Lecture 14: Pollution
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
name some forms of pollution
trash
plastics
lead
environmental chemicals
light pollution
noise pollution
how does the US contribute to waste generation?
US is one of top producers in the world of waste (12%)
each American throws out about 4.5 lbs of trash each day
what are the most common kinds of trash in landfills?
food and plastics
plastic makes up to 40-50% of US waste
plastic waste makes up about 40% of al litter
describe recycling rates and the issues with recyling
US recycling rates are about 32%
only about 4.5% of plastics in the US are recycled (we use to much plastic, but plastic is very difficult to recycle)
how does large plastic affect wildlife?
wildlife may eat plastics like plastic bags, 4-pack rings, or masks, which can kill them or suffocate them
what 2 things make plastic exceptionally detrimental?
slow to decompose - takes about 450 years for a plastic bottle to decompose
not likely to be recycled - about 99% of plastic cutlery is not accepted to be recycled
what are microplastics? where do you find them? why are they a problem?
primary microplastics: plastics that are produced that are less than 5mm (like a microbead in beauty products)
secondary microplastics: larger plastics that have broken down into smaller plastics
found everywhere - in our bodies, air, snow, rain, ocean
problem in marine environments and in humans
many animals in the ocean filter water to gain food and they also filter small plastic particles
how do environmental toxins harm the environment?
rat poisoning ends up harming the raptors and other predators that eat the rats
pesticides and herbicides reach a destination other than their target species because they are sprayed across entire agricultural fields
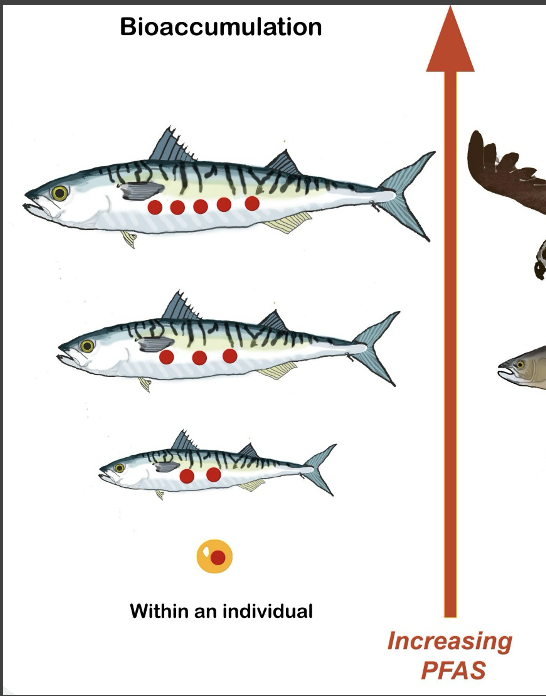
what is bioaccumulation?
when a toxin accumulates in an individual over time
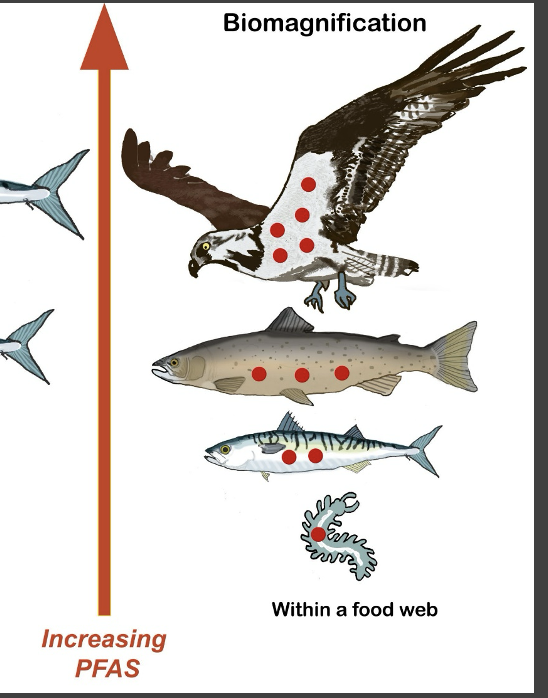
what is biomagnification?
an accumulation of a toxin up the food chain
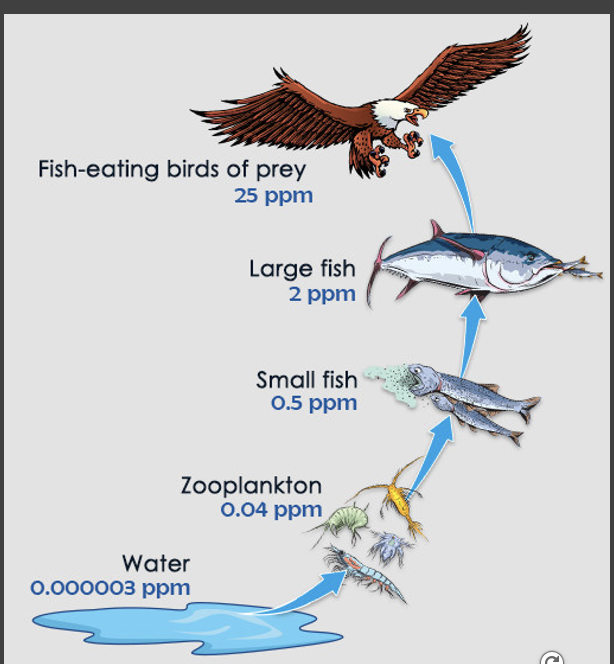
explain the biomagnification of DDT
DDT is a pesticide used in agriculture and to control spread of disease by mosquitos
caused bald eagle eggshells to be very thin
now is considered a carcinogen
banned in the US in 1972
about 1/3 of food is a result of ______
pollinators
how does lead ammunition and tackle harm the environment?
lead toxicosis kills many animals
one of the hardest hit groups are raptors
most often, lead exposure occurs through ingestion of spent ammunition fragments and fishing tackle
what is
the presence of excessive artificial light that brightens the night sky. results from human constructs like street lighting, lights on buildings, flood lights. can be disruptive to wildlife and other organisms. as much as 50% of outdoor lighting is wasted
name 3 groups of organisms that are highly affected by light pollution
cacti/trees
sea turtles
birds
how are cacti affected by light pollution?
some cacti only bloom at high and often only for short intervals. bats and moths are primary pollinators that allow the cacti to reproduce. light pollution can prohibit them from flowering. if flowers do not open or are open even shorter periods, then they may not reproduce
what are the 2 things bringing on an earlier spring? which one has a larger impact on an earlier spring?
rising temps and urban light pollution. light pollution causes a much greater impact
how does light pollution affect birds?
most birds migrate at night, and they rest during the day, so they are attracted to areas with a lot of light
more light = more humans and buildings
if they are in an area with a window facing a green space, they may run into the window thinking it is the green space and die
how does noise pollution harm the environment?
roadways, fireworks,
excess noise makes it difficult for birds to listen for predators and hear other birds
owls and bats use echolocation - noise pollution disrupts this
boats and vessels in the water disrupt marine life by causing internal damage, confusion, making it difficult for them to stay in their social groups, beaching, interrupting communication