Electric charge
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What are the units for charge?
coulombs (C)
What is an electrical conductor?
a material that electric charge can flow through easily
What materials are good electrical conductors & why?
- metals (e.g. copper, steel, graphite, mercury)
- because they contain delocalised electrons which means that have charged particles that are free to move
What is an electrical insulator?
a material that has a very high resistance to the flow of electric current
What materials are good electrical insulators & why?
- rubber, paper, plastic, diamond
- because these materials do not have charged particles that are free to move
What is meant by attraction & repulsion?
- opposite charges attract
- like charges repel
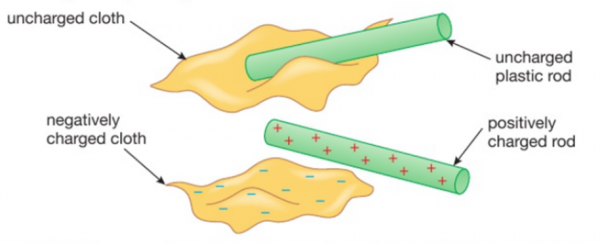
How are materials charged by friction?
- when insulating materials are rubbed against each other & electrons are transferred from one object to the other
- the material that gains electrons becomes negatively charged
- the material that loses electrons becomes positively charged
- the magnitude of the charge on each material is equal since they lose / gain the same number of electrons
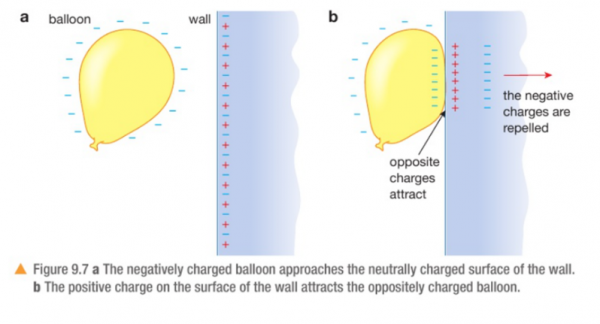
How are materials charged by induction?
- when a charged material charges an uncharged material
- a negatively charged object will repel electrons away from the surface of a neutral object, leaving it with a slight positive charge
- a positively charged object will attract electrons towards the surface of a neutral object, leaving it with a slight negative charge
What happens when the charged object is removed when charging by induction?
the charges redistribute & the other object becomes neutral again
What is static electricity?
- when electric charges are not free to move / stationary
- this occurs best with insulators
What are some uses of static electricity?
- paint spraying
- ink-jet printers
- photocopiers
What are some dangers of static electrcity?
- can cause electric shocks
- if a spark is created it can cause a fire or explosion (e.g. when fueling aircrafts or tankers)