Cell Biology
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Homeostasis
Keeping the internal conditions of the body stable.
Eukaryote
An organism whose cells have a nucleus.
Prokaryote
An organism whose cells do not have a nucleus.
Cell membrane
A thin layer that controls what enters and leaves the cell.
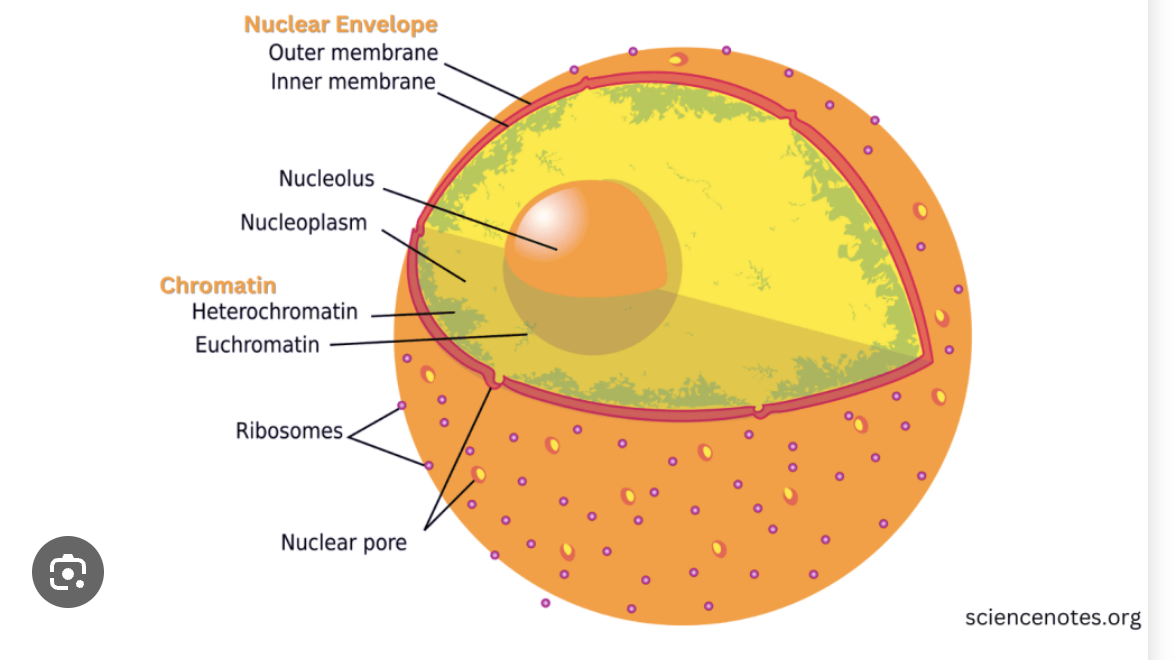
Nucleus
control center of the cell
contains DNA
Cytoplasm
colorless fluid of lipids and proteins
Mitochondria
powerhouse of the cell
processes glucose into ATP for the cells to use
Lysosome
small sacs filled with enzymes
Cilia
fine hair like projections on the surface of a cell
found in lung, respiratory and middle ear tissue
Flagella
sperm cell
longer than cilia
Intracellular Compartment
A space inside a cell with a specific function.
Extracellular Compartment
The space outside cells where fluids and substances are found.
Interstitial Compartment
The space between cells in tissues that contains fluid.
Absorption
The process of taking in substances, like nutrients, into the body or cells.
Excretion
The removal of waste products from the body.
eg. urine moving out
Transport
The movement of substances from one place to another in the body or cells.
Passive Trasport (diffusion and osmosis)
The movement of water across a membrane from where there is more water to where there is less water.
THREE TYPES OF FLUIDS:
1.hypertonic
2.isotonic
3. hypotonic
Active Transport
The movement of substances across a membrane using energy.
Endocytosis
enables large particles to be taken into the cell
Exocytosis
movement of large particles OUT of the cell
response to stimuli
reacting to sound, light and anything going on around it
cell theory
all organisms are composed of one or more cells and is the basic and smallest living unit of organization of all organisms
levels of organization
cells
tissues
organ
organ system
organism
pinocytosis
takes in fluids and solute
phagocytosis
takes in larger substances (bacteria)
secretion
The release of useful substances made by cells or glands.
eg. release of histamines during allergy season
Cell Physiology
activities within the cells that keep the animal alive
solutes
proteins, glucose, blood, electrolytes
homeostasis of the cell
Absorption- The cell ABSORBS what it needs
Excretion- The cell EXCRETES waste it doesnt need
Transport- The cell TRANSPORTS waste to other parts of the body