Biochem
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
What are monosaccharides?
Simple sugars made of one sugar unit. Examples include glucose, fructose, and galactose
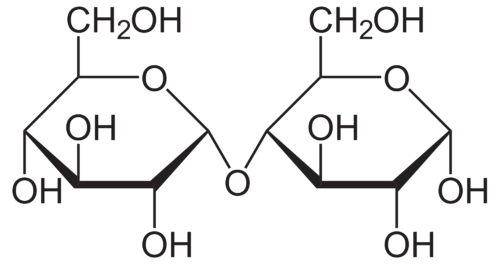
What are disaccharides?
Sugars made of two monosaccharides. Examples: sucrose (glucose + fructose), lactose, maltose.
What are polysaccharides?
Long chains of monosaccharides. Examples: starch, glycogen, cellulose.
What is the main function of carbohydrates in the body?
They provide energy (mainly through glucose).
Where is glycogen stored in the body?
In the liver and muscles.
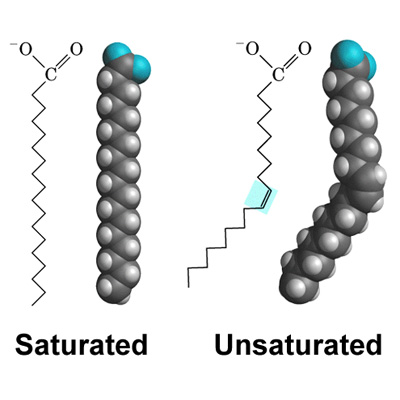
What are fatty acids?
Long hydrocarbon chains that can be saturated (no double bonds) or unsaturated (one or more double bonds).
What are prostaglandins?
Lipid compounds that act like hormones, involved in inflammation, pain, and fever.
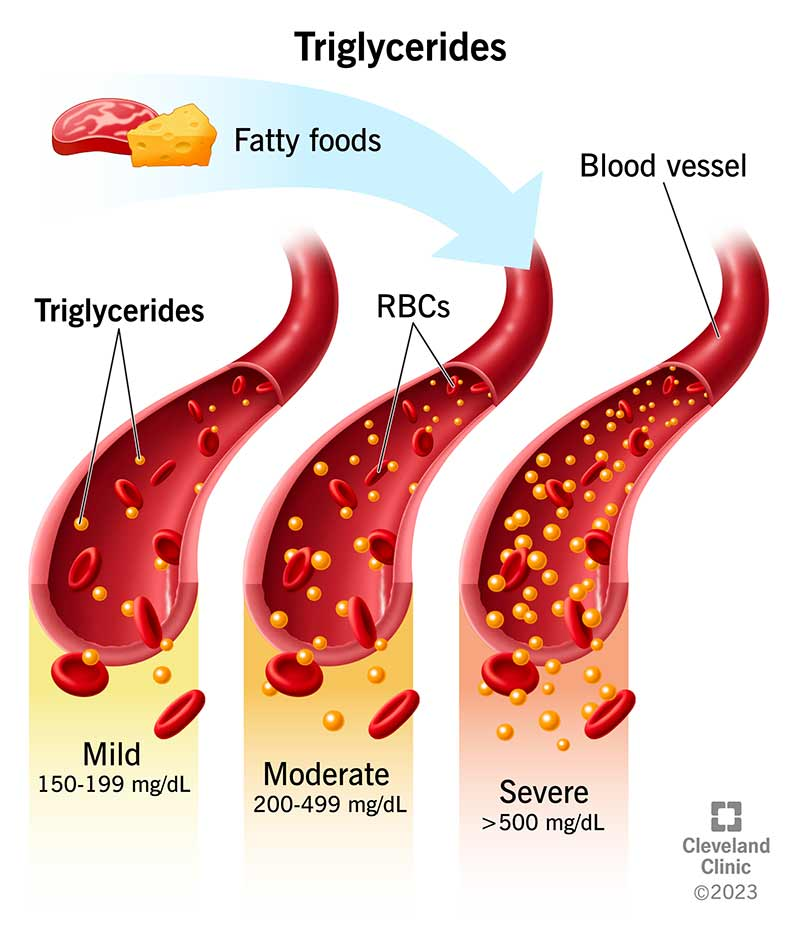
What are triglycerides?
Three fatty acids + glycerol. Main form of stored fat in the body.
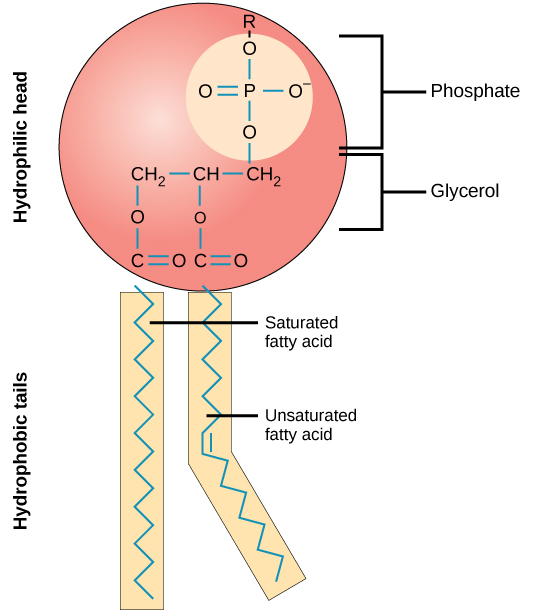
What are phospholipids?
Lipids with two fatty acids and a phosphate group. They form the cell membrane bilayer.
What is cholesterol and what is it used for?
A steroid lipid that helps stabilize cell membranes and is used to make steroid hormones and vitamin D.
What are steroid hormones?
Hormones made from cholesterol, like estrogen, testosterone, and cortisol.
What role do lipids play in cell membranes?
Phospholipids form the membrane structure; cholesterol maintains fluidity and stability.
What are the main functions of proteins?
Structure, enzymes, transport, defense (antibodies), and hormones (e.g., insulin).
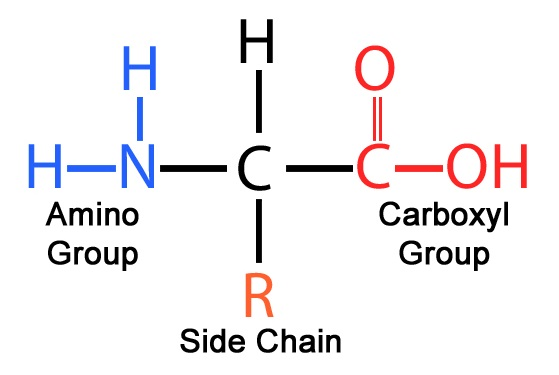
What is the basic structure of an amino acid?
Central carbon, amino group (–NH₂), carboxyl group (–COOH), hydrogen, and variable R group.
How are amino acids classified?
Based on their R group: polar, nonpolar, acidic, or basic. Also classified as essential or non-essential.
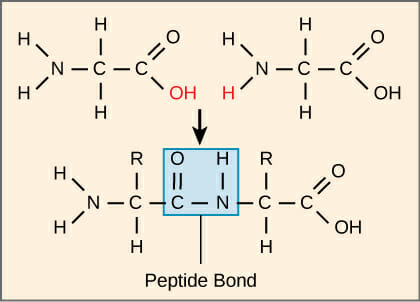
How is a peptide bond formed?
By linking the amino group of one amino acid to the carboxyl group of another, releasing water (condensation reaction).
What’s the primary level of the protein structure
amino acid sequence
What’s the secondary level of the protein structure
alpha helices and beta sheets
What’s the Tertiary level of the protein structure
3D folding
What’s the Quaternary level of the protein structure
multiple polypeptides together
What is protein denaturation?
Loss of structure and function due to heat, pH, or chemicals
What is an enzyme?
A biological catalyst (usually a protein) that speeds up chemical reactions without being used up.
How are enzymes named?
Most end in “-ase” and are named for the substrate or reaction (e.g., lactase breaks down lactose).
What model describes how enzymes and substrates fit?
The "lock and key" model or the "induced fit" model.
What factors affect enzyme activity?
Temperature, pH, substrate concentration.
What are cofactors?
Non-protein helpers for enzymes (e.g., metal ions like Mg²⁺ or Zn²⁺).
What are coenzymes?
Organic cofactors, often vitamins (e.g., B vitamins).
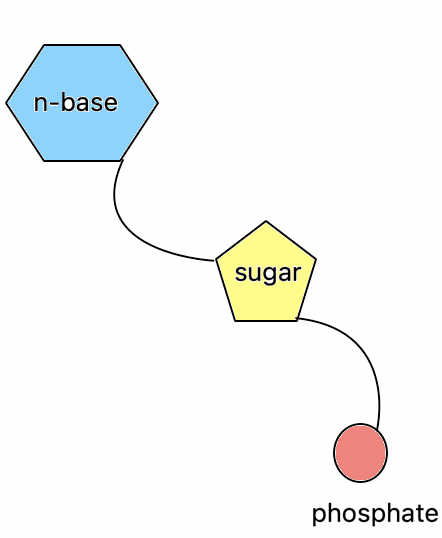
What are the building blocks of nucleic acids?
Nucleotides (sugar + phosphate + nitrogenous base)
What is the structure of DNA?
Double helix with base pairs: A-T and G-C.
What is the structure of RNA?
Single-stranded with base pairs: A-U and G-C.
What is DNA replication?
Process where DNA makes a copy of itself before cell division. Enzyme: DNA polymerase
What is the function of RNA?
Assists in protein synthesis (mRNA, tRNA, rRNA).
What’s the first step of protein synthesis?
Transcription: DNA → mRNA (in nucleus)
What’s the second step in protein synthesis?
Translation: mRNA → protein (at ribosome, using tRNA)
What is a genetic mutation?
A change in the DNA sequence that can affect protein structure and function.
Which gas is produced during cellular respiration?
Carbon dioxide
Which molecule carries genetic instructions from the nucleus to the ribosome?
mRNA
Which molecule brings amino acids to the ribosome during translation.
tRNA

Glucose is a
Monosaccharide - main energy source for the body’s cells. Found in foods like fruits, bread, and pasta.

Fructose is a
monosaccharide - is a simple sugar found in fruits, honey, and some vegetables. It’s known as the sweetest natural sugar
Galactose is a
Monosaccharide -Found in milk

Sucrose is a
Disaccharide (glucose + fructose)
Commonly known as table sugar Found naturally in fruits and also refined in sugarcane and sugar beets
Lactose is a
Disaccharide (glucose + galactose)
Maltose is a
Disaccharide (glucose + glucose)
Starch is a
Polysaccharide (plant energy storage)
Glycogen is a
Polysaccharide (animal / human energy storage)

Cellulose is a
Polysaccharide (plant structure/fiber)
Ribose is a
Monosaccharide (sugar in RNA)
Deoxyribose is a
Monosaccharide (sugar in DNA)