Comprehensive Volcanoes and Minerals: Types, Hazards, and Formation
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
What geological feature results from oceanic lithospheric melting due to a hotspot?
The Hawaiian islands.
What happens if a hotspot is located underneath a continent?
It can lead to volcanic activity and the formation of volcanic features on the continent.
What is the Chicxulub Crater and where is it located?
A crater in Yucatan, Mexico, formed by a meteor impact.
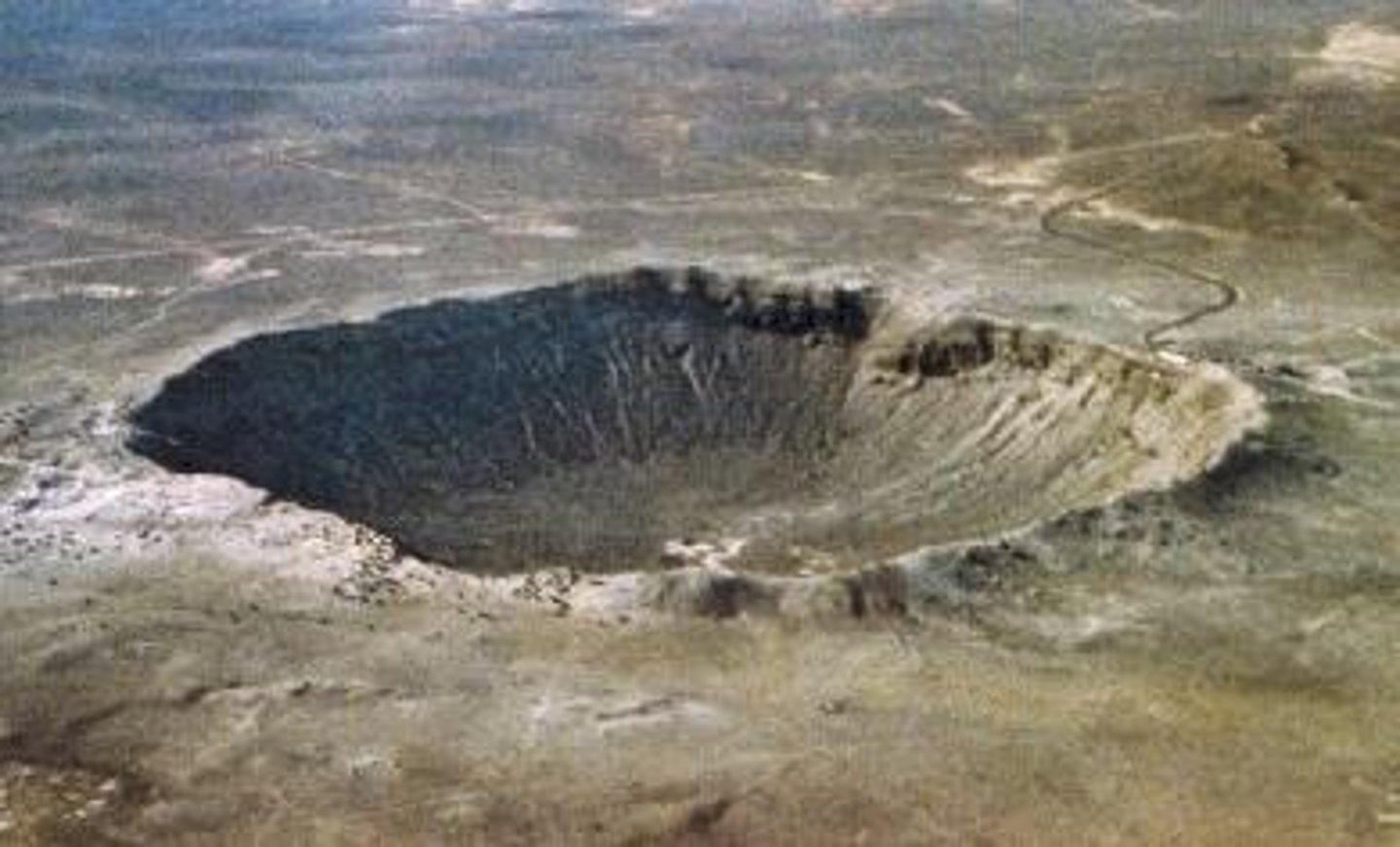

What is the Meteor (Barringer) Crater and where is it located?
A crater in Arizona, formed by a meteor impact.
How do seismic waves travel through different types of rock?
All waves travel faster through harder rock; S-waves cannot travel through liquids.
What are some key components of earthquake mitigation?
Research and hazard maps, earthquake sensors with alert systems, building regulations, preparedness, and education.
What catastrophic event occurred in 79 A.D. at Mt. Vesuvius?
A massive eruption that buried the cities of Pompeii and Herculaneum.
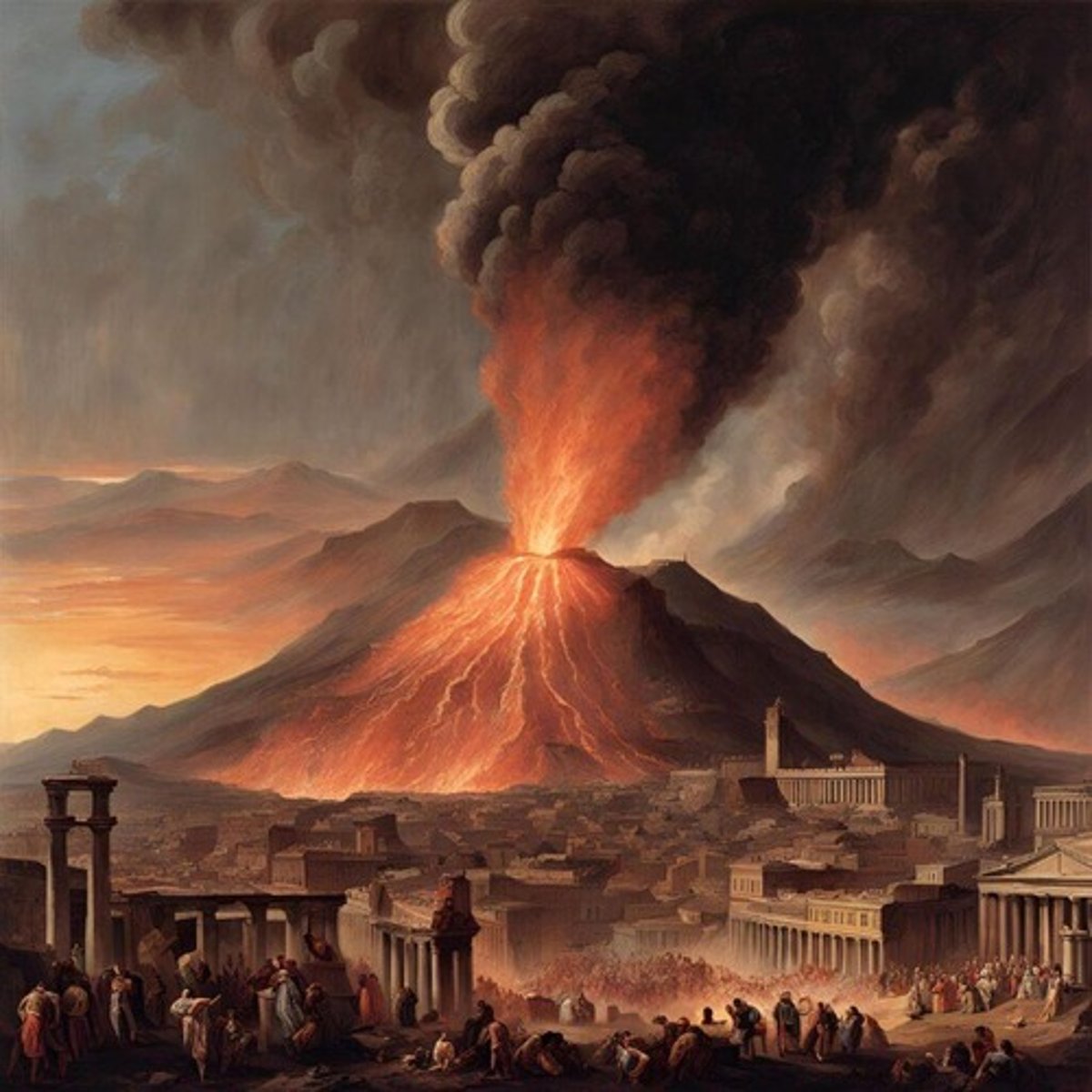

What was the height of the eruption cloud during the Mt. Vesuvius eruption?
Over 32 km.
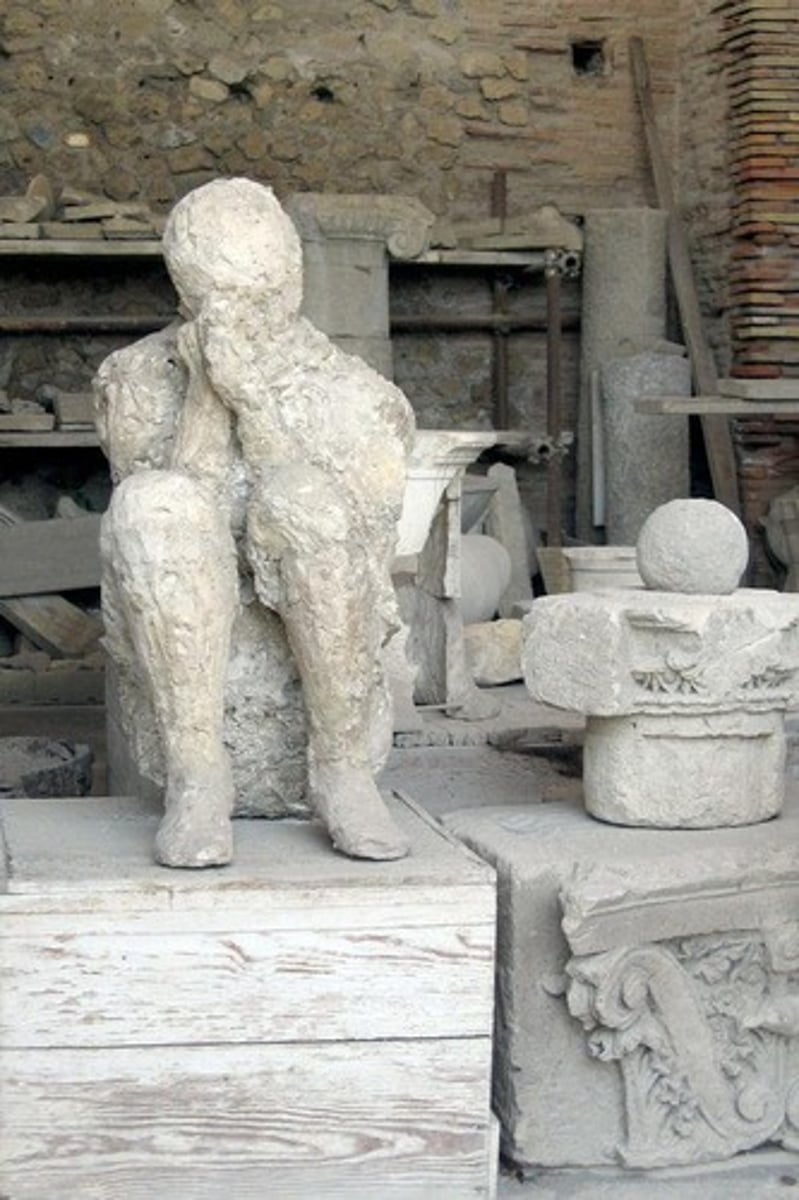
What archaeological discovery was made in Pompeii in 1863?
An Italian archaeologist discovered voids in volcanic ash containing human remains and filled them with plaster.

What was the population of Naples around the time of the Mt. Vesuvius eruption?
Approximately 1 million people.
What was significant about the eruption of Mt. Tambora in 1815?
It was the largest eruption in recorded history, heard 2,600 kilometers away.
What effects did the Mt. Tambora eruption have on the atmosphere?
It released sulfurous gas that mixed with water vapor, creating a haze that blocked sunlight.
What was the estimated death toll from the Mt. Tambora eruption?
Between 71,000 and 90,000 people, many from starvation and disease.
What was the global impact of the Mt. Tambora eruption in terms of climate?
It caused the 'Year without a summer' and led to the world's worst famine in the 19th century.
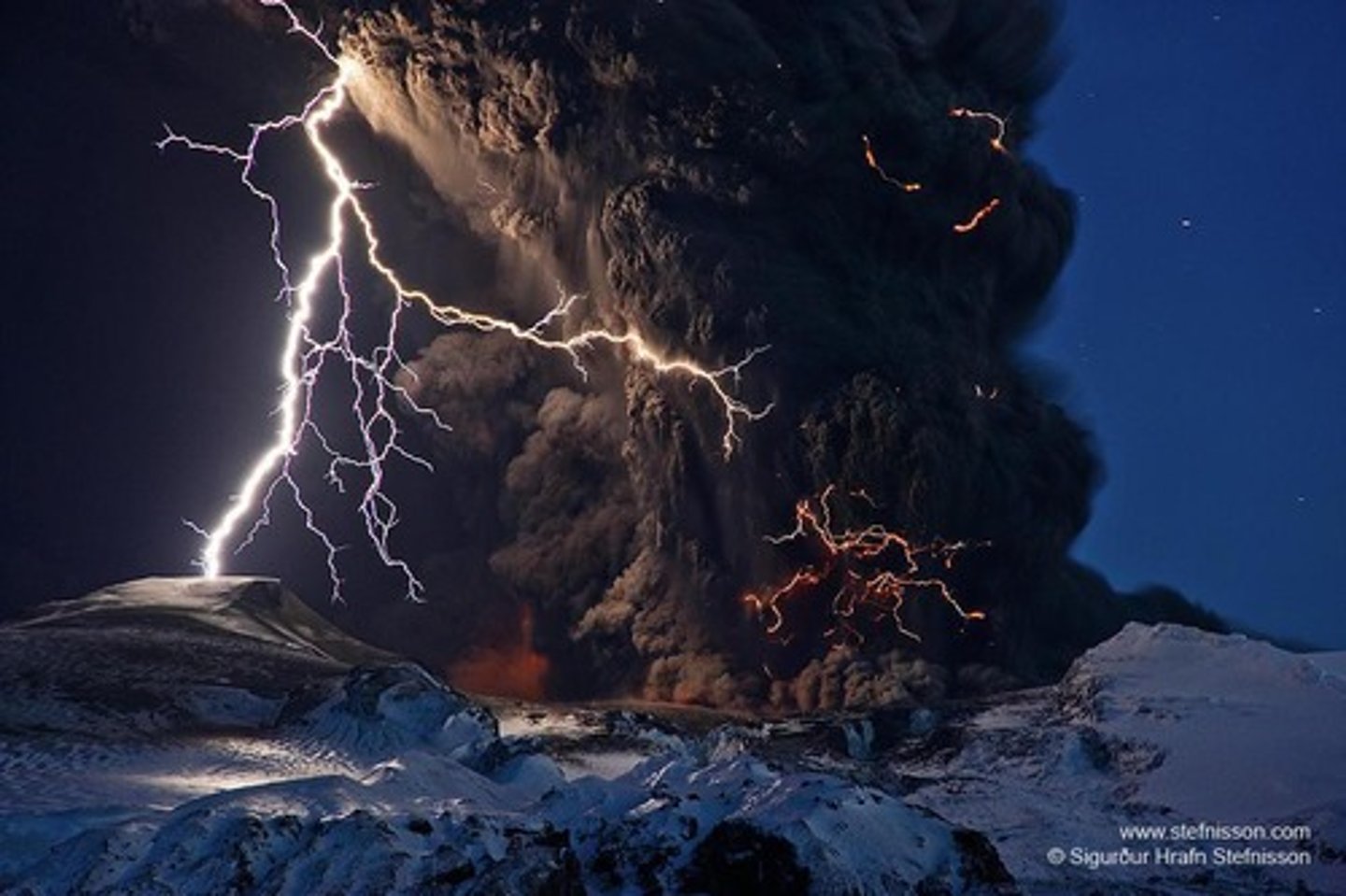

What was the explosive force of the Krakatoa eruption in 1883?
Equivalent to a 200-megatonne bomb.
How many people died as a result of the Krakatoa eruption?
More than 36,000 people.
What was the impact of the Eyjafjallajökull eruption in Iceland in 2010 on air travel?
It caused the shutdown of air travel over Europe for six days, canceling 95,000 flights.
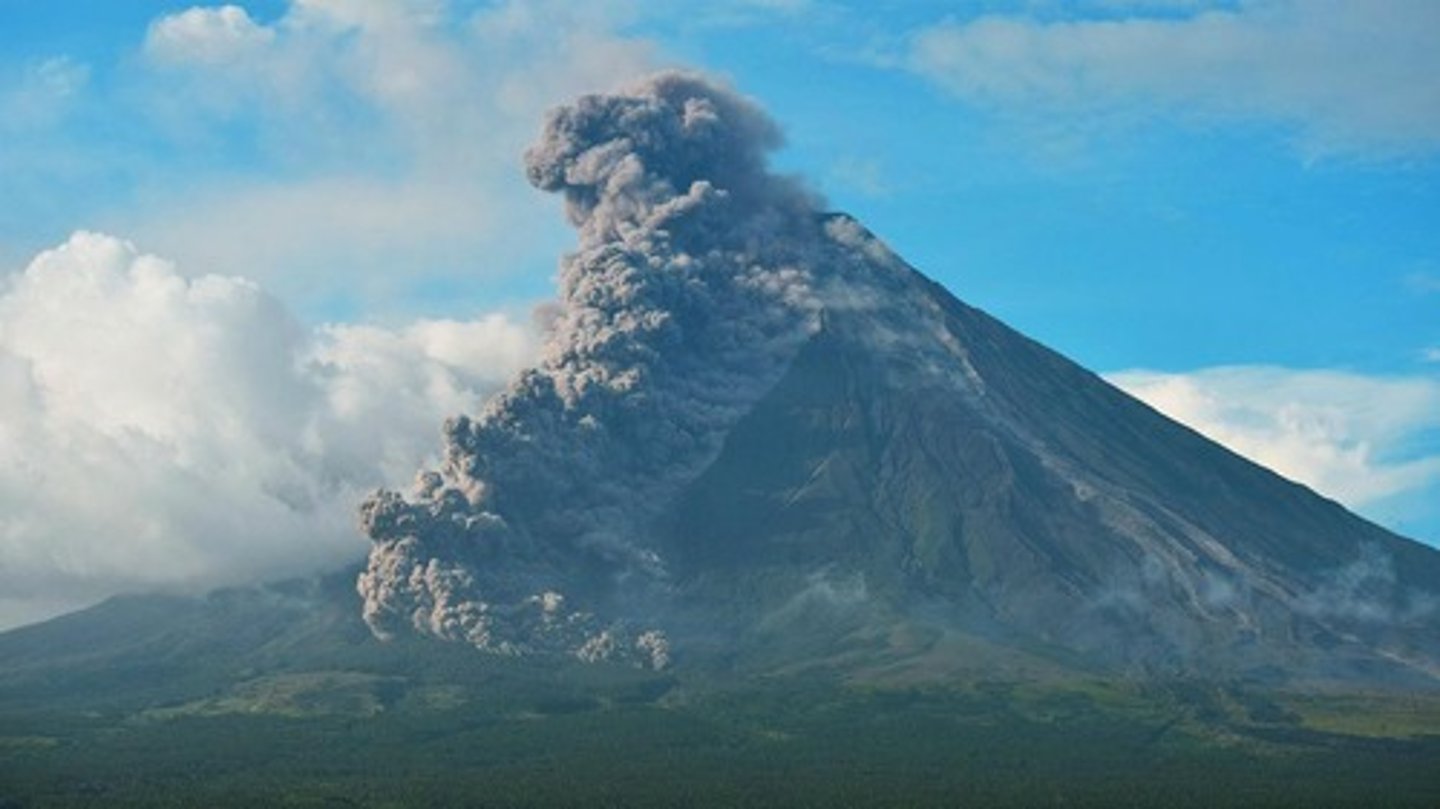

What was the height of the ash plume produced by the Eyjafjallajökull eruption?
Up to 10 km high.
What geological activity occurred during the 2010 Eyjafjallajökull eruption?
Lava flows melted snow, causing explosive activity and significant ash production.
What were the consequences of the Eyjafjallajökull eruption on infrastructure?
It destroyed roads and caused evacuations due to glacial meltwater.
What was the estimated volume of volcanic ash ejected during the 2010 Eyjafjallajökull eruption?
Approximately 250 million cubic meters (250,000,000 m³).
What was the impact of the 2010 Eyjafjallajökull eruption on air travel in Europe?
Air travel was shut down for six days, resulting in 95,000 cancelled flights.
What were the economic losses incurred by airlines due to the 2010 Eyjafjallajökull eruption?
$2 billion lost by airlines.
How many people were evacuated during the 2010 Eyjafjallajökull eruption?
800 people were evacuated, and some farms were abandoned due to poisonous ash.
What is a volcano?
A vent or opening from which lava, solid rock debris, or gases are erupted.
What are the two types of climate forcing agents?
External forcing (changes outside the climate system) and internal forcing (changes within the climate system).
Name two examples of external climate forcing.
Changes in solar radiation and changes in Earth's orbit.
What is magma?
A mixture of molten rock, suspended minerals, and dissolved gases that forms in the crust and mantle.
What is the difference between magma and lava?
Magma is underground, while lava is magma that reaches the surface.
What are the main factors controlling magma behavior?
Magma viscosity, which is influenced by composition and temperature.
What type of eruptions are associated with basaltic magma?
Effusive eruptions, characterized by low viscosity and low gas content.
What type of eruptions are associated with granitic (rhyolitic or andesitic) magma?
Explosive eruptions, characterized by high viscosity and high gas content.
What is decompression melting?
Melting that occurs when pressure decreases, such as at a spreading ridge.
What is flux melting?
Melting that occurs when water or other volatiles lower the melting point of rocks.
What is the Earth's geothermal gradient?
Approximately 25°C per kilometer into the crust.
What is the significance of volcanic eruptions in Earth System Science?
They reveal inner Earth structure, influence atmospheric composition, and redistribute energy.
What is the role of volcanic ash in climate change?
Volcanic ash can change the radiative balance of the atmosphere, affecting climate.
What are the types of volcanoes?
Shield, strato (composite), fissure, cone, caldera, and submarine volcanoes.
What are the three ways that rocks can melt within the Earth?
Decompression melting, thermal (increase heat) melting, and flux melting.
What is the most important property controlling magma behavior?
Magma viscosity.
What volcanic event is known for its climate change impact?
The 1815 eruption of Mt. Tambora in Indonesia.
What happens to magnetic minerals in volcanic rock when heated below their Currie point?
They will realign to current dipole positions.
What is the effect of volcanic eruptions on human society?
They can disrupt travel, commerce, and tourism, and pose hazards to health and safety.
What is the relationship between silica content and magma viscosity?
Higher silica content generally leads to higher viscosity.
What is the impact of glacial floods caused by volcanic eruptions?
They can cause damage to roads and infrastructure.
What are the two main types of volcanic eruptions?
Explosive and effusive eruptions.
What is a primary volcanic hazard?
Hazards that occur directly from the eruption, such as lava flows, pyroclastic flows, tephra falls, volcanic gases, and volcanic bombs.
What is a secondary volcanic hazard?
Hazards triggered by volcanic activity, including lahars, landslides, flooding, and tsunamis.
What are lava flows?
Hot molten rock that destroys everything in their path but usually moves slowly enough for people to escape.
What are pyroclastic flows?
Fast-moving, extremely hot clouds of gas, ash, and volcanic rock fragments that are the most deadly volcanic hazard.
What are tephra falls?
Ash, pumice, and rock fragments ejected into the atmosphere that settle back to the ground, affecting air quality and infrastructure.
What are volcanic gases?
Gases released during eruptions that can suffocate organisms, damage lungs, and contribute to acid rain.
What are lahars?
Fast-moving slurries of water, ash, and debris flowing down valleys, often triggered by melting snow or heavy rain.
What is the Volcanic Explosivity Index (VEI)?
A logarithmic scale from 0 to 8 used to measure and compare the size of explosive volcanic eruptions.
What is volcanic ash?
A mixture of rock, mineral, and glass particles expelled from a volcano during an eruption, which can cause health issues if inhaled.
What is the difference between explosive and effusive eruptions?
Explosive eruptions are characterized by violent outbursts, while effusive eruptions involve the steady flow of lava.
What type of magma is associated with explosive eruptions?
Andesitic to rhyolitic magma.
What type of magma is typically associated with effusive eruptions?
Basaltic magma.
What is a nuée ardente?
A highly destructive, fast-moving, incandescent mass of gas-enveloped particles associated with certain volcanic eruptions.
What geological feature is formed by the subduction of the Juan de Fuca Plate?
The Cascade Range of volcanoes.
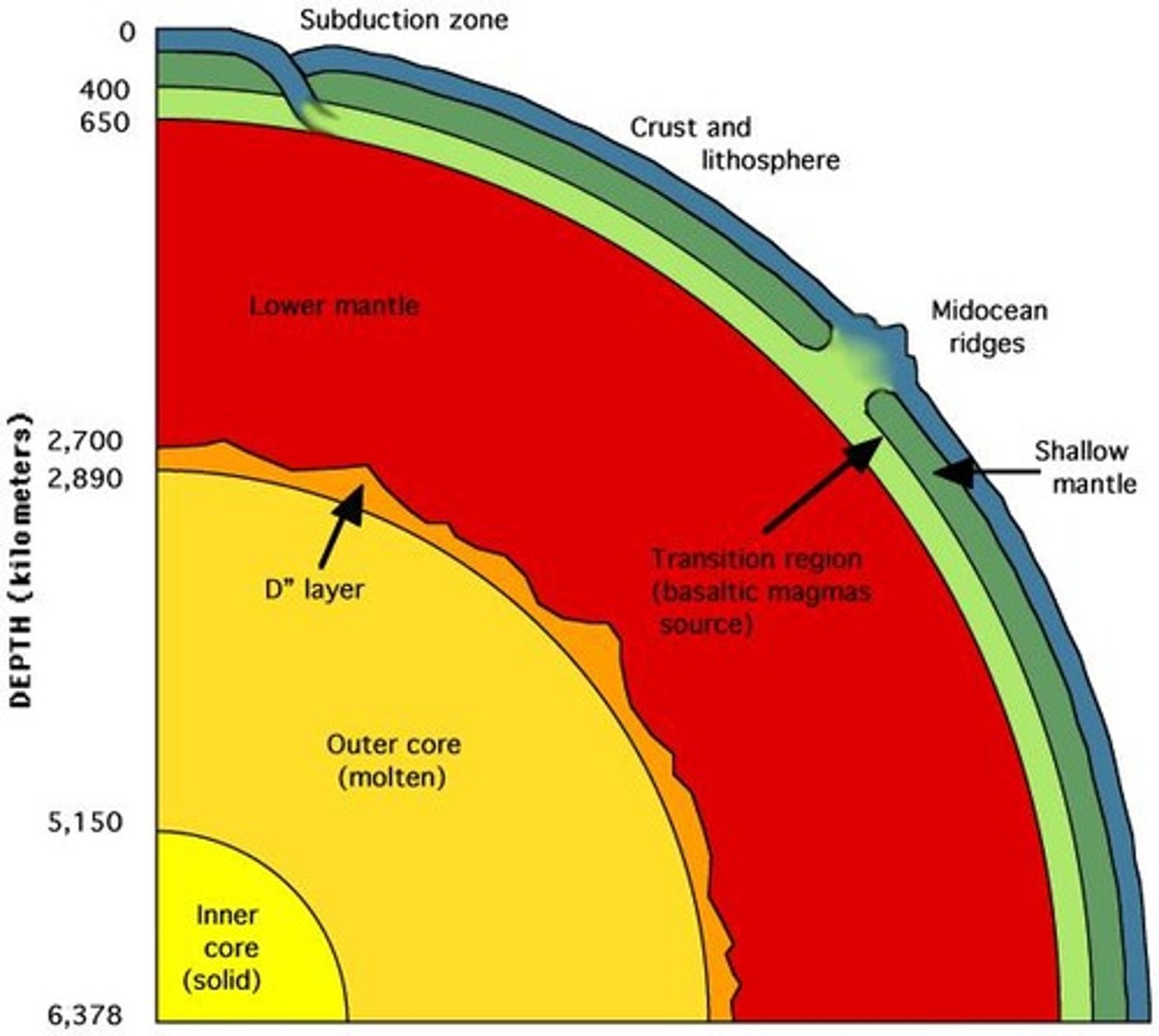
What can trigger a tsunami related to volcanic activity?
Volcanic explosions, landslides, or caldera collapses near water bodies.
What are volcanic bombs?
Larger fragments of rock and lava thrown during explosive eruptions that can cause impact damage.
What are the effects of tephra falls on the environment?
They can affect air quality, damage buildings, harm crops, and disrupt machinery.
What is a volcanic mudflow?
A lahar, which is a fast-moving slurry of water, ash, and debris.
What is the significance of the 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens?
It was a notable explosive eruption that demonstrated the dangers of volcanic activity.
What is the impact of volcanic gases on health?
They can suffocate living organisms and damage respiratory systems.
What is the role of water released from a subducting slab in volcanism?
It causes the overlying mantle to partially melt, forming magma.
What causes magma to form in the Cascade Range of volcanoes?
Water released from the subducting slab causes the overlying mantle to partially melt.
Why is Mount Rainier considered the most threatening volcano in the Cascades?
Due to its elevation (4,392 m), relief, icecap, glacier-fed valleys, and proximity to suburbs of Seattle-Tacoma.
What volcanic hazards could occur during an eruption of Mount Rainier?
Volcanic ash, lava flows, and pyroclastic flows.
What is the greatest risk associated with Mount Rainier?
The potential for generating huge lahars triggered by sector collapse or magma-water-ice interaction.
What are the primary volcanic hazards directly from an eruption?
Lava flows, pyroclastic flows, tephra falls, volcanic gases, and volcanic bombs.
What gases are released during volcanic eruptions?
Gases like H2O, CO₂, SO₂, H₂S, and HF that can suffocate organisms and contribute to acid rain.
What are secondary volcanic hazards?
Hazards triggered by volcanic activity, including lahars, landslides, flooding, and tsunamis.
What is a maar?
A broad, low-relief volcanic crater caused by a phreatomagmatic eruption that fills with water to form a crater lake.
What happened at Lake Nyos in Cameroon in 1986?
A landslide caused the lake to degas, suffocating 1,700 people while they slept.
What is the significance of the Yellowstone volcano?
It has a volcanic explosivity index (VEI) of 8 and has produced massive eruptions over the last 2.1 million years.
What geological process created the Yellowstone volcano?
The North American Plate drifted over a hot spot, generating basaltic magma that melted surrounding granitic rocks.
What are the five characteristics that define a mineral?
Naturally occurring, inorganic, solid, defined chemical composition, and orderly internal structure.
What is the difference between natural and lab-grown minerals?
Lab-grown minerals are not considered true minerals as they are not formed by natural processes.
What is the melting point of granitic rocks compared to basaltic magma?
Granitic rocks melt at about 650 °C, while basaltic magma can reach temperatures of ~1600 °C.
What is the primary use of lab-grown minerals?
They are predominantly used in the jewelry industry and in high-end lasers.
What defines organic compounds?
Organic compounds are carbon-based and typically involve covalent bonds between carbon and other atoms such as hydrogen, oxygen, or nitrogen.
What are examples of organic compounds?
Examples include proteins, sugars, and oils.
What distinguishes inorganic compounds?
Inorganic compounds include most substances formed by geological processes and can contain carbon but are considered inorganic if formed through non-biological processes.
How should 'inorganic' be understood in the context of minerals?
Inorganic is best thought of as 'non-biogenic,' excluding carbon crystals and compounds produced by organisms.
What is a solid solution in minerals?
A solid solution is a continuous mixture between two or more end-member compositions, meaning many minerals do not have a single fixed formula.
What is the chemical formula for plagioclase feldspar?
Its formula is written as (Na,Ca)(Al,Si)₄O₈, varying between sodium-rich Albite and calcium-rich Anorthite.
What is the formula for olivine?
Olivine is written as (Mg,Fe)₂SiO₄, varying between magnesium-rich Forsterite and iron-rich Fayalite.
What do parentheses in mineral formulas indicate?
Parentheses indicate elements that can substitute for one another in the crystal lattice, depending on conditions like temperature and pressure.
Which of the following is a mineral: ice, sugar, or petroleum?
Ice is a mineral; sugar and petroleum are not.
What are the eight most abundant elements in Earth's continental crust?
Oxygen, Silicon, Aluminum, Iron, Magnesium, Calcium, Sodium, and Potassium.
What is the basic building block of silicate minerals?
The silica tetrahedron (SiO₄) is the basic building block of silicate minerals.
What percentage of Earth's crust is made up of silicate minerals?
Silicate minerals make up approximately 90% of Earth's crust.
What are the primary components of a volcano?
A volcano consists of a vent, magma chamber, and erupted material (lava/ash).
What is the difference between craters and calderas?
Craters are small depressions at the vent, while calderas are large collapse features after the magma chamber empties.
What drives volcanic eruptions?
Volatiles, such as dissolved gases, drive eruptions as gas bubbles expand when pressure drops.
How does magma viscosity affect eruption style?
High silica and low temperature result in high viscosity and explosive eruptions; low silica and high temperature lead to low viscosity and effusive eruptions.
What are the primary hazards associated with volcanoes?
Primary hazards include lava flows, pyroclastic flows, ash fall, and gas emissions.
What is a lahar?
A lahar is a mudflow triggered by melting snow/ice or heavy rain on volcanic slopes.