DNA HYBRIDIZATION
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Hybridization
a phenomenon in which single stranded deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) or ribonucleic acid(RNA) molecules anneal to complementary DNA or RNA
hybridize
Lowering the surrounding temperature allows the single-stranded molecules to anneal or ”__________” to each other
DNA PROBE HYBRIDIZATION
generally refers to a molecular biology technique that measures the degree of genetic similarity between pools of DNA sequences
genetic distance or degree of genetic similarity
DNA PROBE HYBRIDIZATION is usually used to determine the ____________ or _____________ between two organisms
gene probe
single stranded piece of DNA complementary to a desired target DNA sequence that is labelled
fluorescent dye or radioactive label
gene probe is usually labelled with _____________ or ____________
Nick translation, Random primed DNA labelling, End labelling of DNA, End labelling of RNA
methods in ASSAYS: PREPARATION OF NA PROBES
Nick translation
used to replace cold nucleoside triphosphates in a double-stranded DNA molecule with radioactive ones (1,2)
3-hydroxyl groups
in nick translation, what is created within the unlabeled DNA (nicks) by deoxyribonuclease 1 (DNAse)
deoxyribonuclease 1
in nick translation, Free 3-hydroxyl groups are created within the unlabeled DNA (nicks) by _____________
addition of dNTPs in 5’ to 3’ direction and removal of nucleotides in 5’ to 3’ direction
two main function of Polymerase 1
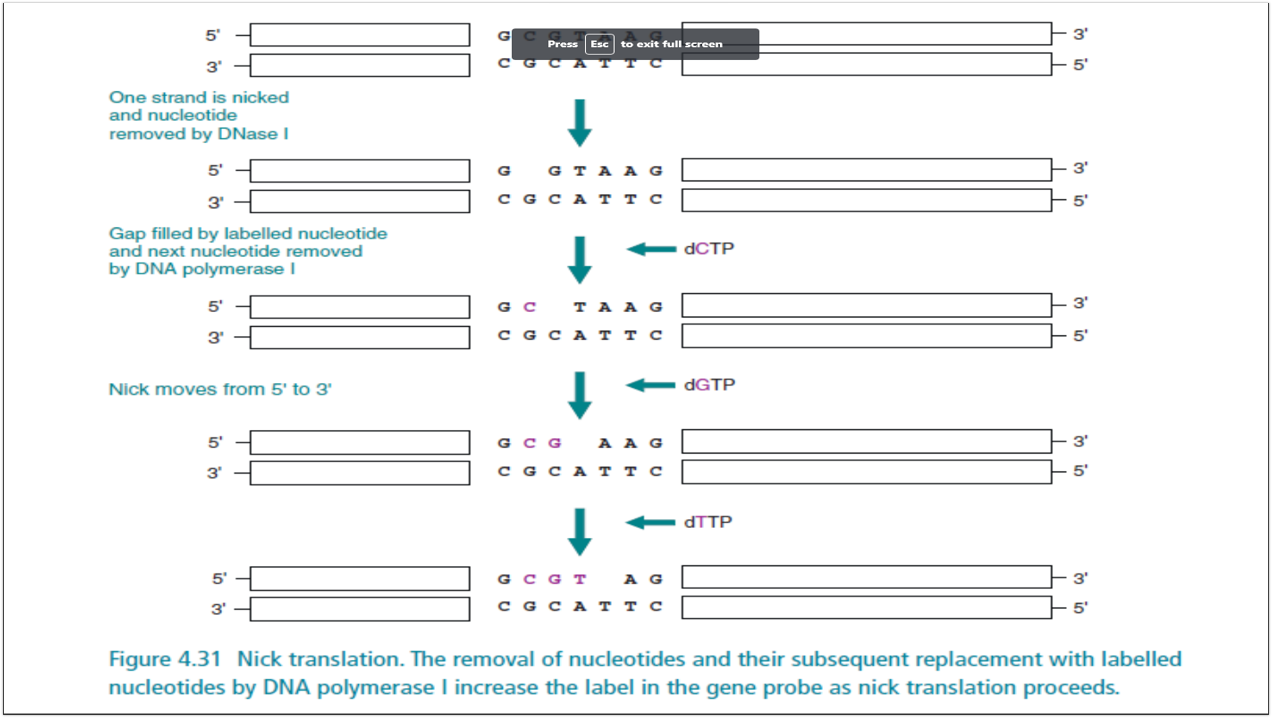
nucleotide is nicked by DNAse 1, polymerase 1 fills the gap with labelled nucleotide, moves in a 5’ to 3’ direction
illustrate NICK TRANSLATION
Klenow fragment of DNA Polymerase
what polymerase is used in Random primer labelling of DNA
it lacks 5’ to 3’ exonuclease activity
why is klenow fragment used in random primer labelling of DNA
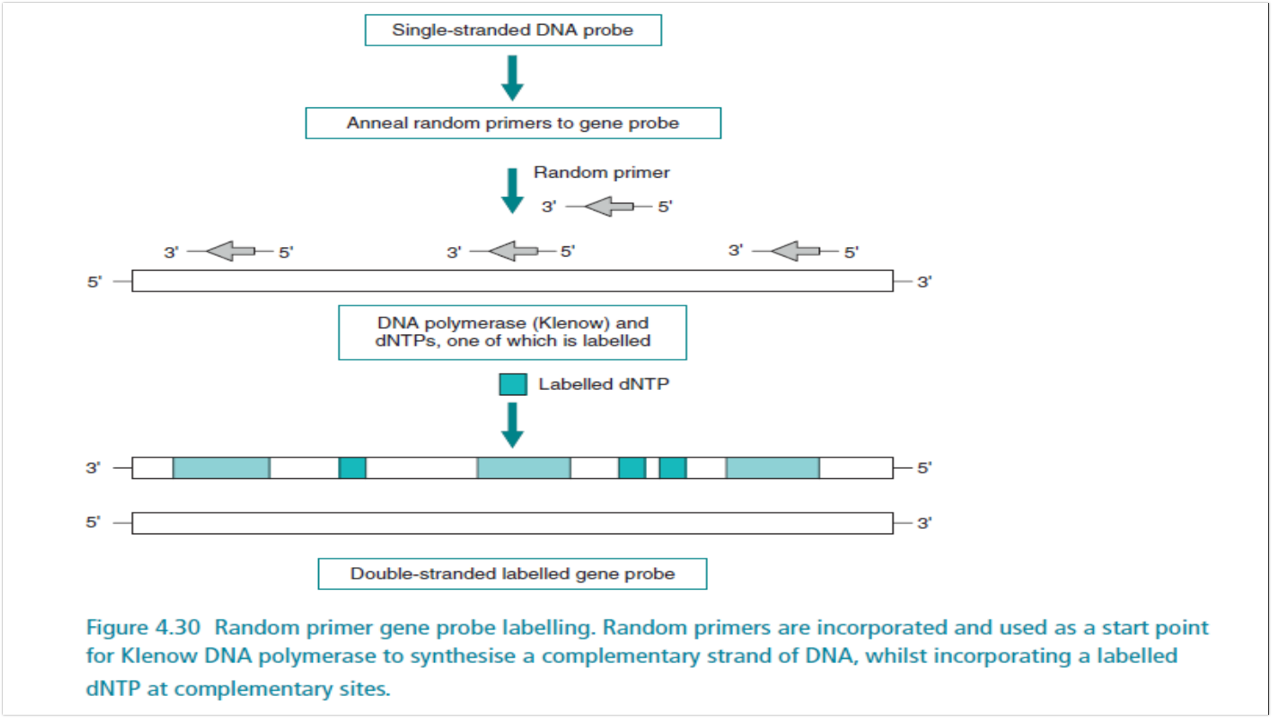
single stranded DNA probe, anneal random primers to gene probe, Klenow DNA polymerase synthesize a complementary strand of DNA with labeled dNTP
illustrate random primed labelling of DNA
5’ or 3’ end labelling
Simplest form of labelling DNA
5’ end-labelling
involves a phosphate transfer or exchange reaction where the 5-phosphate of the DNA to be used as the probe is removed and in its place a labelled phosphate, usually 32P, is added
alkaline phosphatase
used to remove the existing phosphate group from the DNA
polynucleotide kinase
catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group (32^P-labelled) to the 5’ end of the DNA.
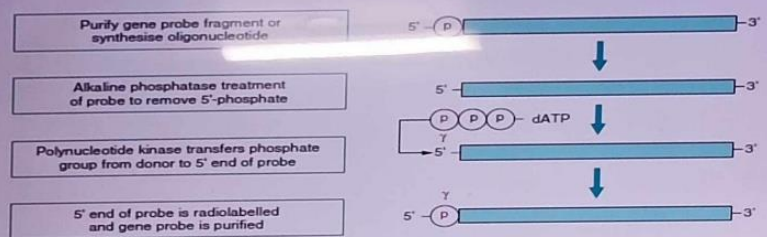
purify gene probe fragment or synthesize oligonucleotide, alkaline phosphatase treatment of probe to remove 5’ phosphatase, polynucleotide kinase transfers phosphate group from donor to 5’ end of probe, 5’ end is radiolabeled and gene probe is purified
Illustrate end labelling at 5’ end
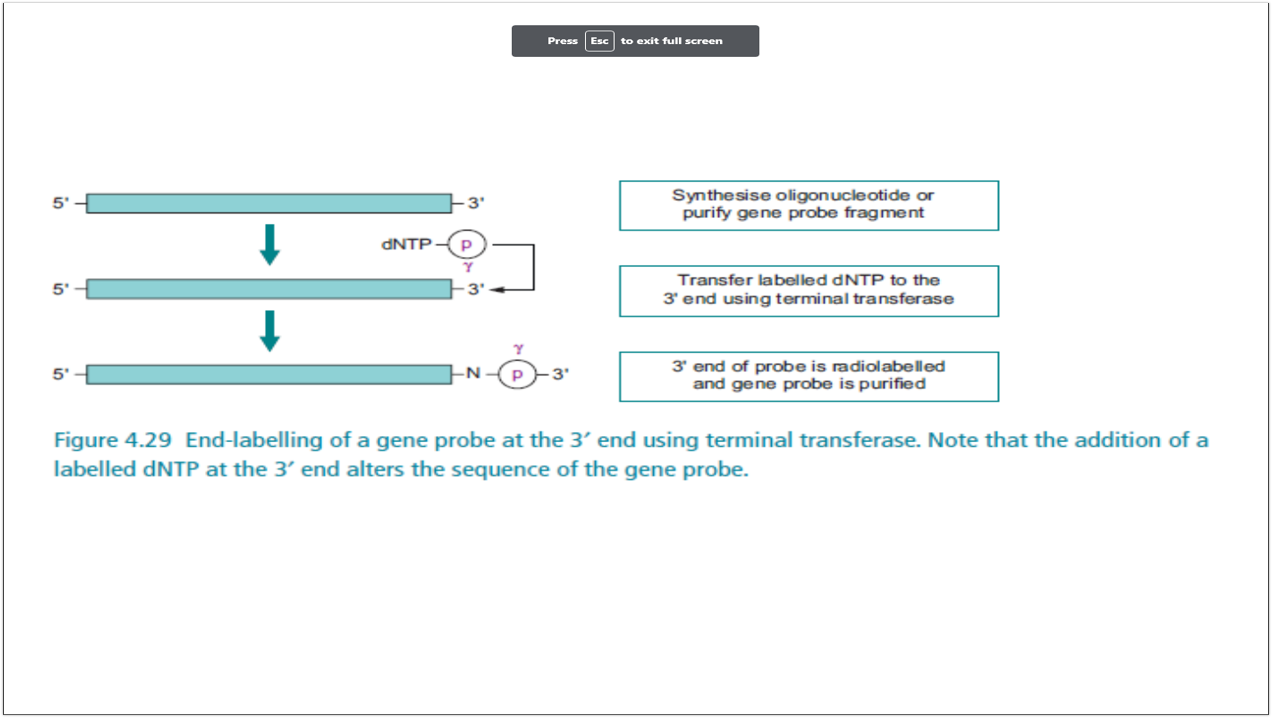
synthesize oligonucleotide or purify gene probe fragment, transfer labelled dNTP to the 3’ end using terminal transferase, 3’ end is radiolabelled and gene probe is purified
Illustrate end labelling at 3’ end
weak hydrogen bonds
The strands of DNA are linked together by ? when acted upon by denaturation
Denaturation, annealing, extension
steps in PCR/ principle in PCR
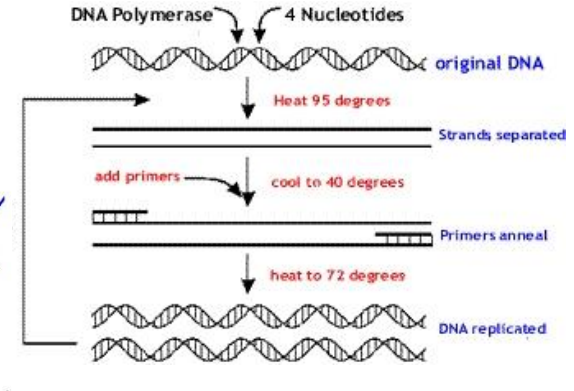
denaturation (95 degrees), annealing (40 degrees, primer anneal), extension (72 degrees, Pol I), dna replicated
illustrate PCR
DNA HYBRIDIZATION
the process of establishing a non-covalent, sequence-specific interaction between two or more complementary acids of nucleic acids into a single hybrid
duplex
two hybrid strands is referred to as a
bacterial taxonomists
DNA-DNA Hybridization values have been used by ___________ since 1960
To determine relatedness between strains and and due to declination of bacterial species
purpose of DNA hybridization
DNA probe to Hybridization to determining the degree of genetic similarity
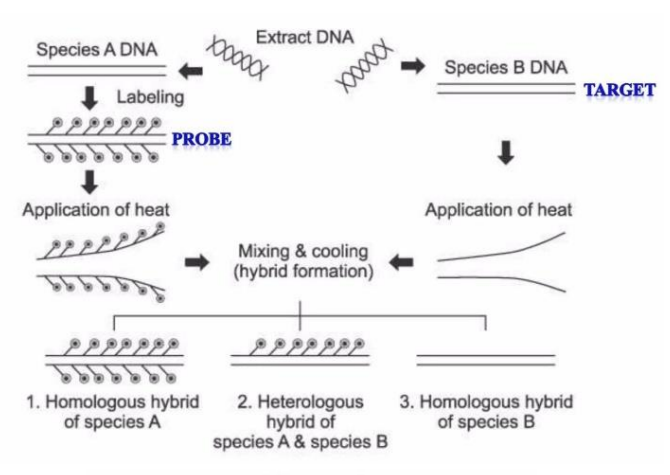
illustrate Hybridization in bacterial taxonomy
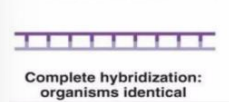
organisms are identical
complete hybridization of two organism strand means
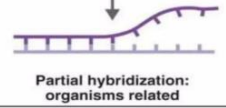
organisms are related
partial hybridization of two organism strand means
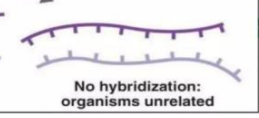
organisms unrelated
no hybridization of two organism strand means
heat to separate strands
combine single strands of DNA
cool to allow renaturation of double-stranded DNA
determine degree of hybridization
steps in dna hybridization two organisms dna for determining degree of genetic similarity
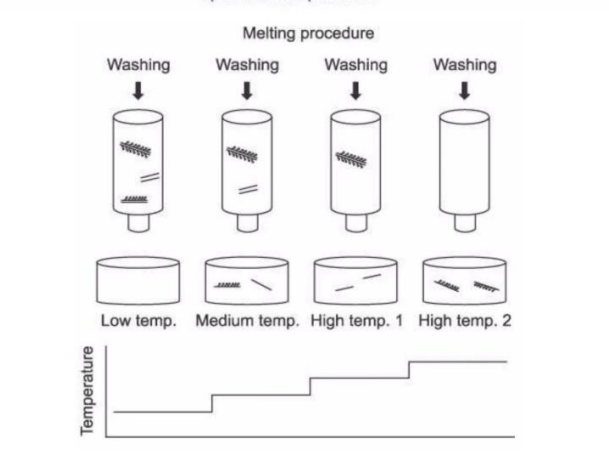
ds DNA bound to the column
the mixture is heated
mixture is heated in small steps
each step - column washed
sequence melt - ssDNA washed off
temp at which labelled DNA comes off the column reflects the amount of similarity between sequences
combined results - determine the degree of genetic similarity between organisms
access melting profile of hybridized DNA steps
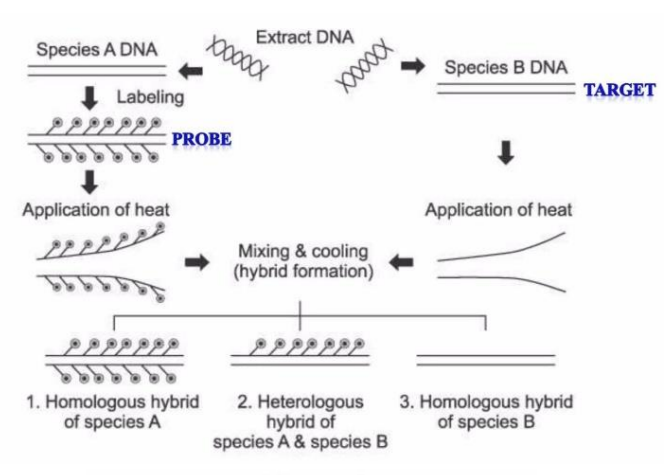
Homologous hybrid
if 2 strands species DNA have a probe attached to it, what type of hybrid is it?
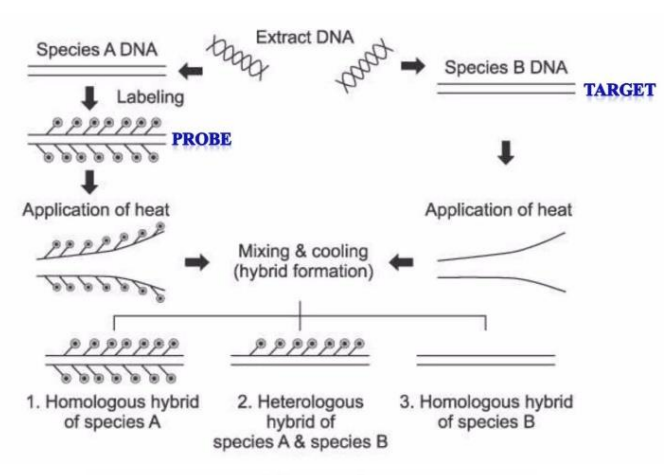
heterologous hybrid
if 1 strand species DNA have a probe attached to it and the other has none, what type of hybrid is it?
Homologous hybrid
if both strand species DNA have no probe attached to it, what type of hybrid is it?

DNA fragmented by bead beating
it ensures randomness in DNA microarray
Agarose gel
used to elute and purify DNA in DNA microarray
T3-T7 promoter primer
In DNA microarray, what is used to amplify PCR