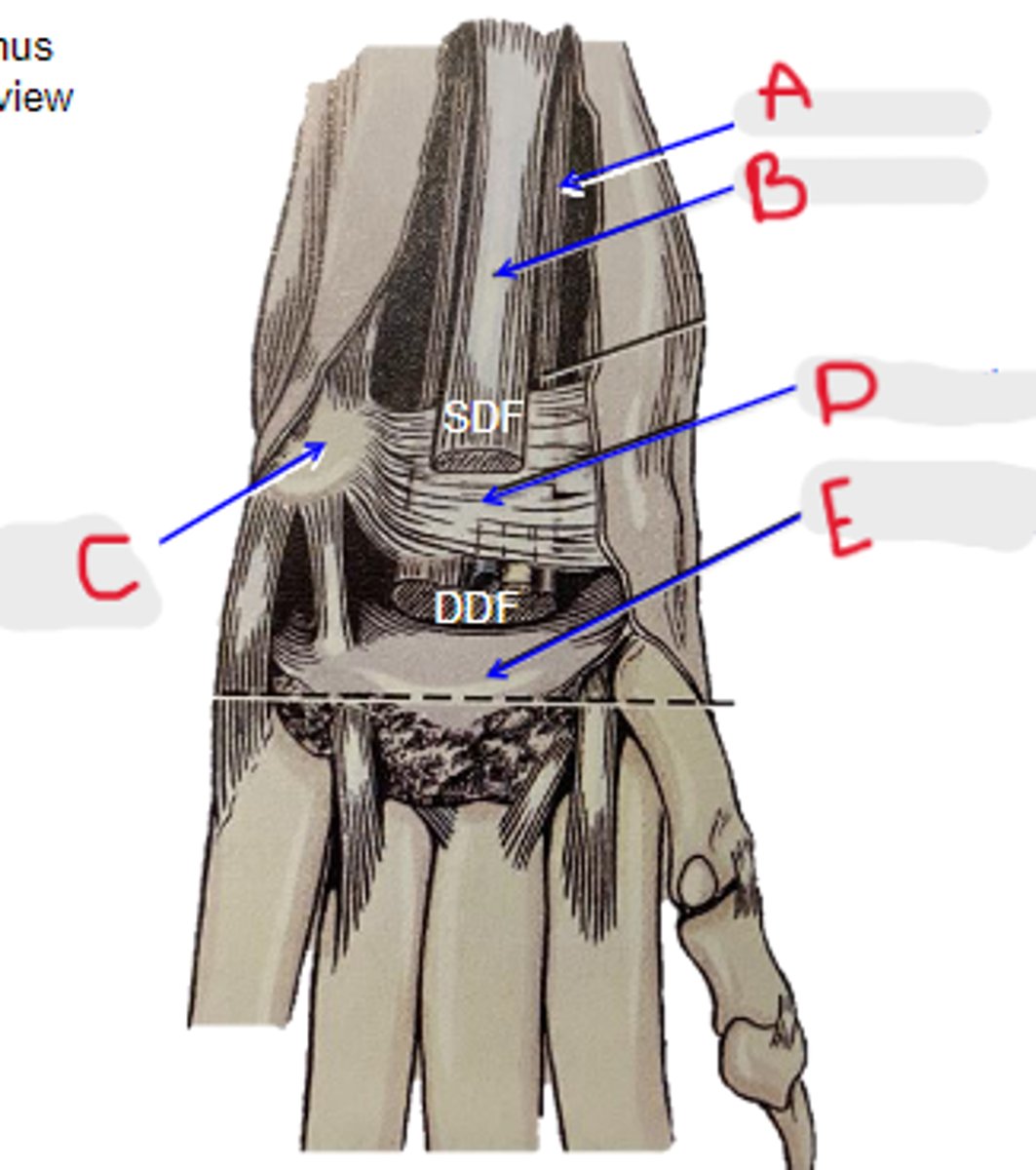
carpal tunnel
What is located in the yellow circle?
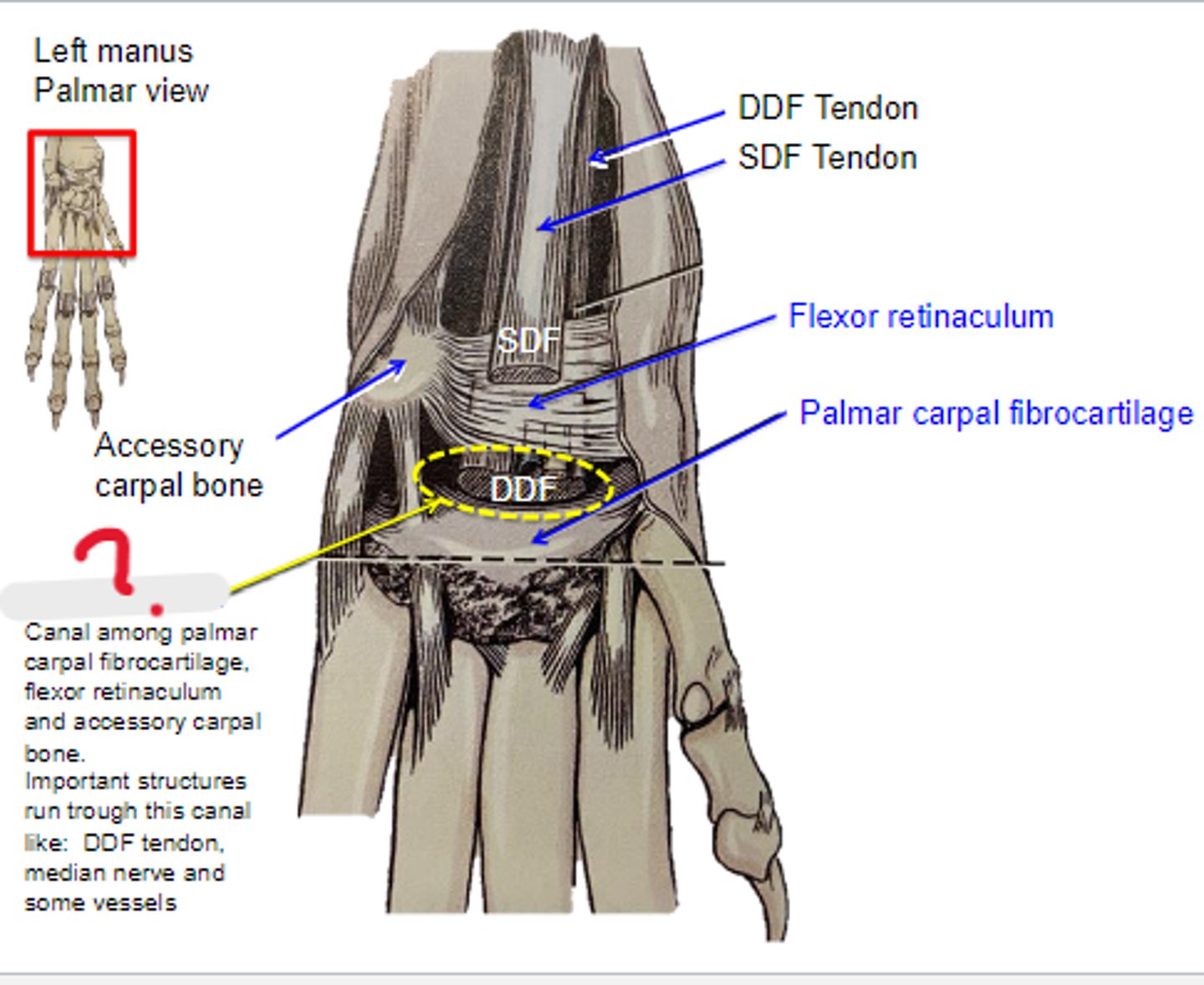
carpal tunnel
Canal among palmar carpal fibrocartilage, flexor retinaculum and accessory carpal bone. Important structures run trough this canal like: DDF tendon, median nerve and some vessels
carpal tunnel syndrome
Common condition that causes numbness, tingling, and pain in the hand and forearm. The condition occurs when one of the major nerves to the hand — the median nerve — is squeezed or compressed as it travels through the wrist.
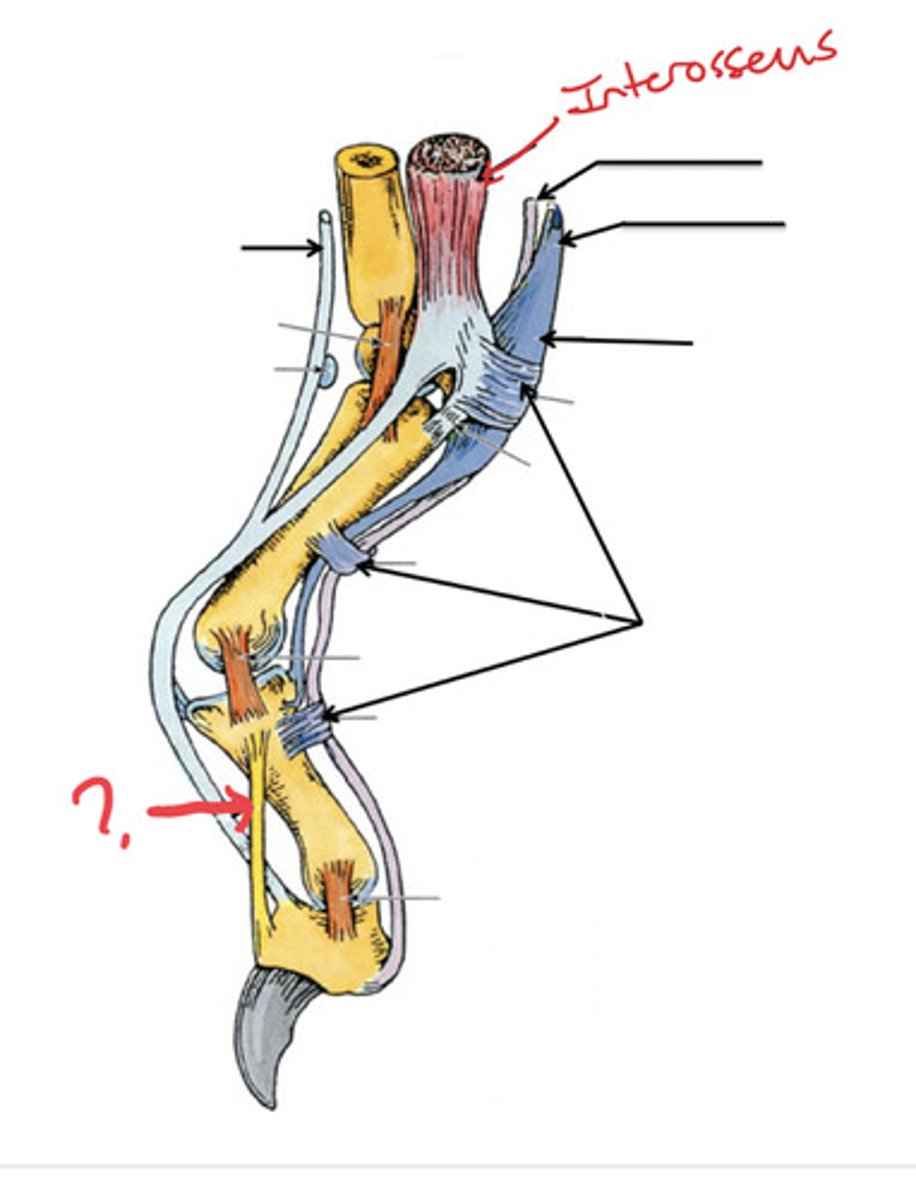
interossei (4) & interosseus (1)
What muscles are shown?
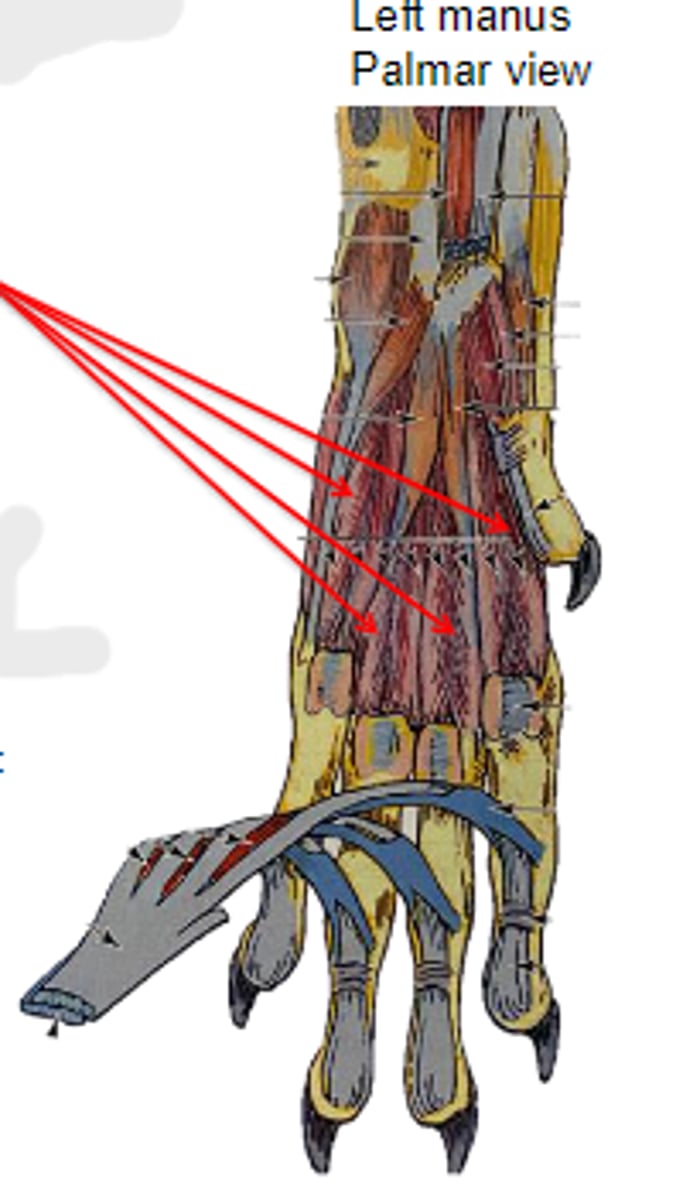
palmar base of respective metacarpal bone
Origin of interossei & interosseus:
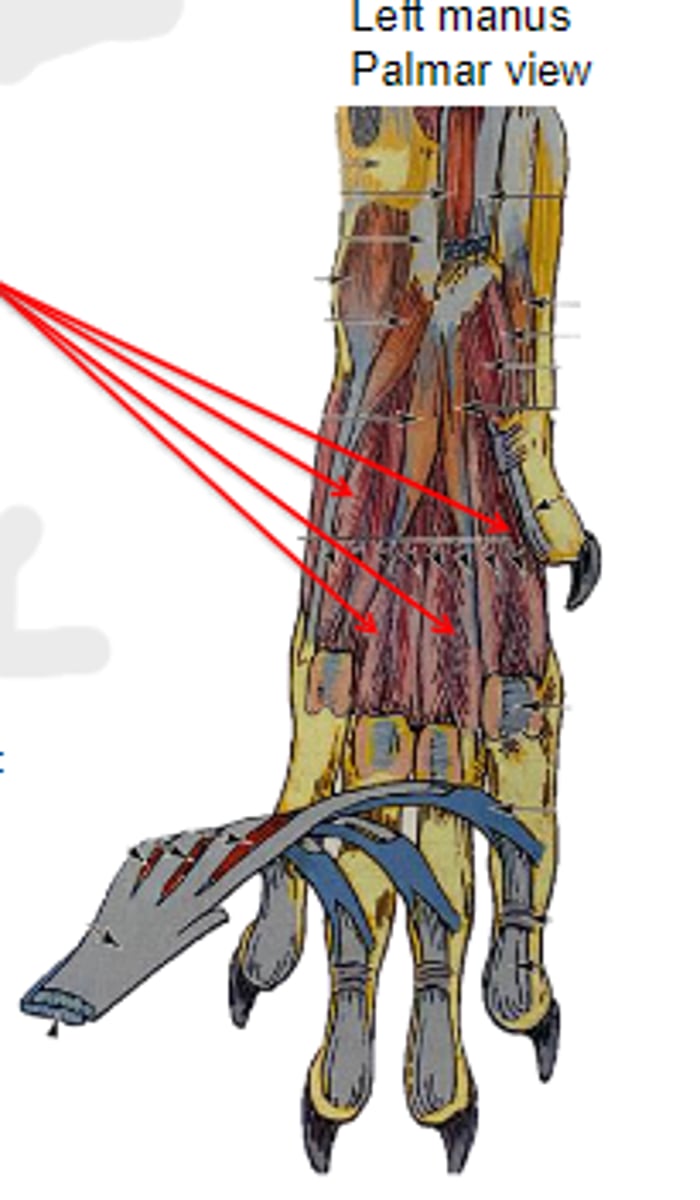
proximal sesamoid bones & palmar base of respective proximal phalanx (tendon of common digital extensor dorsally via extensor branch)
Insertion of interossei & interosseus:
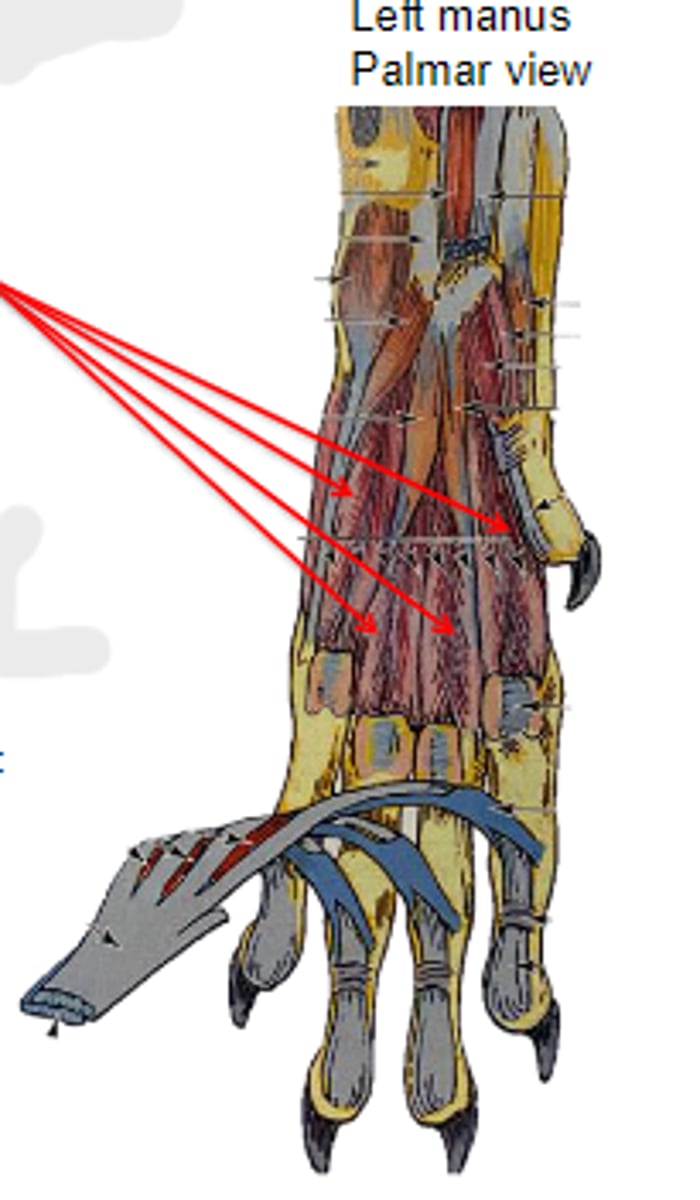
support and flex metacarpophalangeal joint
Action of interossei & interosseus:
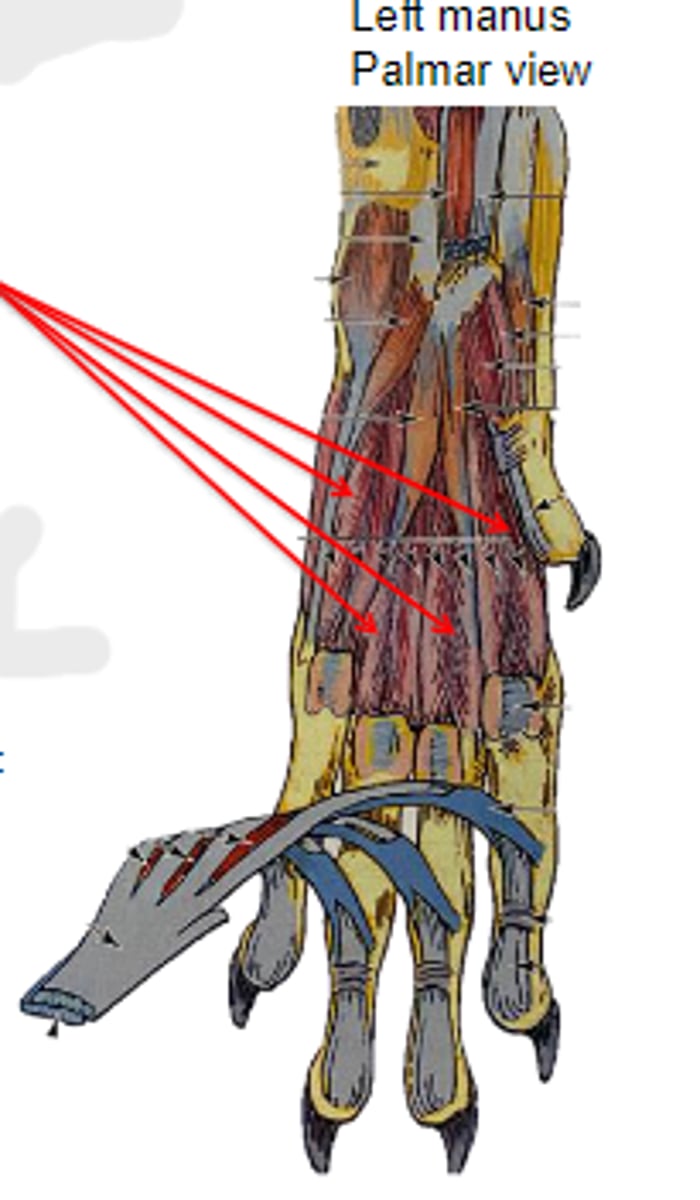
interossei & interosseus
The following are associated with what muscle(s)?
Origin: palmar base of respective metacarpal bone
Insertion: proximal sesamoid bones & palmar base proximal phalanx (tendon of common digital extensor dorsally via extensor branch)
Action: supports and flex metacarpophalangeal joint
interosseus muscle
What is A?
common digital extensor tendon
What is B?
extensor branch of interosseus
What is C?
deep digital flexor tendon
What is A?
superficial digital flexor tendon
What is B?
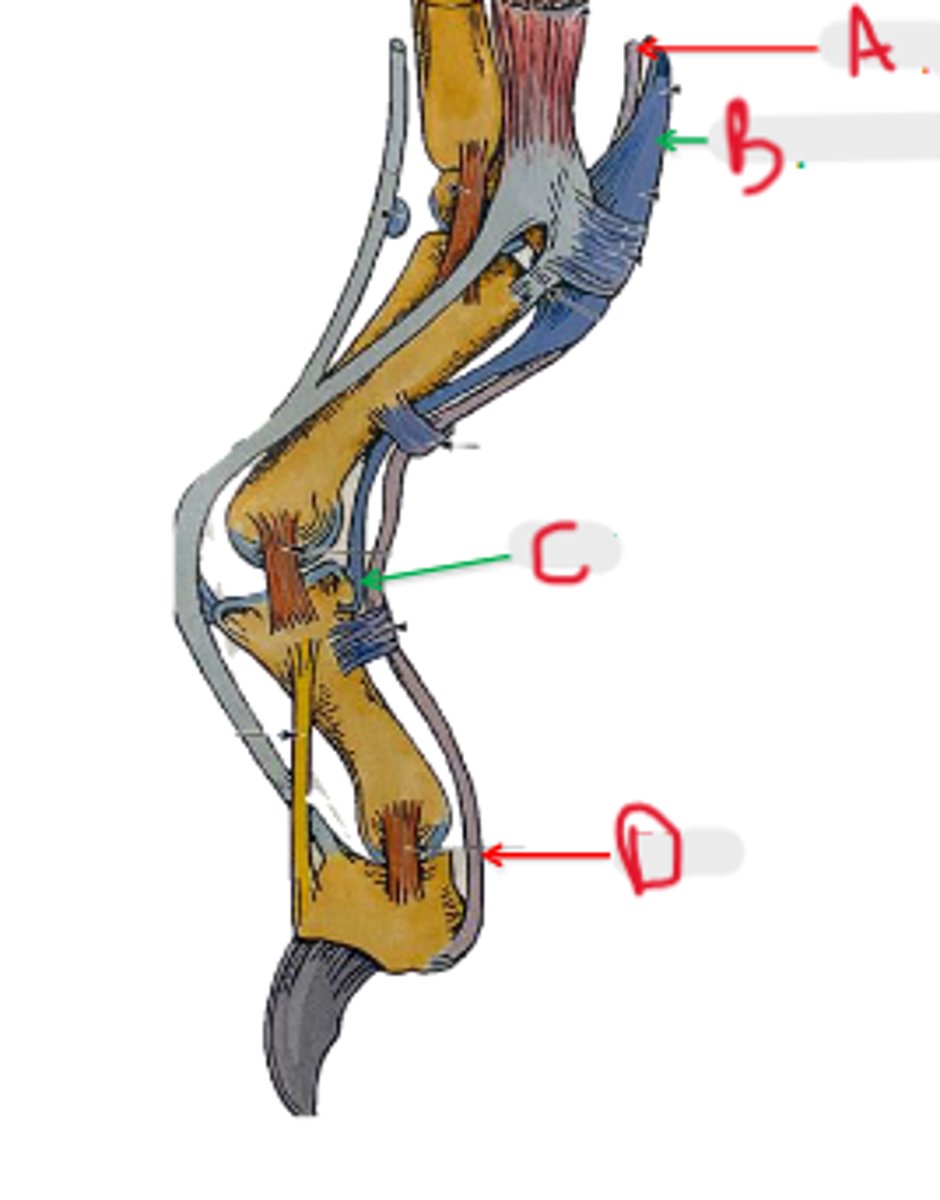
SDF
What is C?
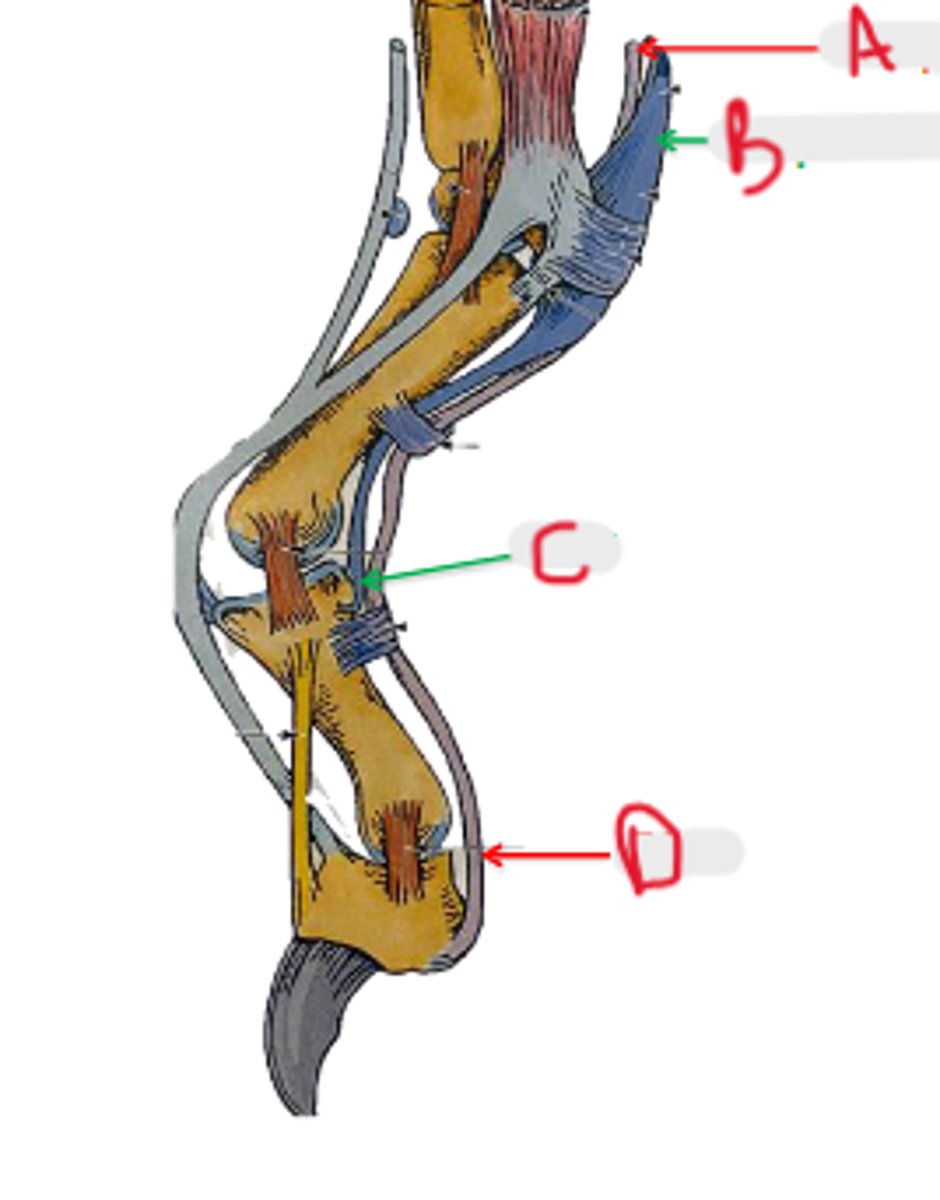
DDF
What is D?
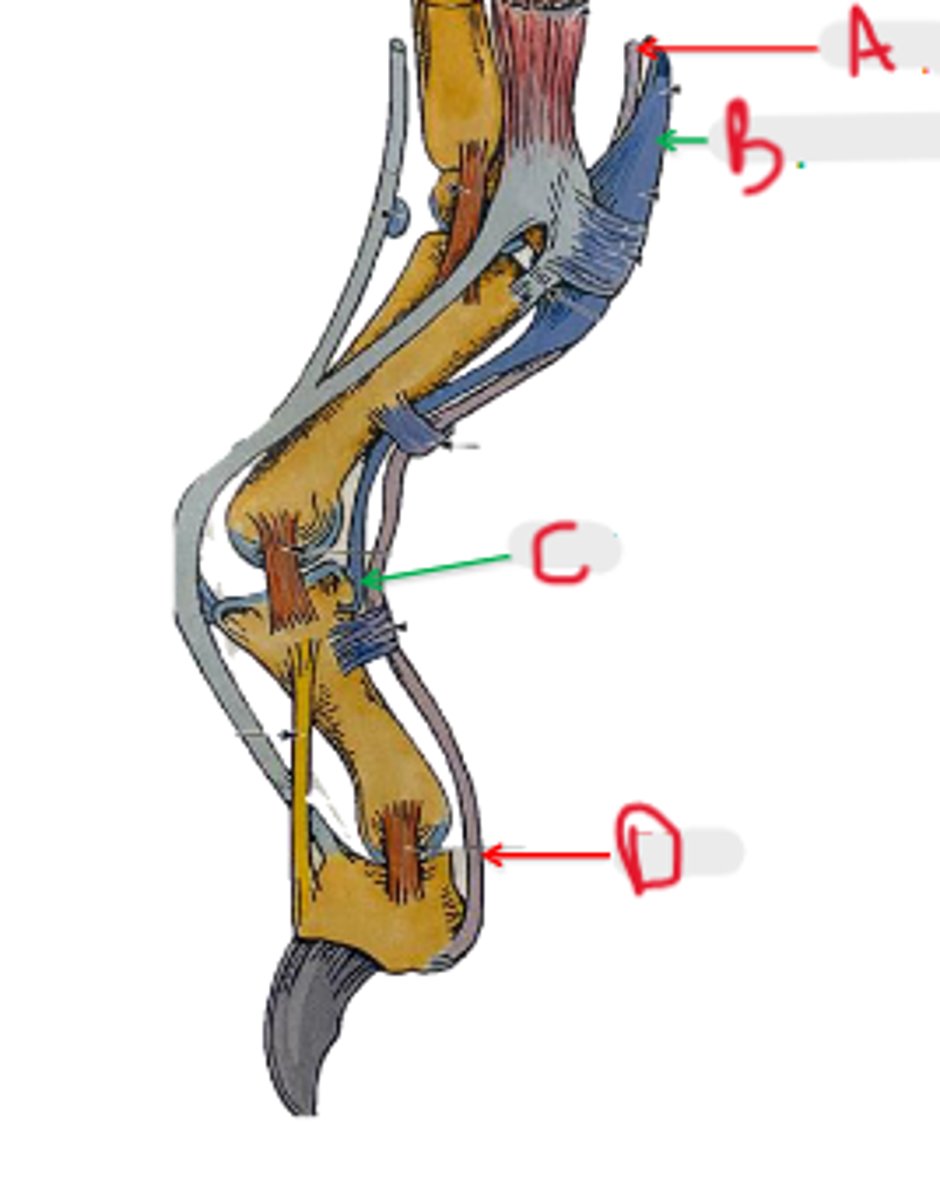
palmar annular ligament
What is A?
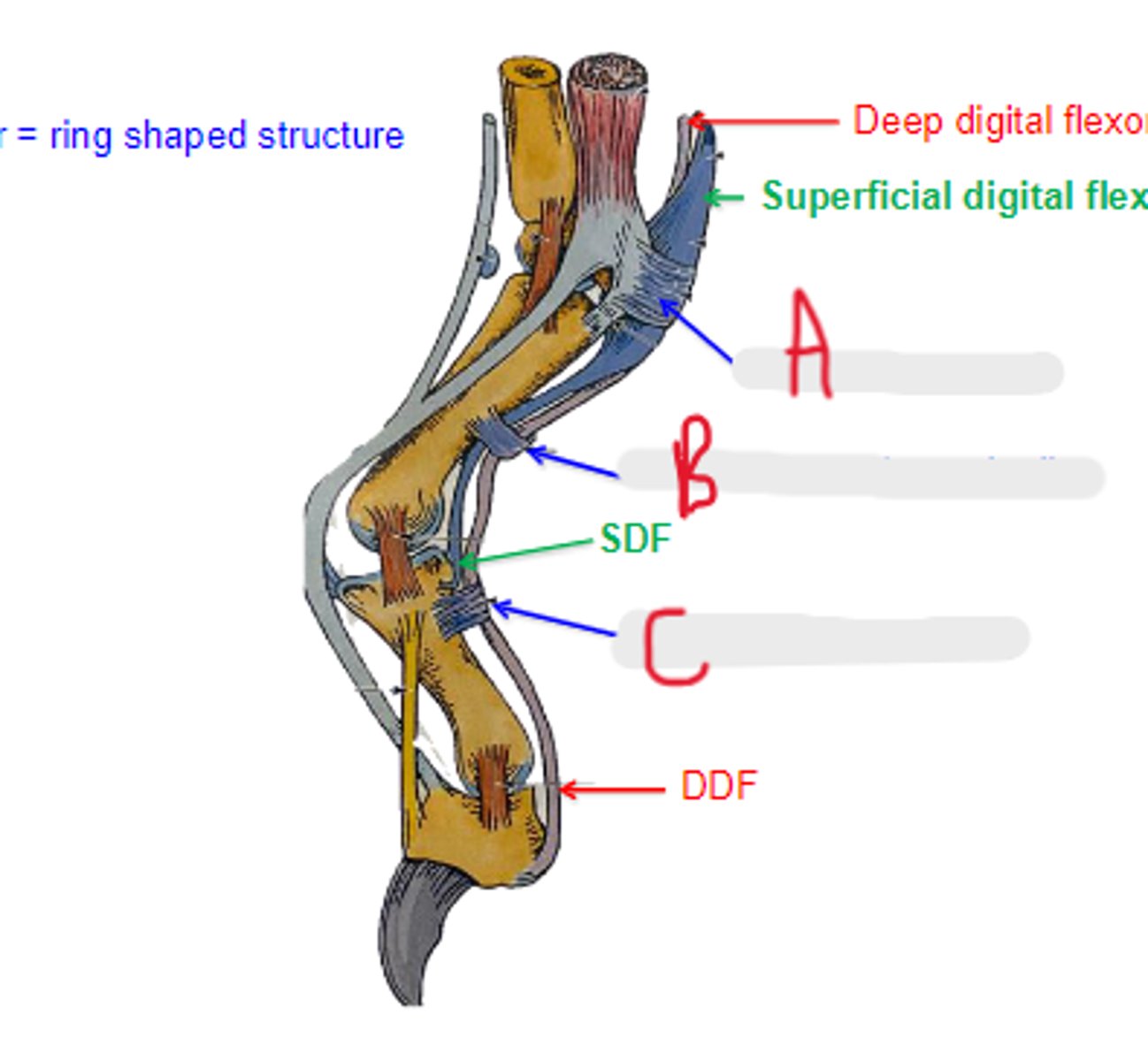
proximal digital annular ligament
What is B?
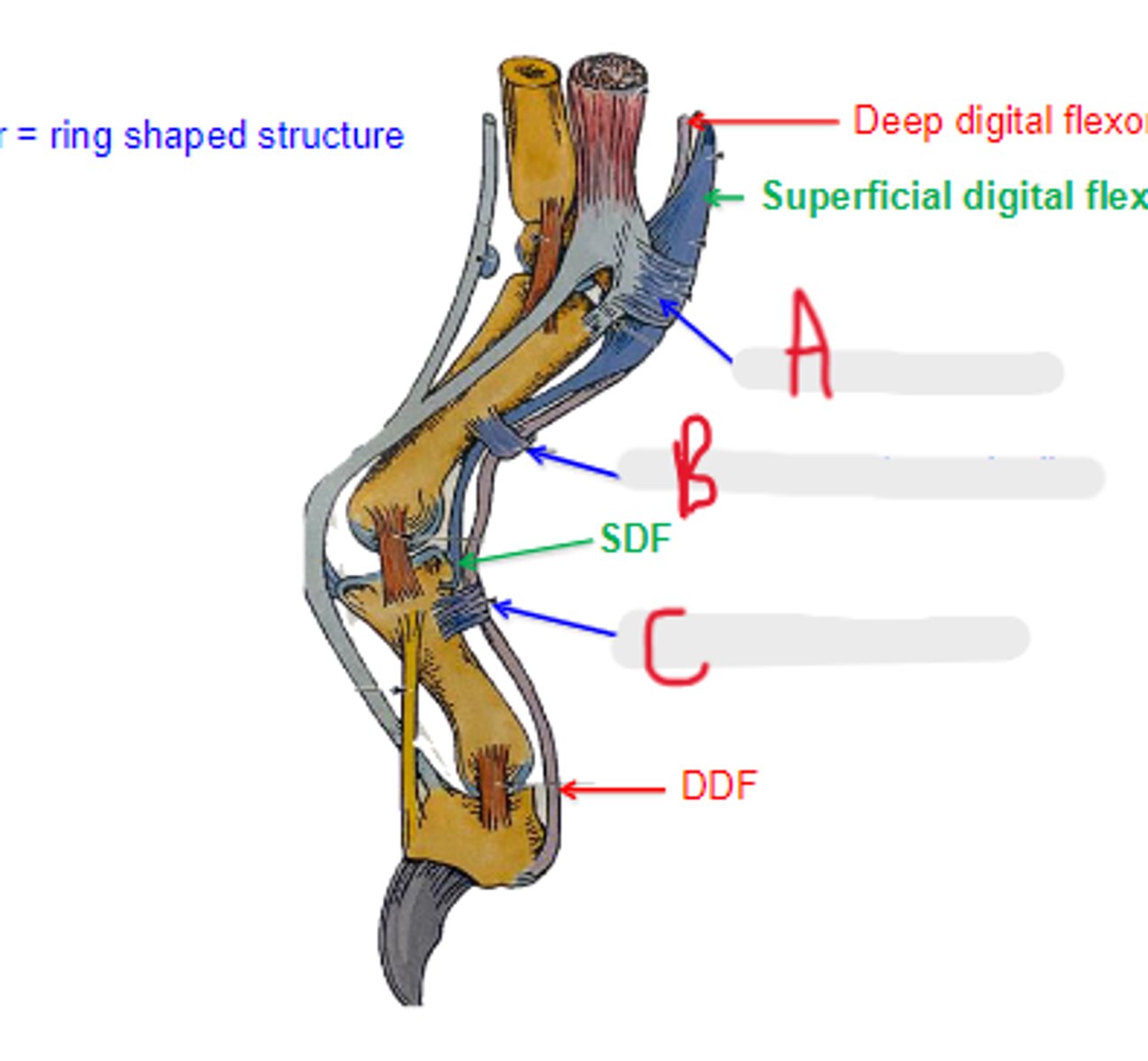
distal digital annular ligament
What is C?
annular
_____ means ring shaped structure
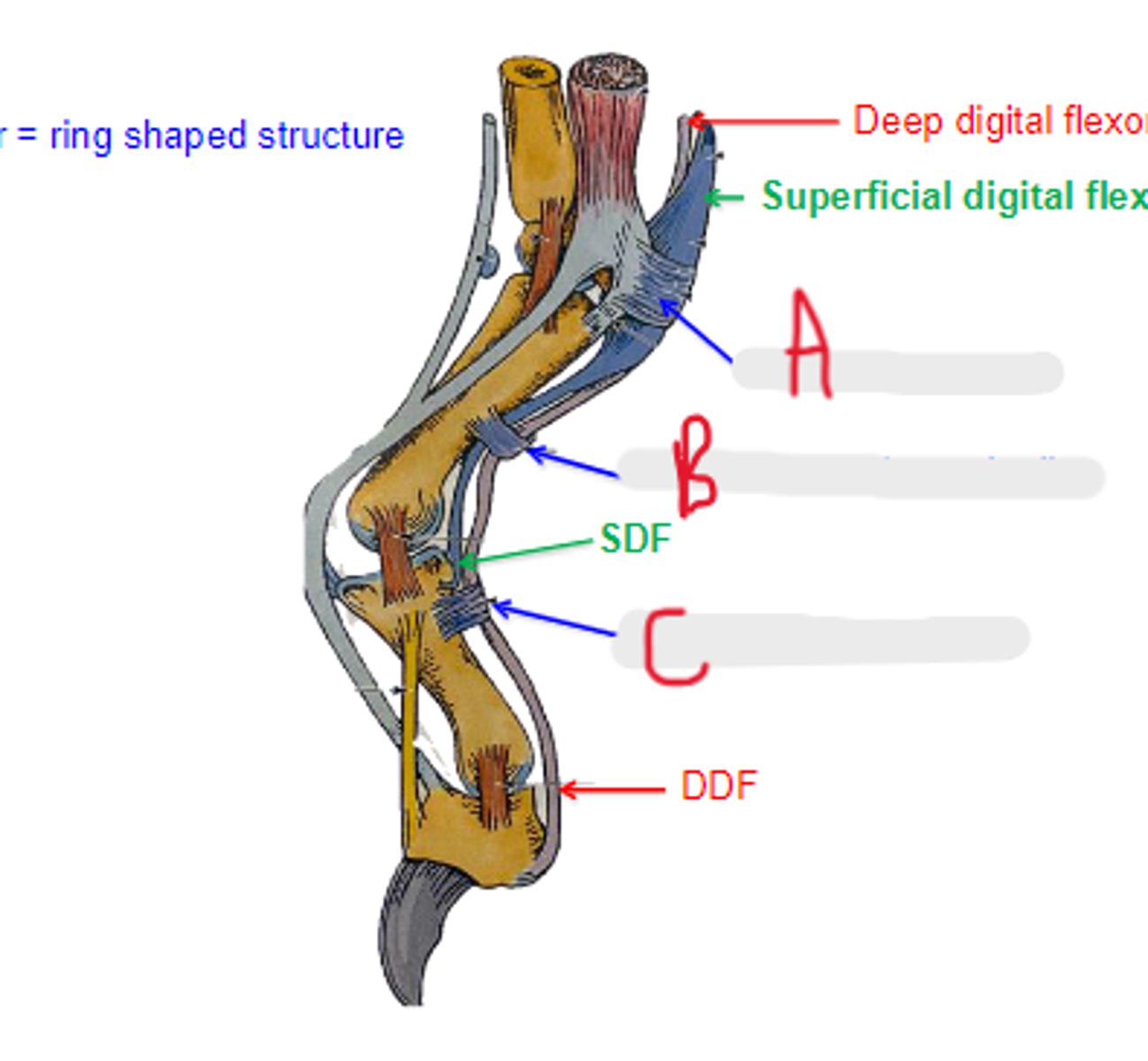
collateral ligaments
What is A?
dorsal elastic ligament
What is the arrow pointing to?
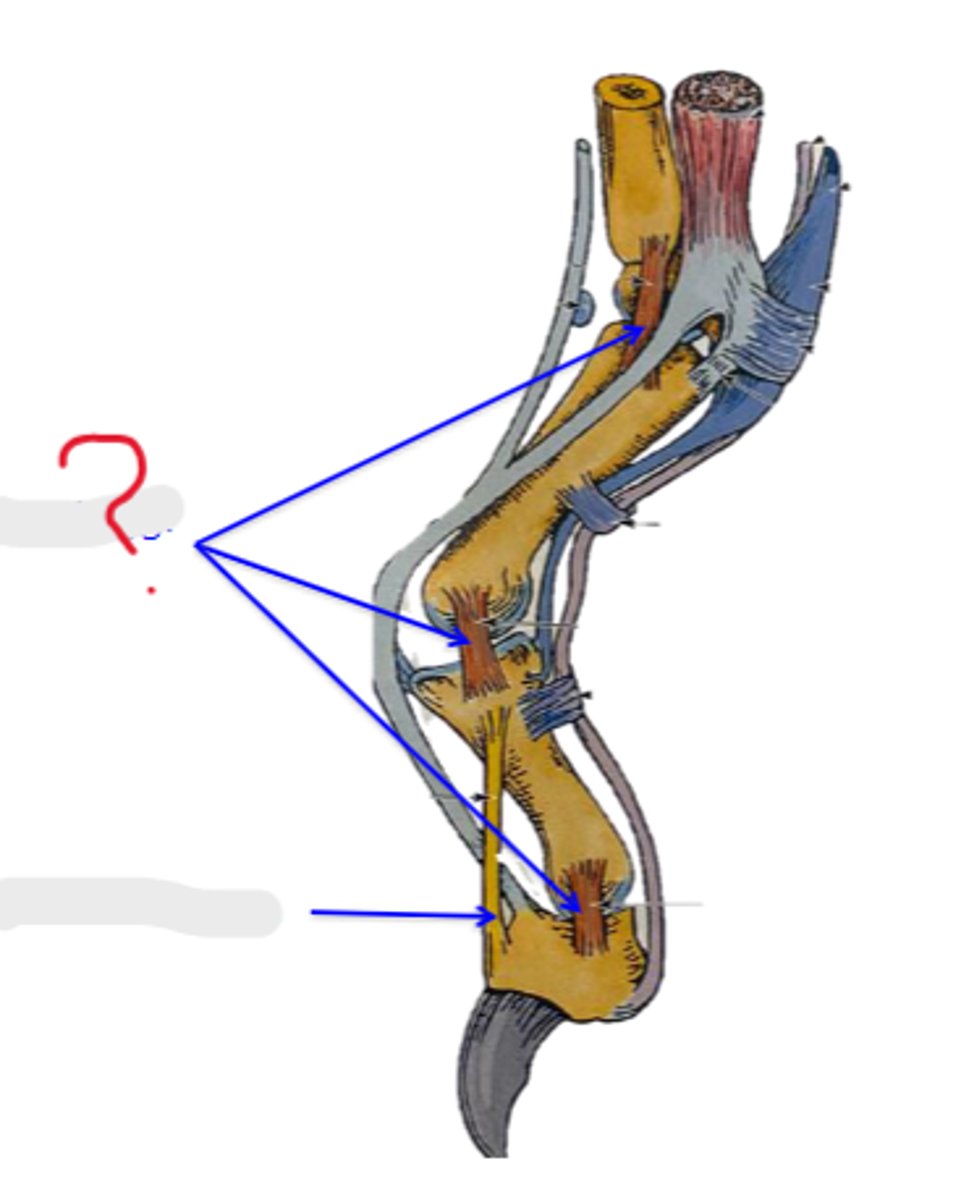
collateral ligaments
What is the arrow pointing to?
extrinsic
[Extrinsic/intrinsic] muscles join the forelimb to the trunk
2 multiple choice options
girdle
Extrinsic muscles are also known as _____ muscles
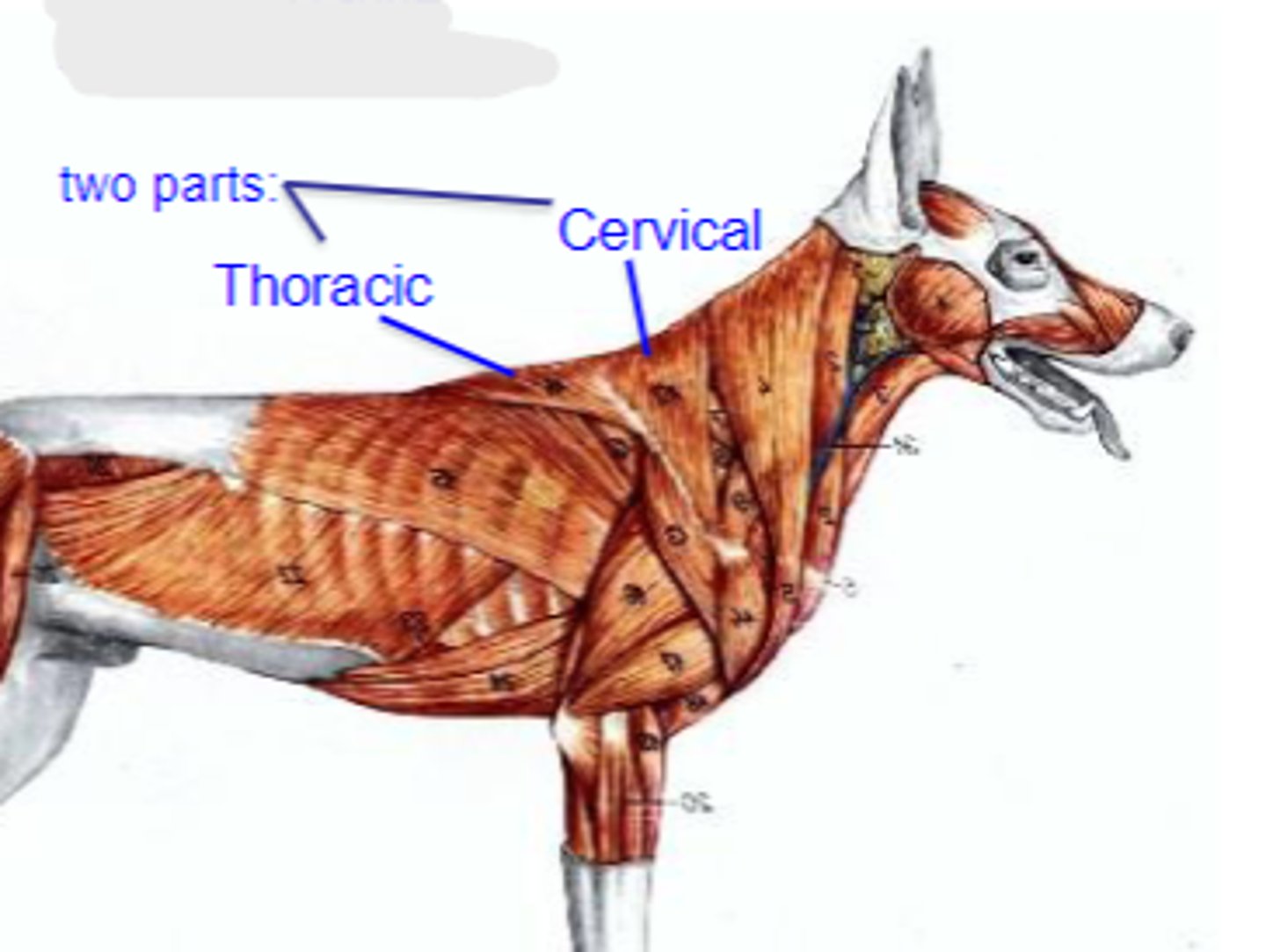
1. thoracic
2. cervical
What are the 2 parts of the Trapezius muscle?
trapezius
What muscle is being shown?
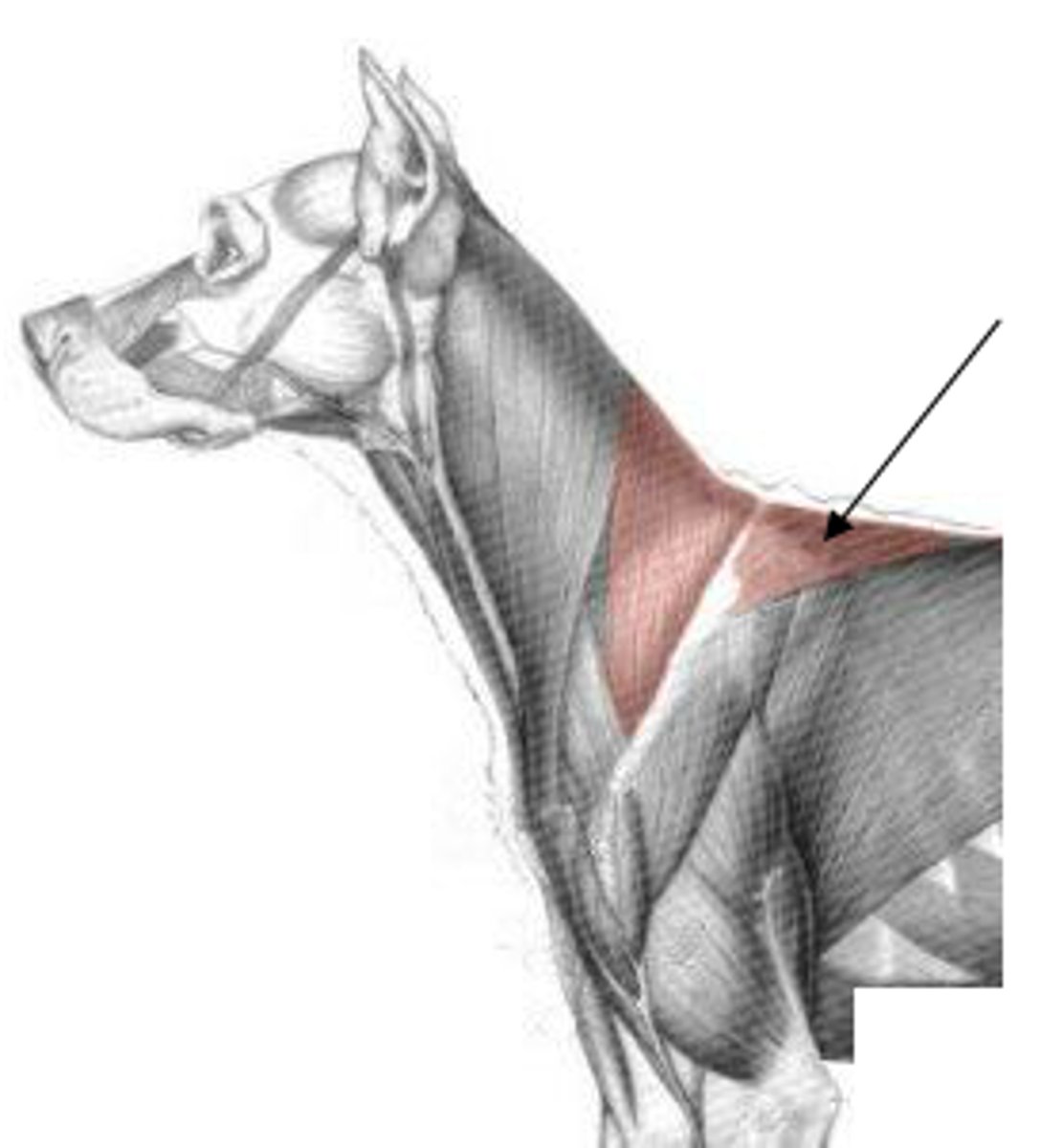
cervical: dorsal midline of neck
thoracic: dorsal midline of thorax
Origin of trapezius:
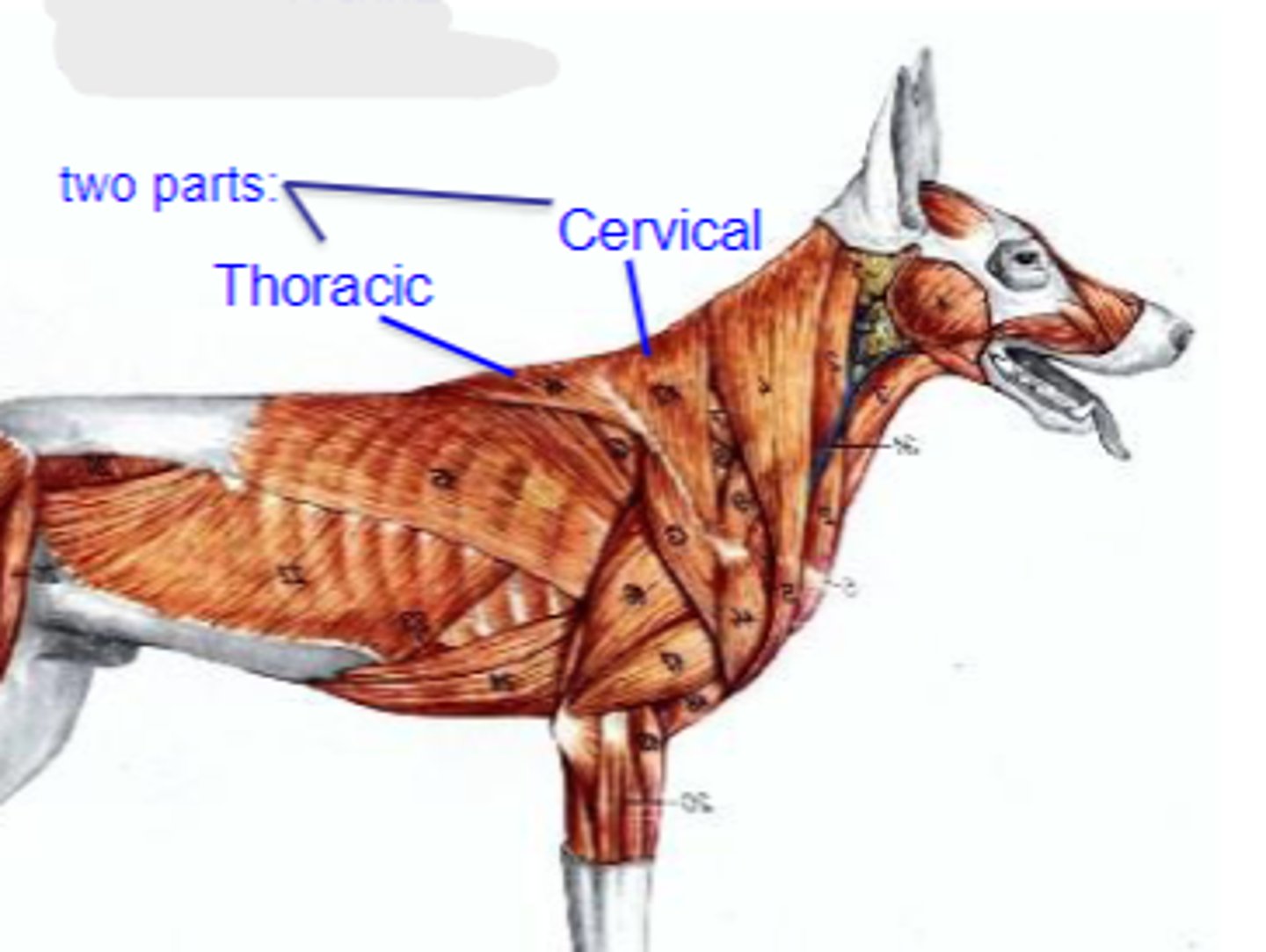
spine of scapula
Insertion of trapezius:
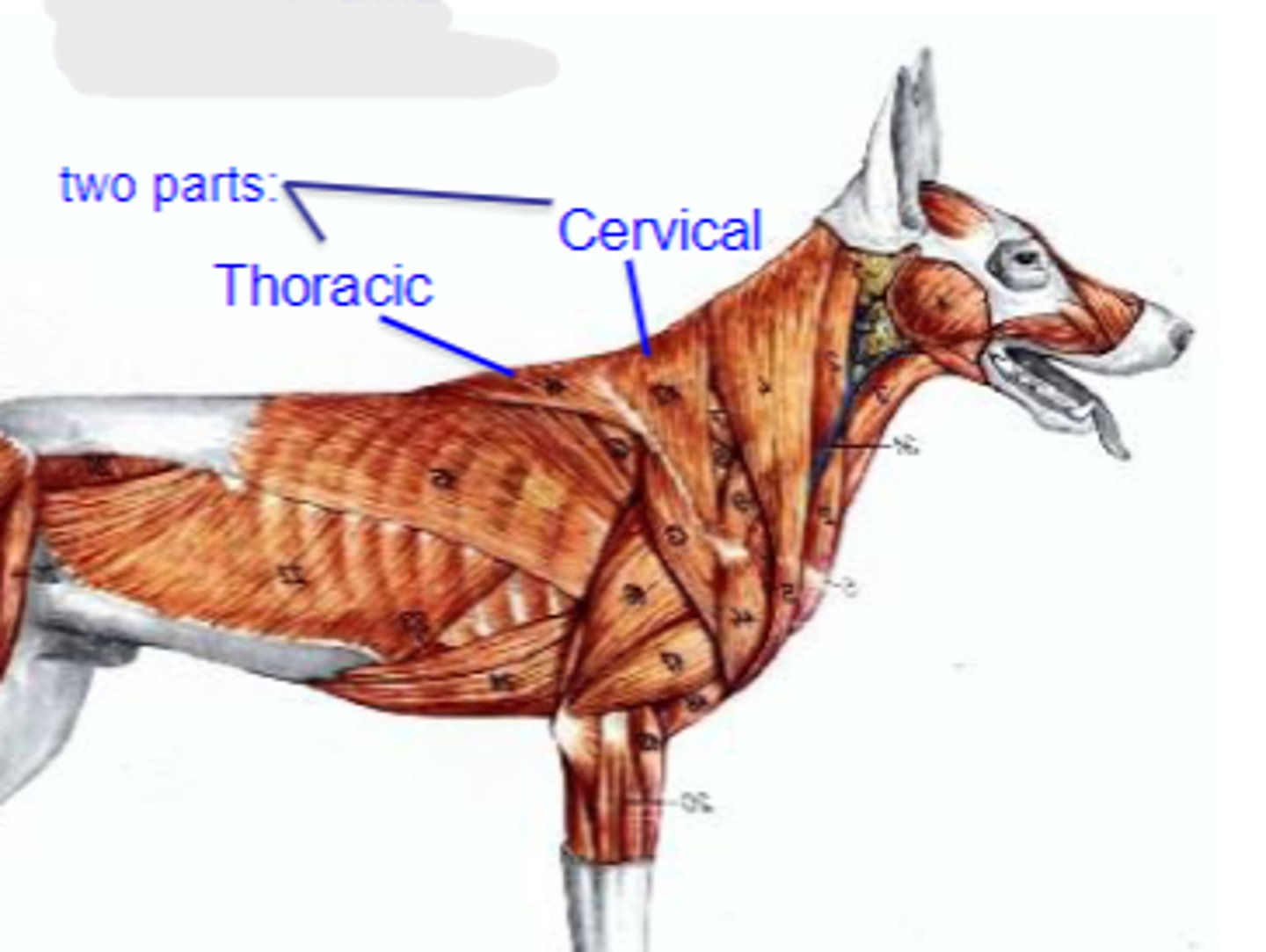
elevate thoracic limb; adduct scapula
Action of trapezius:
trapezius
The following are associated with what muscle?
Origin:
-cervical: dorsal midline of neck
-thoracic: dorsal midline of thorax
Insertion: spine of the scapula
Action: elevate the thoracic limb, adduct the scapula
1. cleidocephalicus
2. cleidobrachialis
What are the 2 parts of the brachiocephalicus?
cleidomastoideus
What is A?
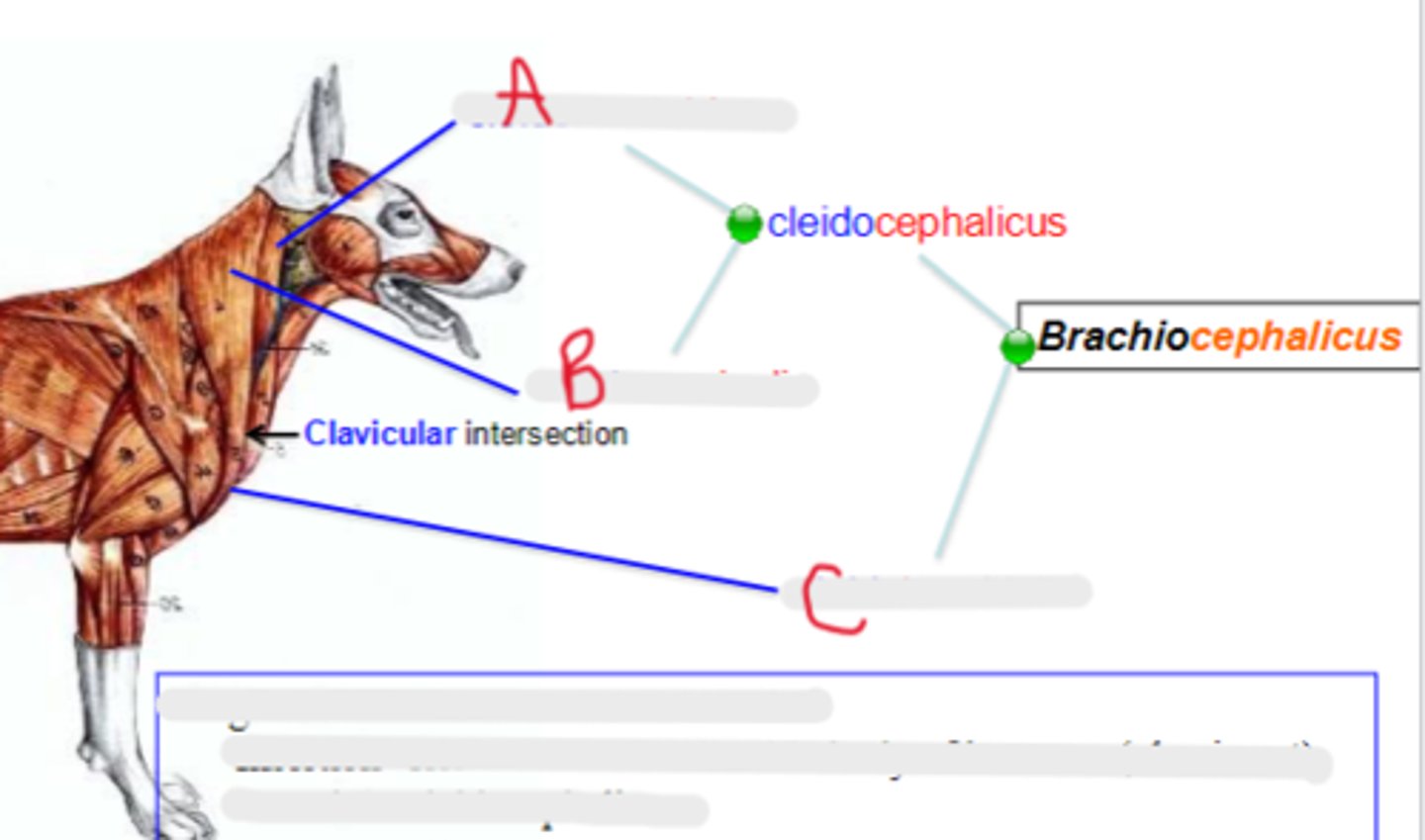
cleidocervicalis
What is B?
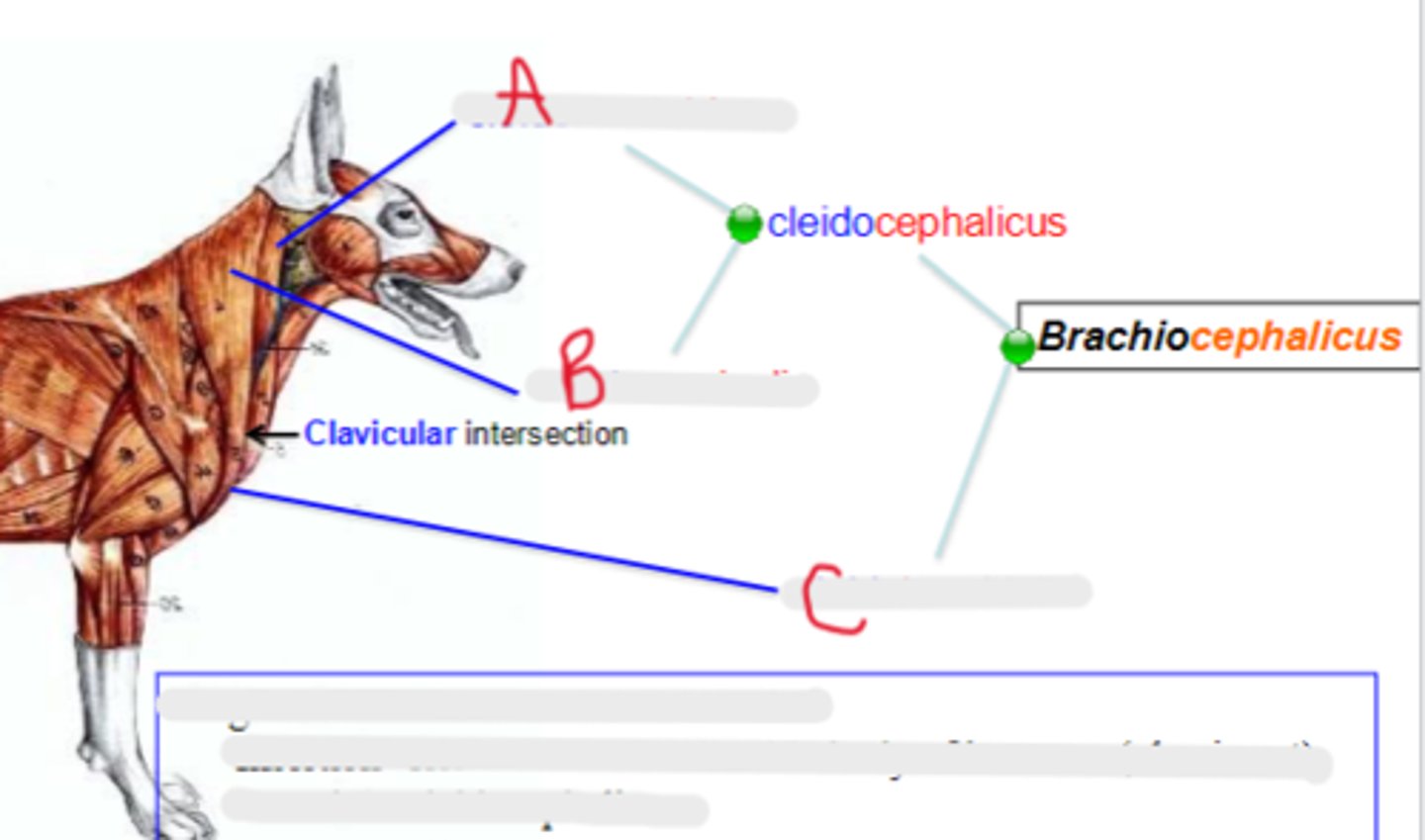
cleidobrachialis
What is C?
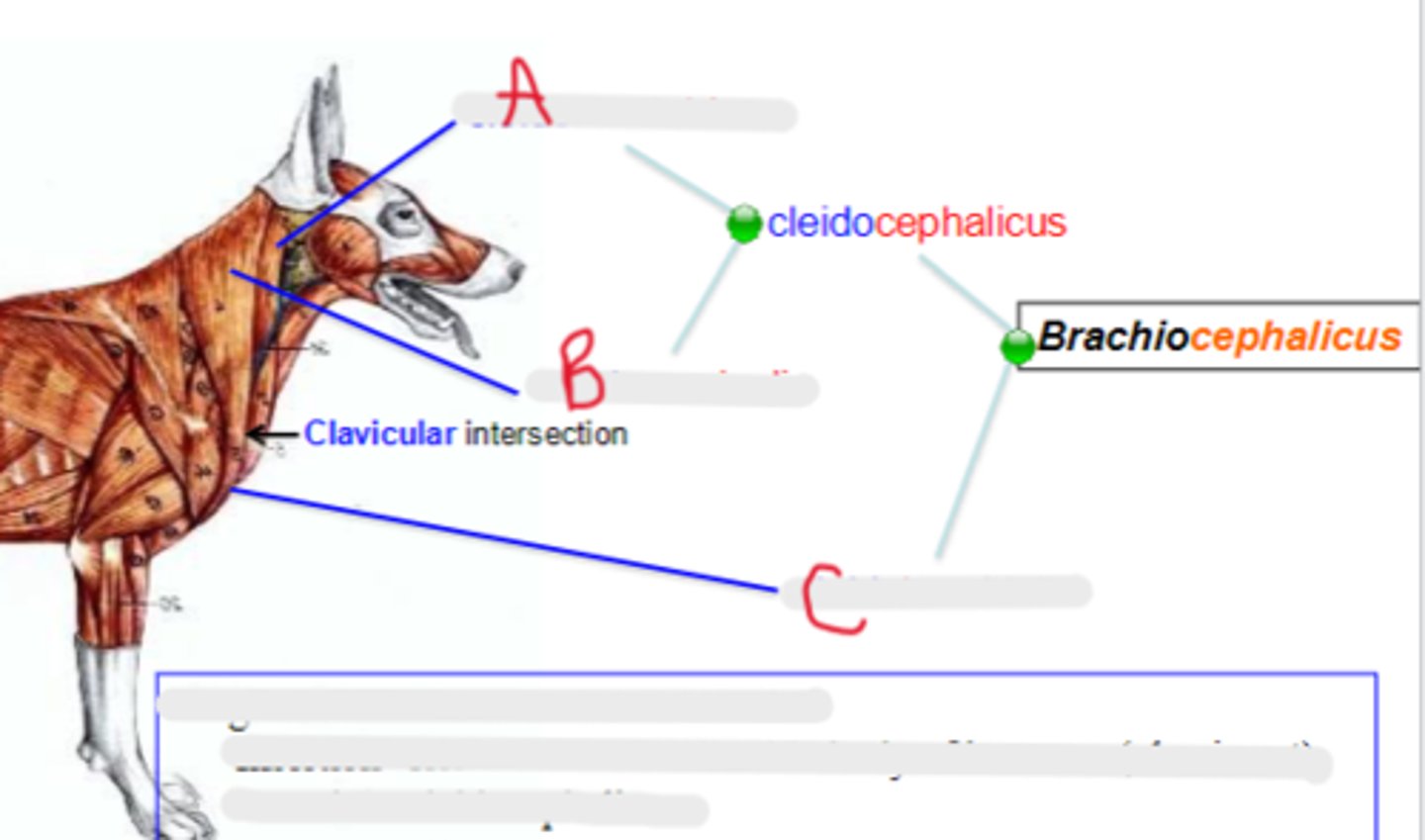
clavicular intersection / clavicle
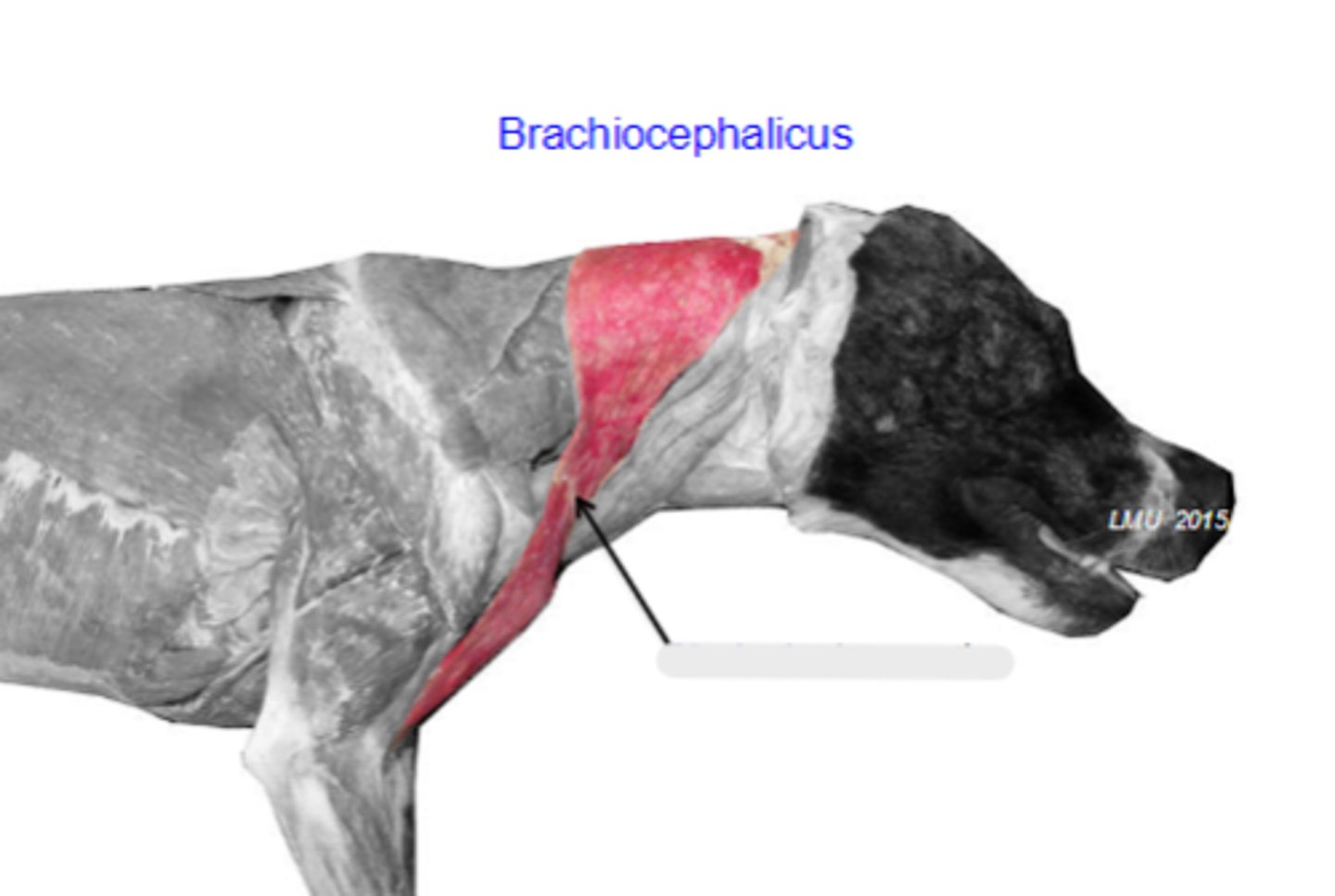
Origin of brachiocephalicus:
distal in body of humerus (ulna in cat)
Insertion of cleidobrachialis:
mastoid part: mastoid process of temporal bone
cervical part: dorsal midline of neck
Insertion of cleidocephalicus:
pull thoracic limb cranially; depress and pull head and neck laterally
Action of brachiocephalicus:
brachiocephalicus
The following are associated with what muscle?
Origin: clavicular intersection / clavicle
Insertion:
- cleidobrachialis: distal in body of humerus (ulna in cat)
- cleidocephalicus:
---mastoid part: mastoid process of temporal bone
---cervical part: dorsal midline of neck
Action: pull thoracic limb cranially; depress and pull head and neck laterally
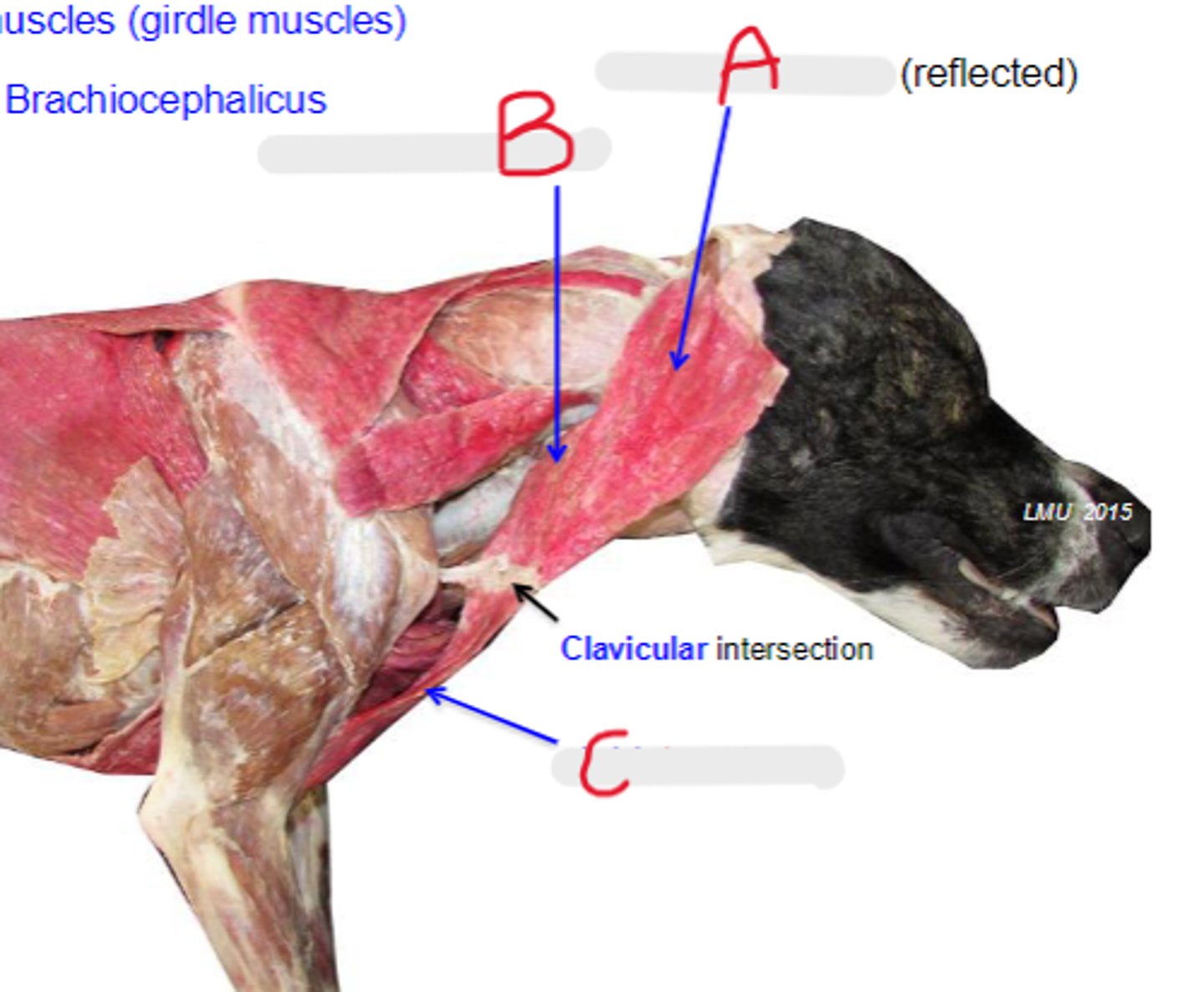
clavicular intersection
What is the arrow pointing to?
cleidocervicalis
What is A?
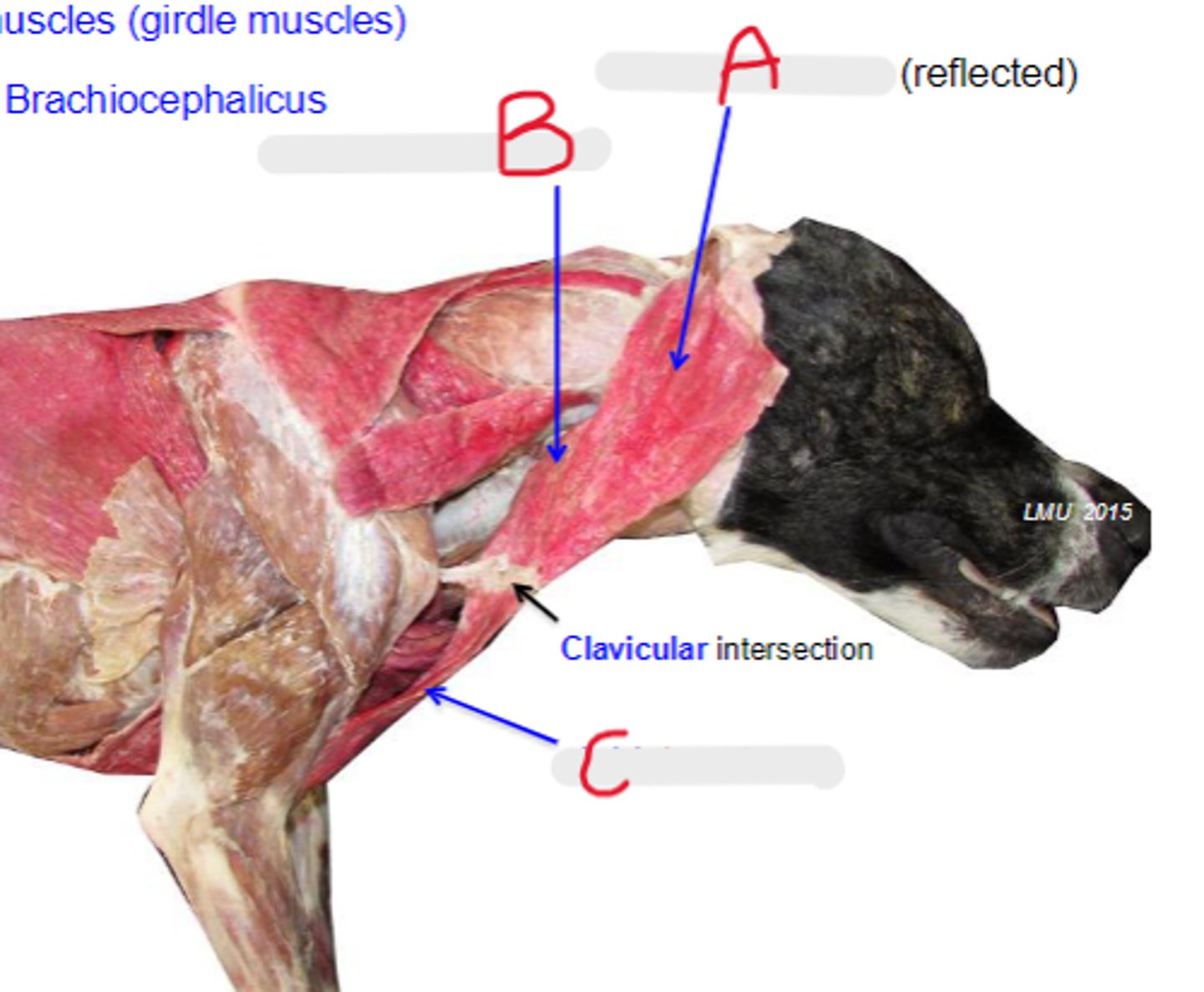
cleidomastoideus
What is B?
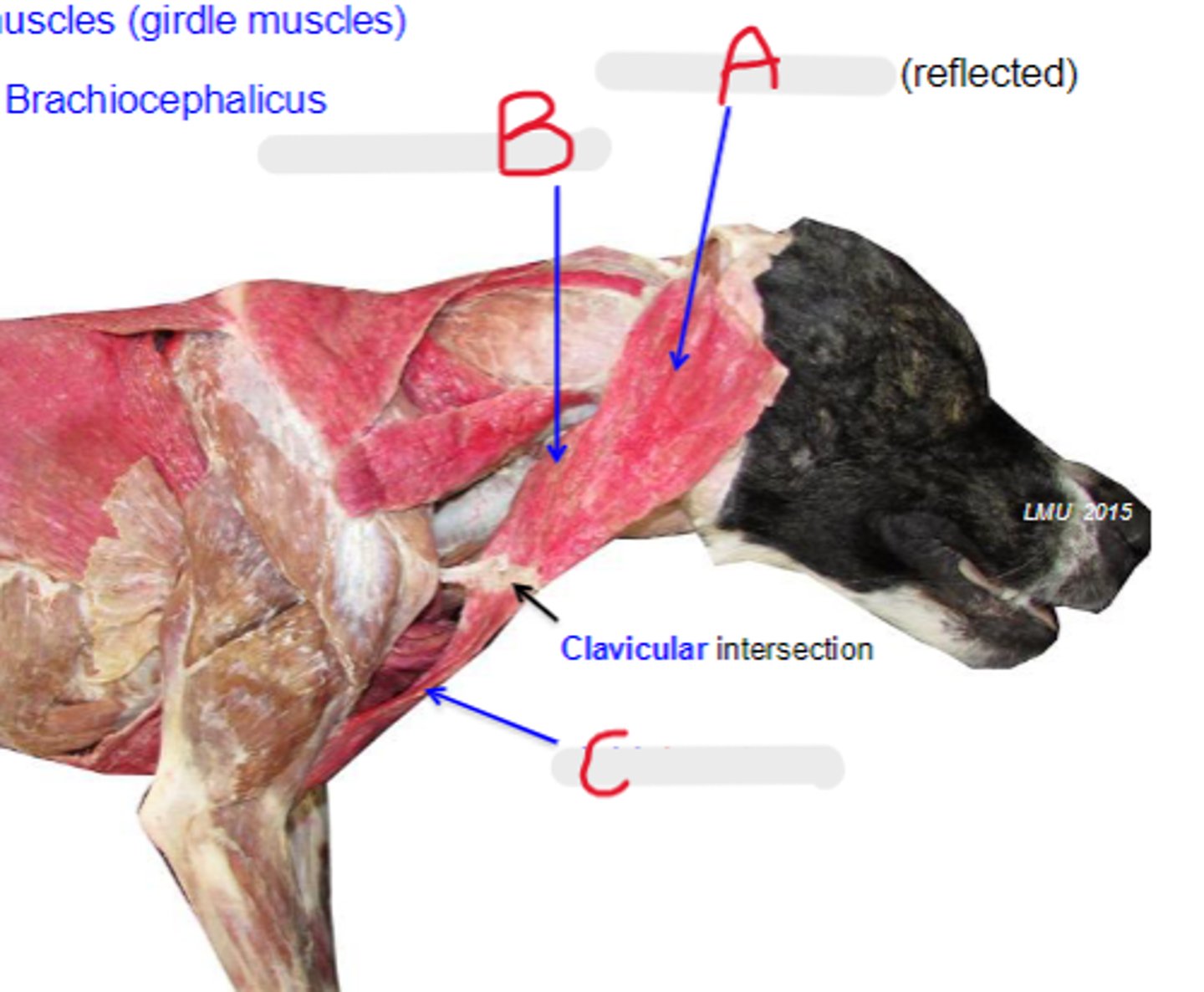
cleidobrachialis
What is C?
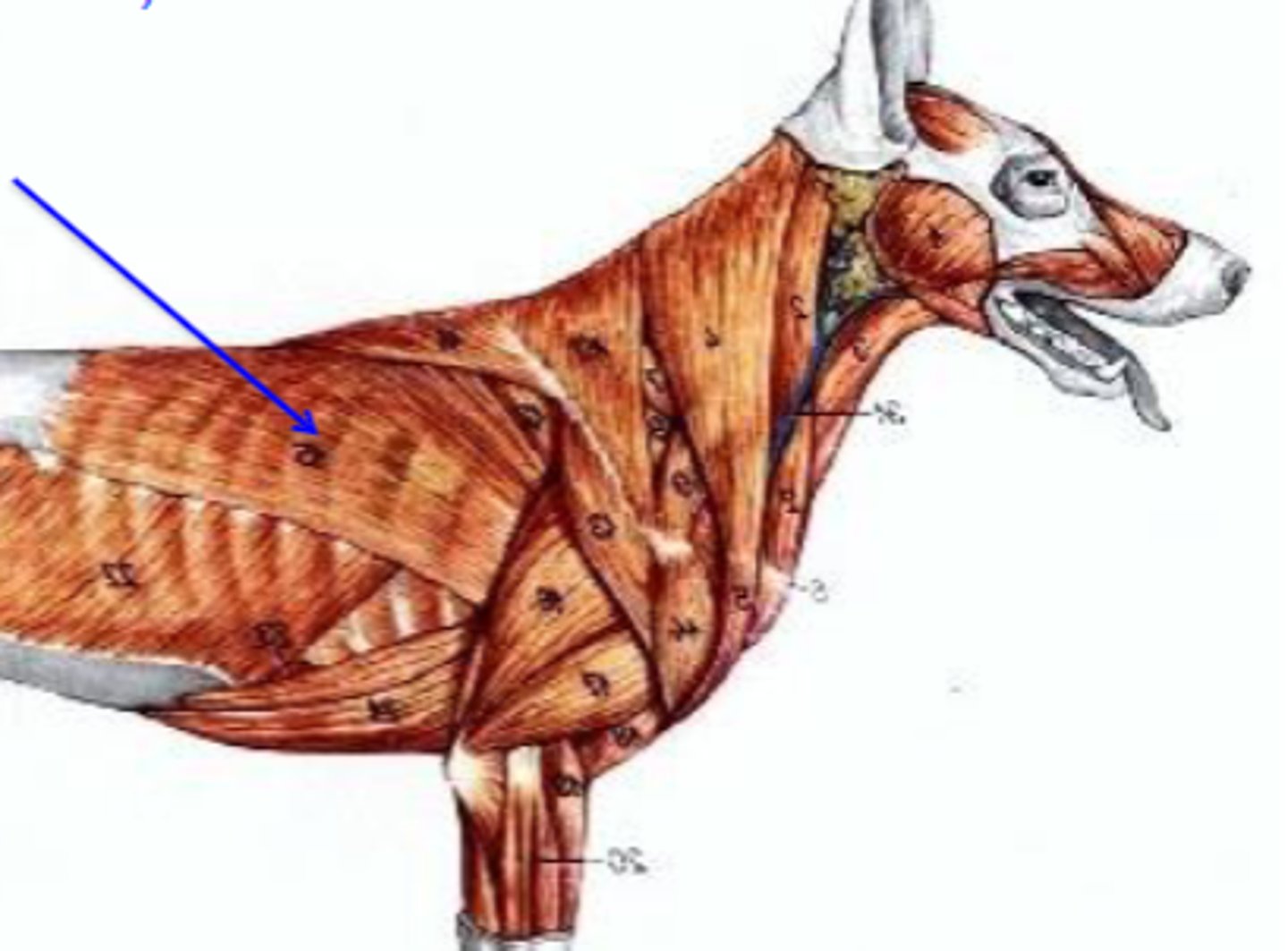
omotransversarius
What muscle is shown?
wing of atlas
Cranial most attachment of omotransversarius:
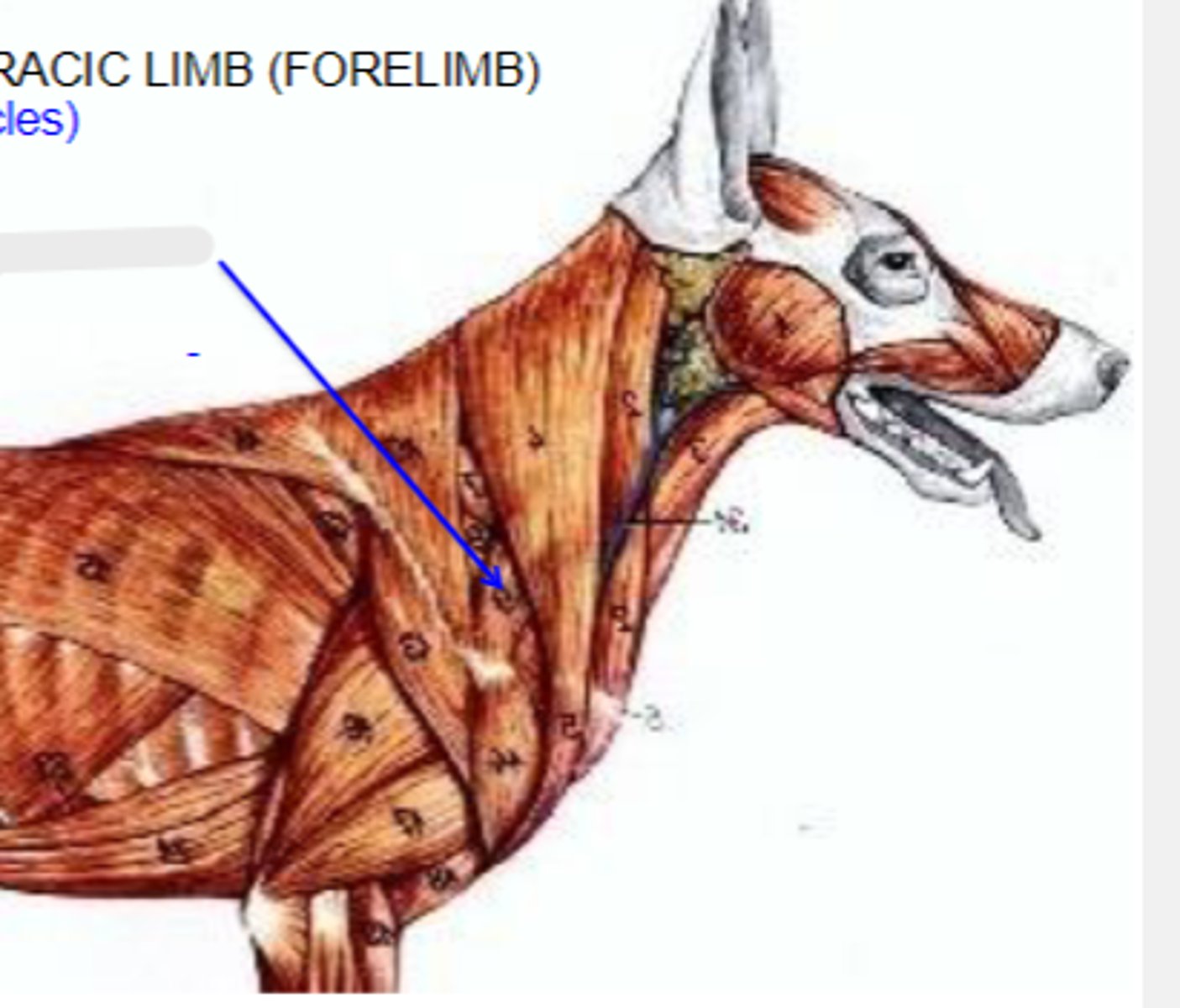
distal spine of scapula
Caudal most attachment of omotransversarius:
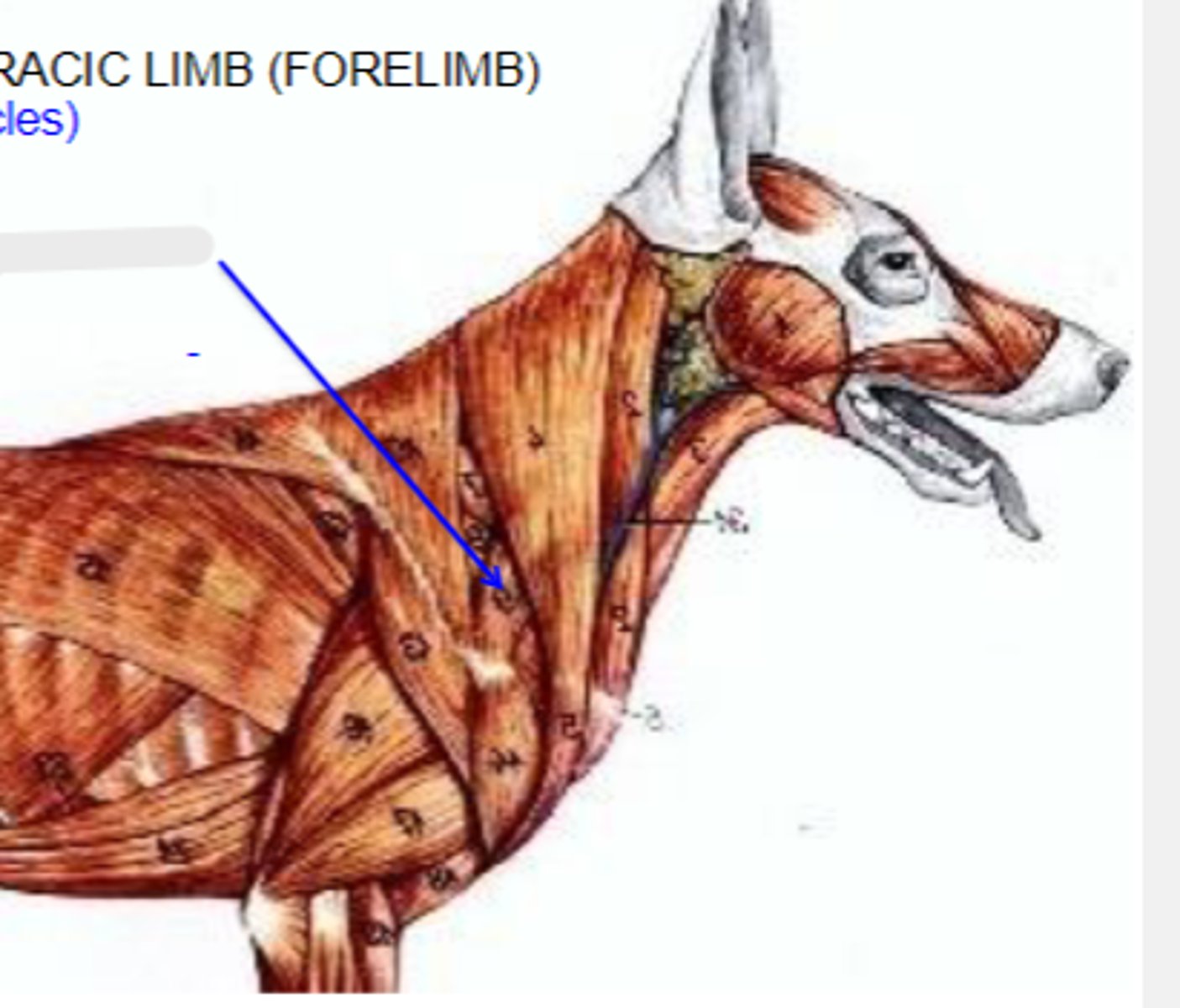
pull thoracic limb cranially; depress and pull head and neck laterally
Action of omotransversarius:
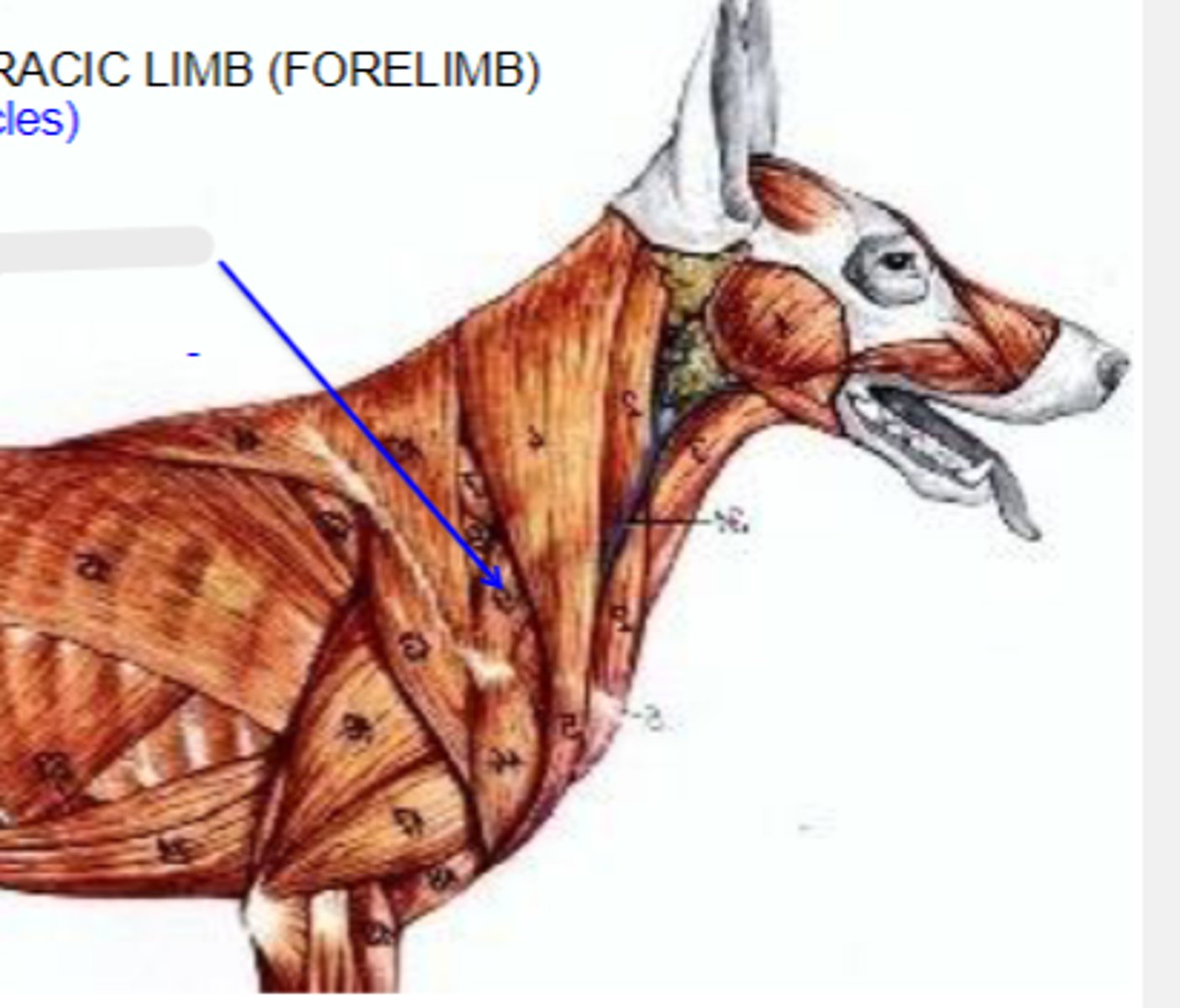
omotransversarius
The following are associated with what muscle?
Cranial-most attachment: wing of the atlas
Caudal-most attachment: distal spine of the scapula
Action: pull thoracic limb cranially; depress and pull head and neck laterally
omotransversarius
What muscle is shown?
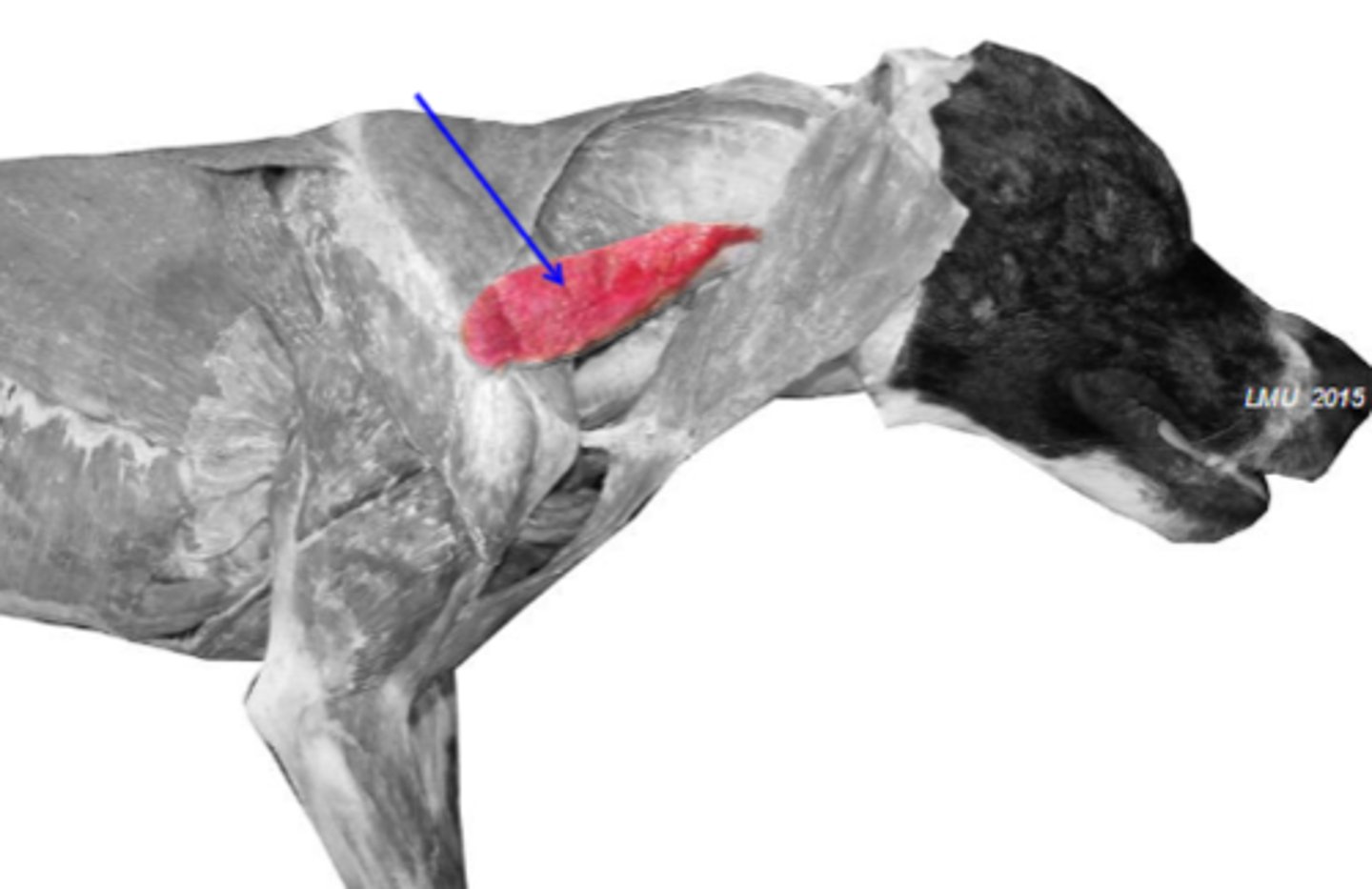
latissimus dorsi
What muscle is being shown?
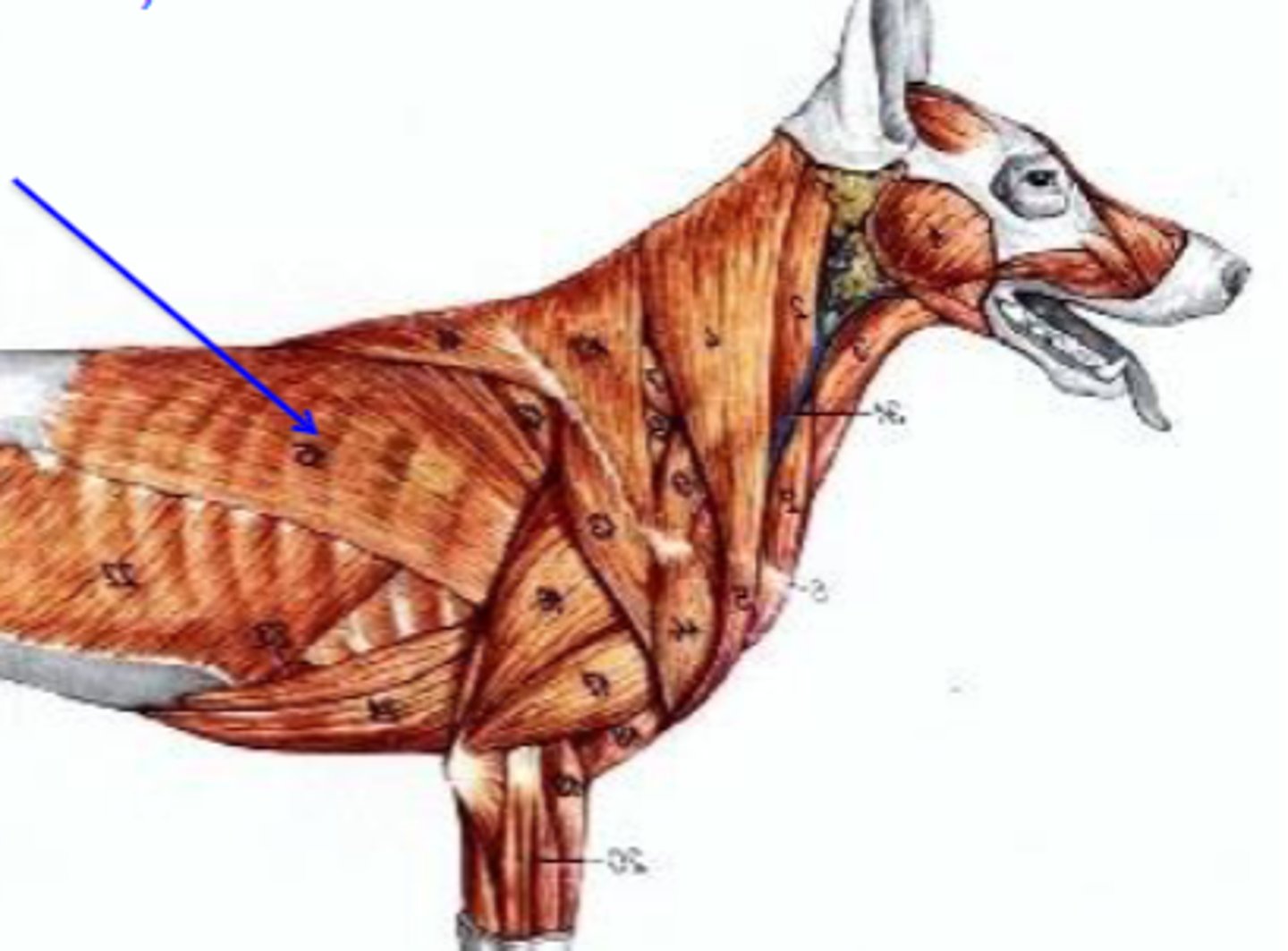
thoracolumbar fascia
Origin of latissimus dorsi: