Gas exchange in humans
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
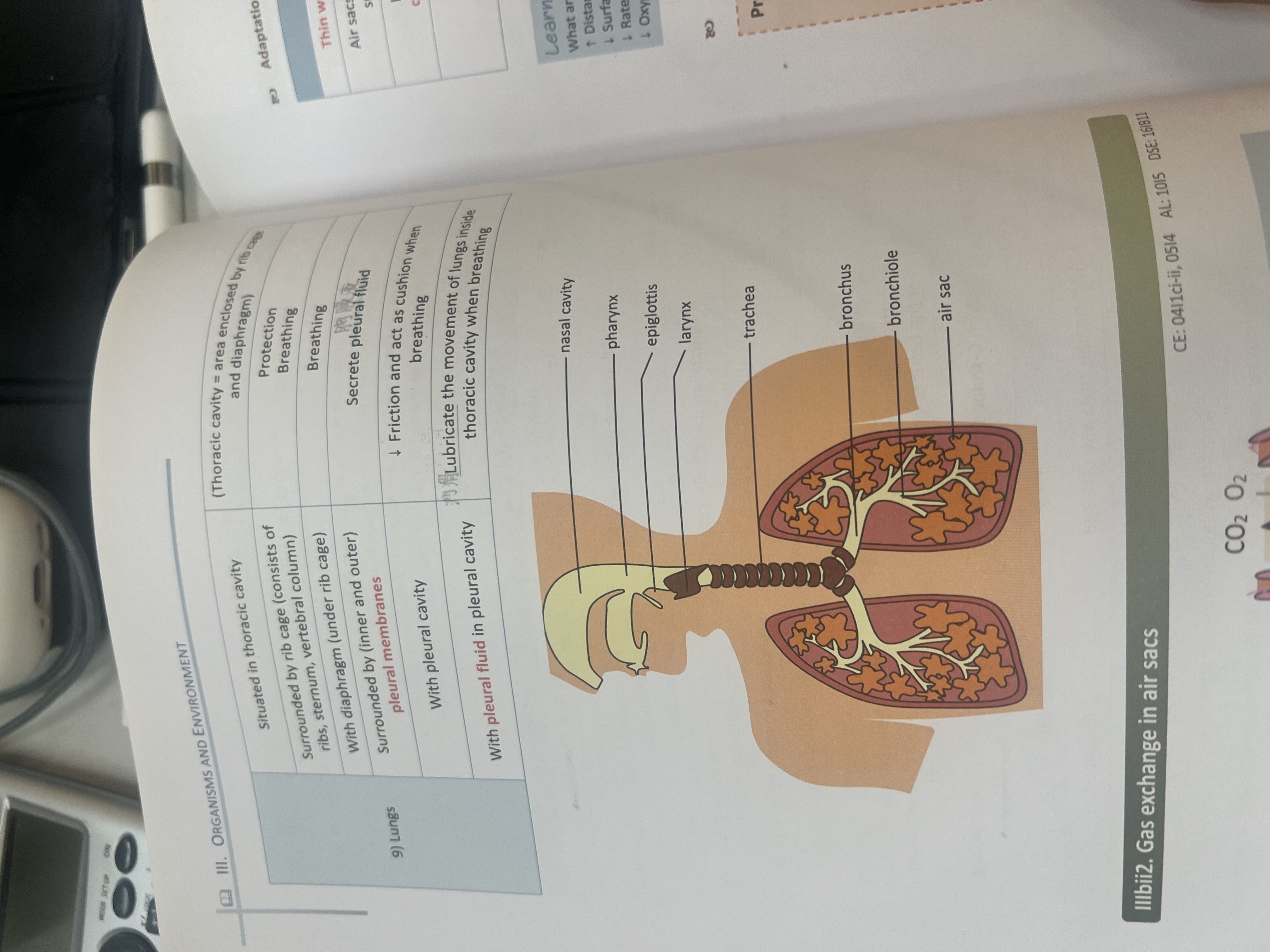
Plan of breathing system

Gas exchange in Air sacs adaption
One cell thick wall of air sacs and capillaries(short diffusion distance )
Large no of air sacs (up surface area for diffusion)
Present of water film (oxygen dissolve in water film so gas diffusion occur effectively
And richly supplied with blood capillaries (maintain steep concentration gradient of gases between air sacs and blood
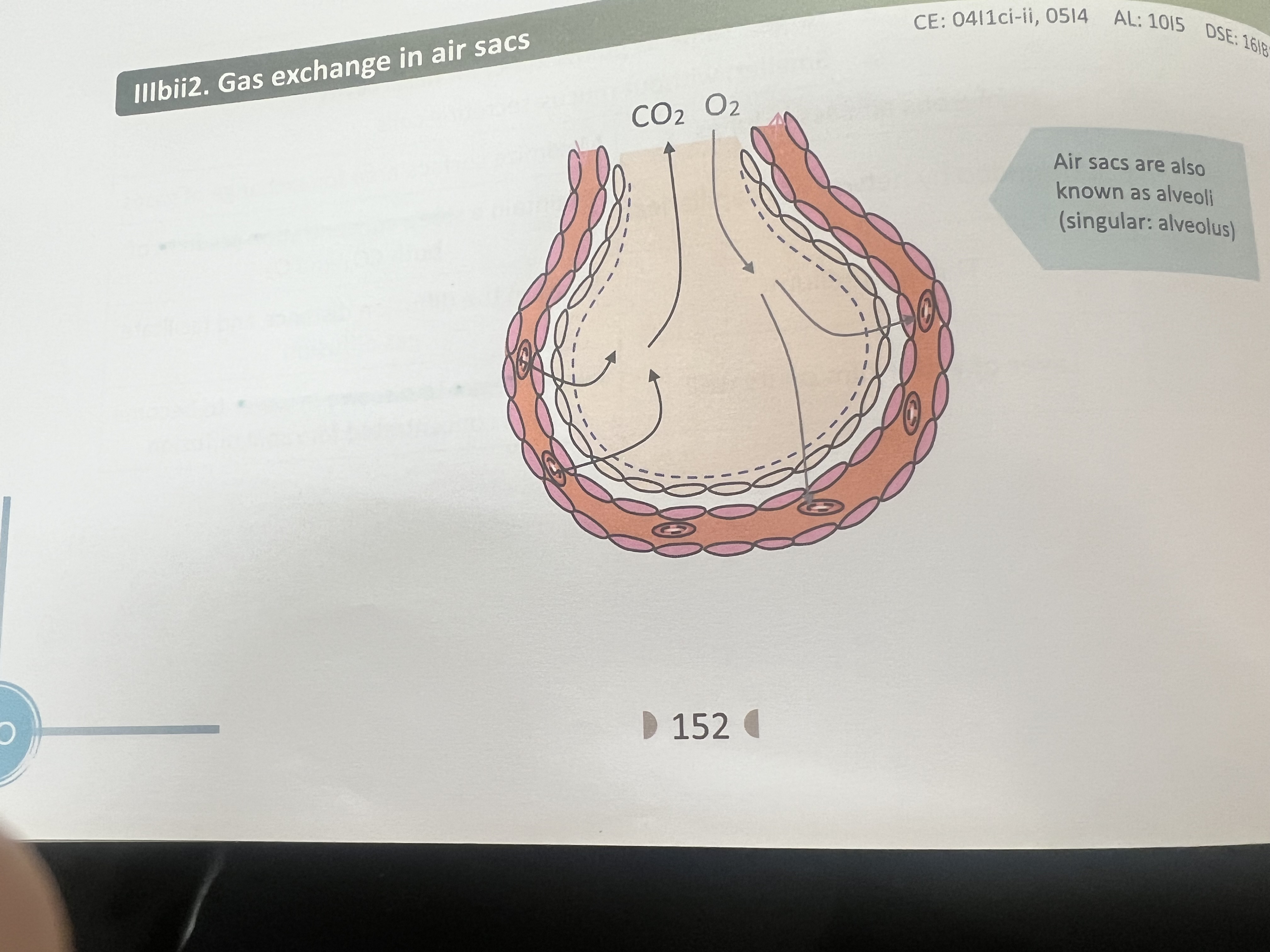
Process of air sacs
Oxygen dissolved in water film-Diffuse to blood through wall of air sacs and capillaries-combine with haemoglobin in rbc co2 diffuse in opposite direction

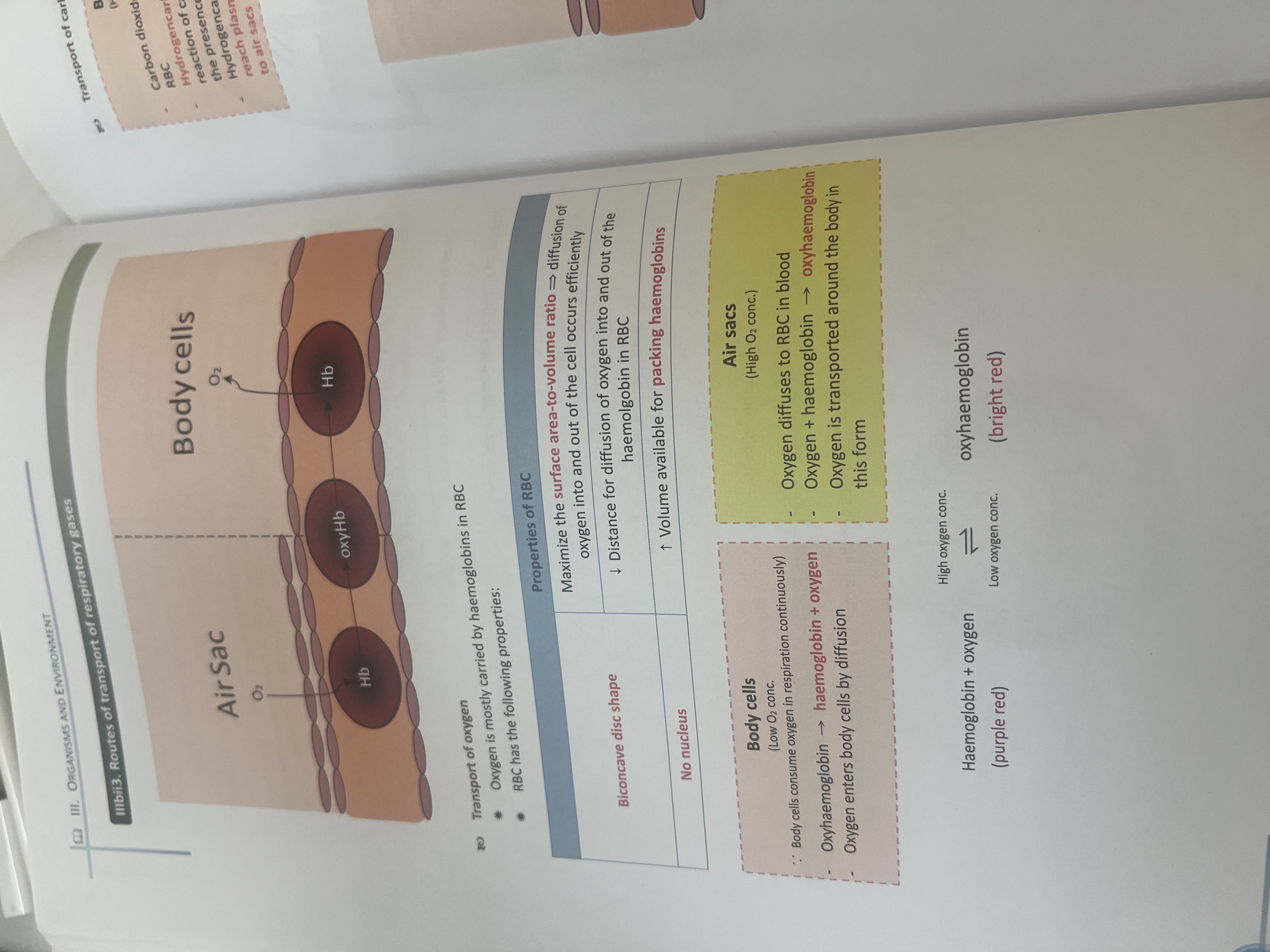
Transport of oxygen
Carried by red blood cell combine with haemoglobin to form oxyhaemoglobin(
(Low oxygen in body cell and high in airs sacs
Transport of carbon dioxide
Transport in form of hydrogen carbonate ions in plasma
Most enter red blood cell and diffuses out into plasma and carries to lungs
(High co2 in body cell and low in air sacs
Red blood cell properties
Bioncave shape to shorten diffusion distance of oxygen in and out of haemoglobin in rbc and increase surface area
No nucleus to carry more haemoglobin
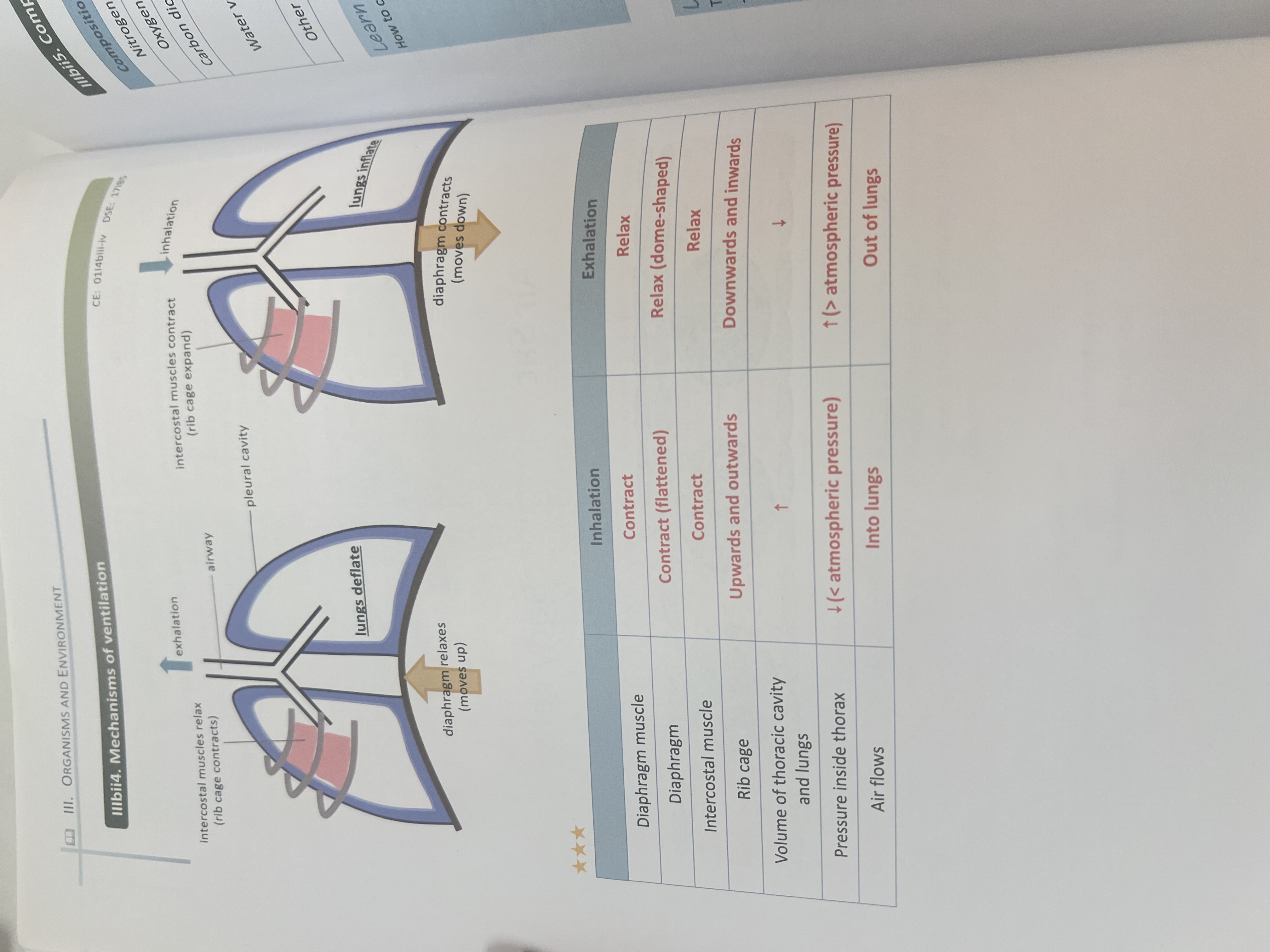
Inhalation and exhalation
Diaphragm muscles contact diaphragm contract
Intercostal muscles contract
Rib cage moves upwards and outwards
Volumes of lungs increase
Air pressure in lung lower than atmospheric pressure
Air flow into lung
Vice versa in exhalation
Circulatory system
Consists of heart blood and blood vessels(artery capillary and vein) double circulation mean blood go through heart twice in one complete circulation
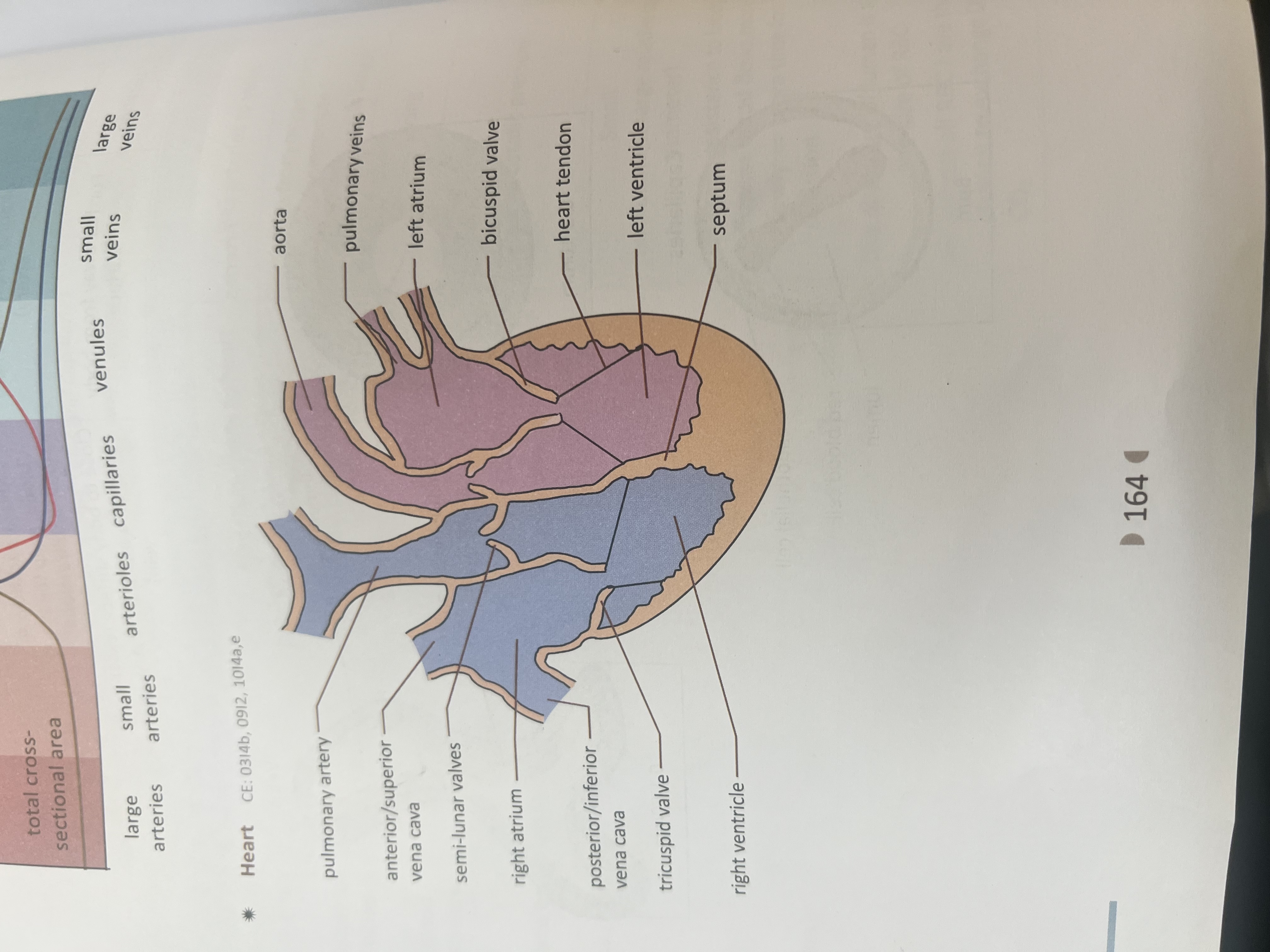
Septum valve left side and right side
Prevent mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood
Prevent back flow of blood from ventricles into atria when ventricles contact
Left is oxygenated right is deoxygenated

Four chamber of heart
Left atrium ,left ventricles ,right atrium and right ventricle
Main function of heart
Pump blood though body and deliver oxygen and nutrients to tissue and remove carbon dioxide and waste
Role of atrium
Atrium receive blood from right atrium(vena cava)deoxygenated blood and left atrium from lungs oxygenated blood (pulmonary vein)
Role of ventricles
Pump blood out of heart-right ventricles to lungs(pulmonary artery ) and left ventricles to body (aorta)
Why Left ventricles thicker than right ventricles
pump blood at higher pressure into aorta to supply entire body
4 main blood vessels connect to heart
Aorta ,pulmonary artery (from heart to other part),pulmonary vein(from body to heart ) , vena cava
What control heartbeat
Sa node ,initiate electrical impulses to regulate heartbeat
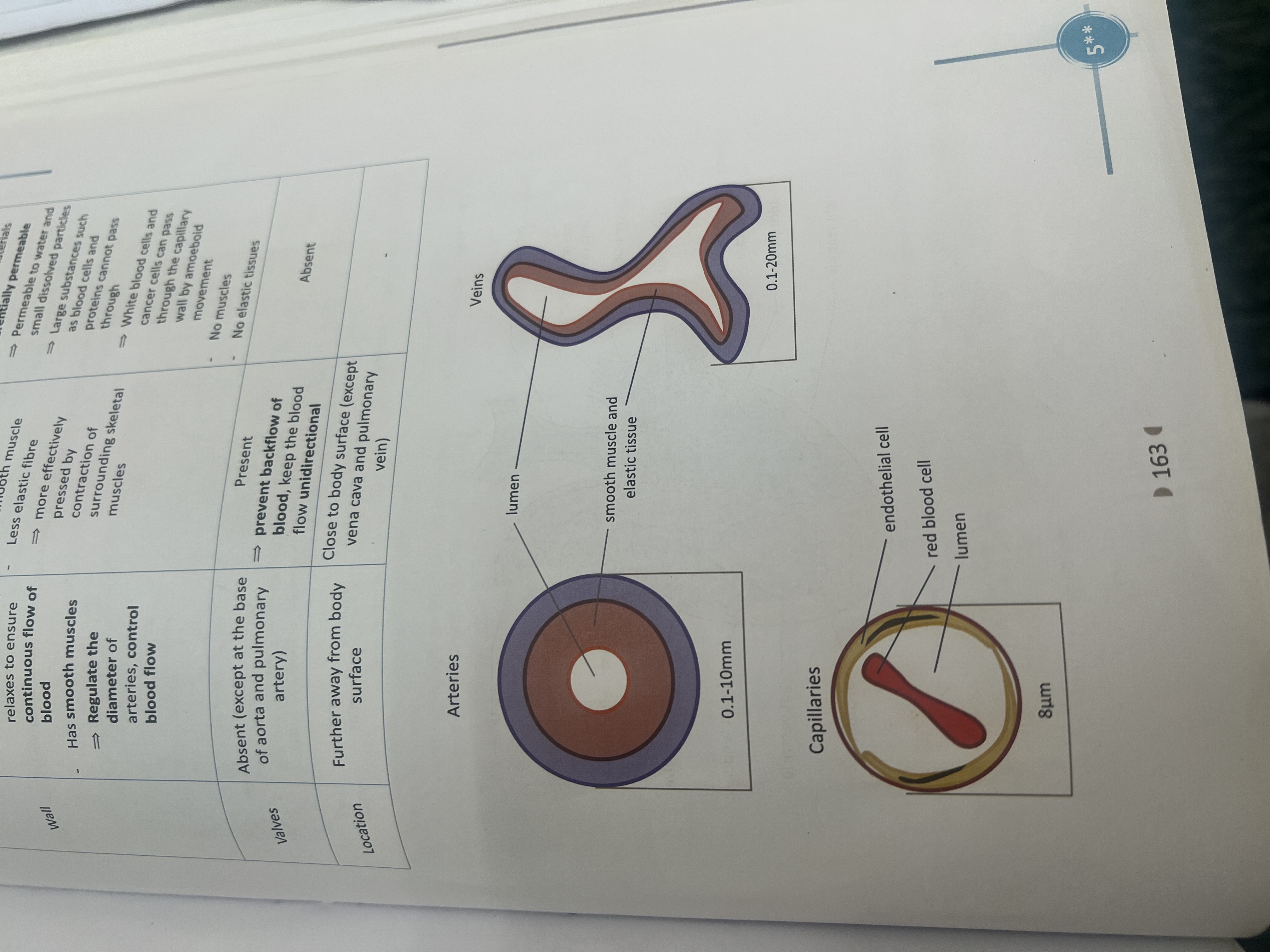
Pulmonary artery
From body to heart
From heart to body high blood pressure force by pumping action of heart smaller lumen and thick wall to withstand high blood pressure
low blood pressure force by the contraction of surrounding skeletal muscles large lumen so blood can flow to heart easily
Thin wall and valves are present to prevent back flow of blood
Lymphatic system(protect against infections)
Consist of lymph vessel (for lymph capillaries)and lymph nodes(formed by wbc when lymph nodes kills pathogens
Capillaries function
Allow exchange of material between blood and body cell

Rbc wbc and platelets function
Carry oxygen
Kill pathogens.
Cause blood clotting
Tissue fluid function
Is blood without rbc and blood platelets and plasma protein
Deliver substance and remove waste from body cell
Where does change of material take place
In dense network of cappillares
Formation of tissue fluid
1.when blood reach arterial end, high hydrostatic pressure by pumping action of heart forces all nutrients except plasma protein rbc out like (oxygen water) though capillary wall
At venous end most tissue fluid is back into capillaries by osmosis water potential of tissue fluid is higher than blood
Blood pressure at venous end is low
The rest of tissue fluid is forced into lymphatic capillaries forming lymph
Importance of lymphatic system
Transport fat and vitamins from lacteal to blood
