Citric Acid Cycle
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
purpose of the citric acid cycle
oxidize the acetyl group of acetyl CoA from pyruvate to CO2 and generate high energy carriers
how many nadh is produced per turn
3 nadh
how many fadh2 is produced per turn
1 fadh2
how many gtp is produced per turn
1
where does glycolysis take place
cytoplasm
where does the citric acid cycle take place
mitochondrial matrix
where does the ETC take place
inner mitochondrial membrane
how is CO2 released
when pryuvate is turned into acetyl CoA
The formation of isocitrate
The formation of alpha-ketoglutarate
pyruvate dehydrogenation rxn
pyruvate + CoA + NAD+ —> acetyl CoA + CO2 + NADH + H+
irreversible
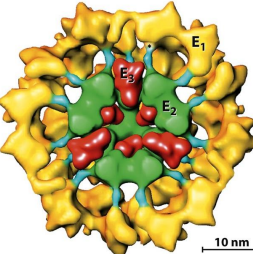
components of pyruvate dehydrogenase
E1, E2, E3
TPP, FAD, NADH, and lipoic acid are all used as cofactors to load an an acetyl unit from pyruvate onto CoA for initiation of the citric acid cycle
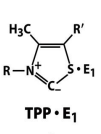
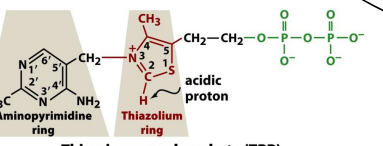
role of TPP
decarboxylation of alpha keto acids
role of lipoic acid
redox and acyl transfer co factor
role of CoA-SH
acetyl carrier
role of FAD
reoxidies to make lipoamide
role of NAD+
final electron acceptor
mechanism in pyruvate dehydrogenation rxn decarboxylation
pyruvate loses CO2, when bound to TPP, forming a hydroxyethyl TPP intermediate
mechanism in pyruvate dehydrogenation rxn acyl transfer
the hydroxyethyl group is oxidized and transferred to lipoamide, forming acetyl lipoamide
mechanism in pyruvate dehydrogenation rxn reduction
lipoamide is reduced by FAD
citrate synthease rxn
Acetyl CoA + oxaloacetate + H2O —> citrate + CoA-SH
is the formation of citrate favorable
yes; it is pushed in the forward direction
mechanism of citrate synthase part 1
oxalacetate binds first, inducing a confirmational change
mechanism of citrate synthase part 2
forms a pocket for acetyl CoA, and generates an enolate anion
acontinase
isomerizes citrate to isocitrate
why is citrate isomerized into isocitrate
citrate is a tert alcohol a poor substrate for oxidation but isocitrate is a good substrate for this.
step1 of citrate to isocitrate
elimination to cis aconitate
step2 of citrate to isocitrate
rehydration to isocitrate (adding water)
what catalyzes the conversion of citrate to isocitrate
4Fe-4S cluster to orient substrate and mediate water release and addition.
isocitrate dehydrogenase
converts isocitrate to alpha ketoglutarate releasing CO2 and generating NADH
alpha ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
converts alpha keto glutarate into succinyl CoA producing another NADH and releasing CO2
succinyl CoA synthase rxn
succinyl CoA + GDP + Pi —> Succinate + GTP + CoASH
near equillibrium
succinyl CoA synthase rxn mechanism
High energy thioester drives phosphorylation of a histidine residue forming a phosphohistidine intermediate. phosphate is then transferred onto GDP via an SN2 mechanism
succinate dehydrogenase (SDH)
oxidizes succinate to fumarate forming FADH2
fumarase
hydrates fumarate to maltate
malate dehydrogenase
oxidizes malate producing oxalacetate generating NADH
pulled forward by rapid consumption of oxaloacetate in citrate synthase step.
forward determining steps
formation of citrate - citrate dehydrogenase
formation of alpha ketoglutarate- isocitrate dehydrogenase
formation of succinyl CoA- alpha ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
structure of pyruvate dehydrogenase
structure of acetyl CoA

structure of TPP+ E1
structure of of lipoamide
structure of TPP
structure of acetyldihydrolipoamide E2 complex
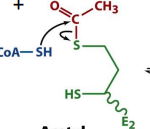
structure of dihydrolipoamide E2
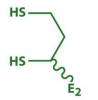
structure of oxaolactetate
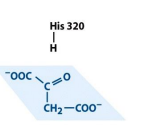
structure of citrate
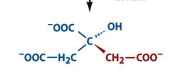
structure of cis aconitase
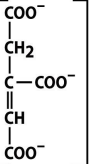
structure of isocitrate

oxalsuccinate
intermediate before forming alpha ketoglutarate in citric acid
structure of oxalsuccinate
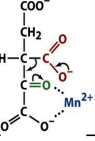
structure of alpha ketoglutarate
structure of succinyl CoA
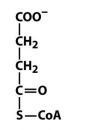
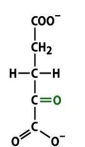
structure of succinate
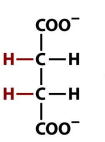
structure of fumarate
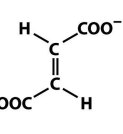
structure of maltate
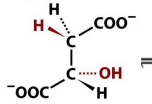
what protein allows for the thioesterfication of PDC
cysteine
lipoamide
area where thioesterification happens to facillitate acetyl co a formation and this has to be regenerated
fumarate to maltate has what type of intermediate
carb anion