Biol 190 Unit 2 Lecture 7
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/76
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
1
New cards
What is a gene?
DNA sequence that encodes a specific protein
2
New cards
What is a genome?
Complete set of DNA in a living organism
3
New cards
How many genomes does every living organism have?
1 genome
4
New cards
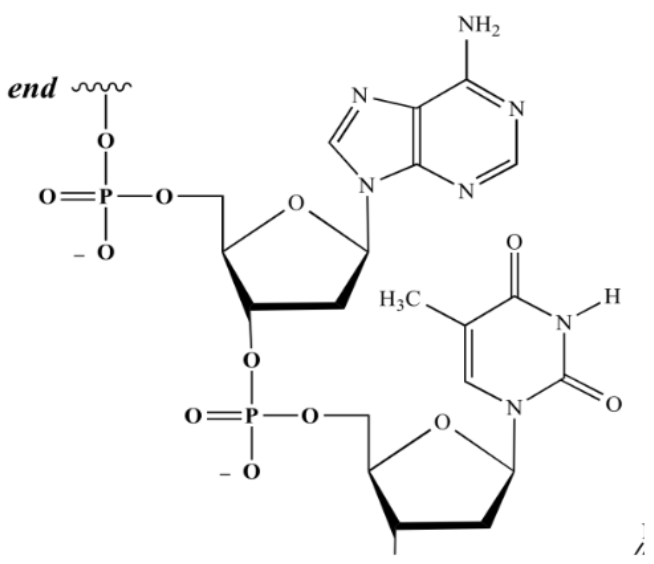
Identify the macromolecule, polymer, monomer, and building block of monomer.
Macromolecule: nucleic acid
Polymer: polynucleotide (ex. DNA and RNA)
Monomers: nucleotide
Building block of monomer: sugar, phosphate, and base
Polymer: polynucleotide (ex. DNA and RNA)
Monomers: nucleotide
Building block of monomer: sugar, phosphate, and base
5
New cards
What are the biological uses of DNA?
\-Permanent storage of genetic information
\-stored in the chromosomes
\-transmission of genetic info
\-stored in the chromosomes
\-transmission of genetic info
6
New cards
What are the biological uses (roles) of RNA?
Temporary; Transmits the genetic information from DNA to the protein synthesizers in the cell
7
New cards
Together, what do DNA & RNA do?
Use the genetic information to direct the creation of new proteins
8
New cards
What are the building blocks of nucleotides?
1. Nitrogenous base
2. A five-carbon sugar (ribose or deoxyribose)
3. Phosphate (mono, di, or tri) group
9
New cards
What are the two classes for the five nitrogenous bases?
Pyrimidine (single rings): Cytosine, Thymine (unique to DNA), Uracil (unique to RNA); Purines (double ring): Adenine, Guanine
10
New cards
What are the two sugars of nucleotides?
1. Deoxyribose (in DNA)- without oxygen 2. Ribose (in RNA)
11
New cards
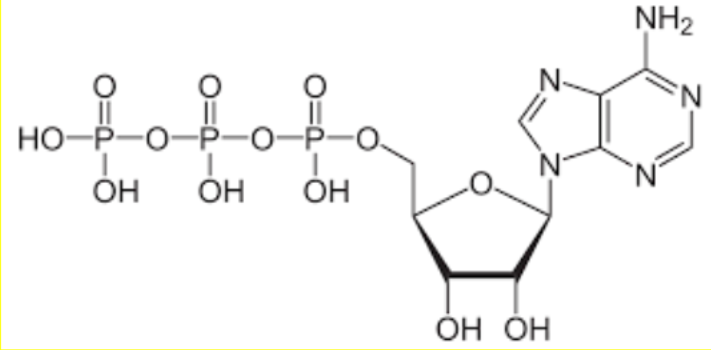
What type of monomer is this? Identify its name.
Nucleotide; ATP (Adenosine TriPhosphate)
12
New cards
What is ATP?
Multifunctional: Builds nucleic acids (DNA & RNA) & energy source for cells
13
New cards
Which part of the nucleotide is rich with potential energy?
Phosphate functional group (5 covalent bonds)
14
New cards
How is energy released from ATP?
Remove a phosphate group (breaks the bond between a phosphate group)
15
New cards
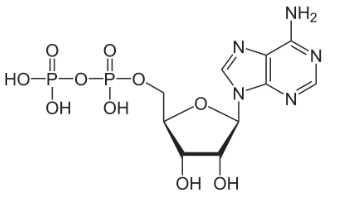
What molecule is this?
ADP (Adenosine Diphosphate)
16
New cards
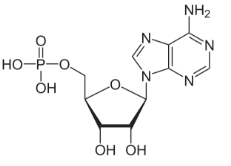
What molecule is this?
AMP (Adenosine Monophosphate)
17
New cards
Which monomer has the least energy out of ATP, ADP, and ADP? Which monomer has the most?
ADP; ATP
18
New cards
What is a nucleoside?
Nitrogenous base + sugar
19
New cards
What is a nucleotide?
Nucleoside + phosphate group
20
New cards
DNA and RNA have \____________
Directionality
21
New cards
What is the beginning of a polynucleotide called? What is the end called?
5' end; 3' end
22
New cards
Where does the beginning and end of a polynucleotide come from?
5' \= fifth carbon on sugar; 3' \= third carbon on sugar (has a free hydroxyl group attached)
23
New cards
What direction are nucleic acids synthesized?
5' to 3' direction
24
New cards
How is a nucleotide linked to form a polynucleotide?
Remove water (dehydration reaction) from OH from 3' end and OH from phosphate group
25
New cards
What is the covalent bond that holds polynucleotides together?
Phosphodiester bonds
26
New cards
What do the covalent bonds between the sugar and phosphate of monomers form?
Strong, stable sugar-phosphate backbone
27
New cards
What are the attributes of DNA vs. RNA?
\-DNA: double-stranded, deoxyribose sugar (lacks an oxygen), Thymine
\
\-RNA: single-stranded, ribose sugar, Uracil
\
\-RNA: single-stranded, ribose sugar, Uracil
28
New cards
What is the shape of DNA?
Double helix- two DNA strands coil around each other
29
New cards
What is the complementary base pairing?
Adenine pairs with Thymine (Apple Trees)
\
Cytosine pairs with Guanine (Chewing Gum)
\
Cytosine pairs with Guanine (Chewing Gum)
30
New cards
How are nitrogenous bases held together?
Hydrogen bonds
31
New cards
Why does uracil not have a complementary base pairing?
Uracil is unique to RNA; RNA is single-stranded
32
New cards
What are the properties of a DNA double helix?
\-DNA strands are antiparallel
\-DNA has polarity (head is different from the tail)
\-complementary strands
\-there are base stacking interactions
\-hydrogen bonds hold together the two strands (can be broken to unzip the DNA)
\-DNA has polarity (head is different from the tail)
\-complementary strands
\-there are base stacking interactions
\-hydrogen bonds hold together the two strands (can be broken to unzip the DNA)
33
New cards
Where does the stability of DNA come from?
Covalent bonds of the sugar-phosphate backbone
34
New cards
What force holds the 2 strands of DNA together?
Hydrogen bonds
35
New cards
What force holds the 1 strand of DNA together?
Covalent bonds
36
New cards
Why would you want to unzip the bonds between 2 strands of DNA?
To make proteins (so cell can see the instructions from the unzipped DNA); DNA is zipped back to protect itself
37
New cards
What are the three types of RNA?
mRNA, rRNA, and tRNA (all are involved in gene expression)
38
New cards
What is the first type of RNA?
Messenger RNA (mRNA)- temporary copy of the gene (the instructions)
39
New cards
What is the second type of RNA?
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)- site/location of gene expression
40
New cards
What are ribosomes made of?
Proteins and ribosomal RNA
41
New cards
What is the third type of RNA?
Transfer RNA (tRNA)- carries around amino acids needed to make proteins
42
New cards
What is the central dogma of molecular biology?
1. Replication (DNA-> DNA)- entire DNA double helix is duplicated
2. Transcription (DNA->RNA)- information to produce a single gene is copied
3. Translation (RNA->Protein)- Functional protein is made
43
New cards
Does all of the DNA go through gene expression?
No, just a gene from DNA will go through transcription to make mRNA; mRNA goes through translation to make proteins
44
New cards
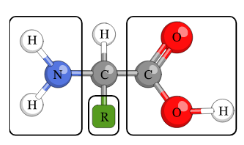
Identify the macromolecule, polymer, monomer, and building block of monomer.
Macromolecule: Proteins
Polymer: polypeptides
Monomers: amino acid
Building block of monomer: C-H, Amino, Carboxyl, (20) R groups (side-chains)
Polymer: polypeptides
Monomers: amino acid
Building block of monomer: C-H, Amino, Carboxyl, (20) R groups (side-chains)
45
New cards
What is the most common macromolecule?
Proteins
46
New cards
What are the eight protein functions?
1. Enzyme
2. Defensive proteins
3. Storage proteins
4. Transport proteins
5. Hormonal proteins
6. Receptor proteins
7. Contractile and motor proteins
8. Structural proteins
47
New cards
Name the function and example of the first type of protein.
Enzymes:
\-Function: Selective acceleration of chemical reactions
\-Example: Digestive Enzymes
\-Function: Selective acceleration of chemical reactions
\-Example: Digestive Enzymes
48
New cards
Name the function and example of the second type of protein.
Defensive proteins:
\-Function: Protection against disease
\-Example: Antibodies
\-Function: Protection against disease
\-Example: Antibodies
49
New cards
Name the function and example of the third type of protein.
Storage proteins:
\-Function: Storage of amino acids
\-Examples: Casein, milk protein; Ovalbumin (egg white)
\-Function: Storage of amino acids
\-Examples: Casein, milk protein; Ovalbumin (egg white)
50
New cards
Name the function and example of the fourth type of protein.
Transport proteins:
\-Function: Transport of substances; transporters across cell membranes
\-Examples: Hemoglobin, iron-containing protein in RBC
\-Function: Transport of substances; transporters across cell membranes
\-Examples: Hemoglobin, iron-containing protein in RBC
51
New cards
Name the function and example of the fifth type of protein.
Hormonal proteins:
\-Function: Coordination of life activities
\-Example: Insulin, pancreatic hormone
\-Function: Coordination of life activities
\-Example: Insulin, pancreatic hormone
52
New cards
Name the function and example of the sixth type of protein.
Receptor proteins:
\-Function: Cell response to stimuli
\-Example: Receptors built into nerve cell membranes detect signaling molecules released by other nerve cells
\-Function: Cell response to stimuli
\-Example: Receptors built into nerve cell membranes detect signaling molecules released by other nerve cells
53
New cards
Name the function and example of the seventh type of protein.
Contractile and motor proteins:
\-Function: Movement
\-Example: Motor proteins allow movement of cilia and flagella
\-Function: Movement
\-Example: Motor proteins allow movement of cilia and flagella
54
New cards
Name the function and example of the eighth type of protein.
Structural proteins:
\-Function: Support
\-Example: Keratin is the protein of hair, horns, feathers, etc.; collagen and elastin
\-Function: Support
\-Example: Keratin is the protein of hair, horns, feathers, etc.; collagen and elastin
55
New cards
What are polypeptides?
Polymers built from amino acid monomers
56
New cards
What does a protein consist of?
One or more properly folded polypeptides; proteins are made by stringing together 20 different amino acids
57
New cards
What is an attribute of amino acids?
All amino acids have the same structure except for the R group
58
New cards
How many amino acids are there?
20 different amino acids
59
New cards
What are the rules to identifying whether an amino acid is hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
1. Find one polar covalent bond in the R group (one PCB makes the entire amino group polar); polar= hydrophilic
2. Charged= hydrophilic
60
New cards
Define essential amino acids
Essential- something your body cannot synthesize for itself; must be consumed; amino acids (8) that must be consumed
61
New cards
How is an amino acid linked to form a polypeptide?
Place a backbone next to another backbone-\> Remove water (dehydration reaction) from OH of carboxyl group and H of amino group
62
New cards
What is the covalent bond that holds polypeptides together?
Peptide bond
63
New cards
What is the backbone of a polypeptide?
Amino group, carboxyl group, C-H
64
New cards
Does a polypeptide have directionality?
Yes, so does DNA and RNA
65
New cards
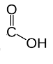
What is the beginning of a polypeptide called? What is the end called?
N-terminus (free amino group NH2); C-terminus (free carboxyl group )
66
New cards
What are the four levels of folding for protein structure?
Primary, Secondary, Tertiary, Quaternary
67
New cards
What is the first level of protein structure?
Primary: the unique sequence of amino acids bonded together by covalent peptide bonds
68
New cards
What is the second level of protein structure?
Secondary: stabilized by hydrogen bonds within the backbone; Two types: 𝛂 helix and pleated sheet
69
New cards
What is the third level of protein structure?
Tertiary: first time using R groups, polar amino acids are exposed to water while nonpolar amino acids form the inside
70
New cards
What do proteins have?
A 3D shape (all using R-groups)
\
Bonds involved:
Hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic interactions, van der Waals interactions, ionic bonds, disulfide bridges
\
Bonds involved:
Hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic interactions, van der Waals interactions, ionic bonds, disulfide bridges
71
New cards
What is protein folding?
An energy independent process; usually to the most energetically favorable structure
72
New cards
What is the fourth level of protein structure?
Quaternary: 2 or more polypeptides that interact together to make a functional protein (e.g. hemoglobin)
73
New cards
What are chaperonins?
Proteins that aid the proper folding of other proteins (protection)
74
New cards
What is a denatured protein?
Secondary, tertiary, quaternary structure bonds broken due to change in: pH, salt content, temperature, and high concentrations of polar or nonpolar substances
75
New cards
Is a denatured protein active or inactive?
Inactive
76
New cards
What is renaturation?
When the denaturant (e.g. heat) is removed, proteins can refold to the correct structure
77
New cards
What is X-ray crystallography?
Method used to determine 3D structure of protein