Water Pollution W6
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Non-marine + marine sewage consequences, biomonitoring
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Types of coastal pollution
microorganisms
oxygen-depleting substances
metals (boats, industrial sources)
hydrocarbons
nutrients
thermal
alien invasive species
litter + rubbish
noise
light
point source nutrient pollution
domestic sewage effluent
industrial discharges incl. detergents
shipping discharges of sewage + wastewater
fish farms (faecal waste from fish + uneaten fish feed)
diffuse source nutrient pollution
agricultural runoff
natural background inputs (rocks weathering, soil leaching, decaying OM)
atmospheric nitrogen oxides
Algal Blooms (HABs)
increased nutrient concentrations
blooms of phytoplankton + other algae produce oxygen in surface waters, then phytoplankton die + sink to seabed
decomposition of phytoplankton uses up more oxygen
anoxia in bottom layers
—> makes shellfish unfit for human consumption
—> cause losses in stock through anoxia/asphyxiation
Antarctica
coliform distributions around research station
sources: local vertebrate populations, human sewage
highlighted persistence of sewage pollution + dispersal motoring needs around sewage outflow
E.coli in Devon (2000)
4 cases of poisoning in resort on same day
girl of 8 yrs died
caused by CSO discharges 2km from beach
benefits of recycling sludge to land
fertiliser - agronomically useful quantities of nutrients
increases soil quality
cheaper than mineral fertiliser
most environmentally sustainable method of disposal
drawbacks of recycling sludge to land
unsure how much microplastics could be transferred to soil
diffuse nutrient pollution (fertiliser can lead to excess phosphorus)
Combined Sewer Overflows (CSO)
Transport domestic, industrial, + surface runoff wastewater.
Happens when heavy, prolonged rainfall causes exceedence of system capacity + act as emergency relief system to prevent flooding + backlogs.
CSO regulations
discharge consents required
consent regards excess rainfall/snowmelt
operation + performance monitored as part of EIP
sewage fungus
mass of filamentous bacteria growing in response to organic inputs (sewage), causes oxygen concentrations in water to drop rapidly
General Quality Assessment (GQA)
Old method of measuring water quality by looking at chemistry, biology, and nutrients. Samples of water taken on monthly basis at intervals 5-8km.
chemical: DO, BOD, ammonia
biological: macro invertebrates
nutrient: nitrates, phosphates, Nitrate Vulnerable Zone (NVZ)
Metals properties
good conductors of heat + electricity
malleable + ductile
16 metals occur in nature in elemental form e.g., gold, silver
non-biodegradable
slightly elevated metals in natural waters cause:
histological or morphological changes in tissue
changes in physiology
changes in circulation
changes in biochemistry
changes in behaviour
changes in reproduction
tradition water quality indicators
dissolved oxygen
pH
temperature
salinity
nutrients e.g., nitrogen, phosphorous
toxicants, insecticides, herbicides, + metals
habitat indicators
riparian :
width,
continuity
extent of shading
species composition
in stream:
measures extent of scouring + bank erosion
presence of woody debris e,g., fallen trees
biological indicators
freshwater
macro invertebrates
benthic algae growth
fish diversity
estuaries
less developed
chlorophyll
coastal embayments
seagrass condition
condition of fringing coral reefs
indicator species
May delineate an ecoregion or indicate an env condition.
can be among most sensitive species in a region + act as early warning.
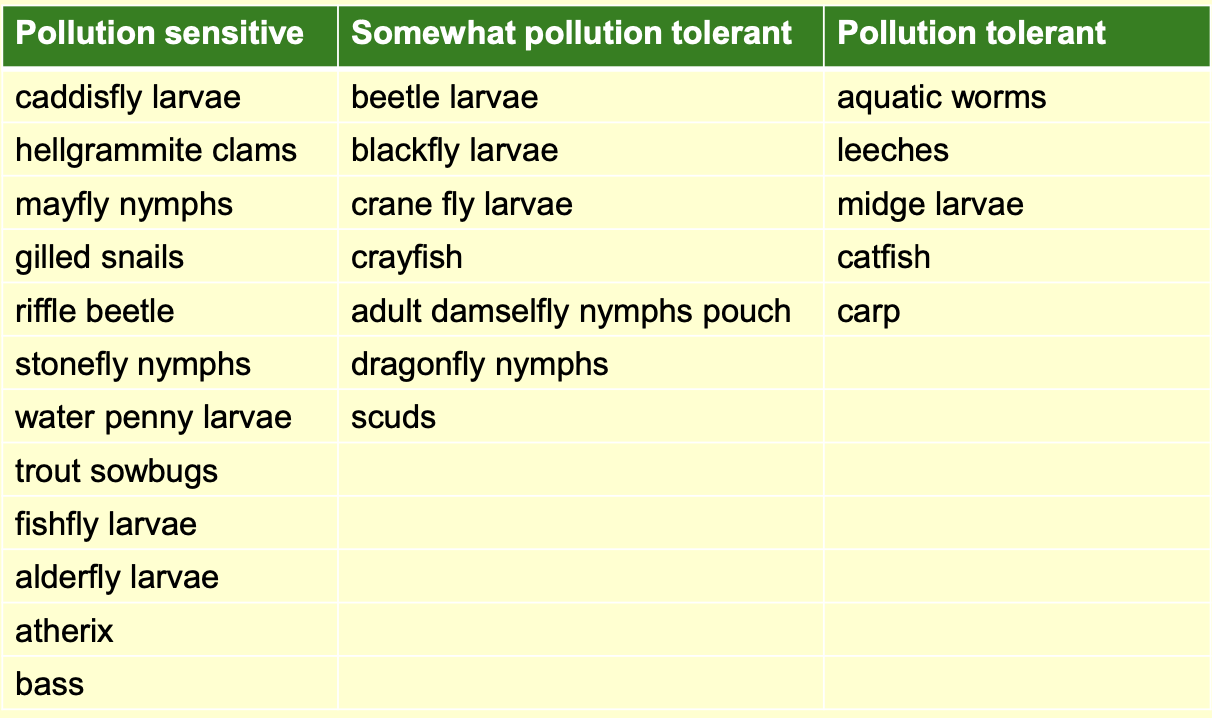
Biomonitors
contain relevant info on the quantitative aspects of the quality of an environment
active bio monitoring
when biomonitors bred in labs are exposed in a standardised form in the field for a define period of time
passive bio monitoring
when organisms already occurring naturally in ecosystem are examined for their actions
advantages of bio monitoring
indicator organisms act as sensitive early warning system
provide direct method of studying effects of pollutants in living organisms
possible to study relationship between concentration of pollutants + effects when both measured at same rate
can determine species and temporal trends in occurrence and intensity of effects of several pollutants in natural env
doesn’t depend on electricity for operation
no expensive equipment
can be done in remote areas
disadvantages of bio monitoring
not useful for assessing exposure to substances that exhibit toxic effects at site of first contact where substances are poorly absorbed
only useful where relationship between waterborne concentrations, internal does and adverse effects is known for specific chemicals
major limitation is lack of detailed info on fate of industrial chemicals
most toxicokinetic data available of animal studies extrapolated to humans
indicator organisms spread over a wide geographical area can cause data interpretation complexities + problems