Module 5.1
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What is gene therapy or delivery?
Gene therapy is an experimental technique that uses genes to treat or prevent disease.
What approaches to gene therapy are researchers currently testing?
Gene replacement
Gene silencing
Gene addition
Gene editing
What are some applications of gene delivery to tissue engineering??
Helping to protect the engineered tissue
Providing stimuli for the engineered tissue to grow and/or differentiate
Why do gene therapy?
Can be more efficient
less expensive
long lasting
therapeutic applications
What are some of the ethical considerations for using gene therapy?
How can “good” & “bad” gene therapy uses be distinguished?
high costs may limit access mainly to wealthy
What are some of the most expensive gene therapies?
Lenmeldy
Skysona
zynteglo
How does gene therapy deliver new genetic material into cells?
It uses vectors—often modified viruses—that naturally enter cells. Their own genes are removed and replaced with the engineered therapeutic gene.
What are viral and non-viral methods of gene delivery?
Viral use:
retroviruses
lentiviruses
adenoviruses
Non-viral delivery
mechanical
electrical
chemical
Compare viral vs. non-viral delivery
Viral delivery:
cost: several fold higher
time: > month
transfection efficiency: > 90%
Non-viral delivery:
cost: low
time: 1 week
transfection efficiency: 1-90%
What are the methods of non-viral delivery?
Mechanical: microinjection
electrical: in vivo/vitro electroporation
chemical: calcium phosphate, protein, other polymers
What are the some common used gene delivery methods?
electroporation
liposomes
calcium phosphate
gold bullets
human artificial chromosomes
What are some physical methods of delivery and there challenges?
direct injection into nucleus - manually injecting is impractical
electroporation - very delicate optimization of power/frequency
ballistic particle delivery (gene gun) - bombard cell w/ nucleotides at high velocity. can physically damage cells
What are the properties of cationic polymers and its advantages?
Properties:
contain positive charged groups
formation of polyplexes w/ dna
Advantages:
relatively inexpensive
ability to incorporate ligands
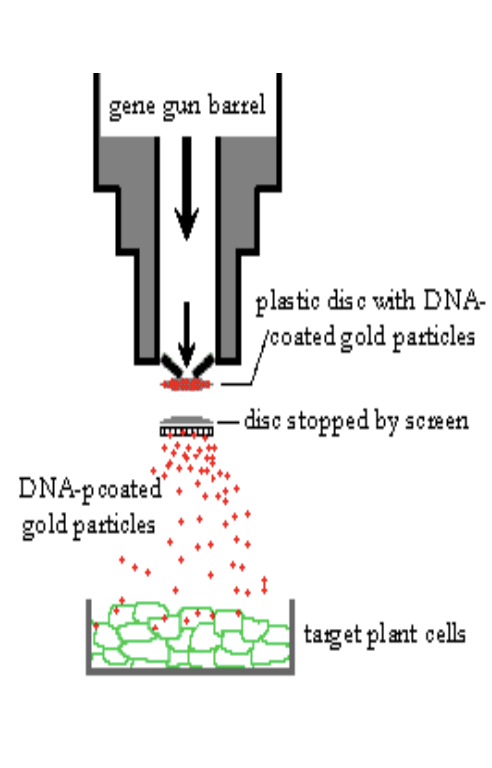
How does the gene gun work?
Gold or Tungsten particles are coated with DNA
• The DNA-coated particles are placed on the end of a plastic bullet
• The plastic bullet is placed in the gene gun
• The target tissue is placed at the end of the barrel • An explosive charge /air pressure propels the particle bullet forward
• The DNA-coated particles are released and strike the target tissue
What are some electroporation based technologies & treatments
cell fusion
biotechnology
electrochemotherapy
transdermal drug delivery
What are the 4 major problems w/ gene therapy?
short-lived of gene therapy - very hard to achieve any long-term benefits w/o integration & even w/ it.
immune response - reduces gene therapy effectiveness
problems w/ viral vectors - fears that viral vector may recover disease-causing ability
multigene disorders - common diseases are caused by combined effects of variations in many genes
How is gene therapy different for different diseases?
Gene transplantation (to patient w/ gene deletion)
Gene correction (to revert specific mutation in the gene of interest)
Gene augmentation (to enhance expression of gene of interest)
Targeted killing of specific cells by introducing killer gene
Gene ablation - targeted inhibition of gene expression
What are the pros and cons of reto/lenti vectors
pros:
stable gene transfer in vitro
cons:
retroviral vectors primarily transduce diving cells
lentiviral vectors transduce dividing and non-dividing cell
insertional mutagenesis/oncogneic potential
What are adenoviruses and problems with adenoviral vectors?
Adenoviruses are non-enveloped viruses containing a linear doube stranded DNA genome.
Problems:
cannot integrate w/ the host cell genome
expression from adenoviral vectors is transient (5-10 days)
What are the key features of adeno-associated virus (AAV)
AAV can infect both dividing & quiescent (non-dividing) cells
it does not stimulate inflammation in the host
does not elicit antibodies against itself
can enter non-diving cells
What are the desired features of viral vectors for in vivo gene therapy?
Efficiency
stability
low immunigenicity/toxicity
How would you treat huntingtons disease?
Using uniQure AMT-130, where it uses AAV vectors to deliver micro-RNAs directly to the brain fro non-selective knockdown of the huntington gene.
What are the challenges in gene therapy?
Immume response (Gelsinger death)
Disrupting important genes in target cells
Commercial viability (developing a new therapy is expensive