The Periodic Table
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Chemical Symbol
An abbreviation that we use to indicate an element or an atom of an element. EX: Chemical symbol for Sodium is Na. Only the first letter of a symbol is capitalized.
The Atomic Mass of an Atom
Is approximately equal to its mass number (a whole number). This is because each proton and each neutron contribute approximately one amu to the mass of an atom, and each electron far less. (The average mass of most elements are not whole numbers because most elements exist naturally as mixtures of two or more isotopes).
The Periodic Law
The properties of the elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers.
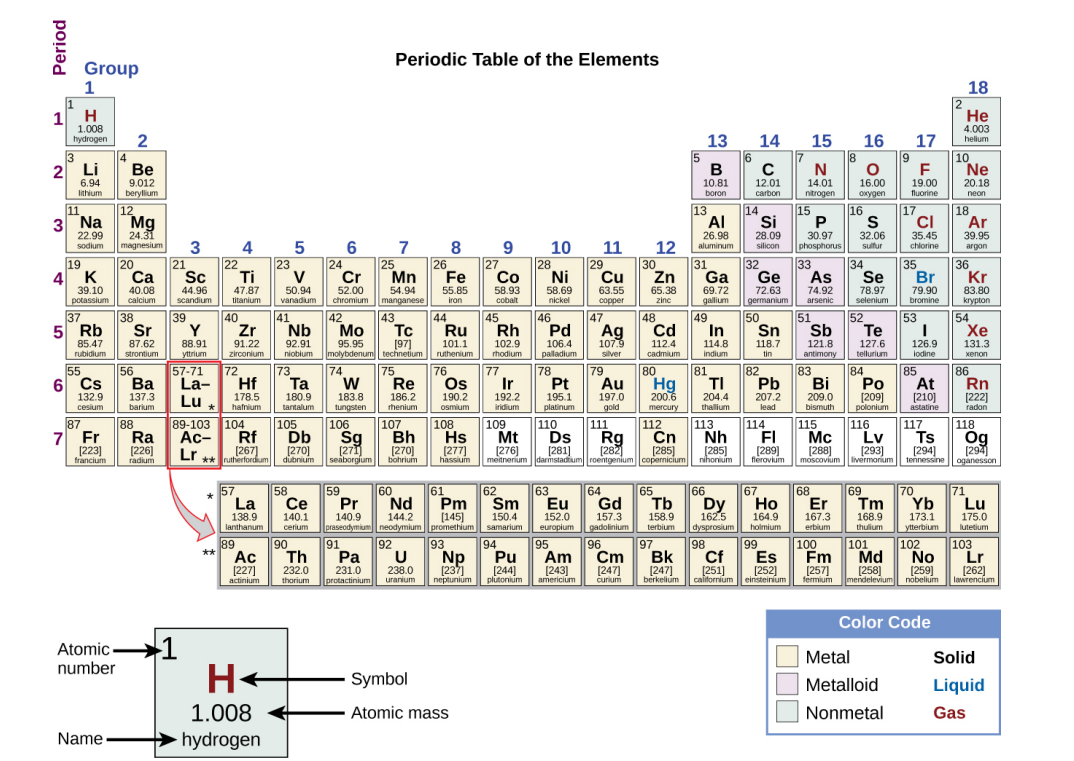
Periodic Table
Arranges the elements in increasing order of their atomic numbers and groups atoms with similar properties in the same vertical column.
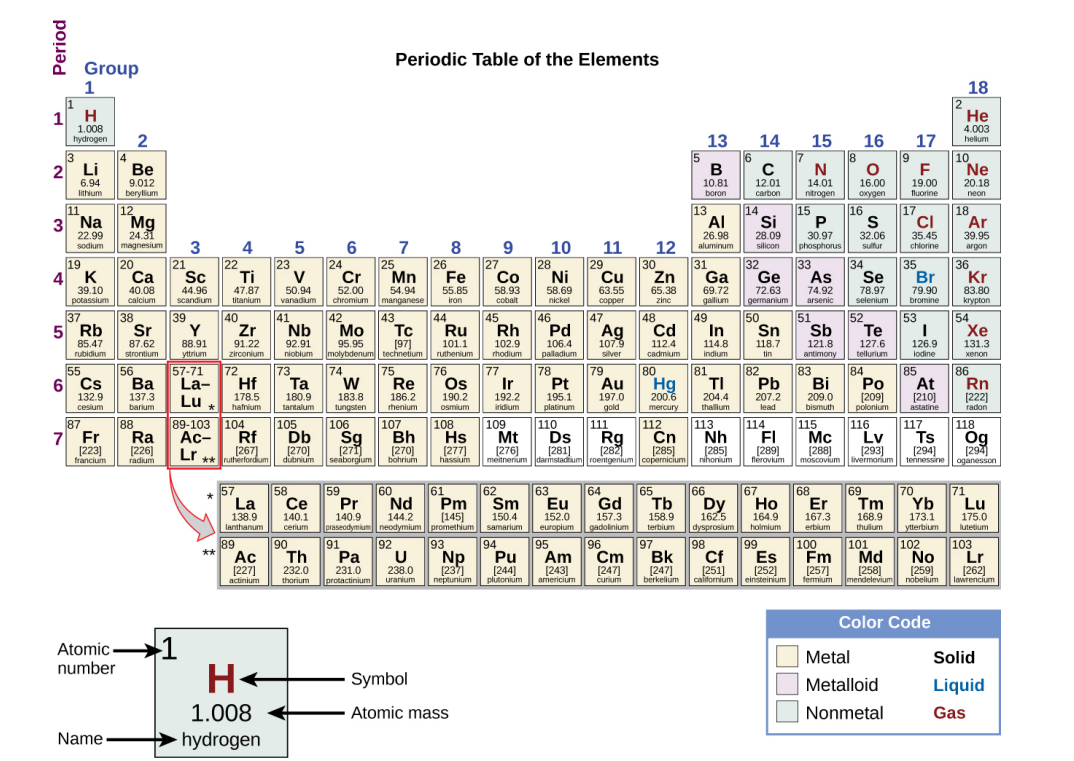
Each Box in the Periodic Table…
Contains its atomic number (Z), symbol, average mass and sometimes its name.
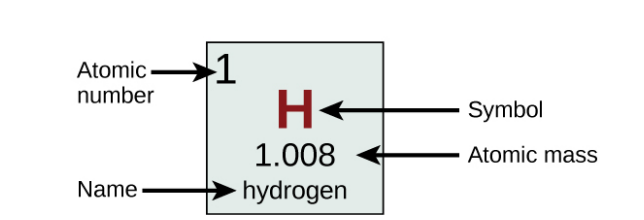
Periods/Series
The 7 horizontal rows on a periodic table in which elements are arranged.
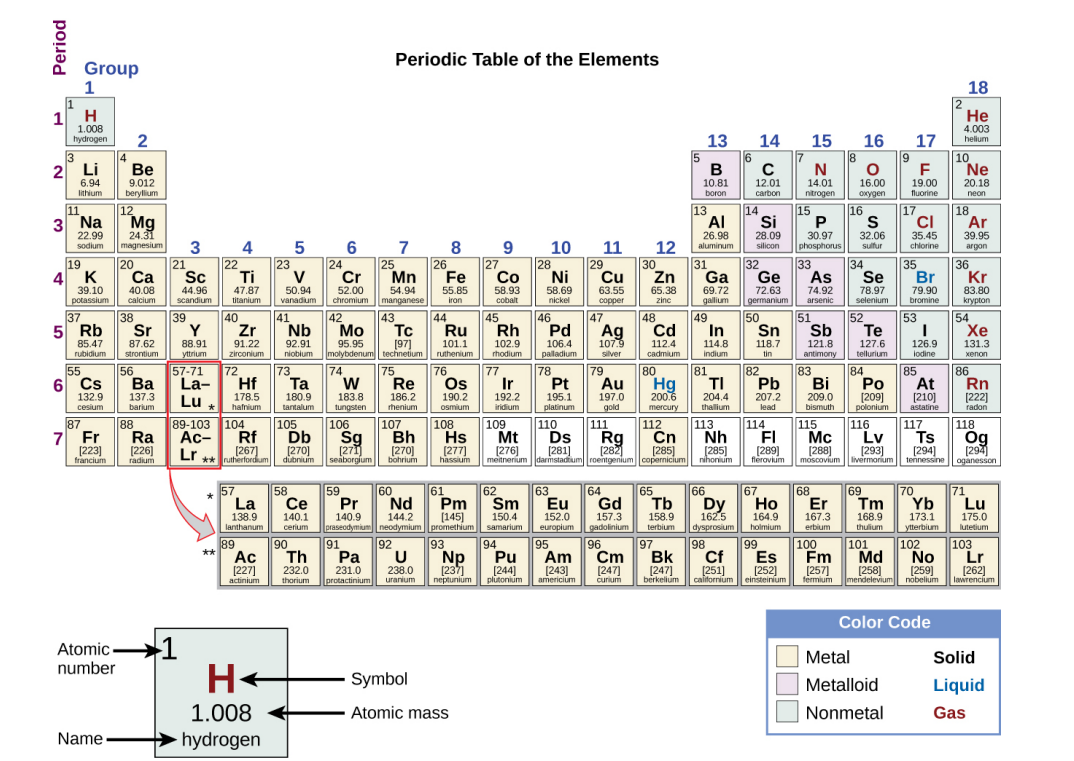
Groups
The 18 Vertical columns in a periodic table.
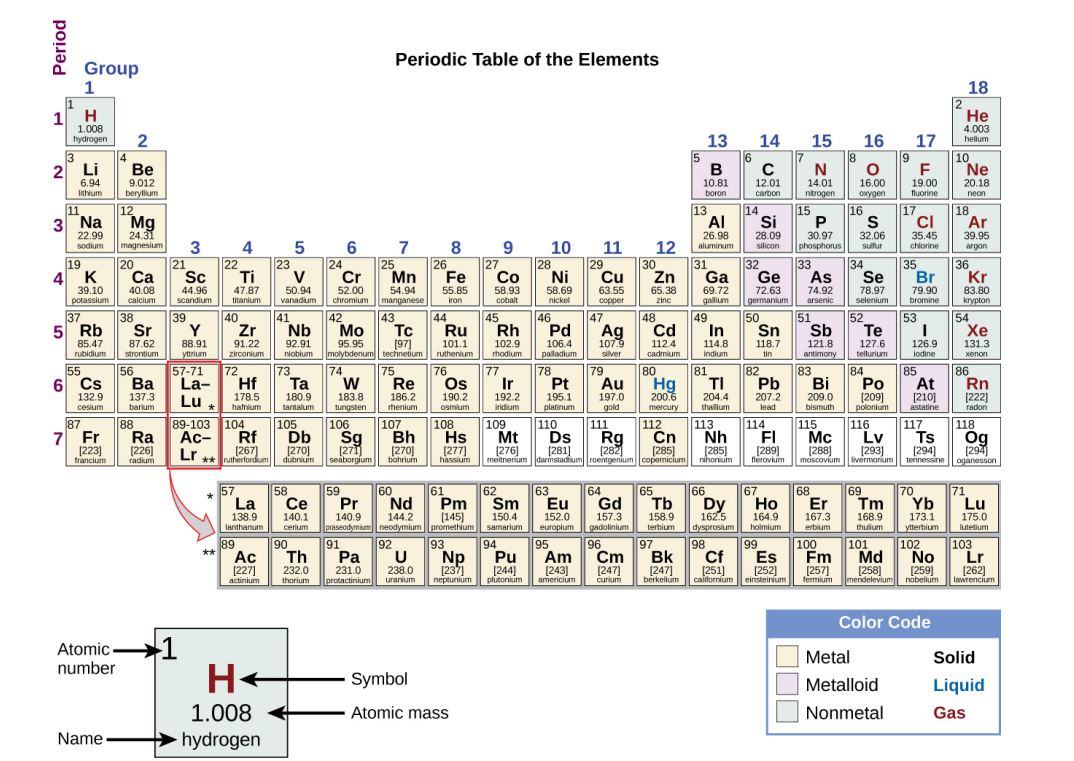
Many Elements…
Differ dramatically in their chemical and physical properties. But some elements are similar in their behaviors. We can sort elements into large classes with common properties.
Metals
Elements that are shiny, malleable (able to be hammered or pressed permanently out of shape without breaking or cracking) and good conductors of heat and electricity. (shaded yellow in textbook).
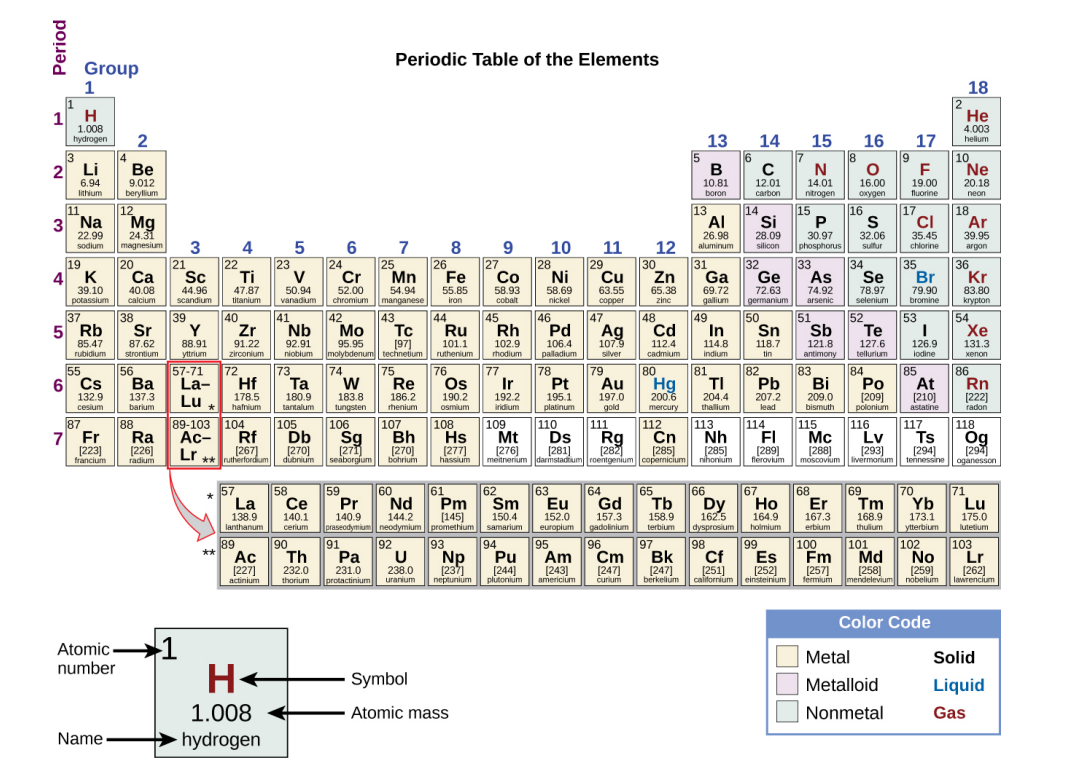
Nonmetals
Elements that appear dull, poor conductors of heat and electricity. (shaded blue in textbook).
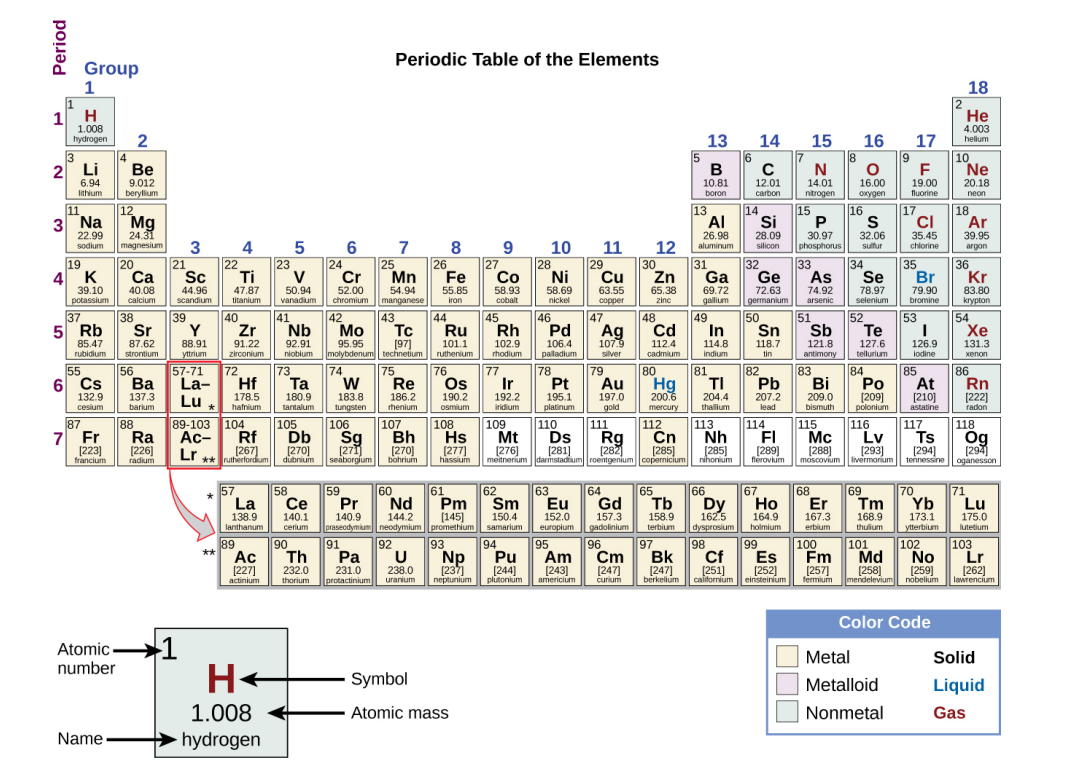
Metalloids
Elements that conduct heat and electricity moderately well, possess some properties of metals and some properties of nonmetals. (shaded purple in textbook).
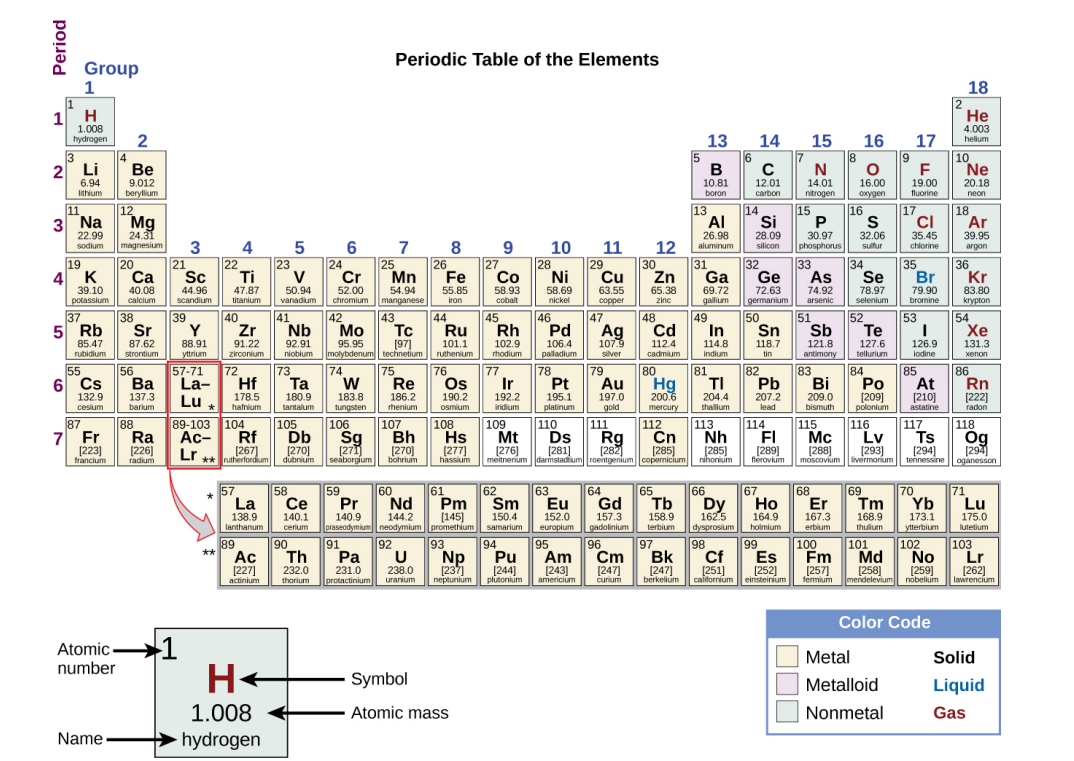
Main Group Elements
(Representative Elements) Groups 1, 2 & 13-18.
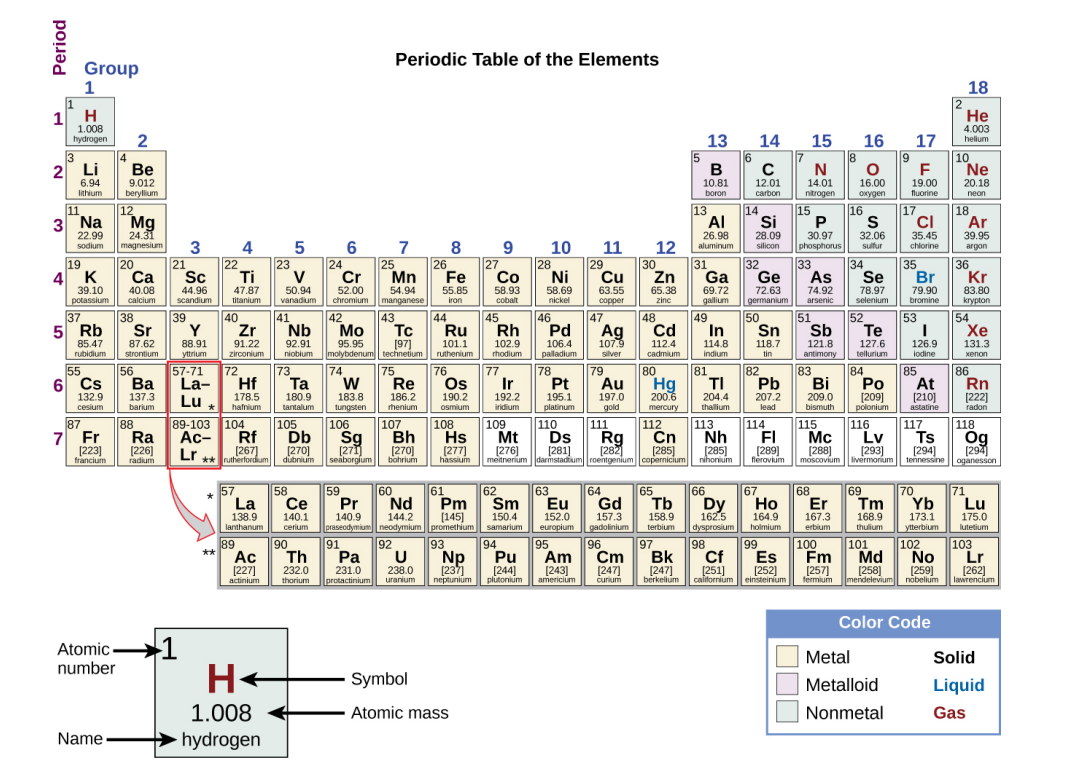
Transition metals
Groups 3-12
Inner Transition metals
(bottom 2 rows) Top Row: Lanthanides. Bottom Row: Actinides.
Alkali Metals
Elements in group 1 form compounds that consist of one atom of the element and one atom of hydrogen (alkali metals).
Alkaline earth Metals
Elements in group 2 form compounds of one atom of the element and two atoms of hydrogen (alkaline earth metals).
Pnictogens
Group 15.
Chalcogens
Group 16.
Halogens
Group 17.
Noble Gases
Group 18.
The Groups can also be referred to by…
The first element of the group. EX: Chalcogens can be called the oxygen group or the oxygen family.
Hydrogen…
Is a unique, nonmetallic element with properties similar to both group 1 & 17 elements. That is why Hydrogen may be shown at the top of both groups or by itself.
Elements in groups often behave…
In a somewhat similar manner due to the number of electrons in their outer shell and their similar readiness to bond.
Elements that consist of entirely unstable, radioactive isotopes…
Have their own atomic mass given in square brackets. (See image). An average weight cannot be determined for these elements because their radioisotopes may vary significantly in relative abundance, or may not even exist in nature. The number in the square brackets is the atomic mass number (an approximation) of the most stable isotope of that element.