Access Control Models
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
What are security models?
general classes of them which abstract away from concrete characteristics of specific domains
Authentication
The process of verifying the validity of something claimed by a system entity
Authorization
a right or a permission that is granted to a system entity to access a system resource.
Access Control
Protection of system resources against unauthorized access.
A process that regulates the use of system resources according to security policy allowing only authorized entities according to that policy.
What could be an authorized entity?
users, programs, processes, or other systems
What do typical access control models focus on?
authorization, i.e., specifying who may do what, and controlling how authorization can change
How is access control achieved?
by using policies
Where can we implement Access Control?
• Locally: used to differentiate inside users from outside users; help users to operate on their own personal data.
• Network: used to give wide access to data and service. (It holds all internet-based services.)
What does a security policy define?
What is allowed.
• It defines those executions of a system that are acceptable, or complementarily, those that are not acceptable
What is a security policy analogous to?
A set of laws
What terms are security policies defined in?
in terms of high-level rules or requirements.
Are policies immeasurable or measurable?
measurable
Where can security policies be enforced?
locally or in a network
What are access control models used for?
• To define a specific set of authorization rights.
• To define a set of policies for a software system to enforce a set of rights to fulfil the security concerns.
• To define a set of run-time system users that are used to assign the defined rights to the other users in the system.
• To protect for all multi-user systems, against violation of:
• Confidentiality (e.g., unauthorized disclosure)
• Integrity (e.g., improper modifications)
• Availability (e.g., service disruption)
What are the main models of access control?
• Discretionary Access Control (DAC) - Defined by the user
• Mandatory Access Control (MAC) - Defined by the system
• Role-based access control (RBAC) and its various extensions. - Defined by the roles
What is the principle behind the Discretionary Access Control (DAC) model?
users own resources and control their access. The owner may change object’s permissions at his discretion and can transfer ownership to other users.
Is DAC flexible?
Yes
What are the security limitations for Discretionary Access Control (DAC)?
open to mistakes, negligence, or abuse as it requires all users to understand mechanisms and understand and respect the security policy. It also does not allow for the control of information dissemination
What type of controls does DAC use?
identity-based controls
What does every object in DAC have?
an owner and a Discretionary access control list (DACL) that contains the permissions of the subjects
Who has full control over the DACL?
the owner
What are the general issues with DAC?
• Managing the policies for a large system is a complex task
• Difficult to understand that the correct accesses are provided to the right users
• The objects and subjects change frequently, thus, also their permissions need to change.
• Access matrix represents the explicit access relation between each individual subject and object, it grows very large very quickly
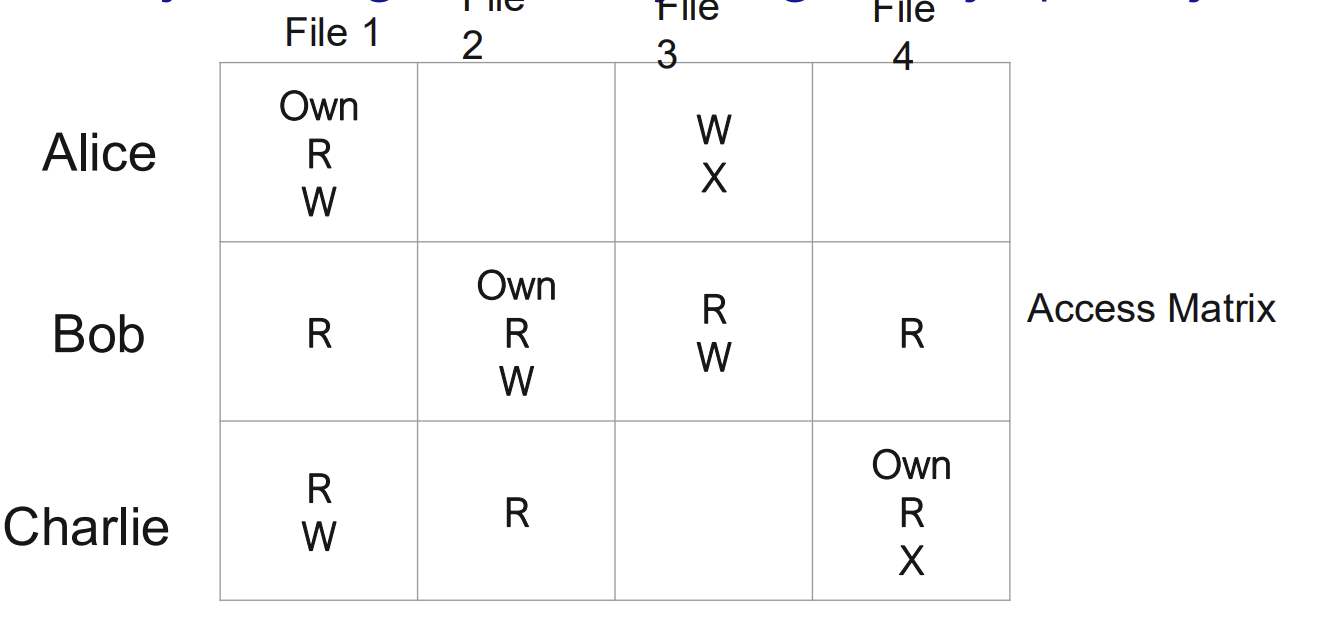
What does MAC stand for?
Mandatory Access Control
What is the main idea behind MAC?
Classification of subjects and objects by security levels.
How are access control decision made with MAC?
by comparing security labels indicating sensitivity/criticality of objects, with formal authorization, i.e. security clearances, of subjects.
How are MAC policies often determined?
with multi-level security policies.
How do MAC and DAC compare?
MAC is more rigid but more secure than DAC
Why is MAC mandatory?
As subjects may not transfer their access rights. The system owner has control not the users.
What does every subject have in MAC?
a profile, which includes the subjects clearance and their need-to know
What does every object have in MAC?
a security label composed of two parts: classification (e.g., sensitivity of the data) and a category (enforcement of need-to-know).
What happens when an entity attempts to access a specific resource?
the OS or security kernel will check the entity's credentials to determine whether access will be granted
What does RBAC stand for?
Role -Based Access Control
What is the main idea behind Rule Based Access Control?
Access is based on user’s role in the organization
Who associates each role to its various permissions?
The administrator
What happens when a user is assigned a rule?
They inherit the permissions associated to the role.
What are the benefits of RBAC?
• Reduces user administration
• Widely used by companies
• Easy to Audit
• Higher Flexibility
• Roles are abstraction of jobs or functions in an organization.
• Increases abstraction in policies. Policies become more manageable
What is the intuition behind RBAC uses?
Abstraction: Many subjects (or objects) have identical attributes, and policy is based on these attributes.
Hierarchy: Often functional/organizational hierarchies that determine access rights.
What is the approach of RBAC?
decompose subject/object relationship by introducing set of roles. Then assign subjects to roles and permissions to objects based on role. This idea can be generalized by introducing a hierarchy on roles (or even users or permissions).
What does RBAC use the notion of “role” as ?
it uses it as the central authorisation mechanism
What is a role in RBAC?
an abstract representation of a group of subjects that are allowed to perform the same operations on the same objects
What are objects in a RBAC system assigned to ?
The objects (i.e., accessible shared data) in the system are assigned to an authorised role
Why do the subjects (users) need to identify themselves?
So they can acquire roles to access and operate on the objects
What are the benefits of role hierarchies?
They simplify policy expression
What are the different types of RBAC?
• Flat RBAC is the simplest but can cause conflicts.
• Hierarchical RBAC simplifies the creation of new roles.
• Constrained RBAC
What are some other types of access control?
• Rule based access control (e.g., Firewalls)
• Temporal Based Access Control (the permissions are valid for a limited amount of time)
• Attributes-Based Access Control (access rights are granted based on policies that combine different attributes)
• A mixture of what we have seen so far.