HOSA CPR/First Aid
1/202
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
203 Terms
How many compressions: breaths do you perform for each cycle of CPR?
30 compressions and 2 breaths 30:2
Total at least 100-120 compressions per minute
How do you treat a cut / gash on a person's arm?
With clean dressing, put gauze pads on the cut.- elevate arm.
Hold for 1 minute and state that you are holding for 1 minute.
If bleeding continues, place more clean gauze pads and hold 1 more minute with more pressure. Bleeding should subside. Judge will sat bleeding stopped.
Wrap arm with some kind of bandage to maintain pressure. Do a pressure wrap" Treat for shock
Triage is ____________
a method of prioritizing treatment when there is more than one victim. Most severe treated first.
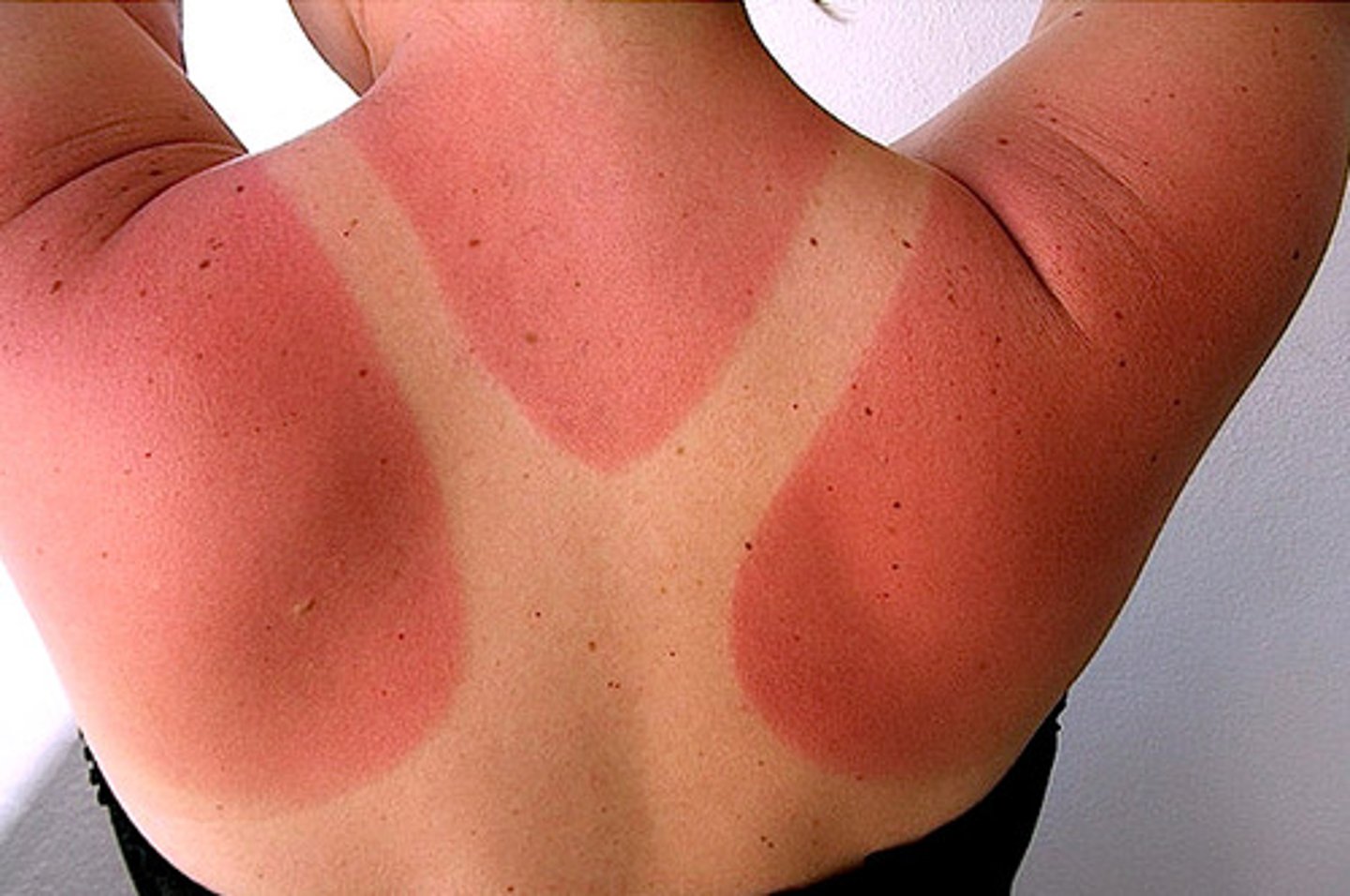
A young man was standing to close to a fire and the hair caught on fire. The fire was extinguished quickly but the skin on the forehead is reddened. Degree of burn is and you should ______.
First Degree Burn - Cool the burn with cool/cold but not ice-cold water or apply cool wet cloths - until pain subsides dry with clean gauze, apply non-stick pad - do not break blisters.

What are the steps to checking an unconscious person?
Make sure scene is safe. Put on PPE
Tap the victim's shoulder while asking "Are you okay?"
Call 911 - get AED - judge might say AED not available. Check for breathing - tell judge
Check for carotid pulse - no more than 10 seconds
Begin CPR if judge says no pulse.
What are signs that indicate a medical emergency?
unusual noise, sight, odor, appearance, or behavior.
List some barriers to action.
- presence of other people
- unsure of victim's condition, type of injury or illness
- fear of catching disease
- fear of doing something wrong
- being unsure when to call 911
Name the 3 C's of first aid.
Use your PPE
Check for medical alert bracelets
-check, call, care.
- Don't forget your PPE before and after treatment. Change gloves when changing victims or verbalize Changing gloves. Use hand sanitizer when done.
-scan the body for ID bracelets or ask patient if they are alert or bystanders

What do you check for prior to administering care to a victim?
- scene safety
- other victims
- bystanders
- signs and clues to what type of injury or condition victim has. Airway, breathing, pulse
Who do you call prior to administering care to a victim?
911 or EMS.
How long should you check a victim's breathing?
10 seconds.
Define implied consent.
the assumption that a victim would give permission to treat them if he or she were conscious.
List some key facts about the transmission of disease.
- can be airborne, in a fluid, or vector (bite)
- injured person must be infected for transmission to occur
- rescuer has to have a break in skin
- there must be sufficient amount of pathogens
Define pathogen.
a disease causing microorganism.
Provide care for first 2 minutes under what circumstances?
- unconscious adult, adolescent, or infant
- witnessed collapse from choking
Call FIRST under what circumstances?
- cardiac emergencies (need AED)
- drowning victims
- witnessed collapse child (need AED)
List the respiratory organs.
- airway (which consists of the pharynx, larynx, trachea, and bronchi, alveoli)
- lungs -alveoli - gas exchange unit
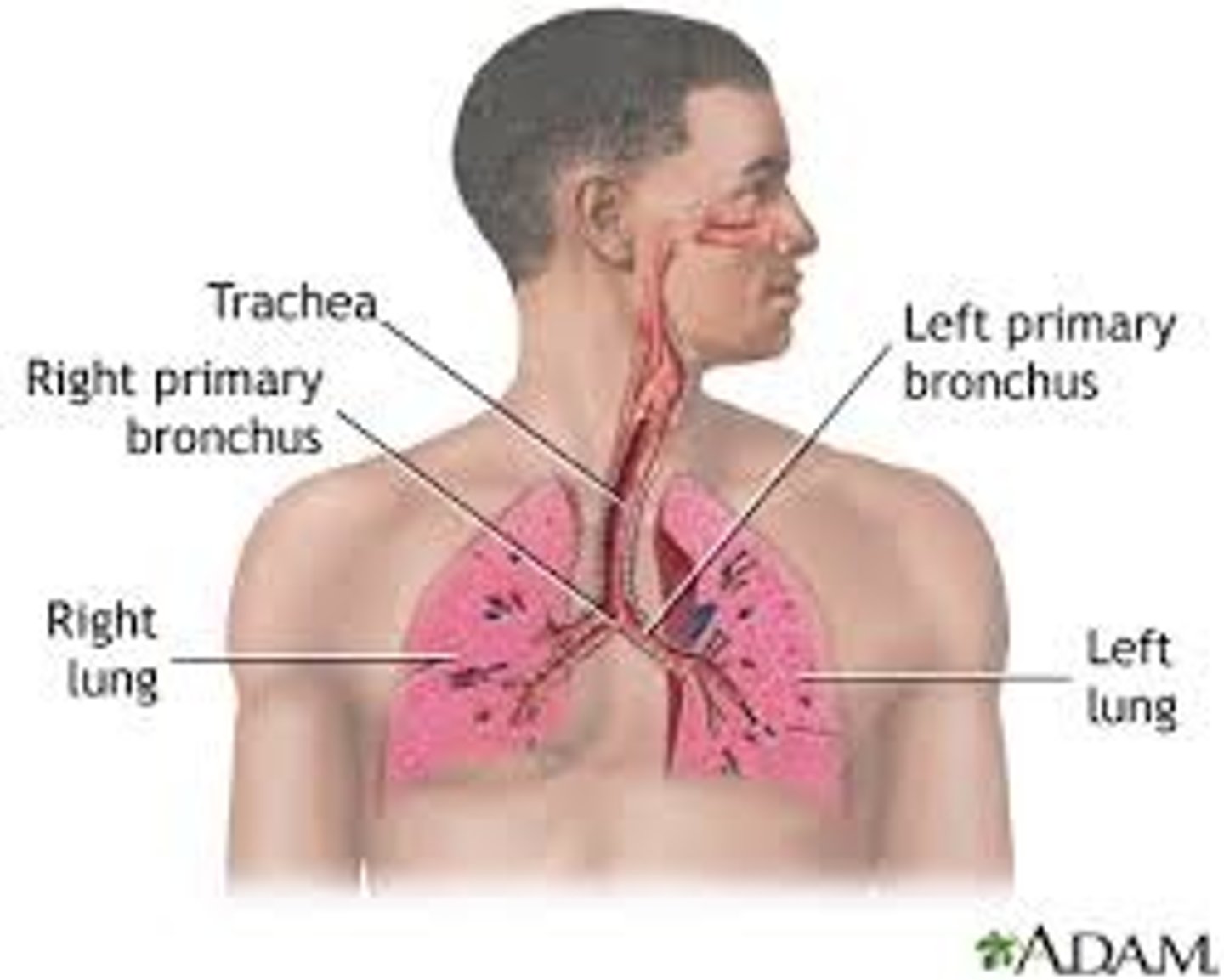
What is the function of the respiratory system?
supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide by breathing.
List some common respiratory system problems.
- asthma
- respiratory distress
- respiratory arrest
List the circulatory organs.
- heart
- blood
- blood vessels, arteries, veins
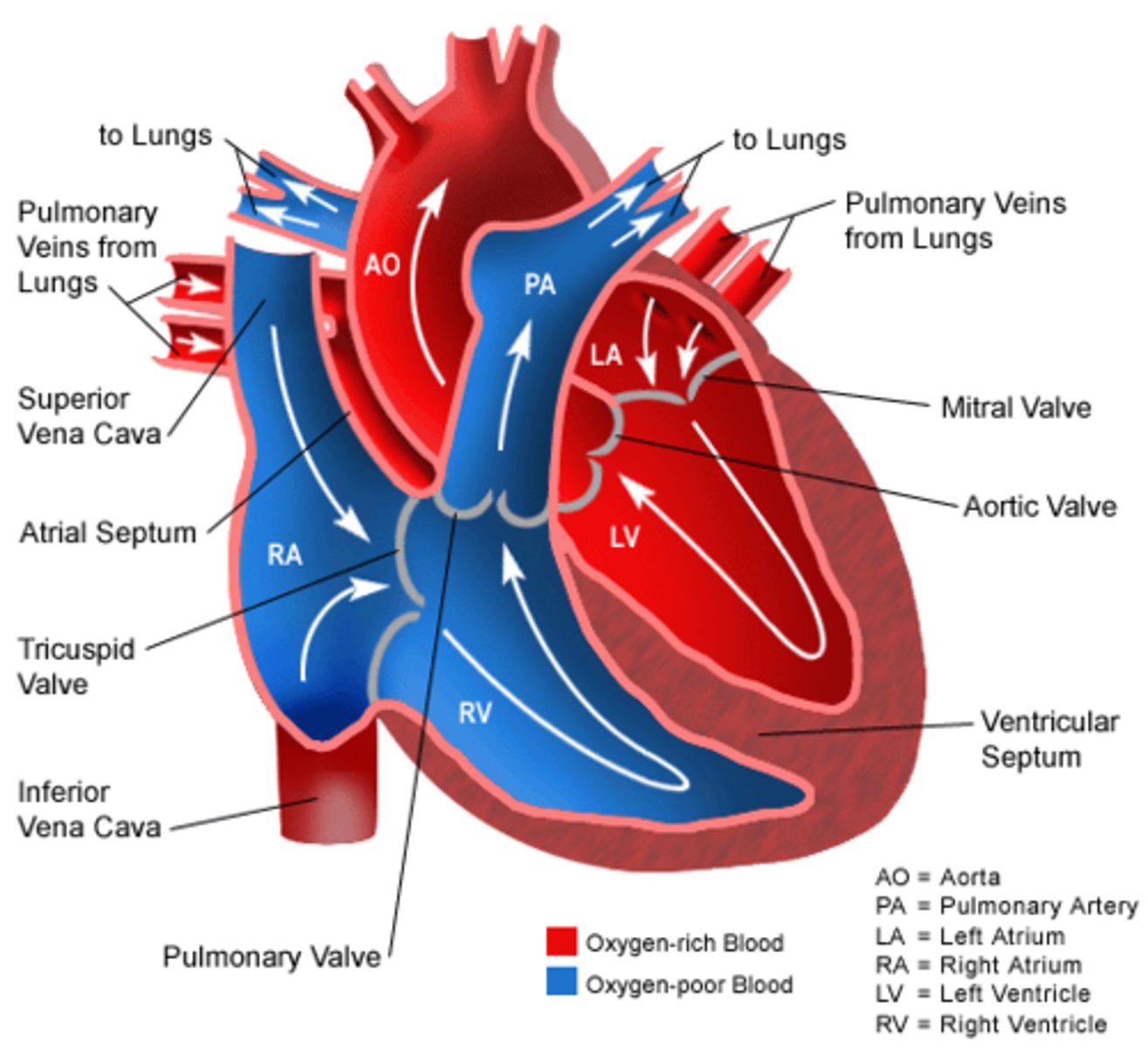
Which direction do arteries pump blood?
away from the heart.
Which direction do veins pump blood?
towards the heart.
What is the function of the circulatory system?
transports nutrients and oxygen to body cells and removes waste products.
List some common circulatory system problems.
- cardiac arrest
- heart attacks
- blood clots
List the nervous system organs.
- brain
- spinal cord
- nerves
_ neurons - unit that transmits nerve impulses
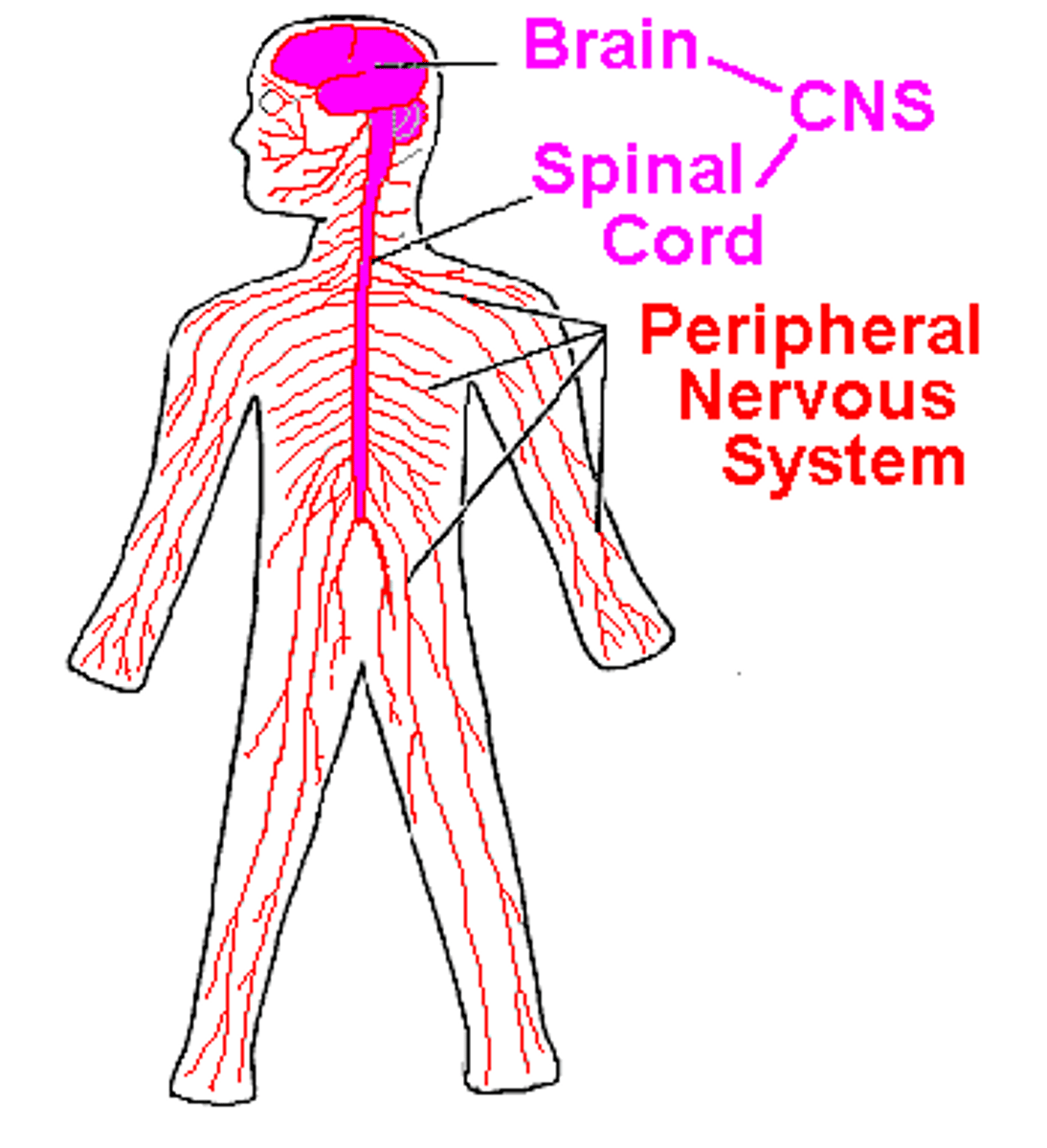
What is the function of the nervous system?
transmits messages to and from the brain to regulate all of the body and its systems.
List some common nervous system problems.
- paralysis
- seizures
- strokes
- concussions
- fainting
- loss of consciousness.
List the musculoskeletal organs.
- bones
- muscles
- ligaments
- tendons
What organs can you strain?
tendons (achilles tendon) - tendon attaches muscle to bone
What organs can you sprain?
ligaments around joints and muscles
What is the function of the musculoskeletal system?
provides framework, protects internal organs, and allows movement and heat.
List some common musculoskeletal system problems.
- breaks
- tears
- sprains
- strains
- fractures
List the integumentary organs.
- skin
- nails
- hair
What is the function of the integumentary system?
prevents infection and dehydration, and regulates body temperature.
List some common integumentary system problems.
1) breaks
2) tears
3) punctures - like a knife wound
4) lacerations - jagged tear
5) abrasions - road rash, scraped skin
6) amputation - loss of body part
7) avulsion -loss of chunk of skin
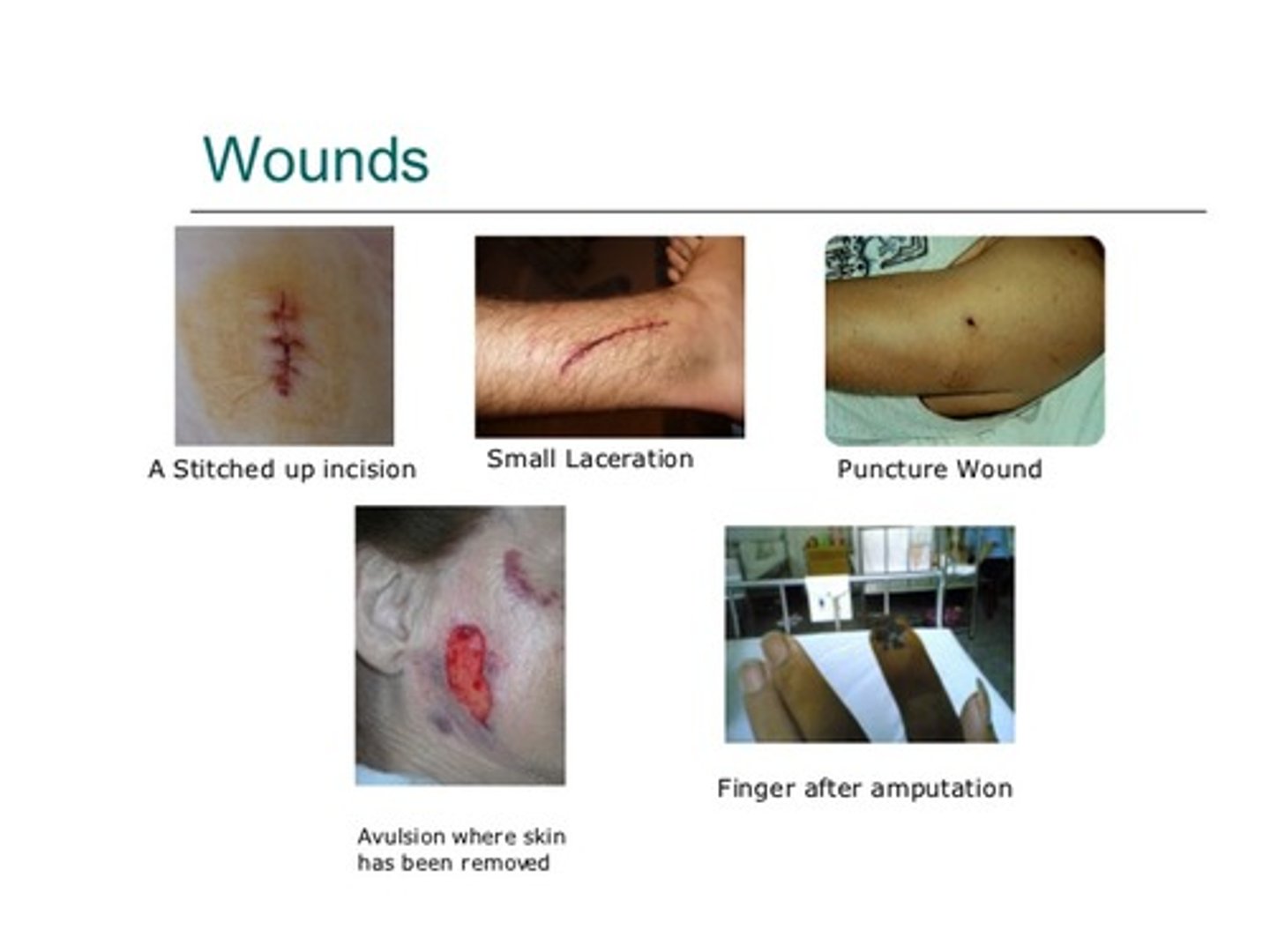
List the digestive organs.
- mouth
- esophagus
- stomach
- intestines
- liver
- pancreas - produces insulin
- gallbladder - secretes bile
What is the function of the digestive system?
breaks down food to supply body with energy.
List some common digestive system problems.
- ulcers
- choking
- allergies
- food poisoning
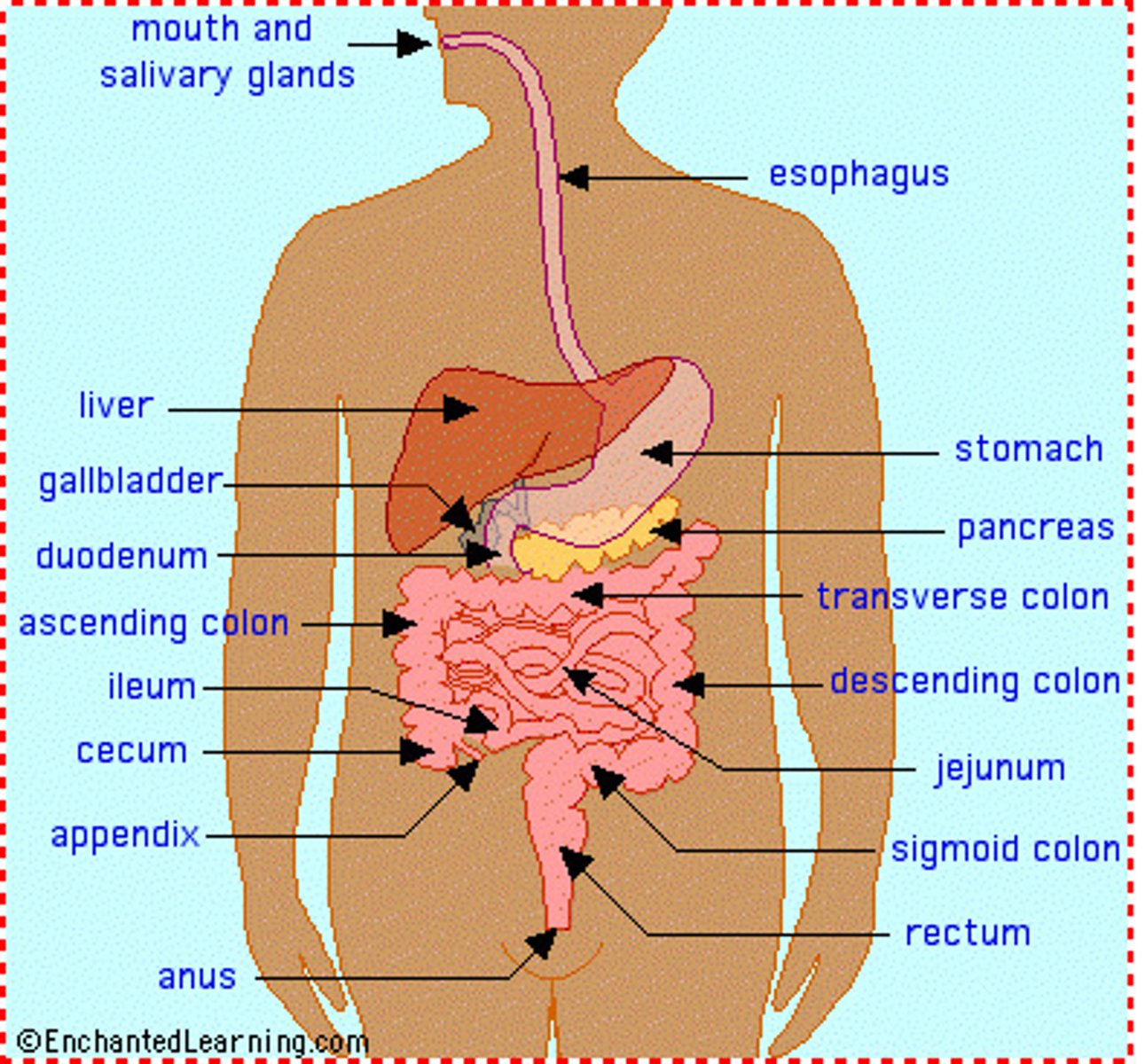
List the endocrine organs.
glands.
What is the function of the endocrine system?
secretes hormones into blood.
List some common endocrine system problems.
- diabetes

List the genitourinary - reproductive organs.
- penis (males)
- testes (males)
- vagina (females)
- ovaries (females)
- uterus (females)
What is the function of the reproductive system?
reproduces offspring
List some common genitourinary system prob
- dehydration
- infections
1. What is the medical term for a bruise?
2. What is another term for a nosebleed?
1. ecchymosis
2. epistaxis
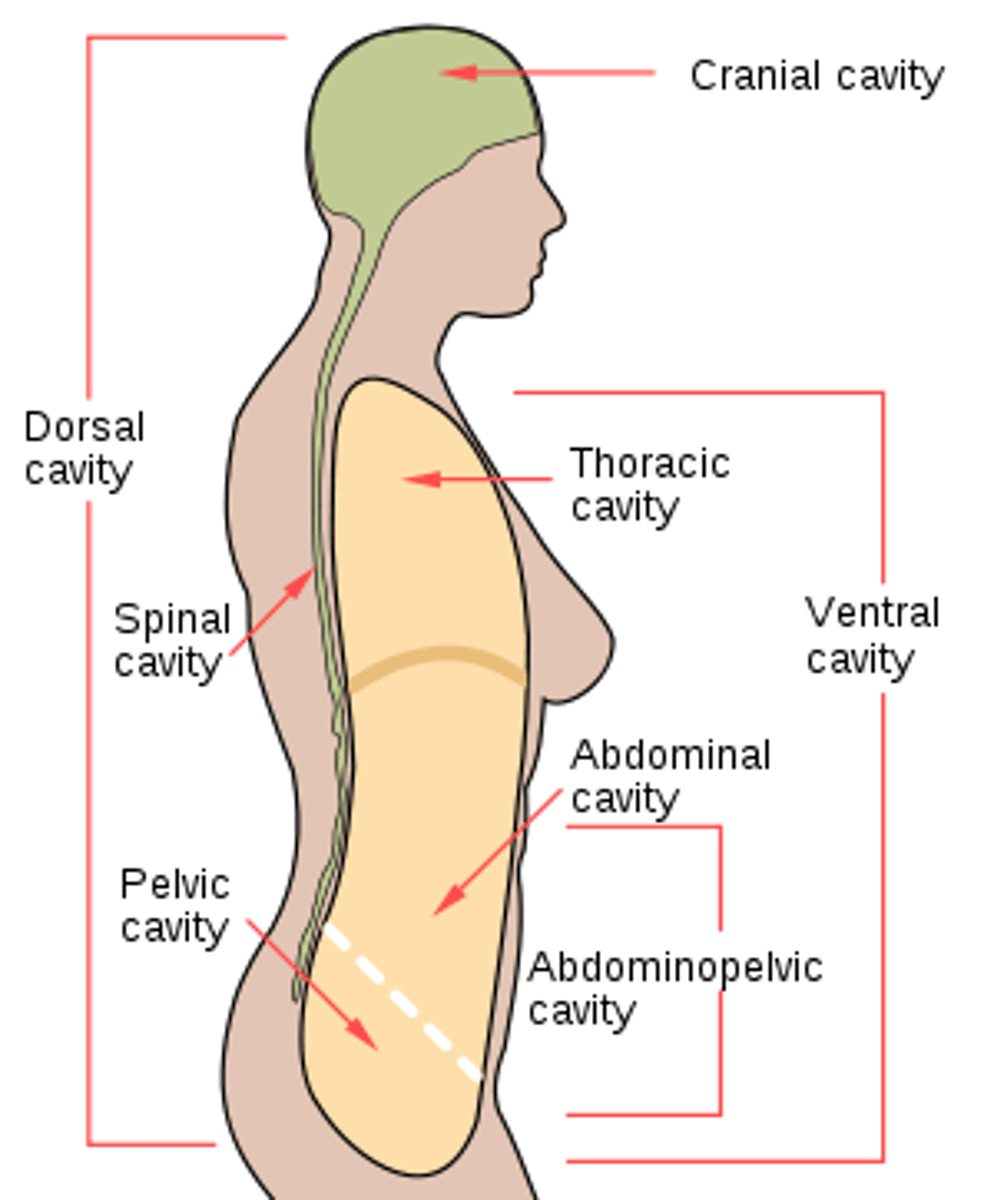
List body cavities from head to toe.
1. cranial
2. thoracic
3. abdominal
4. pelvic
List some common breathing emergencies.
- choking
- illnesses
- asthma
- electrocution
- shock
- drowning
- heart attack
- allergic reactions
- drugs
- emphysema
- bronchitis
- croup
- hyperventilation
Define asthma - bronchoconstriction
a condition that narrows the breathing passages and makes it difficult to breathe, caused by a spasm of the muscle lining in the bronchi and excess mucus.
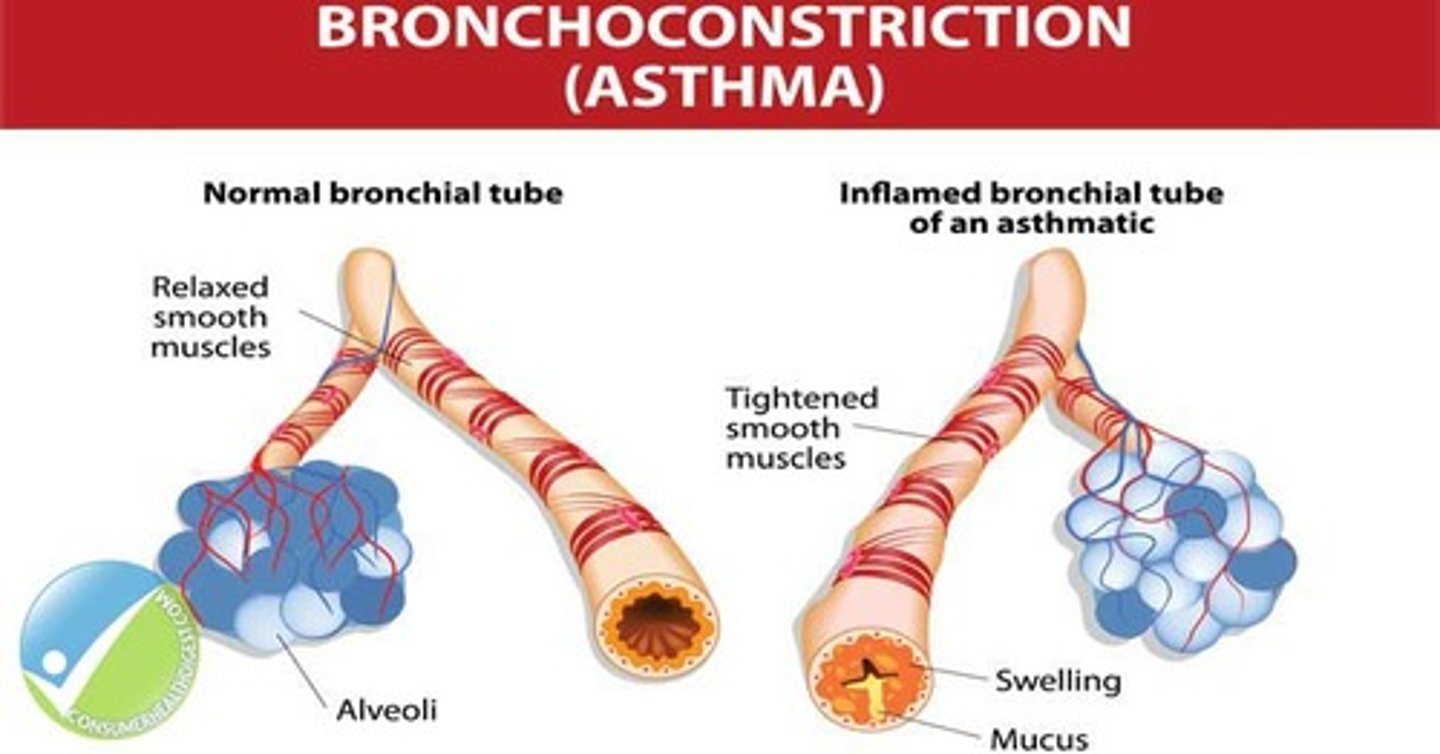
List the signs and symptoms of asthma.
- wheezing
- difficulty breathing
- painful breathing

List the treatments for asthma.
- medications (inhaler, etc.)
- fresh air
Define bronchitis.
a disease resulting in inflammation of the lining of the trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles.
List the signs and symptoms of bronchitis.
- persistent cough
- chest tightness
- difficulty breathing
List the treatments for bronchitis.
- antibiotics
Define anaphylactic shock.
a severe allergic reaction that can restrict and swell a person's chest cavity and cause death.

List the causes of anaphylactic shock.
- insect stings
- certain foods
- medication
List the symptoms of anaphylactic shock.
- chest tightness
- swelling of throat, face, and neck
- difficulty breathing
- dizziness
- confusion.
-hives (urticaria)
List the treatments for anaphylactic shock.
- injection of epinephrine - epi-pen, followed by the activation of EMS
Define croup.
a common viral illness in children that causes swelling of the tissues around the vocal cords, characterized by a "seal bark" type of cough.
List the treatments for croup.
- fresh cool air
- steamy bathroom
Define epiglottitis.
a bacterial infection that causes severe inflammation of the epiglottis.
What are the signs of epiglottitis?
- appear ill
- fever
- sore throat
- the need to sit up in order to breathe
- drooling
- difficulty swallowing
What are the treatments for epiglottitis?
- antibiotics
Define hyperventilation.
occurs when breathing is faster than normal, imbalance of oxygen and carbon dioxide, occurs in nervous people, people who are in shock and tense.
List the treatments for hyperventilation.
- relax the victim, rebreathe air in paper bag
Describe general respiratory distress care.
Call 911.
Help victim rest comfortably.
Monitor ABC's (airway, breathing, and circulation).
Keep victim from overheating or chilling.
Assist victim in taking medications.
Respiratory distress can lead to _____.
respiratory arrest, body system deterioration, cardiac arrest, or death.
List the two types of choking.
anatomical - soft tissue - tongue
mechanical - food or small objects
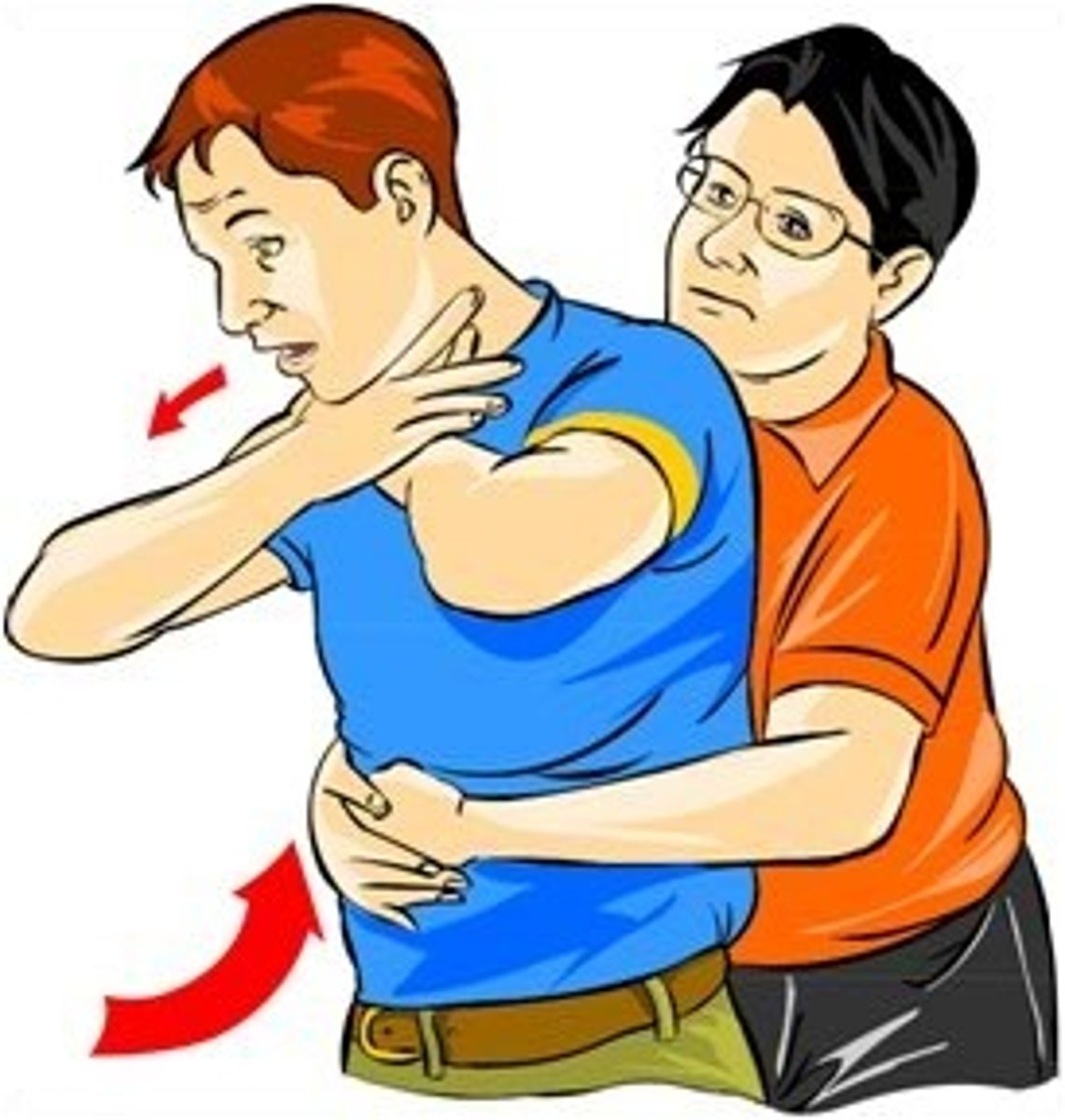
Describe the techniques used to stop choking.
(Heimlich maneuver)
Adult and child - abdominal thrusts till object is expelled / if person becomes unconscious - call 911and continue with chest compressions and check mouth
Infant - 5 back blows and 5 chest thrusts
List the symptoms of a heart attack.
- chest pain
- chest heaviness
- pale skin
- weak pulse
- nausea
- vomiting
- pain radiating to left arm
- indigestion
- shortness of breath
- sweating

Describe proper heart attack care.
Call 911.
Rest victim in comfortable position.
Give victim nitroglycerin under tongue if patient has it.
Give aspirin like bayer aspirin or baby aspirin
Monitor ABC's (airway, breathing, and circulation).
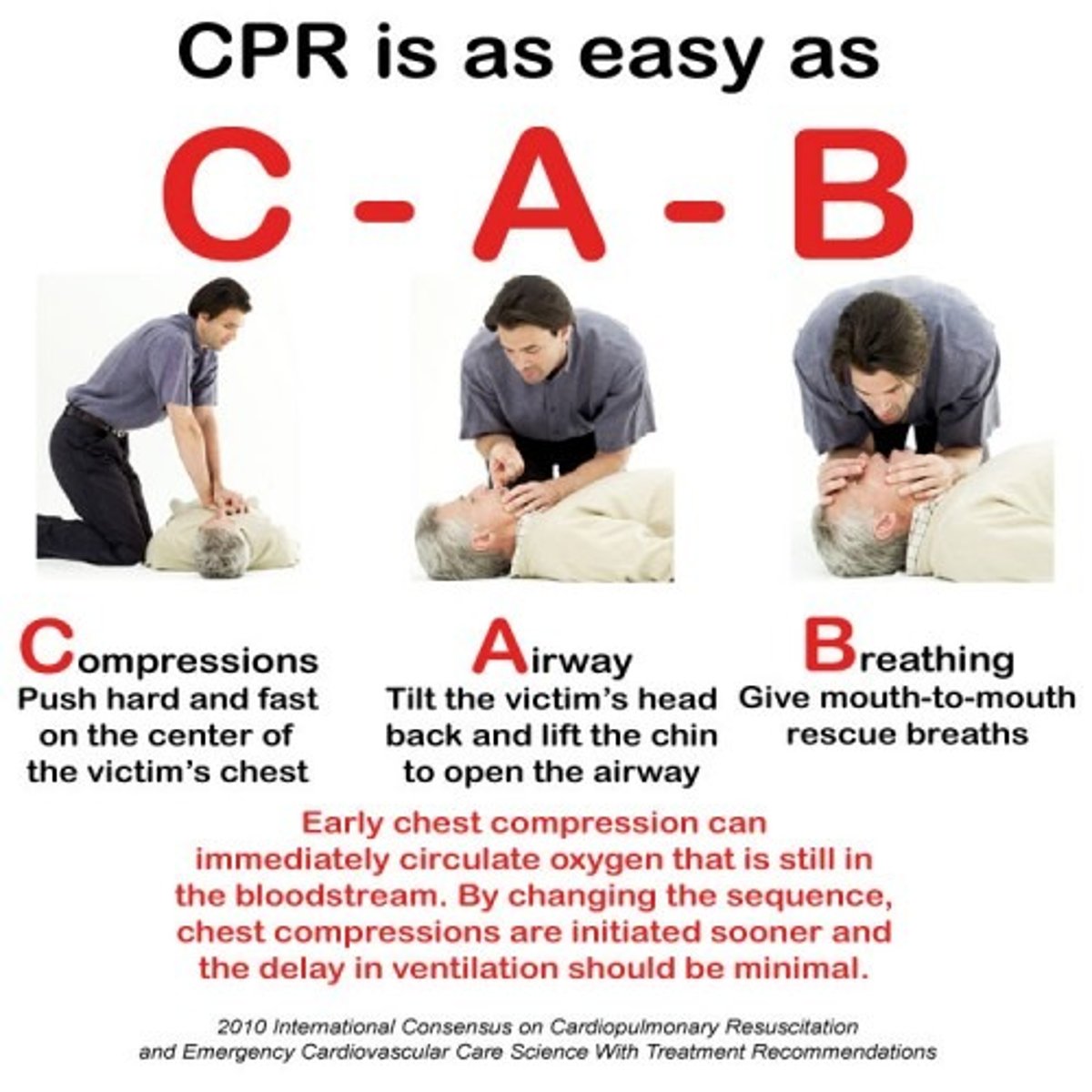
Describe adult CPR (cardiopulmonary resuscitation). guidelines. - 1 and 2 person
No change in compression/breath ratio - 30:2
2 persons - one does 30 compressions and other gives 2 breaths uses bag/mask using the E-C clamp technique
CAB - compression, airway, breathing. 2 hands on middle of chest lower half of sternum
- compress 2 inches
- 30:2 compression to breaths ratio
- 5 cycles in 2 minutes.
-100/120 compressions minute - push hard and fast
- same for one and two person CPR
Describe child CPR guidelines. 1 -person
- 1 or two hands on chest
- rescue breathing rate is one every 3 seconds
- compress 2 inches
- 5 cycles in 2 minutes. Change partner 2 minutes.
- 30:2 compression to breaths ratio
-100/120 compressions minute
- one person CPR
Describe infant CPR guidelines. - 1 person
- 2 fingers on sternum below nipple line
- rescue breathing rate is one every 3 seconds
- mouth covers over mouth and nose during rescue breathing
- compress 1 1/2 inch inches
- 5 cycles in 2 minutes. Change partner 2 minutes.
- 30:2 compression to breaths ratio
-100/120 compressions minute
- one person CPR
Describe the adult chain of survival.
- early activation of EMS
- early CPR
- rapid defribrillation
Turn on AED, PADS, Clear, Charge, Shock
- advanced life support
- post-cardiac arrest care
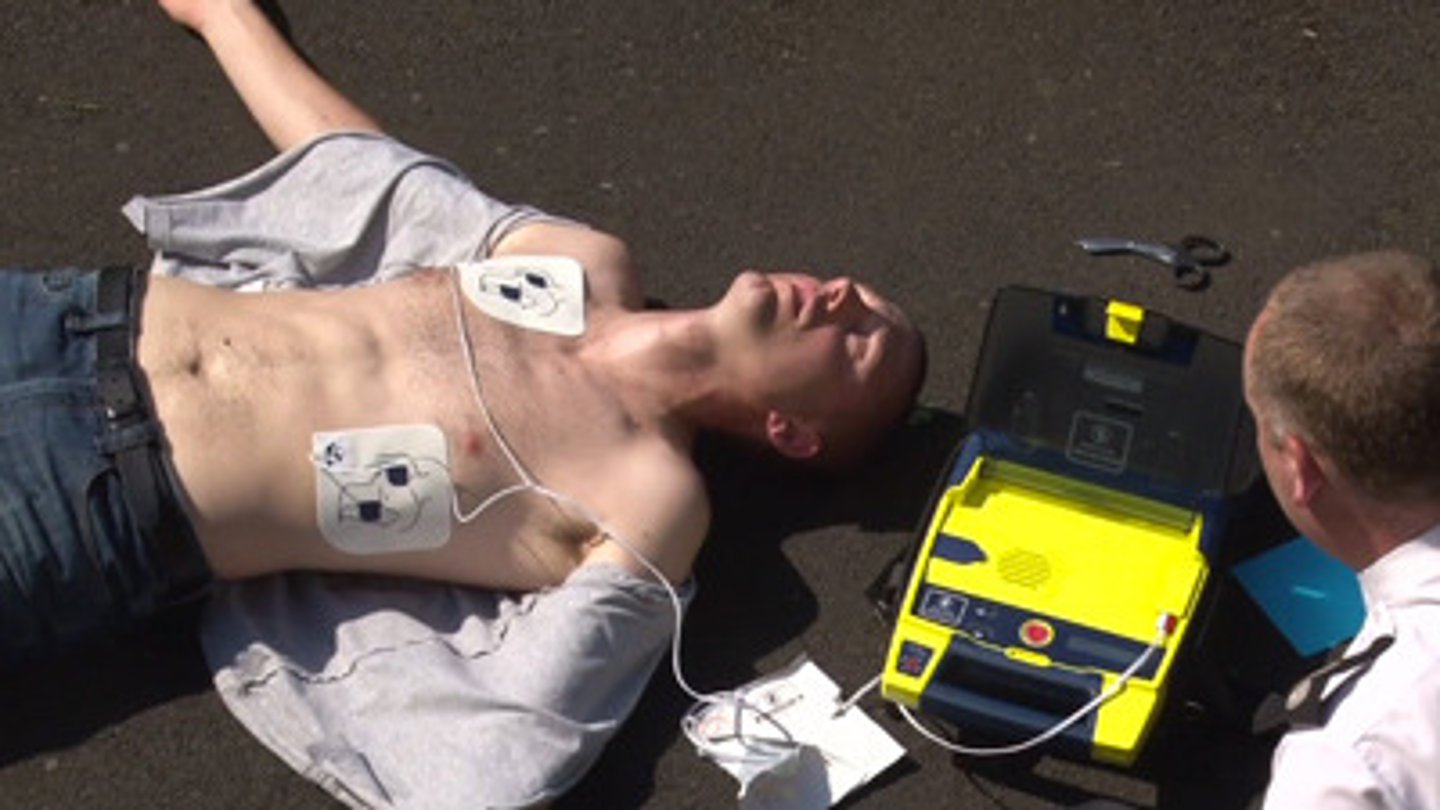

For child and infant CPR with 2 persons - 15:2
2 persons - one does 15 compressions and other gives 2 breaths uses bag/mask using the E-C clamp technique
- hand placement as above for child
- infant - 2 hands encircling the chest
- 15 compressions to 2 breaths ratio 15:2
- 100/120 compressions minute - push hard and fast
When do you stop CPR?
The rescuer should try not to stop. However, he or she may if:
- he or she becomes so exhausted they cannot continue
- someone of equal or greater training comes to take over - EMT
- his or her personal safety is in danger (as in the scene is not safe)
- the victim is pronounced dead by a medical doctor
List some of the causes of cardiac arrest.
- drugs
- respiratory arrest
- drowning
- electrocution
- weak heart
- suffocation
- firearm injuries
- poison
- genetic history factors
Define clotting.
process which blood thickens at a wound site to seal a hole or tear and stop bleeding.
Define direct pressure.
pressure applied on a wound to control bleeding
Define hemorrhage.
loss of a large amount of blood in a short period of time. If a limb is bleeding, a tourniquet can be applied.
List the signs of internal bleeding.
- discoloration
- tenderness
- swollen, hard tissues
- anxiety
- restlessness
- rapid breathing
- cool, moist, pale skin
- nausea
- vomiting
- excessive thirst
- declining level of consciousness
Describe proper closed wound.
Apply direct pressure.
Apply cold pack.
Call 911 if severe.
Describe minor open wound care.
Wash out.
Apply sterile dressing with direct pressure.
Apply antibiotic ointment.
Describe major open wound care.
DO NOT WASH.
Apply clean dressing with direct pressure - do not press on bone
Bandage.
Call 911.
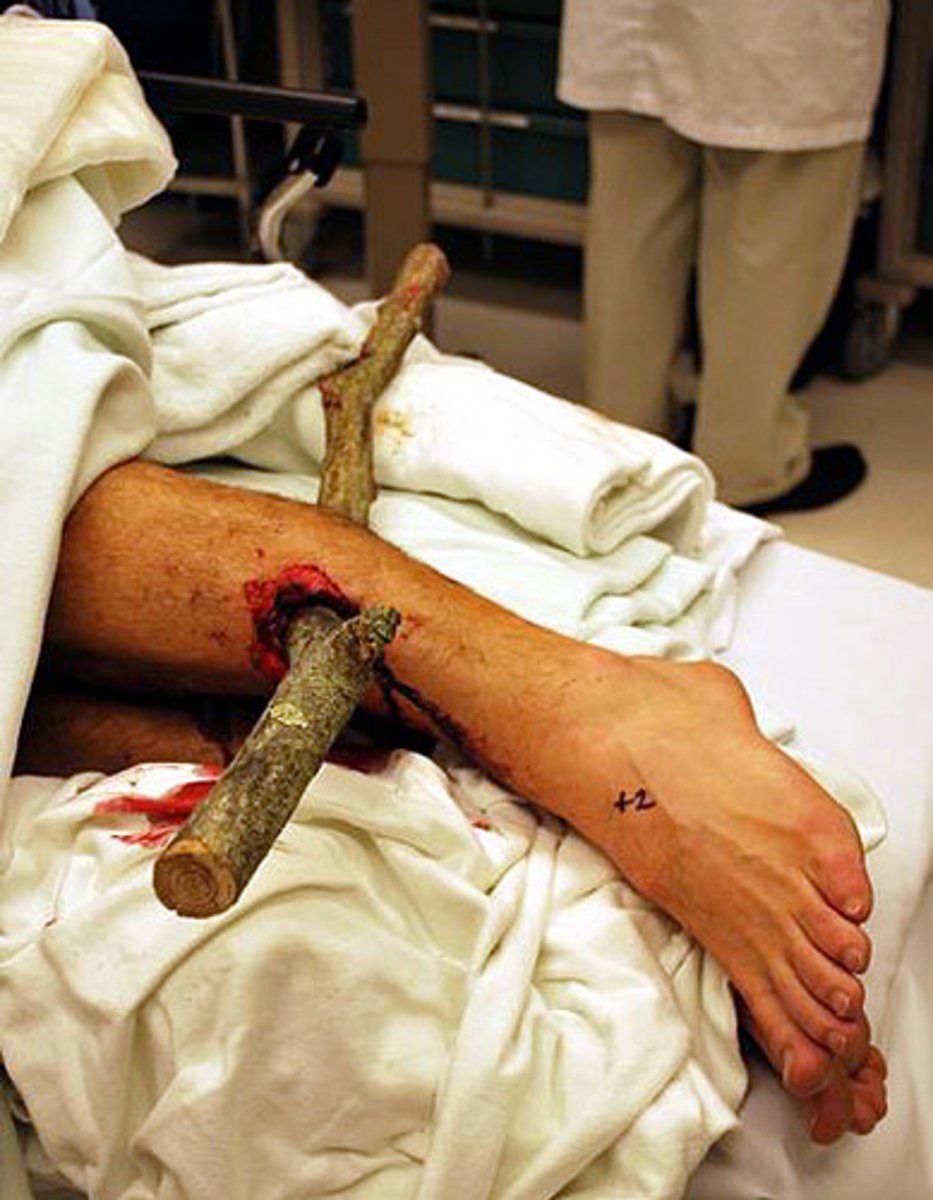
Describe care given for wounds caused by embedded objects.
Do NOT remove object unless it is preventing breathing.
Use bulky bandages around the object to support and minimize bleeding.
Be careful not to further push in or move object.
Control bleeding.
Call 911.
List some of the causes of burns.
- heat
- chemicals
- electricity
- solar radiation. - sun
List the signs and symptoms of first degree burns. (superficial)
- red, dry skin
- area is painful
- area is swollen (superficial)
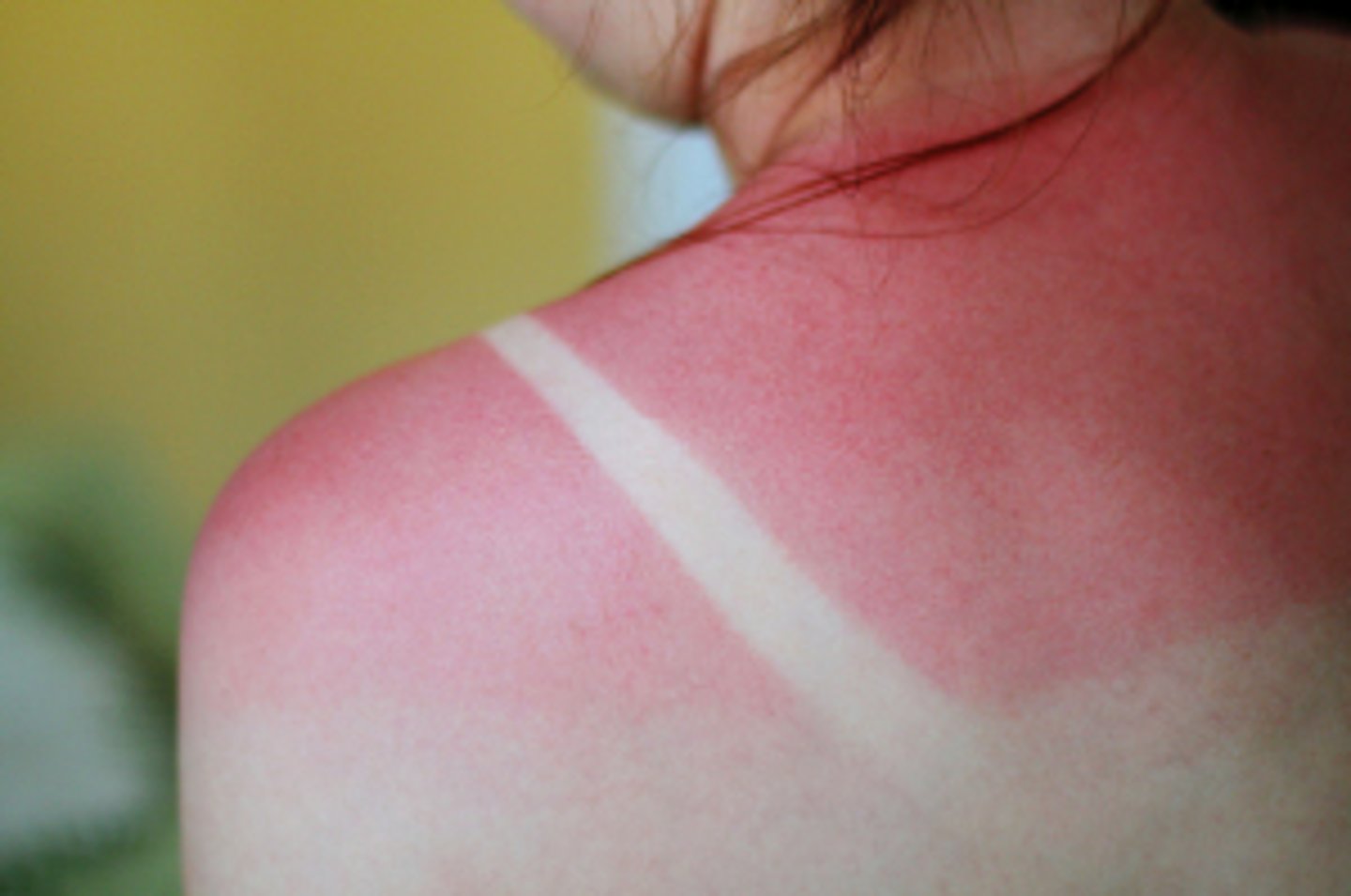

List the signs and symptoms of second degree burns. (Partial thickness)
- red, wet, skin
- open and closed blisters
- skin spotted and blotchy
- area is painful
- area is swollen
- area is deep
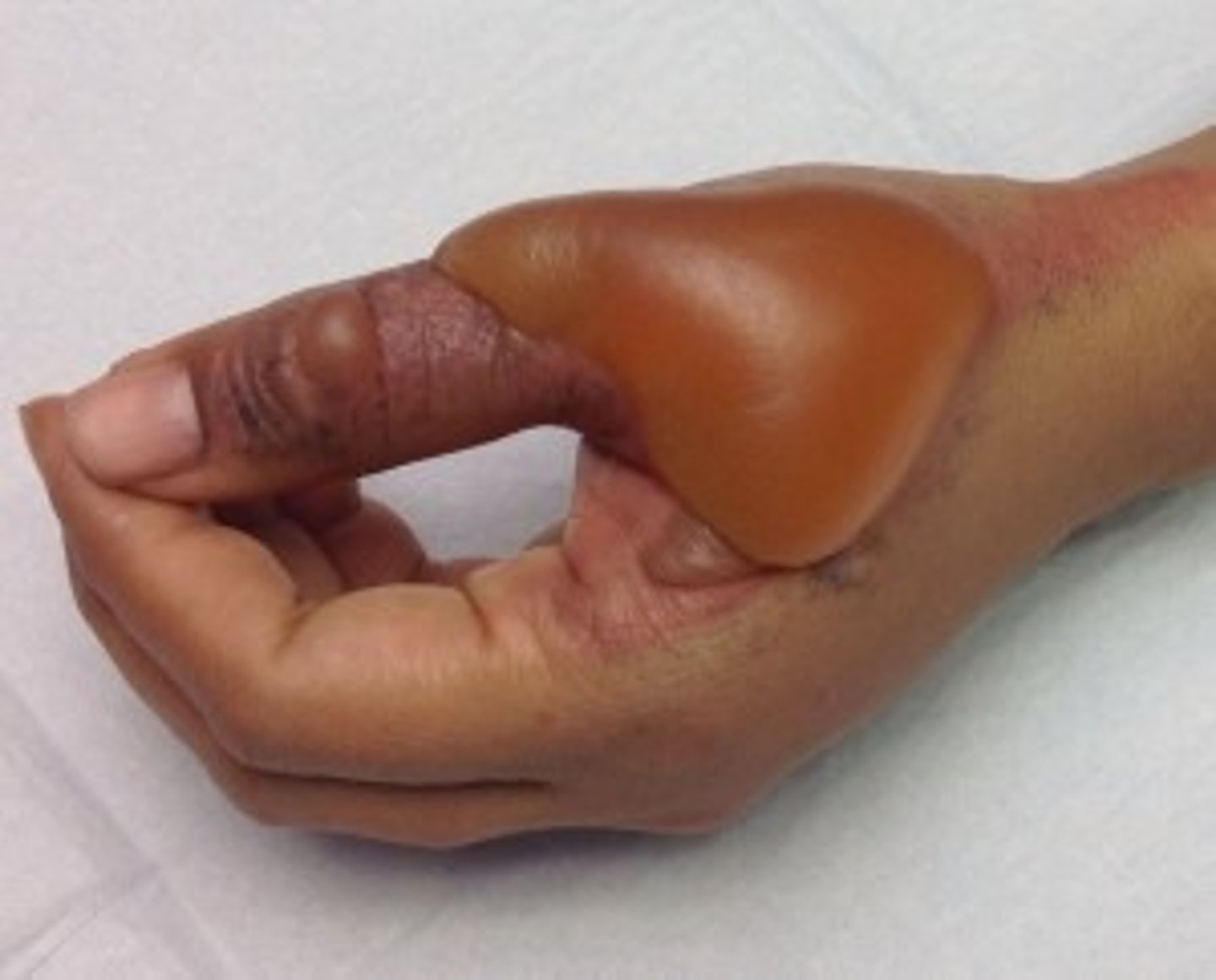
List the signs and symptoms of third degree burns. (full thickness)
- brown or charred skin
- tissue underneath appear white
- may not feel pain
may be life threatening
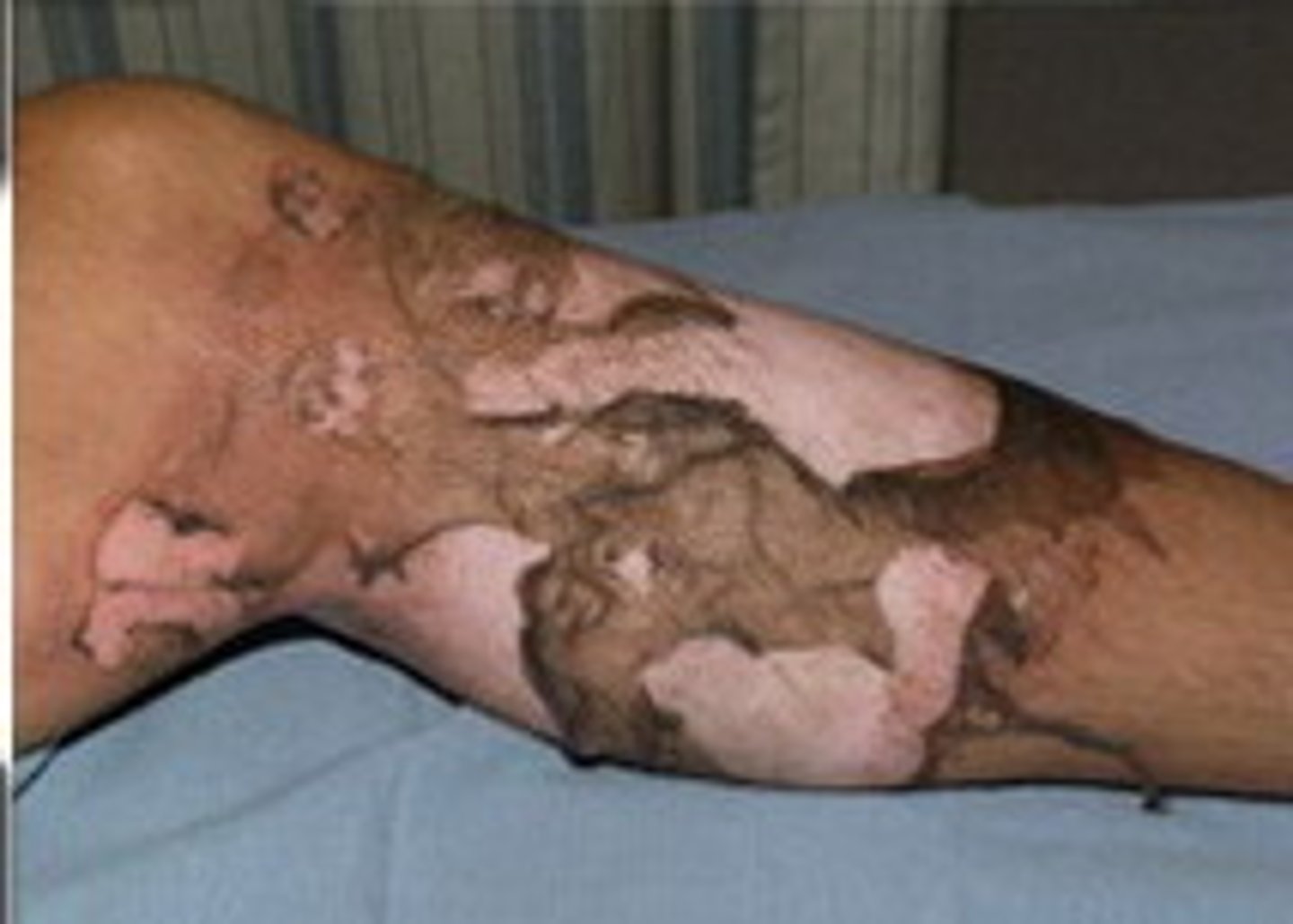
List the critical burn locations.
- face
- hands
- feet
- genitals
- airway
Describe proper burn care.
Stop burning process (extinguish fire).
1st degree or mild 2nd - Cool the burned area with cool water or cool cloths. Cover with non-stick dressing - if c/o pain, continue more cool water
Severe 2nd and 3rd degree - do not use water Cover the burned area with a nonstick bandage. Do not remove stuck clothing.
Minimize shock.
Call 911 if third degree burn.
Describe Rocky Mountain spotted fever.
a serious tick borne disease caused by wood or dog ticks
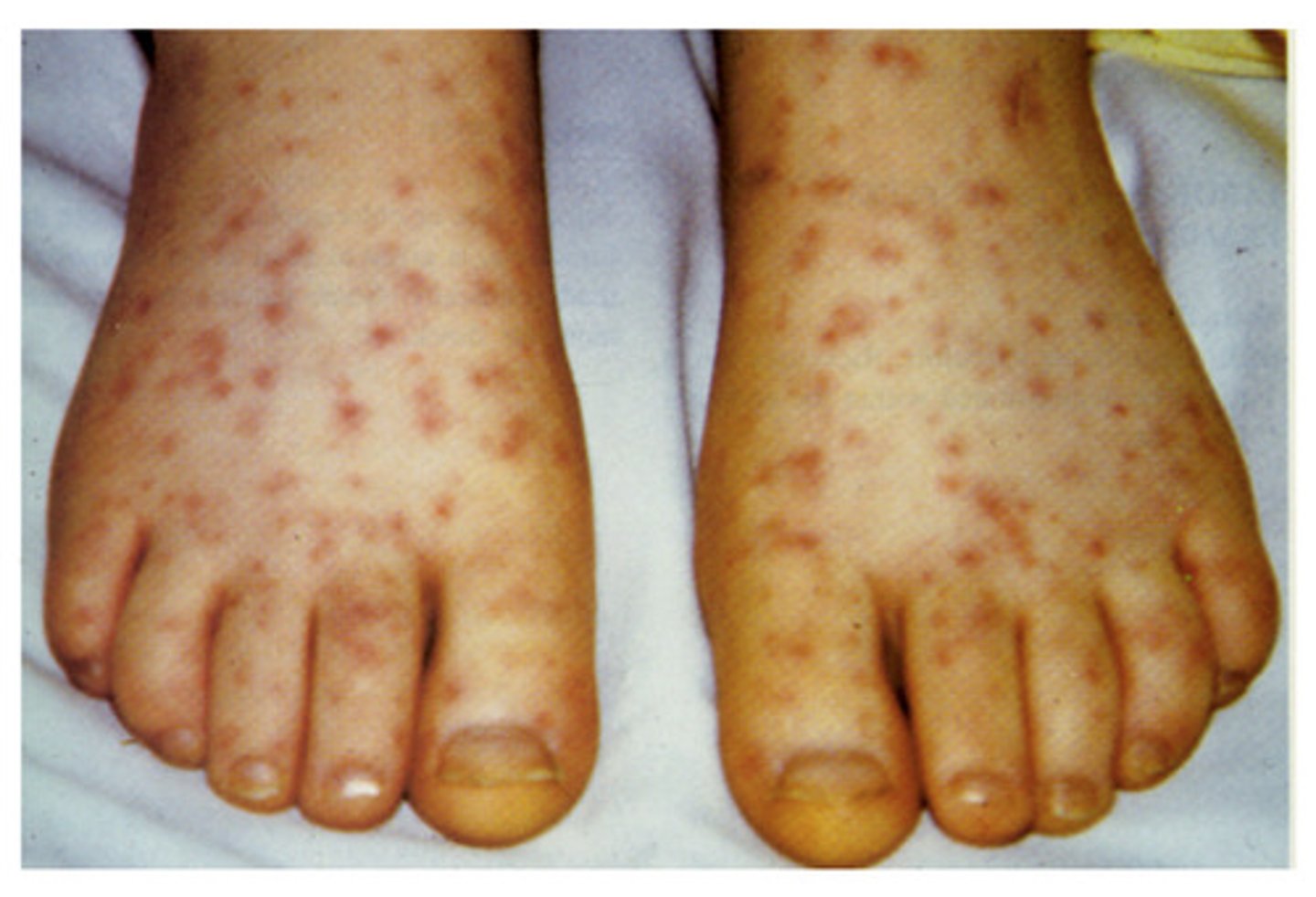
List the signs and symptoms of Rocky Mountain spotted fever.
- spotted rash on ankles or wrists that spreads
- fevers
- chills
- severe headaches
- joint and muscle aches.
early treatment is important because victim could die of kidney failure
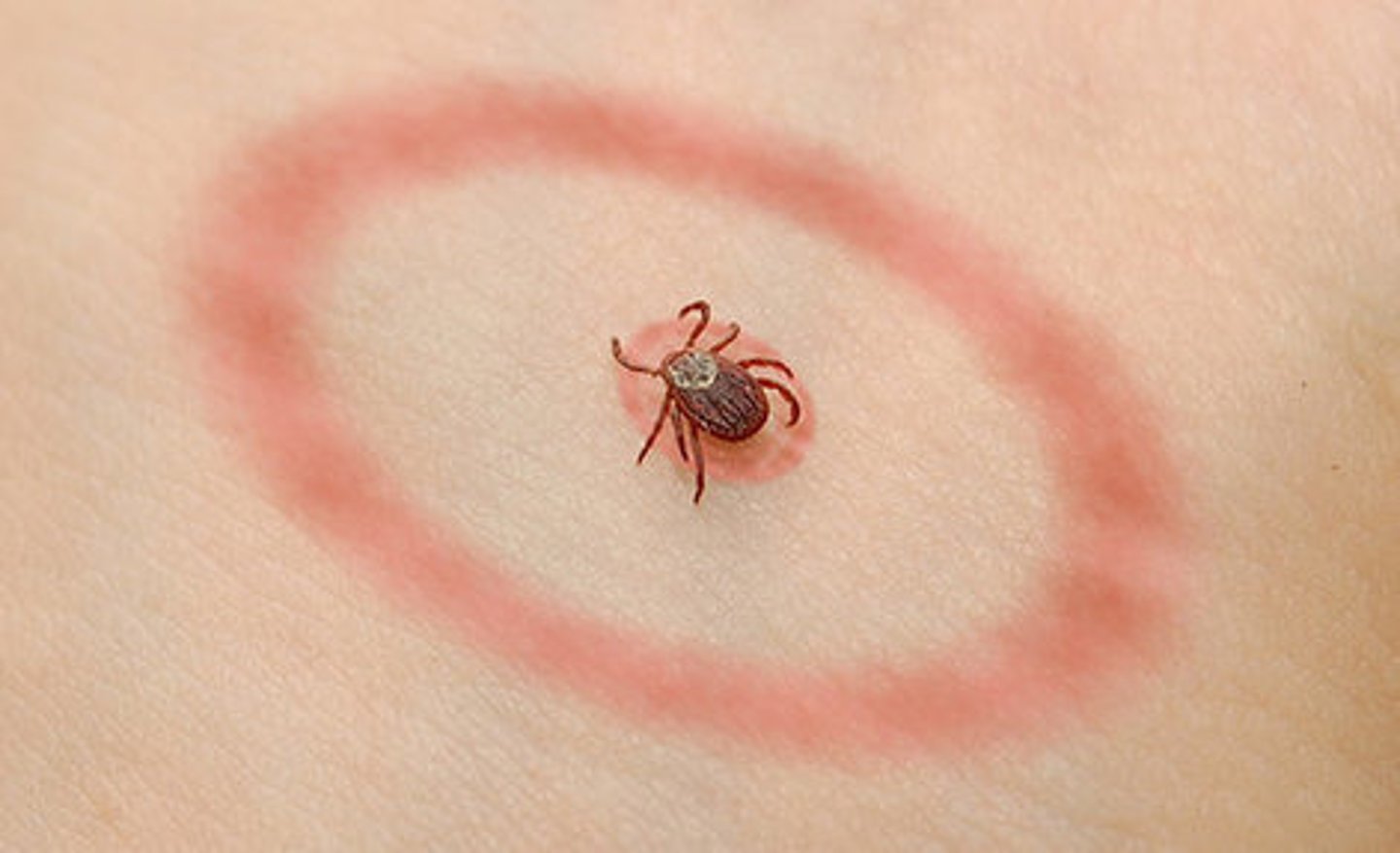
List the signs and symptoms of Lyme disease.
- tick bite
- red rash (with bull's eye appearance)
- fevers
- chills
- headaches
- fatigue
- flu-like symptoms
contracted by deer ticks

List the signs and symptoms of stings and bites.
- stinger present
- bite marks
- pain
- local swelling
- rash
- hives
- nausea
- difficulty breathing
- itchiness
Describe proper care for stings and bites.
Remove stinger by scraping with fingernail or credit card. Only use tweezers with ticks.
Wash wound and cover with bandage.
Apply ice.
Watch for allergic reactions.
Use epi-pen if person has
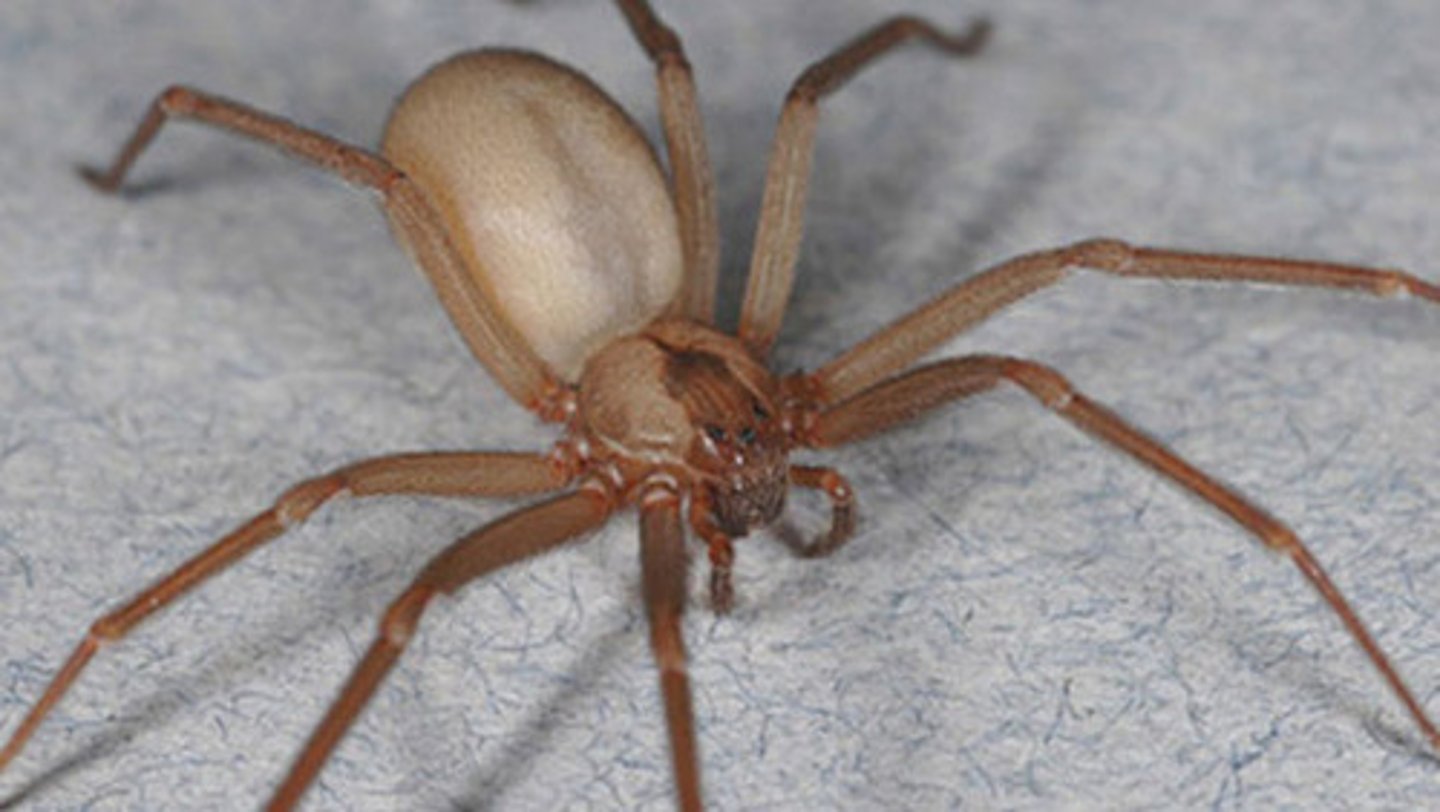
List the signs and symptoms of spider bites.
- bite marks
- sharp pain (black widow)
- swelling and blistering (brown recluse)
- pain
- cramping
- nausea
- vomiting
- difficulty breathing / swallowing
- sweating
- irregular heartbeat

Describe proper care for spider bites.
Call 911 as soon as possible.
Antivenin will be needed
List the signs and symptoms of snake bites.
- fang bite marks
- pain
- burning
- swelling
- tingling
- numbness
Describe proper care for snake bites.
Wash.
Apply ice and immobilize the body part.
Call 911.
Antivenin will be needed if pit viper bite