Exam 3 - Reading questions
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
In the lungs, carbon dioxide leaves the blood and enters the air because the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in deoxygenated blood is _____________ in air.
A
higher than
B
lower than
C
the same as
D
sometimes higher and sometimes lower than
A
Which of these is not part of the upper airway?
A
Nasal vestibule
B
The superior, middle, and inferior meatuses
C
The pharynx
D
The lungs
D
Which of these is not a part of the pharynx?
A
Nasopharynx
B
Oropharynx
C
Linguopharynx
D
Laryngopharynx
C
What structure of the larynx prevents food and drink from going down the trachea?
A
Epiglottis
B
Glottis
C
Pharynx
D
Cricoid cartilage
A
What type of cartilage makes up the rings of the trachea?
A
Elastic cartilage
B
Hyaline cartilage
C
Fibrocartilage
D
Calcified cartilage
B
What does the carina do if someone accidentally inhales food or water?
A
Closes
B
Causes forceful inhalation
C
Causes violent coughing
D
Nothing
C
What type of alveolar cell secretes surfactant to make breathing easier?
A
Type I
B
Type II
C
Type III
D
Macrophage
B
Which lobe is the left lung missing?
A
Superior
B
Middle
C
Inferior
D
Don't choose this option
B
Which lung contains the cardiac notch?
A
Left
B
Right
A
True or False: The pulmonary artery carries oxygenated blood to the lungs.
False
True or False: The parasympathetic nervous system causes bronchodilation.
False
When we first inhale, air pressure in our lungs ____________ because volume _____________.
A
increases; increases
B
decreases; decreases
C
increases; decreases
D
decreases; increases
D
The respiratory cycle:
A
only involves inhalation
B
only involves exhalation
C
is one sequence of inhalation and exhalation
D
involves numerous inhalations and exhalations
C
This is the normal amount of air that enters the lungs during quiet breathing:
A
Inspiratory Reserve Volume
B
Tidal Volume
C
Expiratory Reserve Volume
D
Functional Capacity
B
Why must we always have at least some air (residual volume) in the lungs?
A
To prevent valves from closing
B
To prevent the lungs from collapsing
C
To prevent the bronchioles from collapsing
D
To prevent the alveoli from collapsing
D
The ventral respiratory group:
A
Is involved in normal breathing
B
Is only involved in inhaling
C
Is only involved in exhaling
D
Is involved in forced breathing
D
In any random quantity of normal air, which of these gases will have the highest partial pressure?
A
Nitrogen
B
Oxygen
C
Carbon Dioxide
D
Carbon Monoxide
A
In internal respiration, oxygen and carbon dioxide move across membranes by:
A
Osmosis
B
Diffusion
C
Active transport
D
Conduction
B
In tissues, oxygen leaves the blood and enters tissues because the partial pressure of oxygen in blood is _____________ in tissues.
A
higher than
B
lower than
C
the same as
D
sometimes higher and sometimes lower than
A
Your patient is hyperventilating. What effect will this have on their blood?
A
Increased carbon dioxide and decreased pH
B
Increased carbon dioxide and increased pH
C
Decreased carbon dioxide and decreased pH
D
Decreased carbon dioxide and increased pH
D
The ____________ is another name for the GI tract.
a) Esophagus
b) Stomach
c) Intestines
d) Alimentary canal
d
Match the layers of the alimentary canal with their correct description:
Layers:
A) Mucosa
B) Submucosa
C) Muscularis
D) Serosa
Definitions:
Made of dense connective tissue; it houses blood vessels, nerves, and some glands
Only found in the abdominal cavity; it connects to the visceral peritoneum
Can contain smooth muscle or skeletal muscle depending on which section of the GI tract it is in
The innermost layer; it produces mucus
C3
D2
B1
A4
Structures:
A) Greater omentum
B) Falciform ligament
C) Lesser omentum
D) Mesentery
E) Mesocolon
Descriptions:
Attaches two portions of the large intestine (the transverse and sigmoid colon) to the posterior abdominal wall
Apron-like structure that lies superficial to the small intestine and transverse colon; a site of fat deposition in people who are overweight
Suspends the stomach from the inferior border of the liver; provides a pathway for structures connecting to the liver
Anchors the liver to the anterior abdominal wall and inferior border of the diaphragm
Vertical band of tissue anterior to the lumbar vertebrae and anchoring all of the small intestine except the initial portion (the duodenum)
A2
B4
C3
D5
E1
Where does mechanical digestion occur?
a) The mouth
b) The stomach
c) The small intestine
d) All of the above
D
Which of these does not participate in chemical digestion?
a) The mouth
b) The stomach
c) The small intestine
d) The large intestine
D
Which of these is NOT true of absorption?
a) It involves the movement of nutrients from the alimentary canal into the bloodstream
b) It utilizes epithelial cells of the mucosa
c) It mostly occurs in the large intestine
d) It mostly occurs in the small intestine
C
How many pairs of salivary glands do we have?
3
What macro does Salivary amylase break down?
carbs
What is mumps?
a) A viral infection of the throat
b) A viral infection of the parotid glands
c) A viral infection of the sublingual gland
d) The laryngopharynx
B
Your patient has had all of their wisdom teeth removed. Assuming they still have not lost any others, how many permanent teeth are remaining?
26
28
30
32
28
Which part of the pharynx is not part of the digestive tract?
a) Oropharynx
b) Laryngopharynx
c) Nasopharynx
c
Which of these is NOT true of the esophagus?
a) It runs from the pharynx to the stomach
b) It sits behind the trachea
c) It sits in front of the trachea
d) There is a sphincter located at each end to help make sure food doesn't travel the wrong way
c
In what part of swallowing does peristalsis occur?
a) The voluntary phase
b) The pharyngeal phase
c) The esophageal phase
d) Only after the food reaches the stomach
c
Which of these puts the four sections of the stomach in the correct order from most superior to most inferior (hint: The most superior part is not necessarily where food enters the stomach)?
A. Fundus, Cardia, Body, Pylorus
B. Cardia, Fundus, Body, Pylorus
C. Fundus, Body, Pylorus, Cardia
D. Body, Pylorus, Fundus, Cardia
A: fundus, cardia, body, pylorus
Which phase of gastric secretion begins before food even enters your body?
A. Cephalic phase
B. Esophageal Phase
C. Gastric Phase
D. Intestinal Phase
a
Which of these is not a primary function of HCl in the stomach?
A. Conversion of pepsinogen to pepsin
B. Denaturing proteins
C. Breaking down fatty acids
D. Killing bacteria ingested in food
c
Match the secretion with the cell that produces it. (One will be used twice)
Hydrochloric Acid → ___
Pepsinogen → ___
Gastrin → ___
Intrinsic Factor → ___
HCL —> Parietal cells
Pepsinogen —> Chief cells
G-cells —> Gastrin
Instrinsic factor —> Parietal cells
Which of these is not produced in the stomach?
A. Intrinsic Factor
B. HCl
C. Pepsin
D. Amylase
D
Where do food and digestive enzymes/chemicals from the liver, pancreas, and gallbladder mix?
A. Stomach
B. Duodenum
C. Jejunum
D. Ileum
B
Where does most absorption occur?
A. The oral cavity
B. The stomach
C. The small intestine
D. The large intestine
c
Which of these is in the correct order from largest to smallest?
A. circular folds, microvilli, villi, small intestine
B. small intestine, villi, microvilli, circular folds
C. small intestine, circular folds, villi, microvilli
D. small intestine, microvilli, villi, circular folds
c
Most digestion of dietary fats occurs in the:
A. Mouth
B. Stomach
C. Small intestine
D. Large intestine
c
Which of these puts the parts of the colon in the correct order, matching the direction that food travels through it?
A. Ascending Colon, Sigmoid Colon, Descending Colon, Transverse Colon
B. Ascending Colon, Transverse Colon, Descending Colon, Sigmoid Colon
C. Descending Colon, Transverse Colon, Ascending Colon, Sigmoid Colon
D. Descending Colon, Sigmoid Colon, Ascending Colon, Transverse Colon
b
About how many different species of bacteria live in our large intestines?
A. 10
B. 100
C. 700
D. 10,000
c
Bile helps with digestion of:
A. Carbohydrates
B. Proteins
C. Fats
D. Insoluble Fiber
c
Production of _____________ in the pancreas helps to neutralize stomach acid.
A. Insulin
B. Glucagon
C. Sodium bicarbonate
D. Enteropeptidase
c
5. What is the function of the conchae in the nasal cavity?
a. Increase surface area
b. Exchange gases
c. Maintain surface tension
d. Maintain air pressure
a
6. The fauces connect which of the following structures to the oropharynx?
a. Nasopharynx
b. Laryngopharynx
c. Nasal cavity
d. Oral cavity
d
. Which of the following are structural features of the trachea?
a. C-shaped cartilage
b. Smooth muscle fibers
c. Cilia
d. All of the above
d
11. A section of the lung that receives its own tertiary bronchus is called the ________.
a. Bronchopulmonary segment
b. Pulmonary lobule
c. Interpulmonary segment
d. Respiratory segment
a
4. Which of the following processes does atmospheric pressure play a role in?
a. Pulmonary ventilation
b. Production of pulmonary surfactant
c. Resistance
d. Surface tension
a
17. Gas flow decreases as ________ increases.
a. Resistance
b. Pressure
c. Airway diameter
d. Friction
a
21. When ventilation is not sufficient, which of the following occurs?
a. The capillary constricts
b. The capillary dilates
c. The partial pressure of oxygen in the affected alveolus increases
d. The bronchioles dilate
a
22. Gas exchange that occurs at the level of the tissues is called ________.
a. External respiration
b. Interpulmonary respiration
c. Internal respiration
d. Pulmonary ventilation
c
25. Which of the following factors play a role in the oxygen–hemoglobin saturation/dissociation curve?
a. Temperature
b. pH
c. BPG
d. All of the above
d
32. A full complement of mature alveoli are present by ________.
a. Early childhood, around 8 years of age
b. Birth
c. 37 weeks
d. 16 weeks
a
13. Which of the following stimuli activates sensors in the walls of digestive organs?
a. Breakdown products of digestion
b. Distension
c. pH of chyme
d. All of the above
d
15. Which of these ingredients in saliva is responsible for activating salivary amylase?
a. Mucus
b. Phosphate ions
c. Chloride ions
d. Urea
c
16. Which of these statements about the pharynx is true?
a. It extends from the nasal and oral cavities superiorly to the esophagus anteriorly.
b. The oropharynx is continuous superiorly with the nasopharynx.
c. The nasopharynx is involved in digestion.
d. The laryngopharynx is composed partially of cartilage.
b
17. Which structure is located where the esophagus penetrates the diaphragm?
a. Esophageal hiatus
b. Cardiac orifice
c. Upper esophageal sphincter
d. Lower esophageal sphincter
a
18. Which phase of deglutition involves contraction of the longitudinal muscle layer of the muscularis?
a. Voluntary phase
b. Buccal phase
c. Pharyngeal phase
d. Esophageal phase
d
20. Where does the majority of chemical digestion in the stomach occur?
a. Fundus and body
b. Cardia and fundus
c. Body and pylorus
d. Body
a
23. In which part of the alimentary canal does most digestion occur?
a. Stomach
b. Proximal small intestine
c. Distal small intestine
d. Ascending colon
b
26. Which part of the large intestine attaches to the appendix?
a. Cecum
b. Ascending colon
c. Transverse colon
d. Descending colon
a
28. Pancreatic juice ________.
a. Deactivates bile
b. Is secreted by pancreatic islet cells
c. Buffers chyme
d. Is released into the cystic duct
c
29. Where does the chemical digestion of starch begin?
a. Mouth
b. Esophagus
c. Stomach
d. Small intest
a
31. Where are most fat-digesting enzymes produced?
a. Small intestine
b. Gallbladder
c. Liver
d. Pancreas
d
32. Which of these nutrients is absorbed mainly in the duodenum?
a. Glucose
b. Iron
c. Sodium
d. Water
d
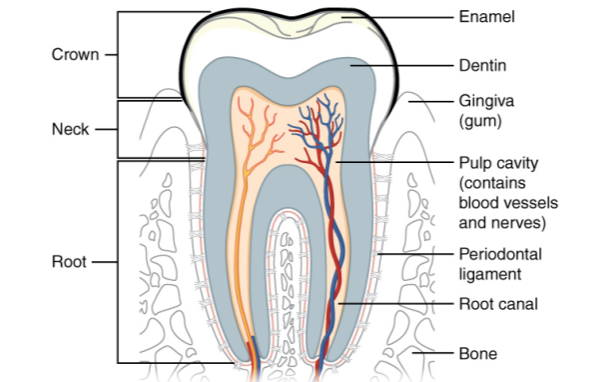
During inhalation, what causes air to move into the lungs?
A) Intra-alveolar pressure increases above atmospheric pressure
B) Intra-alveolar pressure drops below atmospheric pressure
C) Atmospheric pressure drops below intra-alveolar pressure
D) Lung volume decreases
B
Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV) refers to:
A) The air you can inhale past normal tidal inhalation
B) The air left in lungs after forced exhalation
C) The air you can exhale past normal tidal exhalation
D) The total air exhaled after maximal inhalation
C
Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV) is:
A) Air you can exhale past normal tidal exhalation
B) Air you can inhale past normal tidal inhalation
C) Air left in lungs after forced exhalation
D) Air remaining after normal exhalation
B
Residual Volume (RV) refers to:
A) Air you can exhale after normal breathing
B) Air left in lungs after hard exhalation preventing alveolar collapse
C) Air inhaled during maximal inspiration
D) Air moved in a normal breath
D
Forced Vital Capacity (FVC) measures:
A) Air inhaled after normal exhalation
B) Air exhaled after maximal inhalation
C) Air remaining after forced exhalation
D) Air moved in one normal breath
B
Forced Expiratory Volume (FEV) is:
A) Air exhaled in a forced expiration
B) Air left after forced exhalation
C) Air inhaled after maximal exhalation
D) Air exhaled in one normal breath
A
Total Lung Capacity (TLC) represents:
A) Air remaining after normal exhalation
B) Air exhaled in one normal breath
C) Total air in lungs after forceful inspiration
D) Air left after forceful expiration
c
Functional Residual Capacity (FRC) is:
A) Air left in lungs after normal exhalation
B) Air left after maximal exhalation
C) Air inhaled after normal exhalation
D) Air in lungs after maximal inspiration
A
Respiratory rate measures:
A) Air volume moved per breath
B) Number of respiratory cycles per minute
C) Total oxygen exchanged per minute
D) Pressure difference during breathing
b
The apneustic center functions to:
A) Inhibit the dorsal respiratory group (DRG)
B) Stimulate the dorsal respiratory group (DRG)
C) Control expiratory neurons
D) Regulate heart rate
B
The pneumotaxic center functions to:
A) Stimulate the DRG
B) Inhibit the DRG
C) Increase lung elasticity
D) Enhance oxygen diffusion
B
According to Dalton’s Law, the total pressure of a gas mixture equals:
A) Product of all partial pressures
B) Sum of all partial pressures
C) Difference between highest and lowest pressure
D) Average of all partial pressures
B
In external respiration, gas exchange occurs as:
A) O₂ moves from blood to alveoli; CO₂ from alveoli to blood
B) O₂ moves from alveoli to blood; CO₂ from blood to alveoli
C) O₂ and CO₂ both move from blood to alveoli
D) O₂ and CO₂ both move from alveoli to blood
B
In internal respiration, gas exchange occurs as:
A) O₂ moves from blood to tissue; CO₂ from tissue to blood
B) O₂ moves from tissue to blood; CO₂ from blood to tissue
C) Both O₂ and CO₂ move from blood to tissue
D) Both O₂ and CO₂ move from tissue to blood
A
The majority of CO₂ in the blood is transported:
A) Dissolved in plasma
B) Bound to hemoglobin
C) Via the bicarbonate buffer system
D) As carbonic acid
c
During the chloride shift, what happens?
A) Chloride moves into the lumen, bicarbonate into the cell
B) Bicarbonate moves into the lumen, chloride into the cell
C) Both ions move into the cell
D) Both ions move into the lumen
B
In pulmonary capillaries, bicarbonate (HCO₃⁻) is:
A) Converted to CO₂ and exhaled
B) Converted to carbonic acid and stored
C) Converted to O₂
D) Released into plasma unchanged
A
The mucosa layer of the alimentary canal includes:
A) Epithelium, lamina propria, muscularis mucosae
B) Circular and longitudinal layers
C) Dense connective tissue with glands
D) Areolar connective tissue only
A
The muscularis externa consists of:
A) Circular and longitudinal muscle layers
B) Lamina propria and epithelium
C) Areolar connective tissue
D) Dense irregular connective tissue
A
The serosa layer is made of:
A) Dense connective tissue
B) Areolar connective tissue
C) Smooth muscle and glands
D) Simple squamous epithelium only
B
The submucosa layer contains:
A) Circular and longitudinal muscle layers
B) Dense connective tissue with glands, lymph, and blood vessels
C) Areolar connective tissue
D) Smooth muscle and mucous glands only
B
The mesocolon attaches:
A) Small intestine to posterior abdominal wall
B) Transverse and sigmoid colon to posterior abdominal wall
C) Stomach to diaphragm
D) Stomach to transverse colon
B
The greater omentum is located:
A) Deep to the small intestine
B) Superficial to small intestine and transverse colon
C) Attached to the posterior abdominal wall
D) Between liver and stomach
B
The small intestine performs mechanical digestion through:
A) Peristalsis
B) Segmentation
C) Churning
D) Mass movement
Mass peristalsis
The pancreas functions to:
A) Absorb nutrients and secrete bile
B) Produce digestive enzymes and bicarbonate
C) Store bile and secrete insulin only
D) Regulate peristaltic waves
B
The small intestine slows food propulsion to:
A) Increase mechanical digestion
B) Allow digestion and absorption
C) Prevent reflux
D) Facilitate peristalsis
B
The pharynx serves to:
A) Chemically digest food
B) Propel food from oral cavity to esophagus
C) Store swallowed food temporarily
D) Absorb nutrients before swallowing
B