ap human unit 5 and others too
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
intensive farming
agriculture that involves greater inputs of capital and paid labor relative to the space being used
Market Gardening (Truck Farming)
farming devoted to specialized fruit, vegetable, flowers, or vine crops for sale rather than consumption
plantation agriculture
Production system based on a large estate owned by an individual, family, or corporation and organized to produce a cash crop.
mixed crop/livestock systems
a type of agriculture where crops and animals are grown together and crops are used to feed the animals, who in turn produce dung that is used as fertilizer for the crops.
Nomadic herding/pastoralism
Farming system where animals (cattle, goats, camels) are taken to different locations in order to find fresh pastures.
Livestock Ranching
An extensive commercial agricultural activity that involves the raising of livestock over vast geographic spaces typically located in semi-arid climates like the American West.
Mediterranean agriculture
specialized farming that occurs only in areas where the dry-summer climate prevails
township and range
rigid grid-like pattern used to facilitate the dispersal of settlers evenly across farmlands
shifting cultivation (swidden agriculture)
The use of tropical forest clearings for crop production until their fertility is lost. Plots are then abandoned, and farmers move on to new sites.
long-lot system
divides land into narrow parcels that extend from rivers, roads, or canals
Corn Belt
Area in the midwestern United States, roughly covering western Indiana, Illinois, Iowa, Missouri, eastern Nebraska, and eastern Kansas, in which a specific crop is dominant
Metes and Bounds
The type of legal description that relies on a property's physical features to determine and to describe the boundaries and measurements of the parcel.
Milkshed
ring surrounding a city from which milk can be supplied without spoiling
Rural Settlement Patterns
differing densities and arrangements of population in a sparsely populated region
Meta cities
a place with 20 million or more residents.
Megacity
City with more than 10 million people
Metropolitan Statistical Area (MSA)
An area with a city of 50,000 or more people, together with adjacent urban communities that have strong ties to the central city.
Gateway City
a city that serves as a link between one country or region and others because of its physical situation
Offshore Financial Services
financial institutions located outside of the country that offer tax advantages & privacy
urban growth boundaries
a legal border that separates an area where development is permitted from an area where development is forbidden
Forward Capital
A capital city placed in a remote or peripheral area for economic, strategic, or symbolic reasons.
New Urbanism
An urban design movement that emphasizes the pedestrian-friendly return to earlier close-knit neighborhoods and a sense of community
Sun Belt
This region consists of a broad band of states running across the South from Florida to Texas. Beginning in the 1970s, this area experienced rapid economic growth and major gains in population.
Rust Belt
The northern industrial states of the United States, including Ohio, Michigan, and Pennsylvania, in which heavy industry was once the dominant economic activity. In the 1960s, 1970s, and 1980s, these states lost much of their economic base to economically attractive regions of the United States and to countries where labor was cheaper, leaving old machinery to turn brown in the moist northern climate
Brownfields
contaminated industrial or commercial sites that may require environmental cleanup before they can be redeveloped or expanded
Zones of Abandonment/Disamenity Zone
An area with a lack of jobs, declining land values and falling demand that cause people to leave and businesses to close
Environmental Injustice
the unequal distribution of environmental hazards based on racial or socioeconomic status
Public Housing
Housing owned by the government; in the United States, it is rented to low-income residents, and the rents are set at 30 percent of the families' incomes.
Filtering
Process of changing the use of a house, from single-family owner occupancy to renting it out to multiple individuals or families in a lower income class.
Blockbusting
A process by which real estate agents convince white property owners to sell their houses at low prices because of fear that persons of color will soon move into the neighborhood
Steering
Channeling prospective buyers or tenants to particular neighborhoods based upon their race, religion, national origin, or ancestry.
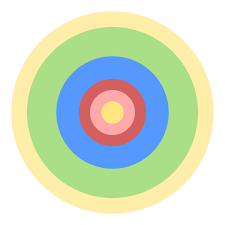
Burgess Concentric Zone Model
A model of the internal structure of cities in which social groups are spatially arranged in a series of rings.
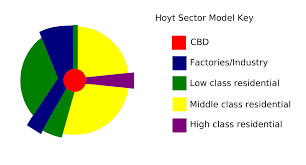
Hoyt Sector Model
A model of the internal structure of a city in which social groups are arranged around a series of sectors or wedges radiating out from the CBD.
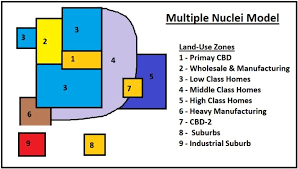
Harris-Ullman Multiple Nuclei Model
A model that recognizes deindustrialization by identifying additional nodes within an urban model as it spreads outward. Each node will act as a point of growth with industries and housing developing nearby.
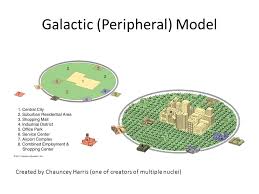
Galactic City Model
Model that is based on deindustrialization and consists of multiple centers which have been connected by an extensive network of highways and edge cities that circle the city.
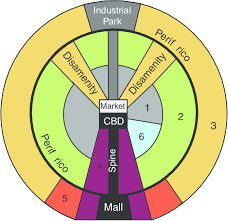
Latin American City Model
The CBD is dominant; it is divided into a market sector and a modern high-rise sector. The elite residential sector is on the extension of the CBD in the "spine". The end of the spine of elite residency is the "mall" with high-priced residencies. The further out, less wealthy it gets. The poorest are on the outer edge.
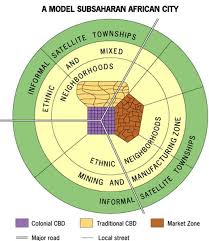
African Cities Model
Usually 3 CBDs - colonial CBD, period market zone, and transitional business CBD. Vertical structure in colonial, one-story buildings in transitional, and informal stands for period market; Ethnic and mixed neighborhoods by mining and manufacturing zones; squatter settlements around the periphery
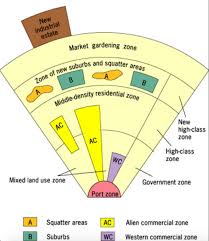
Southeast Asian City Model
The focal point of the city is the colonial port zone combined with the large commercial district that surrounds it. There are seperate clusters of elements of the CBD surrounding the port zone: the government zone, the Western commercial zone, and the alien commercial zone.
crop rotation
the system of growing a different type of agricultural product in a field each season or year to preserve the fertility of the land
First Agricultural Revolution
Dating back 10,000 years, it achieved plant domestication and animal domestication.
linear settlement pattern
a settlement pattern that develop along a mode of transportation such as a road, railroad, or river
Mediterranean agriculture
specialized farming that occurs only in areas where the dry-summer climate prevails
2nd Agricultural Revolution
industrialized agriculture at the time of the Industrial revolution provided many new innovations that allowed large scale farming to exist and an increase in production.
3rd Agricultural Revolution (Green Revolution)
Corresponds with a spike in population growth around the world and the introduction of biotechnology, GMO's, an increased use of fertilizers resulting in very efficient production of agricultural goods
agribusiness
A system of using the economies of scale to consolidate into large scale systems that create efficiencies by reducing cost (land, labor, equipment, seeds, transportation etc.) to maximize profits.
Columbian Exchange
The transfer of plants, animals, diseases, and technologies between the Americas and Europe that followed the discovery of the region by European explorers.
Hybridization
The act or process of mating organisms of different varieties or species to create a hybrid species with specific qualities
genetically modified organism (GMO)
This is an organism whose genome has been altered by the techniques of genetic engineering so that its DNA contains one or more genes not normally found there.
double cropping
Harvesting twice a year from the same field.
Transhumance
A seasonal periodic movement of pastoralists and their livestock between highland and lowland pastures
capital-intensive agriculture
Form of agriculture that uses a variety of mechanical goods to produce large amounts of agricultural goods with very little human labor.
labor intensive agriculture
employs large numbers of people and requires relatively little capital, mechanical goods or machinery to produce agricultural goods.
Pesticides
Chemicals used on crops that kill pests or animals that may harm the crop.
Herbicides
A chemical that targets and destroys unwanted plant species that can disrupt the growth of crops
Fertilizer
a chemical or natural substance added to soil or land to increase its fertility
Feedlot
a plot of land on where livestock are fattened for market
double cropping
Harvesting twice a year from the same field.
capital-intensive agriculture
Form of agriculture that uses a variety of mechanical goods to produce large amounts of agricultural goods with very little human labor.
labor intensive agriculture
employs large numbers of people and requires relatively little capital, mechanical goods or machinery to produce agricultural goods.
Commercial Agriculture
Term used to describe large-scale farming and ranching operations that employ vast land bases, large mechanized equipment, factory-type labor forces, and the latest technology.
arid
extremely dry climate that does not support vegetation.
Wet Rice Dominant
type of agriculture that plants seeds on dry land in a nursery and then moving them to a deliberately flooded field to promote growth
Non Wet Rice dominant
type of agriculture that occurs in areas with little to no precipitation which forces certain crops to be cultivated like wheat, barley, millet, oats or corn that do not need flooded lands to grow.
intensive subsistence agriculture
When a farmer must expend a relatively large amount of effort with little help from technology; to produce the maximum feasible yield from a parcel of land for the family's consumption.
commodity chain
activities involved in the creation of a product: design, production or collection of raw materials, manufacturing and assembly, distribution and sale.
Monocropping
Growing the same crop on the same field year after year
Monoculture
the agricultural practice of producing or growing one single crop over a wide area.
Bid rent theory
explains how the price and demand on real estate changes as the distance from the Central Business District increases.
Commercial Agriculture
Term used to describe large-scale farming and ranching operations that employ vast land bases, large mechanized equipment, factory-type labor forces, and the latest technology.
Von Thunen Model
explains and predicts agricultural land use patterns in a theoretical state by varying transportation cost.
Desertification
the process by which fertile land becomes desert, typically as a result of drought, deforestation, or inappropriate agriculture.
soil salinization
when irrigation water evaporates and leaves an excessive amount of salt in the soil making it infertile.
Slash and Burn (farming technique)
A farming method involving the cutting of trees, then burning them to provide ash-enriched soil for the planting of crops
Aquaculture
The cultivation of seafood under controlled conditions
organic farming
the use of natural substances rather than chemical fertilizers, herbicides, and pesticides to enrich the soil and grow crops
fallow
farming technique where a field is plowed but not sowed to allow the soil time to acquire moisture and nutrients while eliminating weeds and pests before sowing with seeds.
perishable goods
Foods, such as meats, and milk that must be properly wrapped or kept cold until they can be stored in a refrigerator or freezer.
Slash and Burn (farming technique)
A farming method involving the cutting of trees, then burning them to provide ash-enriched soil for the planting of crops
Von Thunen Model
explains and predicts agricultural land use patterns in a theoretical state by varying transportation cost.
organic farming
the use of natural substances rather than chemical fertilizers, herbicides, and pesticides to enrich the soil and grow crops
State
An area organized into a political unit and ruled by an established government with control over its internal and foreign affairs, and being recognized by the international community.
Denomination
A division of a branch that unites a number of local congregations in a single legal and administrative body.
Branch (of a religion)
A large and fundamental division within a religion
Gnostic
Referring to the belief that salvation comes from secret knowledge available to only a select few.
Religion
the belief in and worship of a superhuman controlling power, especially a personal God or gods.