Chapter 10.2: Micro Anat of SKM, Innervation of SKM Fibers, SKM Fiber Rest
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
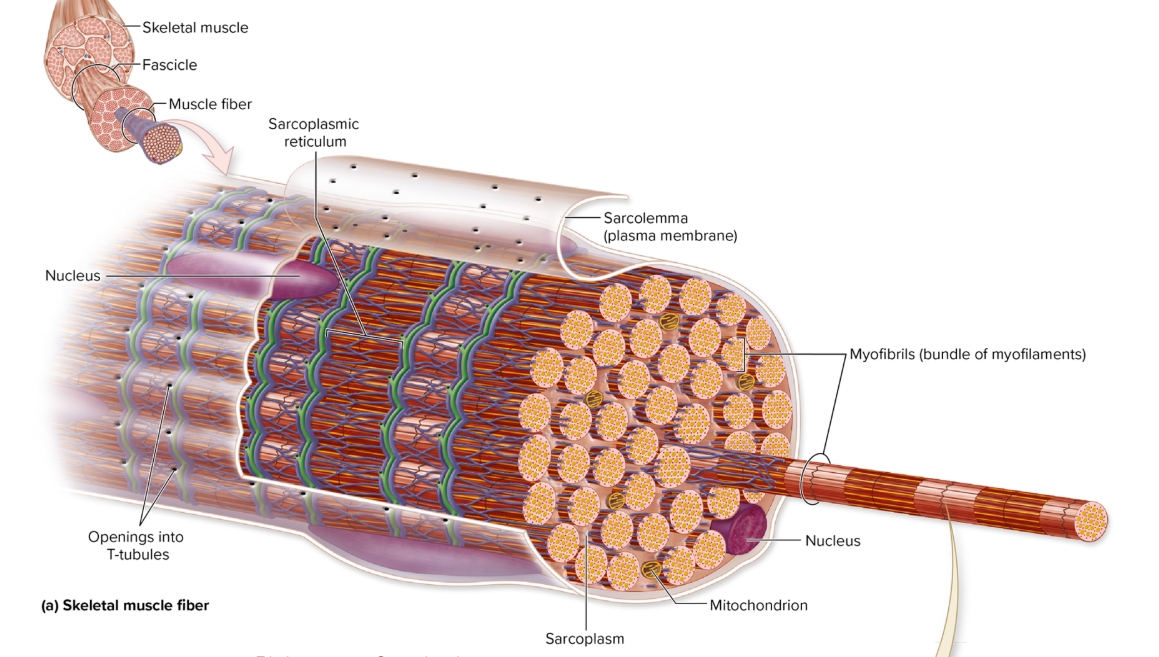
Parts of cell (fiber)
sarcoplasm (cytoplasm)
sarcolemma (plasms membrane)
myofibrils
sarcoplasmic reticulum
myofilaments (thick and thin)
Sarcoplasm
cytoplasm
organelles, contractile proteins, other specializations
multiple nuclei
formed in embryo where myoblasts fuse
some myoblasts become undifferentiated satellite cells to support and repair muscle fibers
Sarcolemma
plasma membrane
voltage-gated ion channels
T-tubules (transverse tubules)
voltage-sensitive calcium channels
Myofibrils
hundred-thousand per cell
bundles of myofilaments enclosed in sarcoplasmic reticulum
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
internal membrane complex similar to smooth ER
terminal cisternae: bind sacs of sarcoplasmic reticulum
reservior for calcium ions
calcium pumps import calcium
triad: two cisternae T-tubule inbetween
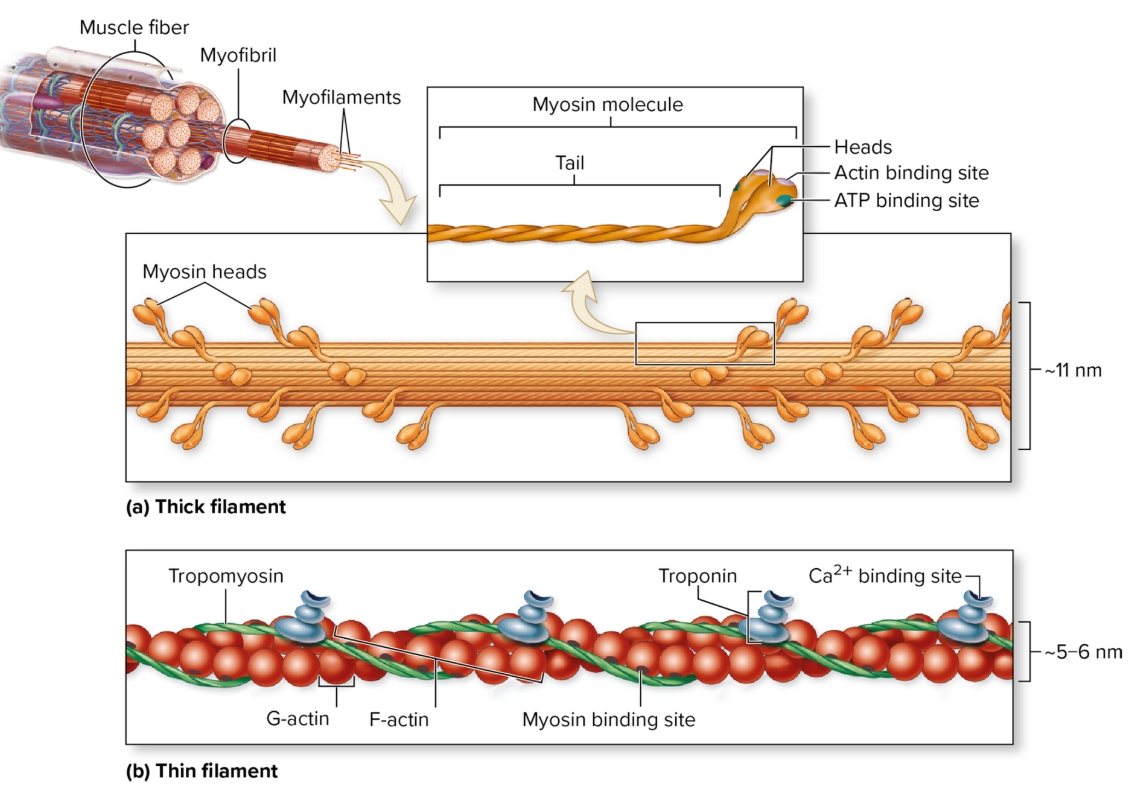
Myofilaments
contractile proteins in myofibrils
thick: bundles of myosin
myosin heads point to end of filaments
thin: twsited strands of actin (F-actin, G-actin)
G-actin = myosin binding site
tropomyosin and troponin
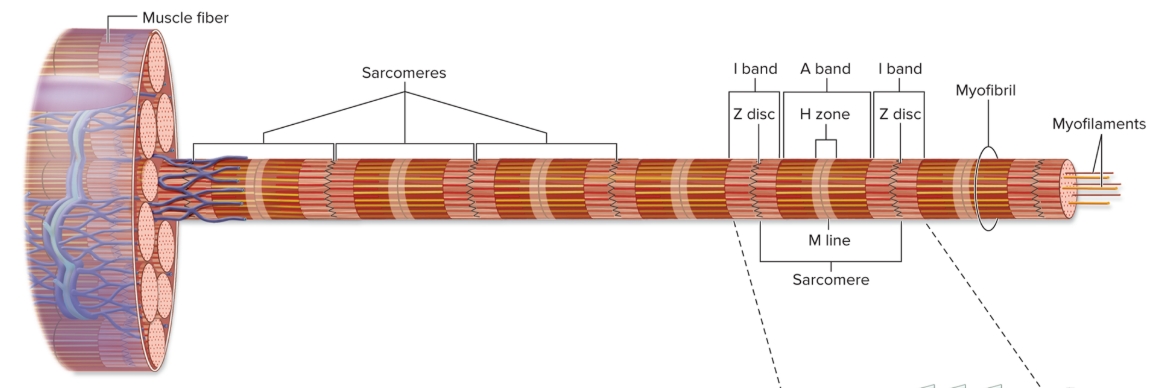
Organization of sarcomere
repeating units of myofilaments
overlapping thick and thin filaments
delineated both ends by Z discs
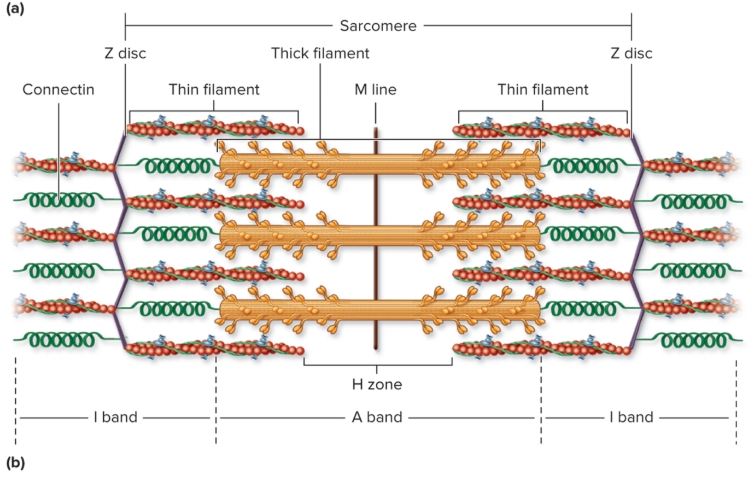
I bands
light-appearing regions contain only thin filaments
bisected by Z disc
get smaller when muscle contracts (disappear maximal contraction)
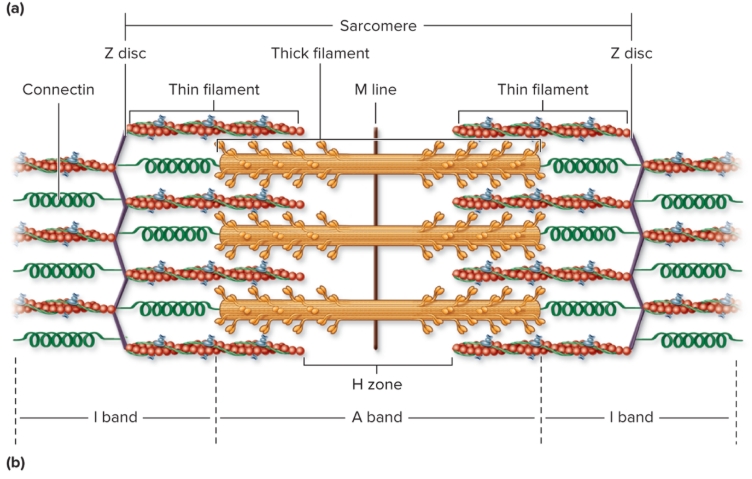
A bands
dark appearing region contains thick filaments and overlapping thin filaments
contains H zone and M lines (central part of sarcomere)
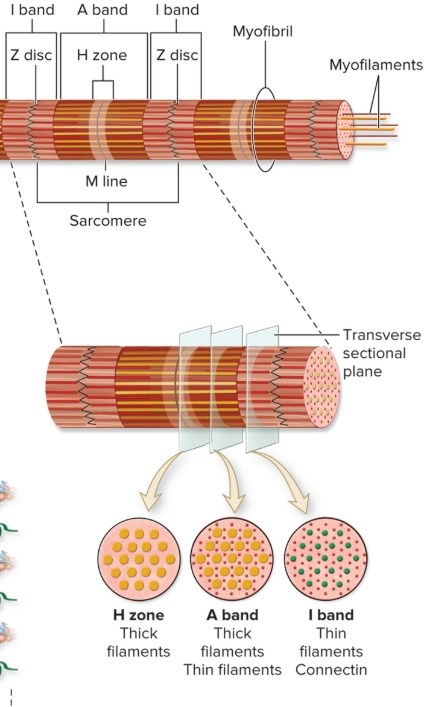
H zone
central portion of A band
only thick filaments
disappear maximal muscle contraction
M line
middle of H zone
protein meshwork structure
attachment site for thick filaments
Connectin
Z disc to M line
stabilizes thick filaments and “springlike” properties (passive tension)
Dystrophin
anchors myofibrils to sarcolemma proteins
abnormalities of these cause muscular dystrophy
Mitochondria and other structures associated with energy production
muscle fibers abdunant mitochondrai for aerobic ATP
myoglobin in cells store oxygen
glycogen stores fuel when quick energy needed
CP gives phosphate to ADP to replenish ATP
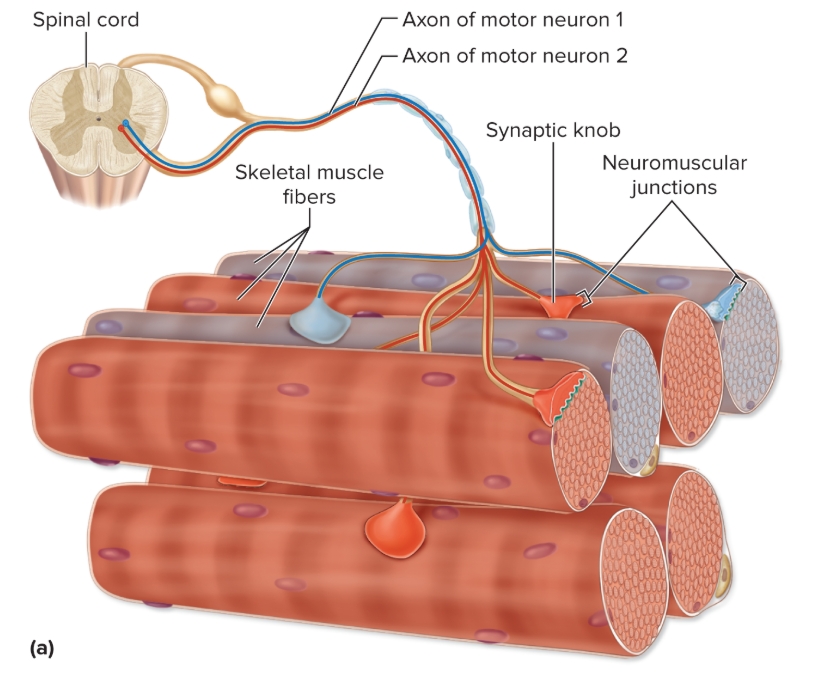
Axons from spinal cord (pr brain)…
innervate numerous muscle fibers
number of fibers neuron innervates varies
Small motor units
less than 5 muscle fibers
prescise control of force output
Large motor units
thousand muscle fibers
production of large force (not precise control)
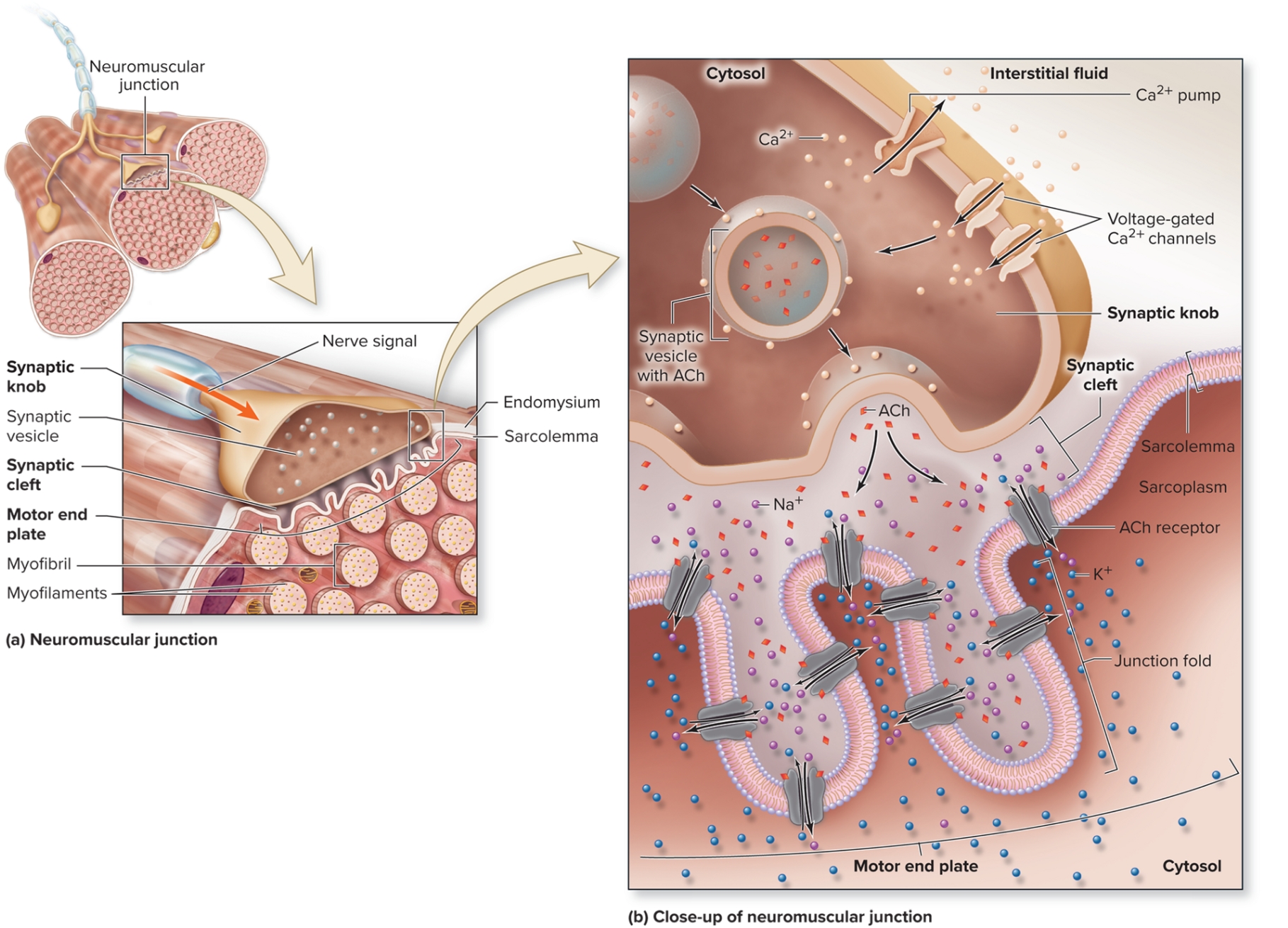
Neuromuscular Junction
location motor neuron innervates muscle (mid-region)
has synaptic knob, synaptic cleft, motor end plate
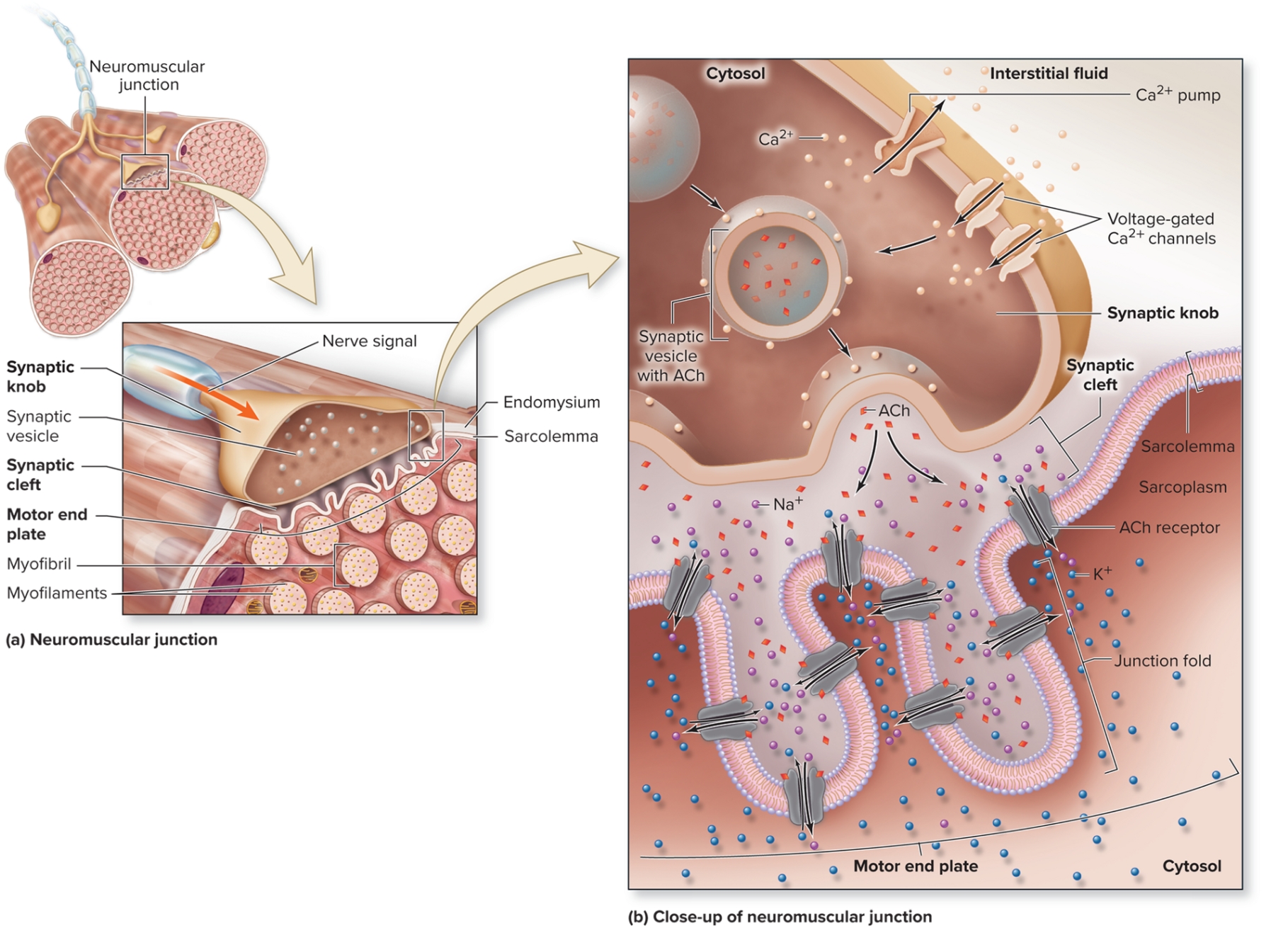
Neuromuscular Junction: Synaptic Knob
expanded tip of motor neuron axon
houses synaptic vesicles
small sacs filled with NT acetylcholine (ACh)
has Ca2+ pumps in plasma membrane (estabilishes calcium gradient)
voltage gated Ca2+pumps
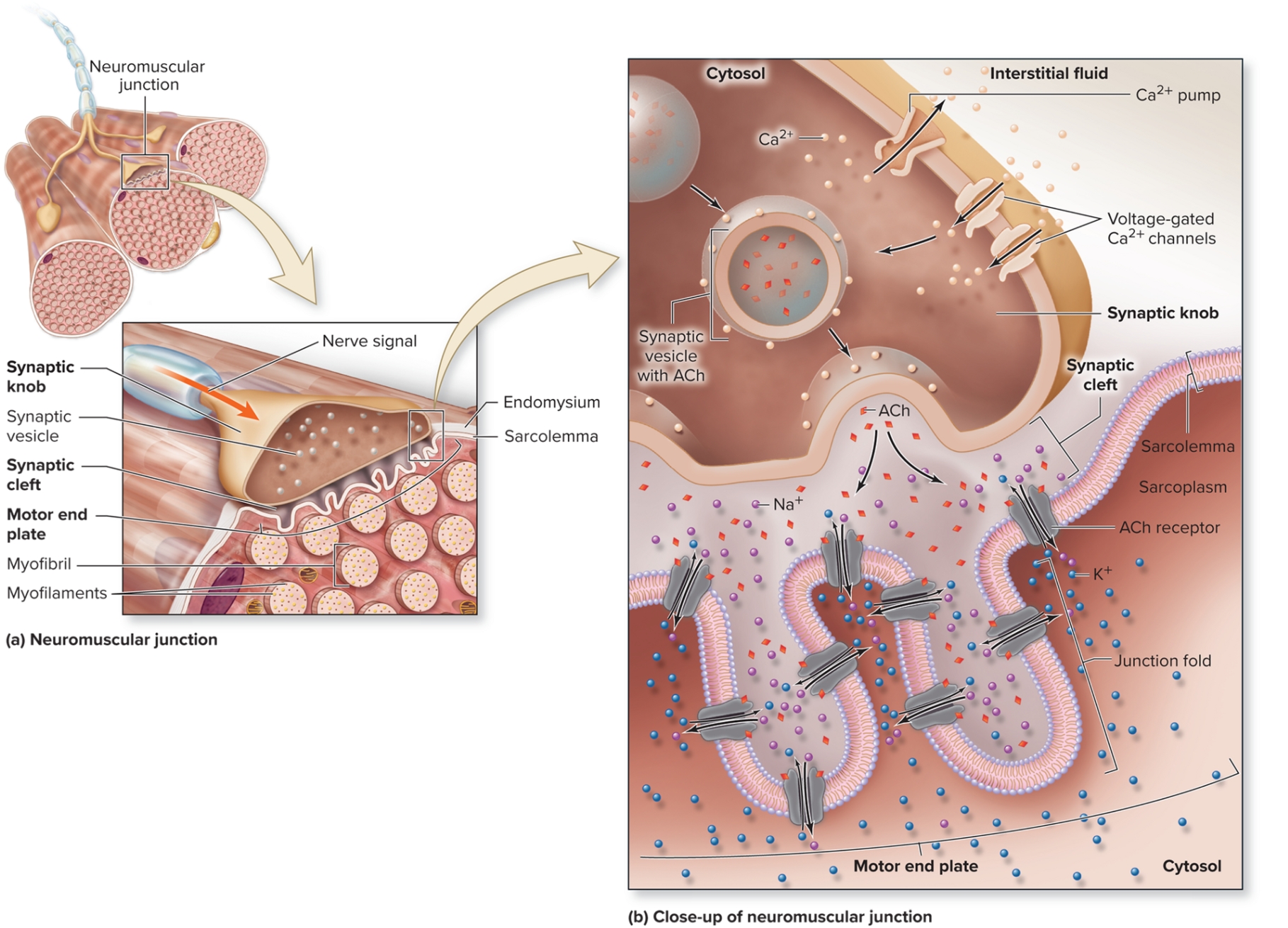
Neuromuscular Junction: Motor End Plate
specialized regions of sarcolemma with numerous folds
many ACh receptors
plasma membrane protein channels, opened bonding ACh, Allow Na+ entry and K+ exit
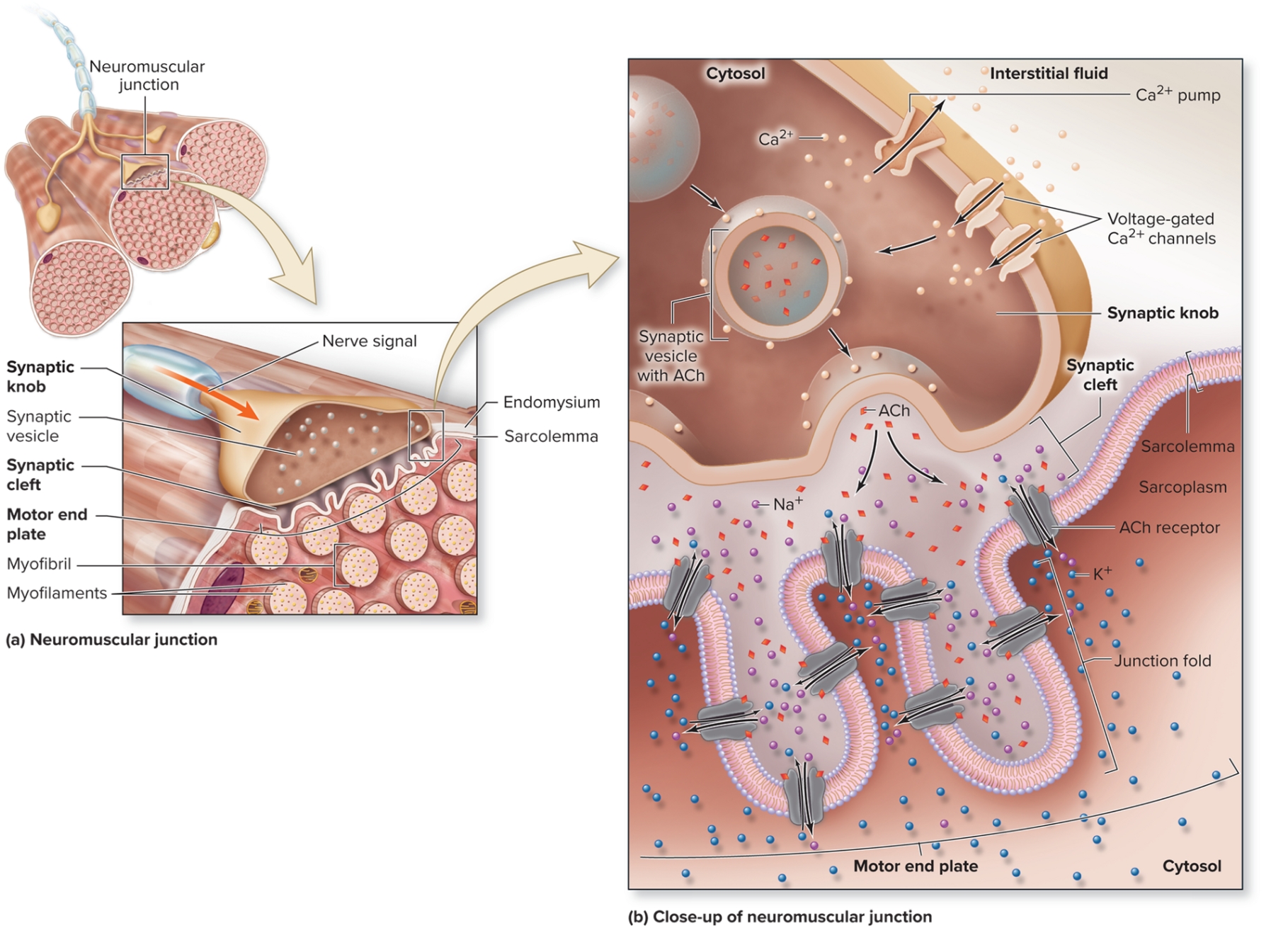
Neuromuscular Junction: Synaptic Cleft
narrow fluid-filled space
separated synaptic knob from motor end plate
Acetylcholinesterase here (breaks down ACh)
Skeletal Muscle Fibers at Rest
resting membrane potential (RMP) = -90 Mv
inside negative compared to outside
established by leak channels and Na/K pumps