BIOS 450 Microbial Fermentation
1/172
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This set of flashcards covers key concepts related to microbial fermentation, its processes, and the types of products generated.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
173 Terms
What are fermentations in microbial metabolism?
are anaerobic metabolisms where microbes balance redox and conserve energy by producing fermentation products, without needing external electron acceptors
How do fermentations conserve energy?
substrate-level phosphorylation reactions
What types of fermentation products are commonly produced?
alcohols (like ethanol and isopropyl alcohol), organic acids (like acetic and lactic acid), and gases (like CO2 and H2).
What differentiates fermentation from anaerobic respiration?
Fermentation occurs in the absence of usable terminal electron acceptors and uses substrate as both electron donor and acceptor, while anaerobic respiration uses external electron acceptors.
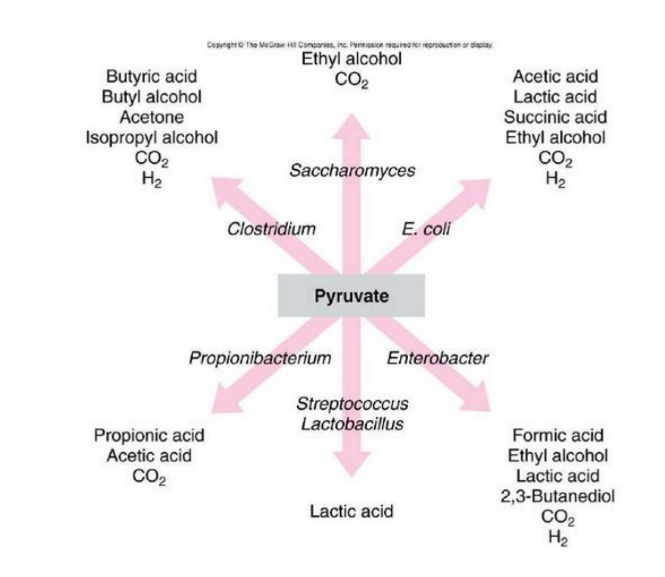
What is the role of pyruvate in fermentation?
In fermentation, pyruvate is reduced to various fermentation products, which are then excreted.
What products can be made from pyruvate?
Pyruvate can be converted into fermentation products such as ethanol, lactic acid, and various organic acids depending on the microorganism and conditions.
What are the pyruvic products from Clostridium?
Butyric acid, Butyl alcohol, acetone, isopropyl alcohol, CO2, H2
What are the pyruvic products from Saccharomyces, and what are they used for?
Ethanol and carbon dioxide. Ethanol is commonly used in alcoholic beverages and as a fuel source, while carbon dioxide is utilized in baking and beverage carbonation.
What are the pyruvic products from E.coli and what are they used for?
Ethanol, CO2, H2 and mixed acids such as acetic acid, succinic acid, formic acid, lactic acid. They are used in biofuel production, food preservation, and fermentation processes and flatulence
What are the pyruvic products from Enterobacter?
Formic acid, ethyl alcohol, lactic acid, 2-3-butanediol, CO2, H2
What are the pyruvic products from Streptococcus and Lactobacillus? What are they used for?
Lactic acid, CO2. They are used in yogurt and fermented dairy products and our own muscles
What are the pyruvic products from Propionibacterium, and what are they used for?
Propionic acid, acetic acid, CO2, and hydrogen gas. They are used in cheese production and contribute to the flavor and texture of Swiss cheese.
What are the two major groups of enteric bacteria based on fermentation products?
Mixed-acid fermenters, which produce acetic, lactic, and succinic acids, and 2,3-butanediol fermenters, which produce butanediol, ethanol, and smaller amounts of acids.
What is the sequence of the anaerobic food chain?
A series of biological processes where microorganisms decompose organic matter without oxygen, producing energy through fermentation and generating products like methane, carbon dioxide, and organic acids.
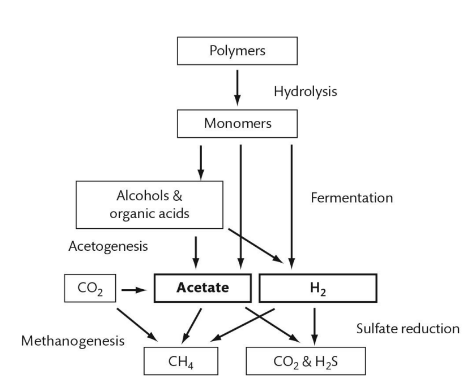
What are the waste products that supply electrons to the anaerobic food chain?
hydrogen, acetate, formate, and CO2
What are the products of the anaerobic food chain?
methane, carbon dioxide, organic acids, sulfate, and terminal electron acceptors
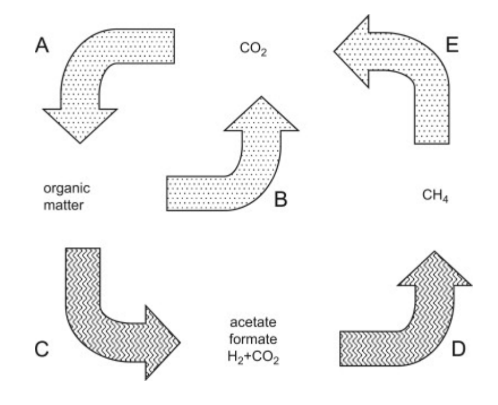
What is A?
Chemolithoautotrophs, phototrophs,
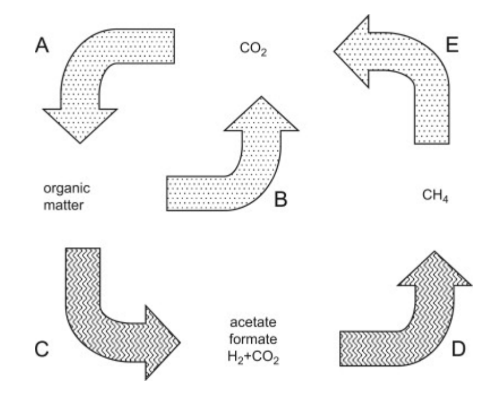
What is B?
Respiration
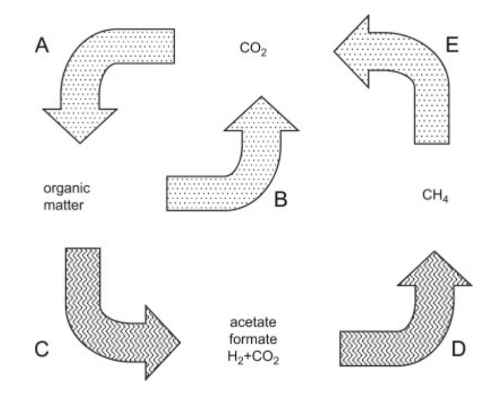
What is C?
Fermentation, acetogenesis
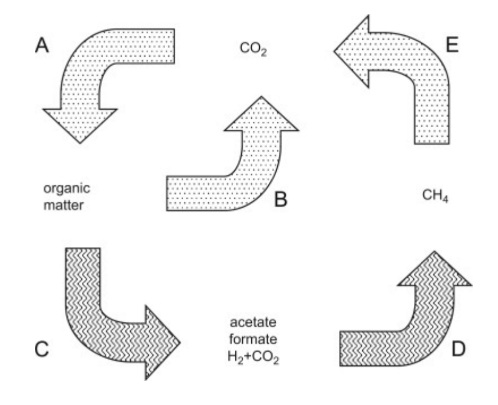
What is D?
Methanogenesis
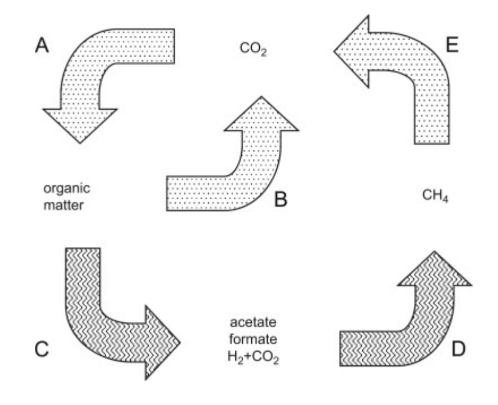
What is E?
Methanotrophy
Name a type of fermentations carried out by microbes
Lactic acid fermentation → yogurt, cheese
Name a type of fermentations carried out by microbes
Ethanol fermentation → wine, beer
Name a commercially valuable product made through fermentations carried out by microbes
enzymes, vitamins, antibiotics
How is insulin produced?
Insulin produced by fermenting microbes with cloned genes from other organisms
Hydrocarbon production
butane, oil, biofuels
What is fermentation?
Anaerobic redox process
What are the goals of fermentation?
Conserve redox balance and conserve energy/make ATP (energy)
Where does fermentation occur?
Wherever organic matter anaerobically decomposes
What are the electron donors and acceptors in fermentation?
organic molecules of medium redox states (sugars, organic acids, amino acids…)
What is formed through fermentation?
A variety of compounds are formed
What is a Stickland reaction?
A type of fermentation where one amino acid is oxidized while another is reduced, typically involving the conversion of amino acids into organic acids and ammonia. It involves multiple compounds
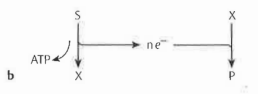
What happens when a single compound is fermented?
Oxidative steps are generally followed by reductive steps
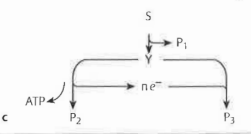
What is branched fermentation?
A type of fermentation that involves multiple metabolic pathways, resulting in the production of various end products, including organic acids, alcohols, and gases from the same substrate. Intermediates are oxidized and reduced
What is the difference between anaerobic respiration and fermentation in terms of how they make ATP?
Anaerobic respiration uses oxidative phosphorylation, and ATP is made from the proton motive force. Fermentation uses substrate-level phosphorylation and makes ATP from an energy-rich intermediate
What are the two reaction series that chemoorganotrophs use to conserve energy?
Fermentation and repsiration
How do fermentation and anaerobic respiration differ in terminal electron acceptors?
Fermentation uses organic molecules as terminal electron acceptors, while anaerobic respiration utilizes inorganic or organic compounds that are not oxygen.
What is fermentation’s electron acceptors?
Fermentation's electron acceptors are substrates that can be the electron donor and acceptor → low energy yield
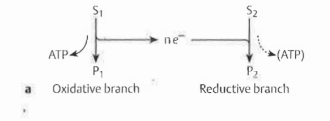
Oxidative vs reductive branch
Oxidative branch focuses on energy-rich compounds through substrate-level phosphorylation
Reductive Branch uses to regenerate electron acceptors for oxidative branches, like NAD+
What is anaerobic respiration electron acceptors?
Anaerobic respiration utilizes inorganic or organic compounds other than oxygen as electron acceptors, allowing for energy production in the absence of oxygen, like NO³-, SO^4-, Fe3+.
What happens if terminal electron acceptors are absent from anoxic habitats?
Fermentation catabolizes organic compounds.
What do energy-rich compounds contain?
An energy-rich phosphate bond or coenzyme A
How does formation during fermentation allow a microbe to make ATP?
By transferring the phosphate bond to ADP by substrate-level phosphorylation.
How is redox balance achieved?
By production of fermentation products from cell
How much energy do fermentation organisms conserve compared to respiratory organisms?
Much less energy
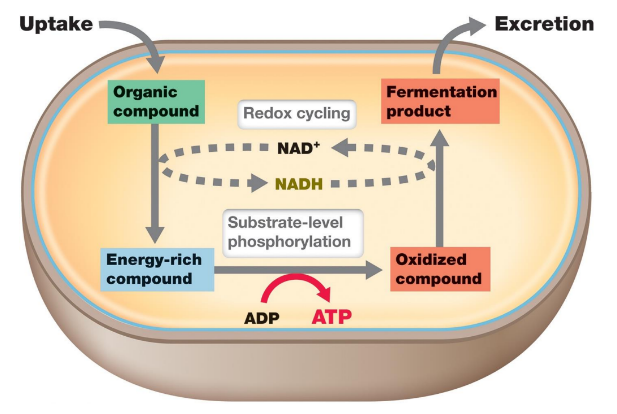
What are the essentials of fermentation?
an uptake of the substrate, a microbe capable of fermenting, the production of ATP through substrate-level phosphorylation, and the regeneration of NAD+ to maintain redox balance.
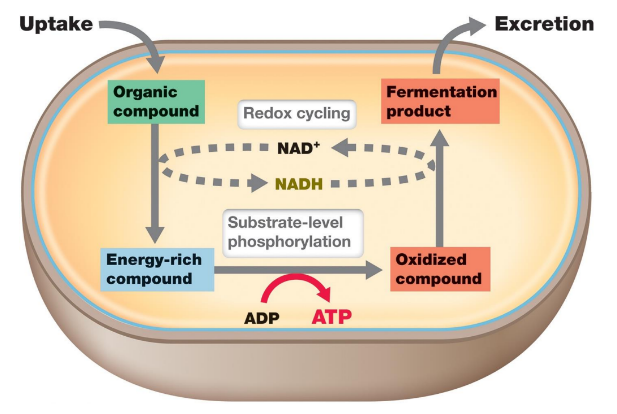
What is the end product from the essential of fermentation?
The uptake of an organic compound makes an energy rich compound from NAD+ regeneration. At the same time, the energy-rich organic compound is converted into fermentation products from turning it into an oxidized compound by converting ADP to ATP
What can the formation of energy-rich compounds allow microbes to do during fermentation
allows mircobes ot make ATP, additional ATP synthesis from substrate-level phosphorylation, and involves coenzyme-A derivatives (e.g., Clostridium butyricum)
What are the energy rich compounds of fermentation?
Acetate and other voltaile fatty acids, like lactic acid
How can redox balance be improved?
Can be improved by producing H2 which is a low reduction potential
What is redox balance associated with
ferredoxin and hydrogenase
Why is H2 important
is a powerful electron donor never wasted in microbial ecosystems
What are the most common substrates for fermenters?
hexoses and pentoses
What are the four pathways are known to convert sugar phosphates to pyruvate (a very versatile intermediate)
E-M pathway
E-D pathway
Phosphoketolase pathway
Combination pathways
Where does the greatest diversity of carbohydrate fermentation stem from?
the different pathways for glucose AND the different modes of pyruvate reduction
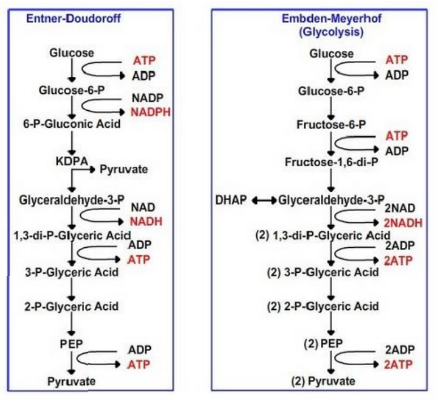
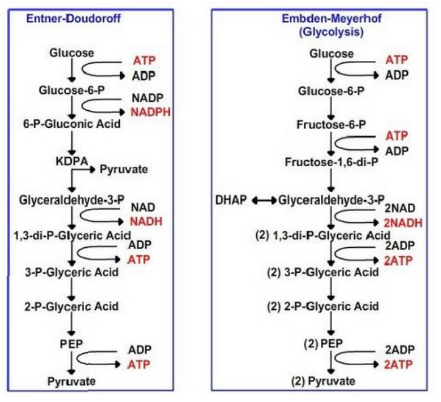
What is the Entner-Doudoroff (E-D) pathway a variant of?
It is a variant of the glycolytic pathway.
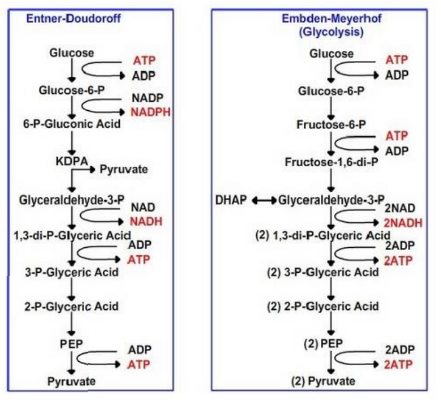
What are the products of glucose 6-phosphate conversion in the E-D pathway?
Pyruvate and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate.
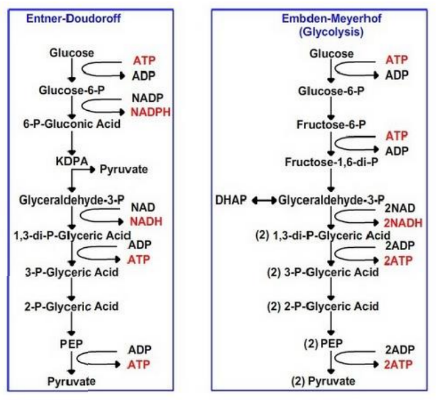
How does the ATP yield of the E-D pathway compare to glycolysis?
It yields half the ATP of glycolysis.
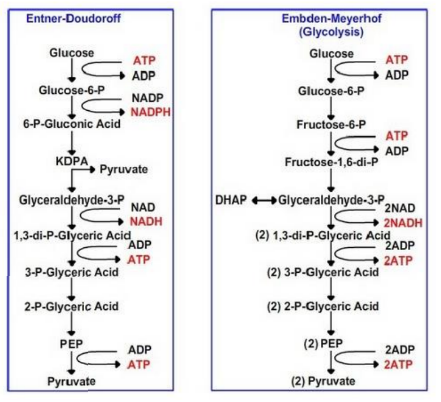
In which organisms is the E-D pathway widespread?
bacteria for sugar catabolism.
How do some enteric bacteria use intestinal mucus, and why is it beneficial to humans?
Some bacteria "farm" mucus to eat, which helps prevent pathogen colonization and supports human health.
What happens to pyruvate during respiration?
It is fully oxidized to CO₂ through processes like the TCA cycle.
What happens to pyruvate during fermentation?
It is reduced to fermentation products, which are then discarded.
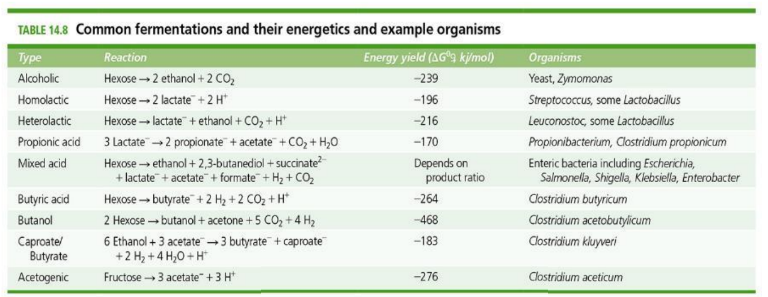
What are the different fermentations?
Different fermentation types include lactic acid fermentation, alcoholic fermentation, and mixed acid fermentation
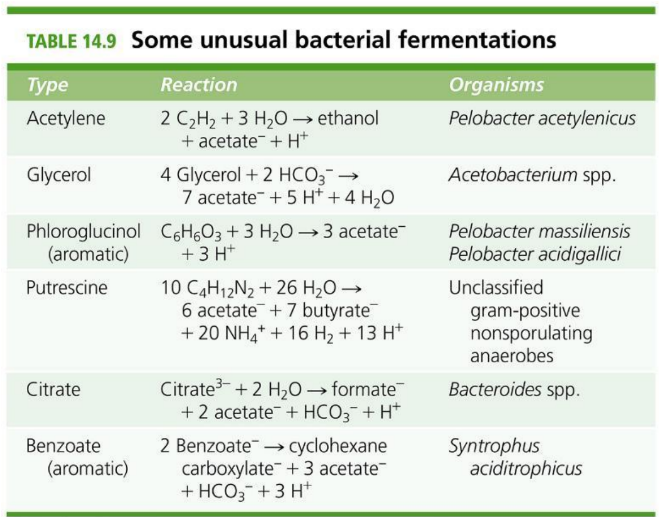
What are some unusual fermentations?
acetylene, glycerol, citrate. benzoate
What do lactic acid bacteria produce?
Lactic acid
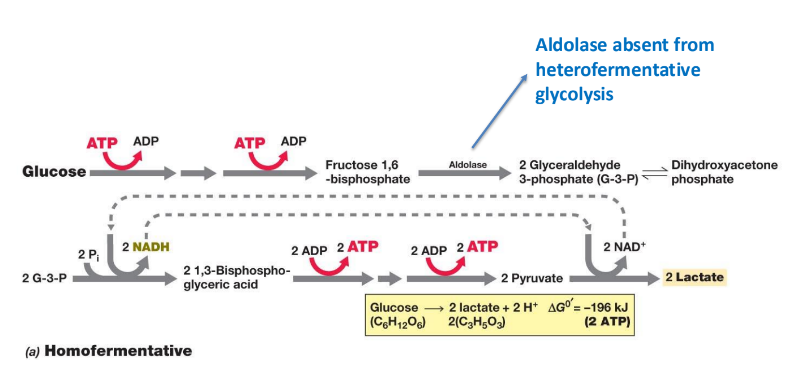
What does homofermentative fermentation yield?
Only lactic acid and 2 ATP per glucose.
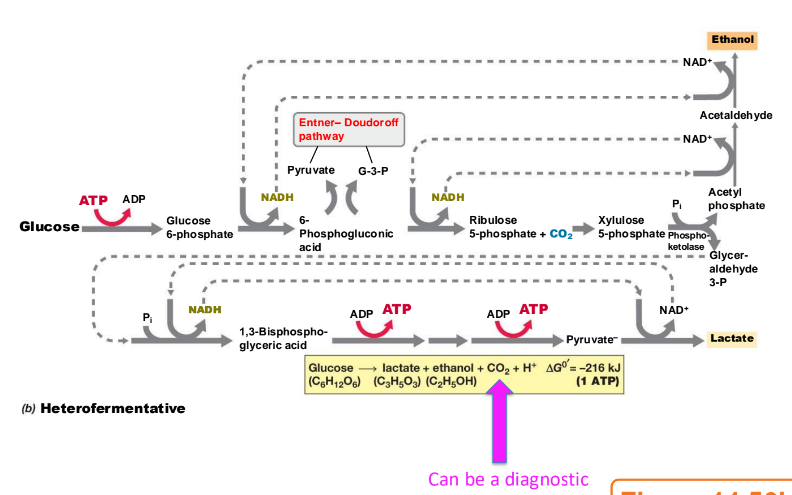
What does heterofermentative fermentation yield?
Lactate, ethanol, CO₂, and 1 ATP per glucose.
What observation can differentiate heterofermenters in culture?
The production of CO₂.
What key enzyme is used in homofermentative but not in heterofermentative lactic acid fermentation?
Aldolase.
What group of bacteria includes lactic acid producers like Lactobacillus?
Firmicutes – specifically the order Lactobacillales.
In what industries are lactic acid bacteria widely used?
Food production and preservation.
How do lactic acid bacteria generate energy?
Through substrate-level phosphorylation only.
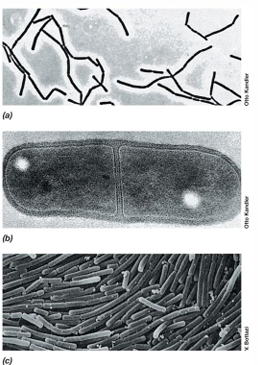
Are lactic acid bacteria sensitive to oxygen?
No, they are aerotolerant anaerobes
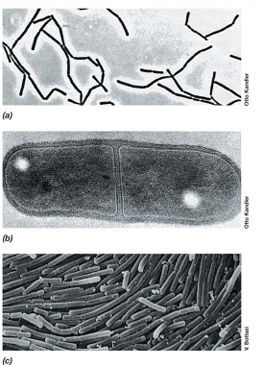
What is a common shape and growth pattern of lactic acid bacteria like Lactobacillus?
Rod-shaped and grow in chains
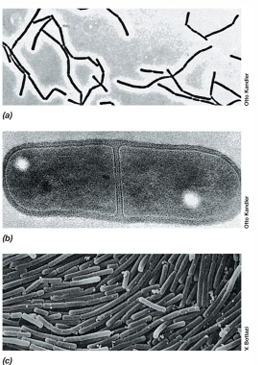
In what kinds of foods are Lactobacillus species commonly found?
Dairy products.
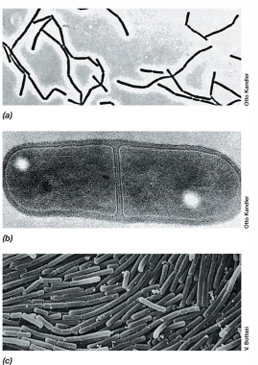
What is the lowest pH at which Lactobacillus can grow, and what does that indicate?
As low as pH 4, indicating resistance to acidic conditions.

True or False: Kimichi is an exmaple of a fermentative food.
True
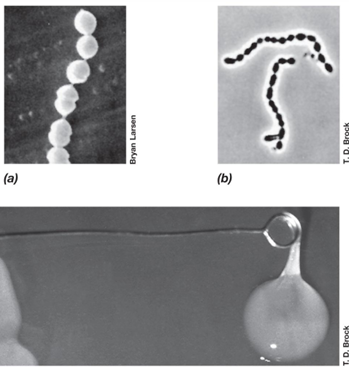
What is the shape and growth pattern of Streptococcus and related cocci?
Coccus-shaped and grow in chains.
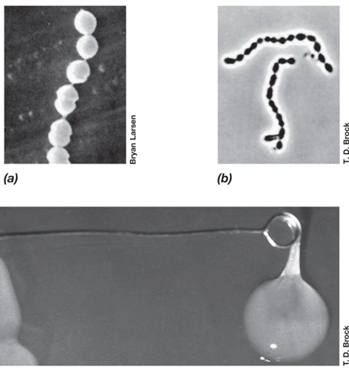
Are Streptococcus species homofermentative or heterofermentative?
Homofermentative.
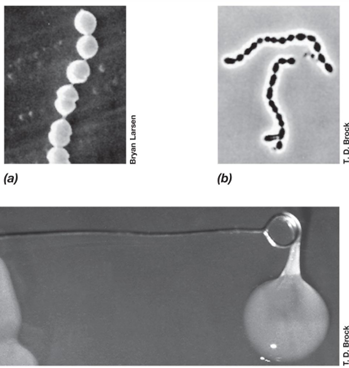
What are some fermented products produced by Streptococcus species?
Buttermilk, silage, and other fermented products.
Q: Which Streptococcus species contributes to dental caries?
A: Streptococcus mutans.
Q: Name a pathogenic species of Streptococcus and the illness it causes.
A: Streptococcus pyogenes, which causes strep throat.
Q: What is the significance of the genus Lactococcus?
A: It is important in dairy fermentation.
Q: What is the typical origin of Enterococcus species?
A: Fecal origin.
Q: What do Peptococcus and Peptostreptococcus ferment, and what type of anaerobes are they?
A: They ferment protein instead of sugar and are obligate anaerobes.

Q: What fermentation type is used by Leuconostoc, and what compounds do they produce?
A: Heterofermentative; they produce flavors like diacetyl and acetoin, like in popcorn.
Q: What types of acids are typically generated in mixed-acid and butanediol fermentations?
A: Acetic, lactic, and succinic acids.
Q. How is pyruvate processed in these fermentations?
A: It is partially reduced and partially cleaved to acetyl-CoA and formate.
Q: Besides acids, what other products are typically formed in these fermentations?
A: Ethanol, CO₂, and H₂.
Q: What neutral product can be produced in some of these fermentations?
A: 2,3-butanediol.
Q: What group of bacteria is characterized by these types of fermentations?
A: Enteric bacteria.
Q: How are enteric bacteria divided based on fermentation products?
A: Into mixed-acid fermenters and 2,3-butanediol fermenters.
Q: What are the characteristic products of mixed-acid fermentation?
A: Acetic, lactic, succinic acid in significant amounts; also ethanol, CO₂, and H₂ (CO₂ and H₂ in equal amounts via formate hydrogenlyase).
Q: Name some genera that are mixed-acid fermenters.
A: Escherichia, Salmonella, Shigella, Citrobacter, Proteus, Yersinia.
Q: Name some genera that are 2,3-butanediol fermenters.
A: Enterobacter, Klebsiella, Erwinia, Serratia.
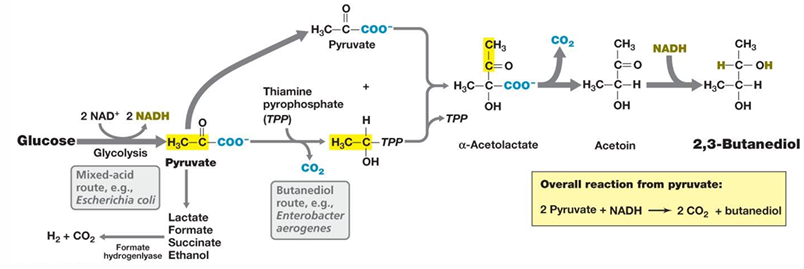
Q: What are the two major fermentation pathways shown for pyruvate in the diagram?
A: Mixed-acid fermentation and 2,3-butanediol fermentation.
Q: What is a key organism associated with the mixed-acid fermentation route?
A: Escherichia coli.
Q: What is a key organism associated with the butanediol fermentation route?
A: Enterobacter aerogenes.