ESS SL IB Review
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
ecocentric, anthropocentric, technocentric
name the three EVS types and what they believe
open (energy and matter in and out), closed (only energy), isolated
what are the three types of systems and describe them
the amount of disorder in a system
define entropy
energy is never destroyed, it only changes forms
define the 1st law of thermodynamics
entropy increases over time
define the 2nd law of thermodynamics
Negative Feedback Loop: predator/prey, body temp
Positive Feedback Loop: permafrost, forest fires
describe the two types of feedback systems. give two examples of each.
strengths: predictions, preparation, consider all the factors
weaknesses: no standard EIA rubric, predictions, sometimes miss a factor
what are EIAs? what are their strengths/weaknesses?
point and non-point source pollution (oil leak in the ocean from a factory; plastic pollution in the ocean)
what are the two main types of pollution? define. examples?
primary/secondary pollutants (oil in the ocean, chlorine in the atmosphere- breaks down O3 in ozone layer)
what are the two main types of pollutants? define. examples?
persistent organic pollutants; long term chemical pollutants (DDT)
what are POPs? how are they harmful. example?
habitat. fundamental and realized niche.
what is a niche? what are the two types? define.
between different/same species
define interspecific and intraspecific interactions.
living v non living. (invasive species, plant life, coral; temperature, pH levels, sunlight, soil quality)
what are biotic/abiotic factors? examples.
the amount of organisms an amount of land can support
define carrying capacity.
the rate of generation of biomass in an ecosystem
define productivity.
the mass or weight of living tissue
define biomass.
generated as trophic levels increase, generated over time
define biomagnification and bioaccumulation.
gross primary productivity, net primary productivity
(amount of photosynthesis undergone; amount of plant growth/biomass)
define GPP, NPP. examples.
gross secondary productivity, net secondary productivity
(total food eaten; energy turned into mass and fecal matter)
define GSP, NSP. examples.
G_P - R = N_P
how do you find respiration?
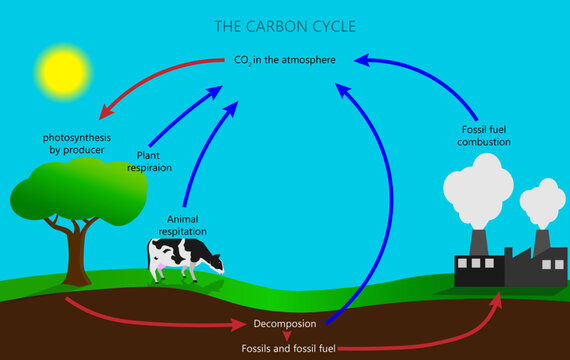
summarize the carbon cycle.
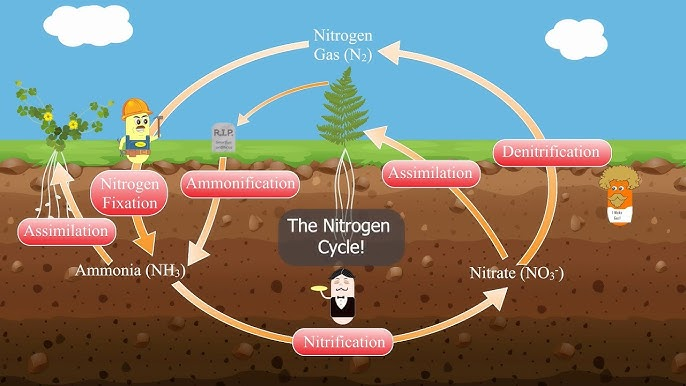
summarize the nitrogen cycle.
zonation: changes as geolocation changes (along a mountainside)
succession: changes over time (eutrophication, after volcano/forestfire)
define zonation and succession. primary and secondary. give examples.
r: reproduce like crazy, low survival, not raised, low on food chain (frogs, insects, fish)
k: care for young, fewer kids, higher survival, higher on food chain (bears, foxes, rabbits)
define r and k-strategists. examples.
used to estimate population for moving organisms
n1 x n2 / nm (catch, mark, release, recapture, count)
what is the Lincoln Index test? when do you use it?
used to calculate species diversity in an area
N(N-1) / sum n(n-1) (total # of species, # of individuals of a specific species)
what is the Simpsons Diversity Index test? when do you use it?
used to estimate the population of a stationary species (plants)
place quadrats randomly over an area. count species within. average to find approx value per quadrat. multiply by area.
what is quadrat sampling? when do you use it?
species, genetic, habitat
what are the three types of biodiversity?
LEDC’s
_EDC’s tend to have higher diversity, which means there is a lot of exploitation
a list of threatened/endangered species
what is the IUCN Red List?
ethics, aesthetics, resources, genetic variation, future generations
why do we conserve nature?
intergovernmental organizations. funded by govt. lots of enforcement. slow to pass laws, etc. can focus on many issues. international agreements.
United Nations Environment Programme, The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN)
define and evaluate IGOs and list examples.
nongovernmental organizations. are volunteer-run/funded, not governmental. use of media, rapid response. only focused on one issue. no legal power.
World Wildlife Fund (WWF), Greenpeace
define and evaluate NGOs and list examples.
flagship: cute, well-known, used as ‘face’ of movement, raise awareness, icon (panda, polar bear, sea turtle, American eagle, national animals)
keystone: vital to ecosystem, it will be destroyed w/o them (coral, elephants, wolves, bees)
define flagship and keystone species. examples.
70, 97
the earth is made of __% water, __% of that is salt water
ground water, springs, lakes,
where does most of our drinking water come from?
the amount of resources we can take without draining the land/ecosystem (annual growth-annual death)
define sustainable yield.
make more reservoirs, redistribution, desalination, rainwater harvesting, irrigation development, water conservation (greywater- used water that can be reused before dumped)
what can we do to conserve drinkable water?
upwelling stirs up nutrients to the top of the ocean
downwelling brings new nutrients back down to the organisms that live at the bottom of the ocean
what does upwelling/downwelling do?
raising fish/aquatic life ‘farms’
define aquaculture.
loss of habitats (mangrove removal), pollution (poop, shells, anti biotics), disease (close contamination), species loss (competition, invasive species if escape)
what are some consequences of aquaculture?
when fertilizer/nitorgen gets into a body of water causing algae blooms which creates deadzones of oxygen and kills everything
what is eutrophication?
minerals, biomass, nutrients, and water
what is soil made of?
oragnic, topsoil, parent rock and bedrock layers. less organic matter, more rock
what are the more general layers of soil and what happens as you go further down?
smallest, bigger, biggest; high, high, high; poor, poor, very good; high, high, low; small, medium, large, low, low, low
what are the comparative sizes, mineral content, drainage, water holding ability, airspace and organic matter of clay, silt, and sand
the best, highest NPP, dark brown
what is loamy soil?
commercial: for profit, lots of excess
substinence: to support a population, just enough
compare commercial and subsistence farming
deforestation (causes erosion), irrigation (causes erosion), pollution (just bad for erosion and nutrient content), intensive grazing (erosion, not strong enough plant growth)
what farming practices are bad for soil and how?
strip cultivation (placing grass inbetween plant rows to prevent wind erosion), crop rotation (trade of nutrients, no drainage), terracing (reduce steepness, crops grown as ‘steps’ on hills, stops wind erosion, slows rainwater), plowing
what farming methods are good for soil and how?
troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere
what are the layers of the atmosphere in order.
troposhpere
what ____sphere do we live in?
the amount of light reflected off of a surface
high: white stuff
low: black/blue/green stuff
define albedo
greenhouse gasses (carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide) get trapped in the atmosphere
what is the greenhouse affect?
good for us, protects us from UV rays
made of O3
decreasing due to propellants/refrigerants
chlorine breaks the O3
what is stratospheric ozone?
an international agreement to lower CTCs in the atmosphere
what was the Montreal Protocol?
bad ozone
it is a secondary pollutant formed when nitrogen oxides and VOCs (volatile organic compounds) interact with light
what is photochemical smog?
burning fossil fuels, high humidity, trappedness
what increases tropospheric ozone?
when bad chemicals come back to earth as rain, snow, fog, etc
what is acid deposition?
more
low pH means more/less acidic?
aquatic organisms, acid deposition goes straight into their habitat and infect them very fast. they are very sensitive to changes in pH
____ are more vulnerable to acid rain because _____
reliable and accessible energy sources
define energy security
tidal, wind, solar, biomass, nuclear power, fossil fuels, hydropower
what are the 7 types of energy sources
unstable economics/political power, cultural attitudes, bad international relations, low tech. development
what are factors that make a country have less energy security?
wildfires, temp rises, erosion, desertification, plants die off, oceans rising and expanding
consequences of climate change?
reduction/stabilization of GHG emissions
define mitigation
lowering energy consumption
alternatives to fossil fuels
reduction of emissions from agriculture
list mitigation strategies for GHGs
increase in carbon sinks’
use biomass as fuel
increase in bioactivity in the oceans
list mitigation strategies for CO2 Removal
exponential
what type of growth does the human population have?
#of births per 1000 people/year
how do you calculate Crude Birth Rate?
#of deaths per 1000 people/year
how do you calculate Crude Death Rate?
how many kids a woman can have over her lifetime
define fertility
expectation of generational legacy
less access to birth control
less education
need more sources of income
have more time to raise them
LEDC have higher birth rates. why?
CBR-CDR/10=RNI
how do you calculate natural increase in a population?
70/RNI
how do you calculate doubling time?
wide/narrow= high/low density
concaves/bulges= increase/decrease
deficits= age specific deaths
name the characteristics of a population pyramid
educate (individual basis): reduce, reuse, recycle, compost, landfills, incinerators
legislate
remediate
how do we try to decrease our SDW?
capital: resources the land offers
income: how much we take
define natural capital and income
useful output/input
how do you find efficiency?
when inputs and outputs are relatively even, and the system is reliable, pre-tipping point
define equilibrium
the process in which food is turned into energy for consumers
define cellular respiration