Biology Test 3
1/166
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
167 Terms
Why does the cis face of the Golgi not face the plasma membrane?
that face receives chemicals from the ER, which is toward the center of the cell
prokaryote
A single celled organism that has no nucleus
Animal cells contain
centrosomes, centrioles and lysosomes
Light microscope
you are wanting to look at a living cell through a microscope
Ribosomes, plasma membrane, peroxisomes
Which of the following organelles are in both plant and animal cells?
Cell wall
Ribosomes
Plasma Membrane
Lysosomes
Peroxisomes
Plasma membrane
Separates cell from external environment; controls passage of organic molecules, ions, water, oxygen, and wastes into and out of the cell
ATP
made in the mitochondria and is the cell's energy source
What does a prokaryotic cell contain:
Plasma membrane, ribosomes, cell wall
Hypotonic
A _______ environment has MORE solute on the outside of the cell.
Plasmodesmata
Intercellular junction unique to plant cells
Cell wall
The _______ is a rigid cover that protects the cell, provides structural support , and gives shape of the cell.
Vesicles and vacuoles
Membrane-bound sacs that function in transport and storage
What are the primary components in the extracellular matrix?
a. Glycoproteins
B. protein collagen
C. chloroplasts
D. Both A&B
E. None of the above
glycoproteins
protein collagen
semipermeable
Plasma membranes are ______ they allow some substances through but not others.
Which of the following is not a component of the endomembrane System?
A. Golgi Apparatus
B. Endoplasmic Reticulum
C. Lysosome
D. Mitochondrion
mitochondrion
What type of microscope is used to see very fine detail inside of cells?
a) scanning electron microscope
b) transmission electron microscope
c) binocular microscope
d) monocular microscope
scanning electron microscope
Hypertonic means
Higher concentration of solutes
diffusion
The net movement of solutes from a region of higher concentration to region of lower concentration
lysosomes
Digestion of macromolecules, recycling of worn-out organelles
What is the Golgi apparatus also called?
the Golgi body
What organelles are included in plant cells, but not in animal cells (select all that apply)
A. Centrioles
B. Plastids
C. Chloroplasts
D. Centrosomes
E. Lysosomes
chloroplasts
rough ER
Produces proteins and release them
Phospholipids have ___________ tails and ___________ heads
hydrophobic (water-fearing) and hydrophilic (water-loving)
Golgi Apparatus
Modifies, sorts, tags, packages, and distributes lipids and proteins
Plants use ________ to store energy.
starch
When viewing specimen through a light microscope scientists use ______________ to distinguish the individual components of cells.
special stains
Which of these is found in a eukaryotic cell but not a prokaryotic cell?
A. Cytoplasm
B. Nucleus
C. Cell membrane
D. Flagella
nucleus
What type of transport is being used when NaCl moves through a semipermeable membrane to an area of higher concentration?
A. Primary Active Transport
B. Secondary Active Transport
C. Tertiary Active Transport
D. Passive Transport
E. Osmosis
Primary Active Transport
A glycoprotein is a ___________ with a ____________ attached to it, while a glycolipid is a _____________ with a ______________ attached to it.
protein
carbohydrate
lipid
carbohydrate
Osmosis
The movement of water across a semi-permeable membrane
Endocytosis
is the process by which large particles, like cells, are taken in by the cell
higher temperature
increases diffusion rate
Mitochondria is considered the __________ or ______ of the cell.
powerhouse
energy factories
cilium (Cilia)
a short, hair-like structure that extends from the plasma membrane in large numbers and is used to move an entire cell or move substances along the outer surface of the cell
Diffusion is movement of ___________
solutes (little particles)
Osmosis is the movement of ____________
water
Which of these can move across the membrane without help?
Salt
Amino acids
Oxygen
Sugar
Estrogen
Water
Oxygen
estrogen
water
What would happen if a cell that contained 0.9% sodium chloride was placed in a solution of 1.5% sodium chloride?
(what doesn’t move, what does move?)
Water is moving (outside)
We are trying to get them balanced
Water can move, making percentages equal
What is different if the concentration of oxygen is 2% outside the cell and 0% inside the cell?
Oxygen goes in to balance
Water is still leaving to balance
“The ________ the hill, the faster the diffusion”
steeper
Peroxisomes
a small, round organelle that contains hydrogen peroxide, oxidizes fatty acids and amino acids, and detoxifies many poisons
hypertonic
extracellular fluid has higher osmolarity than the fluid inside the cell
hypotonic
extracellular fluid has lower osmolarity than the fluid inside the cell
isotonic
extracellular fluid has the same osmolarity as the fluid inside the cell
eukaryotic cell
membrane-bound nucleus and several other membrane-bound compartments or sacs
found in animals and plants
prokaryotic cell
a unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus or any other membrane-bound organelle
bacteria and archaea
ATP ________ energy
releases
ADP _________ energy
requires
What affects diffusion (3):
size, charge, and polarity
Where does the cell get energy for active transport processes?
The cell harvests energy from ATP produced by its own metabolism to power active transport processes, such as the activity of pumps.
What structures does a plant cell have that an animal cell does not have? What structures does an animal cell have that a plant cell does not have?
Plant cells: plasmodesmata, cell wall, large central vacuole, chloroplasts, and plastids
Animal cells: lysosomes and centrosomes
A doctor injects a patient with what he thinks is isotonic saline solution. The patient dies, and autopsy reveals that many red blood cells have been destroyed. Do you think the solution the doctor injected was really isotonic?
No, it must have been hypertonic, as a hypotonic solution would cause water to enter the cells, thereby making them burst.
When viewing a specimen through a light microscope, scientists use _________ to distinguish the individual components of cells.
a beam of electrons
radioactive isotopes
special stains
high temperatures
special stains
The _______ is the basic unit of life
cell
Which of these do all prokaryotes and eukaryotes share?
nuclear envelope
cell walls
organelles
plasma membrane
plasma membrane
A typical prokaryotic cell __________________ compared to a eukaryotic cell.
is smaller in size by a factor of 100
is similar in size
is smaller in size by a factor of one million
is larger in size by a factor of 10
is smaller in size by a factor of 100
Which of the following is found both in eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells?
nucleus
mitochondrion
vacuole
ribosome
ribosome
Which of the following is not a component of the endomembrane system?
mitochondrion
Golgi apparatus
endoplasmic reticulum
lysosome
mitochondrion
Which plasma membrane component can be either found on its surface or embedded in the membrane structure?
protein
cholesterol
carbohydrate
phospholipid
protein
The tails of the phospholipids of the plasma membrane are composed of _____ and are _______?
phosphate groups; hydrophobic
fatty acid groups; hydrophilic
phosphate groups; hydrophilic
fatty acid groups; hydrophobic
fatty acid groups; hydrophobic
The principal force driving movement in diffusion is __________.
temperature
particle size
concentration gradient
membrane surface area
concentration gradient
Active transport must function continuously because __________.
plasma membranes wear out
cells must be in constant motion
facilitated transport opposes active transport
diffusion is constantly moving the solutes in the other direction
diffusion is constantly moving the solutes in the other direction
What are the advantages and disadvantages of light, transmission, and scanning electron microscopes?
The advantages of light microscopes are that they are easily obtained, and the light beam does not kill the cells. However, typical light microscopes are somewhat limited in the amount of detail that they can reveal. Electron microscopes are ideal because you can view intricate details, but they are bulky and costly, and preparation for the microscopic examination kills the specimen. Transmission electron microscopes are designed to examine the internal structures of a cell, whereas a scanning electron microscope only allows visualization of the surface of a structure.
Describe the structures that are characteristic of a prokaryotic cell
Prokaryotic cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane and have DNA, cytoplasm, and ribosomes, like eukaryotic cells. They also have cell walls and may have a cell capsule. Prokaryotes have a single large chromosome that is not surrounded by a nuclear membrane. Prokaryotes may have flagella or motility, pili for conjugation, and fimbriae for adhesion to surfaces
In the context of cell biology, what do we mean by form follows function? What are at least two examples of this concept?
"Form follows function" refers to the idea that the function of a body part dictates the form of that body part. As an example, organisms like birds or fish that fly or swim quickly through the air or water have streamlined bodies that reduce drag. At the level of the cell, in tissues involved in secretory functions, such as the salivary glands, the cells have abundant Golgi.
Why is it advantageous for the cell membrane to be fluid in nature?
The fluidity of the cell membrane is necessary for the operation of some enzymes and transport mechanisms within the membrane
Why does osmosis occur?
To balance the concentrations of solutes on both sides of the membrane or attain a state of equilibrium
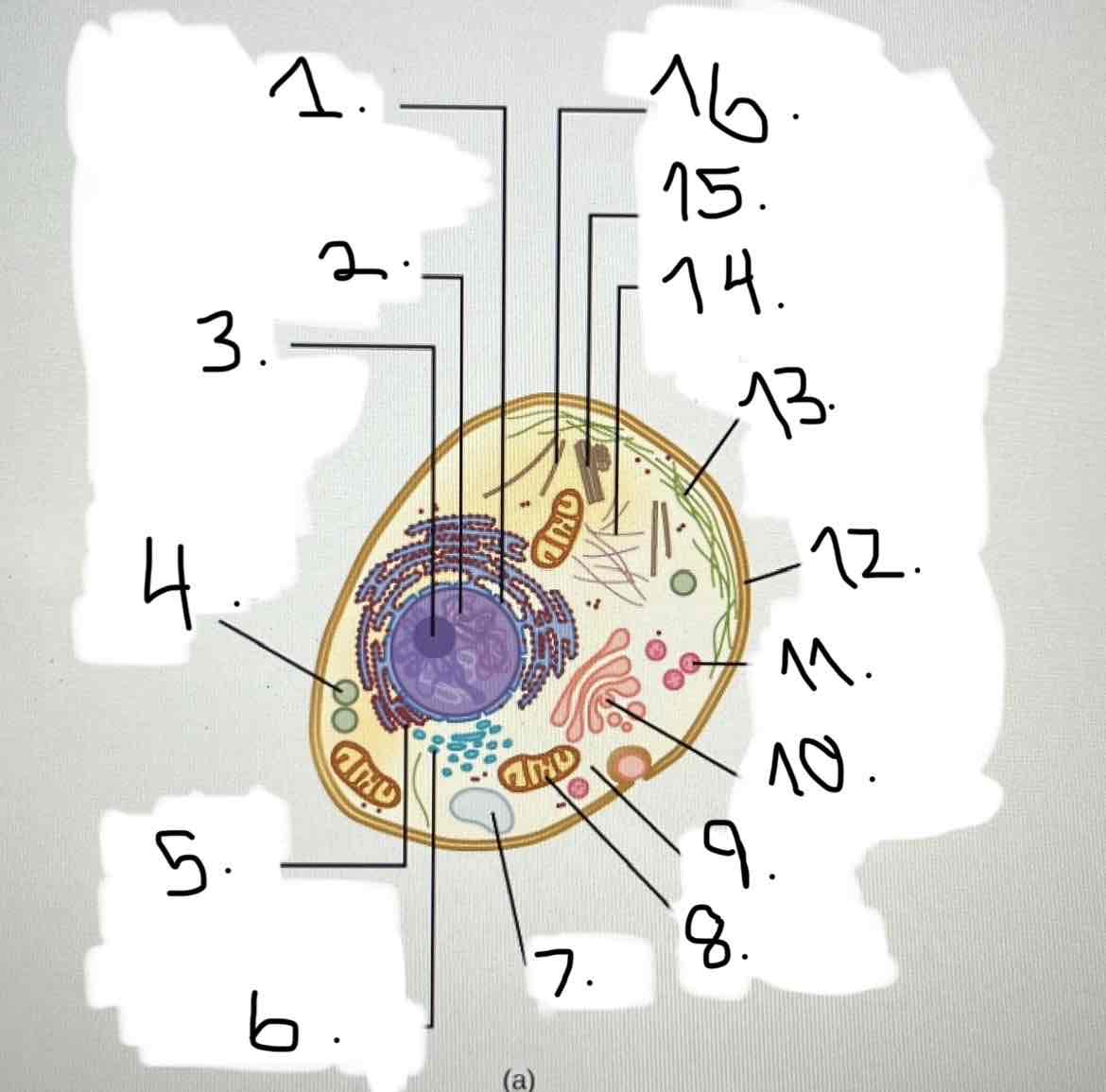
What is 1?
nucleus; nuclear envelope
vacuole
plasma membrane
mitochondria
nucleolus
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
intermediate filaments
cytoskeleton; microtubules
Golgi apparatus
rough endoplasmic reticulum
chromatin
peroxisome
intermediate filaments
cytoplasm
centrosome
lysosome
nucleus/nuclear envelope
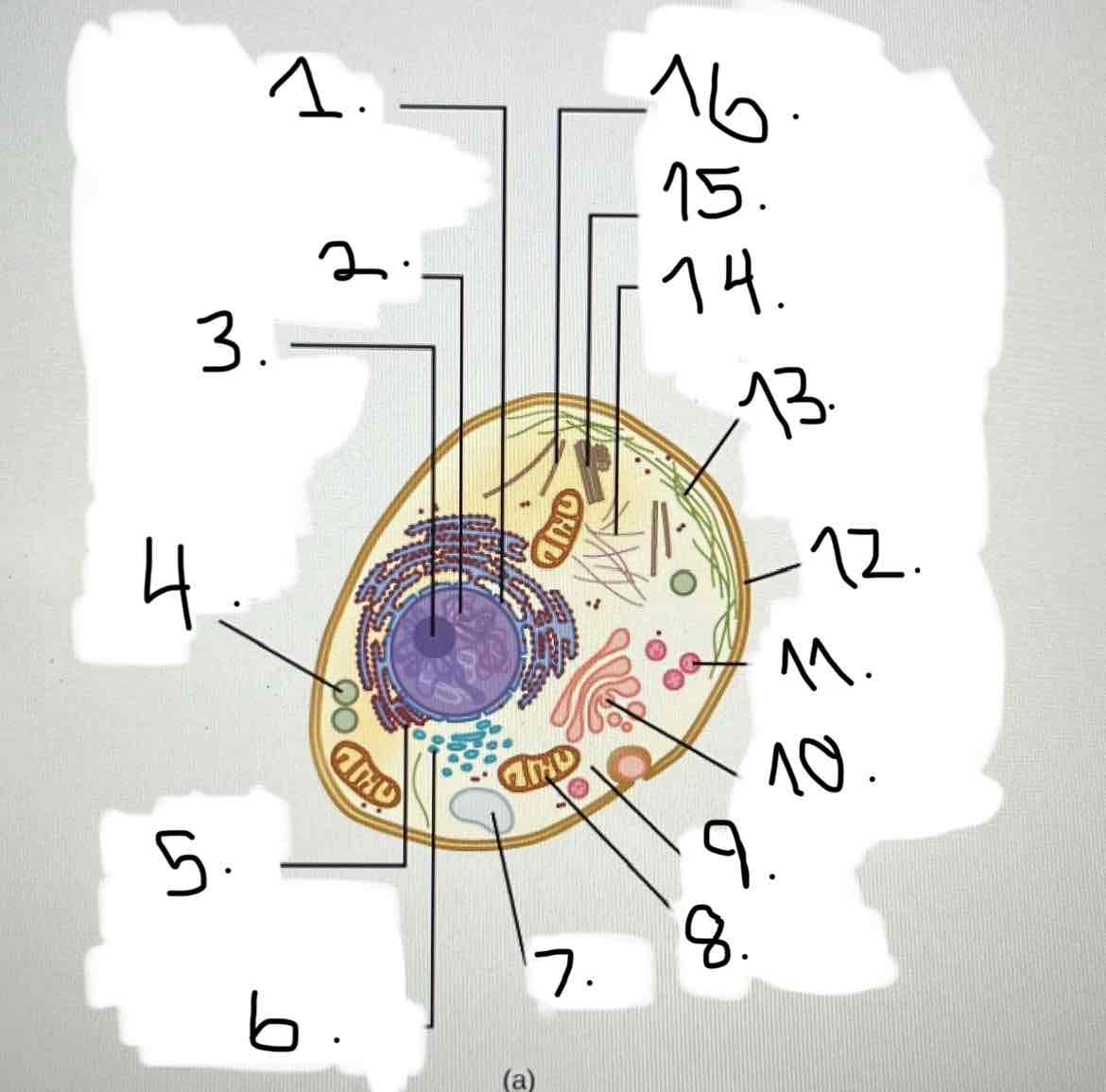
what is 2?
nucleus; nuclear envelope
vacuole
plasma membrane
mitochondria
nucleolus
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
intermediate filaments
cytoskeleton; microtubules
Golgi apparatus
rough endoplasmic reticulum
chromatin
peroxisome
intermediate filaments
cytoplasm
centrosome
lysosome
chromatin
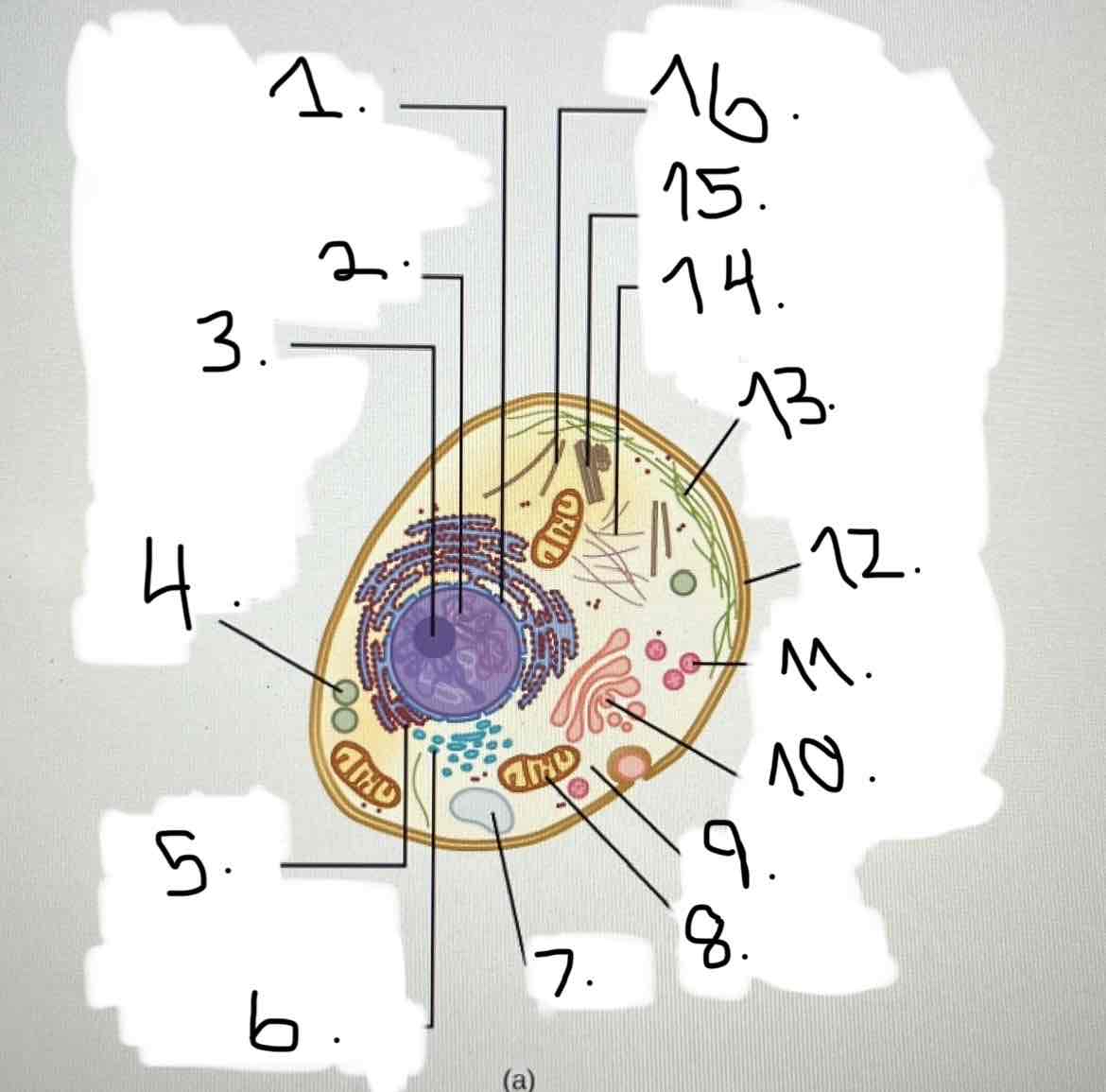
what is 3?
nucleus; nuclear envelope
vacuole
plasma membrane
mitochondria
nucleolus
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
intermediate filaments
cytoskeleton; microtubules
Golgi apparatus
rough endoplasmic reticulum
chromatin
peroxisome
intermediate filaments
cytoplasm
centrosome
lysosome
nucleolus
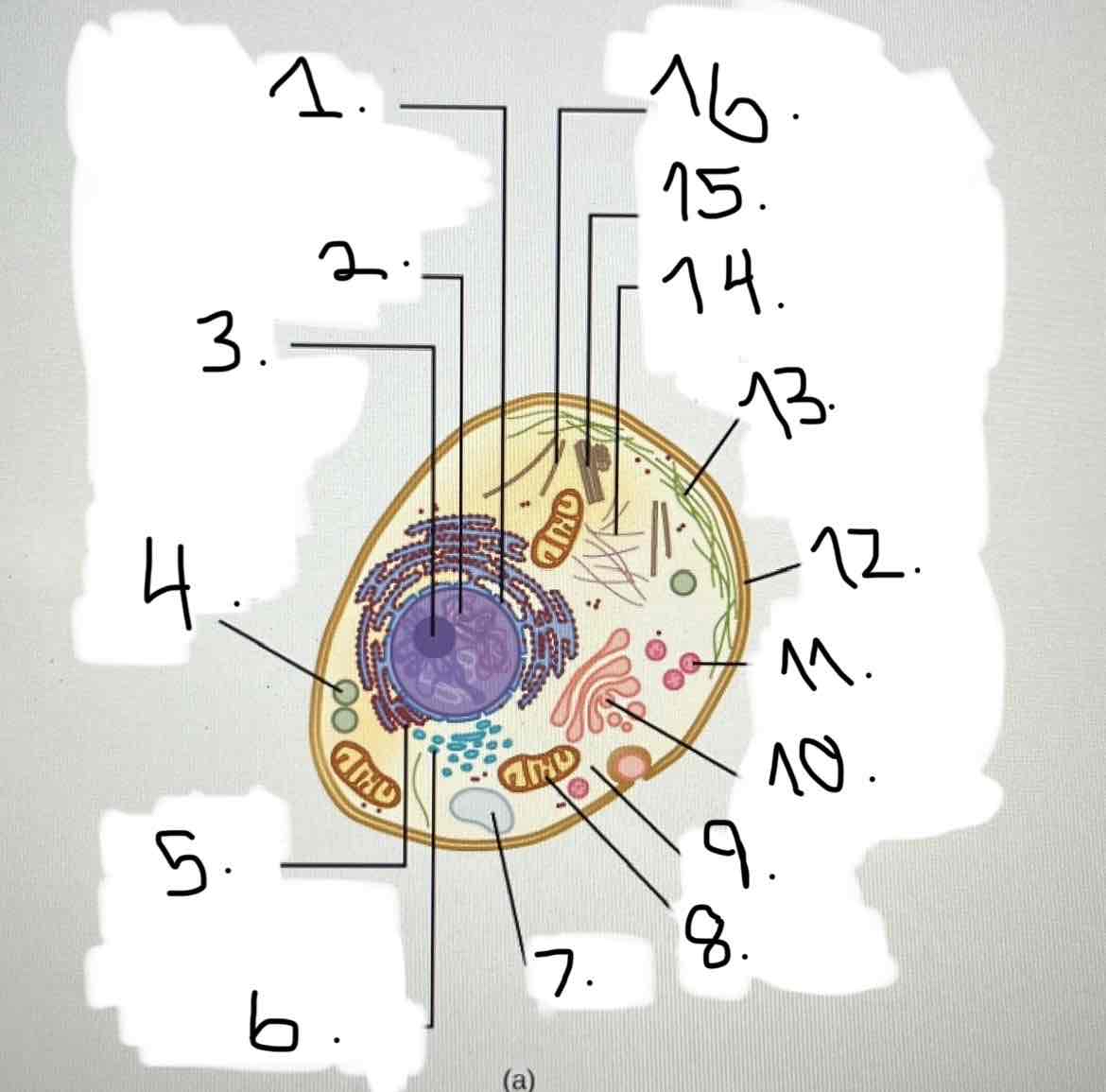
what is 4?
nucleus; nuclear envelope
vacuole
plasma membrane
mitochondria
nucleolus
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
intermediate filaments
cytoskeleton; microtubules
Golgi apparatus
rough endoplasmic reticulum
chromatin
peroxisome
intermediate filaments
cytoplasm
centrosome
lysosome
peroxisome
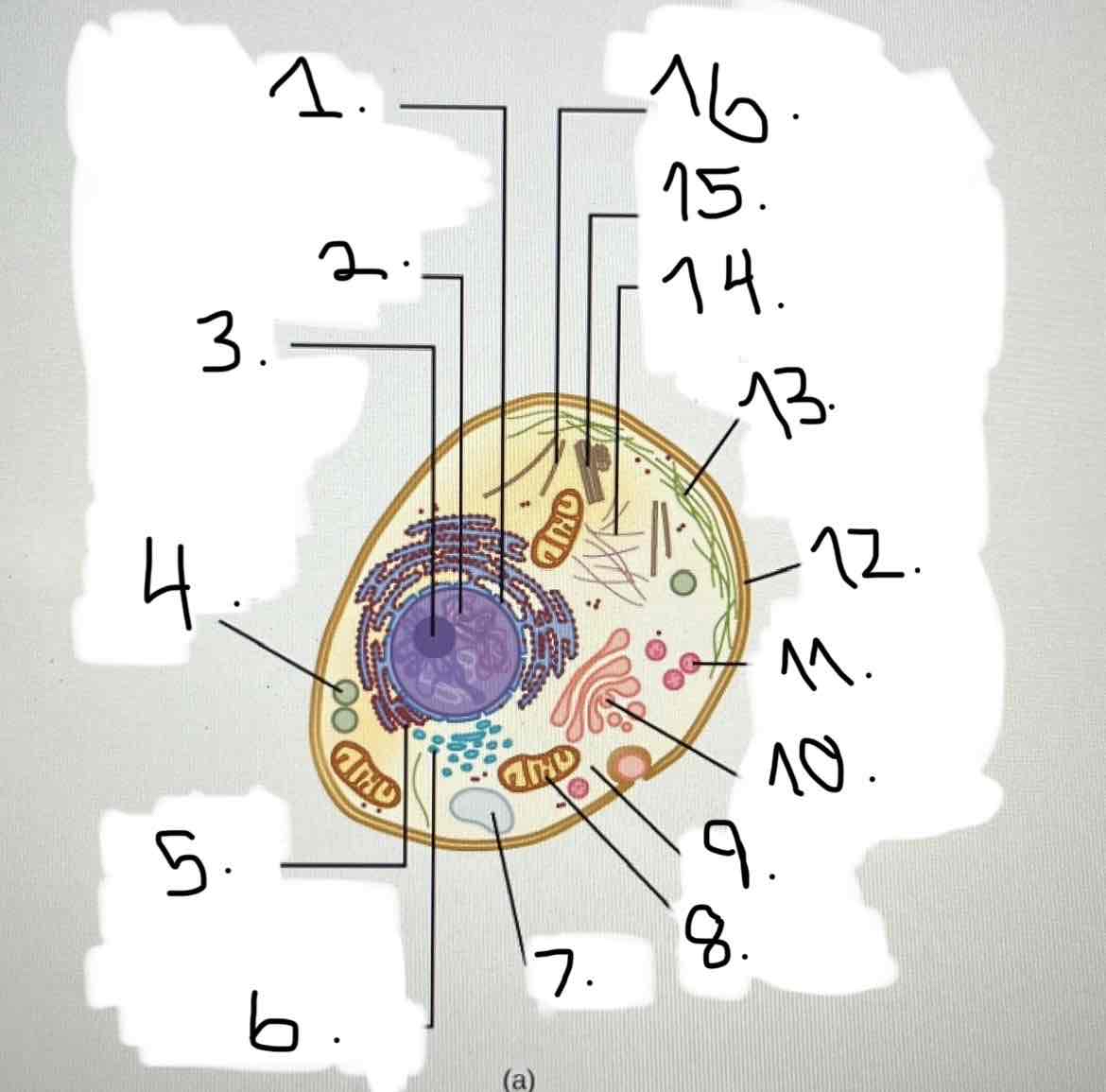
what is 5?
nucleus; nuclear envelope
vacuole
plasma membrane
mitochondria
nucleolus
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
intermediate filaments
cytoskeleton; microtubules
Golgi apparatus
rough endoplasmic reticulum
chromatin
peroxisome
intermediate filaments
cytoplasm
centrosome
lysosome
rough endoplasmic reticulum
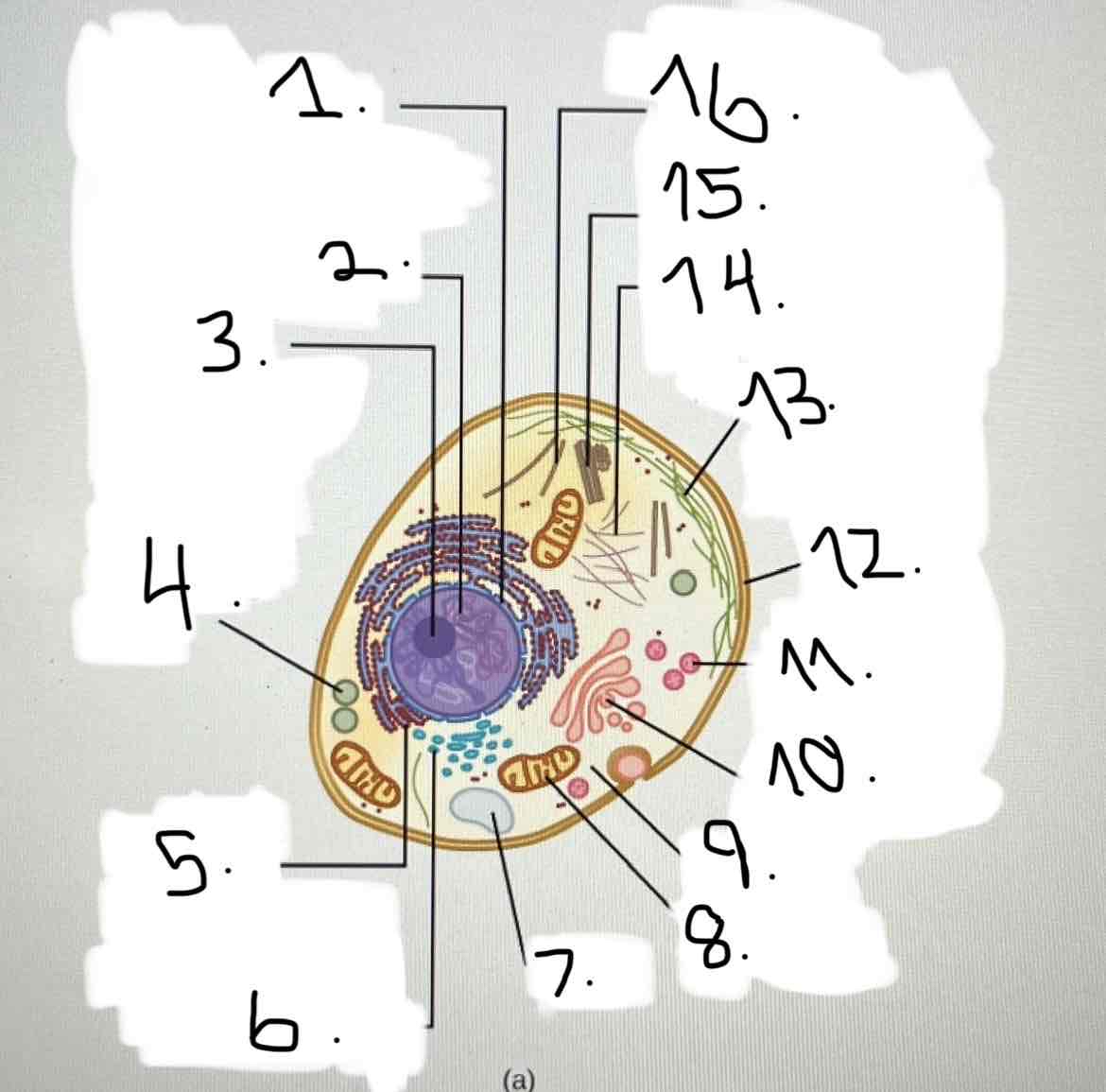
what is 6?
nucleus; nuclear envelope
vacuole
plasma membrane
mitochondria
nucleolus
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
intermediate filaments
cytoskeleton; microtubules
Golgi apparatus
rough endoplasmic reticulum
chromatin
peroxisome
intermediate filaments
cytoplasm
centrosome
lysosome
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
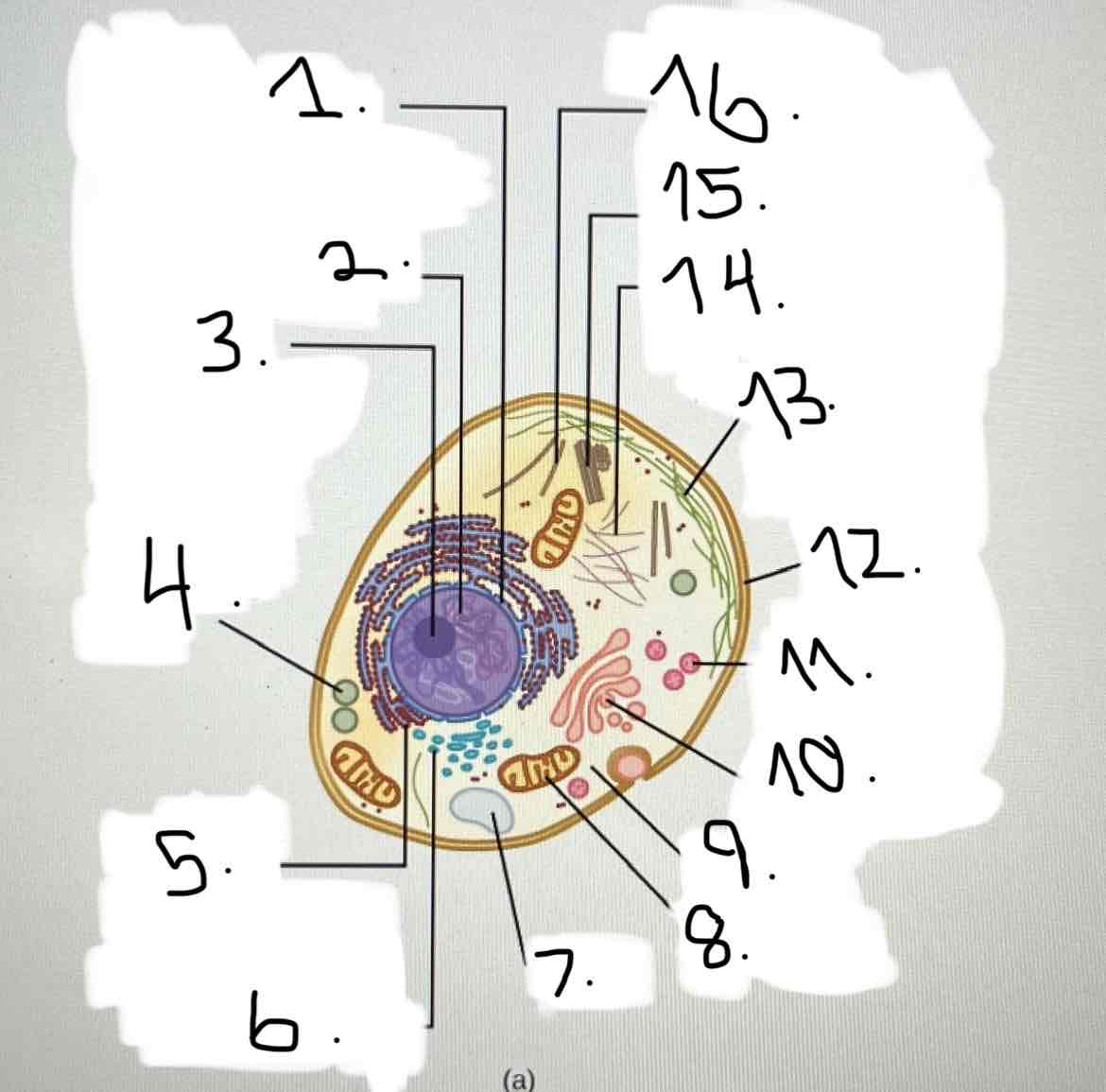
what is 7?
nucleus; nuclear envelope
vacuole
plasma membrane
mitochondria
nucleolus
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
intermediate filaments
cytoskeleton; microtubules
Golgi apparatus
rough endoplasmic reticulum
chromatin
peroxisome
intermediate filaments
cytoplasm
centrosome
lysosome
vacuole
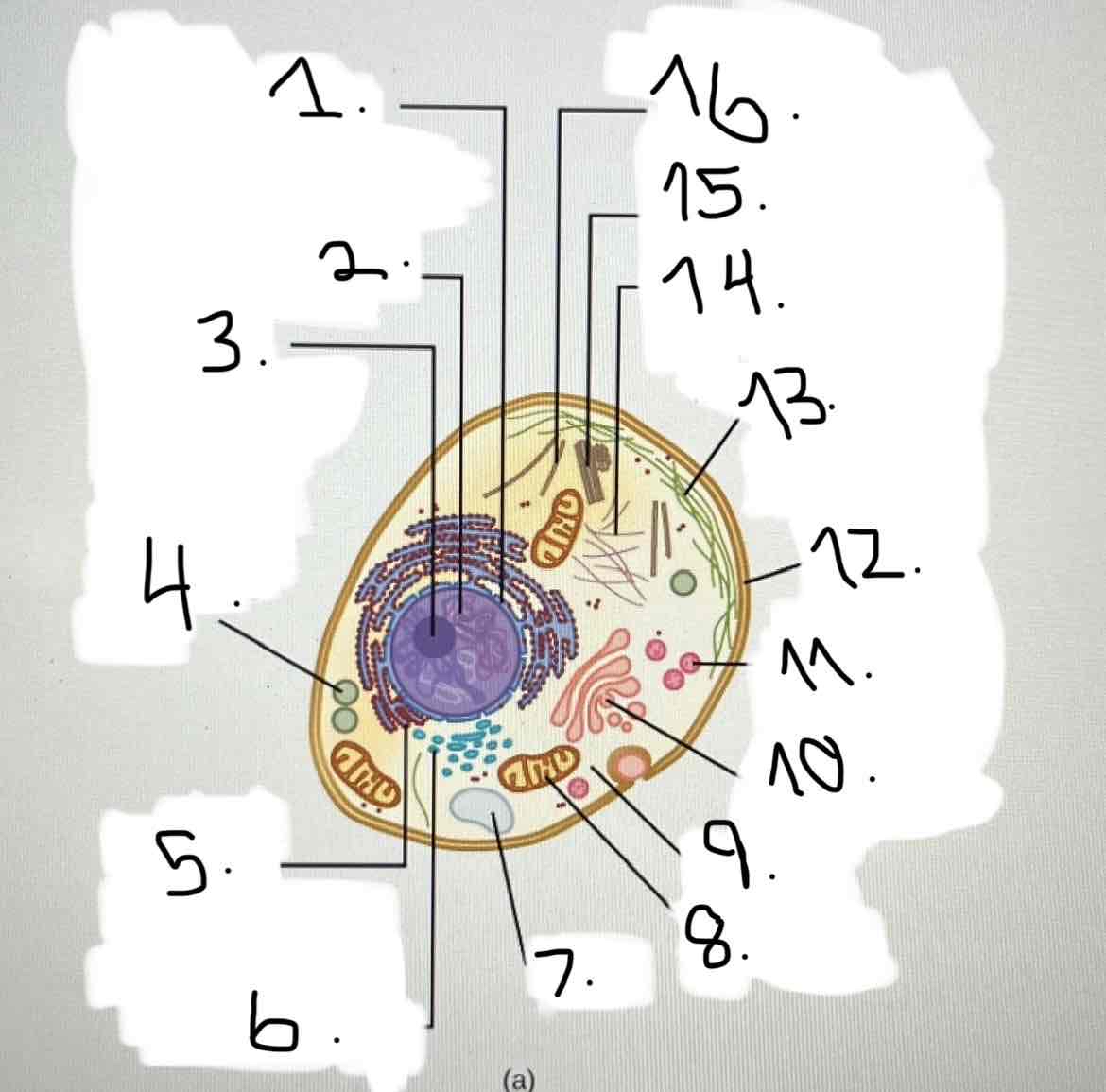
what is 8?
nucleus; nuclear envelope
vacuole
plasma membrane
mitochondria
nucleolus
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
intermediate filaments
cytoskeleton; microtubules
Golgi apparatus
rough endoplasmic reticulum
chromatin
peroxisome
intermediate filaments
cytoplasm
centrosome
lysosome
mitochondria
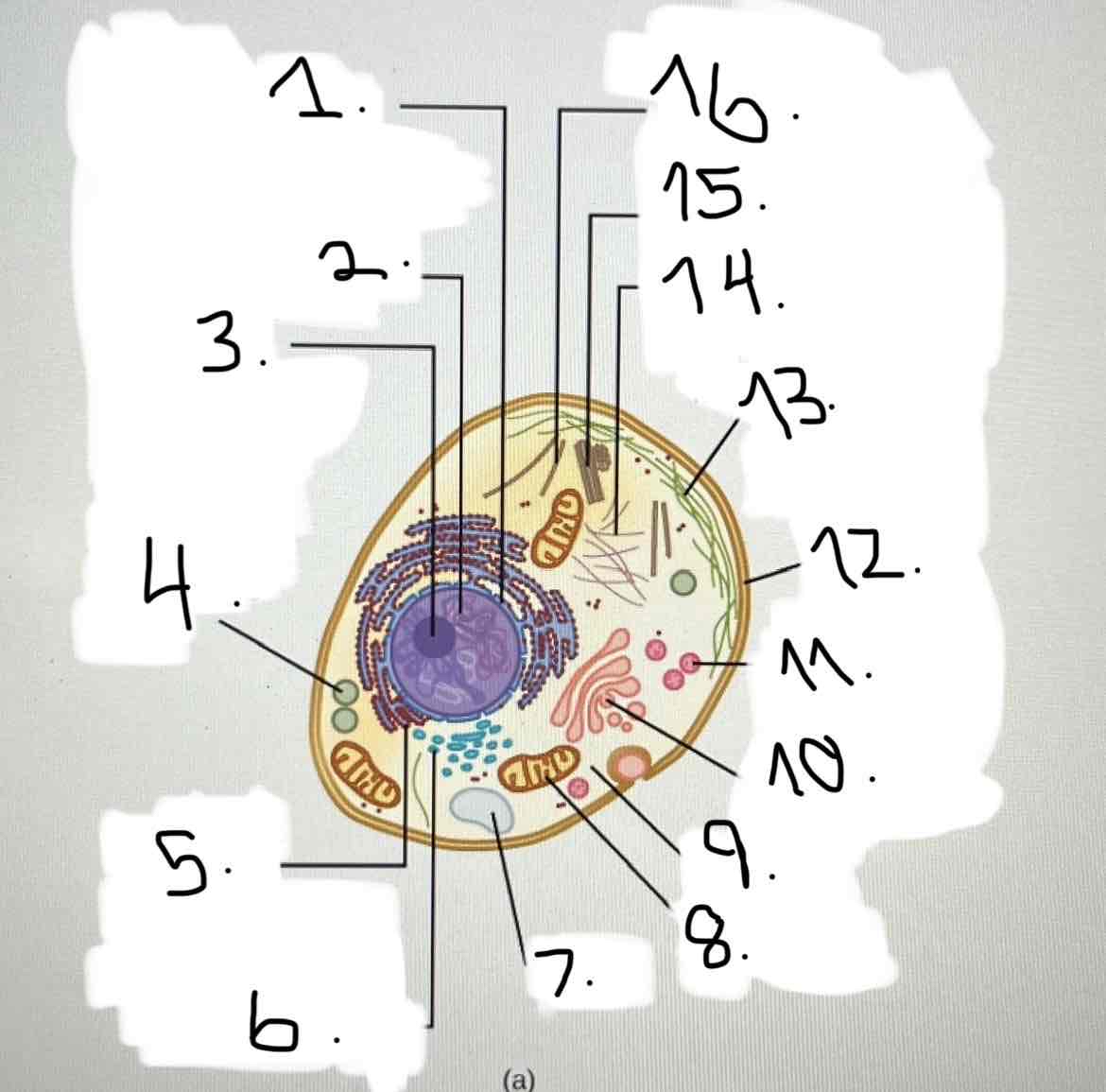
what is 9?
nucleus; nuclear envelope
vacuole
plasma membrane
mitochondria
nucleolus
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
intermediate filaments
cytoskeleton; microtubules
Golgi apparatus
rough endoplasmic reticulum
chromatin
peroxisome
intermediate filaments
cytoplasm
centrosome
lysosome
cytoplasm
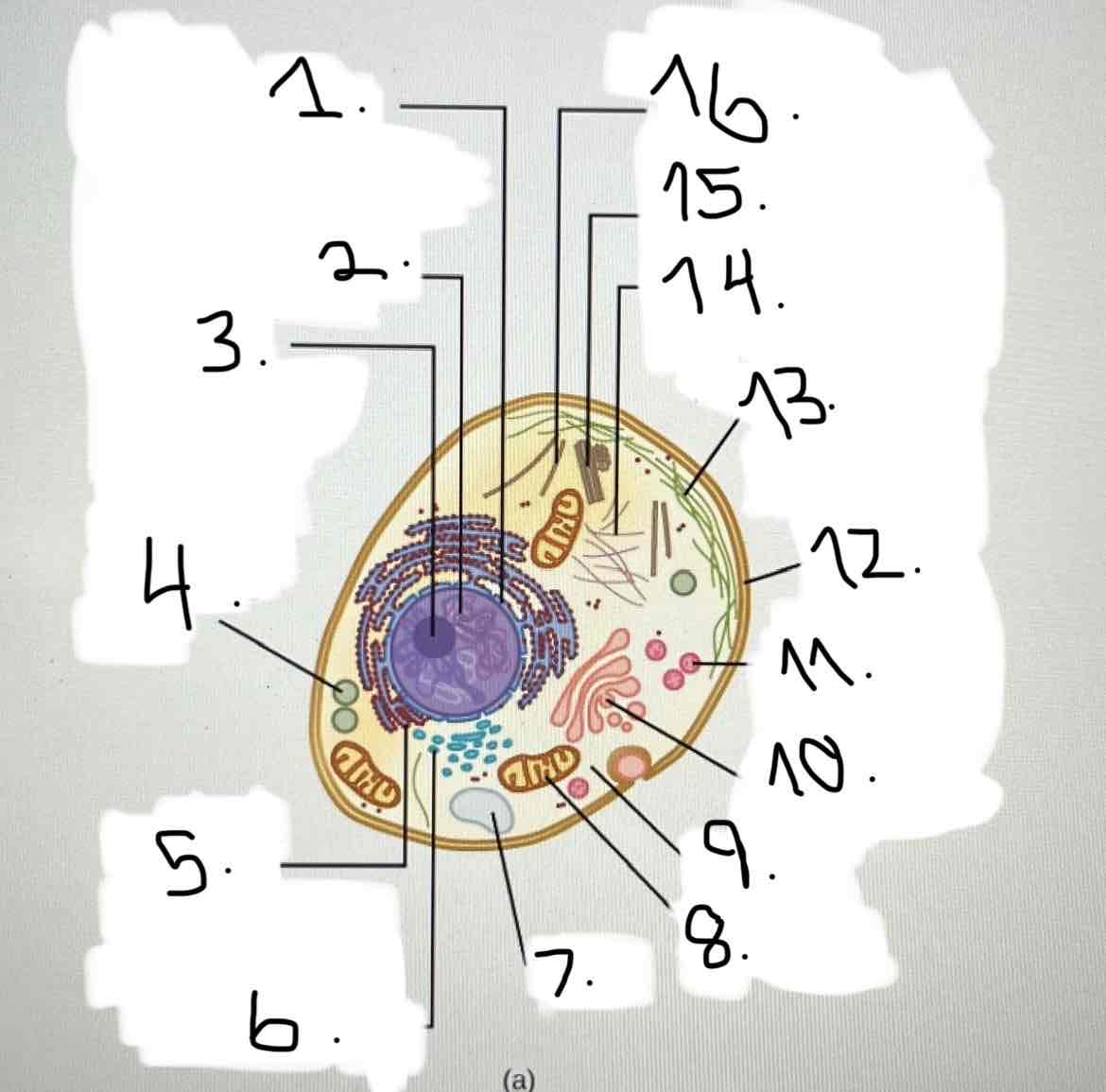
what is 10?
nucleus; nuclear envelope
vacuole
plasma membrane
mitochondria
nucleolus
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
intermediate filaments
cytoskeleton; microtubules
Golgi apparatus
rough endoplasmic reticulum
chromatin
peroxisome
intermediate filaments
cytoplasm
centrosome
lysosome
Golgi apparatus
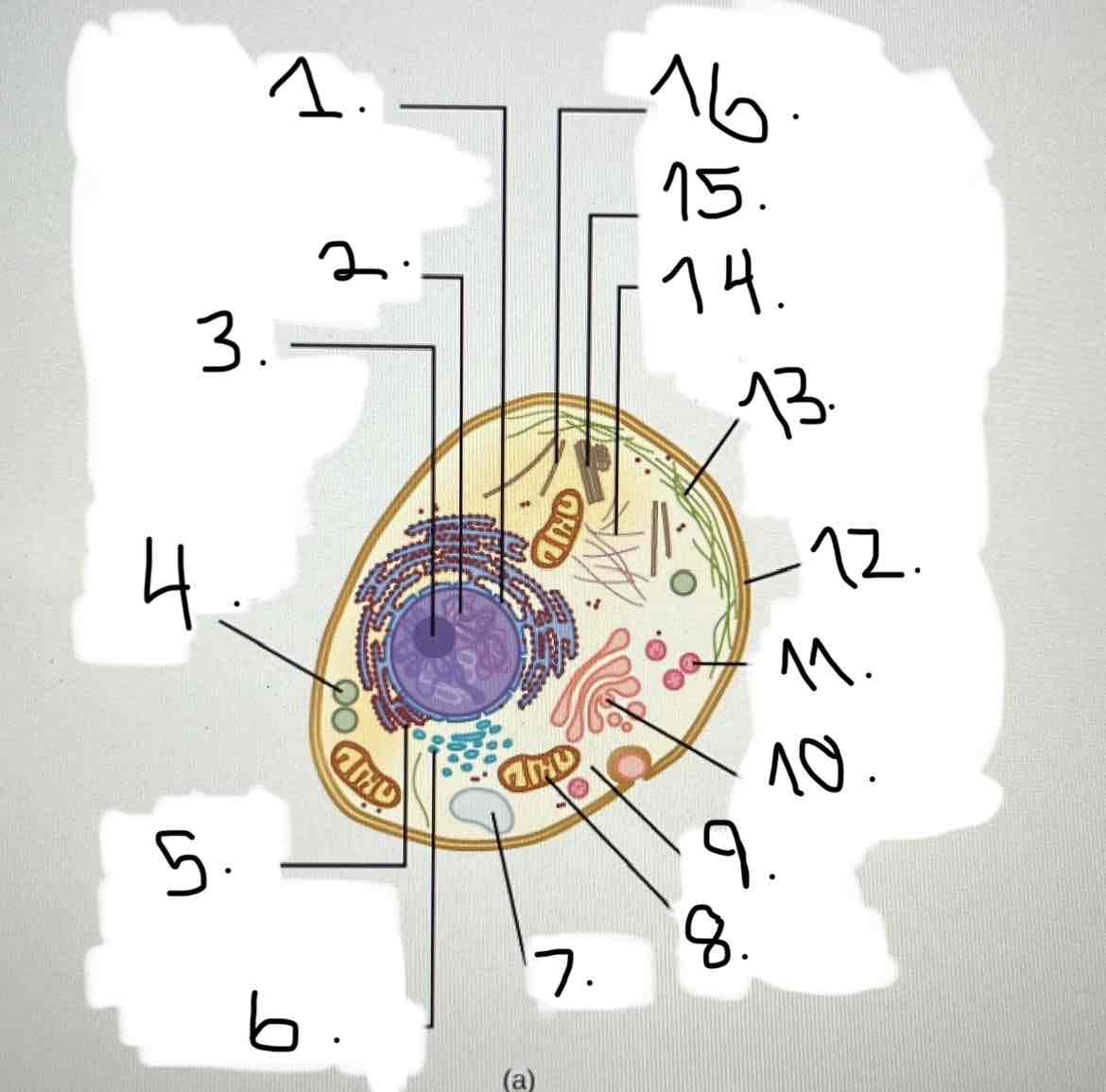
what is 11?
nucleus; nuclear envelope
vacuole
plasma membrane
mitochondria
nucleolus
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
intermediate filaments
cytoskeleton; microtubules
Golgi apparatus
rough endoplasmic reticulum
chromatin
peroxisome
intermediate filaments
cytoplasm
centrosome
lysosome
lysosome
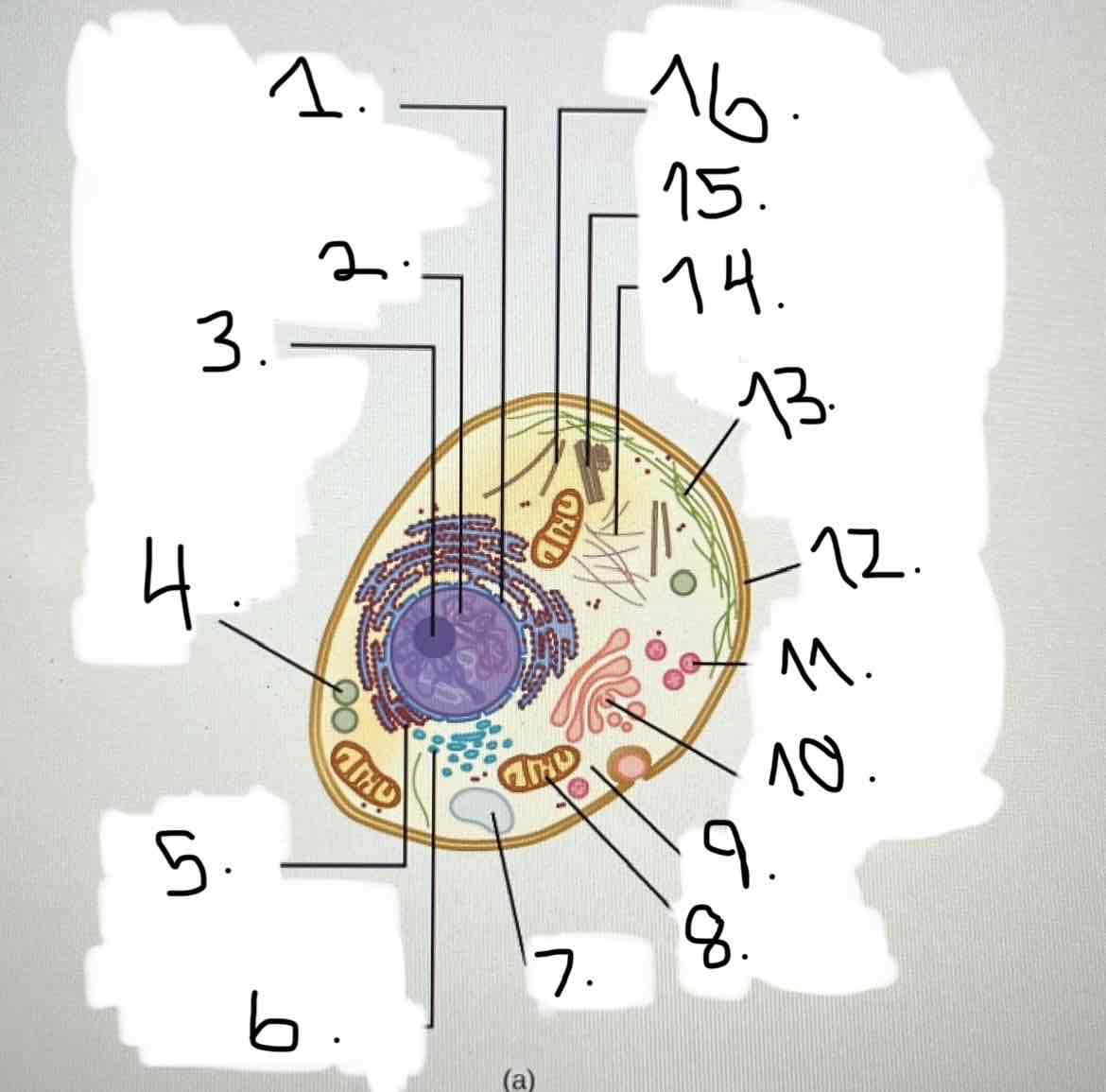
what is 12?
nucleus; nuclear envelope
vacuole
plasma membrane
mitochondria
nucleolus
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
intermediate filaments
cytoskeleton; microtubules
Golgi apparatus
rough endoplasmic reticulum
chromatin
peroxisome
intermediate filaments
cytoplasm
centrosome
lysosome
plasma membrane
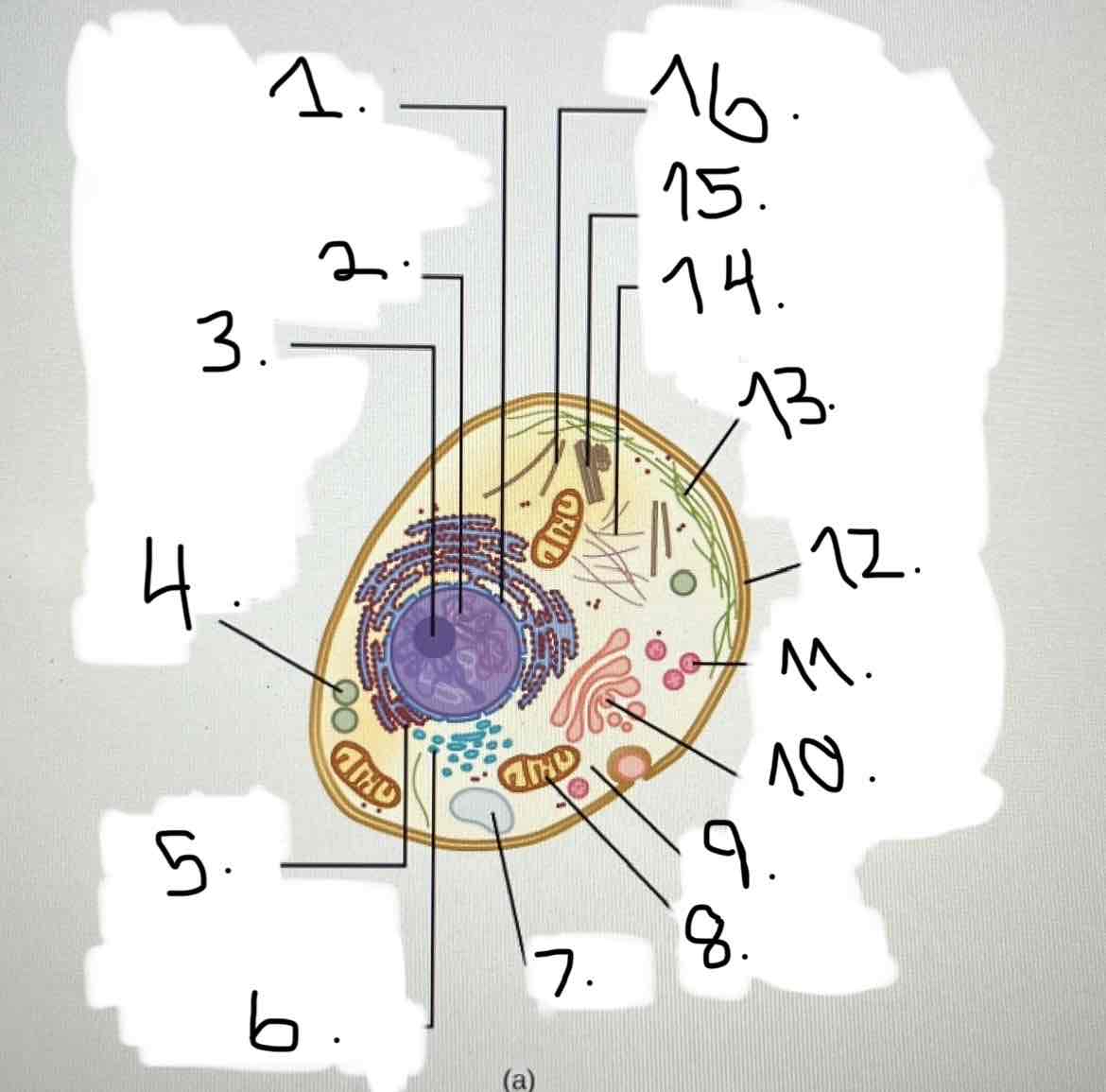
what is 13?
nucleus; nuclear envelope
vacuole
plasma membrane
mitochondria
nucleolus
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
intermediate filaments
cytoskeleton; microtubules
Golgi apparatus
rough endoplasmic reticulum
chromatin
peroxisome
intermediate filaments
cytoplasm
centrosome
lysosome
microfilaments
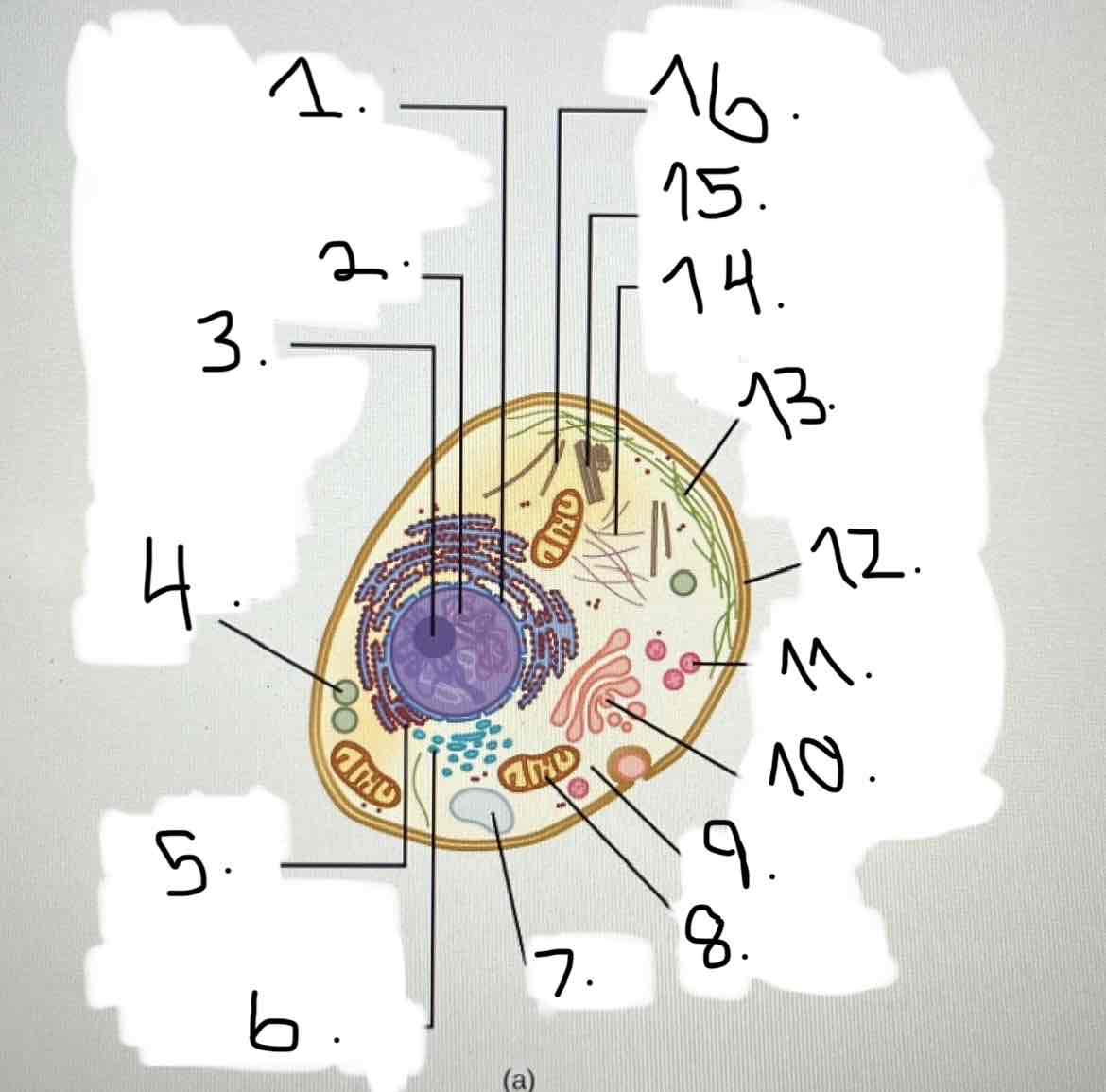
what is 14?
nucleus; nuclear envelope
vacuole
plasma membrane
mitochondria
nucleolus
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
intermediate filaments
cytoskeleton; microtubules
Golgi apparatus
rough endoplasmic reticulum
chromatin
peroxisome
intermediate filaments
cytoplasm
centrosome
lysosome
intermediate filaments
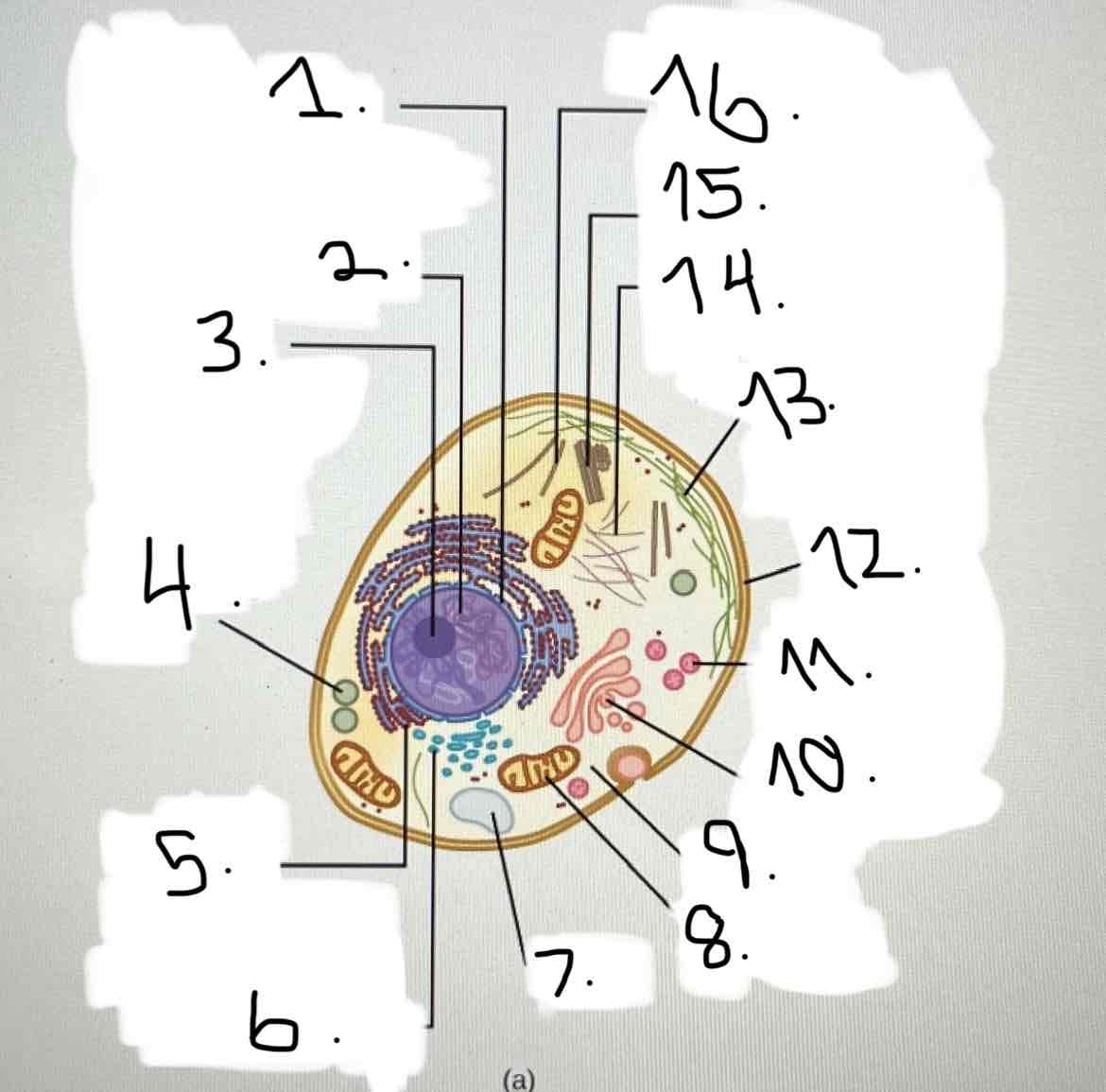
what is 15?
nucleus; nuclear envelope
vacuole
plasma membrane
mitochondria
nucleolus
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
intermediate filaments
cytoskeleton; microtubules
Golgi apparatus
rough endoplasmic reticulum
chromatin
peroxisome
intermediate filaments
cytoplasm
centrosome
lysosome
centrosome
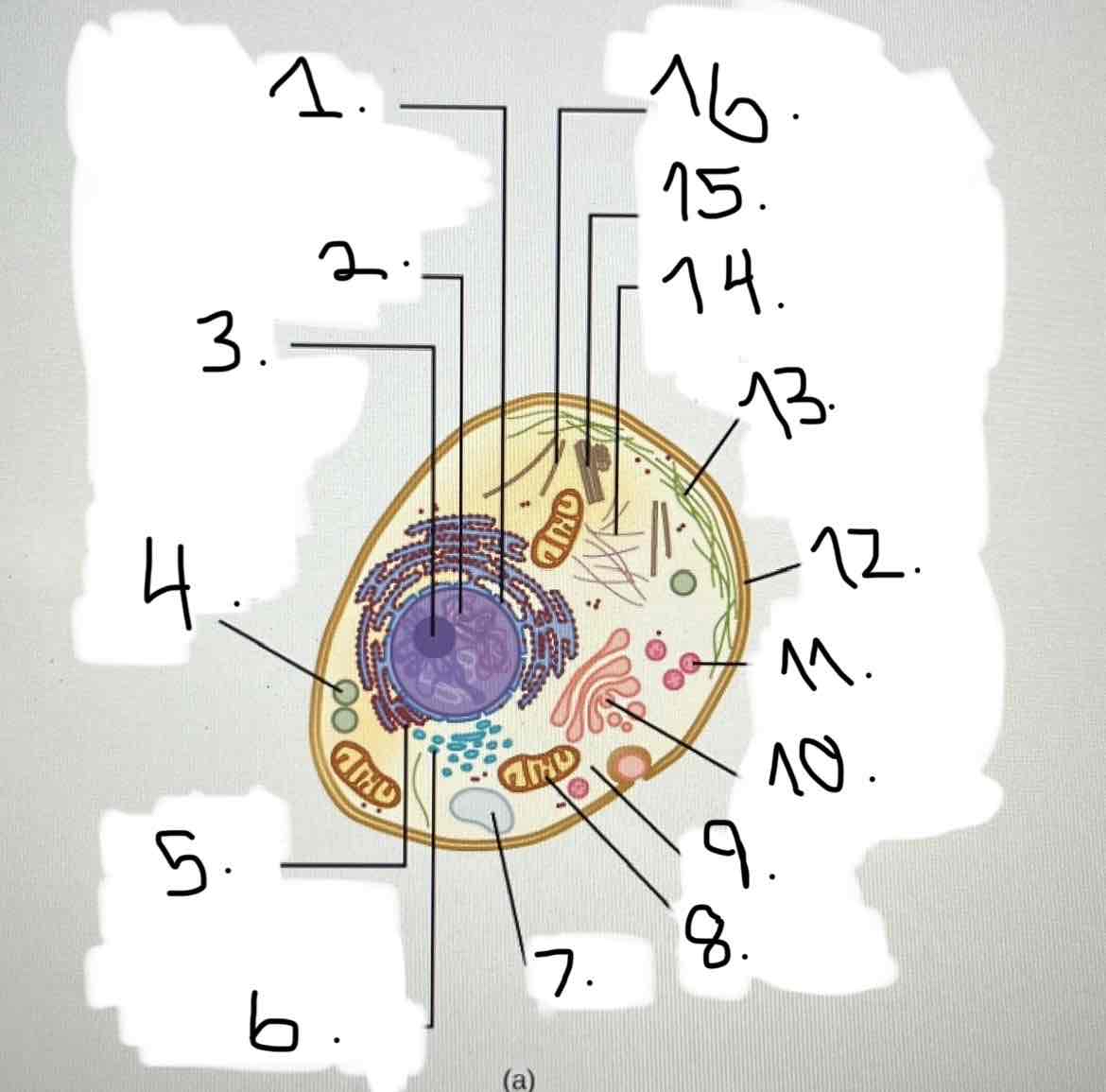
what is 16?
nucleus; nuclear envelope
vacuole
plasma membrane
mitochondria
nucleolus
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
intermediate filaments
cytoskeleton; microtubules
Golgi apparatus
rough endoplasmic reticulum
chromatin
peroxisome
intermediate filaments
cytoplasm
centrosome
lysosome
cytoskeleton; microtubules
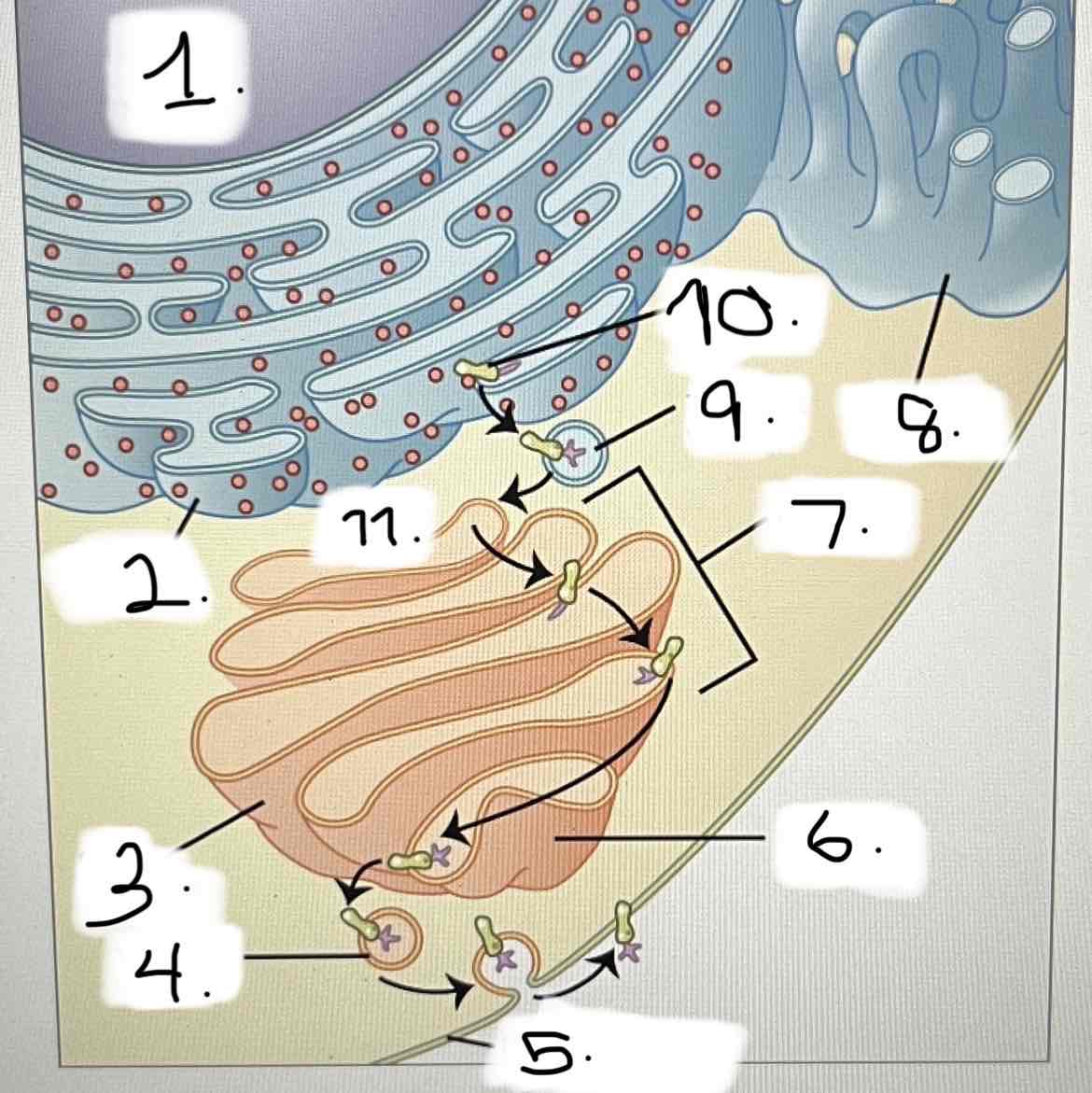
what is 1?
smooth ER
Golgi apparatus
transport vesicle
nucleus
trans face
cis face
cisternae
rough ER
transport vesicle
plasma membrane
protein for export
nucleus
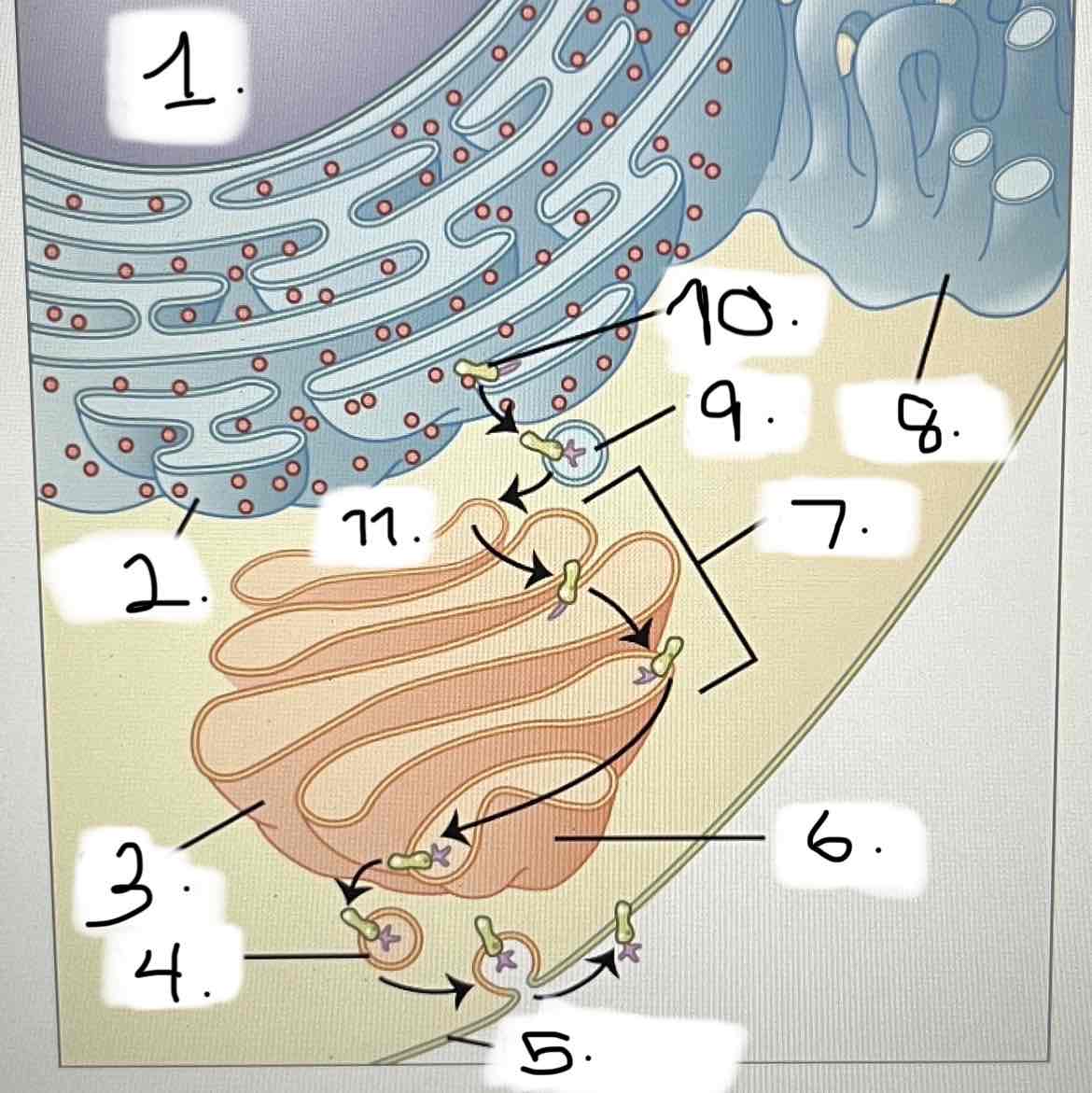
what is 2?
smooth ER
Golgi apparatus
transport vesicle
nucleus
trans face
cis face
cisternae
rough ER
transport vesicle
plasma membrane
protein for export
rough ER
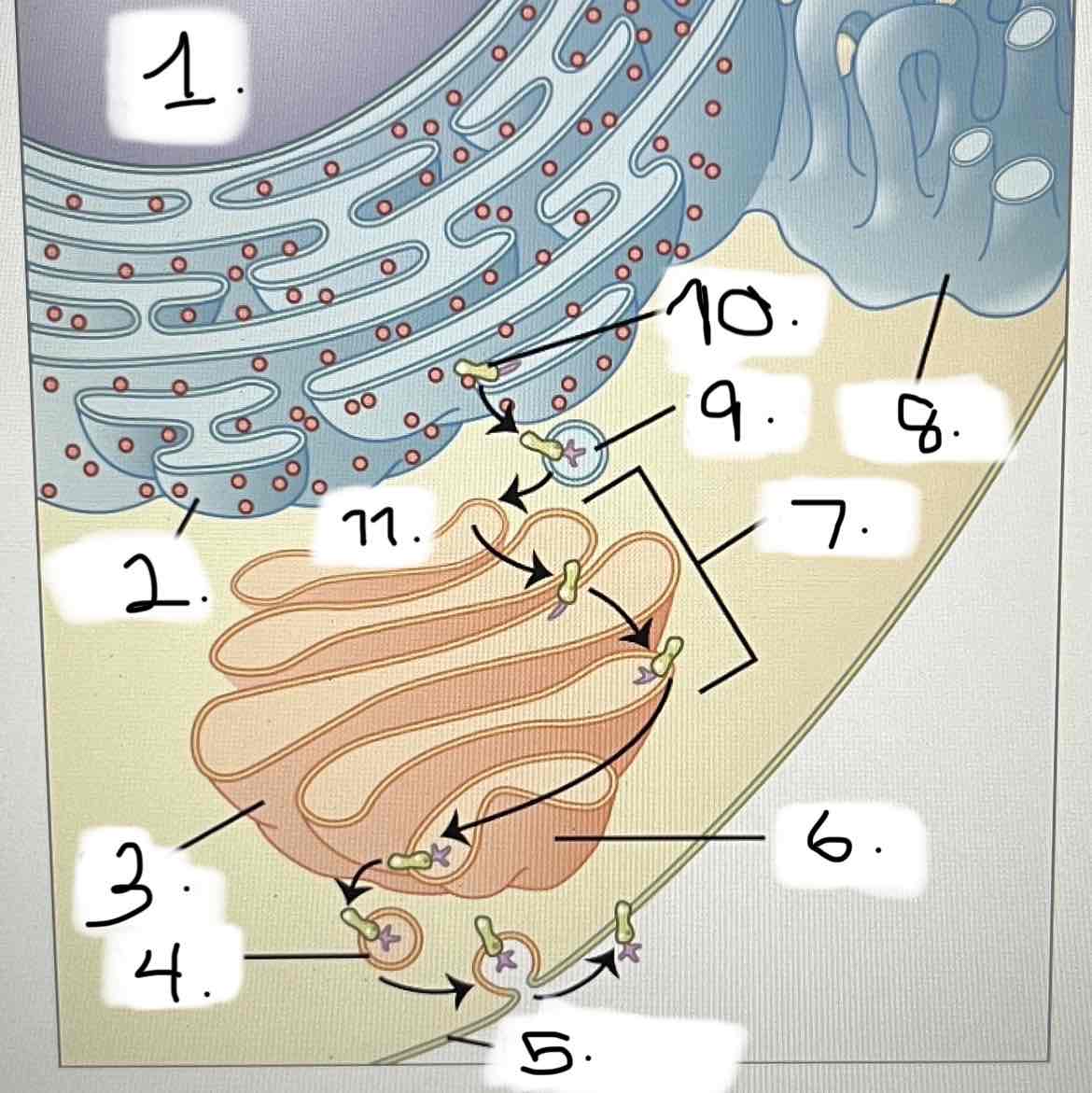
what is 3?
smooth ER
Golgi apparatus
transport vesicle
nucleus
trans face
cis face
cisternae
rough ER
transport vesicle
plasma membrane
protein for export
Golgi apparatus
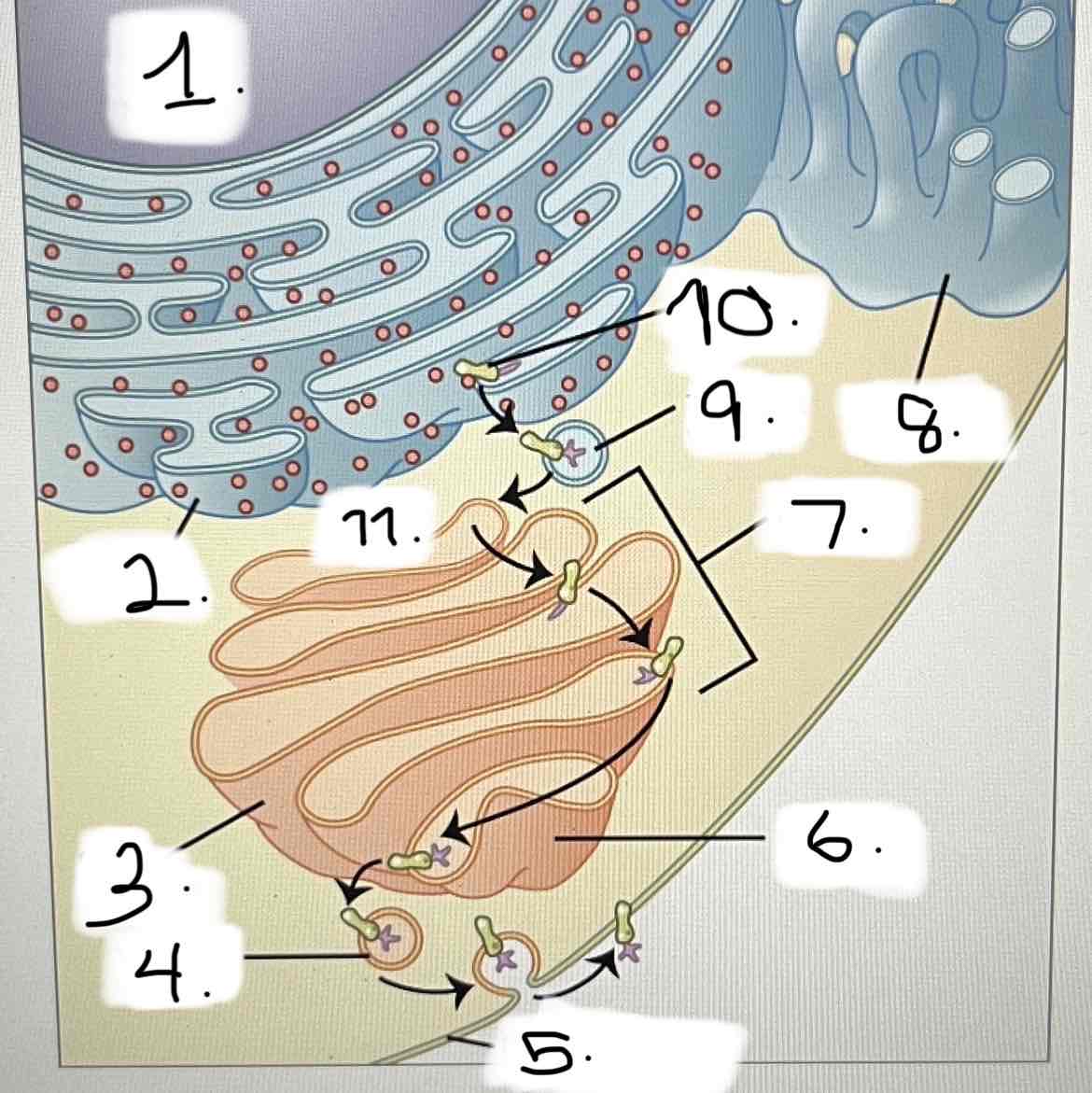
what is 4?
smooth ER
Golgi apparatus
transport vesicle
nucleus
trans face
cis face
cisternae
rough ER
transport vesicle
plasma membrane
protein for export
transport vesicle
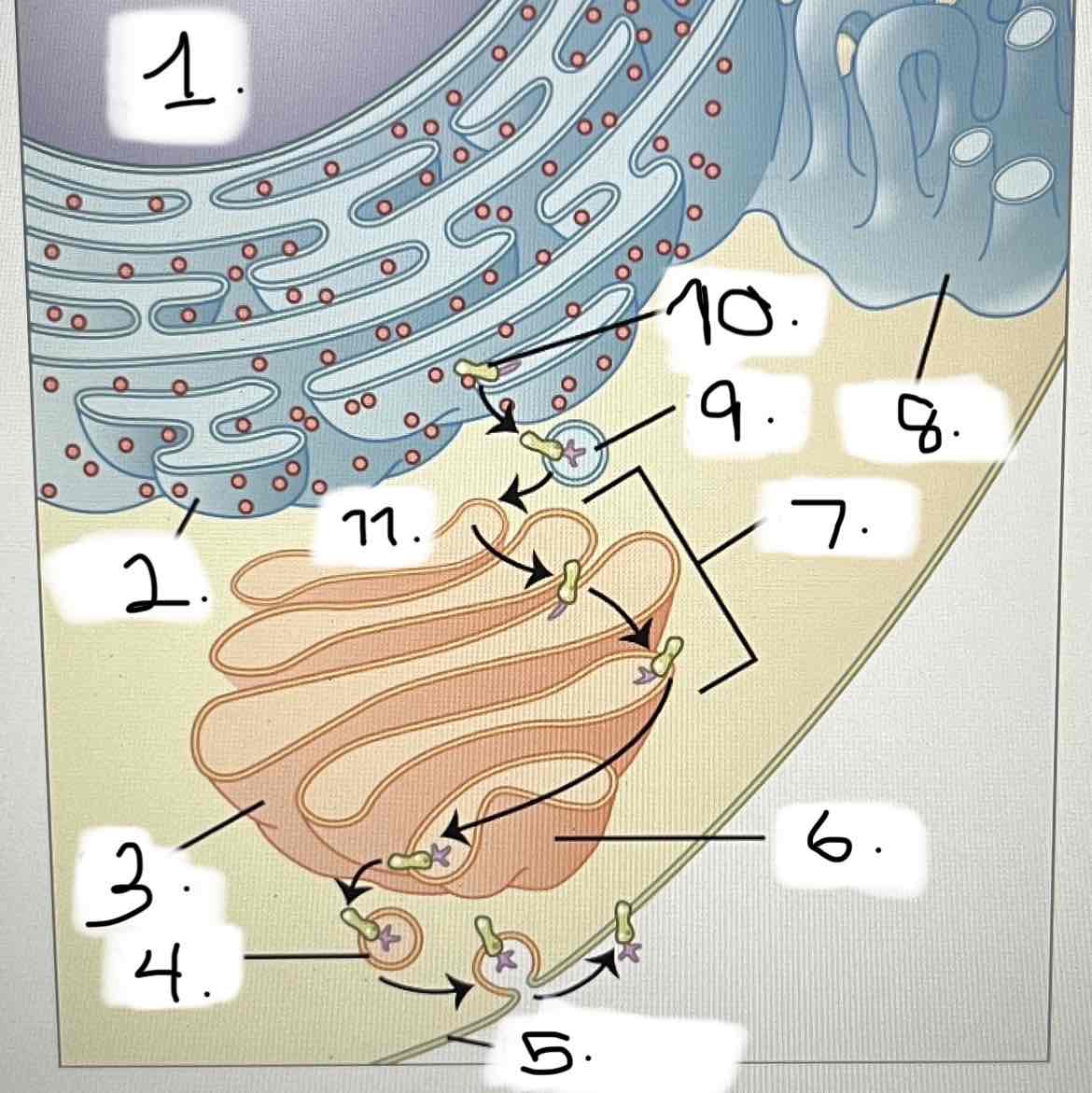
what is 5?
smooth ER
Golgi apparatus
transport vesicle
nucleus
trans face
cis face
cisternae
rough ER
transport vesicle
plasma membrane
protein for export
plasma membrane
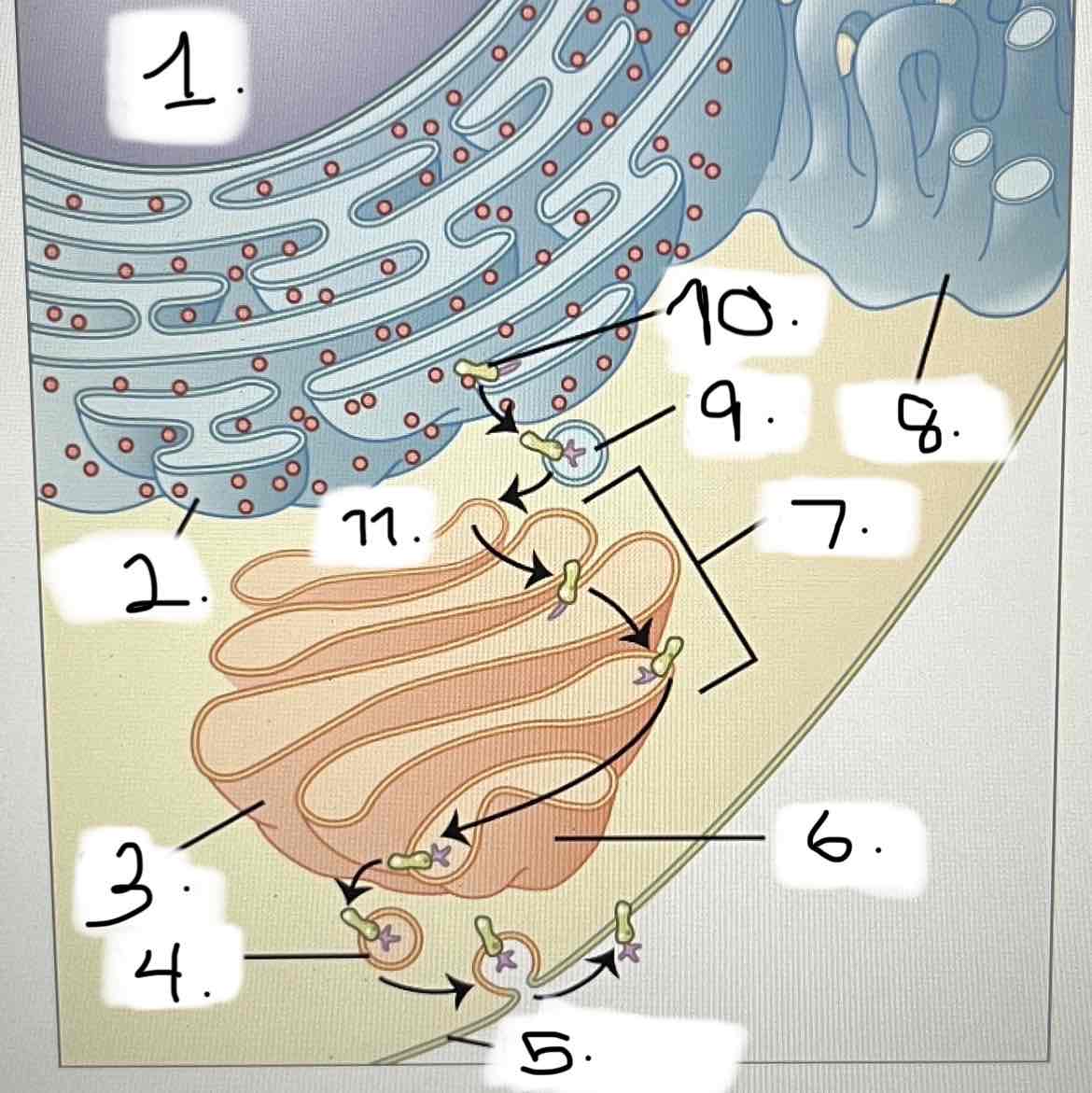
what is 6?
smooth ER
Golgi apparatus
transport vesicle
nucleus
trans face
cis face
cisternae
rough ER
transport vesicle
plasma membrane
protein for export
trans fat
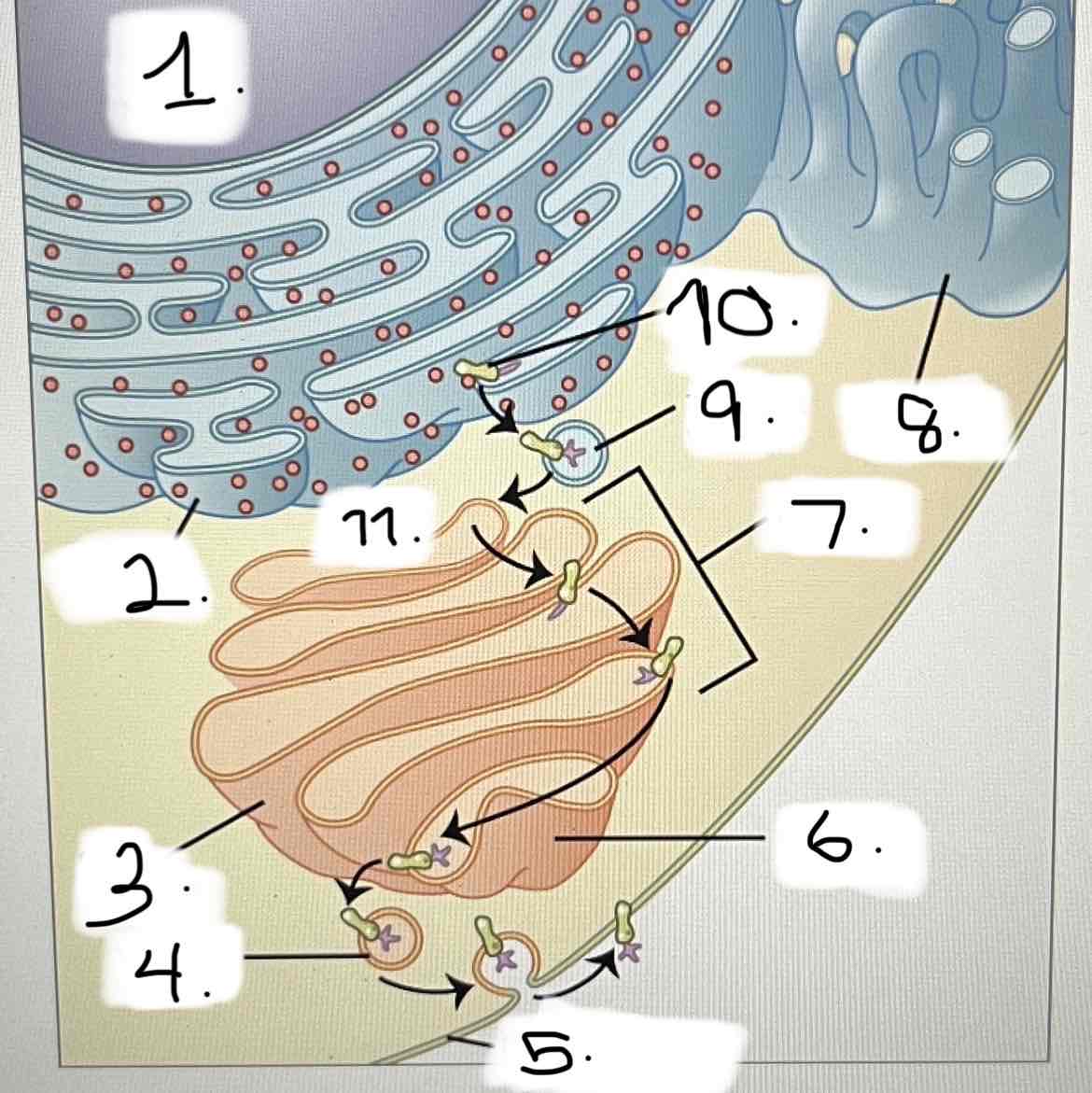
what is 7?
smooth ER
Golgi apparatus
transport vesicle
nucleus
trans face
cis face
cisternae
rough ER
transport vesicle
plasma membrane
protein for export
cisternae
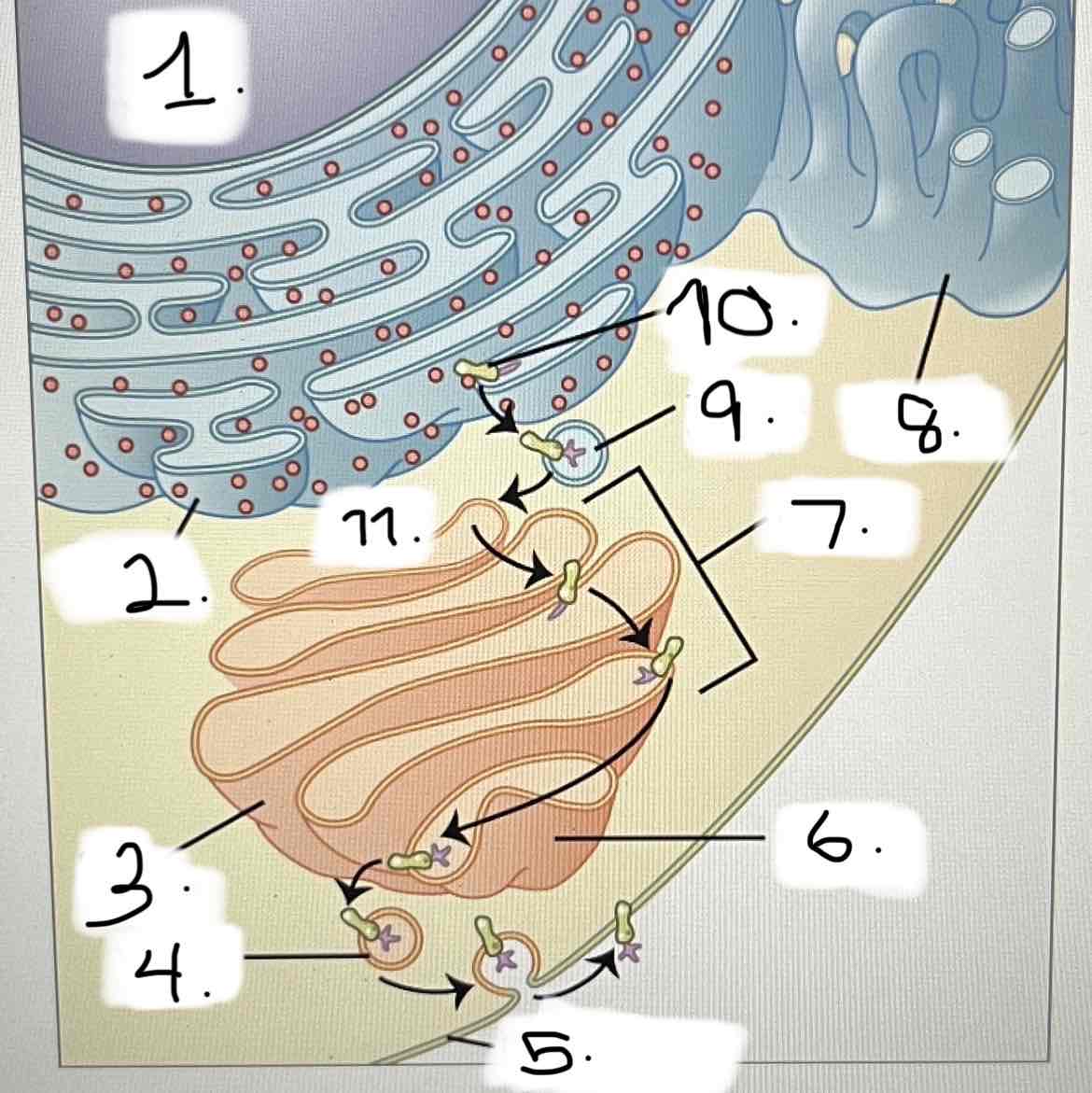
what is 8?
smooth ER
Golgi apparatus
transport vesicle
nucleus
trans face
cis face
cisternae
rough ER
transport vesicle
plasma membrane
protein for export
smooth ER
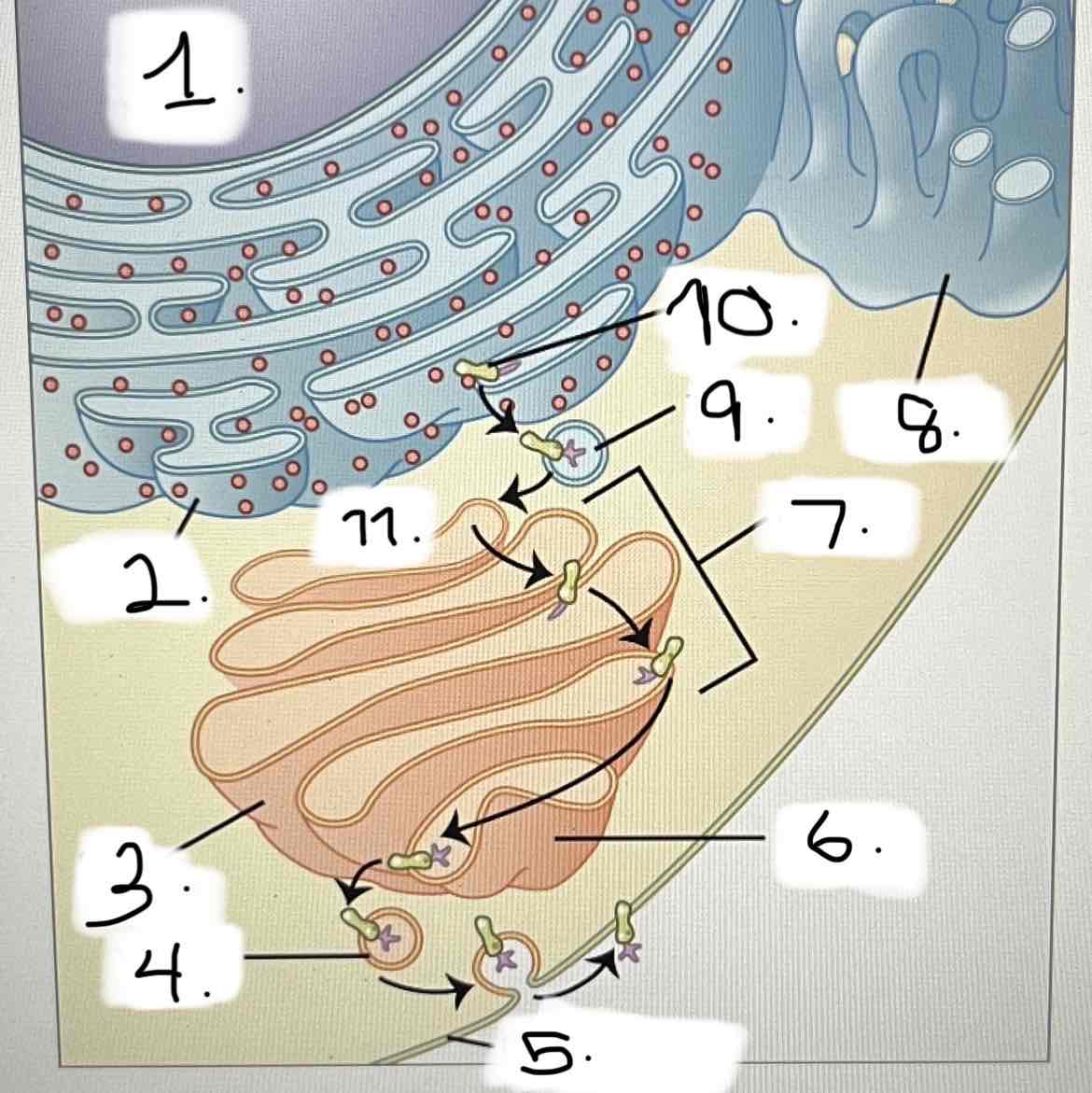
what is 9?
smooth ER
Golgi apparatus
transport vesicle
nucleus
trans face
cis face
cisternae
rough ER
transport vesicle
plasma membrane
protein for export
transport vesicle
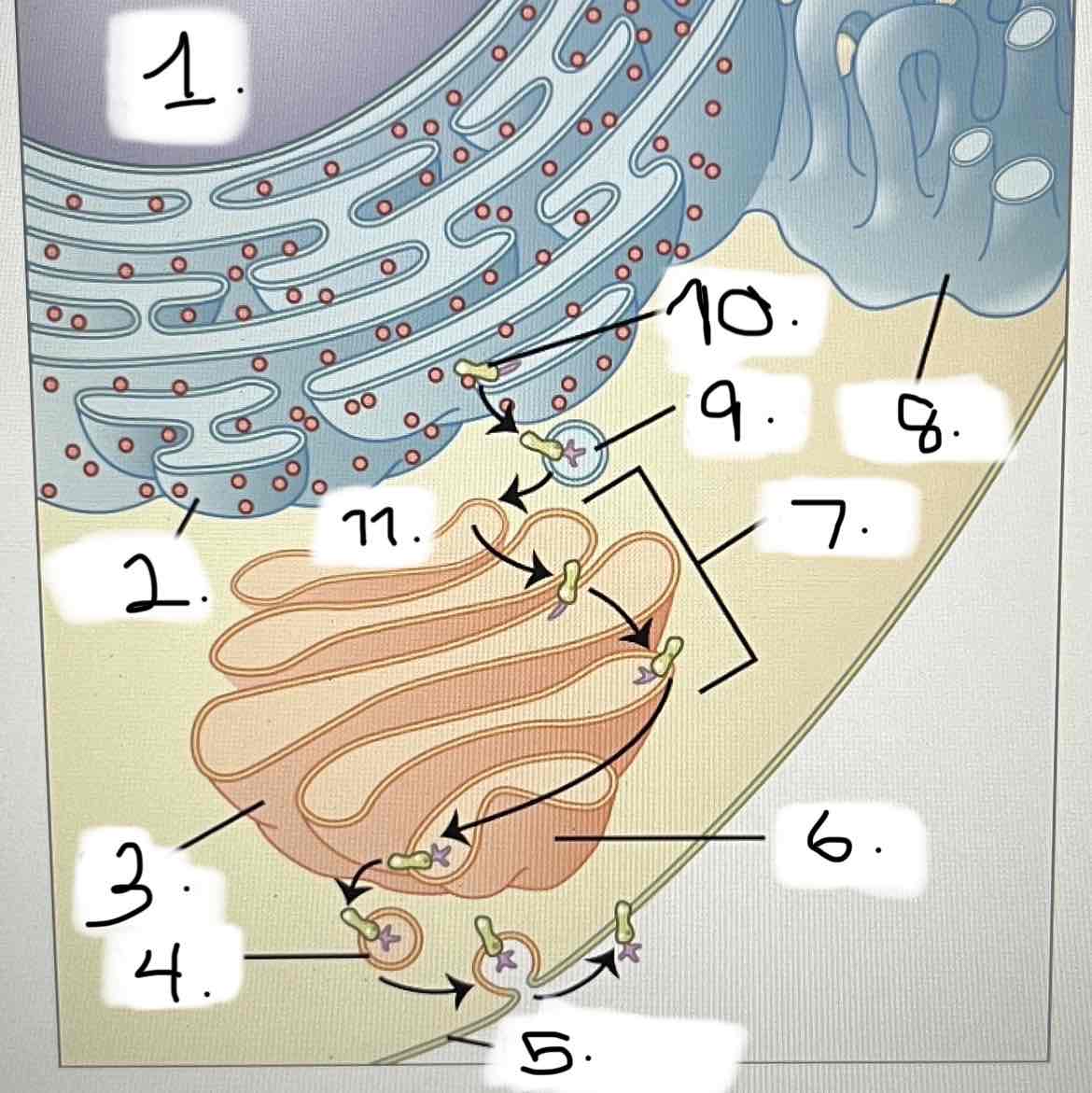
what is 10?
smooth ER
Golgi apparatus
transport vesicle
nucleus
trans face
cis face
cisternae
rough ER
transport vesicle
plasma membrane
protein for export
protein for export
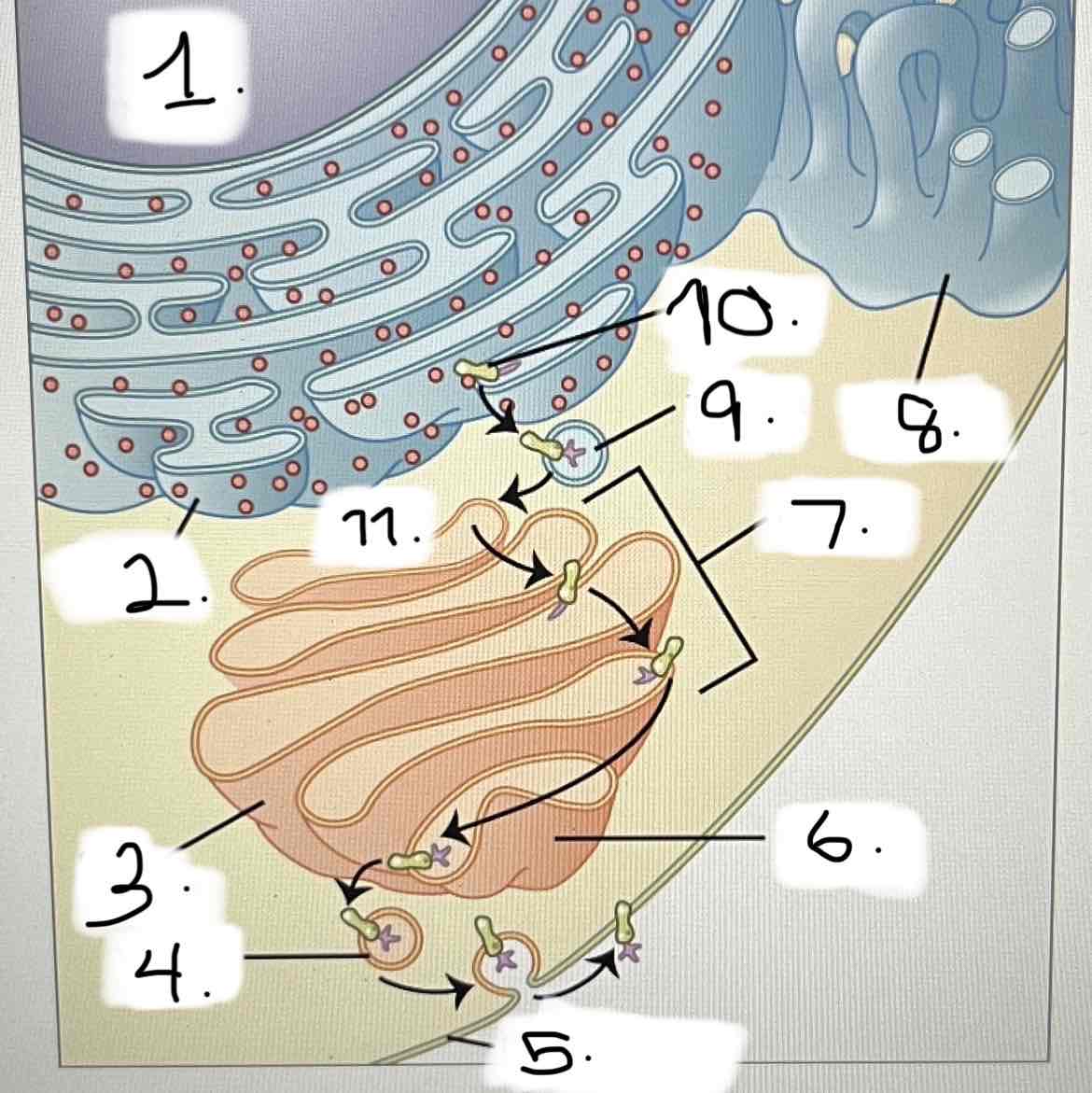
what is 11?
smooth ER
Golgi apparatus
transport vesicle
nucleus
trans face
cis face
cisternae
rough ER
transport vesicle
plasma membrane
protein for export
cis face
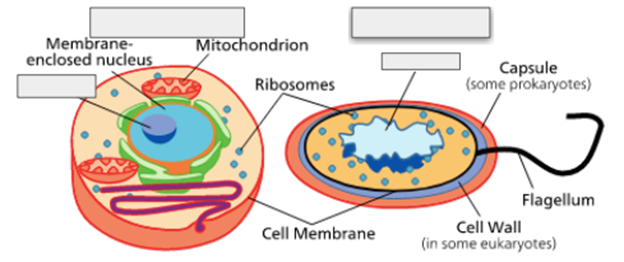
Label the Nucleoid/Nucleus in each picture and identify the cell as Eukaryotic or Prokaryotic
Left: Eukaryotic, nucleus
Right: Prokaryotic, nucleoid
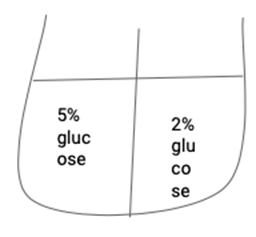
What will happen to the water in this scenario?
Osmosis, water raises to 5% and lowers on 2%
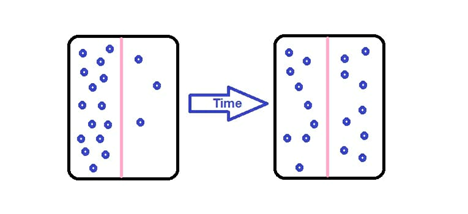
What is shown in the following image? Choose all correct answers. (blue circles are solute)
a. Osmosis
b. Diffusion
c. Passive Transport
d. Active Transport
diffusion
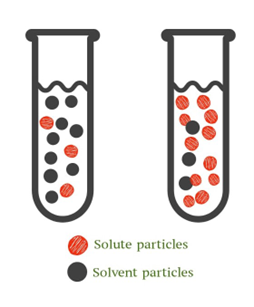
From the picture below, assuming the two containers are connected by a semipermeable membrane. The red being salt and the black being oxygen. Which statement would be true?
A. Water move to the left
B. Salt will move to the left
C. Oxygen will move to the left
D. Water will move to the right
Water will move to the right
A cell in an environment with a higher concentration of solutes outside the cell than inside the cell. Which of the following is correct?
A. The cell is in a hypertonic environment and therefore water will flow into the cell, causing it to swell.
B. The cell is in a hypertonic environment and therefore water will leave the cell, causing it to wilt.
C. The cell is in a hypotonic environment and therefore water will flow into the cell, causing it to swell.
D. The cell is in a hypotonic environment and therefore water will flow out of the cell, causing it to wilt.
D. The cell is in a hypotonic environment and therefore water will flow out of the cell, causing it to wilt.
If a cell is in a hypertonic environment and the solutes are small non-polar molecules, what kind of transport is required to bring those solutes into the cell?
A. Primary Active Transport
B. Secondary Active Transport
C. Passive transport
D. Osmosis
passive transport