StemUp: OCR A A level Biology 6.3.1 Ecosystems
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Describe how the abundance of plants can be estimated and population size can be calculated from this (3)
1. Place quadrats around an area randomly
2. Count number of individual plants contained within quadrat

Describe the capture-mark-release-recapture technique can be used to estimate the population size of an animal species (7)
1. Capture as many individuals as possible in a sample area
2. Mark or tag each individual
3. Release the marked animals back into the sample area and allow time for them to redistribute themselves throughout the habitat
4. Recapture as many individuals as possible in the original sample area
5. Record the number of marked and unmarked individuals present in the sample. (Release all individuals back into their habitat.)
6. Use the Lincoln index to estimate the population size

Compare the movement of energy through an ecosystem with the movement of elements such as nitrogen or carbon (2)
- Energy has linear flow - enters ecosystem from the Sun and transferred to atmosphere as heat
- Elements have to be constantly recycled for plants and animals to grow bc no external source constantly replenishing nutrients like the Sun supplies energy
What is meant by abiotic factors? (1)
Non-living components of an ecosystem
What is amonification? (2)
- Process by which decomposers convert nitrogen-containing molecules in dead organisms, faces, and urine
- Into ammonium compounds
What is an autotroph? (3)
- Organism that produces complex organic molecules (carbs, lipids, proteins)
- Using carbon from simple substances (carbon dioxide)
- Using energy from light or inorganic chemical reactions
What is biomass? (1)
Mass of living material present in a particular place or in particular organisms
What are biotic factors? (1)
Living components of an ecosystem
What are carnivores? (1)
Animal that feeds on other animals
Describe climax community (3)
- The final stage in ecological succession
- The community is in a stable state, with very little change over time.
- It consists of a few dominant plant and animal species
What is meant by "community"? (1)
All the populations of living organisms in a particular habitat
What is meant by "consumer"? (1)
Organisms that get their energy from eating other organisms
What are decomposers? (1)
Organisms that break down dead or decaying organic matter into inorganic ones
What is deflected succession? (1)
When human activity halts the natural flow of succession
What is denitrification? (1)
Conversion of nitrates to nitrogen gas under anaerobic conditions
What are detritivores? (1)
Organisms that feed on detritus (dead and decaying material)
What is meant by niche? (1)
The role of an organism in an ecosystem
What are some examples of biotic factors? (5)
- Feeding of herbivores on plants
- Predation
- Parasitism
- Mutualism
- Competition
What is intraspecific competition? (1)
Individuals of the same species competing with each other
What is intrerspecific competition? (1)
Individuals of different species competing with each other
What are some examples of abiotic factors? (5)
- Temperature
- Light intensity
- Oxygen concentration
- CO2 concentration
- Water supply
- pH
How do plants synthesize organic compounds? (1)
From atmospheric or aquatic carbon dioxide
What do plants use most of the sugars they synthesise for? (1)
As respiratory substrates
What happens to the sugars not used as respiratory substrates in plants? (2)
- They are used to make other groups of biological molecules
- Forming the plant's biomass
What does dry biomass show? (1)
Shows the chemical energy store in an organism
How can dry biomass be measured? (3)
- Can be measured using calorimetry
- Where a dry sample is weighed and burnt in pure oxygen
- The temperature increase of water is used to calculate energy released
What is gross primary production (GPP)? (2)
- The total quantity of chemical energy stored in plant biomass
- In a given area or volume
What is net primary production (NPP)? (2)
- The chemical energy store in plant biomass
- After respiratory losses to the environment have been taken into account
What is the NPP available for? (2)
- Available for plant growth and reproduction
- For consumers in the food chain, such as herbivores and decomposers
What is net production (N) in consumers? (2)
- The total chemical energy stored by consumers after energy losses through faeces, urine, and respiration
- Are subtracted from the energy in ingested plant food
What is primary productivity? (3)
- The rate of primary production
- Measured as biomass in a given area over a specific time
- Such as kJ ha^-1 year^-1
What is secondary productivity? (3)
- The rate of secondary production
- Measured as biomass in a given area over a specific time
- Such as kJ ha^-1 year^-1
How can the percentage efficiency of energy transfer between trophic levels be calculated? (3)

How do farming practices increase the efficiency of energy transfer in the human food chain? (2)
- By reducing respiratory losses
- Such as limiting the movement of animals
What is another way farming practices simplify food chains to increase energy efficiency? (2)
- Simplify food chains by reducing energy loss to non-human food chains
- For example, killing weeds and pests using herbicides and insecticides
What is the role of mycorrhizae in plants? (2)
- Associate with plant roots to increase surface area
- For absorption of water and mineral ions, including phosphate ions
What is the role of free-living nitrogen-fixing bacteria in the soil? (1)
Reduce nitrogen gas to ammonia in the soil
What do mutualistic nitrogen-fixing bacteria do? (1)
Use nitrogen gas to produce amino acids
What is the role of saprobiotic organisms? (2)
- Break down dead organisms
- To release phosphate, ammonia, or ammonium compounds
What do nitrifying bacteria do in the nitrogen cycle? (1)
Oxidise ammonium ions into nitrites and nitrites into nitrates in the soil
What is the role of anaerobic denitrifying bacteria? (1)
Use nitrates in respiration to produce nitrogen gas
Name three biological processes involved in the carbon cycle. (3)
- Decomposition
- Respiration
- Photosynthesis
How does decomposition contribute to the carbon cycle? (1)
Releases carbon dioxide through respiration of decomposers
How does respiration contribute to the carbon cycle? (1)
Releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere as a byproduct of metabolic reactions
How does photosynthesis contribute to the carbon cycle? (1)
Removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and converts it into organic compounds
Give one physical process that affects the cycling of carbon. (1)
Dissolving of carbon dioxide in oceans
Give one chemical process that affects the cycling of carbon. (1)
Formation of carbonate rocks like limestone
Draw and label a diagram of the phosphorus cycle
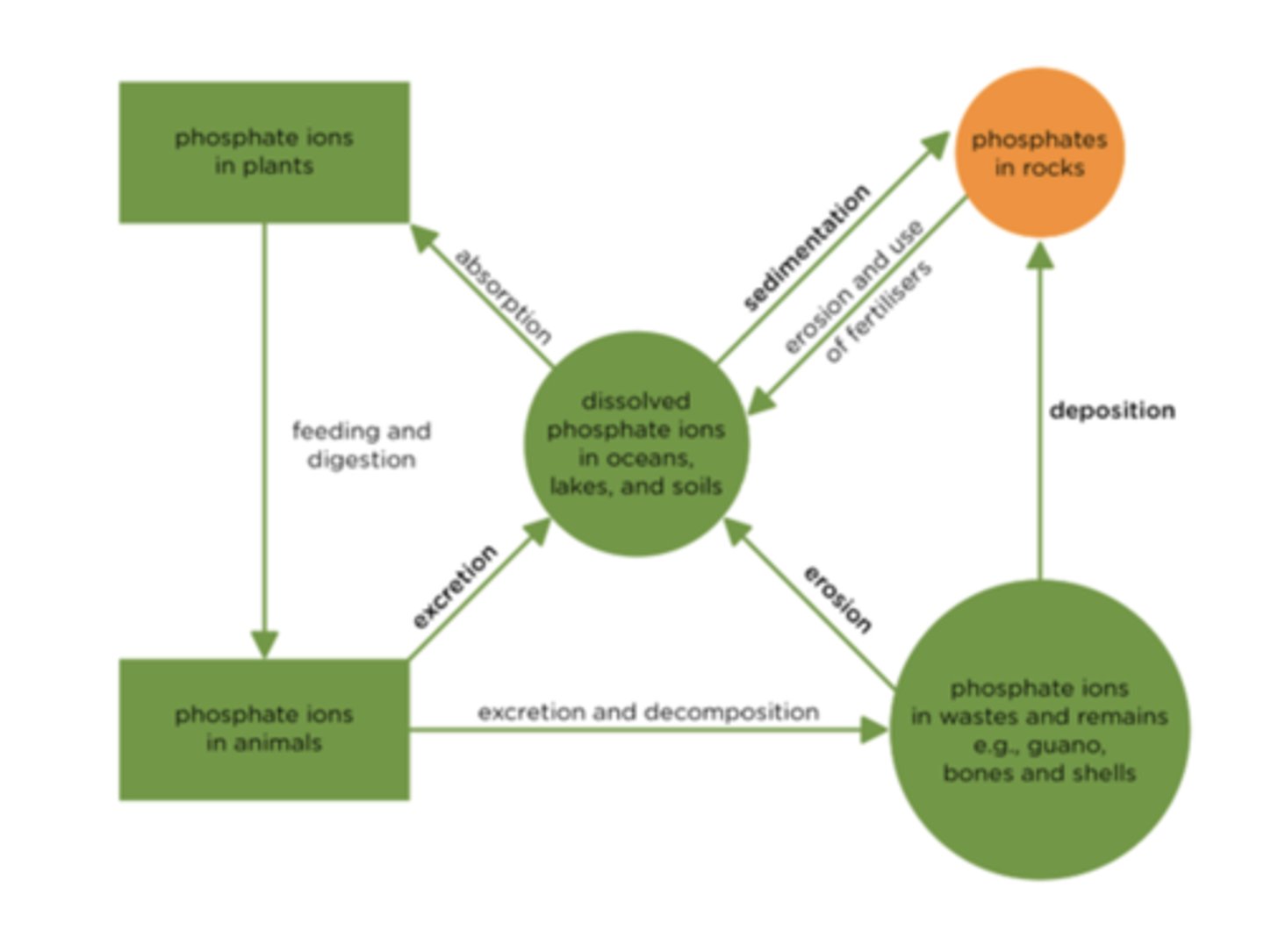
What is absorption in the phosphate cycle? (1)
The process where plants take up dissolved phosphate ions from the soil through their roots
What is sedimentation in the phosphate cycle? (3)
- The process where dissolved phosphate ions in water bodies settle
- To form phosphate-rich sediments
- Which can eventually become rocks
What is erosion in the phosphate cycle? (2)
- The process by which rocks or soil are broken down
- Releasing phosphate ions into water bodies such as oceans, lakes, and soils
What is deposition in the phosphate cycle? (3)
- The accumulation of phosphate ions from wastes and remains
- Such as guano, bones, and shells
- Forming phosphate-rich sediments
What is the role of excretion and decomposition in the phosphate cycle? (2)
- Involve the release of phosphate ions from animal waste and the breakdown of dead organisms
- Returning phosphate to the soil or water
What is erosion and use of fertilisers in the phosphate cycle? (2)
- Contribute phosphate ions to soils
- Which can then be absorbed by plants
Draw and label a diagram of the nitrogen cycle
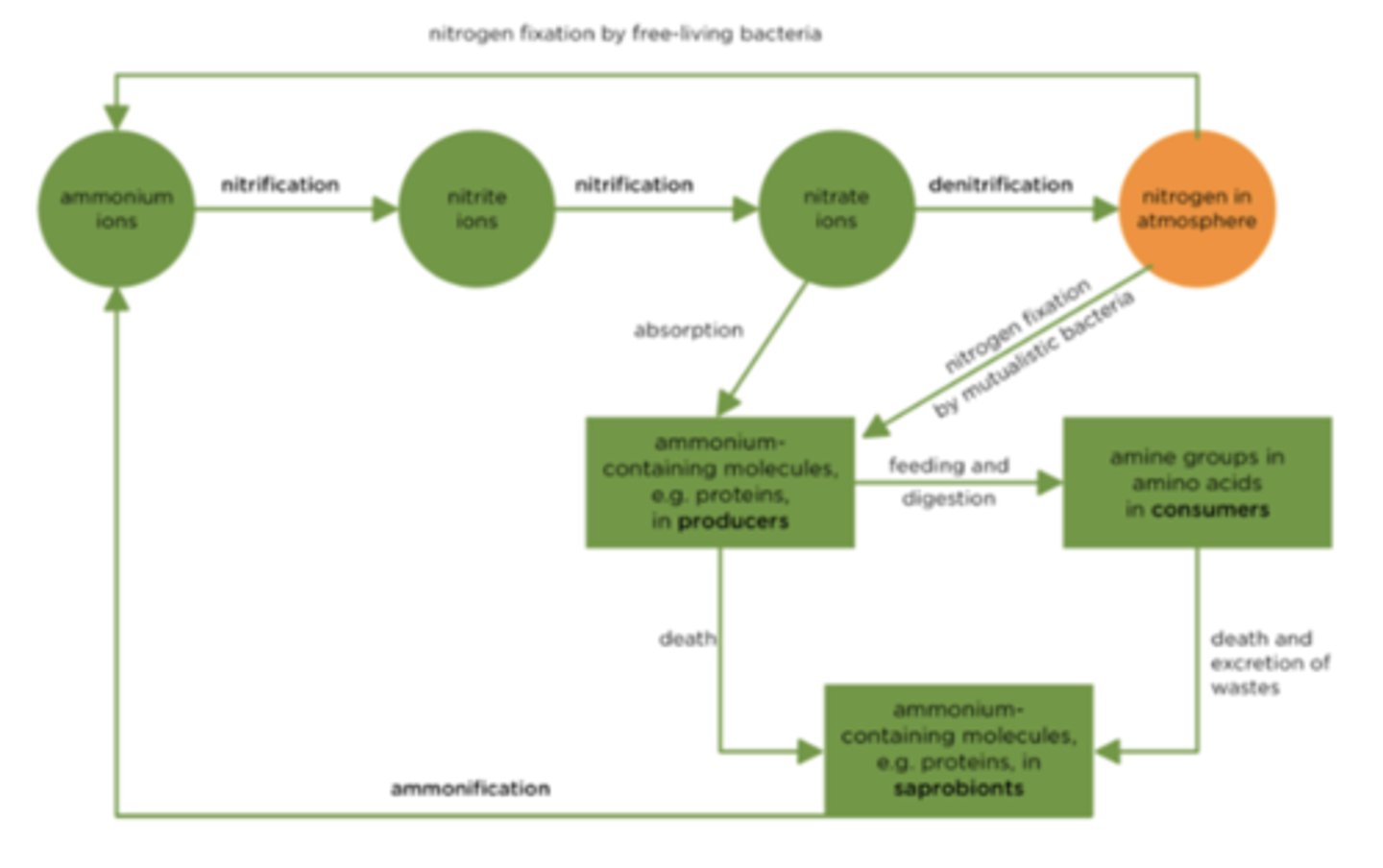
What is nitrification in the nitrogen cycle? (2)
- The process where ammonium ions are first converted to nitrite ions and then into nitrate ions
- By nitrifying bacteria in the soil
Name two microorganisms involved in nitrogen recycling in ecosystems. (2)
- Nitrosomonas
- Nitrobacter
What is the function of Nitrosomonas in the nitrogen cycle? (1)
Converts ammonia into nitrites
What is the function of Nitrobacter in the nitrogen cycle? (1)
Converts nitrites into nitrates
What is denitrification in the nitrogen cycle? (2)
- The process where nitrate ions are reduced and converted into nitrogen gas by anaerobic denitrifying bacteria
- Returning nitrogen to the atmosphere
What is nitrogen fixation in the nitrogen cycle? (2)
- The process where nitrogen gas from the atmosphere is converted into ammonium ions
- By free-living (Azotobacter) or mutualistic (Rhizobium) nitrogen-fixing bacteria
What is ammonification in the nitrogen cycle? (2)
- The process where dead organic matter or waste is broken down by saprobiotic organisms
- Converting nitrogen-containing organic compounds into ammonium ions
What is absorption in the nitrogen cycle? (2)
- The uptake of nitrate ions by producers, such as plants, from the soil
- For use in synthesising proteins
What is eutrophication? (2)
- The process by which a body of water becomes enriched with nutrients
- Leading to excessive growth of algae and other aquatic plants
Describe what happens during eutrophication (9)
1. Leaching and runoff of inorganic fertilisers occurs
2. So there is an increased concentration of nitrates and phosphates in lake
3. Algae bloom on surface of water
4. Which means there is no light for plants on water bed
5. So they can't photosynthesise which causes the death of plants
6. So there will be large quantities of decaying organic matter
7. Therefore, Increased numbers of aerobic saprobionts
8. Aerobic bacteria, fish and invertebrates die as dissolved oxygen is used up by saprobionts and they cannot respire
9. This causes a reduction in species diversity