Communications Exam 1
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
1
New cards
Source Oriented
"Intent" Matters
2
New cards
Receiver Oriented
Intent does not matter
3
New cards
Where is Source-oriented communication used?
Public Relations (Ex; Journalism, Advertising)
4
New cards
Where is receiver-oriented communication used?
Interpersonal, communication, consulting
5
New cards
What are the flaws of source-oriented communication?
Too narrow
6
New cards
What are the flaws of receiver-oriented communication?
too broad, doesn't draw the line between communication & behavior
7
New cards
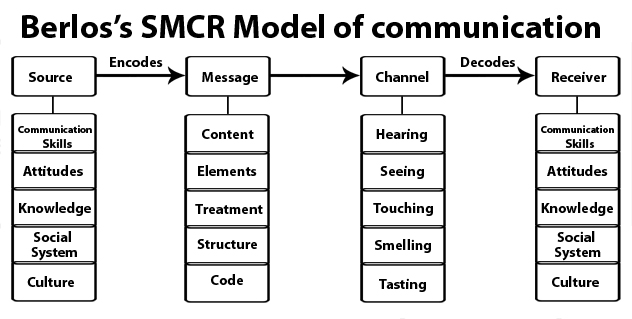
SMCR
Linear/one-way view of communication
8
New cards
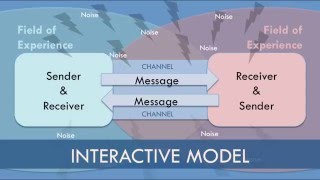
Interactional Model
Communication takes turns
9
New cards
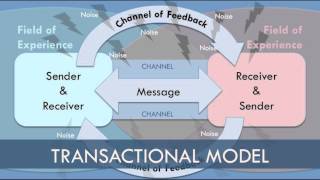
Transaction Model
Communication plays role simultaneously
10
New cards
Function of Theories
Organise Experience, Extend Knowledge, Stimulate and Guide Research, Perform an Anticipatory Function
11
New cards
Rhetorical
Talk is a practical art
12
New cards
Semiotic
Study of Signs in ordinary/everyday life
13
New cards
Phenomenological
personal interpretation that we make as individuals
14
New cards
Cybernetic
Information processing
-expansive look on communication networks
-Where the message went wrong
-expansive look on communication networks
-Where the message went wrong
15
New cards
Socio-Psychological
Cause & Effect on human interaction
16
New cards
Socio-Cultural
Everyday interactions depend heavily on pre-existing social norms/shared cultural patterns
17
New cards
Critical
-Fairness, Injustice, Power
-Language is to keep or break down social order
-Language is to keep or break down social order
18
New cards
Intrapersonal
Communication with oneself
19
New cards
Interpersonal
Imagined Interactions
20
New cards
Paradigm
A grand macro-scale model with a set of assumptions that are shared by many "like theories"
21
New cards
Drawbacks of Paradigm
-Incomplete, oversimplified
-many ways to model a single process
-many ways to model a single process
22
New cards
Covering Laws
-Focuses on numbers
-Makes Generalisations
-Makes Generalisations
23
New cards
Strengths of Covering Laws
-Good at making predictions
-Identifies clear themes in human interaction
-Frequently used
-Allows you to study large group of people
24
New cards
Weaknesses of Covering Laws
-Can appear Linear
-Overemphasized in-groups & outgroups
25
New cards
Rules
Rules you pick to govern your opinion
26
New cards
Strengths of Rules
Strengths of Rules
-Free choice interpretation
-Multiple meanings to any one action
-Diverse perspectives
-Free choice interpretation
-Multiple meanings to any one action
-Diverse perspectives
27
New cards
Weaknesses of Rules
-No clear cut answers
-Doesn't offer any generalised ability
-Doesn't offer any generalised ability
28
New cards
Systems
Patterns of behaviours
29
New cards
Strengths of Systems
-Most aware of the communication context
-Good at giving descriptions of how things are interacted
-Doesn't attempt to make universal generalisations Scope
-Good at giving descriptions of how things are interacted
-Doesn't attempt to make universal generalisations Scope
30
New cards
Scope
Boundaries & limits of the theories explanations
31
New cards
Logical Consistency
Do the principles of theories contradict each other?
32
New cards
Parsimony
Theory as simple as it could be
33
New cards
Utility
Theory is useful, practical, applied
34
New cards
Testability
Can parts of the theory be falsified?
35
New cards
Heurism
Theory stimulating new ways of things
36
New cards
Test of Time
How long has the theory been around? How long has it been used?
37
New cards
Assumptions of Expectancy Violations Theory
-Human interaction is driven by expectations
-When expectations are not met (deviation) becomes aroused or curious
-Evaluations of deviations are mediated by the reward value of the communicator
-When expectations are not met (deviation) becomes aroused or curious
-Evaluations of deviations are mediated by the reward value of the communicator
38
New cards
Critique of Expectancy Violations Theory
Scope: does the throw define its parameters
Utility: Can you use it/can you apply it anywhere
Testability: Have to be able to observe it
Heurism: Stimulated ideas
Utility: Can you use it/can you apply it anywhere
Testability: Have to be able to observe it
Heurism: Stimulated ideas
39
New cards
Expectations
behaviours we can anticipate in a conversation with another person
40
New cards
Arousal
When you notice something was not anticipated as you thought you become more AWARE!
41
New cards
Threat Threshold
Interactant in the conversation feels uncomfortable in the presence of deviation
42
New cards
Violation Valence
Positive or Negative assessment of deviation
43
New cards
Assumptions of Cognitive Dissonance Theory
-Communicators carry rich assortiments of cognitive elements
-What is consonant or dissonant for one person may not be for another
-Dissonance produces tension for change
-Human attempt to deduce dissonance tend to avoid situations that produce it
-More dissonance=Greater pressure to change
-What is consonant or dissonant for one person may not be for another
-Dissonance produces tension for change
-Human attempt to deduce dissonance tend to avoid situations that produce it
-More dissonance=Greater pressure to change
44
New cards
Sources of Consonance
-Reassurance of Security
-Demonstration of Predictability
-The use of Rewards
-Demonstration of Predictability
-The use of Rewards
45
New cards
Sources of Dissonance
-Loss of Group Prestige
-Economic Loss
Loss of Personal Prestige
-Uncertainty of Prediction
-Guilt
-Economic Loss
Loss of Personal Prestige
-Uncertainty of Prediction
-Guilt
46
New cards
Ways Dissonance is reduced
-New elements may be added to cognitive systems to add more "weight" to one side or the other
-Elements may be refined as important
-Consent information may be sought
-Info may be distorted
-Elements may be refined as important
-Consent information may be sought
-Info may be distorted
47
New cards
Critique of Cognitive Dissonance Theory
-Utility(-): Maybe the theory can't be applied
-Testability(-): Validate & Falsify ideas, theory is hard to falsify
-Testability(-): Validate & Falsify ideas, theory is hard to falsify
48
New cards
Anchors
most acceptable position to the receiver on the topic
49
New cards
Latitude of Acceptance
range of all positions that are agreeable to the individuals or audience on that topic
50
New cards
Latitude of Noncommitment
range of all positions toward which individual or audience feels neutral
51
New cards
Latitude of Rejection
range of all positions that are objectionable to an individual or audience
52
New cards
Ego- Involvement
Importance of the issue to the receiver
(As ego involvement increases, the latitude of rejection increases)
(As ego involvement increases, the latitude of rejection increases)
53
New cards
Distortion Process: Assimilate
when something sounds similar we view it as the same
54
New cards
Distortion Process: Contrast
When something is slightly different we see it as VERY different
55
New cards
Critique of Social Judgement Theory
-Heurism (+)
-Testability(+)
-Utility(+)
-Logical Consistency (-)
-Testability(+)
-Utility(+)
-Logical Consistency (-)