vision
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
light
electromagnetic radiation traveling in waves
wall of eye
3 types: fibrous, vascular, inner layer
fibrous
sclera + cornea
vascular
posterior choroid
inner
retina
posterior choroid
membrane that supplies all of the layers w/ blood
iris
circular muscle that controls the diameter of the pupil; helps to restrict light rays to focus; controls how much light enters the retina
Two systems of the iris
parasympathetic
sympathetic
parasympathetic iris
causes the sphincter pupillae muscles in iris to contract (makes pupils smaller) in response to certain conditions like bright light or focusing on close objects
sympathetic iris
causes dilator pupillae muscles in iris so iris can lead to pupil dilation (widens pupil) so more light is allowed in; helpful in low light conditions
pupil
opening that allows light to reach the retina
aqueous humor
fluid behind cornea
in anterior chamber
sclera
outermost layer that forms eyeball
only layer in anterior chamber
extraocular muscles
attached to the eye and skull and allow movement
conjunctiva
membrane inside the eyelid attached to the sclera
optic nerve
axons of the retina leaving eye
cornea
transparent surface covering the iris and pupil
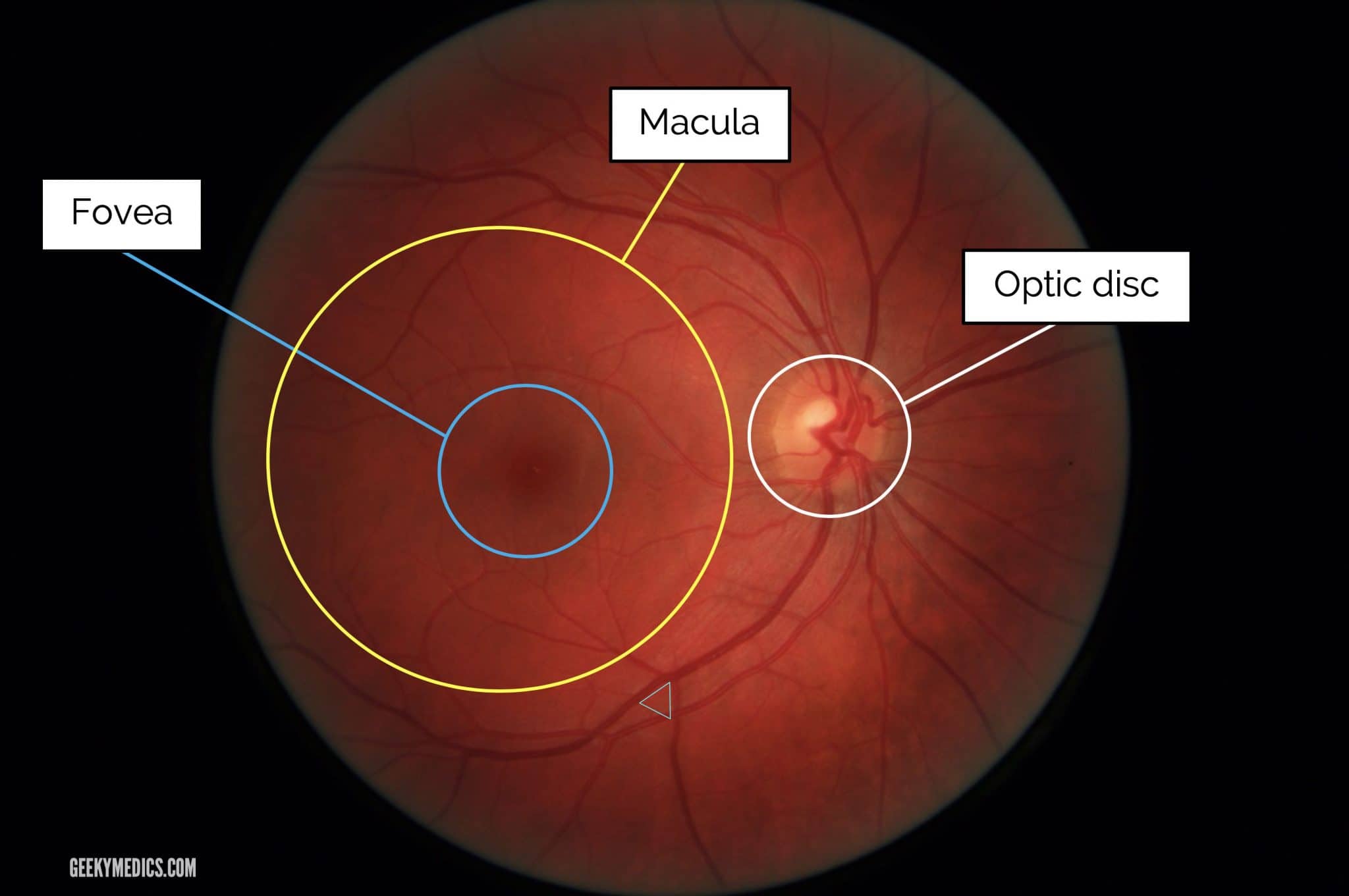
ophthalmoscopic appearance
optic disk
macula
fovea
optic disk
blind spot; no vision possible
blood vessels originate here (shadow retina)
optic nerve fibers exit here
no photoreceptors (rods and cones)
macula
area of retina responsible for central vision (vs. peripheral)
fovea
center of retina
where most cones are
inside macula
lens
transparent surface that contributes to the formation of images
focuses the light that comes through the cornea and pupil and projects it onto retina
ciliary body
attaches to the fibers of the lens
curves / changes shape of the lens
needs to contract too refract lens
allows for focusing
vitreous humor
provides eye spherical shape
lies between the lens and retina in posterior chamber
retina
inner most layer of cell wall in posterior chamber
transduces light energy into neural activity
anterior chamber
has aqueous humor
posterior chamber
has vitreous humor
parts of the eye
pupil
iris
aqueous humor
sclera
vascular layer: posterior choroid
retina
cornea
lens
ciliary body
zonule fivers
vitreous humor
retina
general sequence of events
light entering the eye is focused on the retina
retina coverts light energy into neural activity
axons of the retinal neurons are bundled to form the optic nerves
visual information is distributed to several brain structures that perform different functions
process of vision
light energy is transduced into neural activity
neural activity is processed by the brain
process of image formation
refraction by the cornea
accommodation by the lens
pupillary light reflex
refract
change direction
refractive surface
where light bends
ie. cornea
focal point
where light rays finally cometogether after refraction
refraction by the cornea
distant objects
light rays slow
light rays bend
focal distance
distant objects
light rays run in parallel
light rays slow
aqueous humor and cornea slow light down; light hits the cornea so light changes direction
slowing light down makes light bend = allows for back of eye to focus light to see clearly
light rays bend
still parallel but light diverges away when distance is closer to eye
light bends when it hits the cornea
bends at perpendicular angle to the curve (radius) of cornea
focal distance
distance between cornea to the image / retina; distance between the surface of cornea (where light bends + refractive surface) and the point where the light rays finally come together (focal point)
depends on how curved the cornea is
avg focal point is 2.4cm
accommodation by lens
objects within 9 meters; light rays do not travel parallel, diverge
lens adds refractive power by changing shape of lens
contraction of ciliary muscles
contraction of ciliary muscles
tension of suspensory ligament is released
which then cause lens to round
which causes refraction
greater the curve = greater the refraction
pupillary light reflex
lets us absorb divergent rays
cell types for retina
ganglion cells
amacrine cells
bipolar cells
horizontal cells
photoreceptors
photoreceptors
the only light sensitive cells in retina
transduces light energy into neural signals
ie. rods + cones
bipolar cells
connect photoreceptors to ganglion cells
ganglion cells
fire action potential and send axons to the brain
horizontal cells
receive inputs from photoreceptors and project laterally to bipolar cells
amacrine cells
receives inputs from bipolar cells and project laterally to ganglion cells
cell layers in retina
In order from superficial to deep (relative to incoming light)
ganglion cell layer
inner plexiform layer
inner nuclear layer
outer plexiform layer
outer nuclear layer
pigmented epithelial

ganglion cell layer
has ganglion cells
only cells with action potential
all ganglion cells leave through optic disk to form optic nerve
inner plexiform layer
has amacrine cells
takes signal from 1 bipolar cell and activates multiple ganglion cells
inner nuclear layer
has bipolar cells
outer plexiform layer
had horizontal cells
takes signaling from 1 photoreceptor to multiple bipolar cells
outer nuclear layer
has photoreceptors
has outer segment
outer segment: pigmented epithelial layer
absorbs light that doesn’t get absorbed by retina
(the pigment does the absorption)
characteristics of layer
photoreceptors are only cells that respond to light
ganglion cells are the only output cells
light travels through other cell layers to reach photoreceptors
pigmented epithelium located at back of the eye
rods
long; many disks
photopigment used rhodopsin (found in disk)
higher pigment concentration / more sensitive to light
used in scotopic system / conditions
rhodopsin
photopigment in rods
when hit with quick light the rhodopsin inactivates (can’t see light anymore) “bleaches” can reactivate with another molecular change
cones
shorter; less disks
used in photopic system / conditions
photopigment: opsin
more dense in macula
opsin
used in cones
has 3 ranges: blue, green, red
scotopic system / retina
see in the dark
only uses rods
convergent: where multiple rods signal to a single retinal ganglion cell
photopic system / retina
sees in light
primarily uses cones
1:1:1 - one cone goes to one cell
mesoptic
have ability to see between both systems: photopic and scotopic
phototransduction w/ no light
no light starts the rod
cGMP rises when rod receives no light
rise of cGMP causes sodium channel to open
sodium influx enters rod
causes rod to depolarize
which causes voltage gated calcium channels to open
calcium influx
initiates the NT to release
ophthalmoscopic appearance
optic disk
macula
fovea