2.2.2 - Pyschoactive Drugs: Influence on Conciousness
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What are psychoactive drugs?
these are substances that alter brain function.
- they lead to changing in perception, mood, consciousness, cognition (understanding), or behavior.

What do psychoactive drugs target in the body?
The Central Nervous System (CNR)
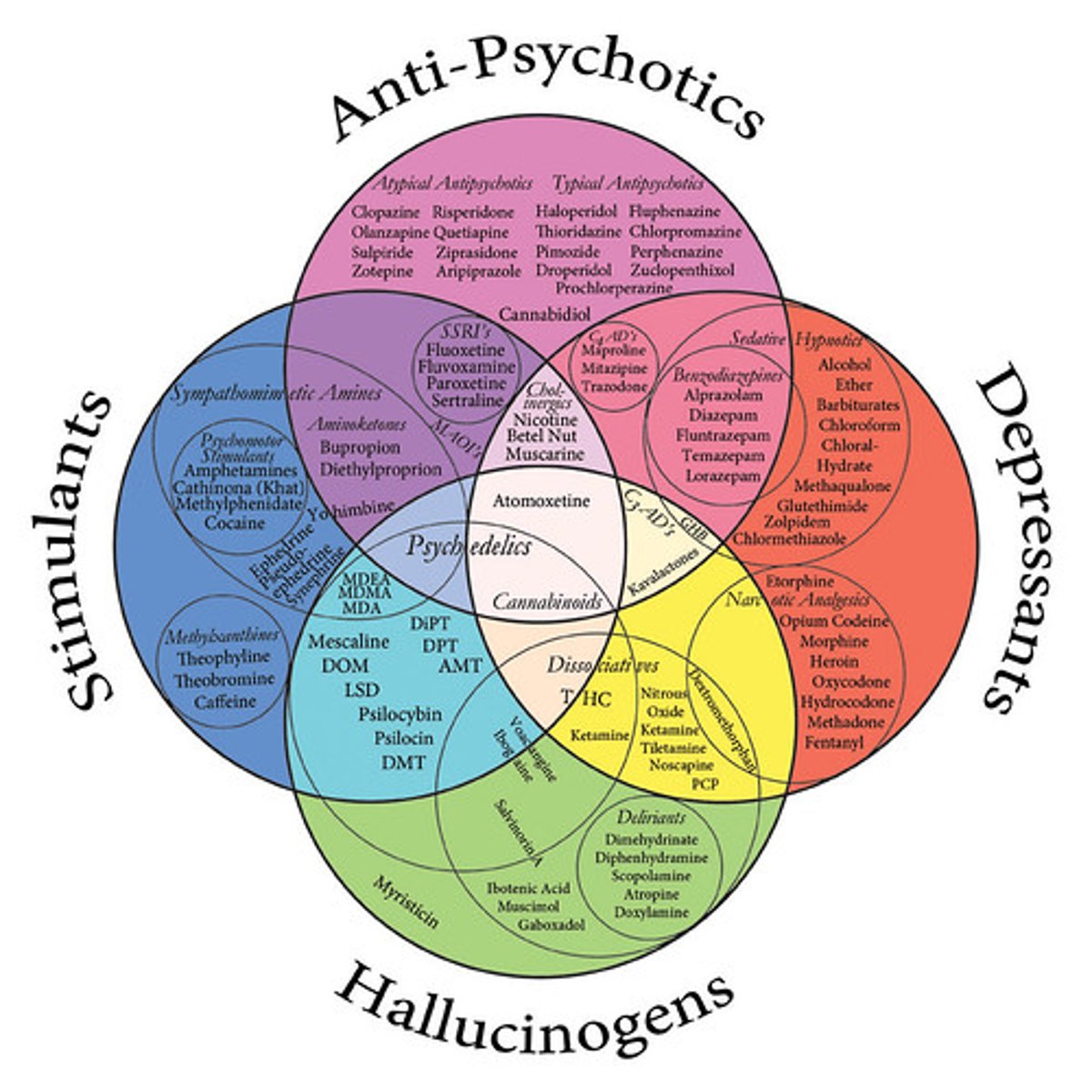
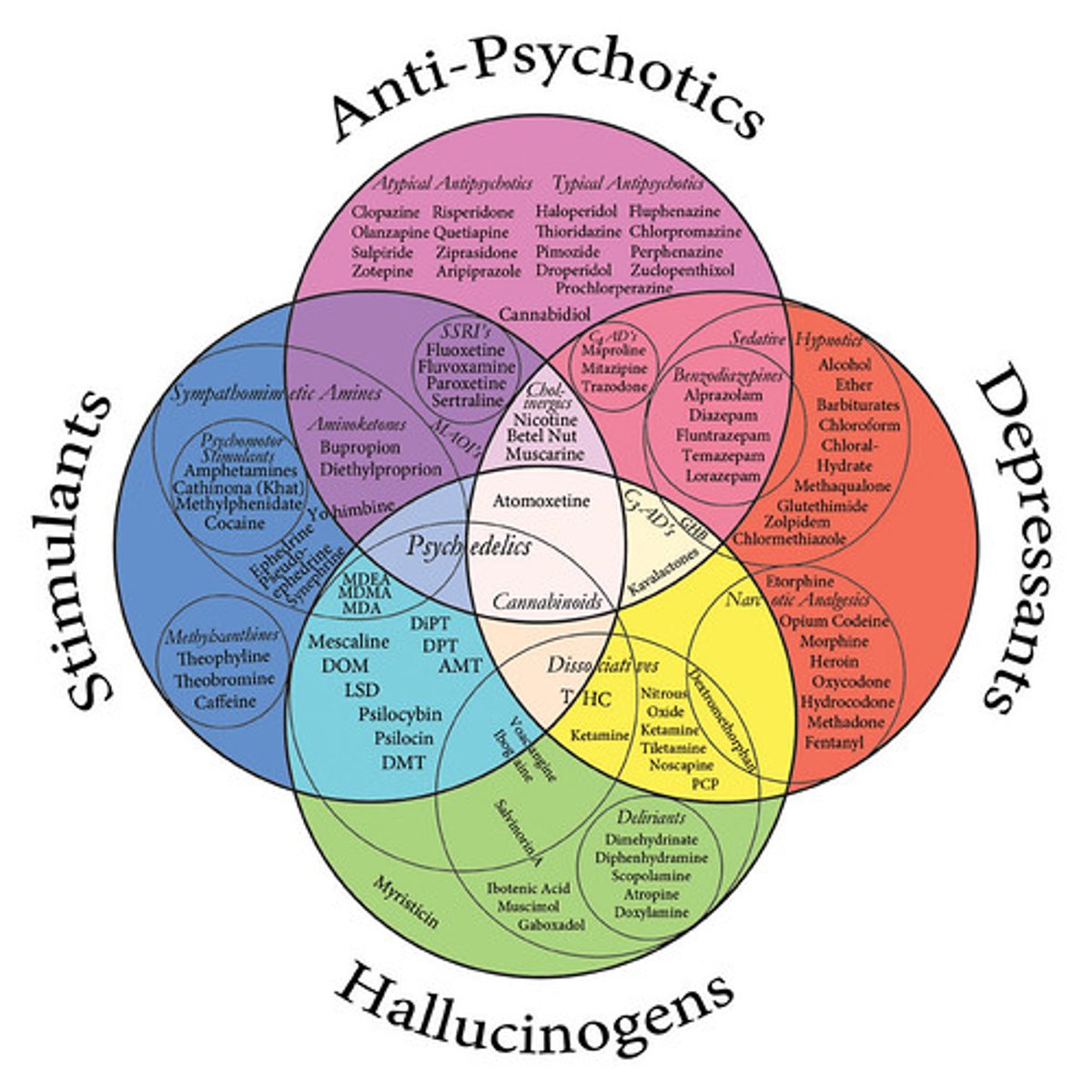
Four categories of psychoactive drugs:
see the chart :)
What does an agonist (substance) do?
these are substances that bind to neurotransmitter receptors to MIMIC their effects.
"AGonists ACTivate"
What does an antagonist (substance) do?
these are substances that bind to neurotransmitter receptors... WITHOUT activating them, BLOCKING the effects of said neurotransmitters
"ANTagonists ANTagonize"
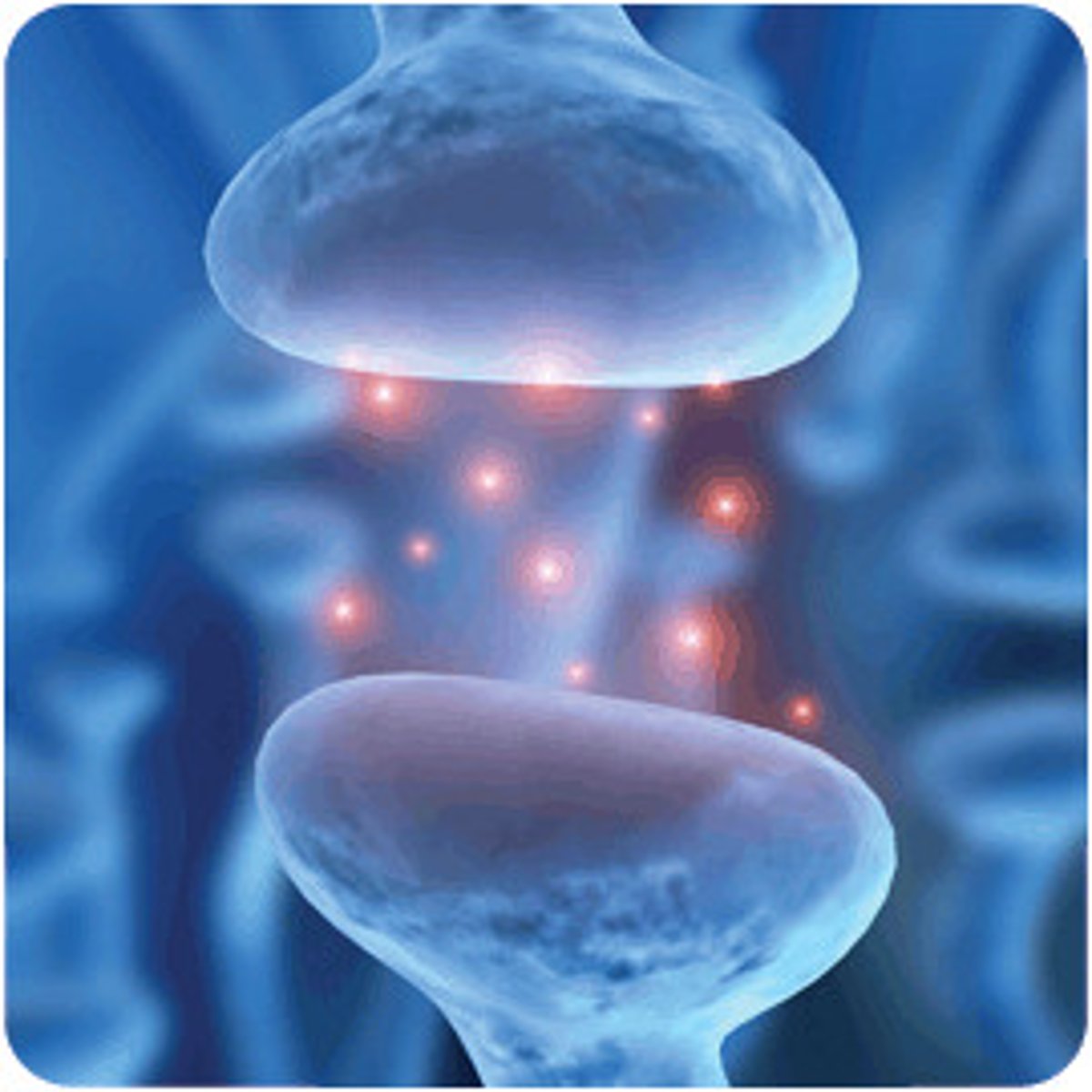
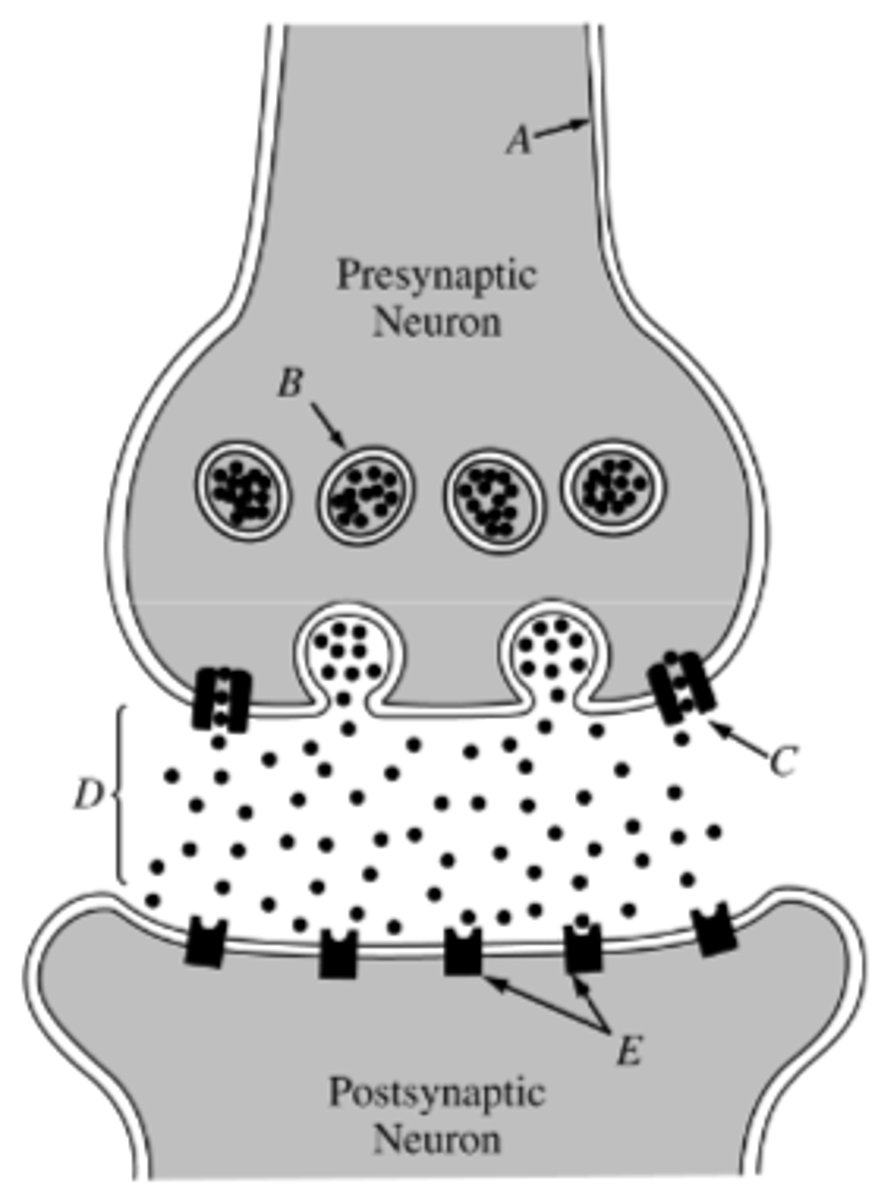
Reuptake Inhibitors:
Medications that block the reabsorption of neurotransmitters into sending neurons, increasing their levels in the brain (concentration). this occurs in the synaptic cleft (synapse) and enhances neurotransmission.
In the picture, C is the Reuptake Inhibitor preventing many of those neurons from moving across the synapse (the gap between neurotransmitters, like a train station between lines!) when the neurons end up making it across the synapse, it is in a greater quantity than before, leading to that higher level of neurotransmission that alters the processing of... said process.
What are stimulants, and what do they do?
these are drugs that increase neural activity and arousal.

Stimulant Drugs lead to what states of being?
heightened alertness, attention, and energy levels

Name a few of the most common stimulant drugs:
Caffeine
Amphetamines (Adderall, etc.)
Methamphetamine (e.g., crystal meth)
Cocaine (in all forms)
Methylphenidate (e.g., Ritalin, Concerta, etc...)
MDMA (Ecstacy, Molly)
Nicotine (lots of products.)
Modafinil (Provigil, etc.)
Ephedrine (found in some cold medications, dietary suplements)
Phentermine (weight-loss meds, via perscription)
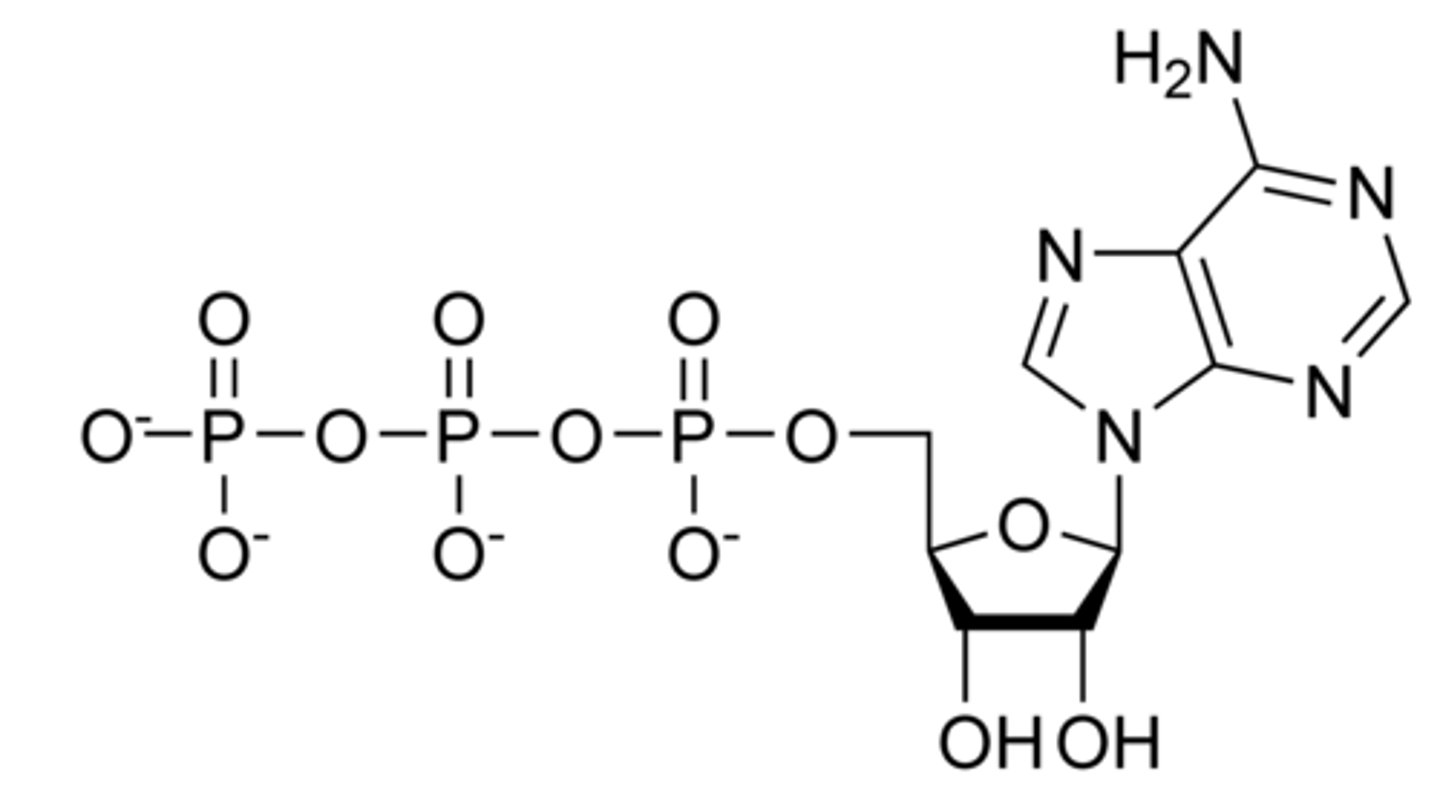
What is caffine?
- what is it found in?
- what does it increase/slow?
A natural stimulant that acts on the central nervous system (CNR)
- found in coffee, tea, and some sodas like Coca-Cola
- increases alertness and reducing fatigue

What neurotransmitter does caffine block?
adenosine
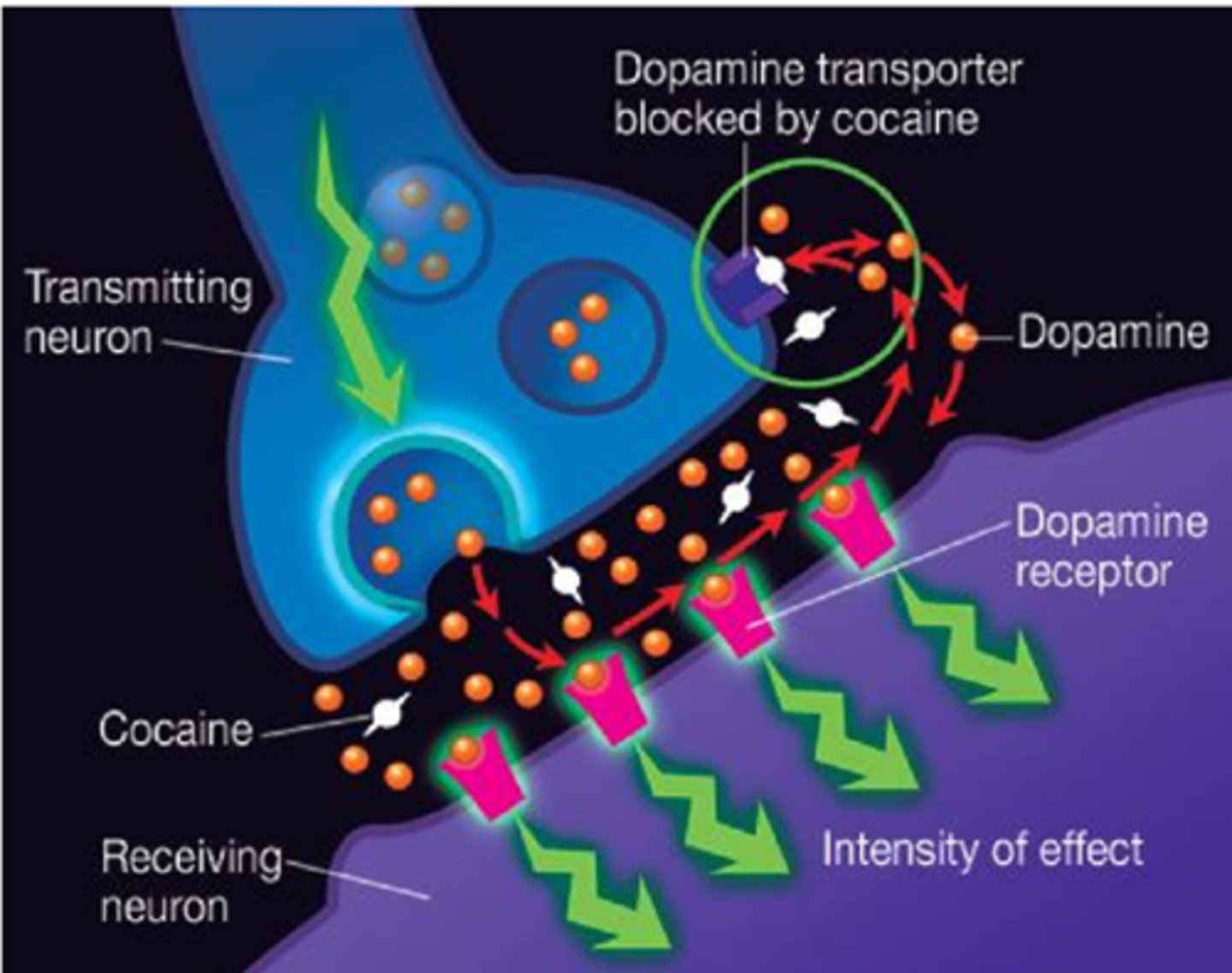
What is cocaine?
- what is it found in?
- what does it increase/slow?
a powerful stimulant derived from the coca plant.
- found in cocaine products, the pure substance
- this increases neural activity, leading to euphoria, increased energy, and alertness

How does cocaine work?
It blocks the reuptake* of dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine.
What do depressants increase/slow?
these are drugs that slow neural activity and bodily functions.
- induce relaxation, sedation and lower inhibitions (tendencies)
Name a few depressants:
Alcohol
Benzodiazepines (e.g., Xanax, Valium, etc...)
Barbiturates
Antipsychotics (e.g., chlorpromazine, etc..."
- primarily used to treat psychotic disorders, they also have sedating effects.
Antidepressants (e.g., trazodone, amitriptyline...)
Certain antidepressants, particularly those with sedative properties, can act as depressants.
Antihistamines - certain over-the-counter products have sedating effects, are used as sleep aids.
What is alcohol?
- What does it increase/slow?
- this leads to...
a depressant drug that slows down neural activity in the CNR.
- impairs judgement, coordination, and cognitive functions
- relaxation, euphoria, and in higher doses, intoxication.

What are hallucinogens?
these are drugs that alter perception, mood, and cognitive processes, often causing hallucinations (hence the name) and profound changes in consciousness.
Name a few of the most common hallucinogens:
LSD
Psilocybin (the shrooms)
DMT
Mescaline (the San Pedro cactus, etc...)
Ayahuasca
Ketamine
2C-B
MDMA (Ecstasy)
- while primarily known as an empathogen, can also produce hallucinogenic effects with higher doses.
What is marijuana?
- what does it contain, and what does that alter?
- this drug leads to...
a psychoactive drug derived from the cannabis plant.
- contains THC; alters mood, perception, and cognition
- relaxation, altered perception of time, heightened sensory experiences

Is marijuana a hallucinogen?
No--- not a true hallucinogen.
- It has some hallucinating effects in certain individuals, with certain doses, but it is not considered to be the primary affect.
What are opiods?
- what do they act on?
psychoactive drugs that act on opiod receptors in the brain in body
What does opiod consumption produce?
pain relief, euphoria, sedation
Name a few of the most common opiods:
Morphine
Codeine
Oxy/Hydro codone
Hydromorphone
Fentanyl*
Methadone, Tramadol, Buprenorphine
Heroin
What is heroin?
- what is it derived from?
- what does it produce?
a highly addictive opiod drug derived from morphine.
- produces intense euphoria, pain relief, and sedation
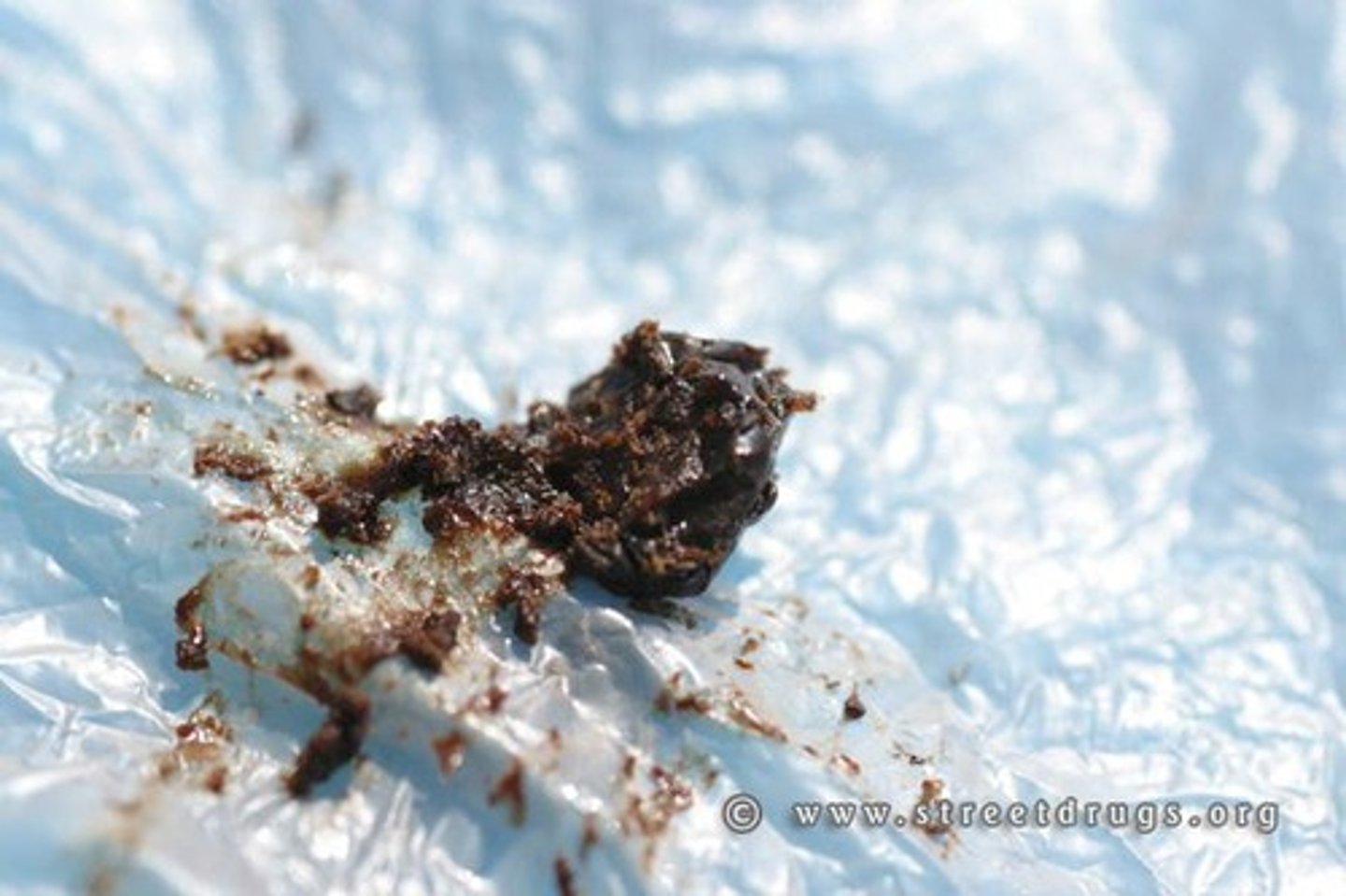

How does heroin take effect? What does it bind to?
Heroin binds to opiod receptors in the brain.
- here, it changes the brain's reward system.
Tolerance:
a condition where increasing amounts of a psychoactive substance are needed to achieve the same effects.
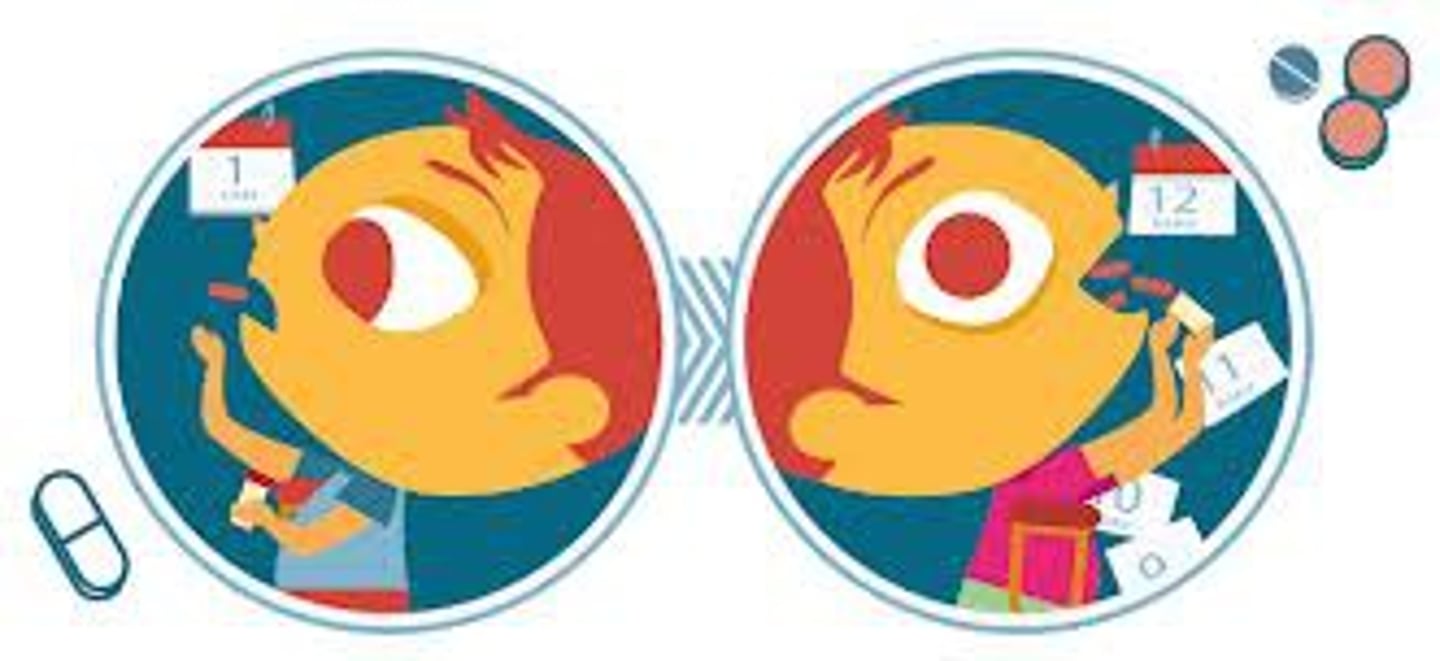

Why does tolerance occur?
The brain adapts to the drug, leading to its reduced sensitivity to just normal doses over time.
- needing to drink 2 cups of coffee instead of just one.
Withdrawal:
the onset of symptoms when a person stops using a psychoactive substance after prolonged use.
Symptoms of withdrawal:
physical discomfort, psychological distress, cravings for the drugs once in use
Addiction:
a chronic brain disorder characterized by compulsive drug seeking and use, despite harmful consequences.
- involves changes in the brain's structure and function
- leads to a loss of control over drug consumption
Bonus!
What does Walter White cook in the most nominated show of all time, Breaking Bad?
blue crystal methamphetamine
