Personality Disorders
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
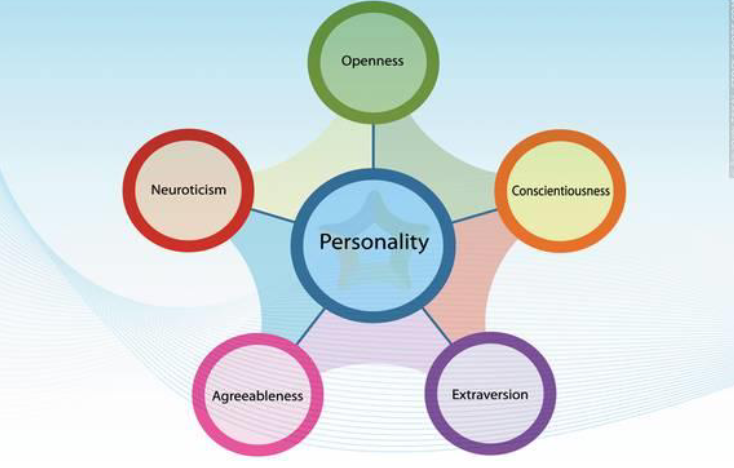
5 - Factor model
Openness: try new things and open to new experiences
Conscientiousness: more careful, attention to detail, managing time
Extraversion: Outgoing and put your selves in new experiences and people
Agreeable: Easy to get along with and problem solve; and go along with ideas
Neuroticism: Negative emotions and affect emotions. High in neuroticism higher risk for anxiety; more tense or moody
All not inherently good or bad
General Feature of Personality Disorder
Chronic interpersonal difficulties
Problems with one’s identity or sense of self
Inability to function adequately in society
Enduring pattern of behavior must be
Persuasive
Stable
Long duration
Cause clinical significant distress or impairment in functioning
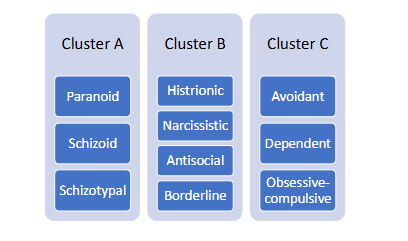
There are three Clusters
Cluster A: odd or eccentric behaviors
Cluster B : erratic behavior
CLuster C: Anxious or fearful behavior
Move away from clusters and more dimensional
10% will meet the criteria for personality disorder; most common is cluster c and least common is cluster b
PDs: Dimensions vs. Categories
All disorders are categories to some extent (based on DSM - V criteria, either have it or not)
But, there’s been a recent push for dimensional approaches to personality and PDs
Dimensional seems better for research purposes, but hard to decide cutoffs for treatment
Challenges in PD Research
Difficulties in diagnosing
how much time do you need for it to be a characteristic of their being or going through something at the moment
Difficulties in studying the causes
So why were categories kept as opposed to dimensions?
Possible Causes
Biological
Temperament
Genetics
Psychological
Learning -based habits
Maladaptive cognitive styles
Social
Parents
Abuse
Society
Treatment Options
PDs are hard to treat
Not many well-researched, very effective txs
Treatment Options
PDs are hard to treat
Not many well-researched, very effective txs
Cluster A
Paranoid
Schizoid
Schizotypal
Common features:
People often seem odd or eccentric
Unusual behavior
Paranoid PD
pervasive distrust of nearly all others
fear of malevolent malevolent in others
reads hidden meanings into interactions
Persistently bears grudges
quick to counterattack over little things
Paranoid PD: Causes
Psychodynamic:
parent’s persistnet, unreasonable demands create a hostile environment
beleive others can’t be trusted —> feel angry
Cognitive:
hold broad assumptions: “people will hurt you if given the chance”
Biological: genes; twins were most likely to share paranoia
Psychosocial
Drugs
Trauma
Abuse
Paranoid PD: Treatments
psychodynamic:
help client develop satisfying relationships
help clients “re-establish self- cohesion”
Cognitive-Behavioral:
practice anxiety-reduction skills
improve interpersonal skills
reappraise others’ motives and behaviors
Schizoid PD
Pervasive pattern of detachment from social relationships
Restricted range of emotional expressions
Uninterested in others (freinds, romantic partners)
Indifferent to praise OR criticism
Schizoid PD: Causes
Psychodynamic:
unaccepting, abusive parents —> unsatisfied need for human contact
cope with abuse by avoiding all contact
Cognitive: lack social, cognitive, or emotional depth to respond appropriately to others even if they are just intelligent
Biological
Heritablility
Impaired affiliative system
Not the type to participate in research
Schizoid PD: Treatments
Cognitive-Behavioral:
emotion education
recording pleasurable experiences
social skill practive
group therapy
Schizotypal PD
discomfort with close relationships
excessive social anxiety does not diminish with increased familiarity associated with paranoid fears, not negative self-judgement
Odd patterns of thinking
ideas, not delusions, of reference
Eccentric behaviors
ex. wearing an odd assortment of clothes
Sometimes perceived to be a prodromal form of schizophrenia
Schizotypal PD: Causes
Biological:
attention and memory issues contribute
ex: some are similar to those seen in schizophrenia
Increased dopamine activity
enlarged brain ventricles
loss of grey matter
Sociocultural:
family conflicts may contribute
Early trauma
Schizotypal PD: Treatments
Cognitive-Behavioral:
help clients evaluate unusual thoughts
help clients summarize instead of digressing in conversations
social skills training
increase positive social contacts
Biological:
antipsychotic drugs in low doses help with unusual thoughts
Schiziodtypical want to make relationship while schiziod did not
ideas of reference: take random occurrence and give personal meanning
and delusions or reference: radio that message was meant for specifically you