Ramp Function (Part-I)
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Time-Scaling Property of the Unit Impulse
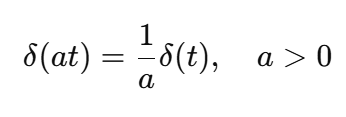
Rectangular Pulse Approximation of the Impulse
The unit impulse δ(t) is the limit of a rectangular pulse with:
Duration Δ → 0
Amplitude 1/Δ
Constant area equal to 1
Impulse Strength
The strength of an impulse is defined by the area under it.
An impulse aδ(t) has strength a
Impulse as a Test Signal
The impulse function is used to probe system behavior because the system response to an impulse reveals its natural (transient) characteristics.
Impulse Response
The output of a system when the input is a unit impulse is called the impulse response.
Parallel LRC Circuit Driven by an Impulse
An impulsive current input causes an instantaneous change in capacitor voltage because the capacitor acts as a short circuit at t = 0
Instantaneous Voltage Change Due to Impulse For an Impulse Current I0δ(t)
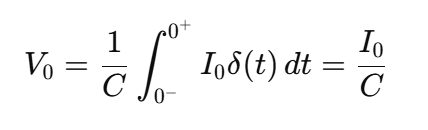
Transient Response
The portion of a system response that exists after the impulse input has ended is called the transient response.
Duality of Series and Parallel LRC Circuits
Series and parallel LRC circuits are duals when their governing equations for current and voltage have identical mathematical forms.
δ(-t) = δ(t)
Unit Impulse as an Even Function
Sifting Property of the Unit Impulse
The impulse extracts the value of a function at a specific time:
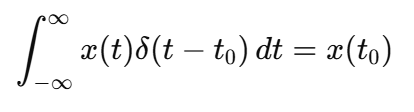
Time-Shifted Impulse
A shifted impulse δ(t - t0) occurs at time t = t0 and and samples the signal at that instant.
δ(t) = [d/dt]u(t)
Derivative of the Unit Step
The unit impulse is the derivative of the unit step
Integral of the Unit Impulse
The unit step function is the integral of the unit impulse:
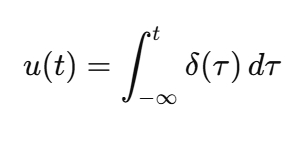
Derivative of the Unit Impulse (Doublet)
The first derivative of the impulse is called a doublet, denoted δ^(1) (t)
Integral of the Doublet
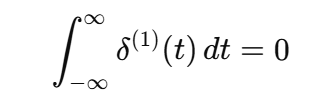
Sifting Property of the Doublet
The doublet extracts the derivative of a function:
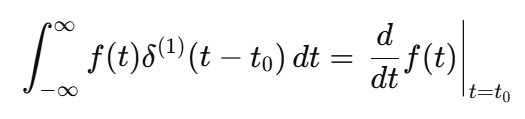
Higher-Order Derivatives of the Impulse
The n-th derivative of the impulse is denoted δ^(n) (t)
Generalized Sifting Property
For the n-th derivative of the impulse:
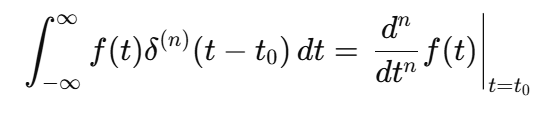
Ramp Function
A signal that increases linearly with time after t = 0.
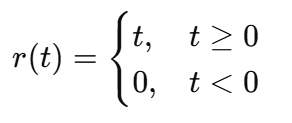
r(t) = t u(t)
Ramp Function Using Step Function
Discrete-Time Ramp Function
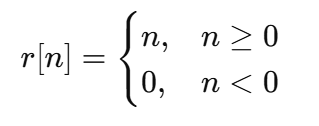
Step Function
What is the derivative of a ramp function?
Impulse Function
What is the derivative of a step function?
Step Function
What is the integral of an impulse function?
Ramp Function
What is the integral of a step function?