3: Lipids + Carbohydrates Role in Health + Disease
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
maintaining homeostasis requires metabolic regulation that coordinates the use of _______ _______
nutrient pools
homeostasis adjusts the ______ and _______ rates to maintain physiological levels while also meeting essential demands
production consumption
How is homeostasis analogous to a bucket with a hole?
water going into the bucket = what we produce from our diet (energy consumed)
hole on the side = clearance and oxidation (energy expended)
water left in bucket = macromolecules left in blood and tissues (energy stored)
the ability to maintain adequate, but not excessive, energy stores
caloric homeostasis
if fuels are consumed in excess of energy needs, the fuels are STORED
excess energy molecules are ultimately converted to ________ which are stored in __________
triacylglycerols
adipocytes
triacylglycerols represents energy that is _________
fuel is expended as ________, _________, and _______ which are oxidized in the citric acid cycle
stored
amino acids, fatty acids, monosaccharides
excessive energy storage beyond what is needed during fast leads to an accumulation of _______________ leading to enlarged ___________ which increase _________ ___________
triacylglycerols
adipocytes
body weight
In 24 hours you …
consume 120 moles of dietary fatty acids
oxidize fatty acids for energy at 2 moles per hour
excrete (via urine + feces) at an average rate of 0.5 moles per hour
the concentration of free fatty acids is the SAME at the beginning and end of the day
Assuming no changes in other fatty acid consumption routes, what must be the effect on triglyceride pools in this person?
120- 2(24) - 0.5(24) = 60 remaining fatty acids to be stored
each triglyceride = 3 fatty acids so
60 fatty acids /3 = + 20 triacylglycerols to storage pool
energy balance is controlled by both BEHAVIORAL and BIOCHEMICAL factors
list some examples of each
behavioral = diet, exercise
biochemical = short term + long term signals, resting metbaolic rate + hormones
which organ plays a KEY role in caloric homeostasis
where does it send short term andlong term signals to?
Brain
GI tract
B cells of pancreas
fat cells
what is the difference between the short term and long term signals sent from the brain to the GI tract, pancreas, and fat cells?
both signals target the brain’s ______ _________, a group of neurons in a region of the ___________
short = active DURING meal
long = report on OVERALL energy status of body
arcuate nuerons hypothalamus
small peptide hormones secreted from the ____________ signal distal organs such as the _______ and __________
from: small intestine
to: pancreas and brain
what are two examples of short term signals that relay feelings of satiety from the gut to various regions of the brain, REDUCING the urge to eat
cholecystokinin (CKK)
Glucagon like peptide - 1 (GLP-1)
CCK and GLP-1 are released are small hormones released by the __________ that bind to their GPCRs in the _________ ________ which relay hunger/satiety signals
small intestine
peripheral neurons
satiety
GLP-1 signals both the _________ and ______ while CKK signals the __________
GLP-1 = brain AND pancreas (increase insulin)
CKK = brain
stimulates the secretion of pancreatic enzymes and bile salts from the gall bladder
CCK
ENHANCES glucose- induced insulin secretion and INHIBITS glucagon secretion
GLP-1
Does insulin increase or decrease the following:
___________ glycogen
____________lipogenesis
____________lipolysis
increase
increase (from triacylglycerides from fatty acids to be stored)
decrease
how does insulin effect the muscle?
increase glucose uptake
increase glycogen synthesis
what does insulin stimulate the ADIPOSE TISSUE to do?
increase lipogenesis
decrease lipolysis
increase glucose uptake and storage
what does insulin stimulate the LIVER to do?
increase glycogen synthesis
decrease glucose release to the bloodstream
decrease gluconeogenesis
increase lipogenesis
what does insulin stimulate the BRAIN to do?
inhibit hepatic glycogenoLYSIS
inhibit lipolysis
decrease appetite
_____________ decreases energy storage activating ______ to catalyze the hydrolysis of triacylglycerols to fatty acids
glucagon
lipases
What do GLP-1 Agonists like the following do?
Mounjaro
Wegovy
Trulicity
Ozempic
increase insulin release from pancrease
inhibit glucagon release from pancreas
DECREASE rate of stomach emptying (digestion)
increase satiety (fullness)
do GLP-1 agonists increase or decrease the rate of stomach emptying (digestion)?
DECREASE digestion to decrease your appetite
signal molecule that communicates the status of triacylglycerol stores
leptin
what is the difference between GLP-1 and leptin?
leptin communicates the amount of TRIACYLGLYCERIDE stored in the body
insulin communicates the status of GLUCOSE in the blood
leptin is secreted from ________ in direct proportion to the amount of _____ present
adipocytes \
fat
when leptin binds to its receptors it increases the sensitivity of the ________ and the ______ to INSULIN
stimulating the ____-________ of FATTY ACIDS
decreasing triacylglycerol synthesis
muscle and liver
b-oxidation
does leptin increase or decrease triacylglycerol synthesis?
DECREASE
increases b-oxidation of fatty acids using them for energy
adipokine secreted by adipose tissue in direct relation to fat mass
leptin
SEQ Leptin Action
fat mass increases
leptin inhibits appetite stimulating peptides _______ and _________ secretion
Leptin activates ________- producing neurons which increases ________ expression suppressing appetite
NPY and AgRP
POMC- —→ MSH
which hormones when stimulated induce appetite?
NPY
AgRP
a psychological condition experienced after an evening meal and throughout night’s fast
fasted-fed cycle
what are the three stages of the fasted-fed cycle?
well - fed (POST prandial)
early fasting (POST absorptive)
refed state
during which part of the fasted-fed cycle are the following levels at their highest
glucagon
insulin
glucose
liver glycogen
fasted
fed
fed
fed
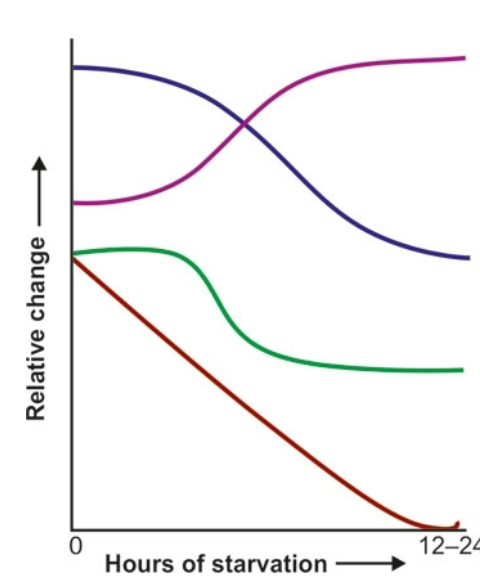
what do each of the curves represent if the x axis going from left to right represents hours of starvatio?
blue = insulin
purple = glucagon
green = glucose
red = glycogen in liver
state that immediately follows the absorption of glucose from the previous meal when blood-glucose concentration begins to drop
leads to
_______ in insulin secretion
_______in glucagon secretion
post-absorptive (early fasting)
decreased
rise
what happens to insulin and glucagon levels in the post-absorptive state?
post absorptive is another word for fasted state
decrease insulin
increase glucagon
what are the 5 roles of glucagon
increase glycogenolysis (glycogen breakdown)
decrease glycogen synthesis
inhibit fatty acid synthesis
increase gluconeogenesis in LIVER
BLOCK glycolysis (use a different source for ATP)
PYRUVATE—>
**oxaloacetate**
phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP)—>
Fructose 1,6- bisphosphate —>
**fructose 1,6- biphosphate 1 (FBP1)**
Fructose 6- Phosphate
Glucose 6- Phosphate—>
**Glucose 6-phosphatase**
GLUCOSE
the following describes the events of which process?
glycolysis
GLUCOSE
*hexokinase / glucokinase*
glucose 6- phosphate —>
fructose 6- phosphate —>
* phosphofructokinase 1 *
fructose 1,6- bisphosphate —_>
phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) —->
*pyruvate kinase*
PYRUVATE
the following describes the events of which process?
glycolysis
__________ and ___________ are reciprocally related
glycolysis and gluconeogenesis
which enzyme is key in the regulation of glycolysis?
which enzyme is key in regulation of gluconeogenesis?
phosphofructokinase
fructose 1, 6 bisphosphotase
does the following conversion occur in the fasted or fed state?
Fructose 6- phosphate —→
** PHOSPHOFRUCTOKINASE ENZYME *
Fructose 1, 6- bisphosphate
fed — glycolysis
does the following conversion occur in the fasted or fed state?
Fructose 1, 6 bisphosphate —→
**Fructose 1,6 bisphosphatase enzyme **
Fructose 6-phosphate
fasted— gluconeogenesis
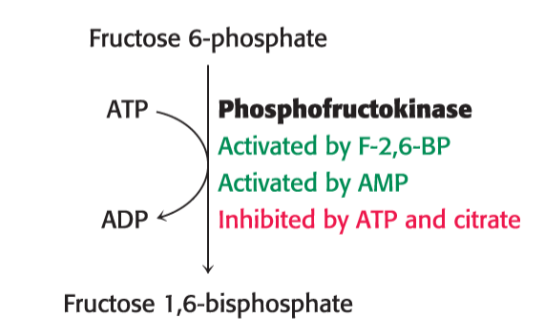
is this the key step in glycolysis or gluconeogenesis ?
does the following occur in the fasted or fed state ?
glycolysis
fed
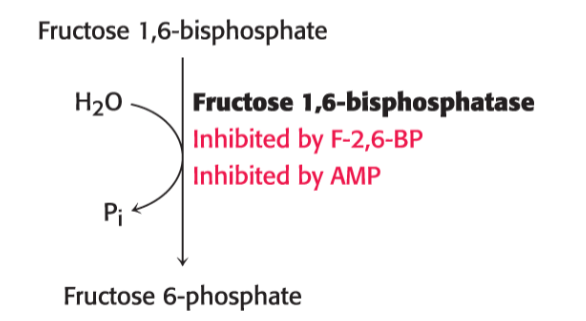
is this the key step in glycolysis or gluconeogenesis ?
does the following occur in the fasted or fed state ?
gluconeogenesis
fasted
SEQ: eating after LONG fast
does the liver immediately absorb glucose from the blood?
is the liver in a gluconeogenesis state or glycogenolysis state?
what happens to the excess glucose that remains after glycogen stores are replenished?
NO leaves glucose in the blood for other tissues
still gluconeogenesissis
glucose is used to synthesize fatty acids
the conversion of frucose 6-phosphate to fructose 1,6-bisphosphate by phosphofructokinase is
inhibited by?
activated by?
inhibited by Citrate + ATP (dont need to do glycolysis)
activated by AMP and F-2, 6-BP
the conversion of 1,6-bisphosphate to fructose 6-phosphate to fructose by Fructose 1,6 bisphosphotase is
inhibited by?
F-2, 6-BP
AMP
disease resulting from the disruption of caloric homestasis
overproduction of glucose by liver and UNDERUTILIZATION by organs — stays in blood
where does this disease gets its name from?
diabetes mellitus
frequent urination
10 hour fast
no dietary glucose
constant glucose concentration
glucose oxidized for energy 2000 moles per hour
no excretion of glucose
gluconeogenesis = 100 moles per hour
glyycogen consists of 1,000 glucose molecules
assuming no change in glucose production or consumption, what must the effecr be on liver glycogen pools in this person by the end of this fast
100 (10) - 2000 (10) = -19000 moles of glucose
-19000/1000 = -19 moles of glycogen
diabetes leads to increased _______ elevation and slower ___________ after a meal
glucose
clearance

which curves respond to a patient with diabetes? what is noticibely different with those with diabetes vs. those without
black = healthy
colored = diabetic
levels of glucose in the blood are larger AND sustained don’t go down as quick as healthy individual
diabetic individuals have HIGHER levels of insulin, but they are resistant to them
which type of diabetes is insulin- dependent?
type 1
these patients rely on medicinal insulin as they do not produce them on their own as opposed to type 2 individuals who HAVE insulin but have grown resistant
diabetes caused by the destruction of the insulin secreting B cells of the pancreas
_______ disorder
begins before age ______
autoimmune
20
type _____ diabetes occurs later on in life than type ___ diabetes and accounts for 90% of cases in the world
what is a predisposing factor of this form of diabetes?
2 1
obesity
cluster of pathologies including
insulin resistance
hyperglycemia
dyslipidemia (high triacylglycerols)
predecessor of type ___ Diabetes
metabolic syndrome
2
conditions in which tissues OTHER THAN adipose tissues accumulate fat
which tissues often accumulate fat?
often results in _______ resistance and _______ failure
hepatic steatosis
liver and muscle
insulin pancreatic
storage capacity of _______ ________ can be exceeded leading to lipid accumulation in other tissues such as … leading to ______ ____________
adipose tissue
blood vessels
liver
pancreas
muscle
excess tissue triglycerides can disrupt signal-transduction pathways leading to _________
insulin resistance
excess fat accumulation in peripheral tissues
SEQ events leading up to insulin resistance:
overnutrition + inactivity
increased _______ ______ supply —→
increased _____ ______
increased triacylglycerols and mitochondrial overload
what follows increased levels of triacylglycerol?
what is the consequence of mitochondrial overload?
fatty acids
fatty- acetyl coA
increased DAG and Ceramide
decreased glucose uptake by transporter GLUT4
what happens during a mitochondrial overload following an excess of fatty acids
decreased _______
increased _____-_______
increased ______
increased ______
what does all of this lead to?
decreased free CoA bc/ now all acyl-CoA
increased B-oxidation (TCA cycle flux)
ROS
acylcarnitines
decreased glucose uptake by GLUT4
what three downstream factors are increased due to increased fatty acid supply leading to decreased GLUT-4 uptake and insulin resistance ?
the following stimulate stress-induced _______ ________
DAG (diacylglycerols)
Ceramides
Mitochondrial overload
serine kinases
ketogenic diets are used as therapeutic option for which demographic?
children with drug-resistant epilepsy
keto diets are rich in _______ and low in __________ with adequate amounts of proteins
rich in fat
low in carbohydrates
research in mice studies suggests keto diets can be used to
improve memory
extend lifespan
weight loss
SEQ Regular Diet / NOT ketogenic
eat carbohydrate —> ________levels rise
pancreas secrete ______ and ______is stored in tissues
_________
glucose
insulin glucose
energy
Ketogenic Diet:
eat ____—> glucose level falls
______ releases stored __________
______ ______ travel to liver
liver produces _______ that give ENERGY
fat
lipases triacylglycerols
fatty acids
ketones
would you want high or low insulin levels on a ketogenic diet and why?
LOW bc/ insulin promotes lipogenesis (formation of triacyl glycerides from fatty acids)
the goal of ketogenesis is to promote lipolysis and covert stored triacylglycerols into fatty acids to be converted into ketones and used for energy
the liver will not produce _____ ______ if there is insulin present
ketone bodies
the liver produces ketone bodies from _______ ______ when _______ signaling is low
acetyl CoA
insulin
what three molecules are known as ketone bodies?
acetoacetate
acetone
d-3-hydroxy-butyrate
SEQ Ketogenesis starting from acetyl-CoA from fatty acids
acetyl-CoA
—> acetoacetyl CoA using enzyme ____________
—> 3-hydroxy-3methyl-glutaryl CoA using ________
—> Acetoacetate using ________________ CLEAVAGE enzyme
—> D-3-Hydroxy-butyrate using ________
OR acetoacetate decarboxylated into
3-ketothiolase
hydroxymethylglutaryl CoA synthase
hydroxylmethylglutaryl CoA
D-3 hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase
acetone
the _________ converts _________ into ketone bodies
liver fatty acids (specifically acetyl CoA from them)
what is the primary fuel that predominates during starvation?
ketone bodies from fatty acids
SEQ Ketone formation:
_______ acids —>
__________ ________ —>
ketone bodies into blood stream—>
ketone go to cells of _______ , ___________, ___________
ketones converted into _______________ which goes into the citric acid cycle
what is produced at the end of the citric acid cycle?
fatty
acetyl CoA
heart, renal cortex, brain
acetyl CoA
H2O + CO2 + ATP
dietary consumption of ______ _____ increases cardiovascular disease
trans fats
changing in relative risk of coronary heart disease for each ___% energy from carbohydrate that is isocalorically replaced with fatty acids
what are the different types of fatty acids that exists?
1
trans fat
saturated
monounsaturated
polyunsaturated
most dietary trans fats derive from industrial _________ ____________ vegetable oils which are less expensive that ______ fats and nonhydrogenated vegetable oils
partial hydrogenated
animal
what are some advantages of partial hydrogenated vegetable oils over nonhydrogenated vegetable oils?
what is a popular example of a partially hydrogenated vegetable oil?
longer half life
greater solidity at room temp
stability during repeated deep-frying temperature
margarine
are naturally occurring fats cis or trans?
are cis or trans fatty acids a straight chain?
cis (carbons of double bond same side)
trans = straight chain = processed
full hydrogenation of cis fatty acids leads to the formation of
partial hydrogen of ciis fatty acids leads to the formation of
full = saturated fat
partial = unsaturated fat
trans fats are made through the partial hydrogenation of cis fats and unsaturated fats are made from full hydrogenation of cis fats
what is meant by hydrogenation?
adding H2 gas to oil with high heat and pressure
dietary trans fats are dangerous because of their interactions with which types of cells?
reactions with these cell types ultimately leads to _____________(fatty plaque build up) and ____________
macrophages
endothelial cells
hepatocytes
adipocytes
ATHEROSCLEROSIS and INFLAMATION
increased lipid and lipoprotein levels
systemic inflammation
endothelial function
adiposity
glucose— insulin homeostasis
are all metabolic risk factors associated with _____________
trans fatty acids (TFA)
___________ molecules have a rigid planar steroid ring structure with a polar _____ that interacts with the hydrophilic head of phospholipids
cholesterol
hydroxyl (OH)
what happens once the OH of cholesterol interacts with the polar head group of the phospholipid bilayer?
cholesterol‘s hydrophobic ring structure is implanted into the hydrophobic tails and increases stiffness with its rigidity
the 27 carbon atoms of cholesterol are synthesized from ____________ in a step process in the ______ and _________
acetyl CoA
3
liver and small intestine
is cholesterol only introduced in the body through diet?
NO can be synthesized de novo as well
the rate of cholesterol synthesis is mediated primarily by changes in the amount and activity of ________ _____ which is the enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of ____________ (intermediate)
HMG CoA
mevalonate
what is 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA reductase?
HMG CoA
enzyme that catalyzes synthesis of cholesterol intermediate (mevalonate)
does cholesterol travel freely though the blood stream?
no MUST be transported with lipoprotein
the means by which cholesterol and triacylglycerols are transported in body fluids to tissues for use as fuel or for storage
lipoproteins
fatty acid constituents of the triacylglycerol components of the lipoprotein particles are incorporated into phospholipids for ____________ ___________
membrane synthesis
cholesterol is a precursor to many _______ hormones BUT its nucleus is unable to be degraded by _____ so it MUST be used or excreted by the ______
steroids
cells
liver
lipoprotein particles consist of
a core of ___________ lipids
shell of more _______- lipids and proteins
protein components of lipoprotein particles (_______) have 2 roles
solubilizing _______ lipids
containing cell- targeting _______
hydrophobic
polar
hydrophobic
signals
particles that are a major carrier of cholesterol in the blood and regulate de novo cholesterol synthesis in peripheral tissues
Low-Density Lipoproteins