Physics Midterm 1
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
unit conversions
giga (G)
mega (M)
kilo (k)
centi c
milli (m)
10^9
10^6 (think million)
10^3 (think money k = 1000)
10^-2
10^-3
what is displacement
the change in the particles position over a time interval
dont are about the path taken only change in point
also a vector quantity (has magnitude and dir)
what is the magnitude of a vector
its the numerical amount of the vector without regard to its direction; it is always a positive quantity.
what are the x and y components of the displacement vector
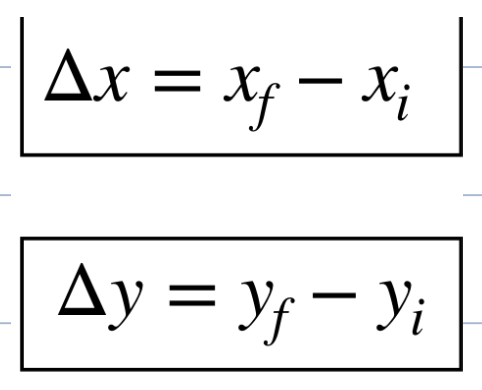
what does the sign mean for the displacement vector
The sign of a displacement vector indicates the direction of the displacement in relation to a chosen coordinate system
what does the sign mean for the velocity vector
The sign of a velocity vector indicates the direction of motion in relation to a chosen coordinate system
what does the sign of the acceleration mean for the acceleration vector
The sign of an acceleration vector indicates the direction of acceleration in relation to a chosen coordinate system.
how to find the magnitude of a vector from its x and y components
use the pythagorean theorum and then take the absolute value of the number
how does vector multiplication by a scalar work component wise
When a vector is multiplied by a scalar, each component of the vector is multiplied by that scalar, effectively scaling the vector's magnitude while maintaining its direction.
if its a negative number the vector changes direction
what is the direction and magnitude of the velocity vector
the direction is the direction of the motion and the magnitude is the speed at which the object is moving
what is the units for velocity
m/s
how does vector addition work component wise
Vector addition involves adding corresponding components of two or more vectors. The result is a new vector where each component is the sum of the respective components from the original vectors.
what is the magnitude and the direction of the acceleration vector
the magnitude is the rate of change of the velocity or the derivative of it and the 2nd derivative of the positon and the direction is the direction in which velocity changes.
what does the acceleration vector tell us
how the velocoty of an object is changing at any instant in time
how do you calculate the x and y comp of acceleration
slope of tangent line to vx vs t graph and vy vs t graph
so positive velocity slope means pos accel and neg velocity slope means neg accel
what is the turning point
an object with opposite velocity and acceleration will eventually stop and change direction, this is the turning point
and the velocity if 0 at this point
what does the acceleration tell us about the position vs time graph
its concavity, pos accel is concave up and neg is concave down
what are the units for acceleration
m/s²
over a given amount of seconds how does the m/s change
how to calculate average acceleration
Average acceleration is calculated by dividing the change in velocity by the time interval over which the change occurs.
how do you think about acceleration in relation to the velocity and if the object is speeding up or down
think of it as pulling or pushing on the velcity, therefore if the acceleration is in the same direction as velocity, the object is speeding up; if opposite, it is slowing down.
how to find vector components when given their magnitude and angle in the pos x dir

how to find vector components when given their magnitude and angle in the neg x dir
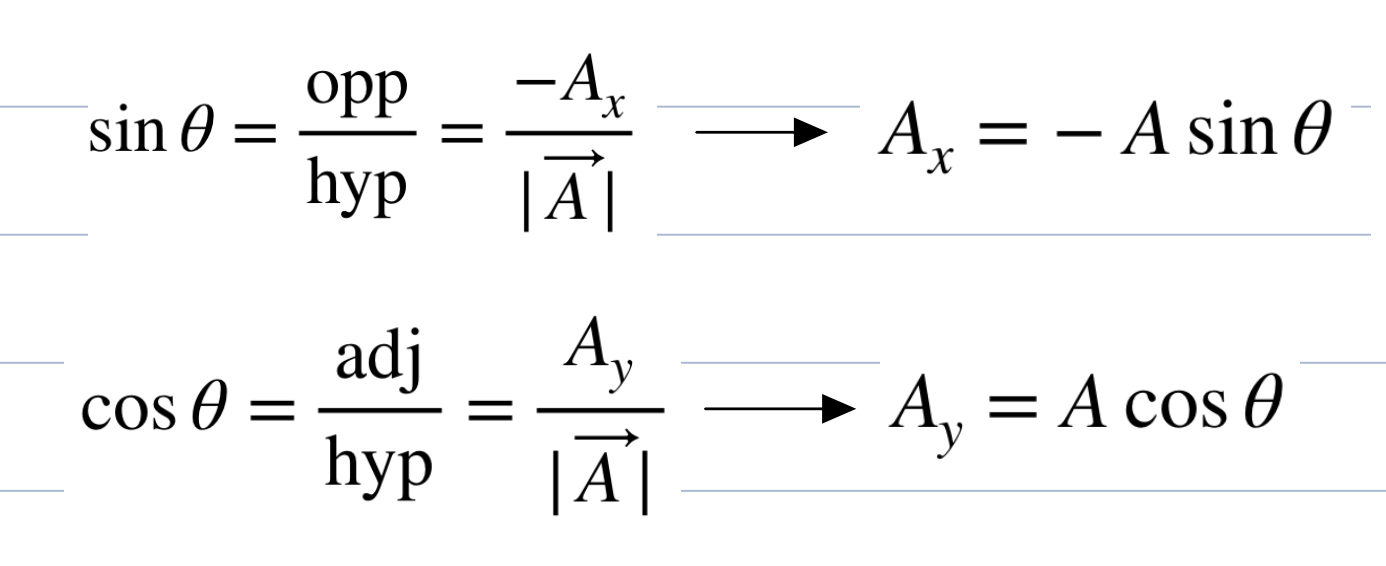
what is cos, sin and tan
cosine is the adjacent side over the hypotenuse, sine is the opposite side over the hypotenuse, and tangent is the opposite side over the adjacent side.
how do you add the two magnitudes of vectors
decomppose the vectors add component wise and then apply pythag theorum to get magnitude of new vector
how do you find the angle when given x and y components
take the inverse tangent of y comp / x comp
what do you do to the angle output if you want to find the angle of a vector in the neg x direction (2/3 quad)
add 180 degrees to the angle output.
if velocity is constant what is the acceleration
0
what are the x and y components of the velocity vector
the derivative of the position or the slope of the tangent line

what does a steeper slope mean for a position graph
It indicates a greater velocity, meaning the object is moving faster. A steeper slope represents a rapid change in position over time.
what is uniform motion
Motion at a constant speed in a straight line, where the position of an object changes uniformly over time.
how do you find the x component of uniform motion
since the velocity of uniform motion is constant (straight slope) then the x comp is equal to the

what is the position of an object at any time in uniform motion
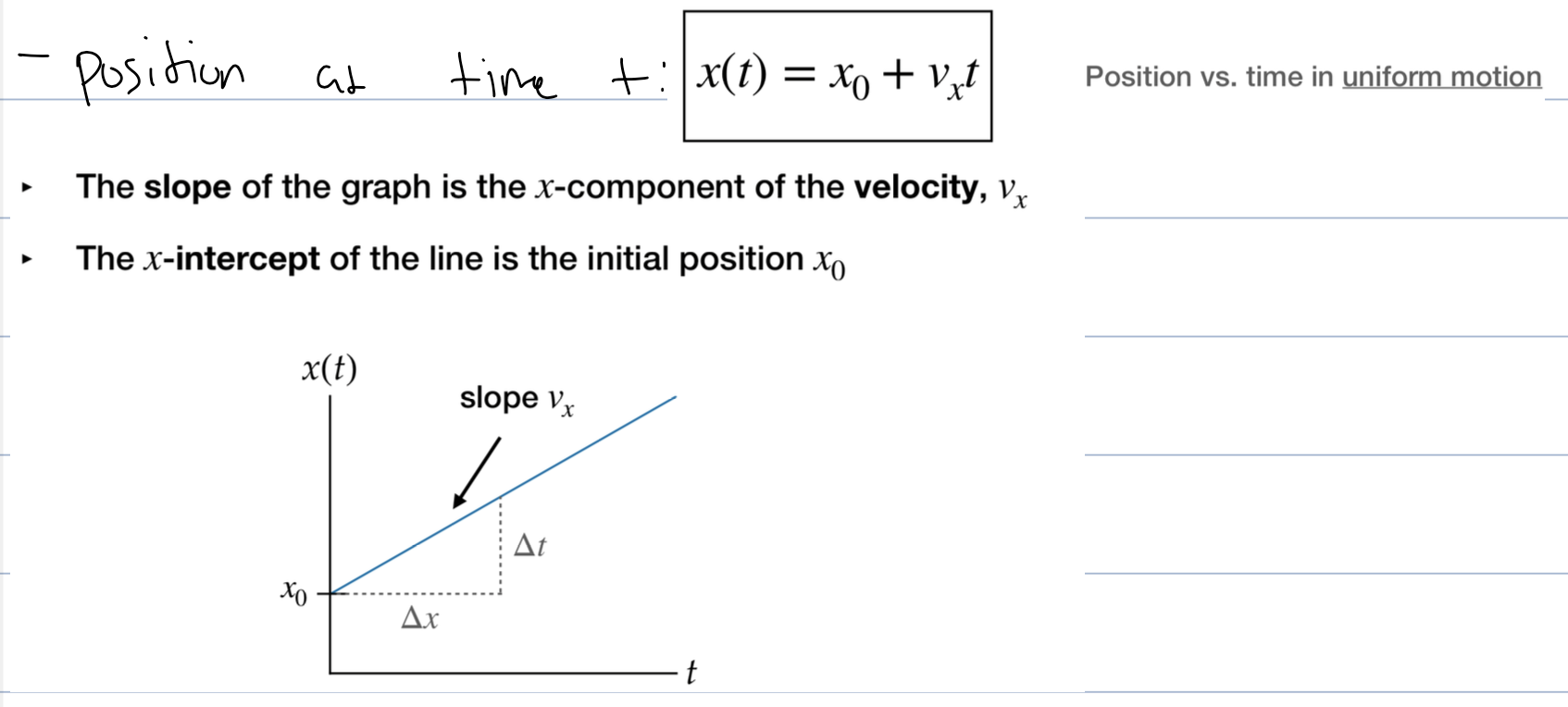
how to calculate displacement in uniform motion

make sure to only calculate the area of time being asked
what does it mean if the velocity goes below 0
It indicates that the object is moving in the opposite direction to the reference point, often referred to as negative velocity.
tips for solving kinematics problems

what is constant acceleration motion
an object under the influence of gravity will move in constant acceleration motion down
what are the eq for constant acceleration
velocity comp:
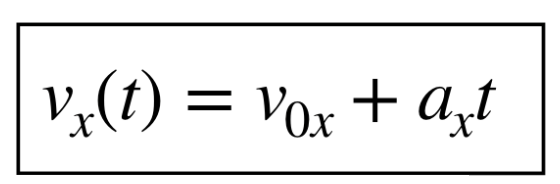
position at time of an object moving with const accel
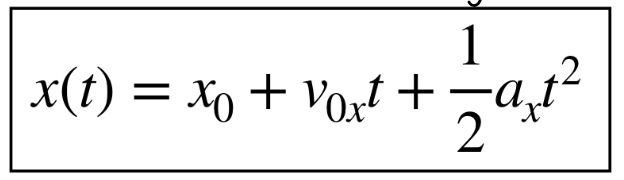
what is the equation without time (for when time isnt needed)
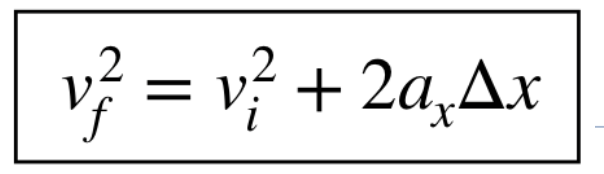
when you have constant acceleration and velocity and accel start in opposite directions hwo long does it take to get to max position and back to inital position
it take double the max position to get back to initial position from start
what is free fall motion
vertical motion under the influence of gravity alone
it is one dimentional constant acceleration motion
what is the dir and magnitude of the gravitational acceleration
constant with a mag of 9.8 and is pointing down
g is always positive because it is the magnitude of the acceleration
what is the y and x comp of accel in free fall motion
since our y axis is pointing up it is -g, the x comp is 0 because there is no change in the x direction
what are the equations for free fall motion

what is the quadratic formula

what are important points about free fall motion
at any given height an object will have the same speed moving down as it is up
dont mistake v=0 at the ground (think its the instant before contact)
what is projectile motion
a two dimensional motion where we have to account for both horizontal and vertical motion of a particle
what are the coordinate axes in projectile motion
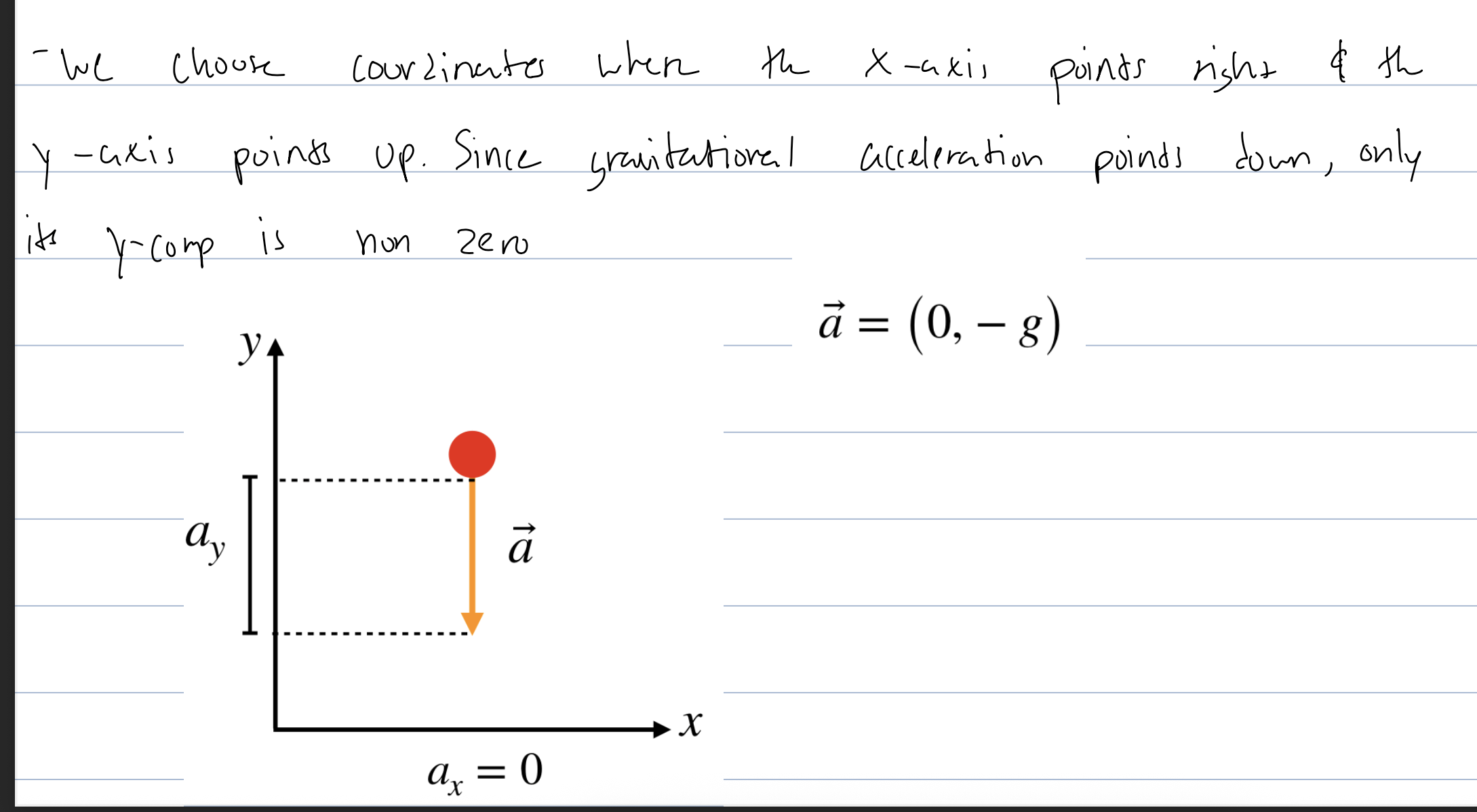
what are the 2 independent but simultaneas motions in projectile motion
horizontal: since ax is 0 the motion in the x direction is uniform motion
vertical: in the y dir we have free fall motion, ay = -g
since the two motions occur simultaneously we will often use time to relate them (solve for time from one then plugging into the other)
what are the standard equations for projectile motion

how to find x and y comp of projectile motion
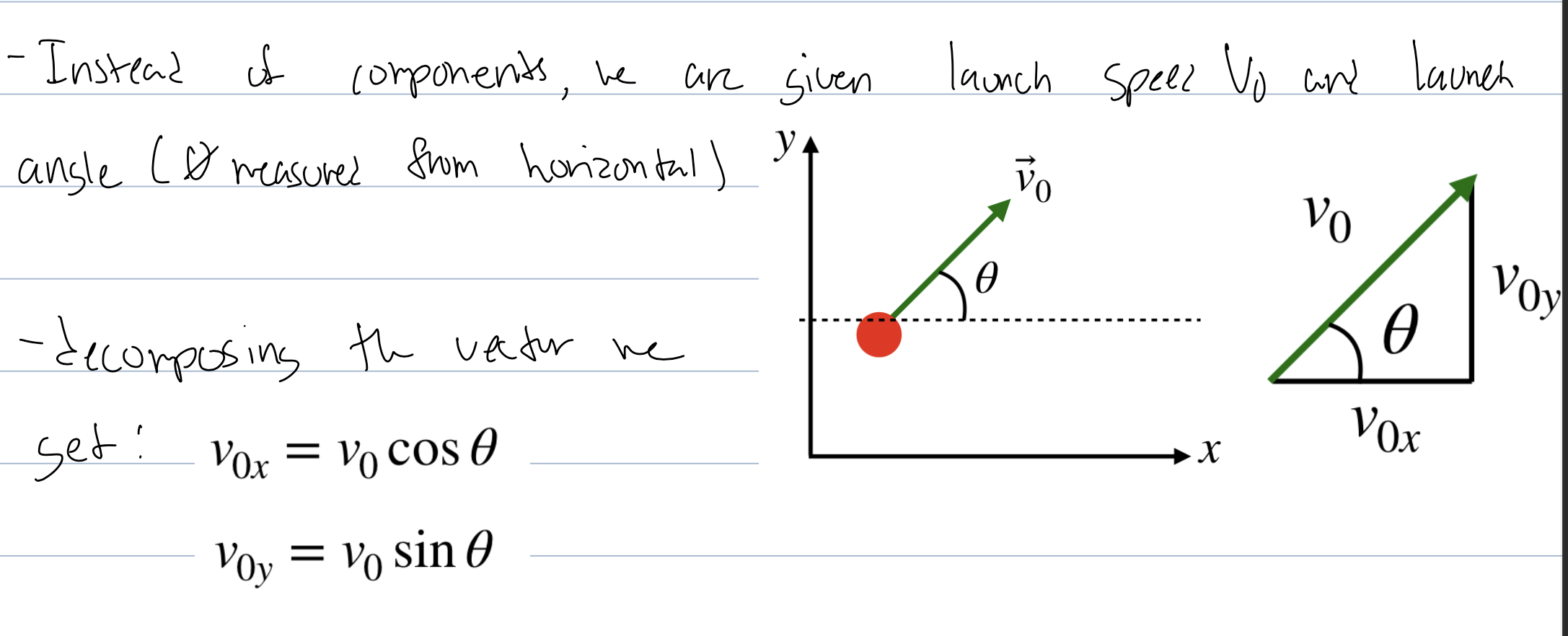
what are the equations for projectile motion with the x and y comp as angles

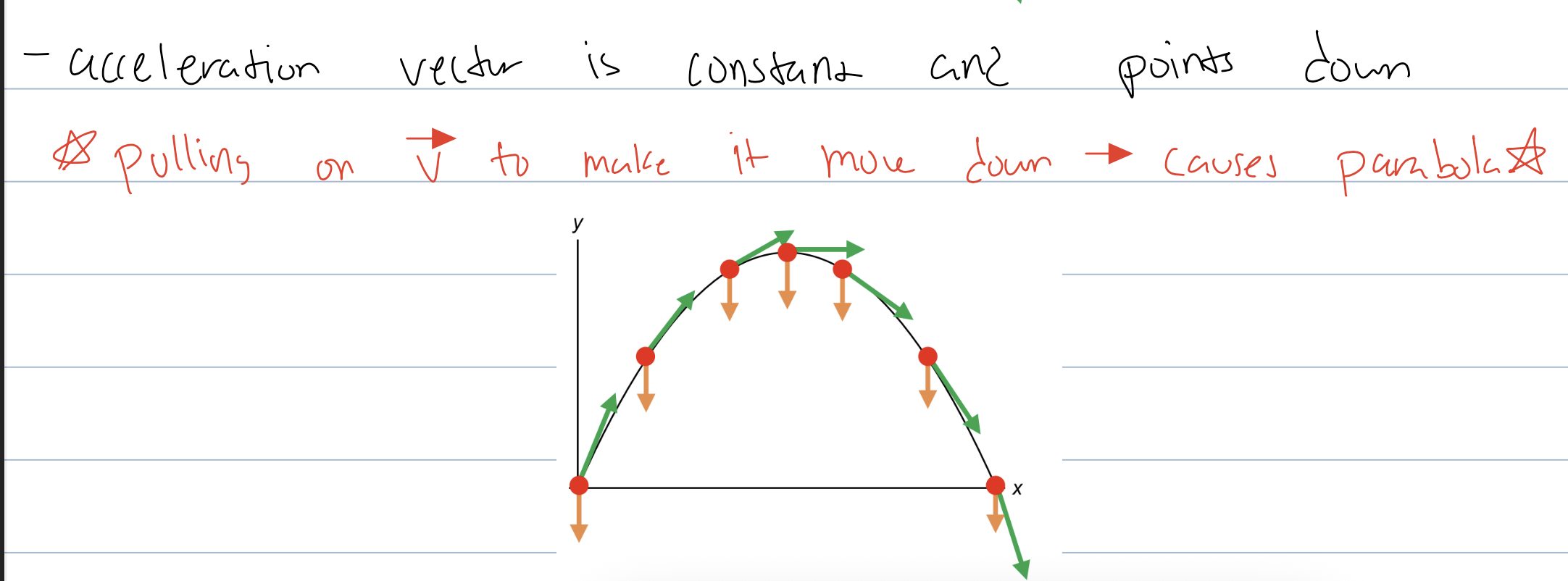
how does the acceleration of projectile motion cause its trajectory
what is uniform circular motion
motion in a circle at constant speed
how is UCM periodic motion
it repeats at regular time intervals
what is the period (T) of UCM
the time it takes for the motion to repeat
what is each full circle in UCM
revolution or cycle
what is the frequency of UCM
the number of revolutions per unit time
frequenccy measures the rate of repetition: higher frequency means the motion repeats more often
how is frequency related to the period (eq)
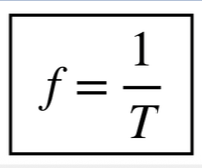
what are units of frequency in UCM
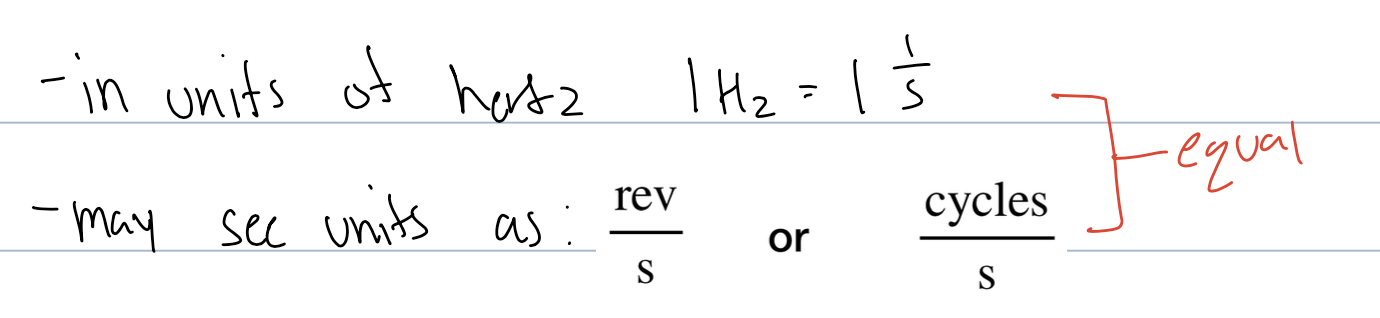
what is the arc length in ucm
The distance traveled by an object moving along a circular path, measured in radians.
what is the velocity in UCM
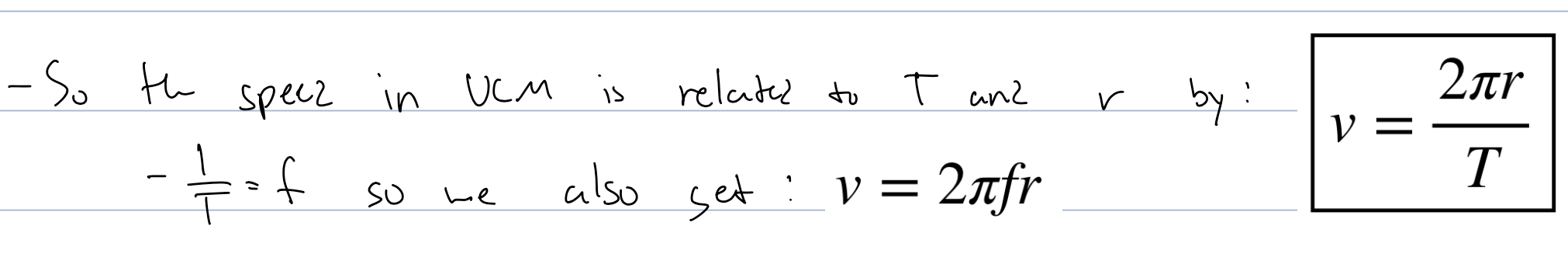
how does the accel relate to the path of UCM and what is centripetal acceleration (ac)
since velo is const changing direction the accel is changing too. Therefore always pointing towards the middle and pulling the velocity around the circle.
what is eq for Ac
