Inner Ear Anatomy
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
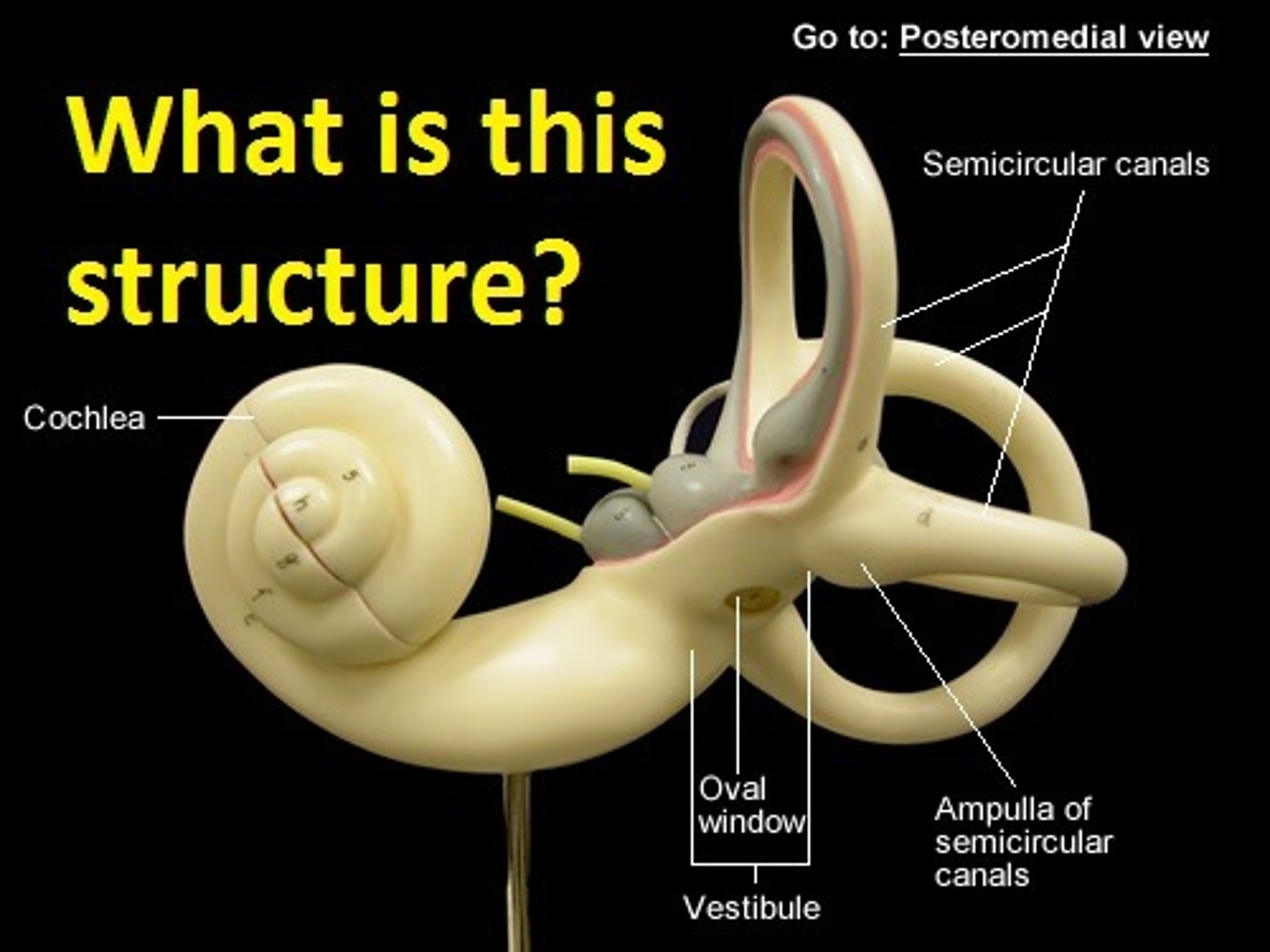
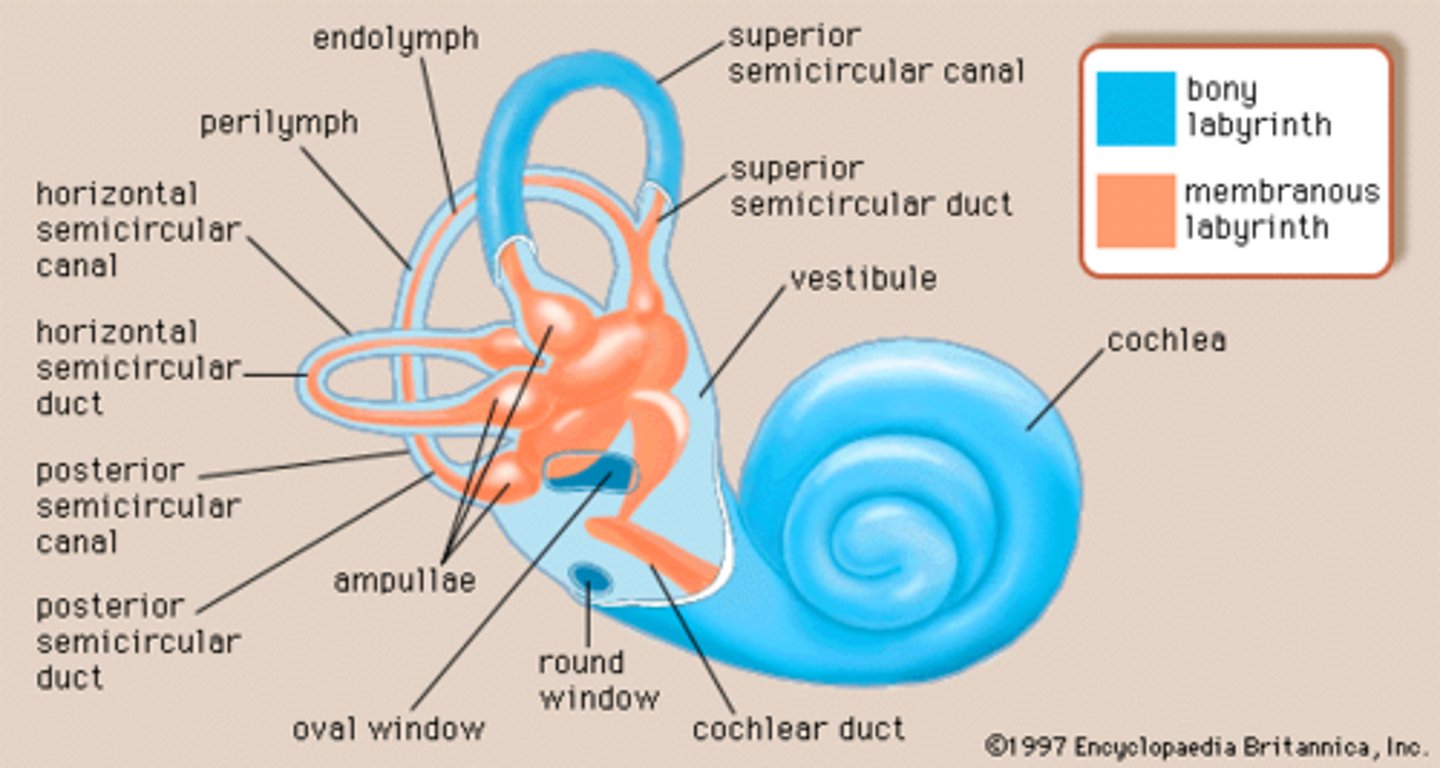
bony labyrinth
intercommunicating bony cavities located in the inner ear filled with perilymph
membranous labyrinth
closed system of membranous tubes/sacs/ducts inside the bony labyrinth. filled with endolymph
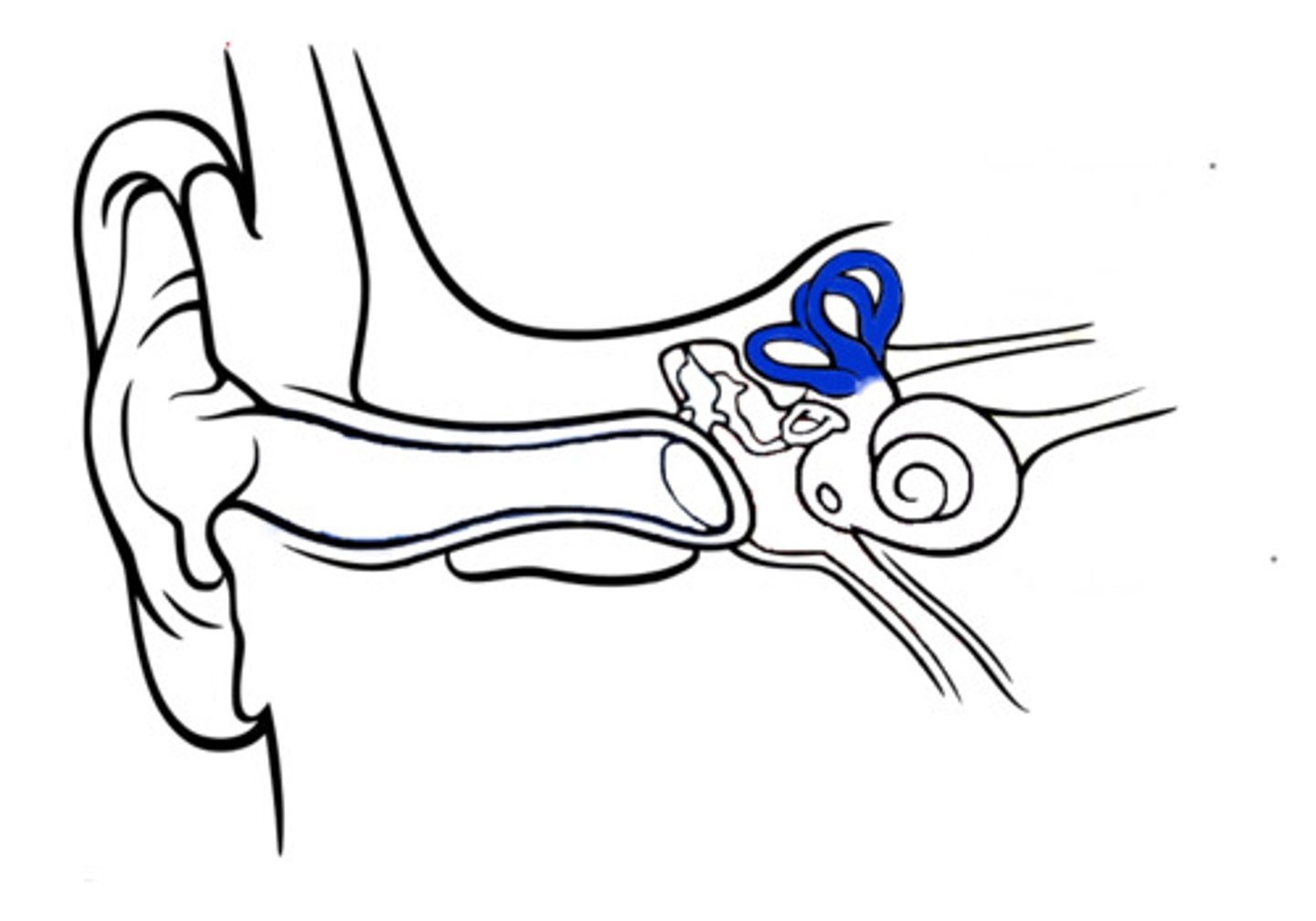
vestibular system
semicircular canals, utricle, saccule. located next to the cochlea. allow sensation of rotation/motion/balance
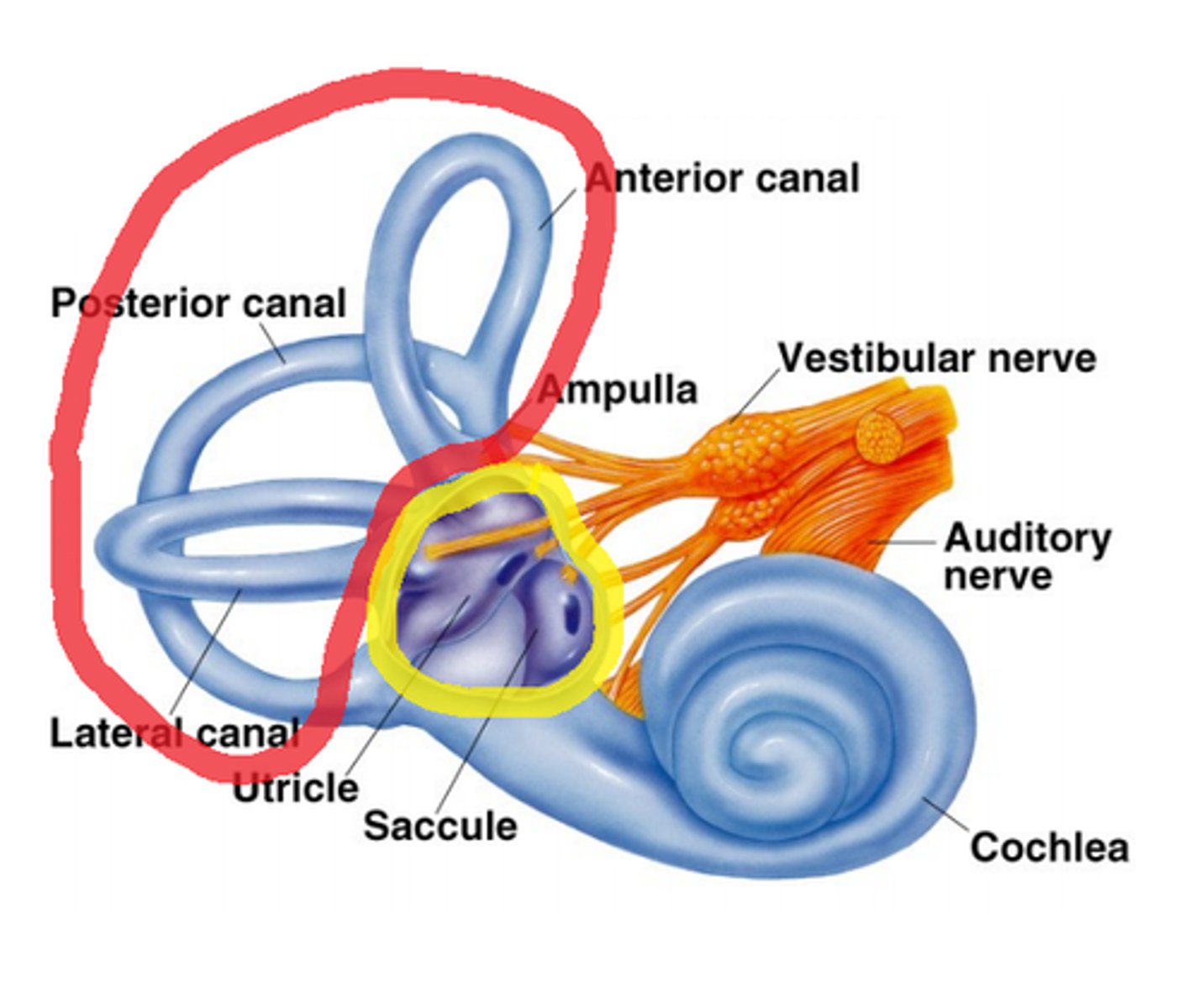
semicircular canals
three fluid-filled canals (loopy things) that sense rotational head movements
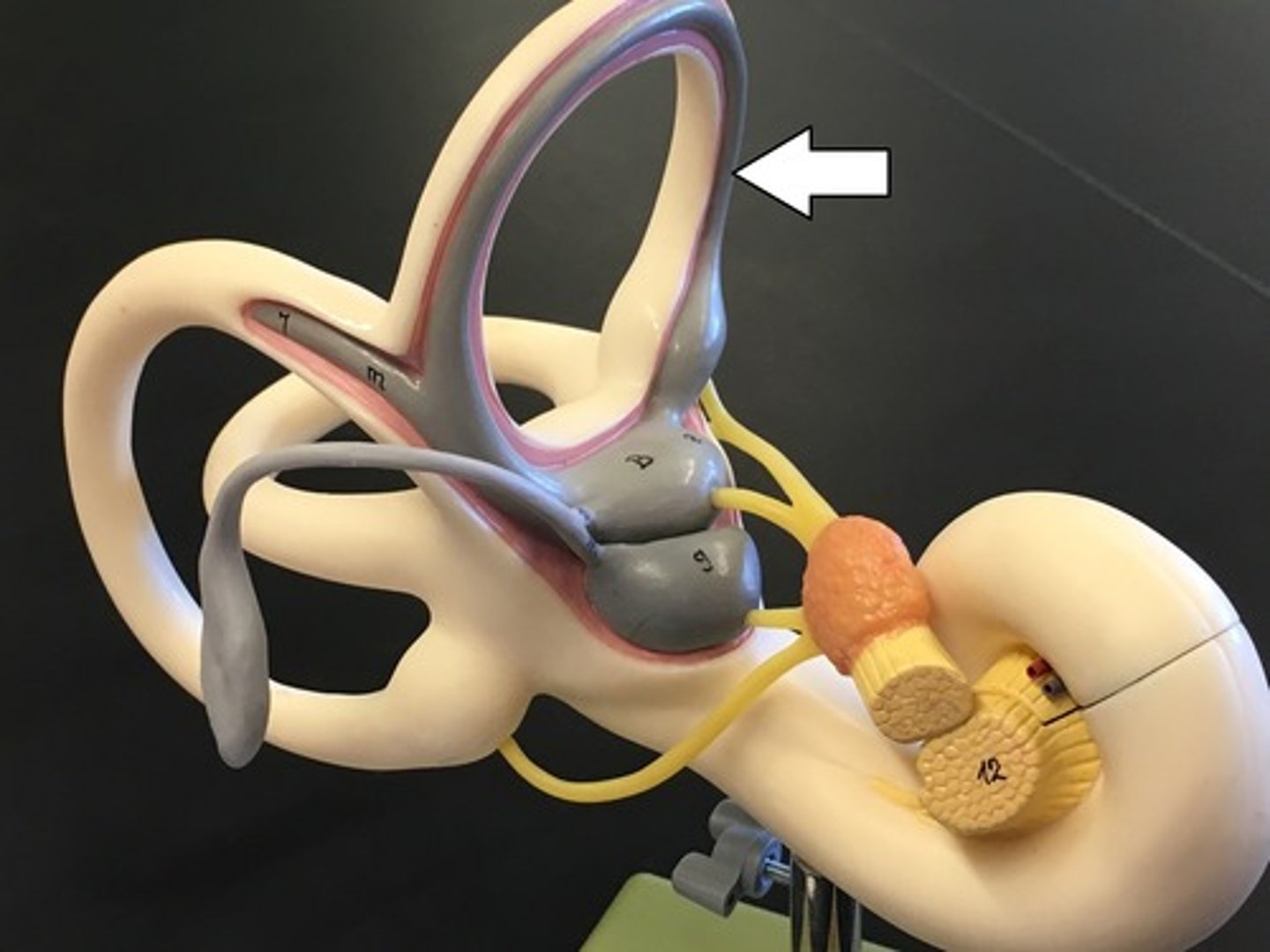
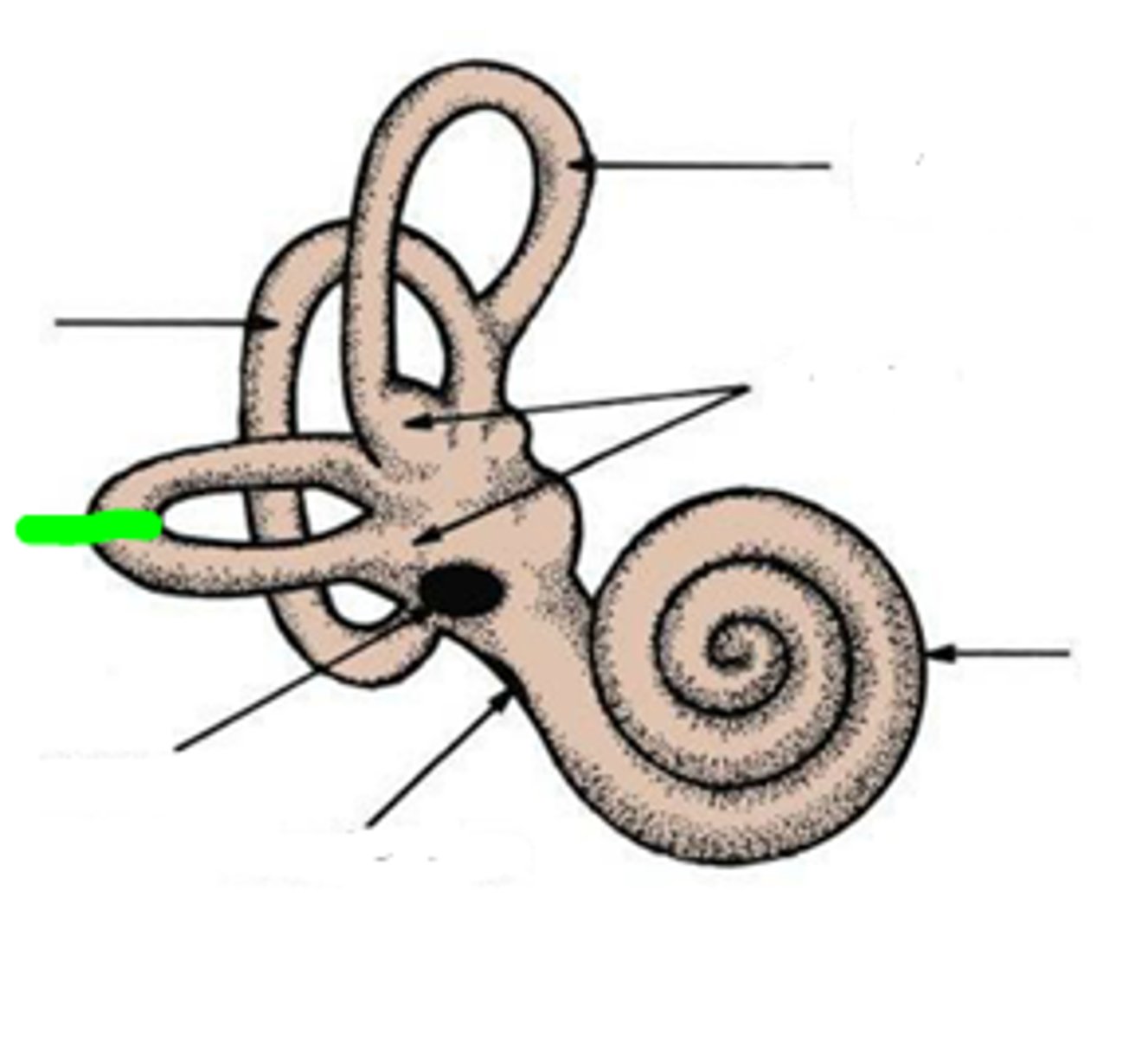
anterior/superior semicircular canal
detects "nodding yes" movement. non-ampullated end unites with non-ampullated end of posterior SCC to form the crus commune
posterior semicircular canal
Detects tilting the head to the side, or cartwheels. lower ampullated end communicates w the vestibule
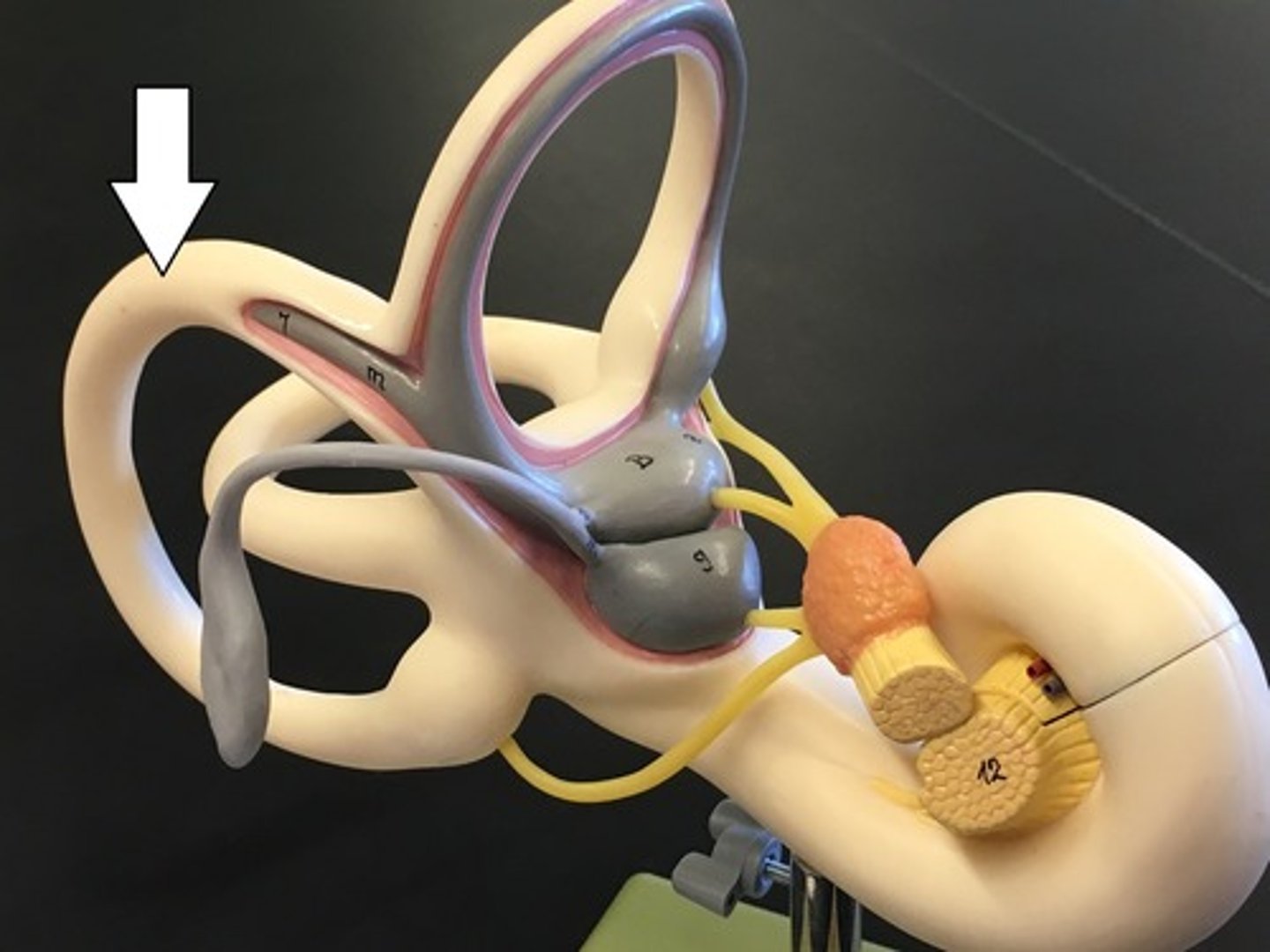
lateral semicircular canal
both ends open into vestibule
ampullae
bulbous expansions at the base of each canal in the inner ear that contain the sensory organs for balance and head rotation
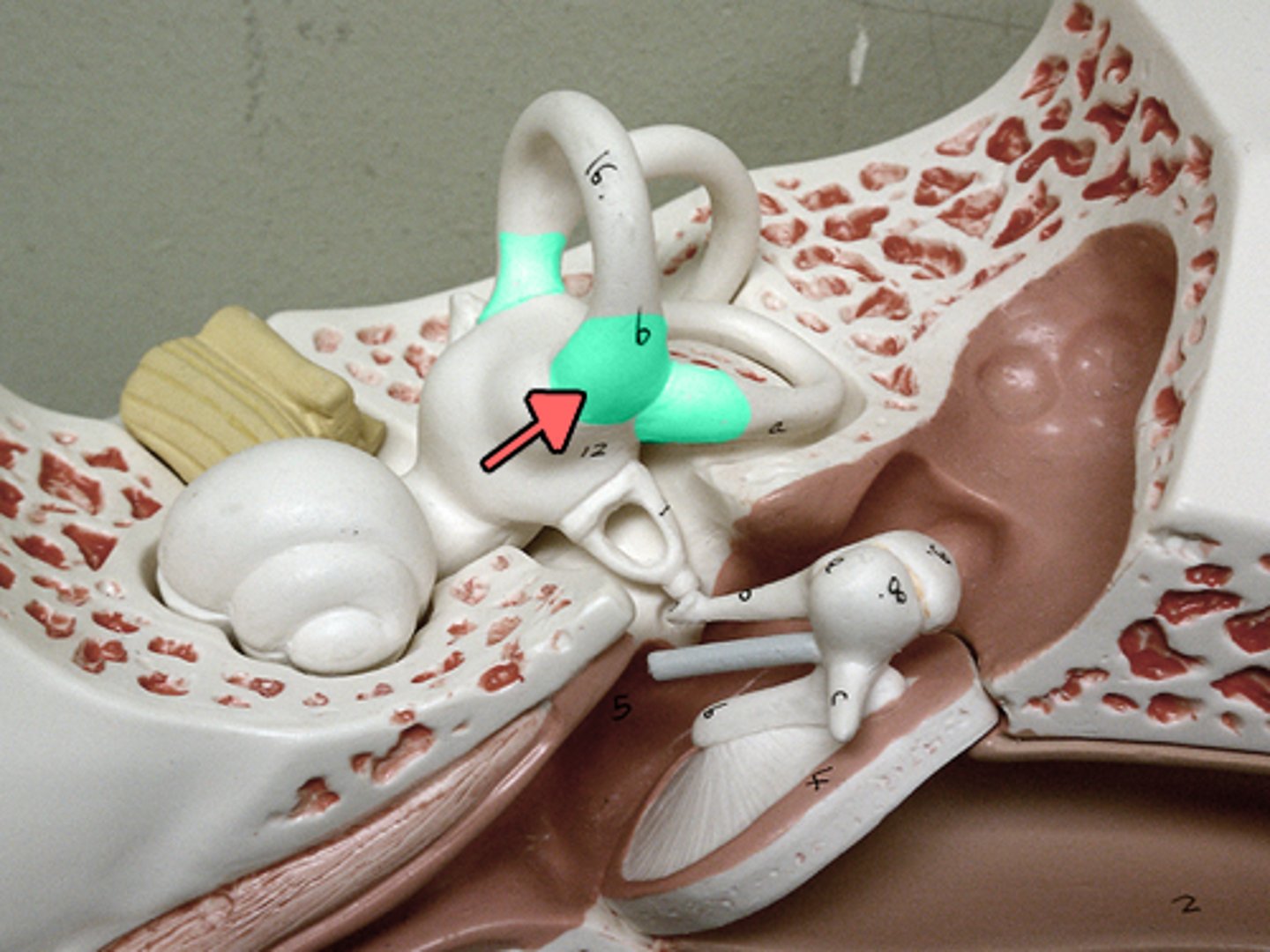
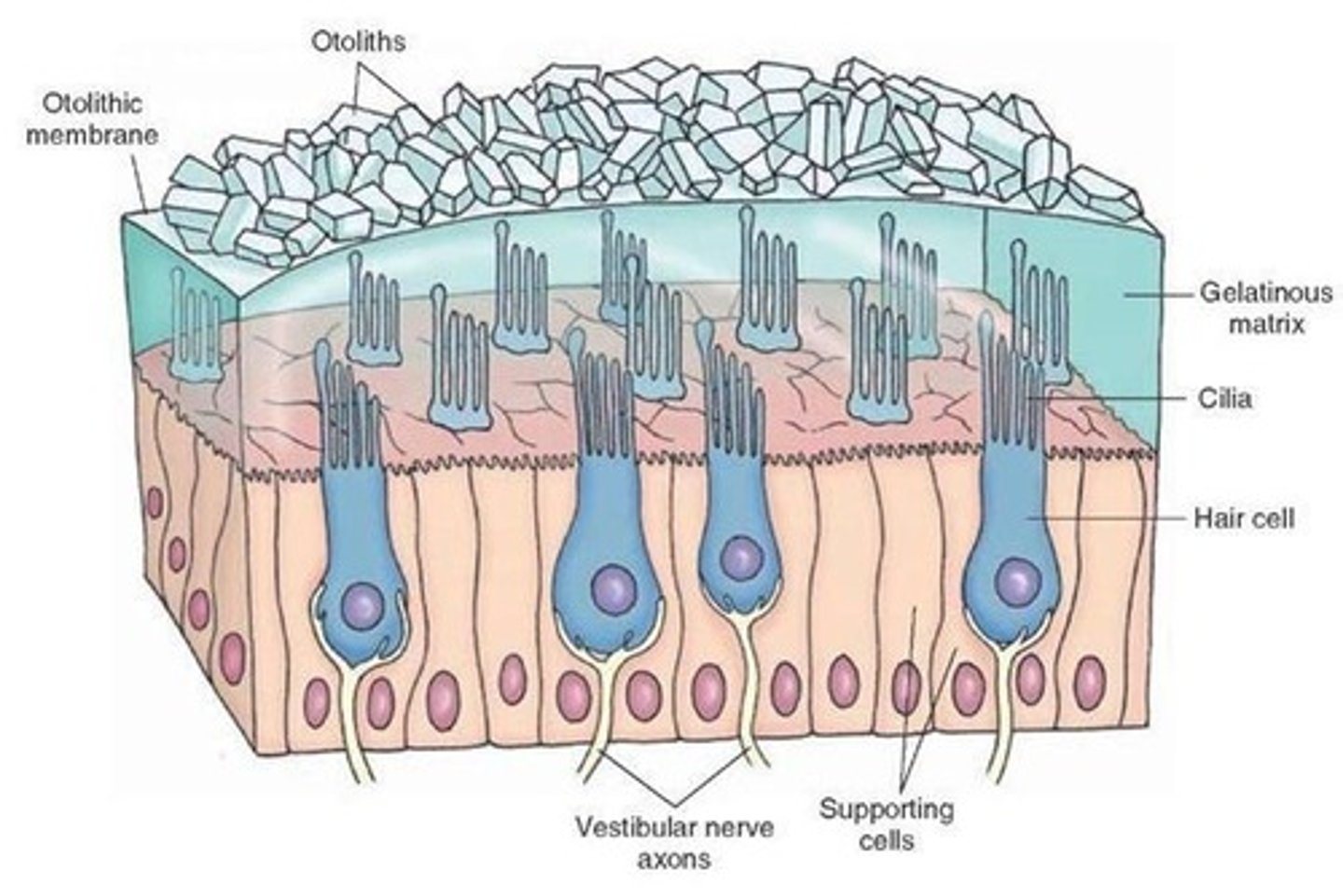
otoliths (ear rock)
sit in ampullae surrounded by hair cells. as head moves, otoliths stimulate hair cells which send signals to brain of movement.
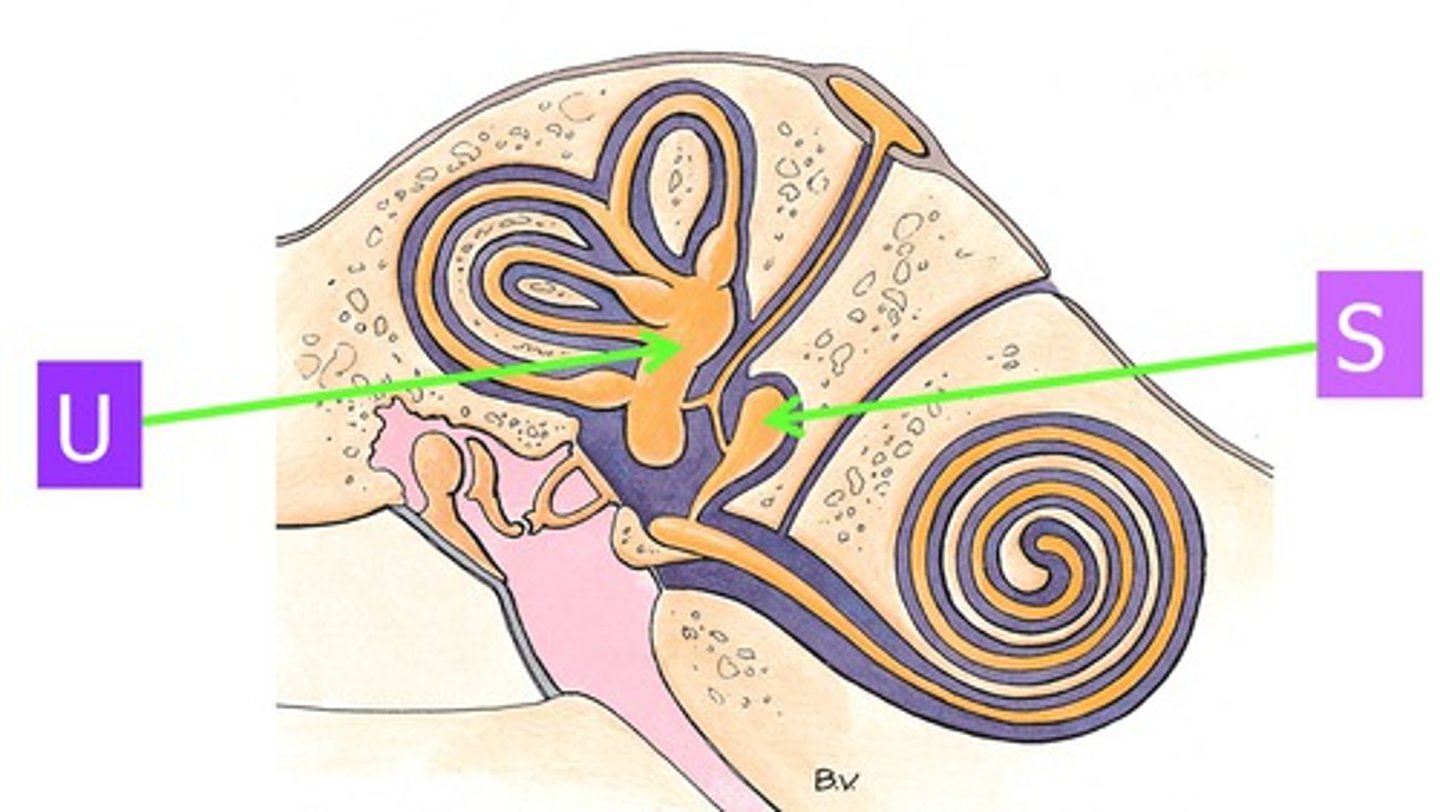
utricle
the larger of two sacs within the membranous labyrinth of the vestibule in the inner ear
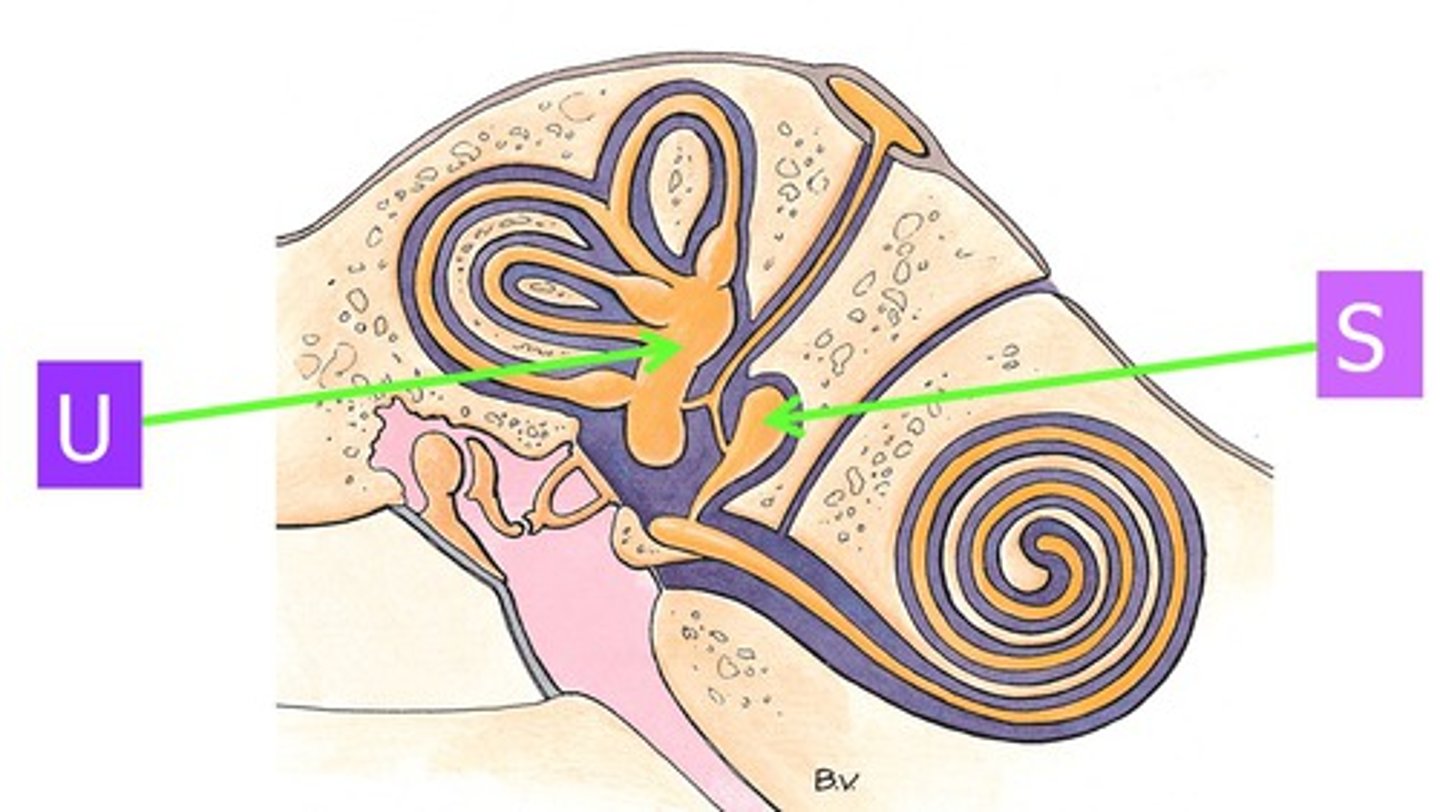
saccule
the smaller of two sacs within the membranous labyrinth of the vestibule in the inner ear
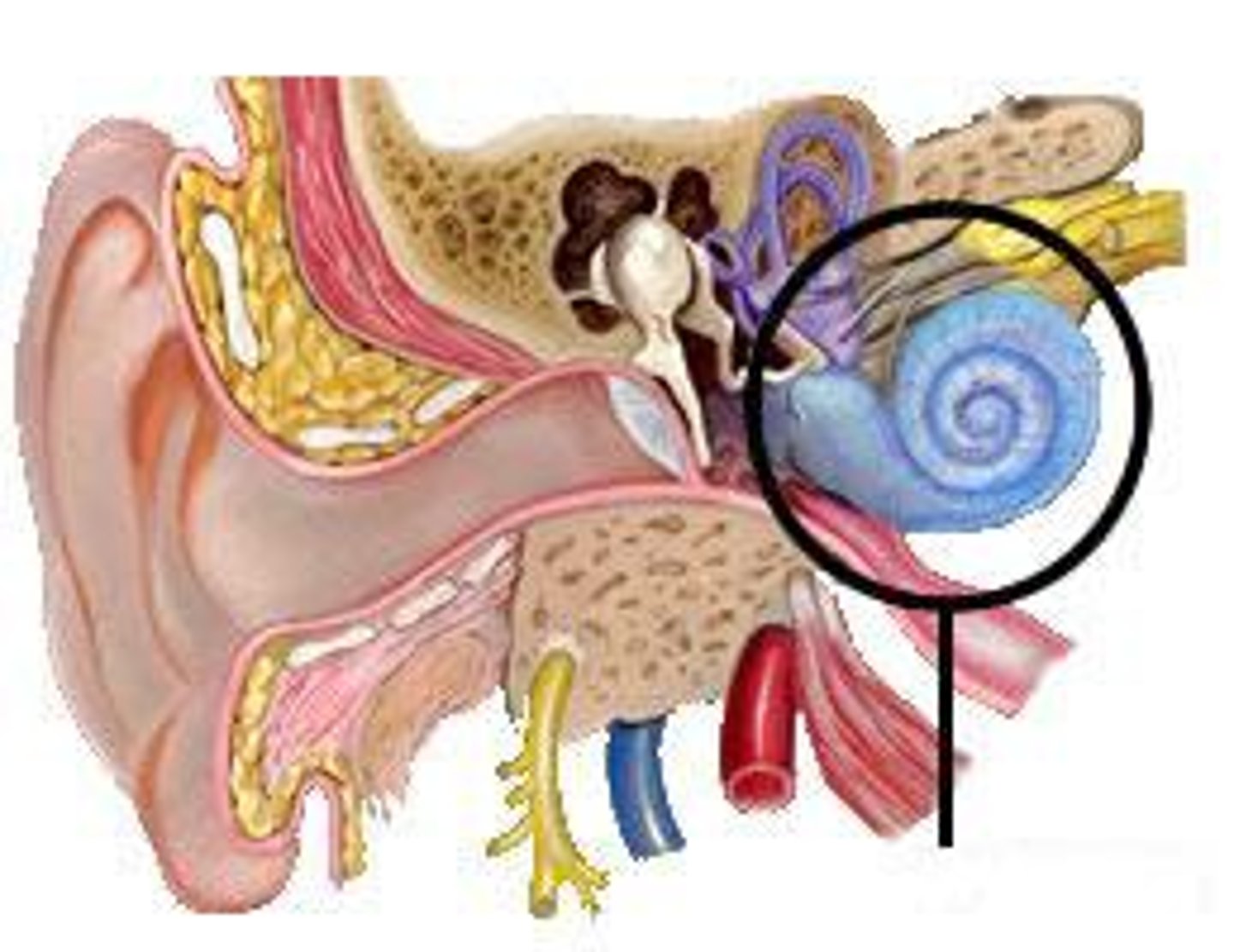
cochlea
a coiled, bony, fluid-filled tube in the inner ear through which sound waves trigger nerve impulses
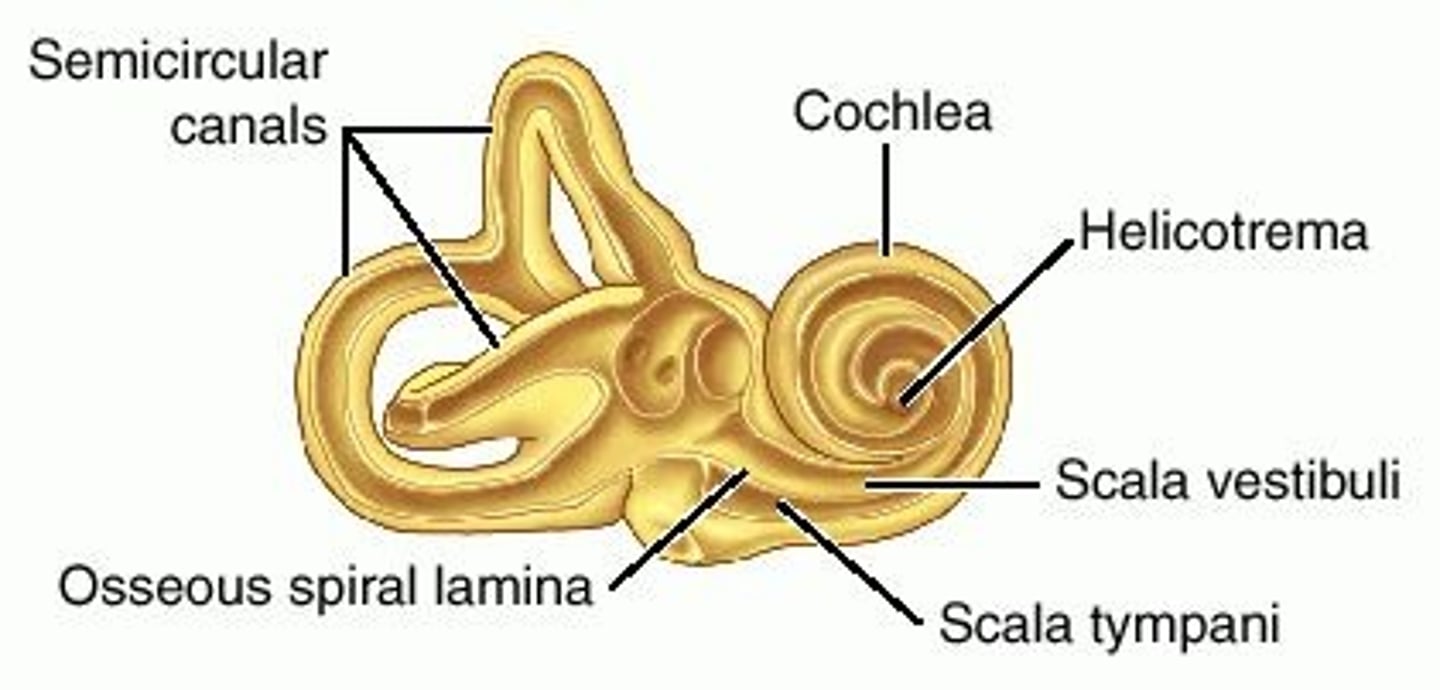
helicotrema (spiral hole)
the opening that connects the scala vestibuli and scala tympani chambers at the apex of the cochlea.
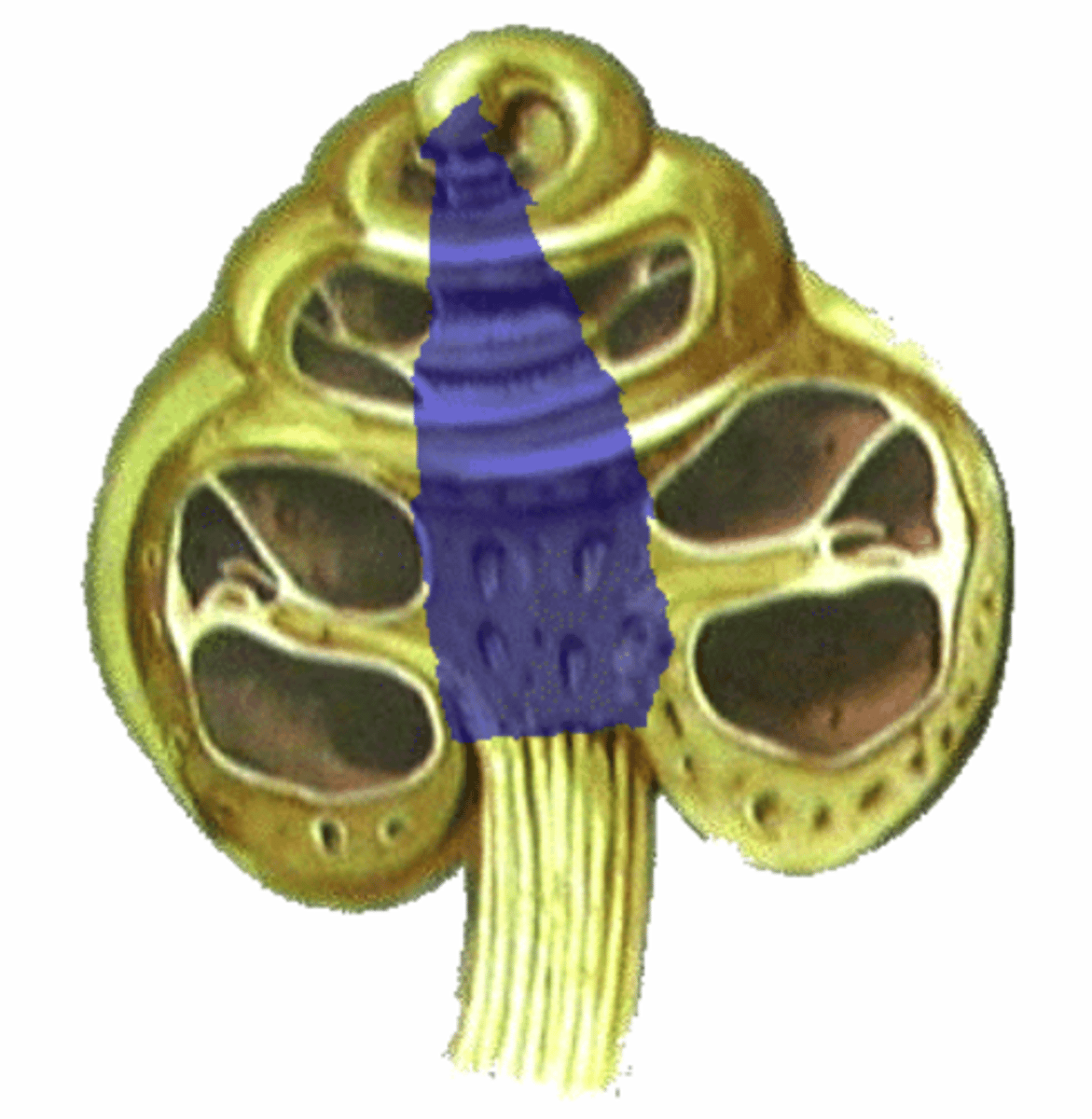
modiolus
bony core that cochlear canal spirals around. elongated cone
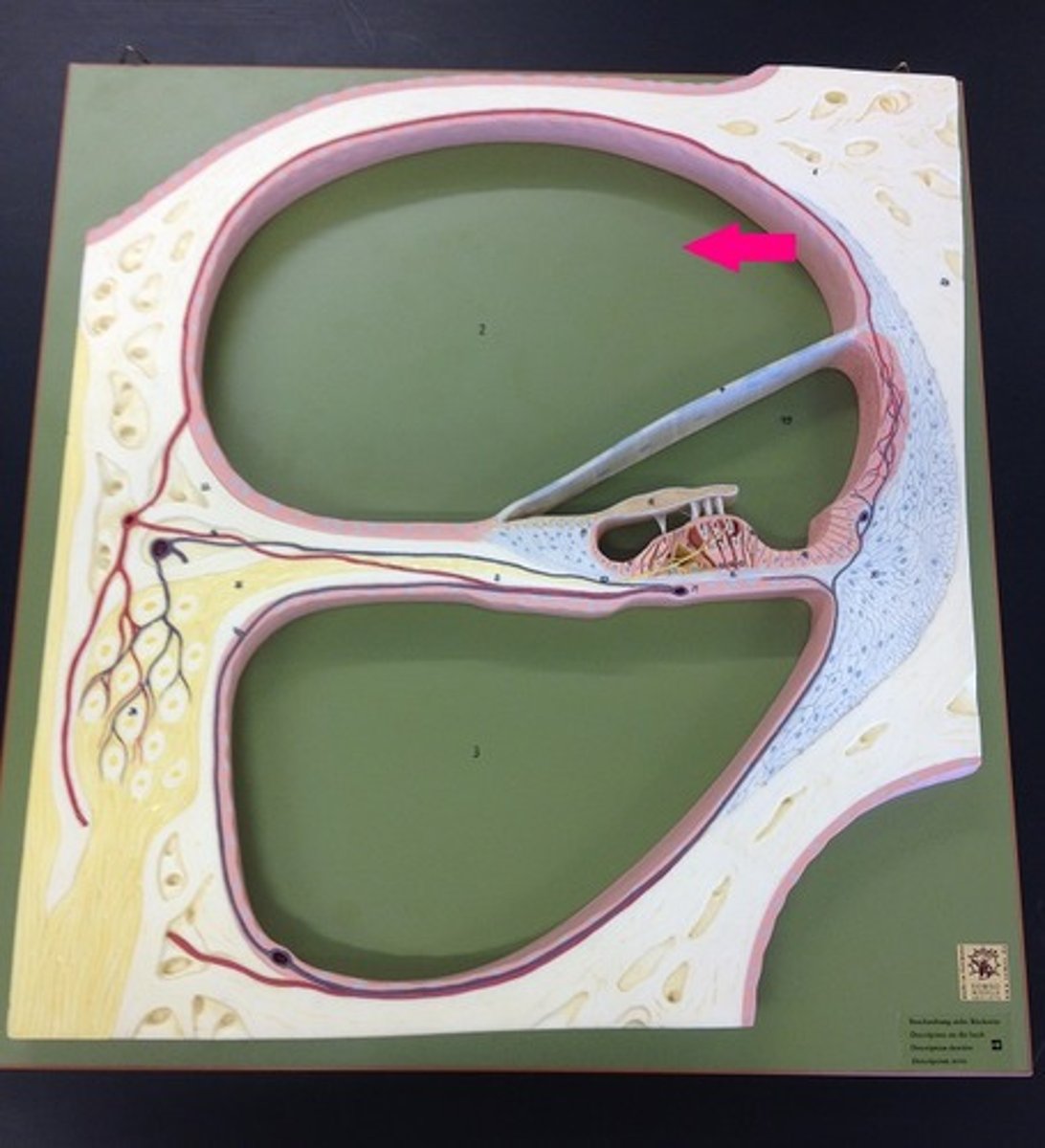
scala vestibuli/vestibular duct
perilymph-filled top chamber of cochlea. Closest to vestibular system.

scala tympani
perilymph-filled cochlear chamber that connects to the round window
scala media
Middle chamber of the cochlea; filled with endolymph
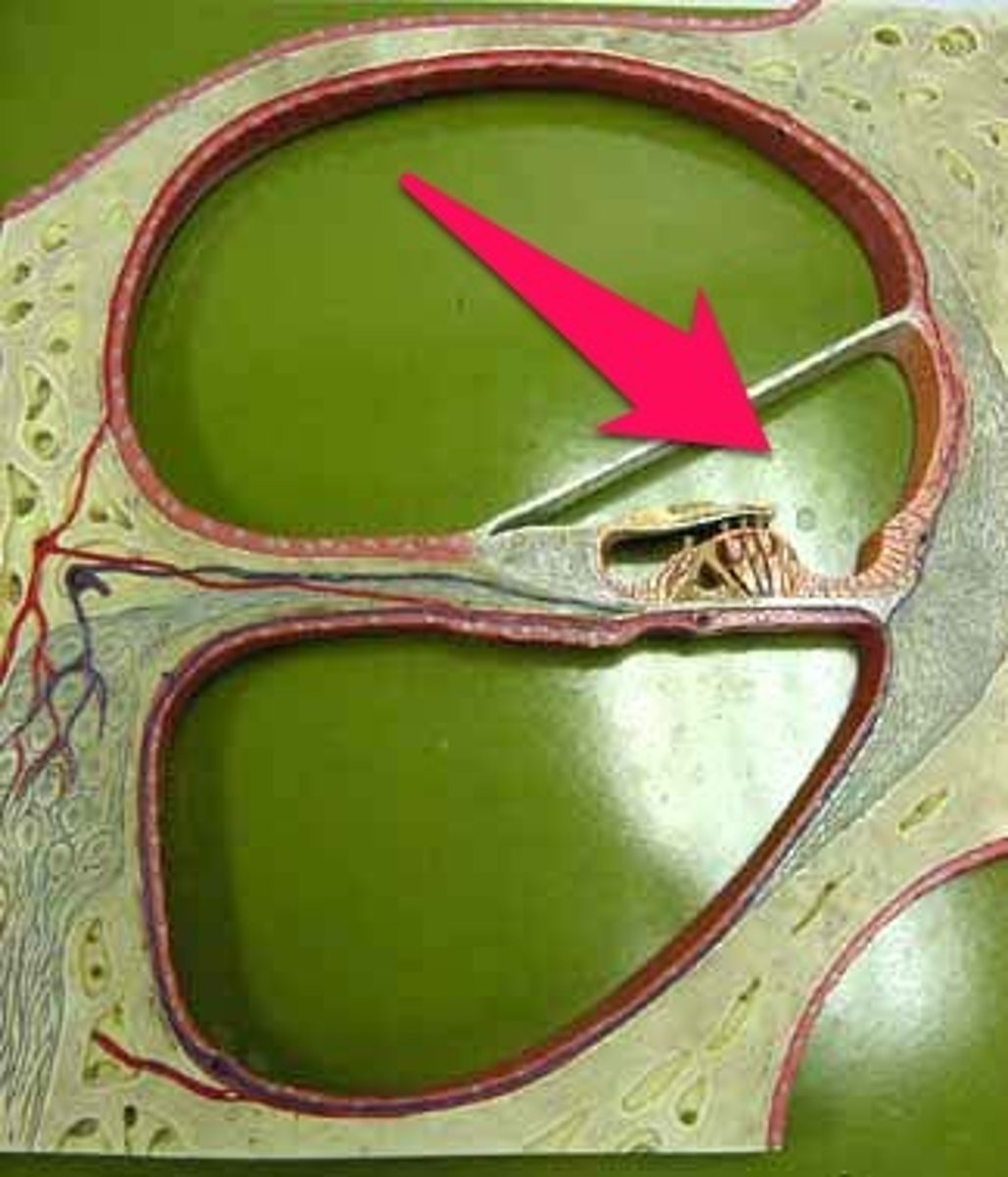
perilymph
fluid that fills the bony labyrinth of the inner ear
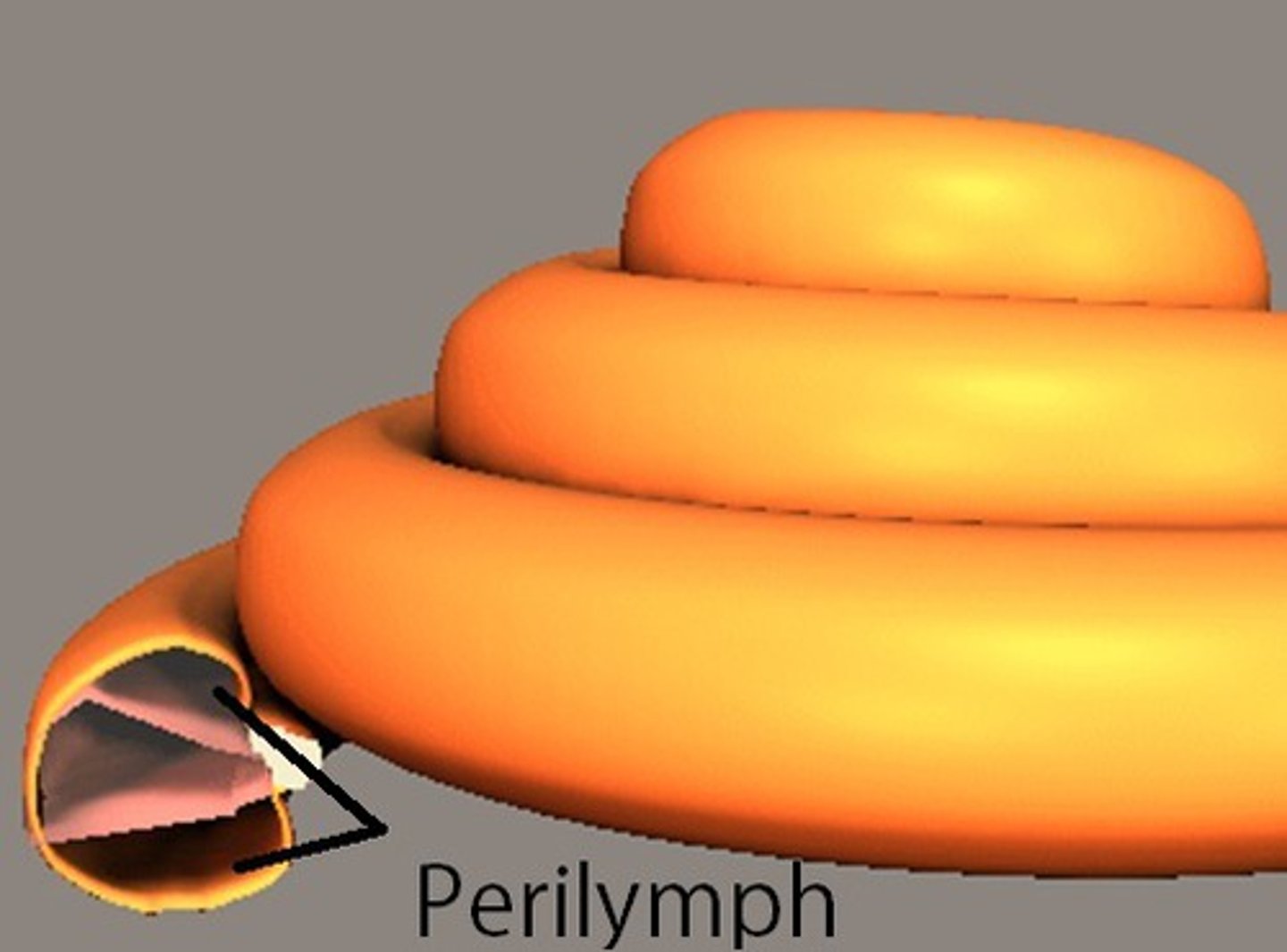
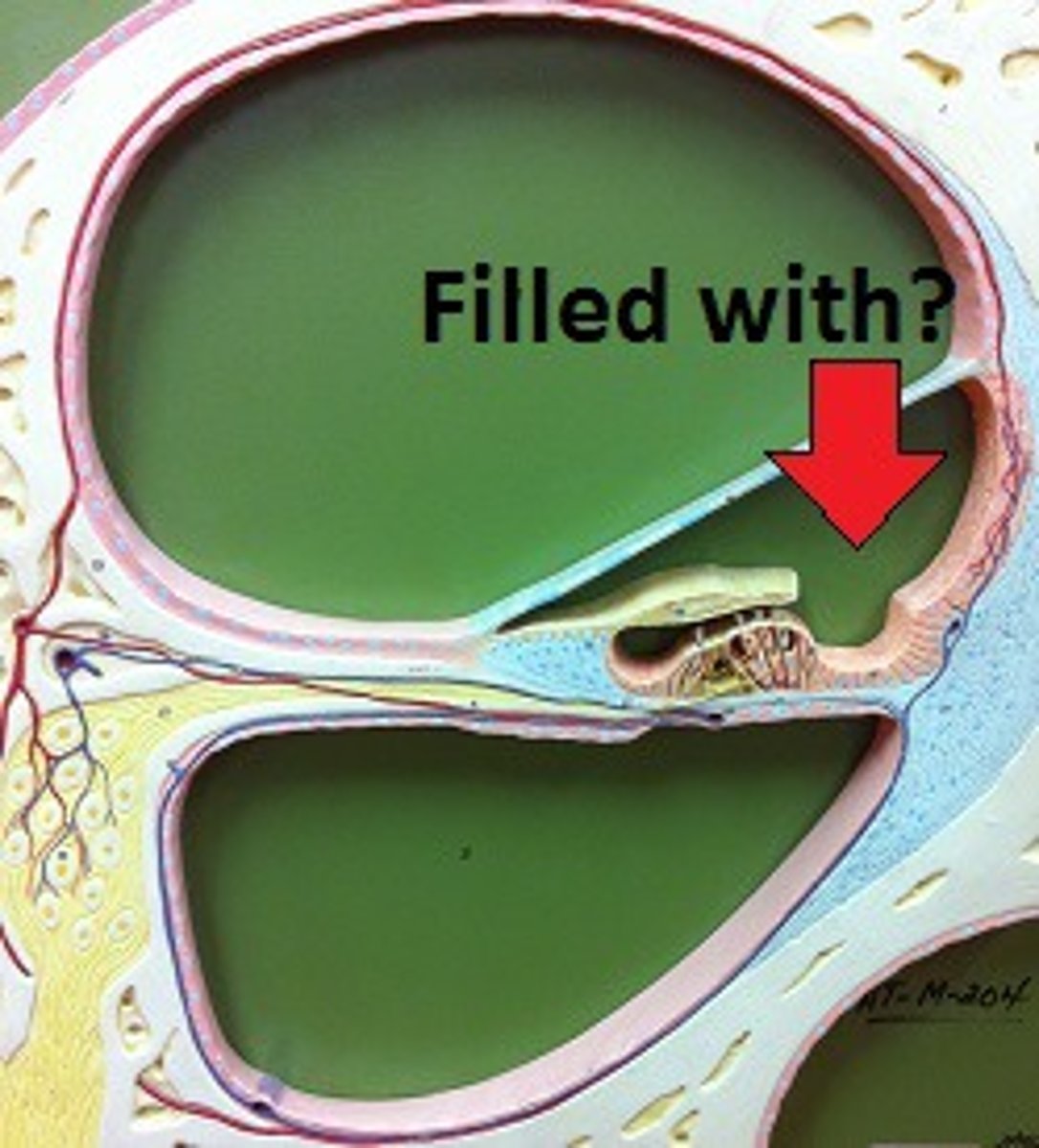
endolymph
fluid within the membranous labyrinth of the inner ear
stria vascularis
external wall of cochlear duct composed of mucosa that secretes endolymph
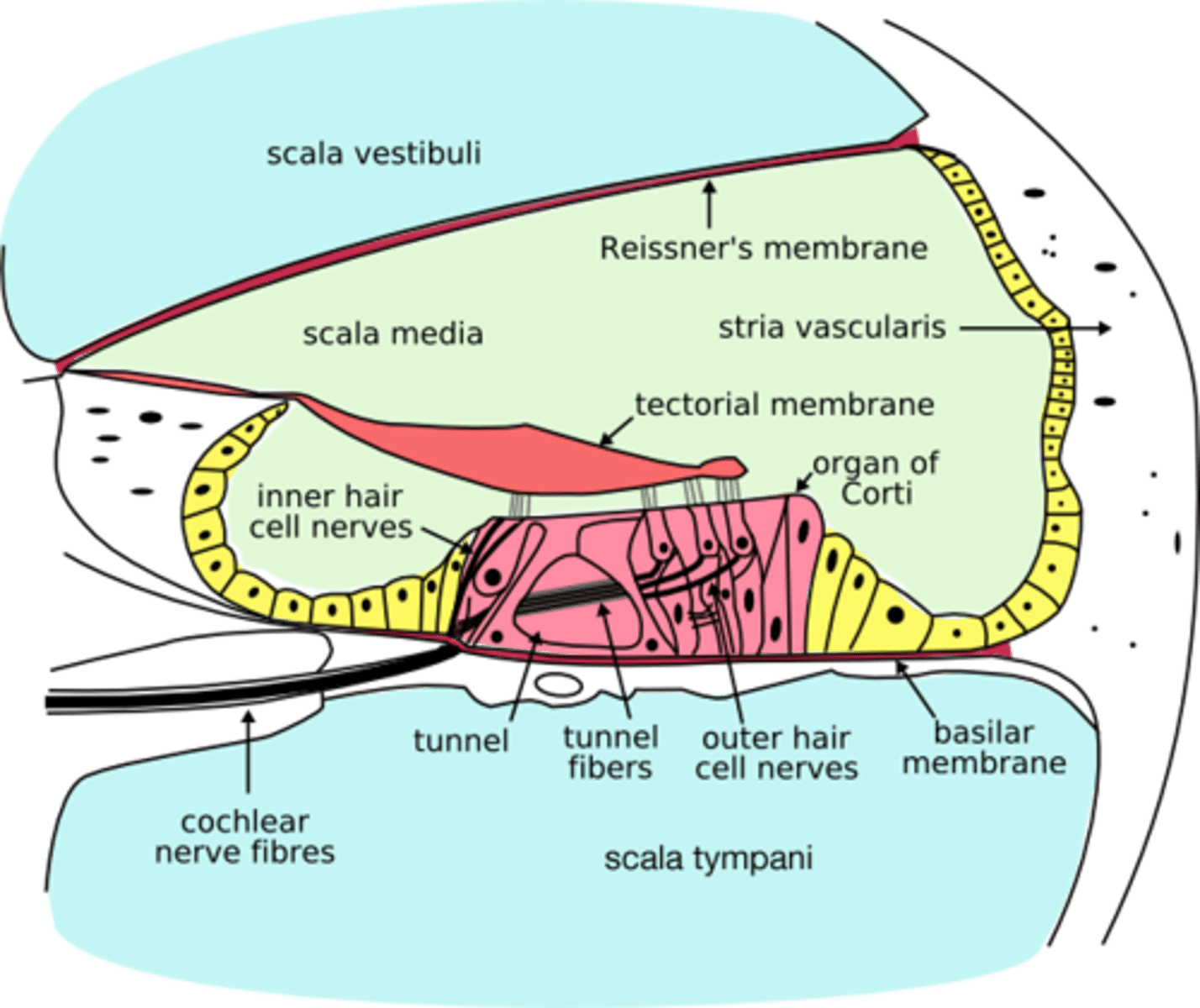
Reissner's membrane (vestibular membrane)
membranous separation between scala vestibuli and scala media
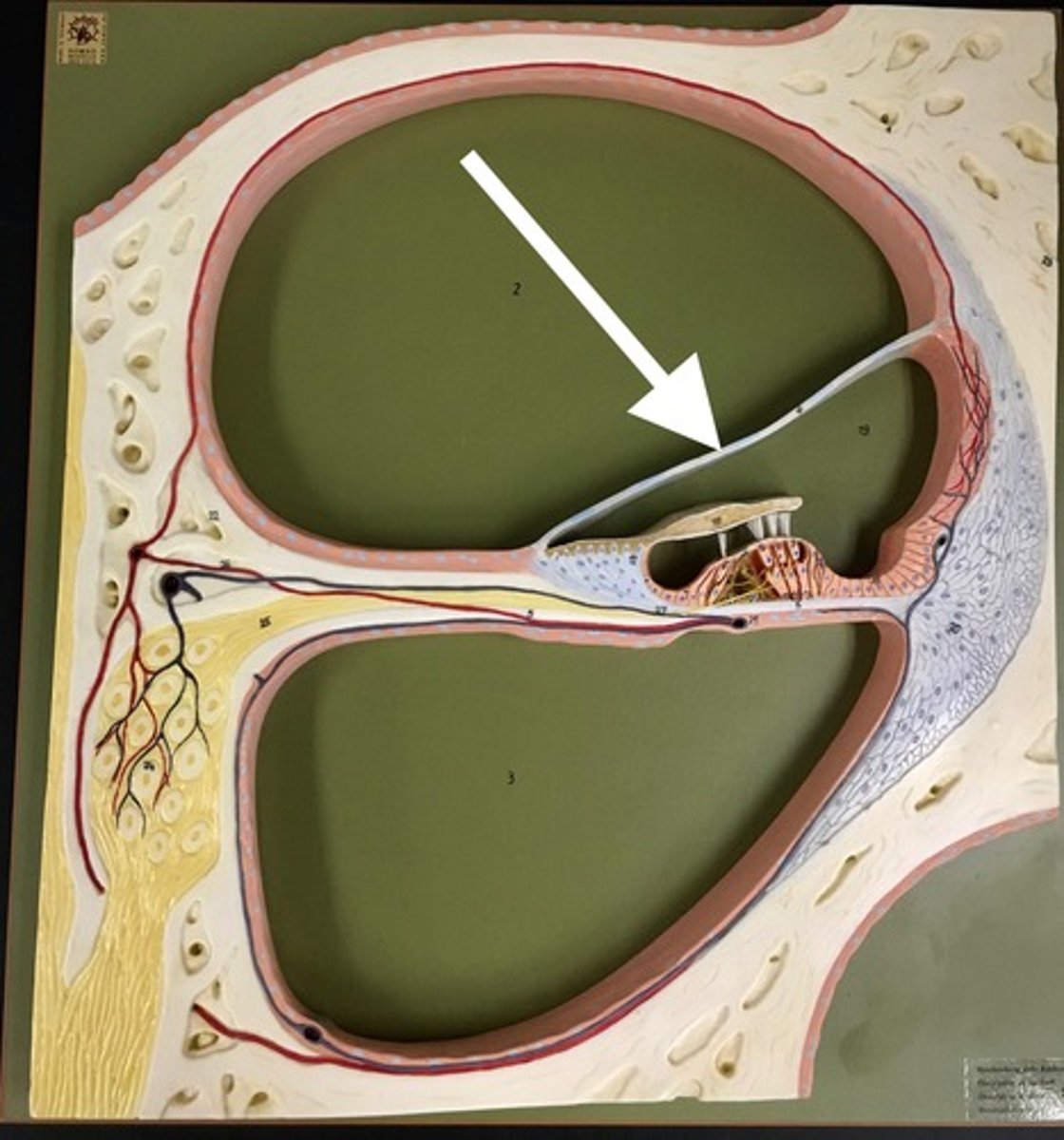
spiral lamina
bony shelf that projects from the modiolus
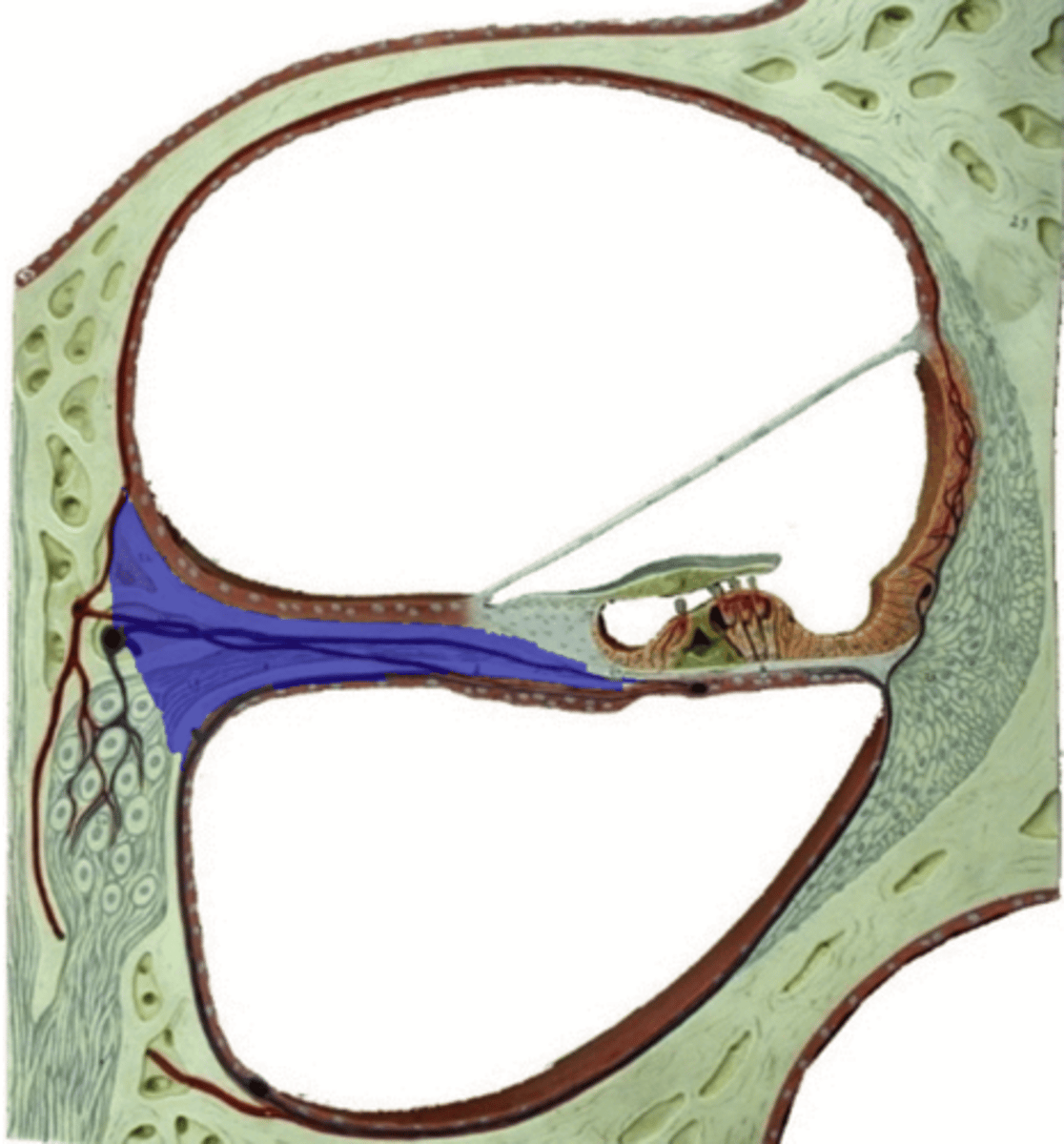
spiral ligament
fibrous connective tissue on the lateral wall of the cochlear duct that supports the lateral edge of the basilar membrane
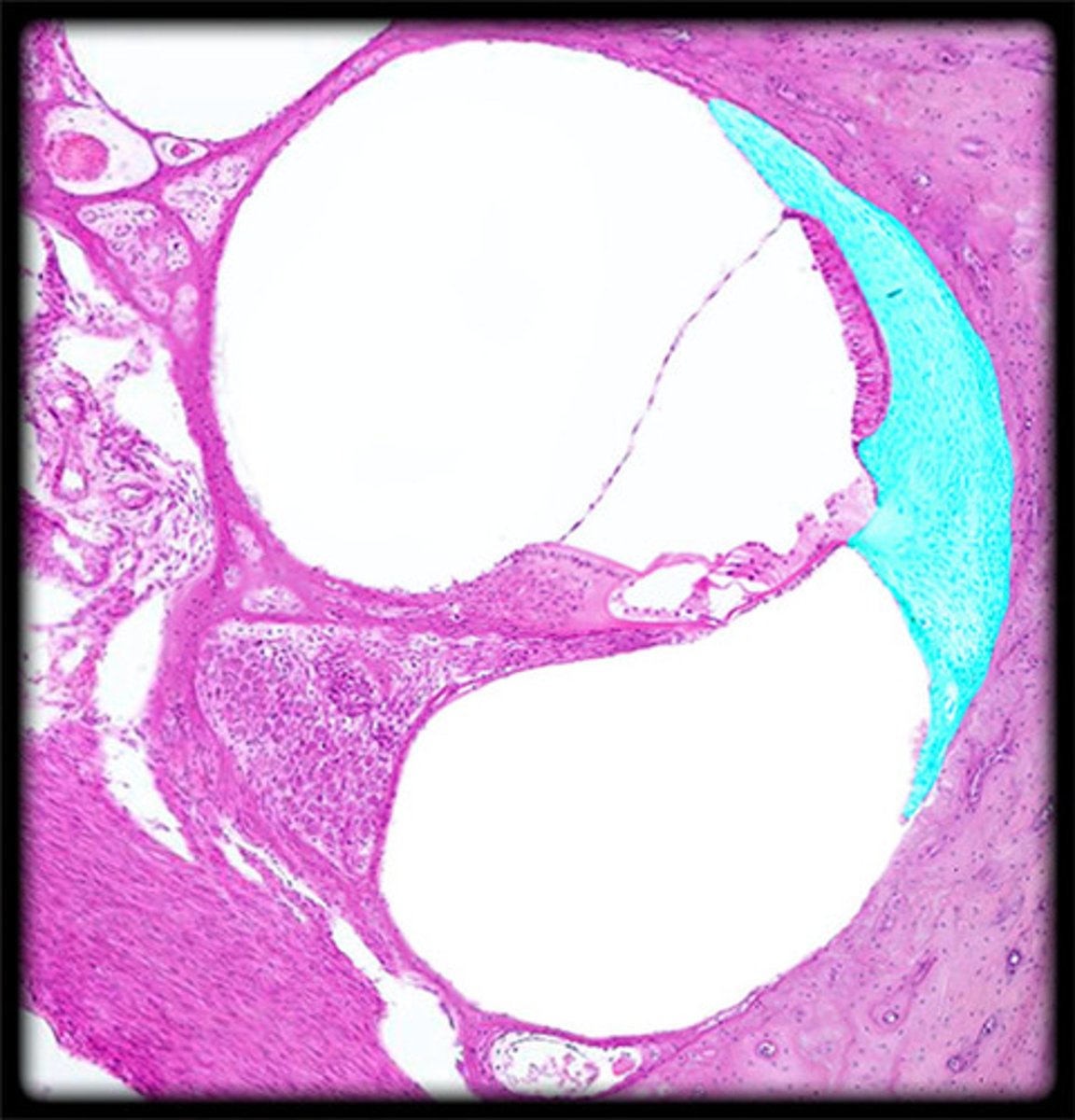
spiral limbus
ridge of fibrous connective tissue that connects to tectorial membrane
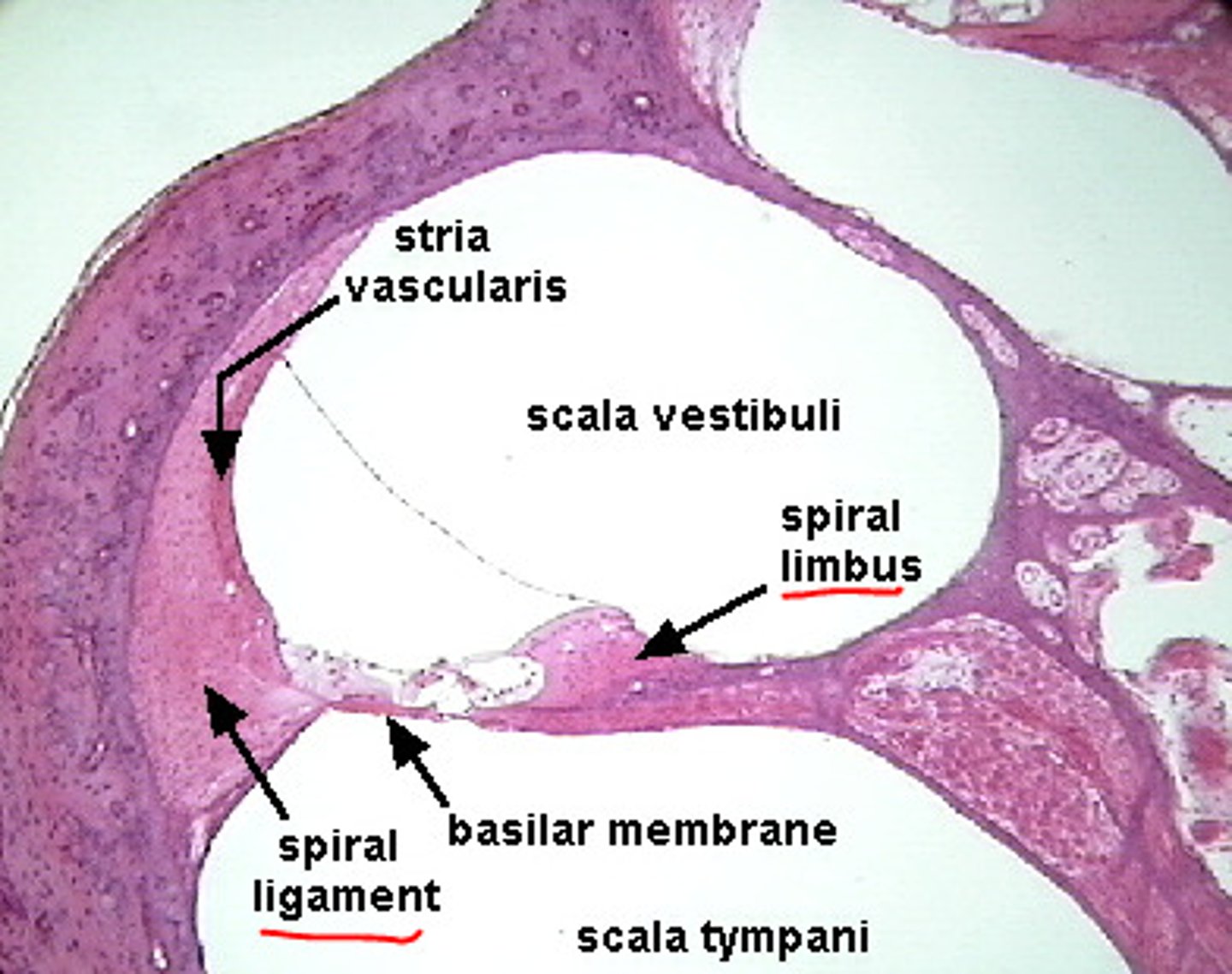
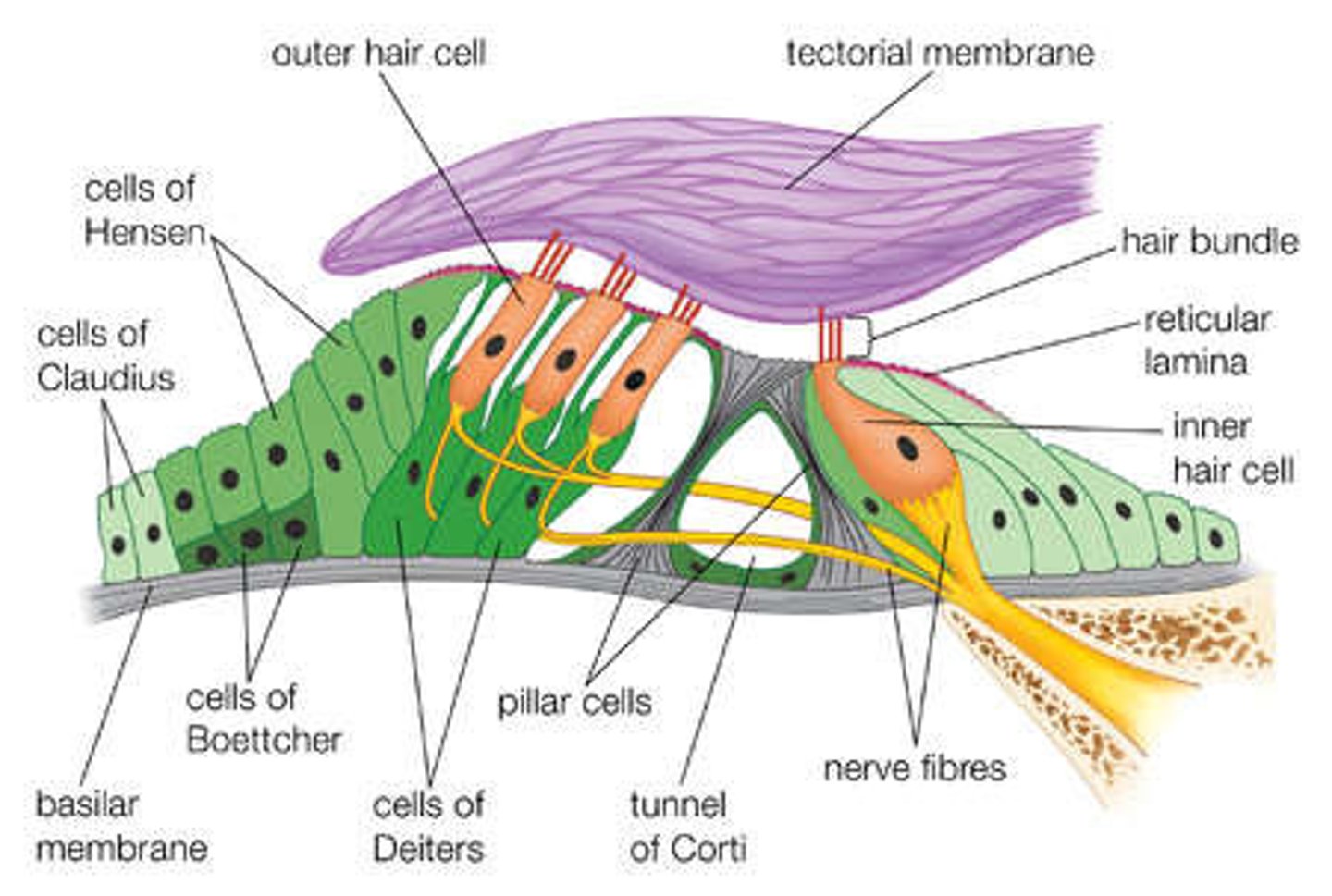
basilar membrane
runs the length of the cochlea in the inner ear and holds the hair cells.
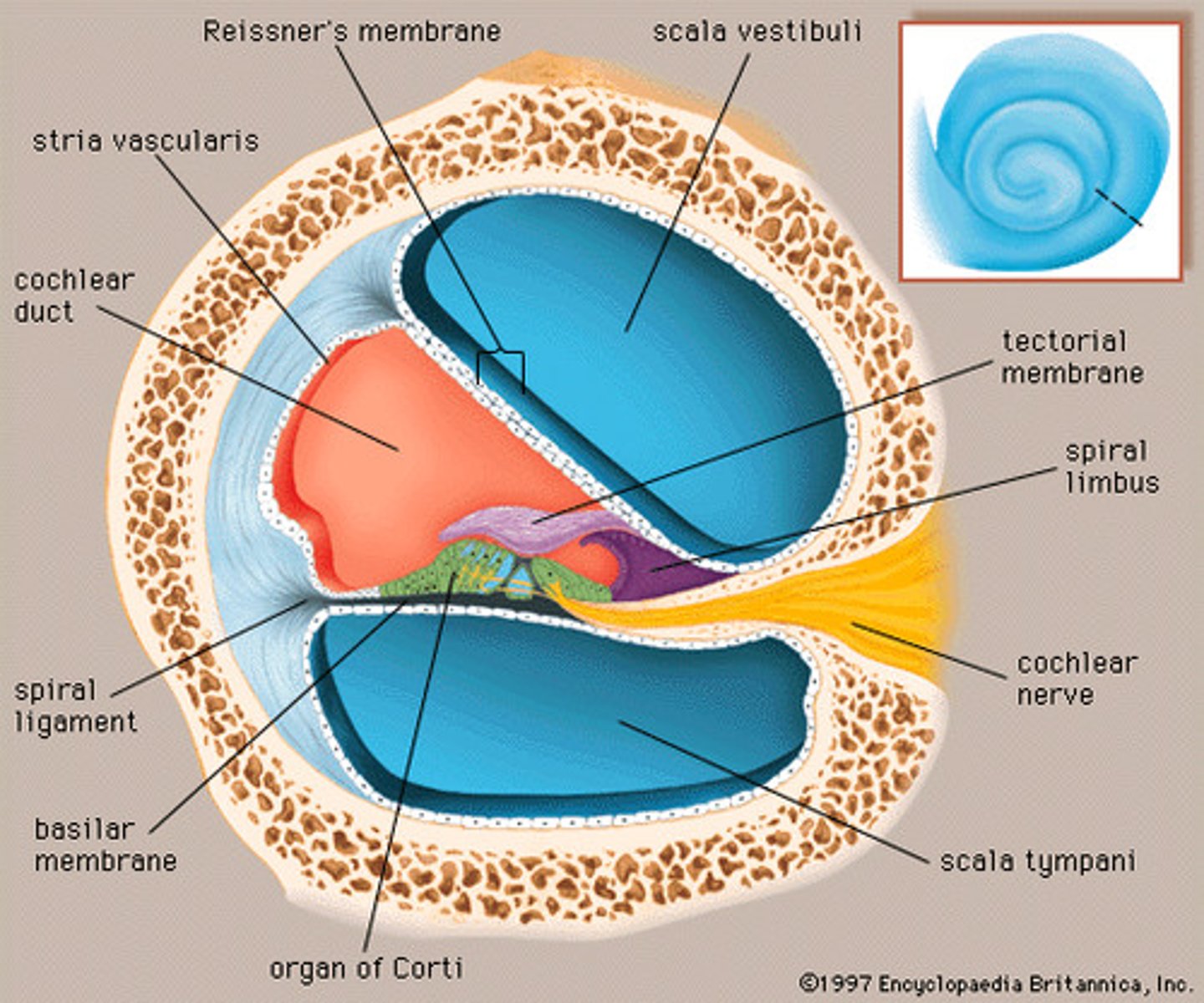
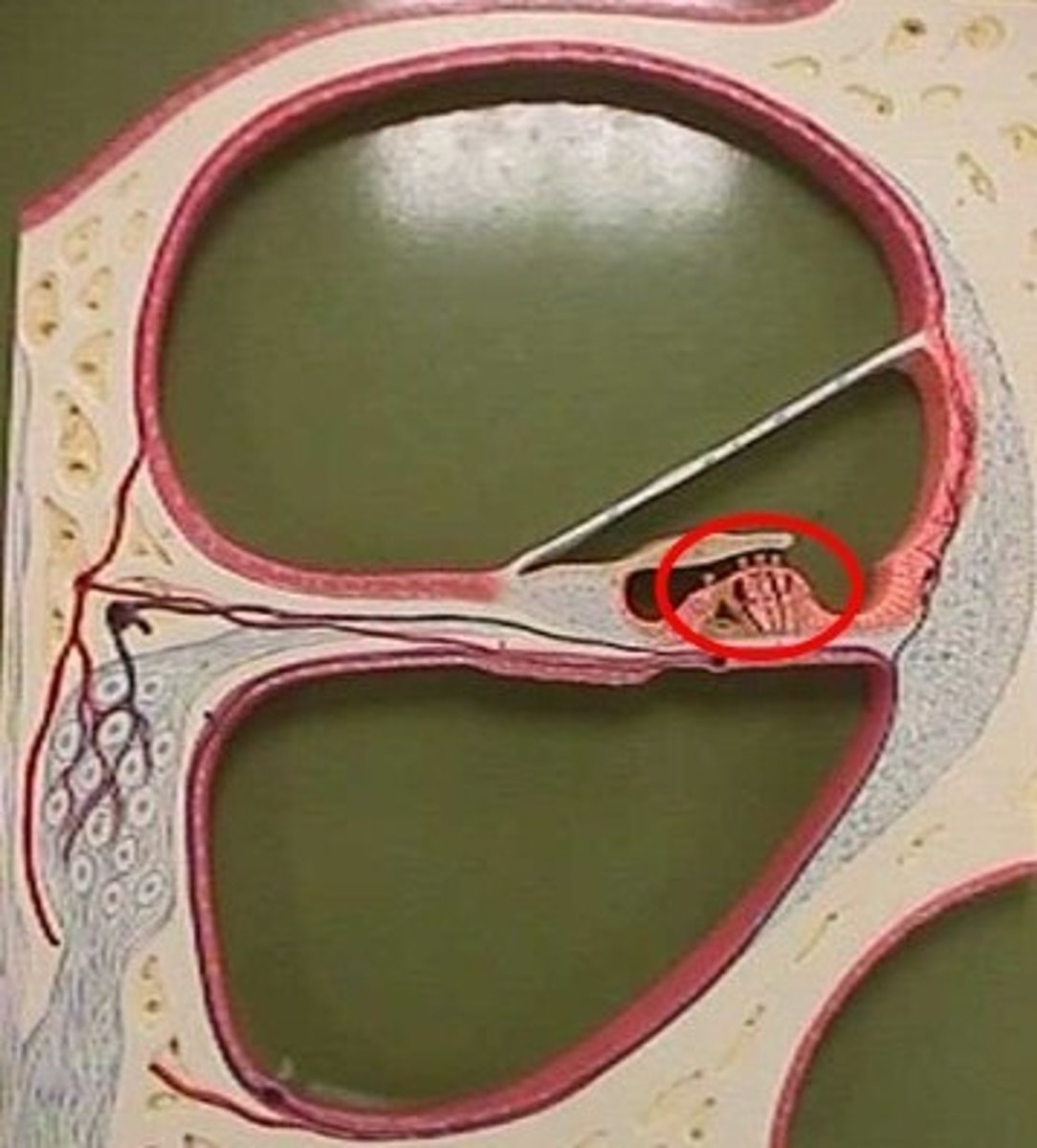
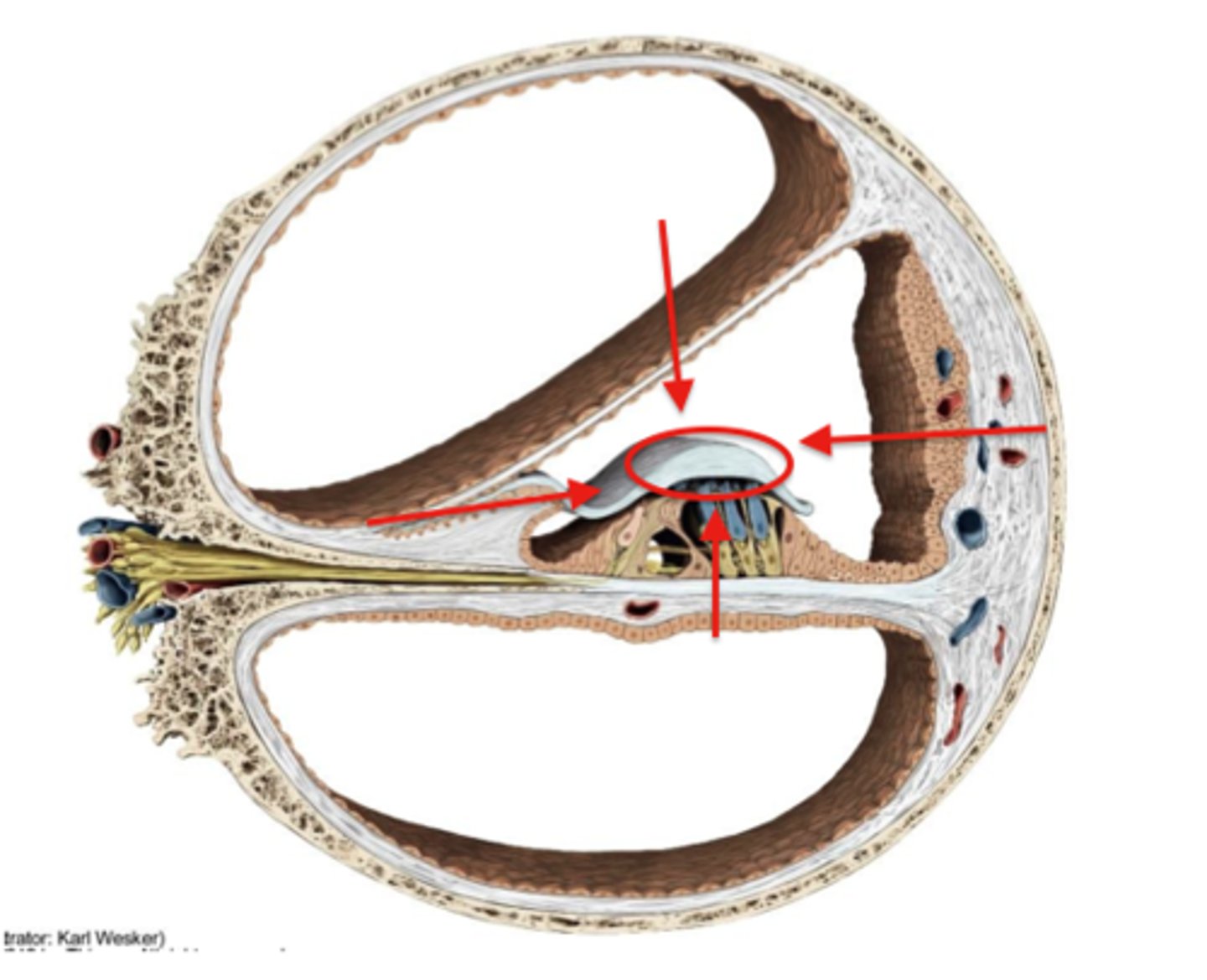
organ of corti
Center part of the cochlea, containing hair cells, canals, and membranes
tectorial membrane
gelatinous, ribbon-like structure sitting atop the organ of corti
tunnel/pillars of corti
triangular part of corti (space=tunnel, pillars=pillars)
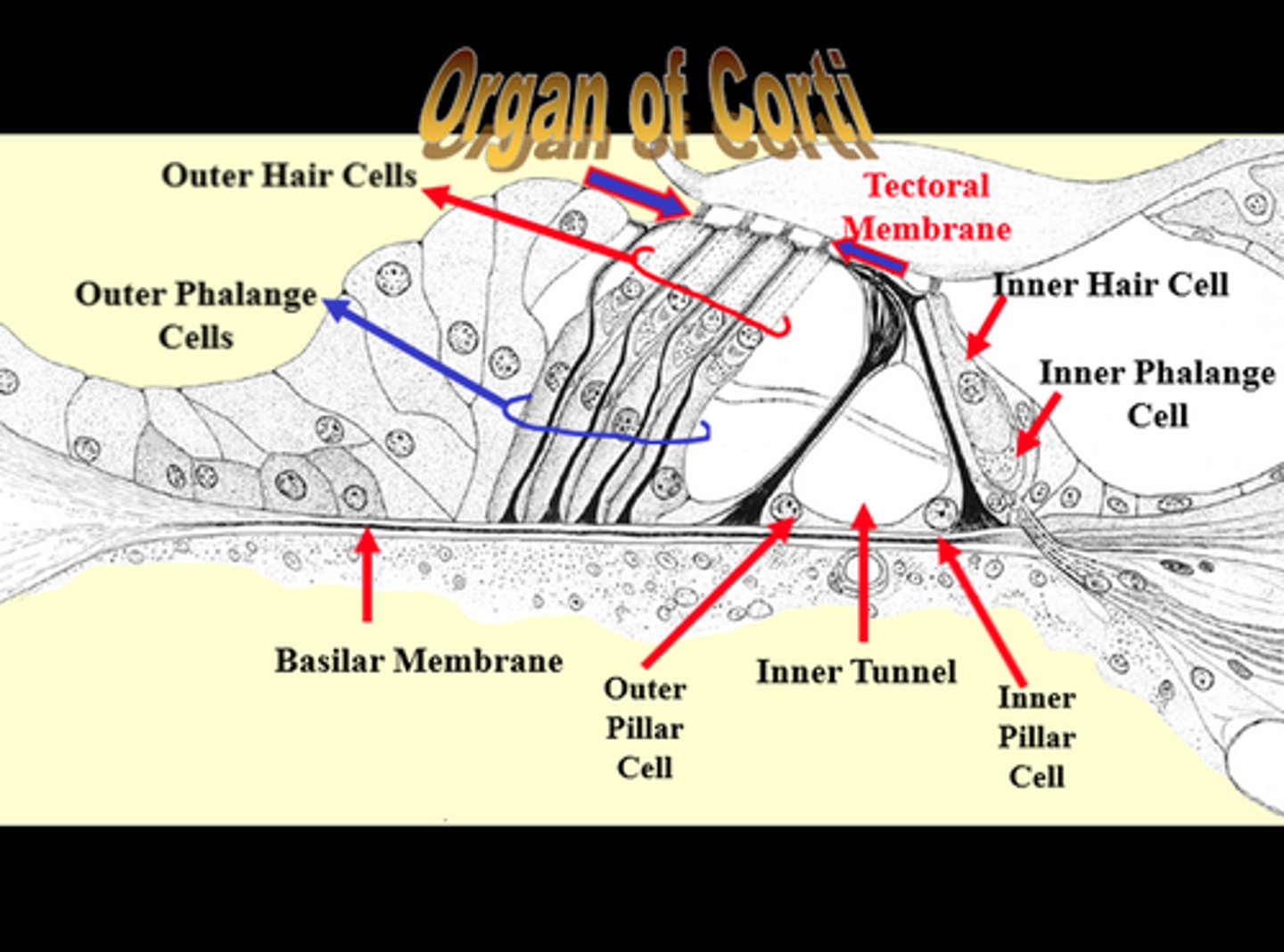
inner hair cells
neurons in the organ of Corti; responsible for auditory transduction
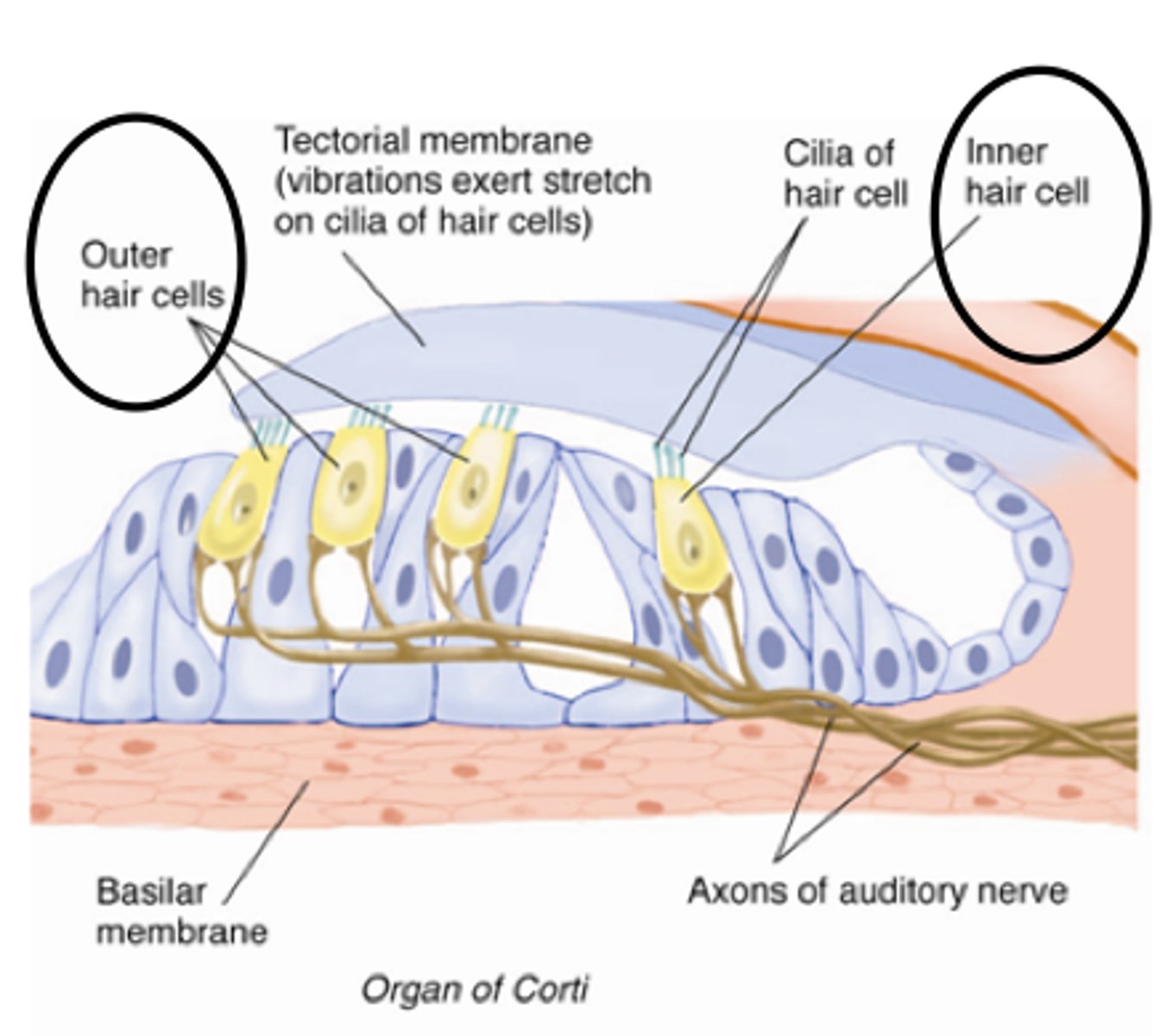
outer hair cells
neurons in the organ of Corti; serve to amplify and sharpen the responses of inner hair cells