Archaeological demography and paleodemography
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Archaeological demography
An interdisciplinary subject focused on understanding past populations through the archaeological record/material culture (Chamberlain, 2009)
The Juvenility Index
A method of understanding fertility rates in the deep past by taking the number of older child remains and comparing it to the number of adult remains, with infant and young child remains removed to prevent bias (Chamberlain, 2009)
Isonymy
The sharing of surnames, it is a simple way of measuring inbreeding based on married pairs who share a surname, and is useful when marriage records are available (Madrigal, 2002)
The formula for calculating population change
Starting population + (births – deaths) + (immigrants – emigrants)
The Wahlund effect
The presence of a subdivision(s) within a population, resulting from an isolation mechanism such as preferential mating among families (Madrigal, 2002)
Population
A population with shared and distinct characteristics like being relatively endogamous, reproduce with each other, share territory, shape its members lives, and share social/cultural heritage), is not the same as group
What does demography study?
It studies groups as aggregates, group structure and composition through things like birth cohorts, age and sex composition, and ethnic composition, etc
How is demography used?
It is used in a variety of disciplines (academic or applied) and uses specialised techniques and theory, which are applied to populations
How is anthropological demography different from regular demography?
Anthropological demography is concerned with describing, interpreting, explaining, and comparing demographic patterns, not just describing and comparing
Anthropological demography aims to look at changes in subsistence and how demography changed, epidemiological transitions over long periods, and other trends over time
What are the three forces of demographic change?
Migration, which could be replaced with marriage, birth, and death, which are all holistic and influenced by culture
What are the three key concerns of anthropological demography?
What makes populations grow, shrink, or stay the same?
Who makes up a particular group?
How are groups spread over space (dense or sparse, urban or rural)?
What data sources do anthropological demographers use?
Headstones, human remains, census data, tax assessments, etc (and often multiple)
What do historical records provide data on?
Age, sex, illness duration, birthplace, religion, socioeconomic status, etc
What makes human populations and groups hard to study?
The complexity of human populations
What are the five reasons demography is important?
It is the basis for understanding any community
Quantitative study supports qualitative study
Birth, death, migration, and disease are universal human experiences
Population structures are the outcome of social behaviour
Understanding the past allows us to predict and plan for the future
According to Chamberlain (2009), what are the four data sources used by archaeological demographers and what do they show?
Human remains to look at movement/migration, genetic relations, and mortality/burial patterns
Paleoenvironmental records to estimate environment carrying capacity, relative population size/density
Material culture, artefacts, and settlement size/distribution can show how/where people lived and relative population density
Historical and ethnographic information sometimes to get an absolute population size/distribution
According to Chamberlain (2009), how does archaeological demography compare to paleodemography?
Compared to paleodemography, archaeological demography focuses more on connecting qualitative and quantitative data, and on incorporating social and cultural perspectives
According to Chamberlain (2009), why does the Juvenility Index work?
Changes in fertility rates/population growth rates typically lead to changes in age distributions, which is usually represented in age-at-death distributions
According to Madrigal (2002), how can gene flow be assessed using archives?
Surnames can act like genetic markers, so looking at archives and tracking where surnames appear can show patterns of mating, inbreeding, and migration
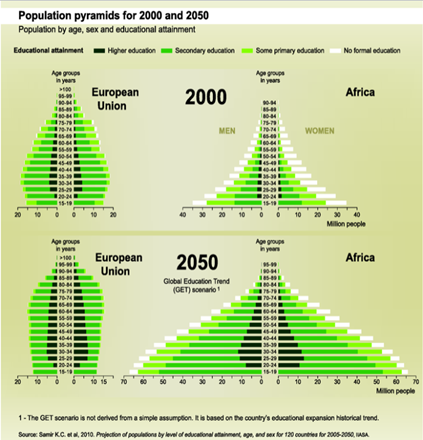
What does this graph show?
A population pyramid showing the population structure of the EU and Africa in 2000 and 2050 based on age, sex, and educational attainment
It shows how these structures are likely to shift over time