Understanding Disordered Eating and Eating Disorders
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
Disordered Eating
Variety of unhealthful eating behaviors.
Eating Disorder
Psychiatric condition with extreme body dissatisfaction.
Binge Eating
Consuming large amounts of food in short time.
Anorexia Nervosa
Severe restriction of food intake leading to weight loss.
Bulimia
Binge eating followed by purging behaviors.
Female Athlete Triad
Combination of disordered eating, amenorrhea, and osteoporosis.
Seasonal Affective Disorder
Depression linked to seasonal changes affecting appetite.
Portion Size Effect
Larger portions lead to increased food intake.
Cognitive Factors
Mental processes influencing eating behaviors.
Signal Sensory Modulation
Brain's response to food-related sensory inputs.
Gut Hormones
Hormones regulating hunger and satiety signals.
Adipose Tissue
Fat storage affecting energy balance and hunger.
Palatability
Pleasantness of food affecting consumption.
Rigid Exercise Routine
Inflexible physical activity patterns related to eating.
Obsessive Calorie Counting
Excessive focus on caloric intake and restriction.
Self Worth
Value based on body shape and weight.
Body Image Disturbance
Misperception of one's body size or shape.
Food Restriction
Limiting food intake to control weight.
Purging
Eliminating food from the body to prevent weight gain.
Anxiety about Foods
Fear or distress related to certain food types.
Inflexible Meal Times
Strict adherence to specific eating schedules.
Chronic Dieting
Long-term restriction of food intake affecting health.
Symptoms of Chronic Dieting
Preoccupation with food, weight, and calories.
Health Risks of Chronic Dieting
Includes poor nutrient intake and low energy.
Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)
Rate of energy expenditure at rest.
Eating Disorders
Psychiatric conditions with complex origins.
Anorexia Nervosa
Eating disorder characterized by extreme weight loss.
Bulimia Nervosa
Binge eating followed by purging behaviors.
Binge Eating Disorder
Recurrent episodes of uncontrolled eating.
Symptoms of Binge Eating Disorder
Includes negative self-esteem and chaotic eating.
Health Risks of Binge Eating Disorder
Increased risk of obesity and related diseases.
Family Environment
Influences development of eating disorders.
Unrealistic Media Images
Contributes to body image dissatisfaction.
Sociocultural Values
Cultural norms affecting eating behaviors.
Personality Traits
Individual characteristics linked to eating disorders.
Genetic Factors
Hereditary influences on eating disorder risk.
Normal Eating Definition
Baseline for identifying eating disorders.
Continuum of Eating Attitudes
Range of perspectives on eating and body image.
SAD (Seasonal Affective Disorder)
Mood disorder linked to seasonal changes.
Symptoms of SAD
Depression with cravings for high-carb foods.
Dopamine Receptor Activity
Linked to binge eating and weight gain.
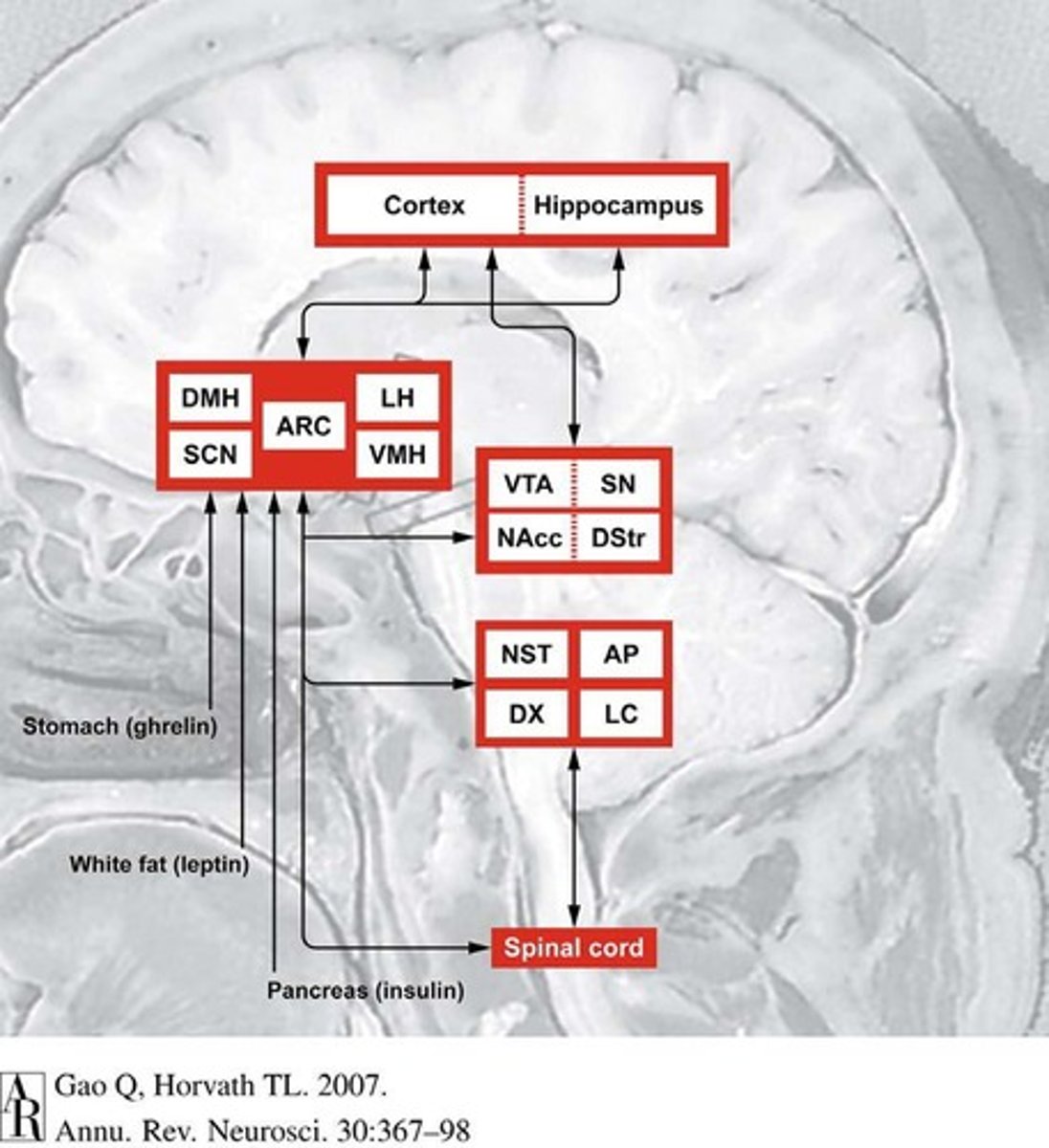
Brain Areas in Food Regulation
Regions controlling appetite and food intake.
Opioid Peptides
Neurotransmitters involved in reward and reinforcement.
Mesolimbic dopamine system
Brain region involved in reward and addiction.
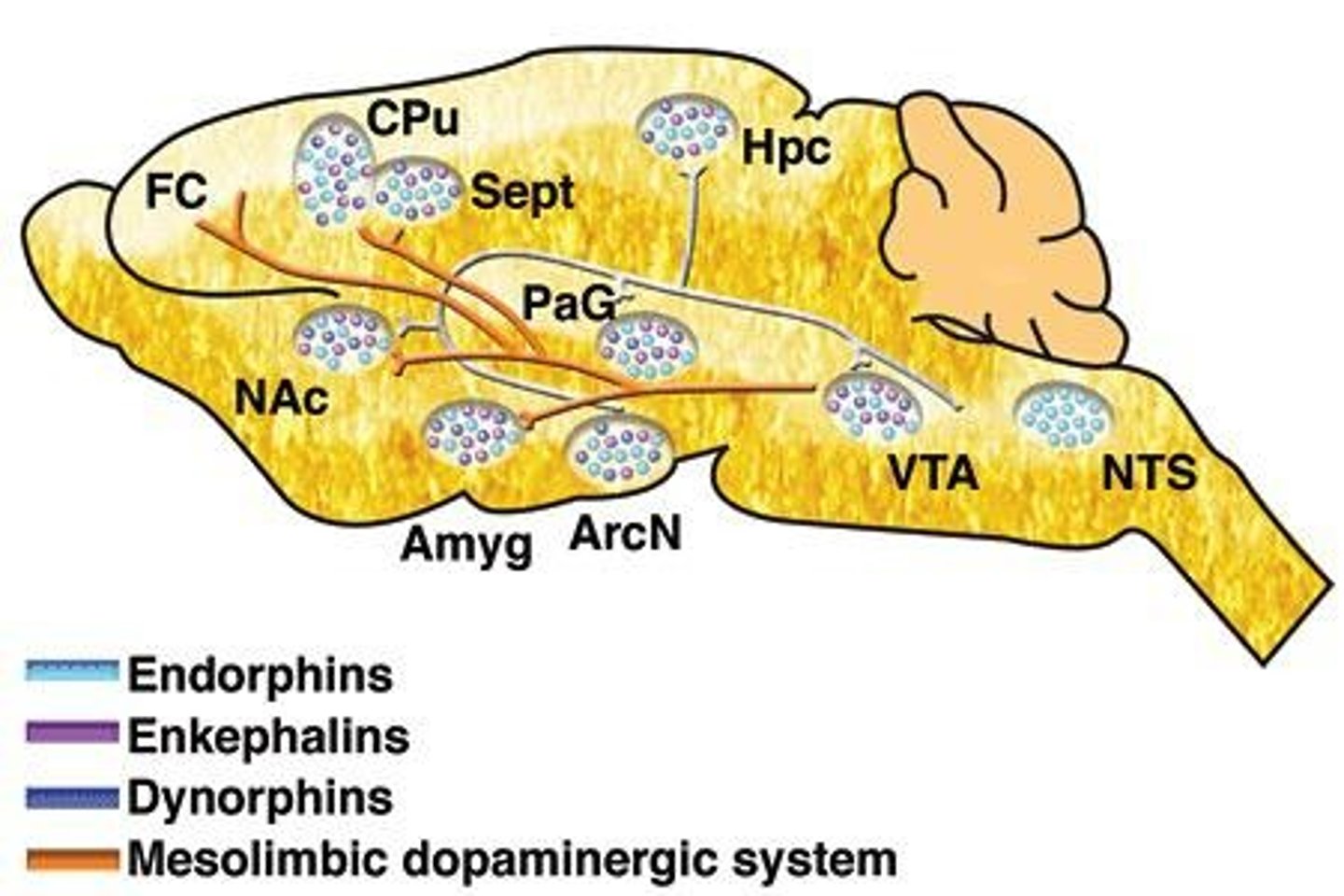
Ventral tegmental area (VTA)
Part of the mesolimbic system linked to pleasure.
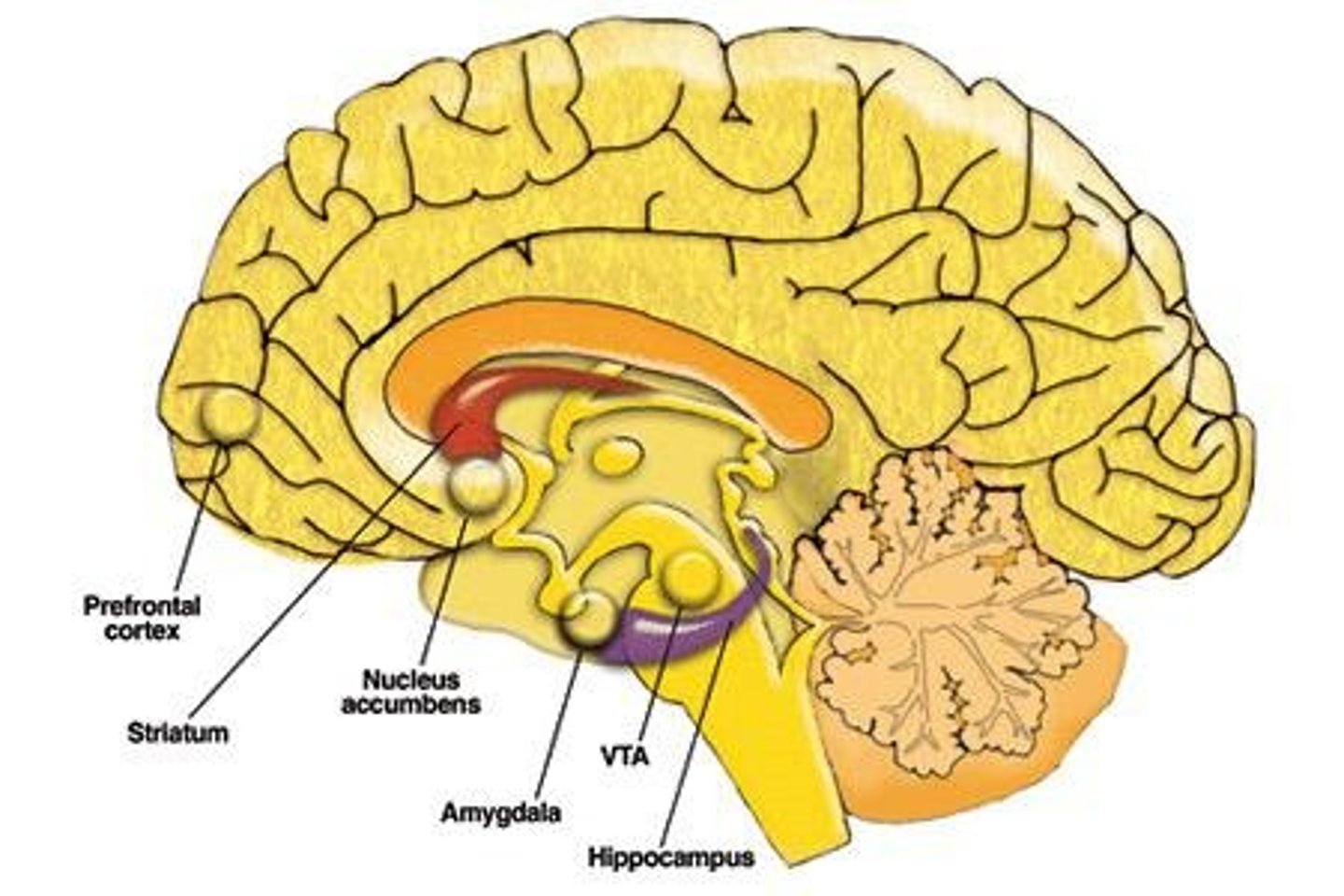
Nucleus accumbens
Key area for processing rewards and motivation.
Prefrontal cortex
Region for decision-making and impulse control.
Amygdala
Brain structure involved in emotional processing.
Striatum
Region associated with movement and reward.
Hippocampus
Critical for memory formation and learning.
AgRP neurons
Neurons that stimulate appetite and food intake.
Ethanol-induced overeating
Increased food consumption due to alcohol intake.
Female Athlete Triad
Combination of disordered eating, amenorrhea, osteoporosis.
Amenorrhea
Absence of menstrual periods for at least three months.
Anorexia nervosa
Disorder characterized by extreme weight loss behaviors.
Bulimia nervosa
Binge eating followed by compensatory purging behaviors.
Binge eating
Consuming large amounts of food rapidly.
Purging
Methods to eliminate food from the body.
Electrolyte imbalance
Disruption of sodium and potassium levels in the body.
Cardiovascular problems
Heart-related issues due to eating disorders.
Gastrointestinal problems
Digestive issues resulting from disordered eating.
Dental problems
Oral health issues caused by purging behaviors.
Health risks of anorexia
Includes electrolyte imbalance, hypothermia, sleep disturbances.
Health risks of bulimia
Includes dental problems, calluses, and gastrointestinal issues.
Team approach treatment
Involves patient, physician, and counselors for recovery.
Healthy diet
Balanced intake of nutrients to maintain optimal weight.
Hypothalamus
Brain region regulating hunger and energy balance.
Leptin
Hormone signaling satiety, produced by fat cells.
VMH
Ventromedial hypothalamus, controls satiety signals.
LH
Lateral hypothalamus, stimulates hunger and food intake.
Parabiosis
Surgical joining of two organisms for study.
Blood Brain Barrier
Protective barrier preventing harmful substances in brain.
Appetite
Desire to eat, influenced by external factors.
Hunger
Physical sensation indicating need for energy.
Gut Brain Axis
Communication pathway between gut and brain.
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome
Disorder caused by alcohol exposure during pregnancy.
Head Circumference
Measurement indicating brain growth and development.
Semistarvation
State of inadequate nutrient intake over time.
Cachexia
Weight loss and muscle wasting despite adequate intake.
Sarcopenia
Age-related loss of muscle mass and strength.
Wasting
Loss of lean body tissue due to malnutrition.
Malnutrition
Deficiency or imbalance in nutrient intake.
Anabolic Block
Inability to gain lean mass during refeeding.
Nitrogen Loss
Excess nitrogen excretion indicating protein deficiency.
Refeeding Syndrome
Complications arising from rapid refeeding after starvation.
Intellectual Impairment
Reduced cognitive function due to nutritional deficiencies.
Attention Deficit Disorder
Condition characterized by inattention and impulsivity.
Learning Disabilities
Challenges in acquiring knowledge and skills.
Delayed Development
Lag in reaching developmental milestones.
Cravings
Desire for specific foods influenced by emotions.
Habits
Routine behaviors affecting food choices and intake.
Food Availability
Accessibility of food impacting consumption patterns.
Hormonal Signals
Chemical messengers regulating hunger and satiety.
Neural Signals
Nerve impulses influencing appetite control.
Cognitive Factors
Mental processes affecting eating behavior and choices.
Ghrelin
Hunger hormone produced in the stomach.
CCK
Hormone signaling satiety, produced in the intestine.
Peptide YY
Hormone that reduces appetite after eating.
Leptin
Hormone from adipose tissue regulating energy balance.
Insulin
Hormone regulating glucose levels and appetite.