What happens to solar radiation once it enters at the TOA?
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Does the atmsophere behave like a black body?
No, unlike Earth’s surface. the atmosphere allows reflection, scattering, transmission (certain wavelengths) and absorption (certain wavelengths) of EM waves
Outcome: Absorption
solar radiation is absorbed by air molecules (some), aerosol particles (some), and cloud droplets
What certain wavelengths are absorbed in absorption?
UV-B light by ozone in the stratosphere, visible light by black carbon aerosols (soot), by air molecules and by cloud droplets, and infrared radiation by water vapor molecules, CO2 and others
Absorption can be described by:
absorptivity, α: the fraction of the incident radiation on an object that is absorbed by the surface/object
Outcome: reflection
light sent backwards by an interface between two different media
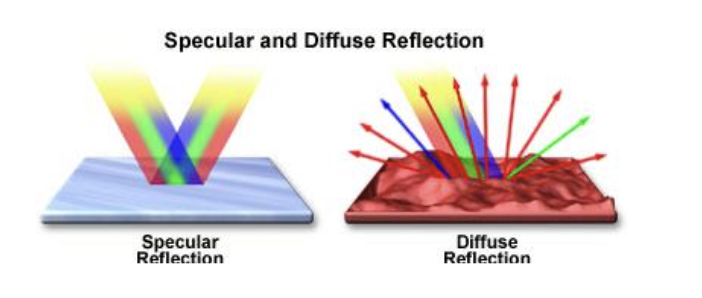
What two things can reflection be?
specular, mirror effect: reflection at a specific angle; or diffuse, reflection in many directions — backscattering
What is albedo?
represents reflectivity of a surface to solar radiation given as a ratio A
What does α depend on?
depends on type of surface and on angle of solar irradiance
What is the A ratio?
amount of solar radiation reflected/ amount of incident solar radiation
What is the mean value of albedo of the Earth at TOA?
about 30%
Which has a higher albedo? Thick clouds or thin clouds?
Thick clouds because they contain more droplets/ice crystals and hence more reflective surfaces
Outcome: Scattering
deflection of light in all directions by air molecules, small particles, droplets etc.
Scattering by air molecules:
air molecules scatter solar radiation into all directions —> difuse light
What if the size of a molecule is very small in scattering?
if the molecule is very small compared to wavelength of light then it is described by Rayleigh scattering
Rayleigh scatter? What does this mean?
Characterized by a strong wavelength dependence (scaling with ~λ-4), this means that shorter wavelengths of the visible range (blue, violet) are scattered more effectively than longer wavelengths (orange, red)
What is λ-4 dependence largely responsible for?
the color of the sky at different times of the day
Why is the sky blue?
clear skies are blue due to preferential scattering of blue wavelengths by air molecules and by tiny aerosol particles (according to Rayleigh theory)

Why is the sunset red?
when the sun is low in the sky, the path of light through the atmosphere is longer, so almost all blue light is scattered to the sides
During the sunset what are the solar beam that reaches the observer?
Only orange and red light is left in the solar beam, excessive scattering of the blue light on its way to the observer
Why is blue light depleted on the way to the observer during the sunset?
due to its preferential scattering by air molecules
What is the Mie Theory (non-slective scattering)
scatter all wavelengths efficiently followed by larger aerosols and cloud droplets are comparable in size to the wavelength of visible light

What is a visible representation of the Mie theory?
clouds and haze appear white
Why do clouds appear white?
cloud droplets scatter all wavelengths of visible light efficiently and so appear white
Why do some thicker clouds appear darker?
because more incident light is scattered back upwards and some of the light that is not scattered is absorbed in the cloud, only a small amount of light is transmitted through a thick cloud