Intro to Supply Chain Final Exam - Devinoff
1/124
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Final Exam Fall Semester
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
Chapter 9
Chapter 9
Which transportation mode has the lowest per unit cost?
Pipeline
How does net rate pricing benefit large-volume shippers in the transportation industry?
Large-volume shippers can negotiate significant discounts against published rates, reflecting the bargaining power of their higher volumes.
Which transportation mode is the most reliable?
Pipeline
Which of the following best describes the significance of intermodal transportation in logistics and supply chain management?
It represents the use of multiple transportation modes to execute a single shipment, highlighting its flexibility and efficiency.
Which transportation mode has the lowest per unit cost?
Pipeline
Which of the following best describes the role and regulation of exempt carriers within the transportation sector?
Exempt carriers specialize in transporting commodities that are exempt from certain economic regulations but not from safety regulations.
The transportation term of sale known as Free on Board (F.O.B.) Origin requires that the seller retain ownership of the product from the point of origin until it reaches the buyer's destination.
False.
Which of the following BEST describes the services provided by Third-Party Logistics (3PL) companies?
They warehouse and distribute your products, and potentially perform some other value-added processes.
Which warehouse location strategy would most likely be used if a company has many more customers than suppliers?
Market Positioned Strategy
What was the primary outcome of the deregulation movement in the U.S. transportation industry starting from the 1970s?
Deregulation allowed transportation companies to set their own rates and negotiate directly with shippers, enhancing competition.
Chapter 10
Chapter 10
What is a significant risk when choosing a country with unstable currency for a facility location?
Erroneous cost projections
A Deemed Export is the release of technology or source code that is subject to the Export Administration Regulations, to a US citizen located in the United States
False
Material that is imported through the use of a Foreign Trade Zone (FTZ) must be removed from the FTZ within 1 year to avoid fines or sanctions being imposed by US Customs and Border Protection on the Importer of Record.
False
Which global facility type is described as a factory set up to take advantage of government incentives, and/or reduced tax/tariff barriers, to meet regional or local market needs?
Server Factor
If a company wanted to import materials duty-free, for use in the production of their end items, and then export them to other countries, they would most likely utilize?
Foreign Trade Zone
Which of the following is NOT one of the twelve pillars of competitiveness?
Recreation
Which of the following is a key difference between taxes and tariffs in the context of global location decisions?
Taxes apply to profits within a country, while tariffs apply to imported goods.
Penalties for international trade violations can be substantial. Which of the following is NOT a typical penalty for these types of violations?
Capital Punishment
If a company wants to locate one factory in a major geographic location and another factory in a different geographic location to better serve its customers, which of the following best represents the MOST CRITICAL factors in evaluating potential locations to meet that goal?
The location's proximity to major customers, the quality of the infrastructure, and the local labor market's efficiency.
Which one of the following is NOT a Quality of Life issue used to help make global location decisions?
Infrastructure (e.g., roads, ports, utilities, institutions, etc.)
What are global location quality-of-life issues?
1) Social Environment
2) Culture
3) Recreation
4) Public Safety
5) Mobility
Which of the following activities can be performed (i.e., permitted activities) in a Foreign Trade Zone (FTZ)
1) Testing
2) Destruction
3) Exhibition
4) Salvage
5) Manufacturing
A business that provides storage and related warehouse functions to companies on a short or long-term basis for a month-to-month fee, is known as a?
Public Warehouse
A warehouse operation that receives products from different plants or suppliers, stores them, and then combines them with similar shipments from other plants or suppliers for further distribution, is known as a?
Consolidation Warehouse
A variation of warehousing that handles the shipping, receiving, and storage of goods on a contract basis for a fee., is known as a?
Contract Warehouse
A storage facility that is owned by the company that owns the goods being stored in the facility, is known as a?
Private Warehouse
A warehouse operation that divides full truckloads of items from a single source or manufacturer into smaller, more appropriate quantities for use or further distribution, is known as a?
Break-Bulk Warehouse
Focused on product development and engineering for products that they manufacture
Contributor Factory
A factory set up for manufacturing or assembly in a country where labor and/or raw materials are less expensive, for eventual import back into the manufacturer's home country
Offshore Factory
Factory set up in an area with an abundance of advance suppliers, competitors, research facilities, etc.
Outpost Factory
A factory set up to take advantage of government incentives, and/or reduced tax/tariff barriers, to meet regional or local market needs
Server Factory
Manufactures products at low cost but with skilled workers and significant managerial resources
Source Factor
Which of the following are newer technologies and trends in transportation (i.e., within the last 25 years)?
1) Driverless trucks
2) Platooning
3) Vertically Folding Shipping Containers
4) Driver Monitoring
5) Drone Deliveries
An organization that puts buyers and sellers from different countries together and handles the export/import arrangements, documentation and transportation
Trading Company
An organization that operates like a freight forwarder but only uses scheduled ocean liners
Non-Vessel-Operating Common Carrie
An organization that moves global shipments through customs and handles the documentation
Customs Broker
An organization that physically moves goods to and from foreign destinations
International Freight Forwarder
What transportation intermediary is a nonprofit cooperative which arranges for members' shipments?
Shippers' Association
What transportation intermediary is an outsourced provider that manages all, or a significant part, of an organization’s logistics requirements (including transportation) for a fee
Third Party Logistics Company
What transportation intermediary consolidates LTL shipments into FTL shipments (i.e., they take small shipments from multiple companies and consolidate them into larger shipments)?
Freight Forwarder
What transportation intermediary purchases blocks of rail capacity and sells it to shippers?
Intermodal Marketing Company
What transportation intermediary brings shippers and carriers together?
Transportation Broke
What are the five (5) primary functions of a warehouse?
1) Receiving
2) Picking
3) Packing
4) Shipping
5) Storage
Which mode of transportation is the most flexible, providing the most accessibility?
Truck
Which mode of transportation is the fastest over a long distance?
Air
Which mode of transportation has the lowest per-unit cost?
Pipeline
Which mode of transportation is the most reliable?
Pipeline
Which mode of transportation has the most capability?
Rail
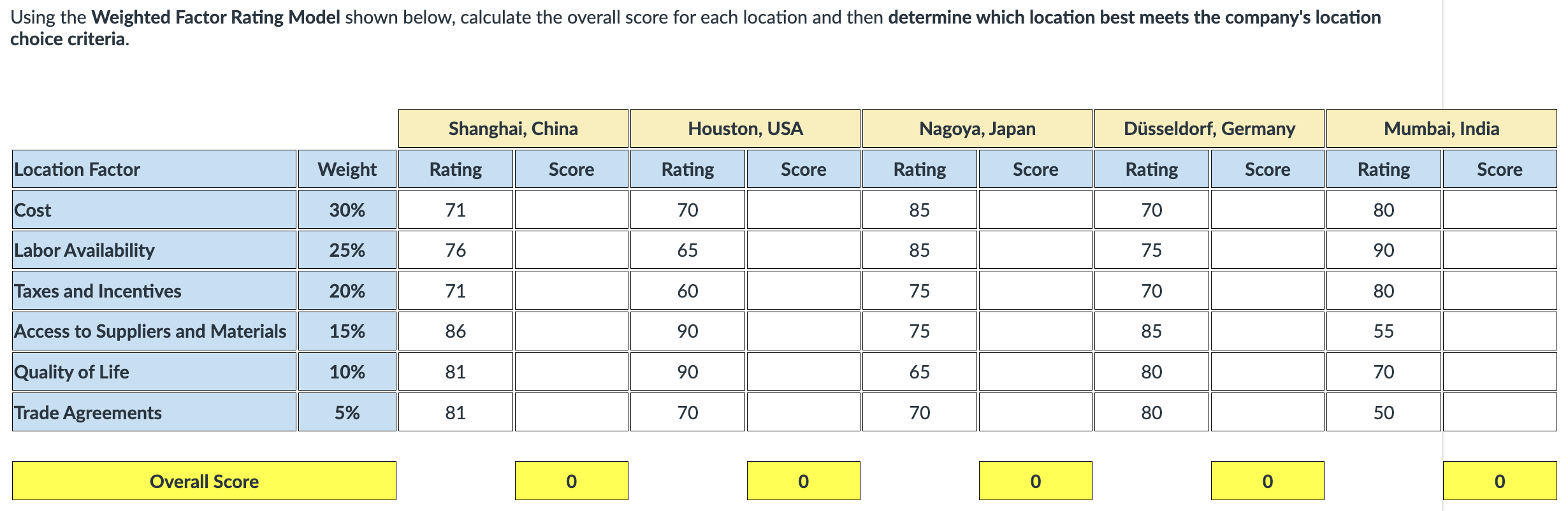
Using the Weighted Factor Rating Model shown below, calculate the overall score for each location and then determine which location best meets the company's location choice criteria.
Nagoya, Japan
Customs Brokers:
Move global shipments through customs and handle documentation.
International Freight Forwarders:
Move goods to and from a foreign destination.
Trading Companies:
Put buyers and sellers from different countries together and handle export/import arrangements, documentation, and transportation.
Non-Vessel-Operating Common Carriers (NVOCC):
Operate like freight forwarders but use only scheduled ocean liners.
Name the five modes of transportation.
Name five (5) services offered by 3PL's.
1) Inbound Transportation
2) Outbound Transportation
3) Warehousing
4) Pick and Pack
5) Freight Forwarding
What is a Third Party Logistics (3PL) company?
A Third-party Logistics company is an outsourced provider that manages all, or a significant part, of an organization's logistics requirements for a fee.
What is the World Trade Organization (WTO)
The WTO deals with the global rules of trade between nations. Its main function is to ensure that global trade flows smoothly, predictably, and as freely as possible.
Where is the World Trade Organization located
Geneva, Switzerland.
What is the mission of U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP)?
Its mission is to safeguard America's borders, protecting the public from dangerous people and materials while enhancing the Nation's global economic competitiveness by enabling legitimate trade and travel.
What is Intermodal Transportation?
It is sometimes referred to as the sixth mode of transportation, but it is really the use of multiple modes of transportation to execute a single transport shipment.
What is a Deemed Export?
Deemed Export is the release of technology or source code subject to the Export Administration Regulations to a foreign national located in the United States.
What is Cross-Docking?
Cross-docking is the logistics practice of unloading materials from an incoming truck or railcar and loading these materials directly onto outbound trucks or railcars, with little or no storage in between, which reduces inventory investment and storage space requirements.
Chapter 11
Chapter 11
Which of the following is a required element of an effective CRM initiative?
Segmenting customers
Through the use permission marketing programs, customers are allowed to select the type of communications companies can make with them, and even choose to be completely eliminated from both e-mail and traditional mailing lists
True
Which of the following best describes how a website self-service portal enhances the effectiveness of a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) program?
It provides customers access to their account information and the ability to update personal details, thereby improving data accuracy.
Which of the following is NOT a reason companies need a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) program?
To ensure that product prices are consistently lower than competitors.
Customer Service is?
1) Performance Measure
2) Activity
3) Philosophy
Finding a new customer costs 5-10 times as much as keeping an existing customer
True
The good customer service video featuring the cab driver highlights the importance of what element in delivering exceptional customer service?
The role of personalization and attention to detail in exceeding customer expectations.
Call centers play a crucial role in customer service by performing various functions. Which of the following is NOT a specific function of a call center?
Manufacturing products based on customer feedback to meet demand.
Companies should invest time and effort in developing CRM programs for every customer
True
Why is it crucial for companies to ensure that their intermediate customers (e.g., wholesalers) are adequately trained and informed?
To ensure intermediate customers accurately represent the company's products and prevent misinformation from being circulated.
Chapter 12
Chapter 12
How does the concept of a blended delivery system apply to a restaurant's operation, and what does it reveal about managing service supply chains?
Blended delivery systems combine high and low customer contact elements, necessitating different management strategies to optimize performance in both customer-facing and operational areas.
Implicit services involve such aspects as the attitude of the servers, atmosphere, waiting time, and convenience, as well as other similar aspects
True
Considering the example of banking, what role do facilities and equipment play in enhancing the service offering?
The physical location, layout, and available equipment significantly affect customer perceptions of service quality, contributing to overall satisfaction.
Themed restaurants such as the ESPN zone, Rainforest Café, and Chuck E. Cheese, are all examples of Entertailment facilities
False
What role does the layout strategy play in managing a service supply chain effectively?
Layout strategy facilitates easy customer navigation to desired services or products, potentially improving service efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Which of the following best represents the most significant challenge in measuring and improving service quality within the service industry?
The subjective nature of quality assessment in services, as perceptions of quality can vary greatly among customers, complicating quality improvements.
When a customer takes their automobile to a car wash, the car wash provides state utility to the vehicle
True
The three general service strategies are?
Differentiation, Focus, and Cost Leadership
Why does the labor content in services complicate efforts to improve productivity?
High labor content limits the scalability of productivity improvements due to the inherent limitations of human performance.
Balking occurs when customers decide to leave the queue after some length of waiting time in the queue
False
Queues formed virtually with technology. Customers can use smartphones to place their names in a real-time electronic queue like at a restaurant. This type of queuing has provided a great deal of flexibility and allows for reduced stress levels on the part of the customer.
Mobile Queues
These queues are set in a fixed position, such as a supermarket checkout line, airport, or bank. In some cases, queue management systems can be organized with a take-a-ticket number, allowing a person to walk around and wait for their number to be called.
Structured Queues
When people form queues informally in various directions and locations. These queues are seen in retail stores, at an airport waiting for a taxi, people waiting for an ATM, etc.
Unstructured Queues
Which of the following are goals or benefits of Customer Relationship Management (CRM)?
1) Increase Revenue
2) Access to updated customer information and personalized interactions
3) Automation of repetitive tasks
4) Increase customer loyalty and retention
5) Faster responses to customer inquiries
If an Automobile Service Repair Shop that operates for twelve (12) hours per day, has a total of six (6) workstations available, and the average automobile repair job takes one-and-a-half (1.5) hours to complete, what is their daily Service Capacity (i.e., how many cars/customers can this service operation accommodate per twelve (12) hour day)?
48 (12 hours a day x 6 work stations = 72 / 1.5 hours per repair = 48)
Occurs when a company sells an additional related or complementary product or service to an existing customer after the initial purchase
Cross-Selling
Involves persuading a customer to buy a more expensive item or upgrade a product or service to make the sale more profitable. It also involves selling the customer extra features or add-ons to the product they are already buying
Up-Selling
The practice of dividing a customer base into groups of individuals that are similar in specific ways relevant to marketing
Customer Segmentation
The process of customers changing their buying preferences because they find better or cheaper products and services elsewhere
Customer Churn
An approach to selling products and services in which a customer explicitly agrees in advance to receive marketing information
Relationship Marketing
Instead of eliminating excess capacity during times when capacity exceeds demand, service providers can take which of the following actions?
1) Use demand management techniques to shift demand from peak demand periods into non-peak periods
2) Doing training or cross-training of employees
3) Doing other jobs
A common line is formed. The customer at the head of the line proceeds to the single service provider who completes the required service for the customer.
Single Channel, Single Phase
A common line is formed, and the customer at the head of the line proceeds to the first available service provider (from a group of service providers), who provides part of the service, and the customer is then passed-off to the next service provider in sequence, and so on, until the full service is completed.
Multiple Channel, Multiple Phase