Standing Waves (Part-I)
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Standing Wave
A wave pattern formed by the superposition of two identical waves traveling in opposite directions
Resulting in fixed nodes and antinodes with no net propagation of the wave pattern.
Resonance
A phenomenon in which a system oscillates with large amplitude when driven at a frequency equal to one of its natural frequencies.
Node
A fixed point in a standing wave where the displacement is always zero for all times.
Antinode
A point in a standing wave where the displacement oscillates with maximum amplitude.
Constructive Interference
Interference that occurs when waves are in phase, causing their amplitudes to add and produce a larger resultant amplitude.
Destructive Interference
Interference that occurs when waves are out of phase by π radians (180°), causing their amplitudes to cancel.
y(x, t) = 2Asin(kx)cos(ωt)
Standing Wave Equation
This equation describes a standing wave formed from two identical traveling waves moving in opposite directions.
In-Phase Condition (Standing Waves)
The condition when the two waves are in phase
t = n(T/2)
Value of the t, in the In-Phase Condition of the Standing Waves
Out-of-Phase Condition (Standing Waves)
The condition when the two waves are 180° out of phase
t = ((2n + 1)T)/4
Value of the t, in the Out-of-Phase Condition of the Standing Waves
Node Positions
Locations where
sin(kx) = 0
where x = n(λ/2)
n = 1, 2, 3, ….
Antinode Positions
Locations where
sin(kx) = ±1
where x = n(λ/4)
n = 1, 3, 5, ….
μ = dm/dx
Mathematical representation of Linear Mass Density
Linear Mass Density
Mass per unit length of a string
μ
Symbol that represents the Linear Mass Density
F_T
Symbol that Represents the Tension in the String
v = ((F_T)/μ)^1/2
Mathematical Representation of the Wave Speed on a String
t = 0T
(1)
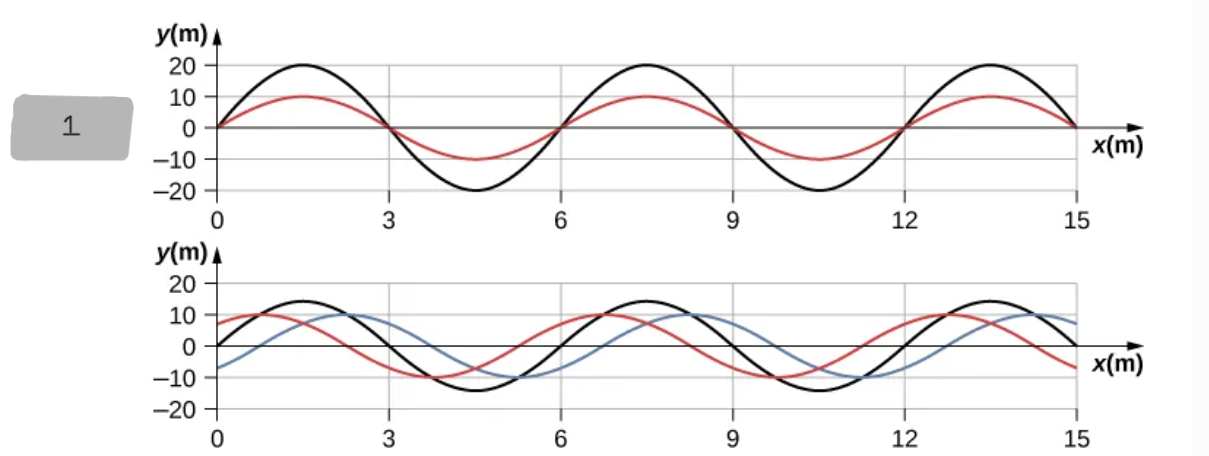
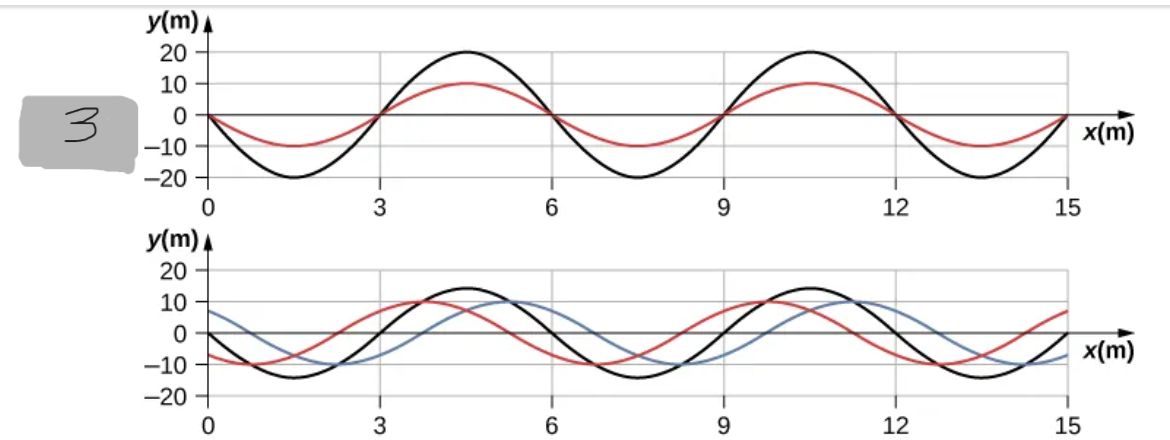
t = (1/4)T
(2)
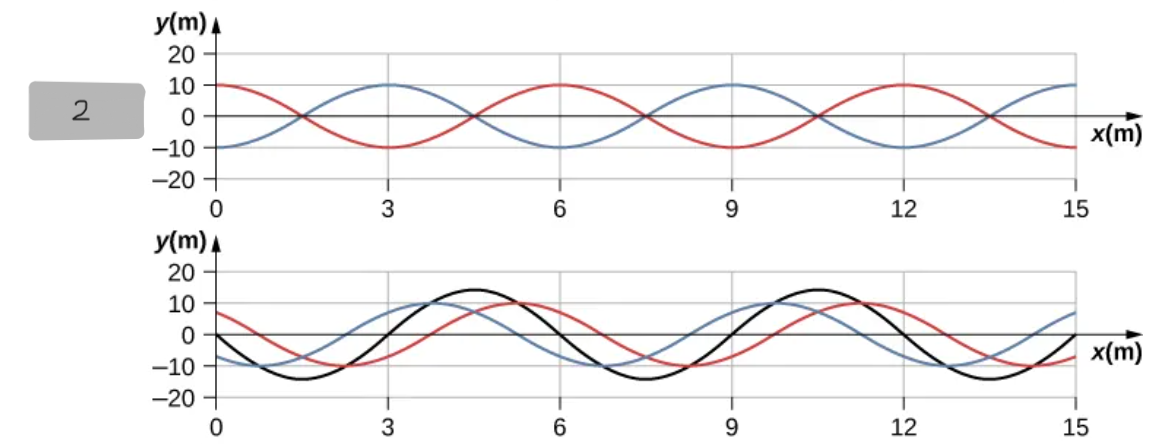
t = (1/2)T
(3)
t = (3/4)T
(4)
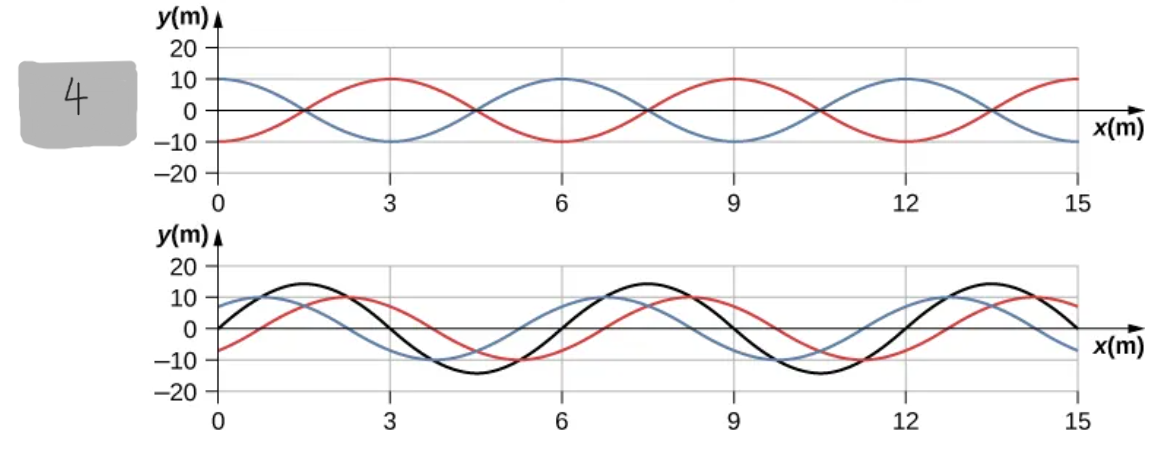
String Vibrator
(i)
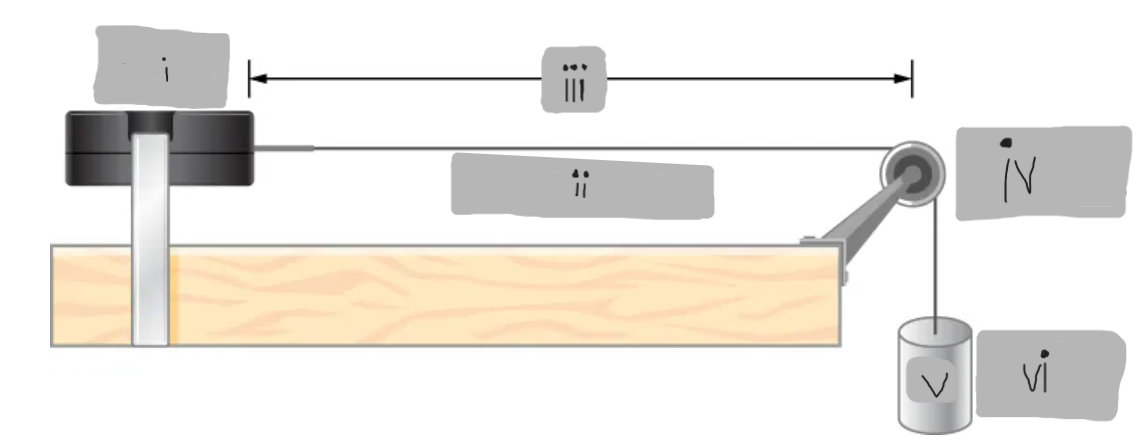
μ = dm/dx = constant
(ii)
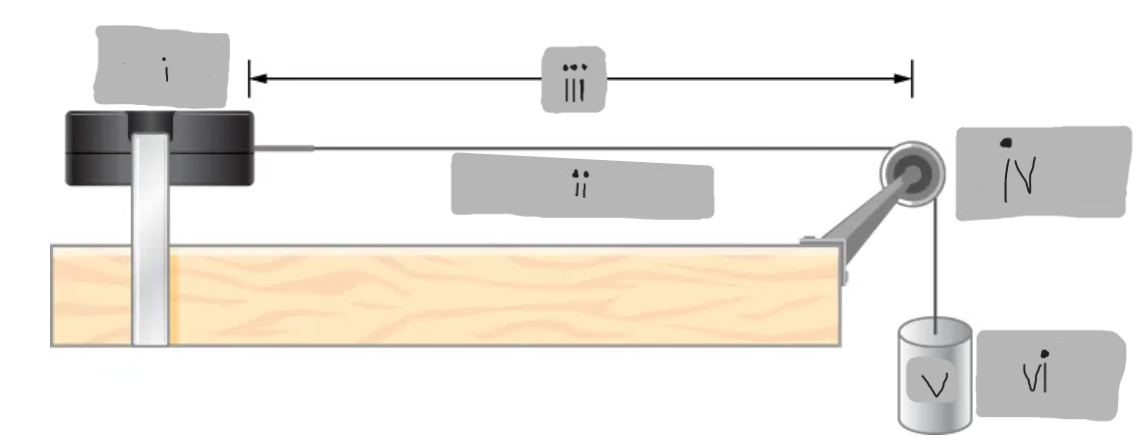
L
(iii)
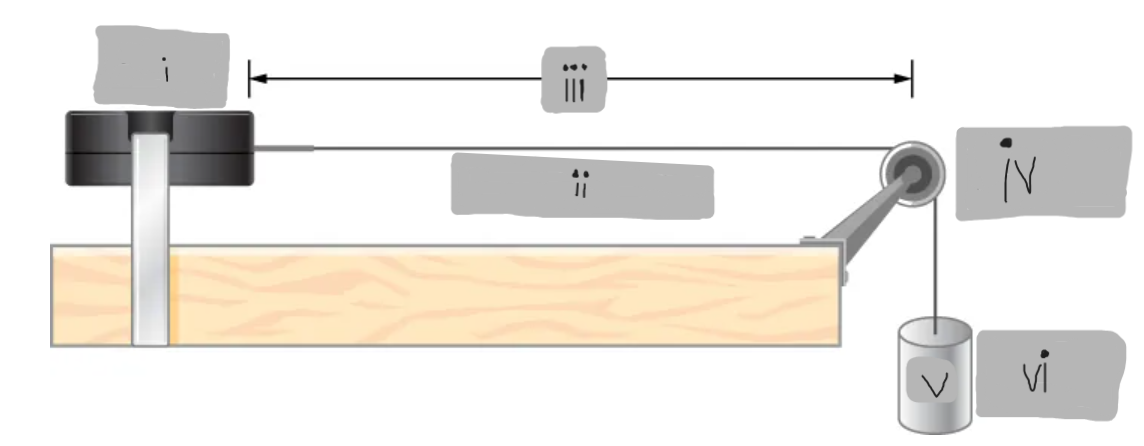
Frictionless Pulley
(iv)
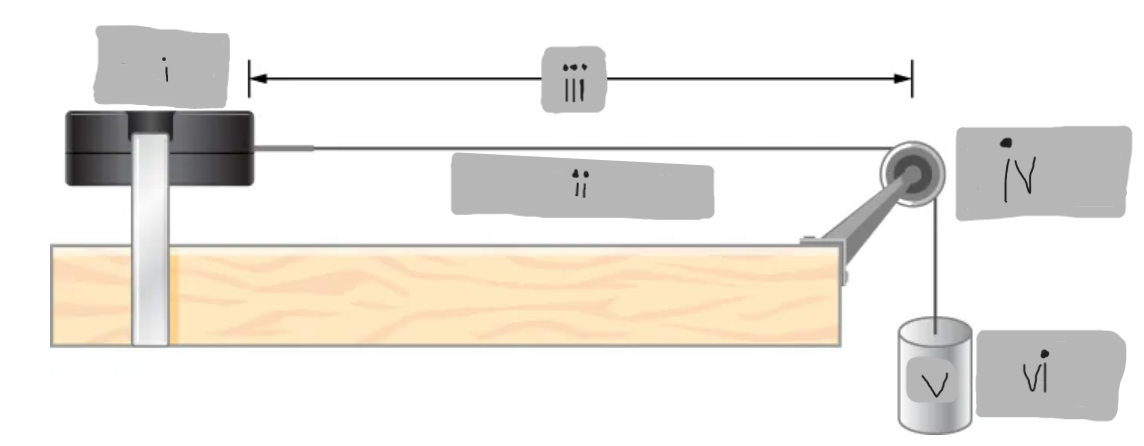
m
(v)
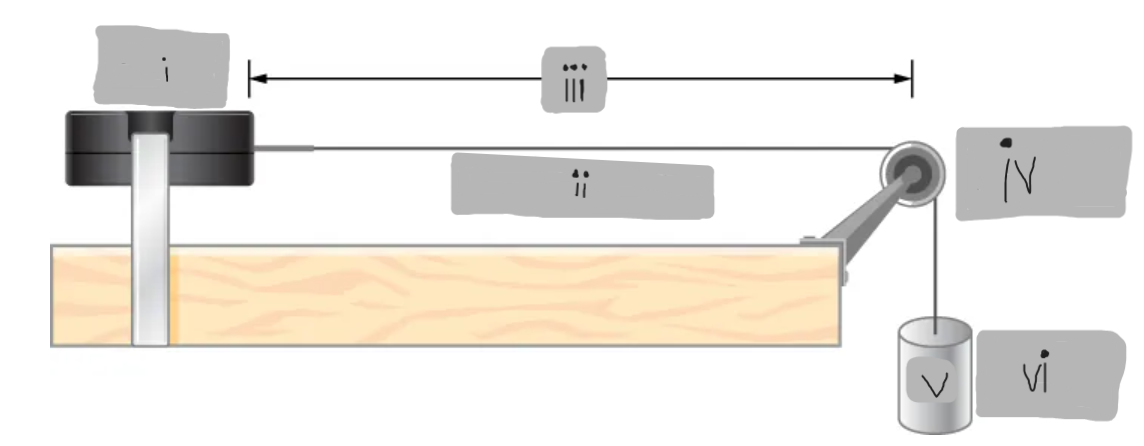
Hanging Mass
(vi)
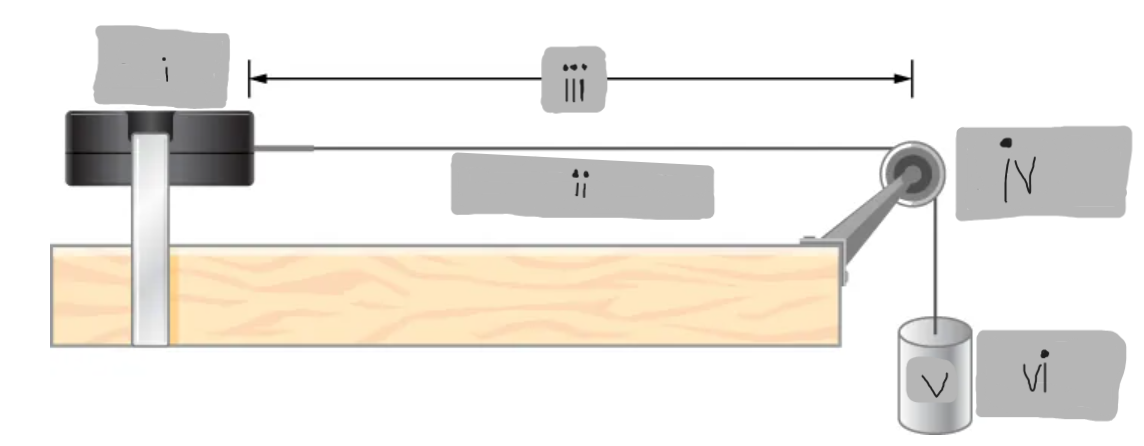
Boundary Conditions (Fixed Ends)
Conditions where both ends of a string are fixed, forcing nodes to exist at both ends.
Fundamental Mode (First Harmonic)
The lowest-frequency standing wave mode, where half a wavelength fits in the string length
λ1 = 2L
Mathematical Representation of the Fundamental Mode
f1 = v/(2L)
Fundamental Frequency: The frequency corresponding to the first harmonic.
Harmonic Number (Mode Number)
An integer n that labels standing wave patterns, with higher values corresponding to higher frequencies and more nodes.
f_n = (nv)/(2L)
Mathematical Representation of the nth Harmonic Frequency (String)
λ_n = (2L)/n
Mathematical Representation of nth Harmonic Wavelength (String)