brain and behavior exam 1
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
"What is phrenology?"
"Phrenology is a pseudoscience that involves reading bumps on the skull to determine a person's personality and character traits."},
"What is the leading cause of disability and second leading cause of death worldwide?"
"Brain Injury and Disease.
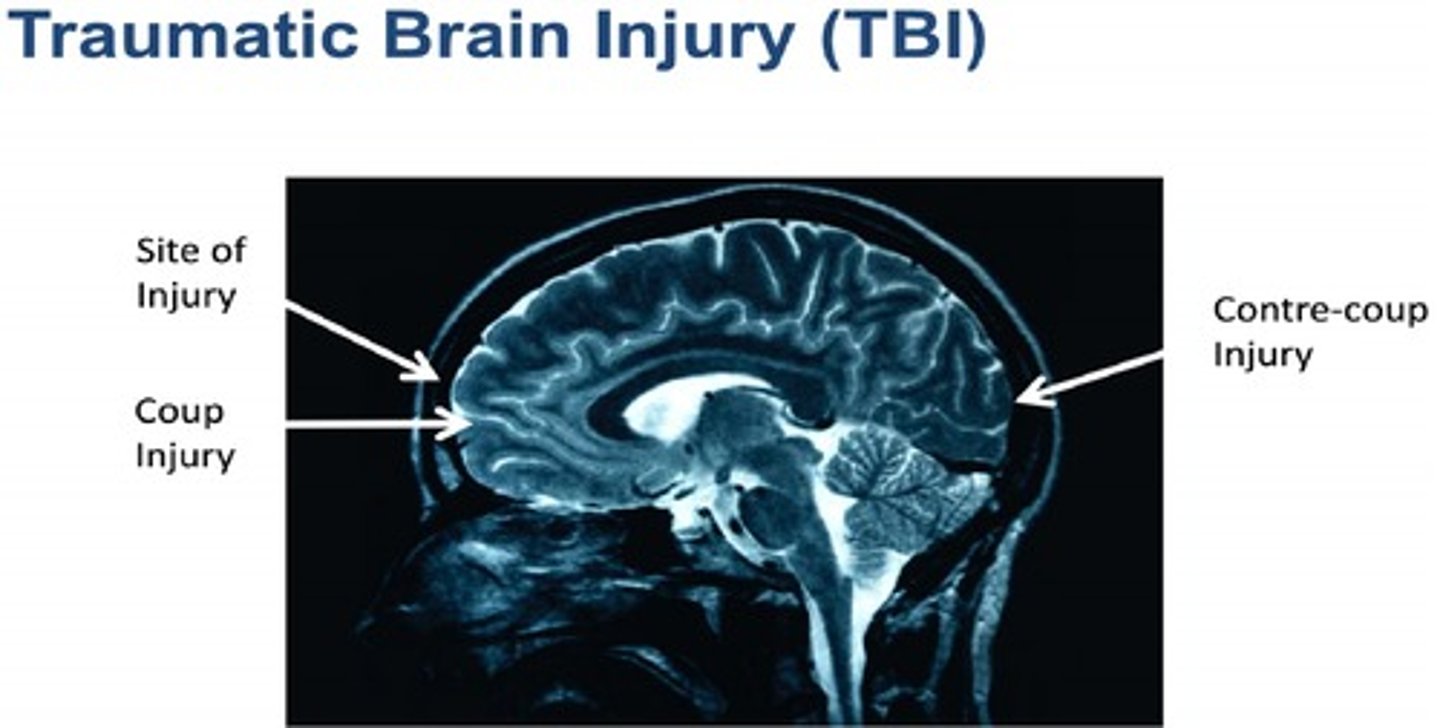
"What is a TBI and how many US residents are treated for it each year?"
A TBI (Traumatic Brain Injury) is an injury to the brain caused by an external force. Approximately 1.7 million U.S. residents are treated for TBI each year."},
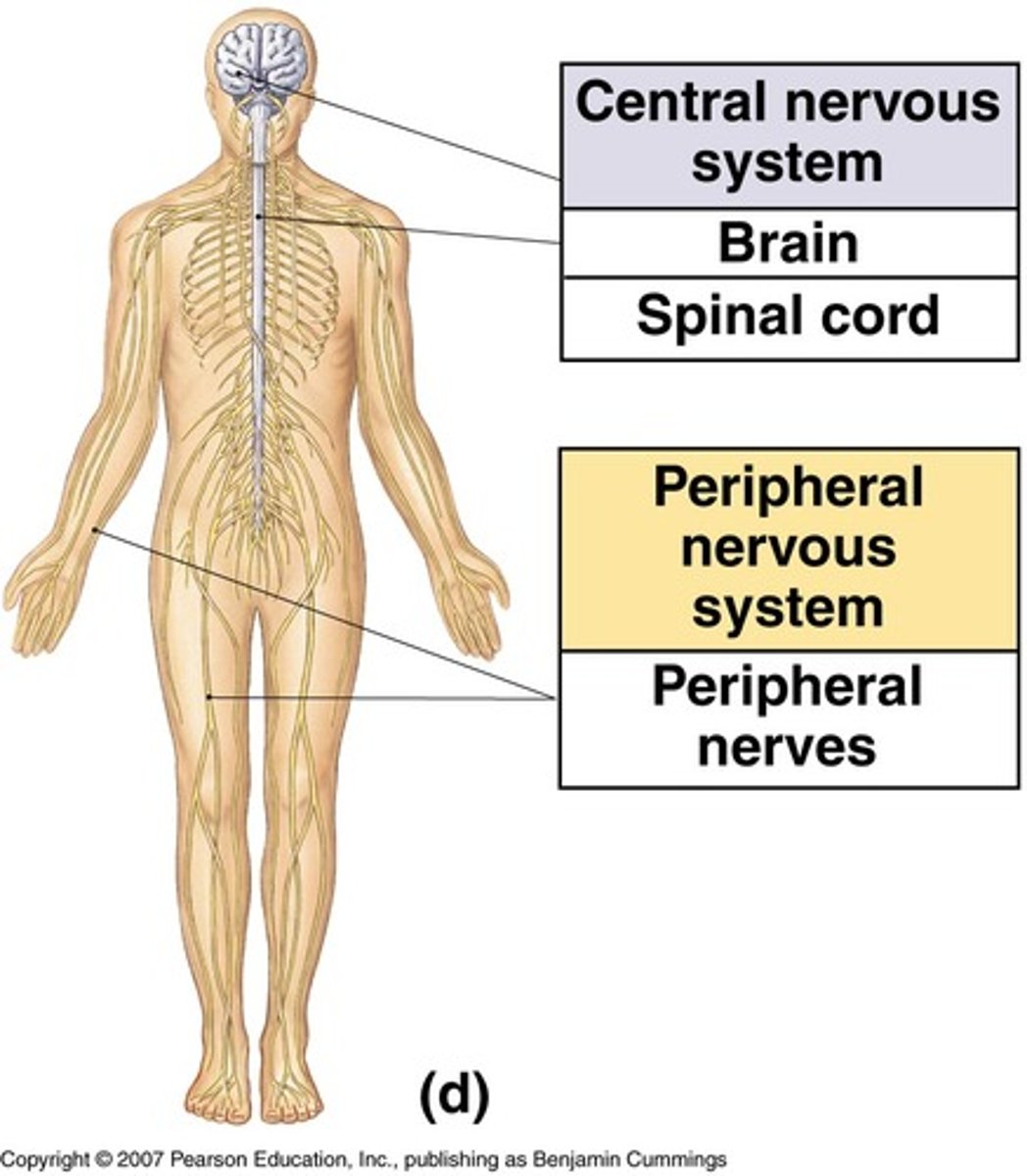
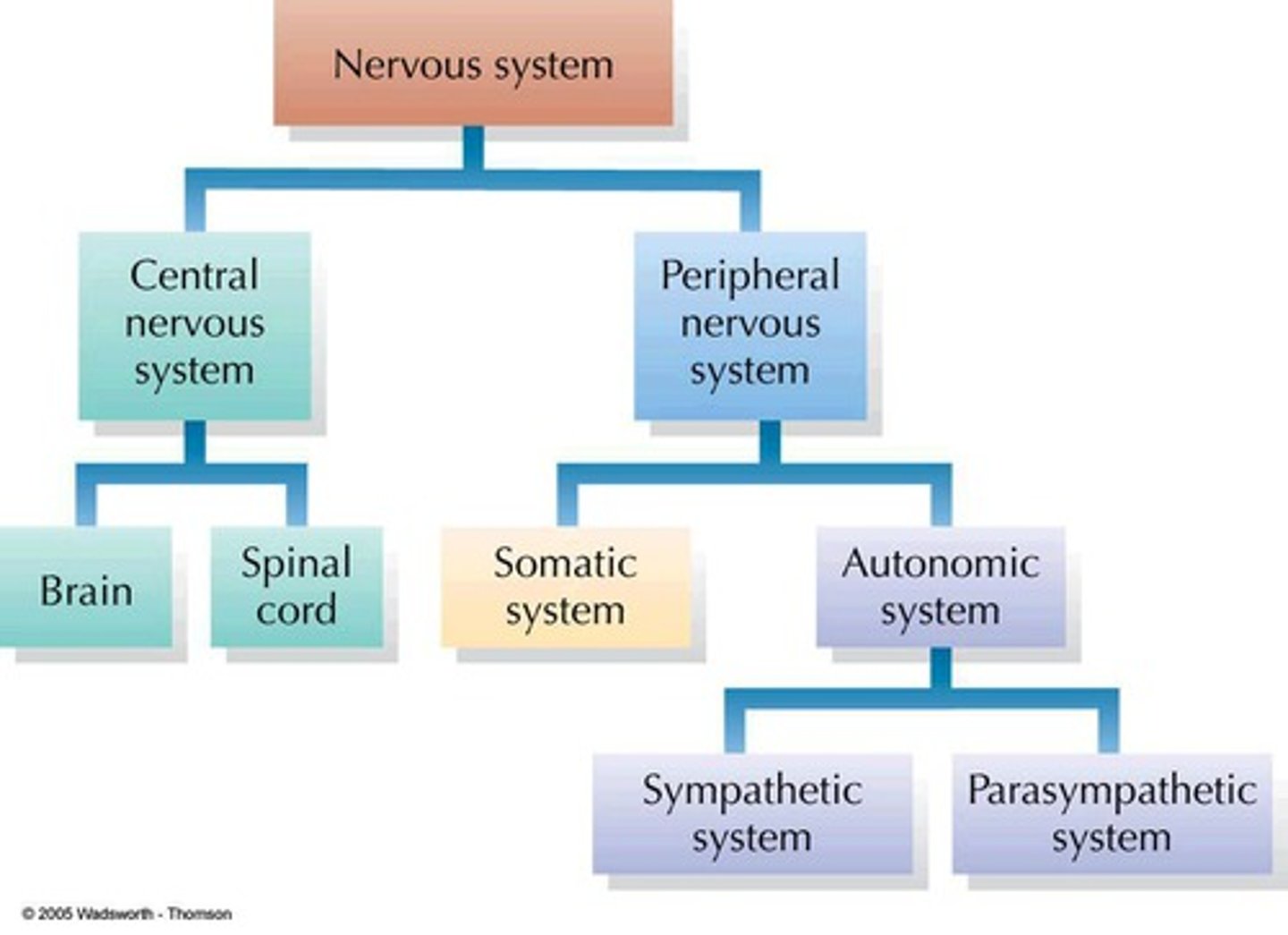
"What are the differences between the CNS and PNS?",
"The CNS (Central Nervous System) includes the brain and spinal cord, while the PNS (Peripheral Nervous System) includes all other nerves. The CNS interprets and responds to signals from the PNS, which carries information to and from the CNS."},
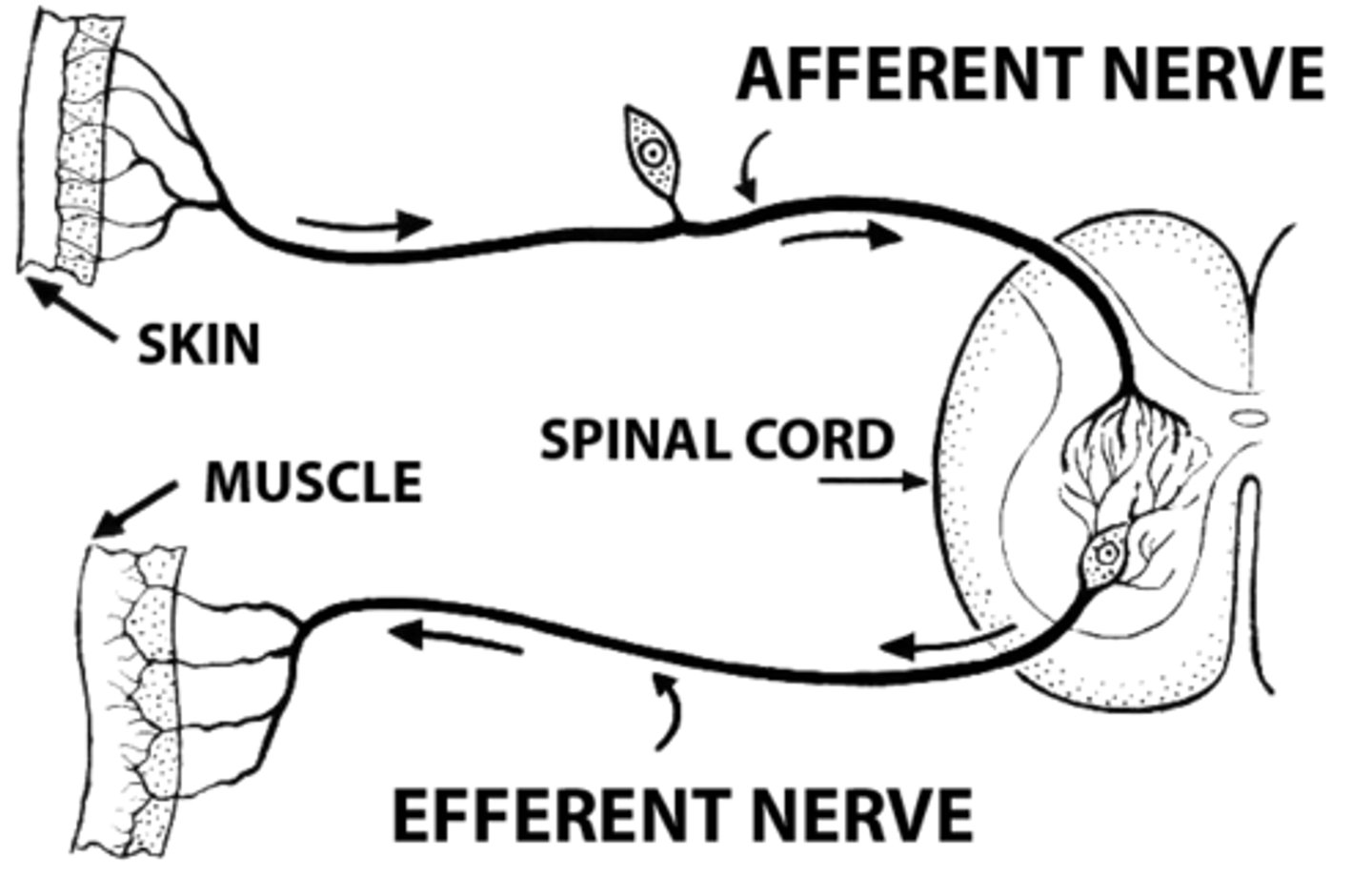
"What are afferent and efferent neurons?",
"Afferent neurons carry sensory information to the CNS, while efferent neurons carry motor commands away from the CNS."},
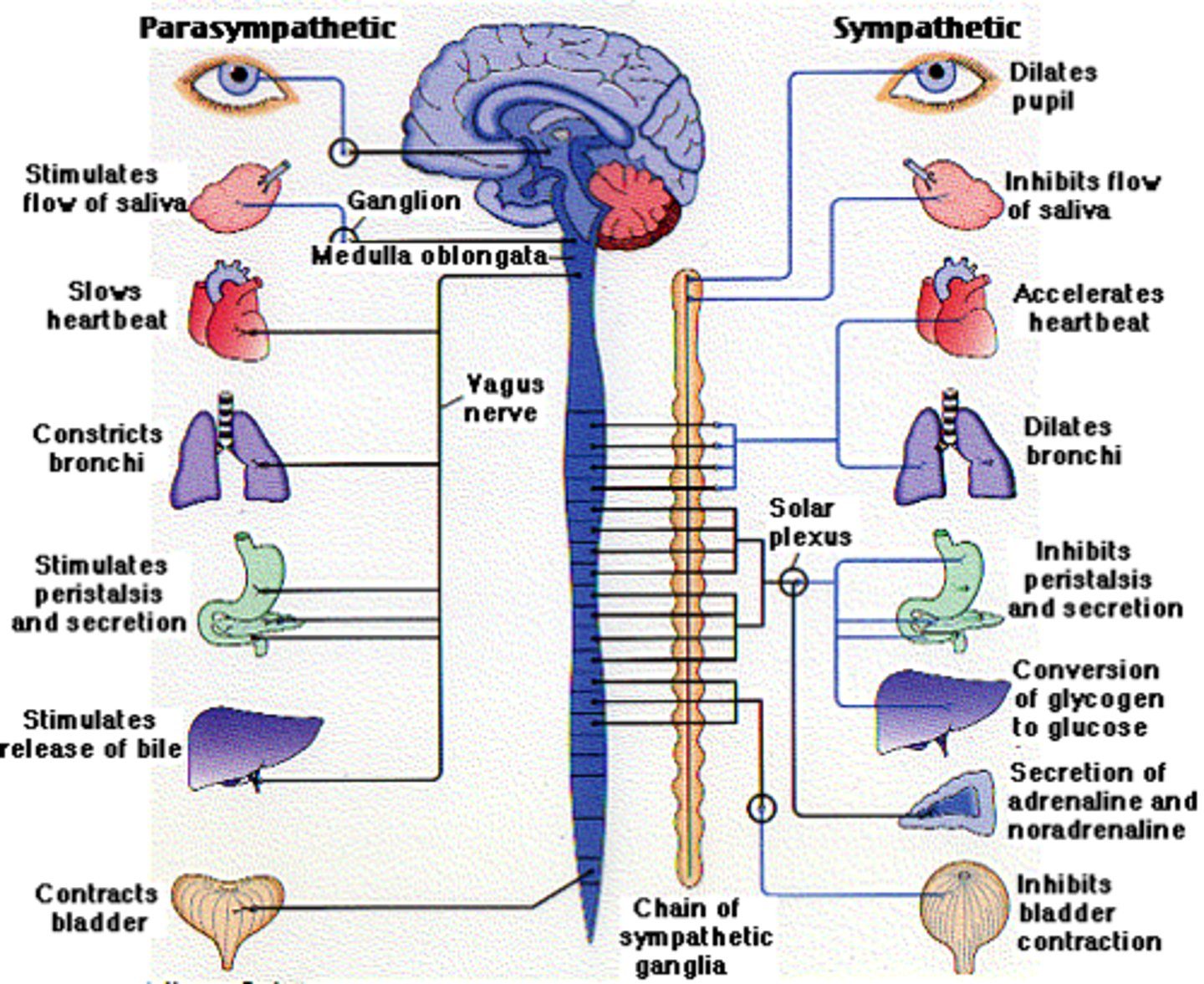
"What are the subsystems of the PNS and their functions?"
"The PNS has the somatic and autonomic nervous systems. The somatic nervous system controls voluntary movement and sensation. The autonomic nervous system, divided into the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems, regulates involuntary functions like heart rate and digestion."},
"What are the subsystems of the CNS?
The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord. The spinal cord facilitates reflex actions, while the brain controls higher-level functions."},
What are the three common definitions of consciousness?
1) Awareness of the environment, 2) Self-awareness, 3) States of alertness (awake, relaxed, altered, sleeping, brain death)."},
"What is the Rouge Test?"
A self-awareness test where a mark is placed on an animal's forehead. If the animal recognizes itself in a mirror and tries to remove the mark, it is considered self-aware."},

Which animals have passed self-awareness tests?
Killer whales, great apes (when raised in captivity)."},
"What is the difference between materialism, dualism, and mentalism?
Materialism (Darwin) argues behavior is explained solely by the nervous system. Dualism (Descartes) states the mind and body are separate but interact. Mentalism (Aristotle) believes consciousness shapes experience."},
Where did Aristotle believe the mind was located?
Aristotle thought the mind was in the heart and that the brain was responsible for cooling the blood."},

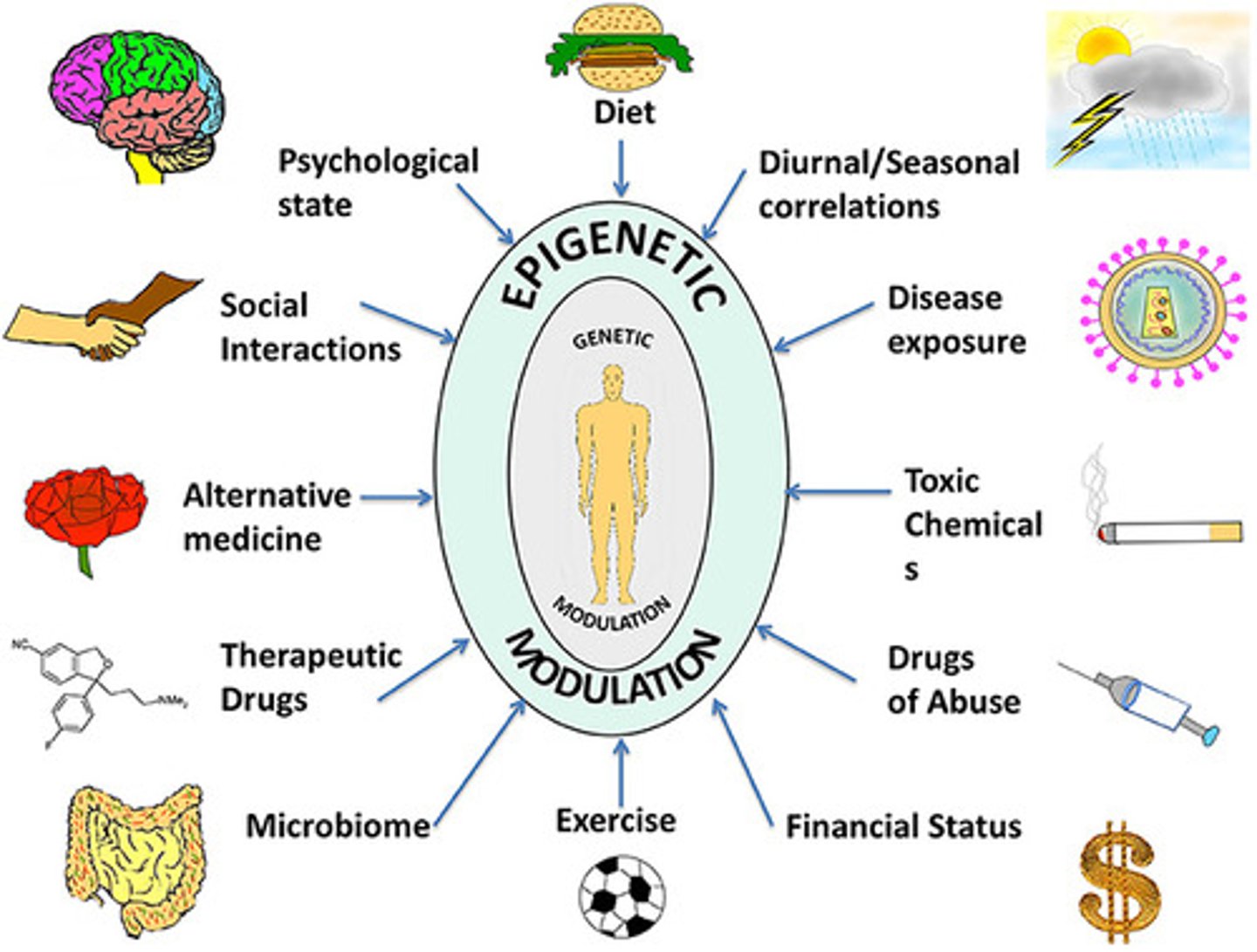
What is epigenetics?
Epigenetics refers to changes in gene expression without altering the DNA sequence. Factors such as stress, diet, and sleep can influence these changes.
What is Hebb's Rule?
Neurons that fire together, wire together.' This principle states that frequently used neural pathways strengthen over time."},
What is the function of the brainstem?"
"Controls basic life functions such as breathing and heart rate."},
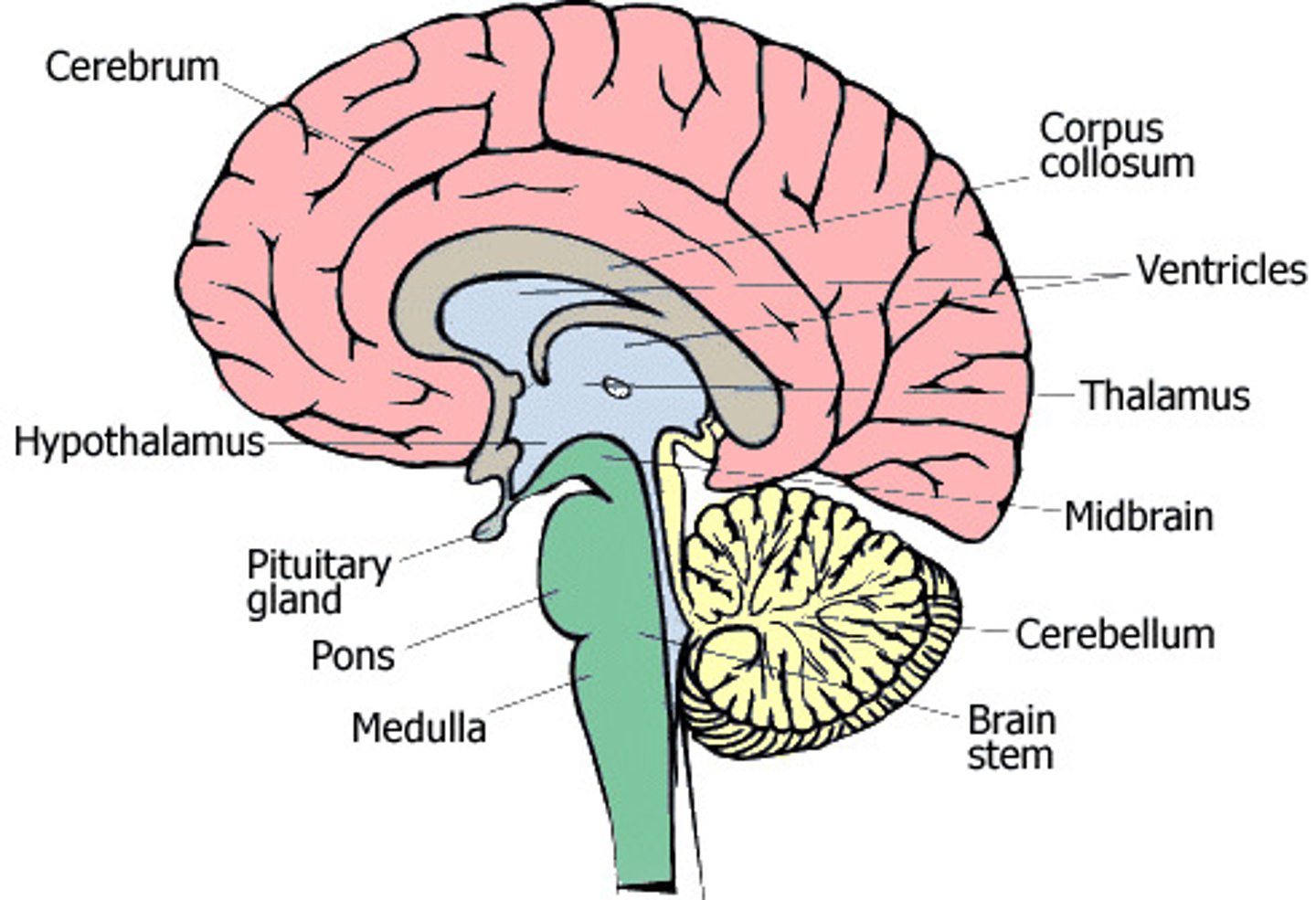
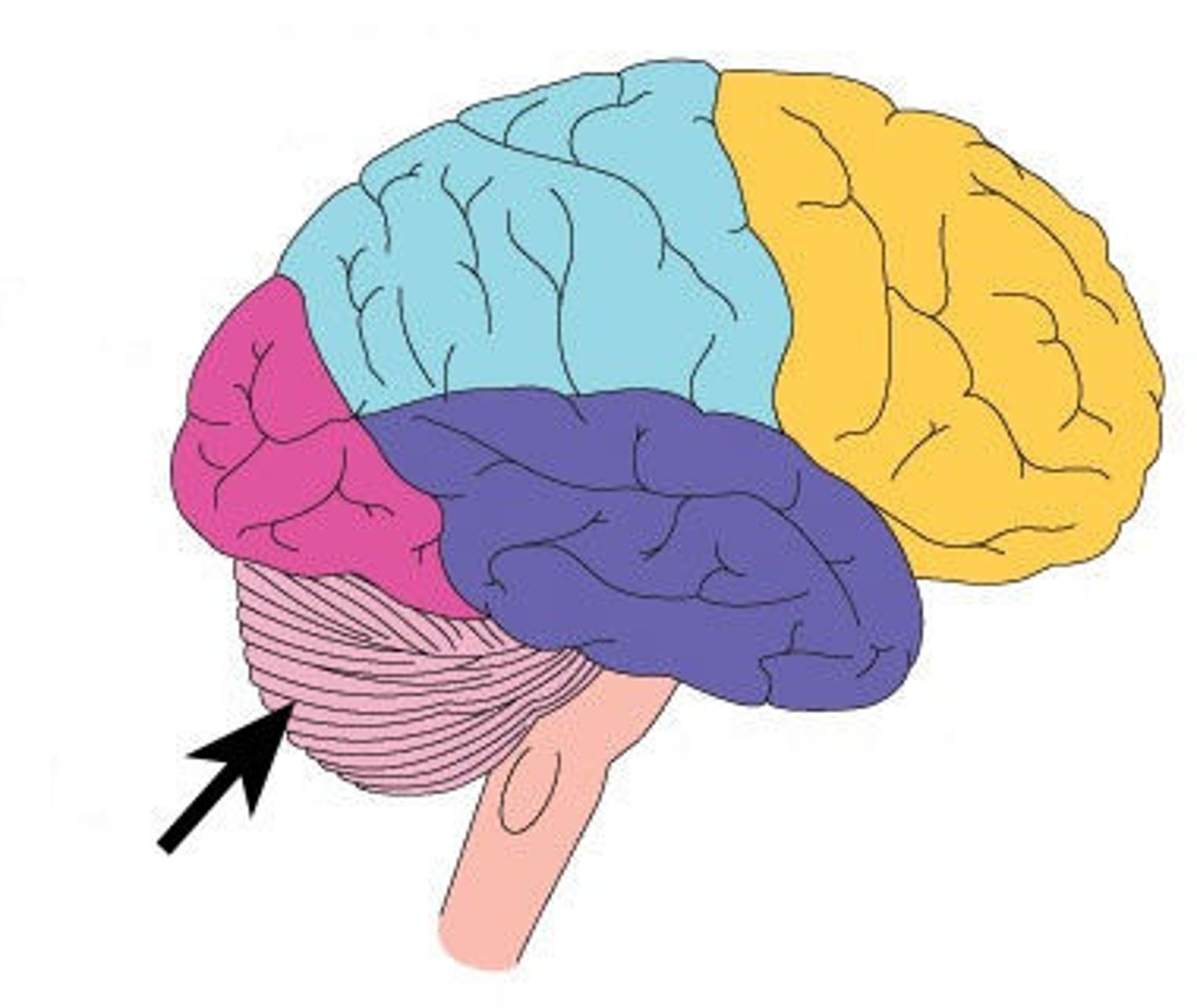
What is the function of the cerebellum?
Controls motor coordination, balance, and voluntary movement. It is the first structure affected by alcohol."},
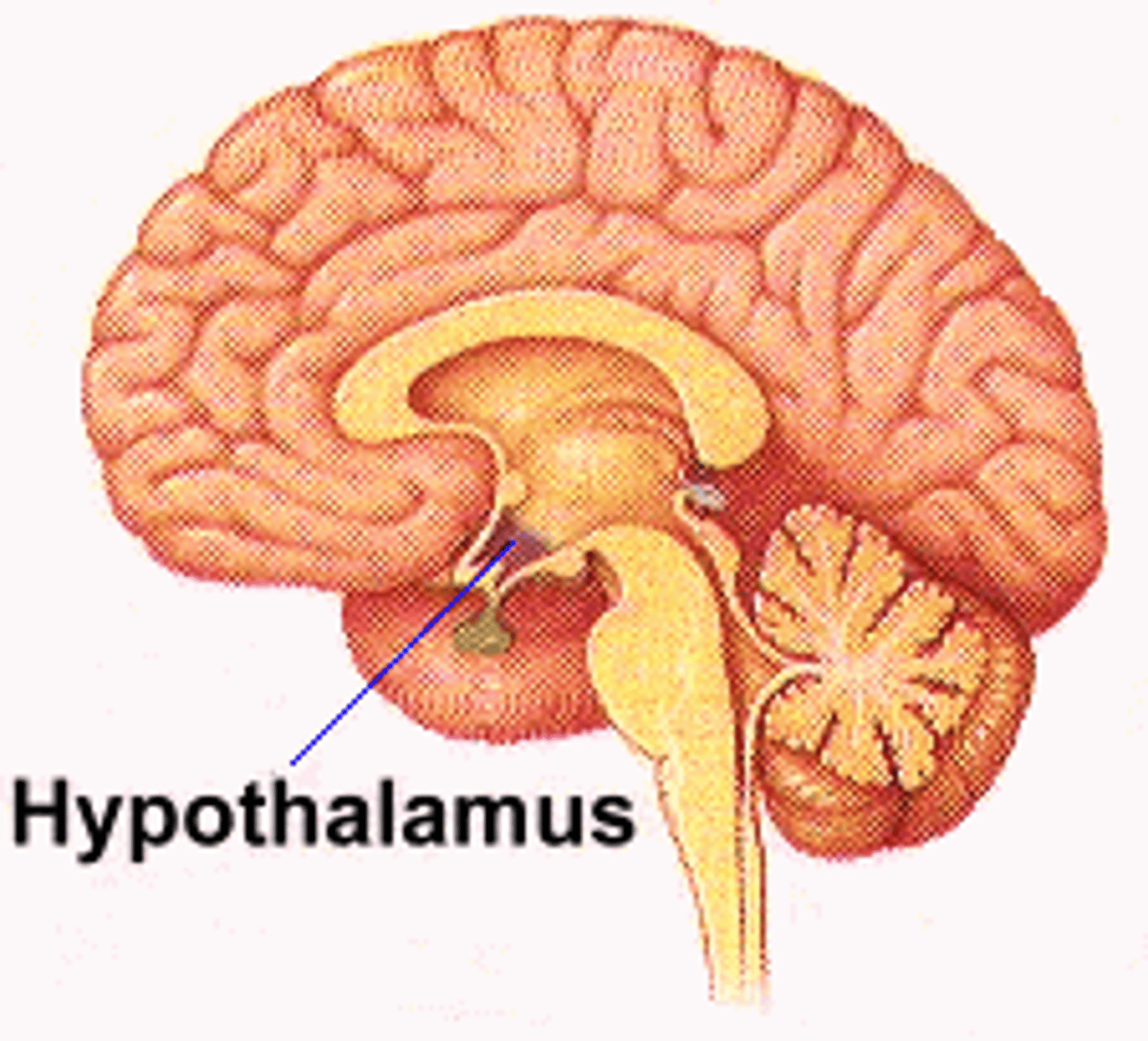
What does the hypothalamus regulate?
"Regulates hormone production via the pituitary gland. Controls hunger, thirst, sleep, and body temperature."},
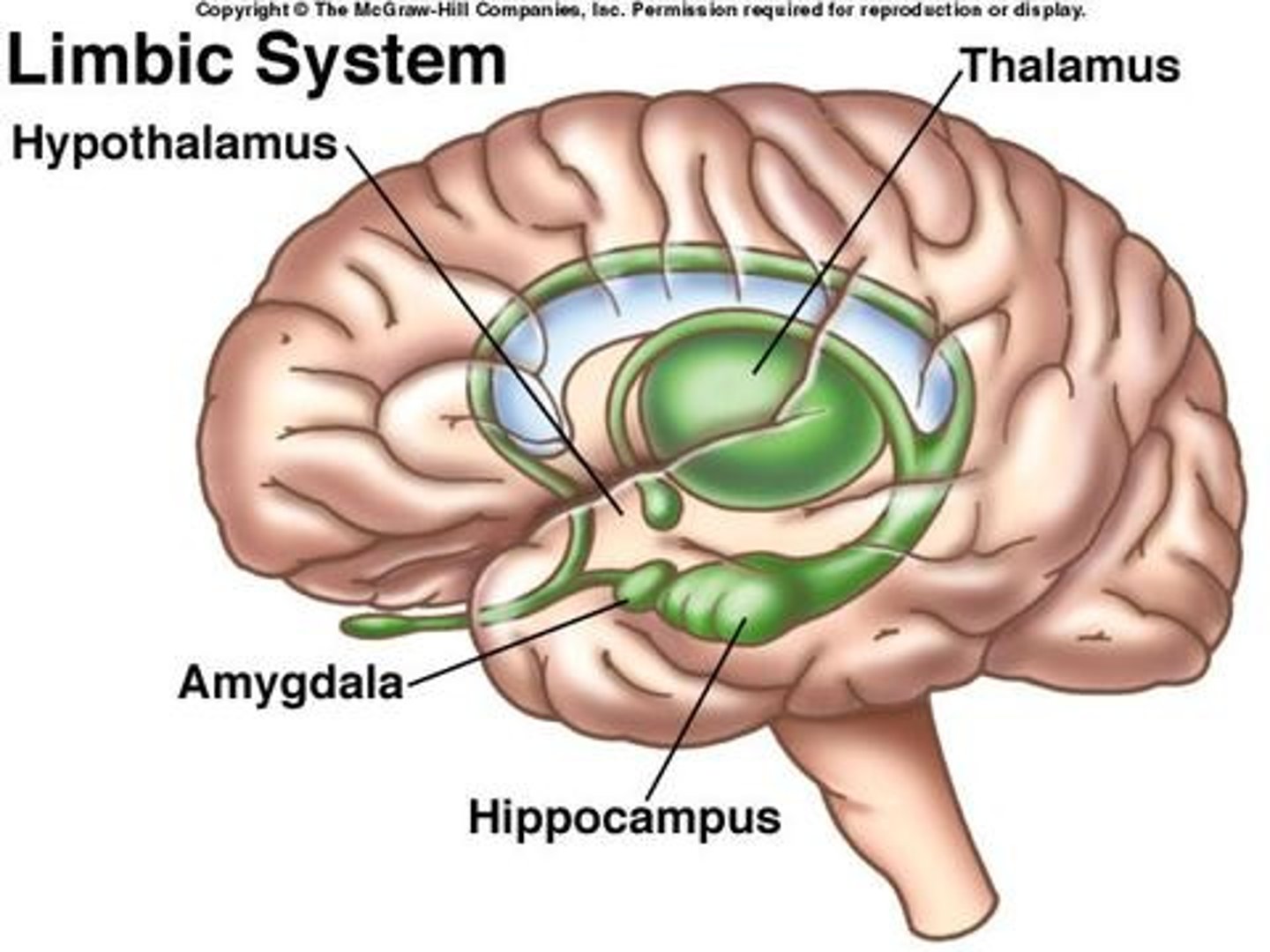
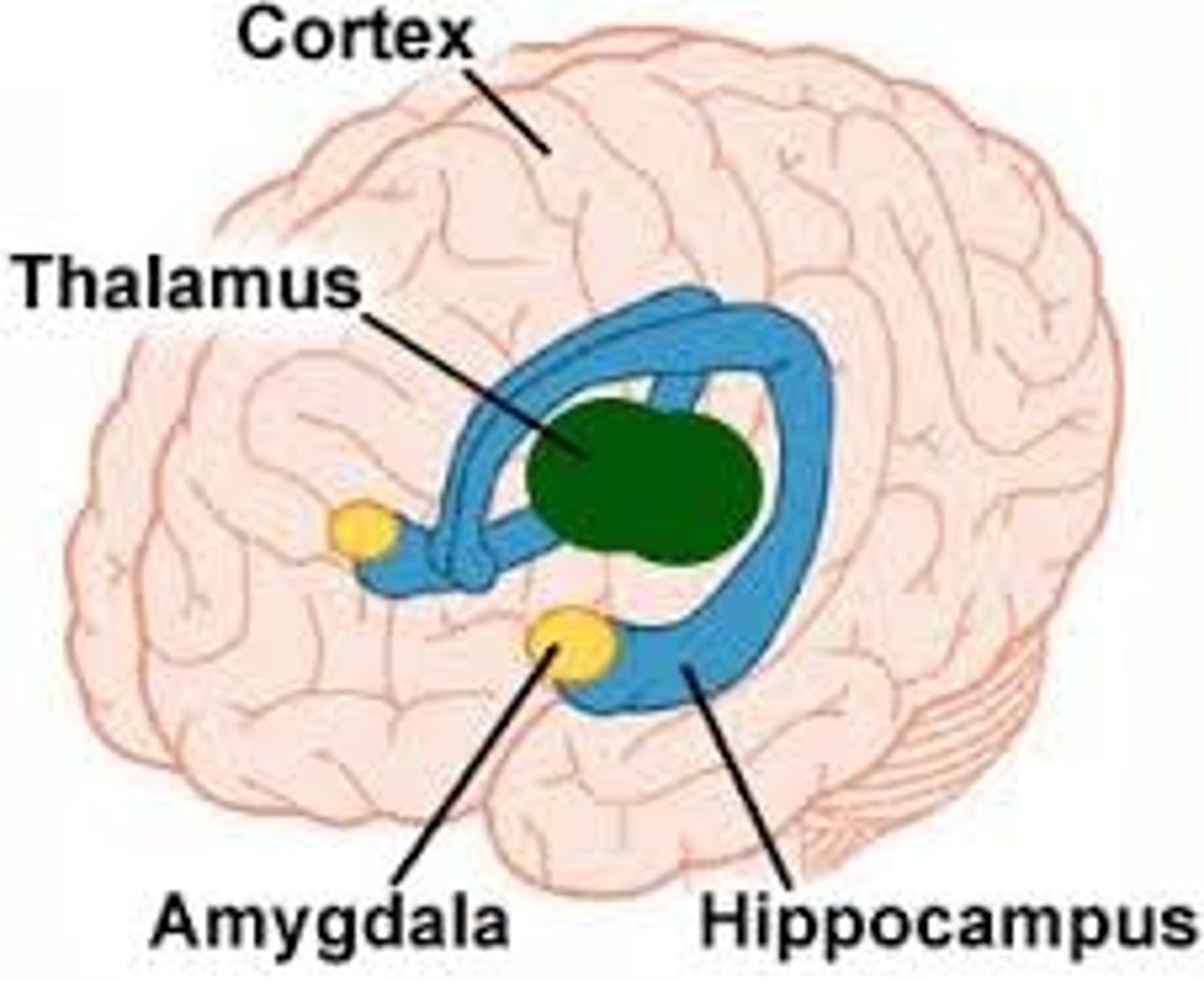
What is the function of the limbic system?
Regulates emotions, memory, and motivation. Includes the hippocampus and amygdala."},
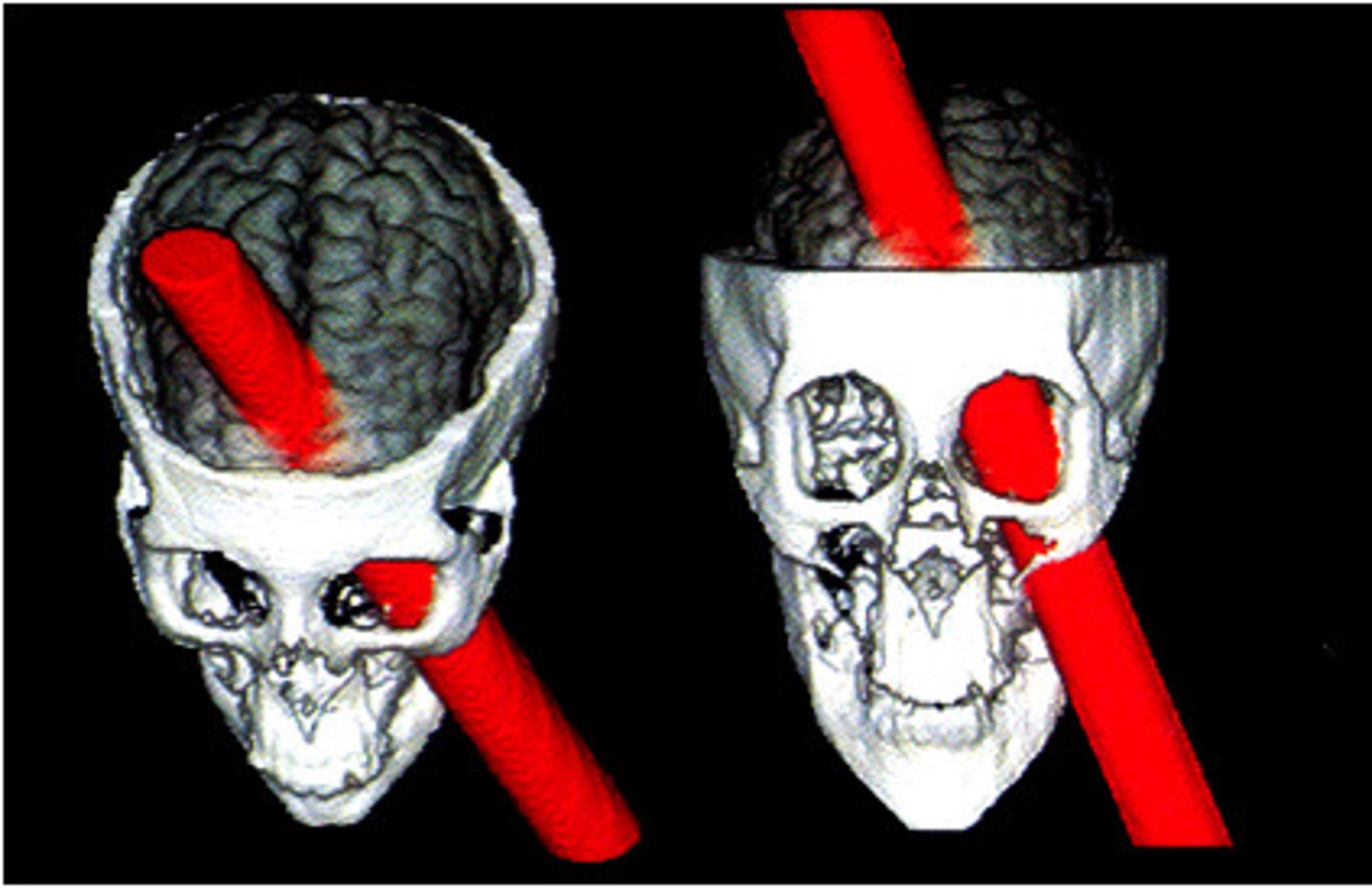
What happened to Phineas Gage?"
He survived a brain injury in which an iron rod passed through his skull, damaging his frontal lobe. His personality changed, becoming more impulsive and aggressive."},
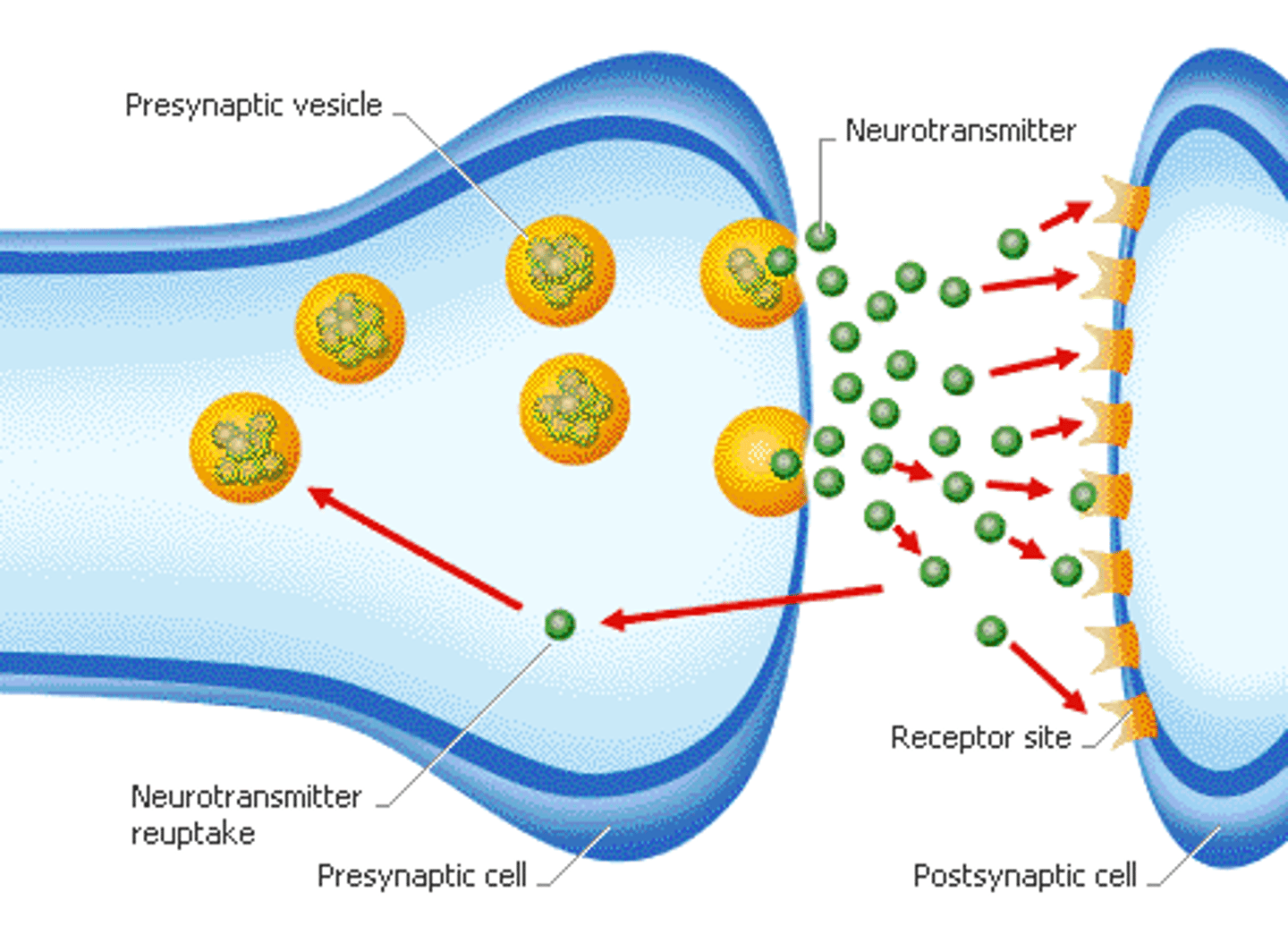
What is the function of neurotransmitters
Neurotransmitters are chemicals that transmit signals between neurons, affecting mood, behavior, and cognitive functions."},
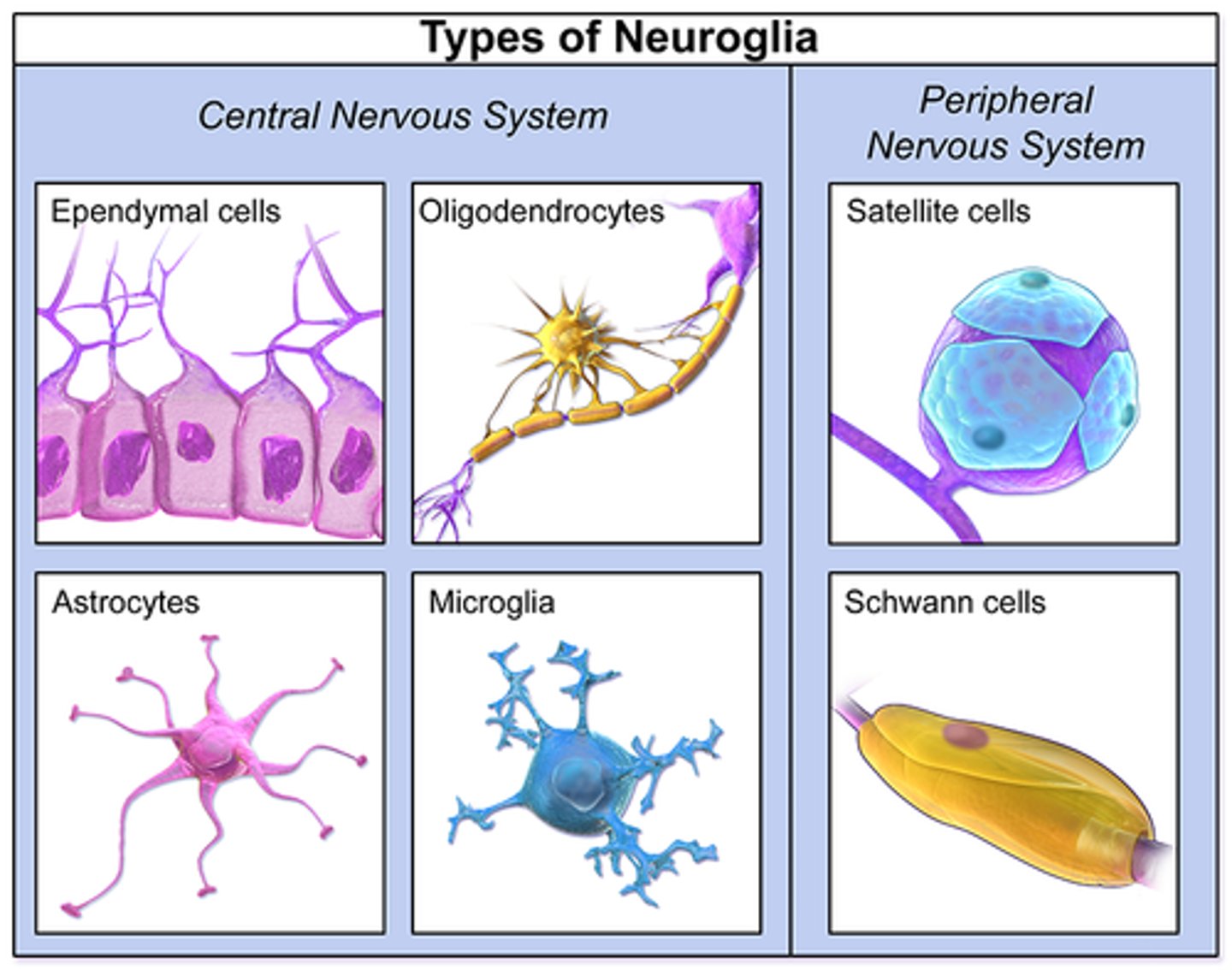
hat are the five types of glial cells
"Astrocytes, Oligodendrocytes, Microglia, Schwann Cells, and Ependymal Cells."},
"What neurotransmitter is primarily associated with the reward system?"
Dopamine.
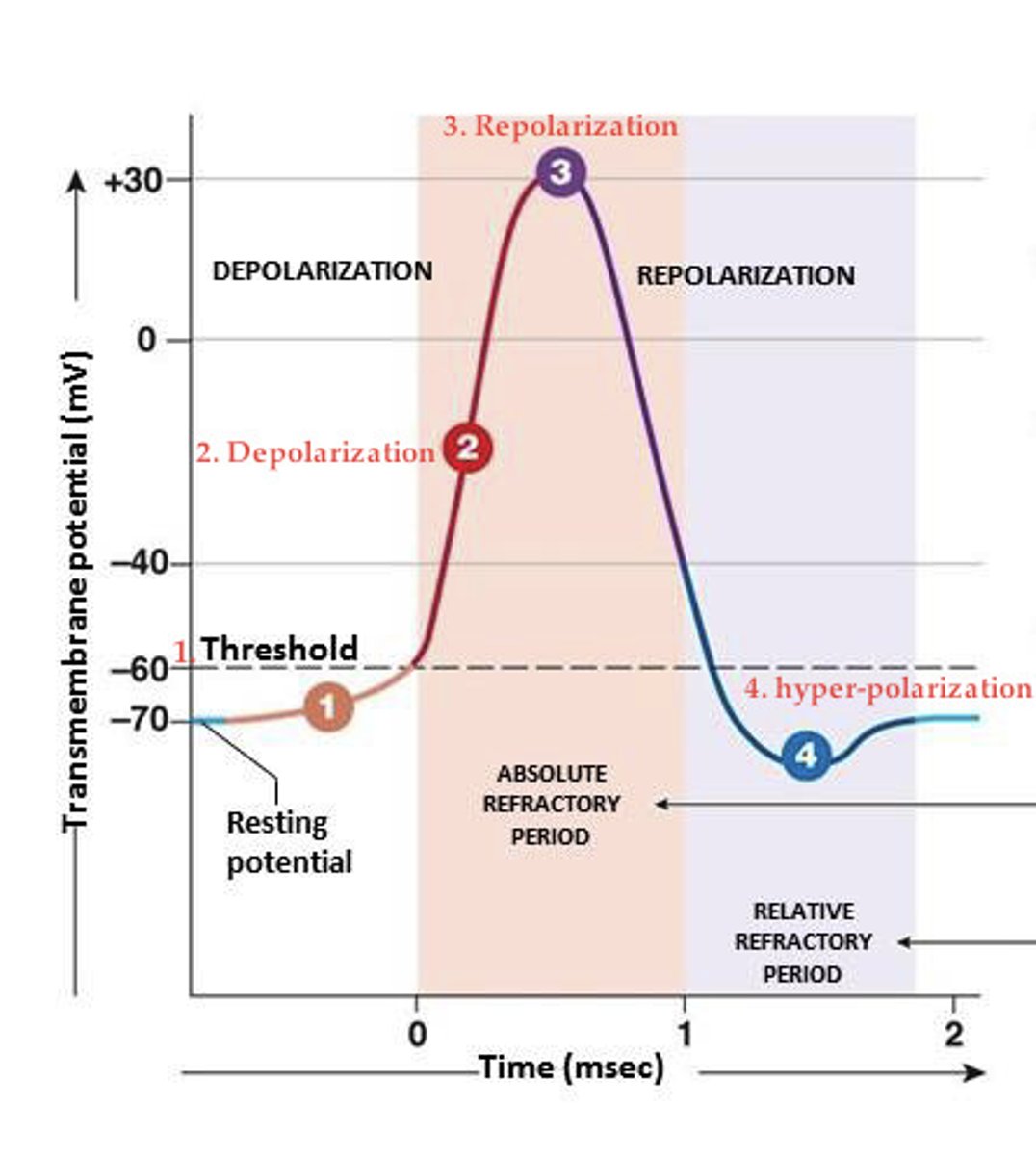
What is an action potential?
An electrical impulse that travels down the neuron's axon, allowing it to transmit information."},
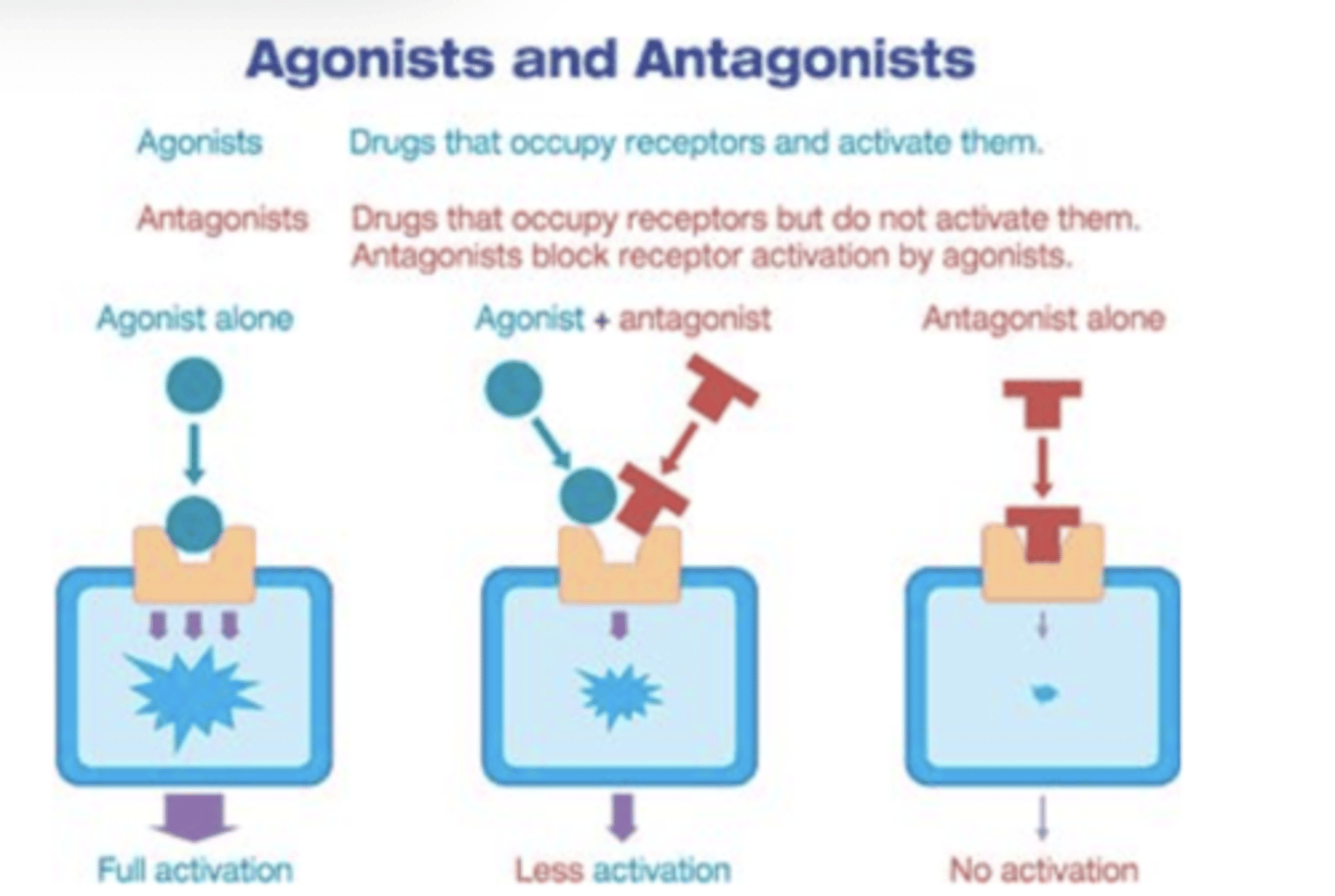
What is the difference between an agonist and an antagonist drug?
Agonists enhance neurotransmitter activity, while antagonists inhibit it."},
What neurotransmitters are involved in drug addiction?
Dopamine (reward system), serotonin (mood regulation), and endorphins (pain relief).
"What is the blood-brain barrier?"
A protective barrier that prevents harmful substances from entering the brain while allowing essential molecules through."}, ]
![<p>A protective barrier that prevents harmful substances from entering the brain while allowing essential molecules through."}, ]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/34c428a5-4cab-440a-9d5c-2f488498ee50.jpg)
"What is neuroplasticity?
The ability of the brain to change and adapt in response to experience, learning, or injury

What are the main parts of a neuron?
Dendrites, cell body (soma), axon, myelin sheath, and synaptic terminals."),
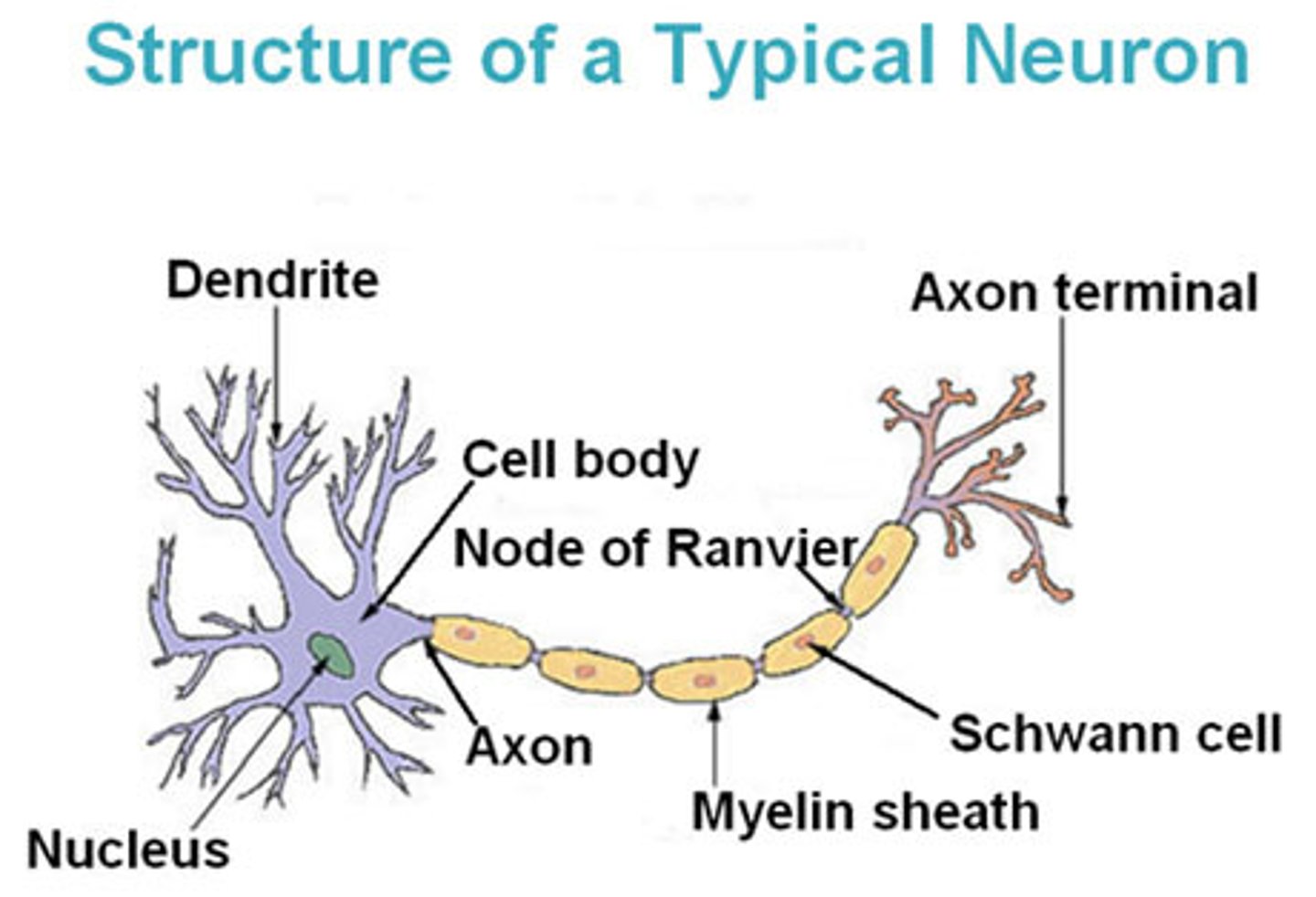
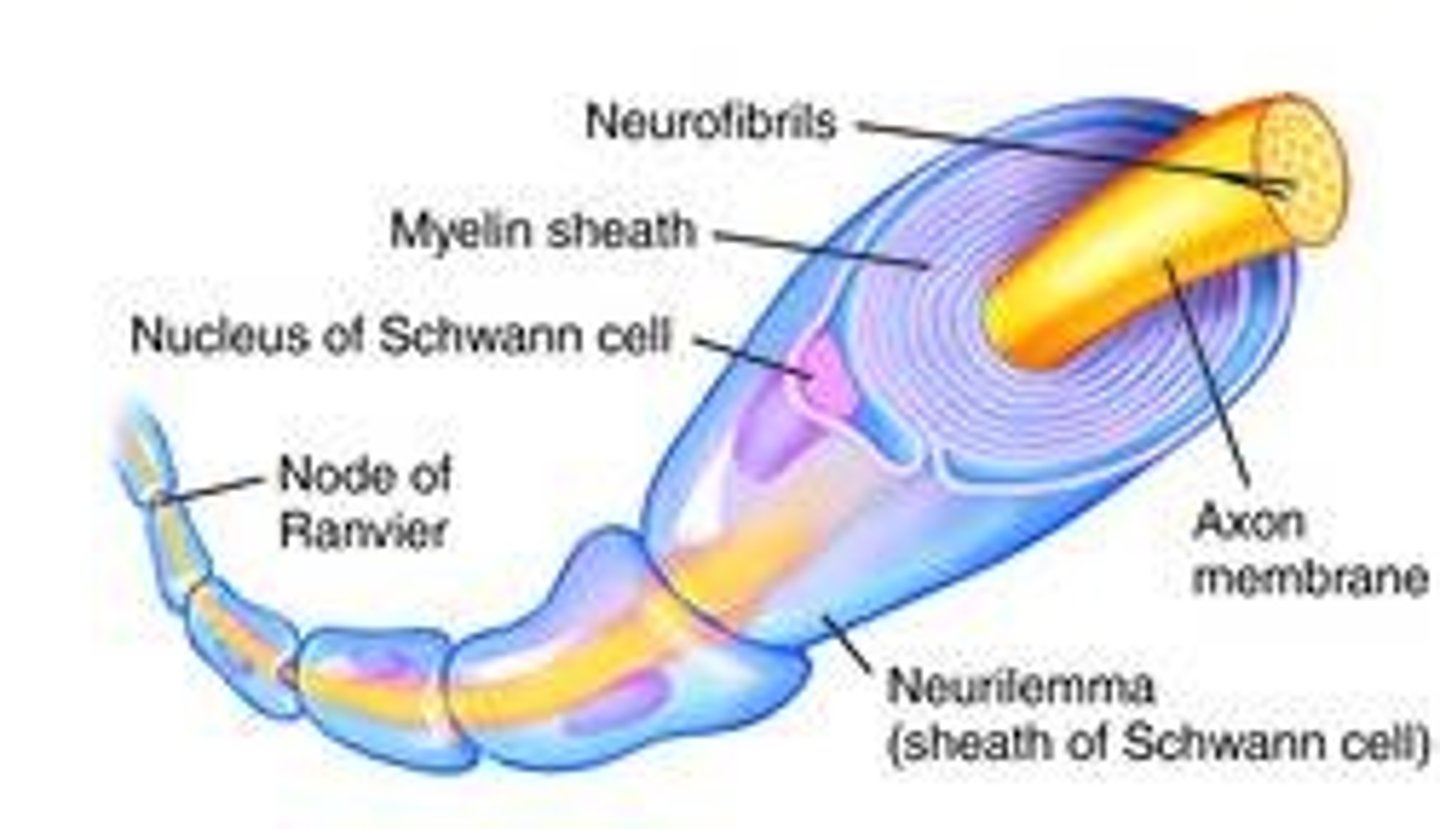
What is the function of the myelin sheath?
To insulate the axon and speed up neural transmission.
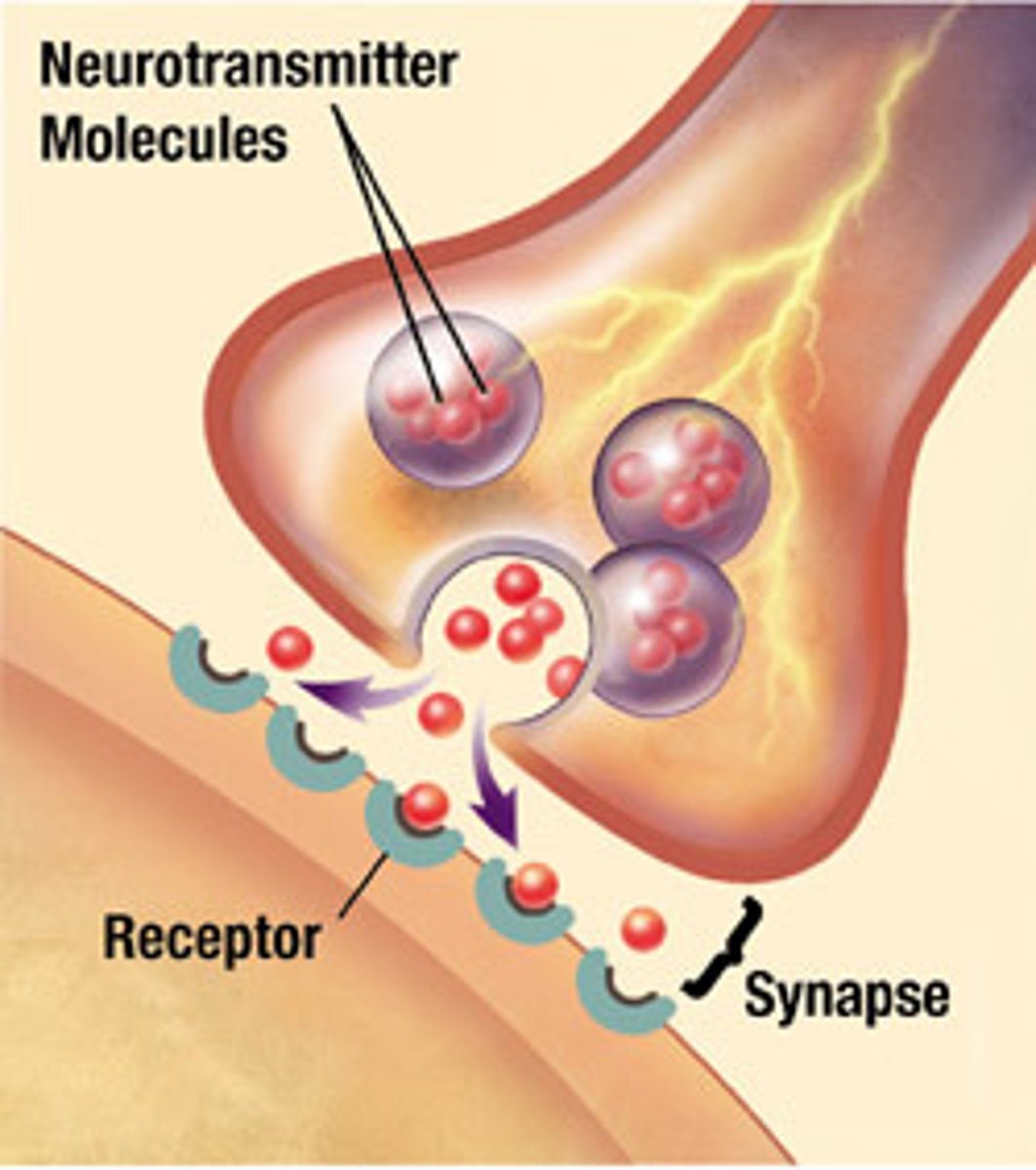
What are neurotransmitters?
Chemical messengers that transmit signals across a synapse from one neuron to another."),
What is the primary effect of stimulants on the brain?"
Increase activity in the central nervous system, leading to increased alertness and energy."
"How does cocaine affect the brain?"
Blocks the reuptake of dopamine, leading to an accumulation of dopamine and intense euphoria."),
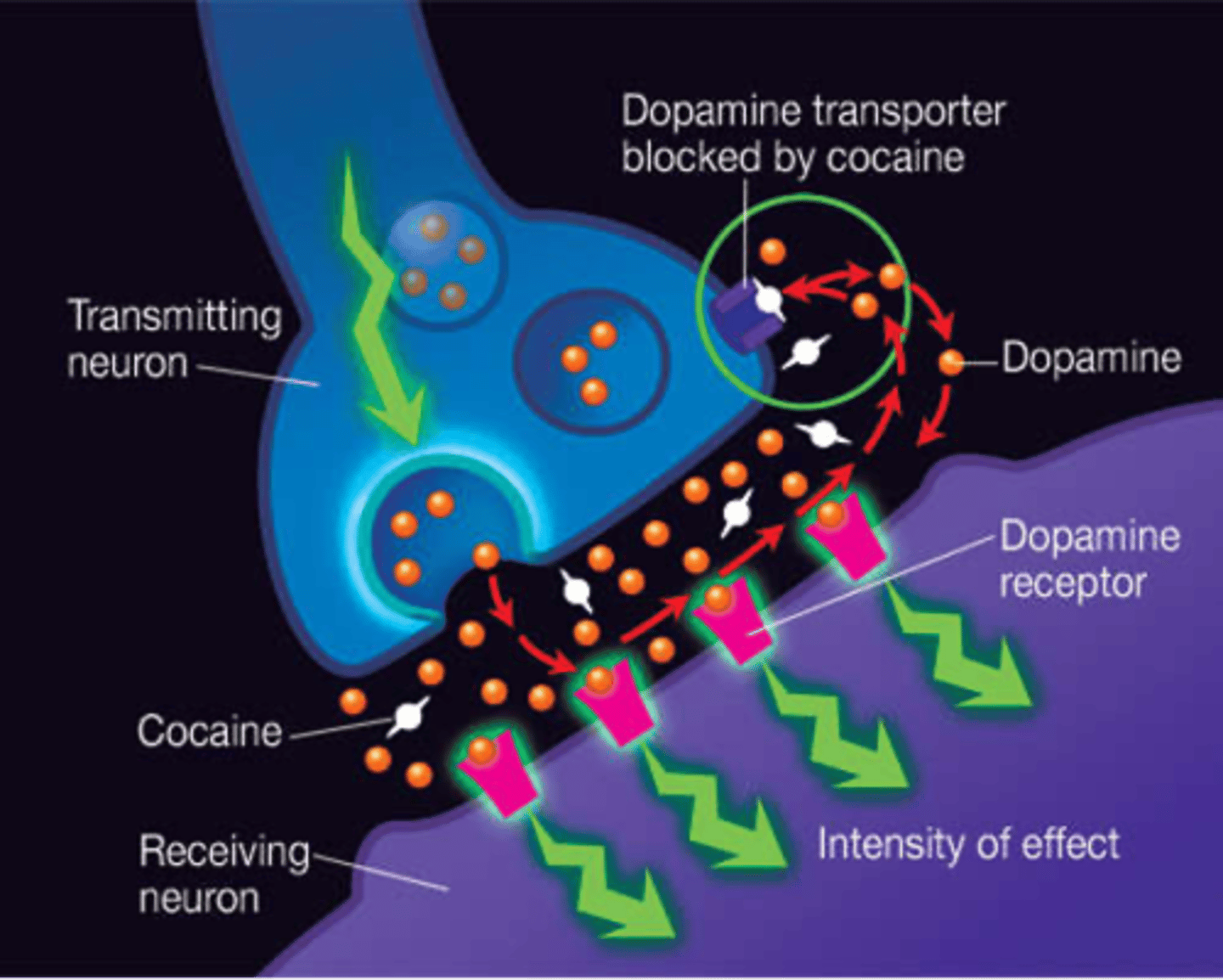
What neurotransmitter does heroin primarily affect?
Heroin affects the opioid receptors and increases dopamine release, causing intense pleasure and pain relief."),
How does alcohol affect the brain?
depresses the central nervous system by enhancing the effects of GABA and inhibiting glutamate.
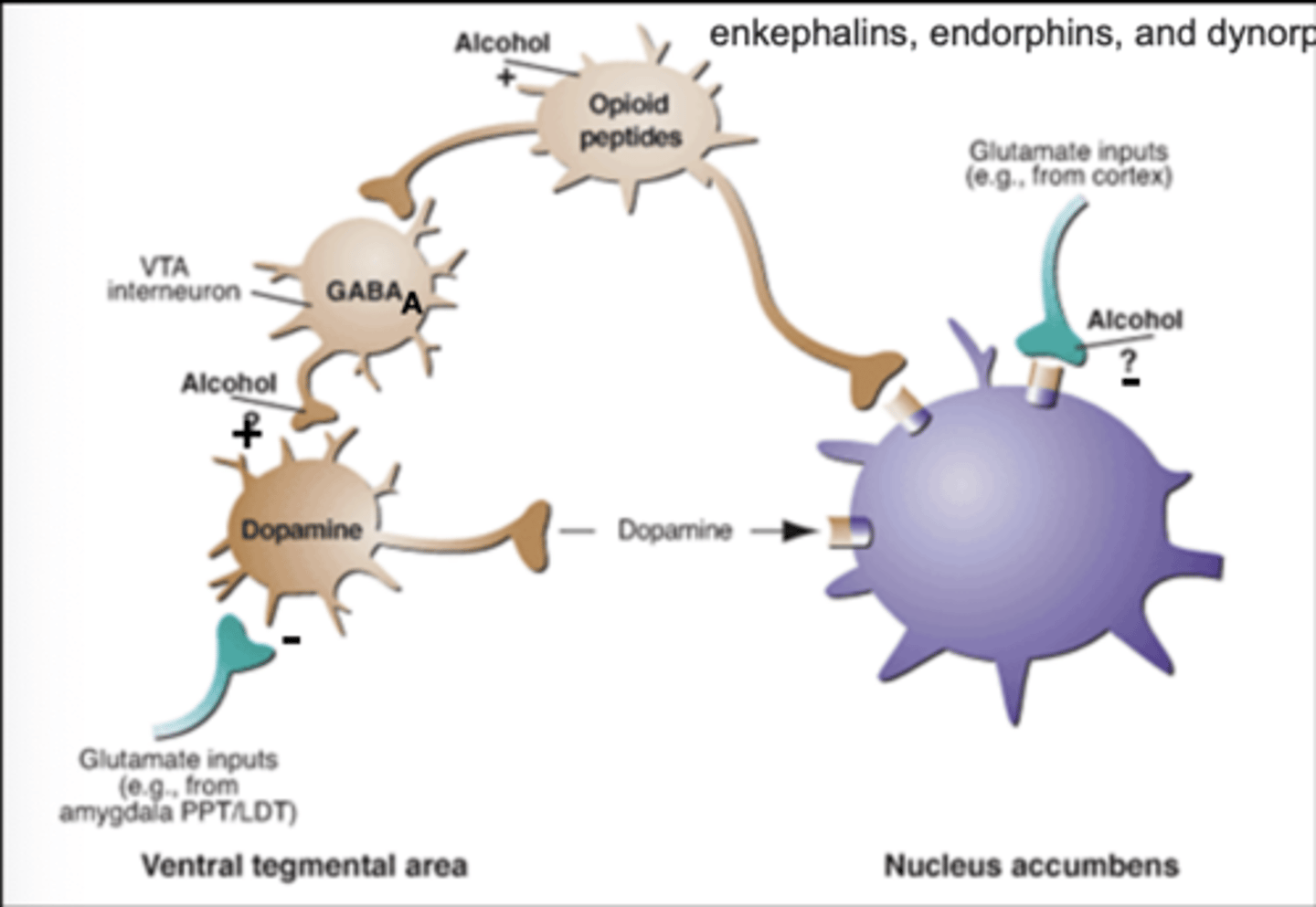
What is the effect of LSD on neurotransmission?
LSD primarily affects serotonin receptors, causing altered perceptions and hallucinations.
How does marijuana affect the brain?
THC binds to cannabinoid receptors, affecting memory, mood, and perception.
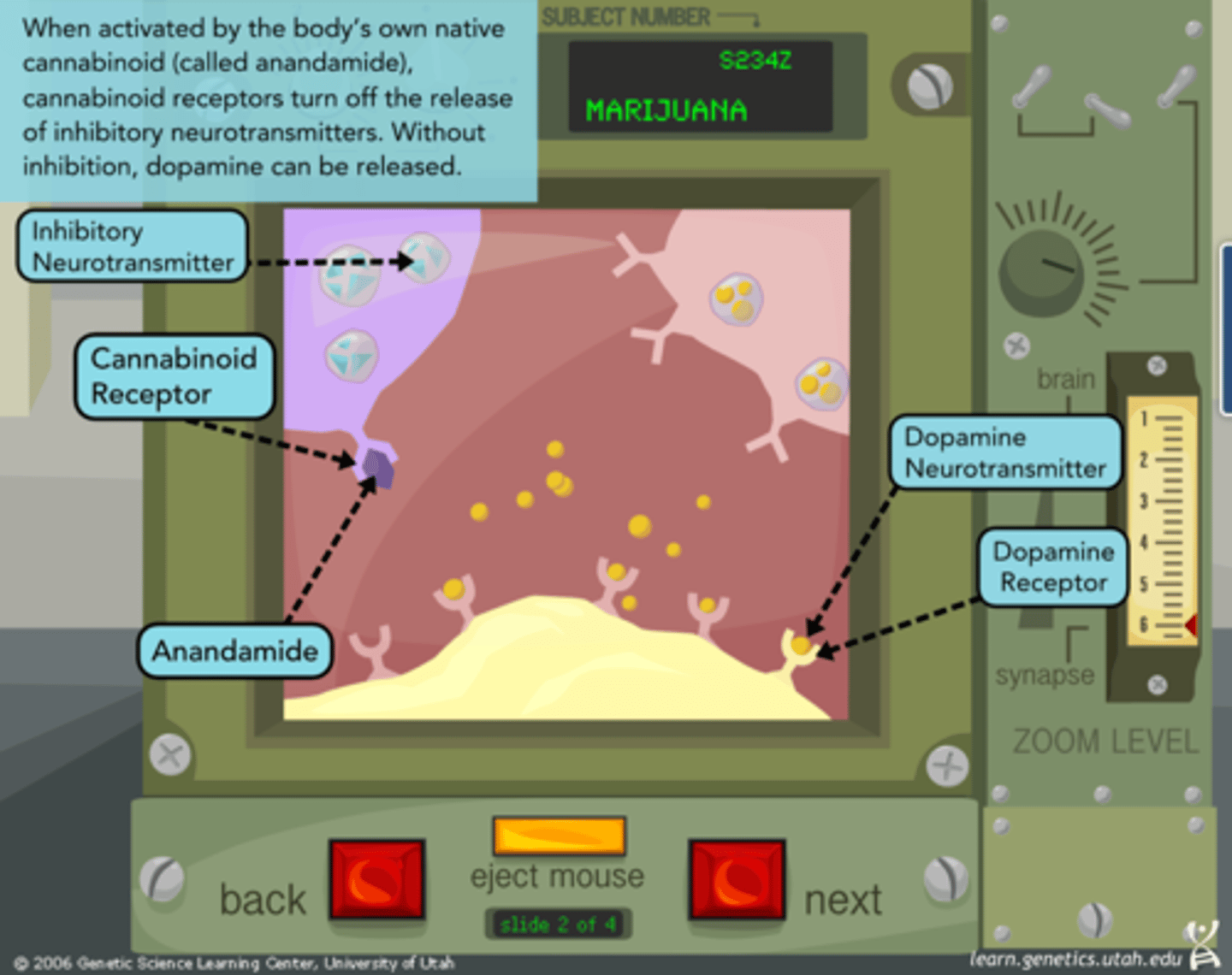
"What are the long-term effects of methamphetamine use?
Neurotoxicity, dopamine depletion, cognitive impairments, and structural changes in the brain."),
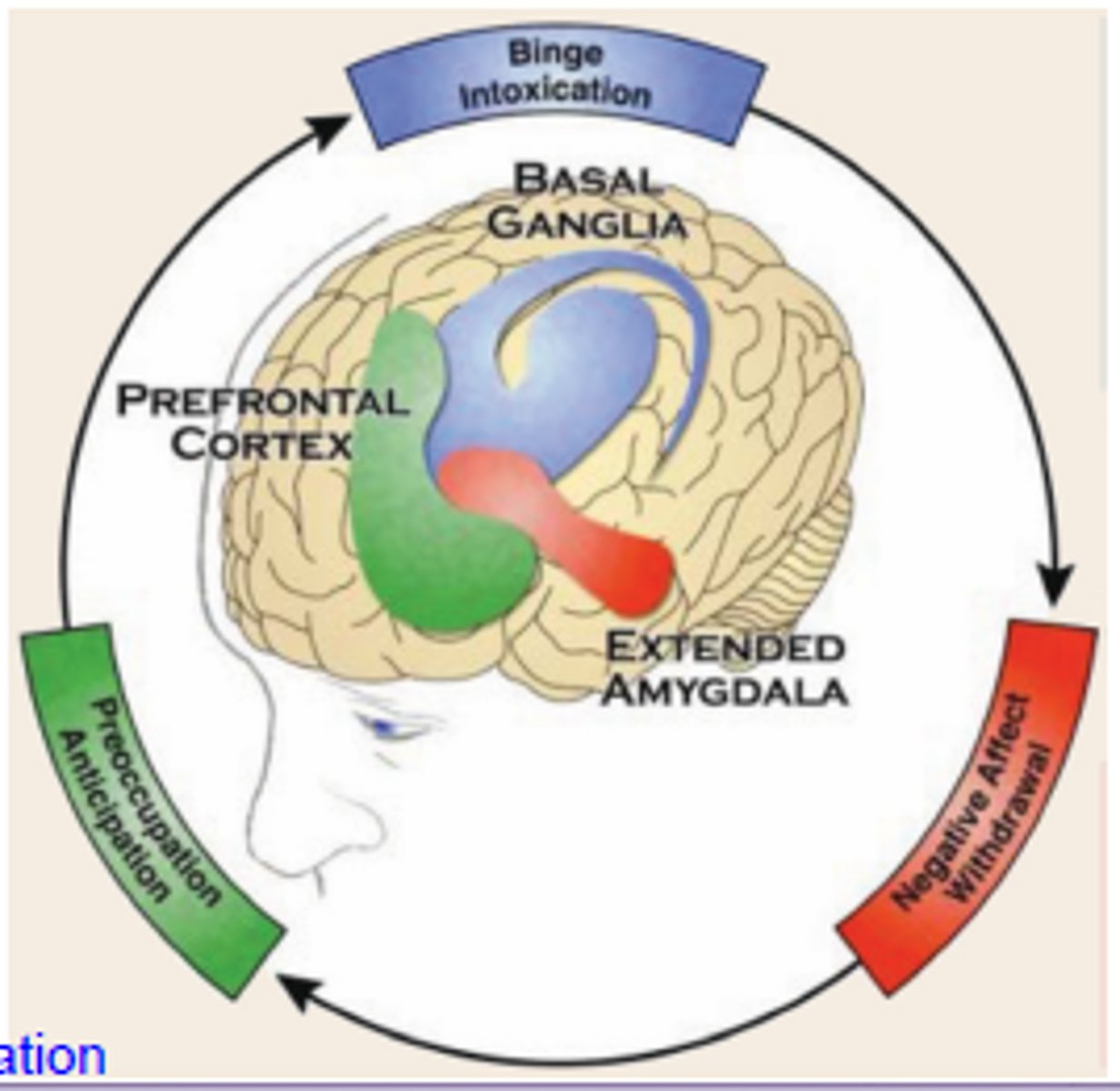
"What role does the prefrontal cortex play in addiction?
Regulates impulse control and decision-making, often impaired in addiction, leading to compulsive drug use.
How does nicotine affect neurotransmitters?
Nicotine stimulates acetylcholine receptors, leading to dopamine release and increased alertness
What is the difference between physical and psychological dependence?
Physical dependence involves withdrawal symptoms, while psychological dependence involves cravings and compulsive use.

olfactory nerve 1
Sensory; brings information from the olfactory bulb to perceive chemical smells.
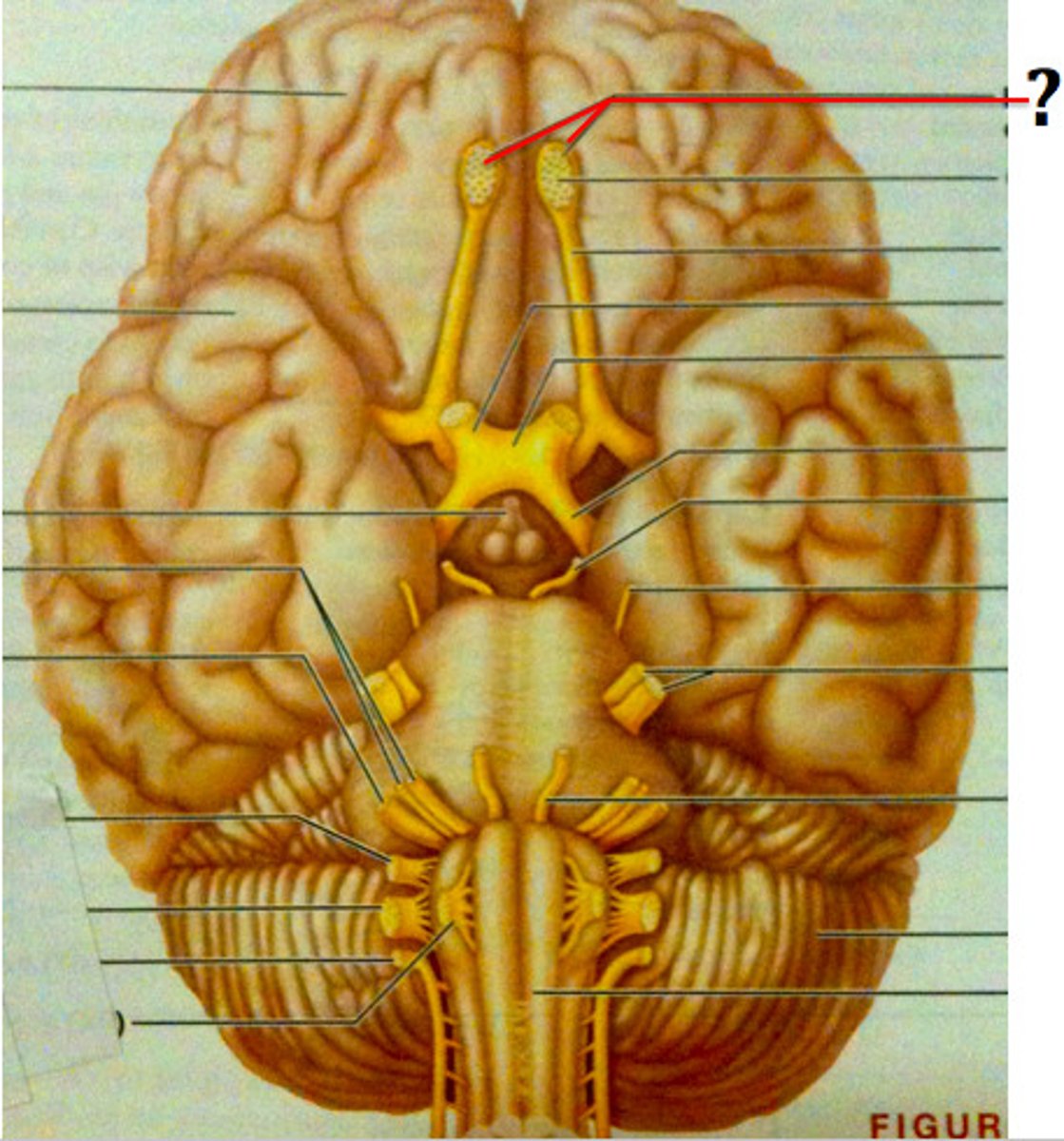
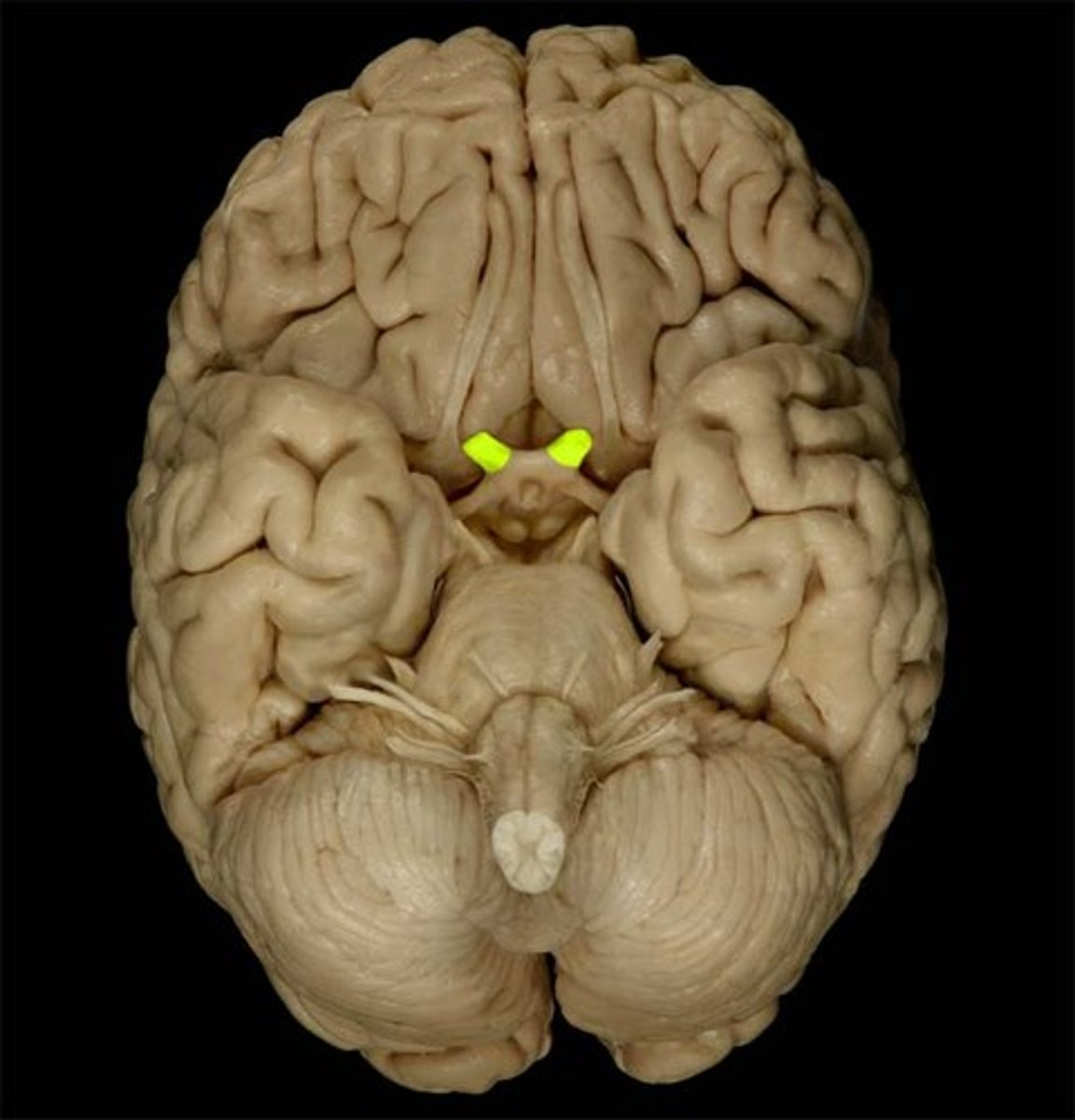
optic nerve (2)
Sensory; transmits visual information from the retina to the lateral geniculate nucleus of the thalamus.
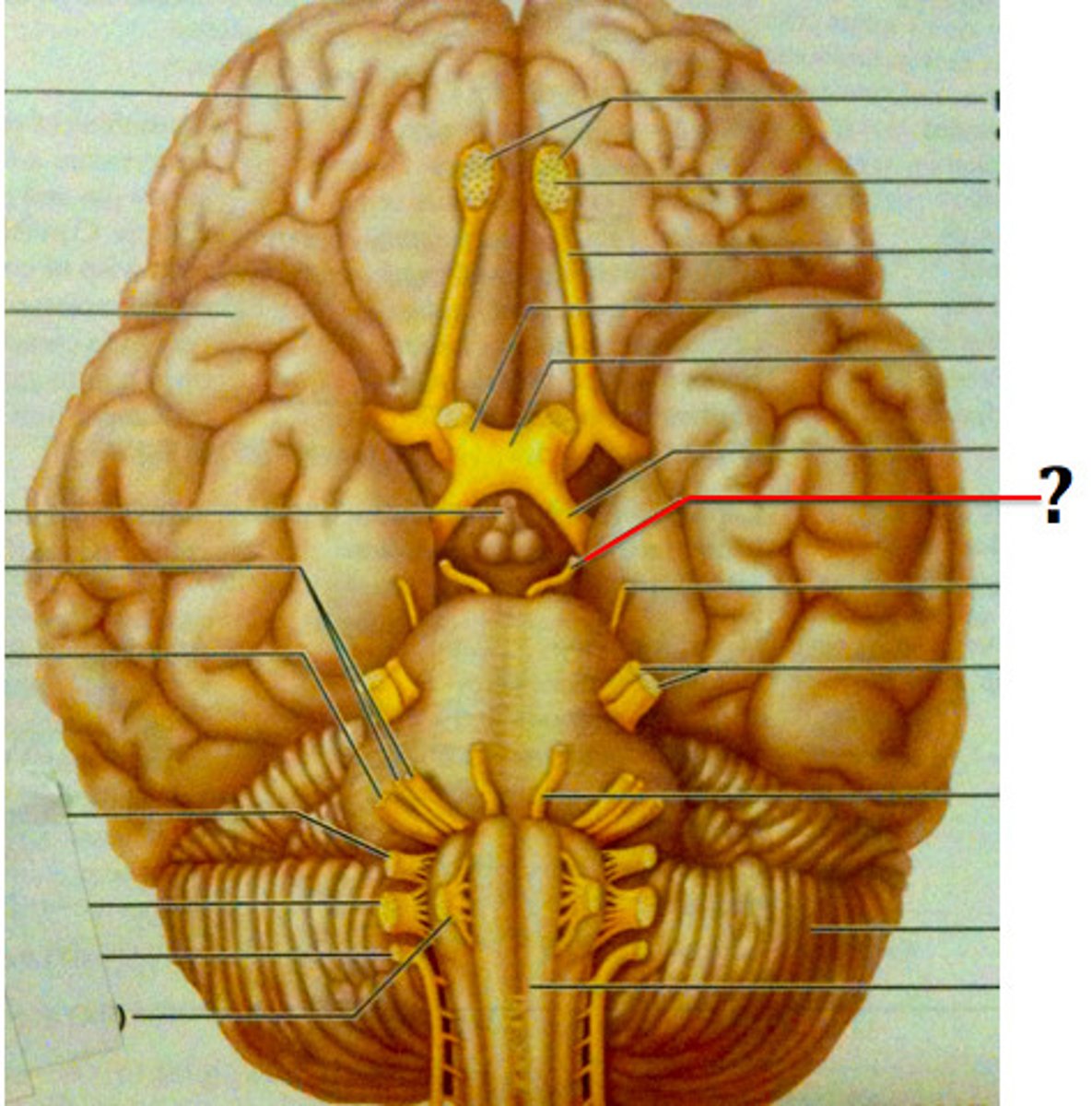
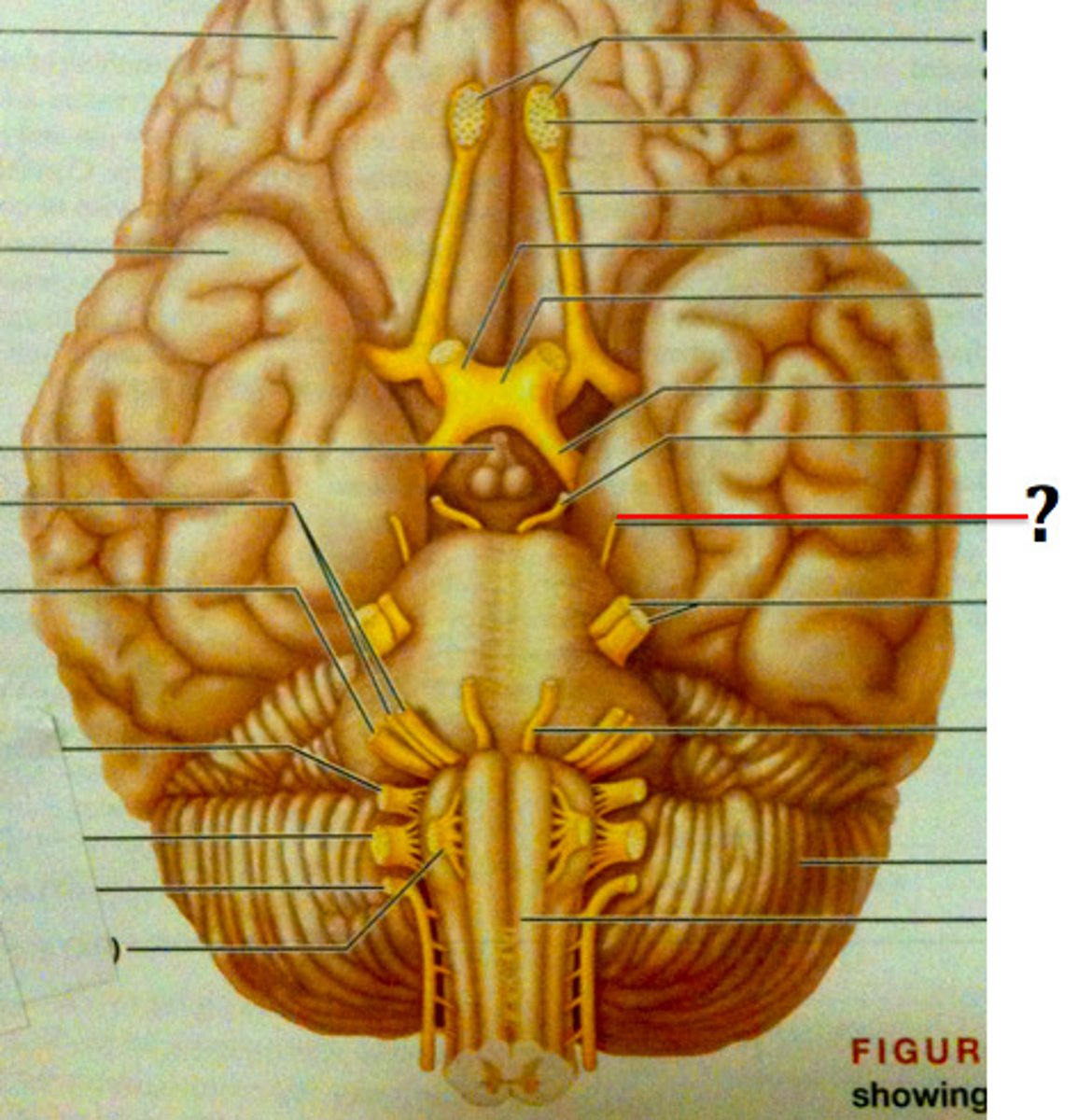
Oculomotor Nerve (III)
Motor; controls eye movement, eyelid movement, and pupil constriction.
Trochlear Nerve (IV)
Motor; controls the superior oblique muscle, which affects eye movement.
Trigeminal Nerve (V)
Sensory & Motor; detects sensation in the face and aids in chewing.
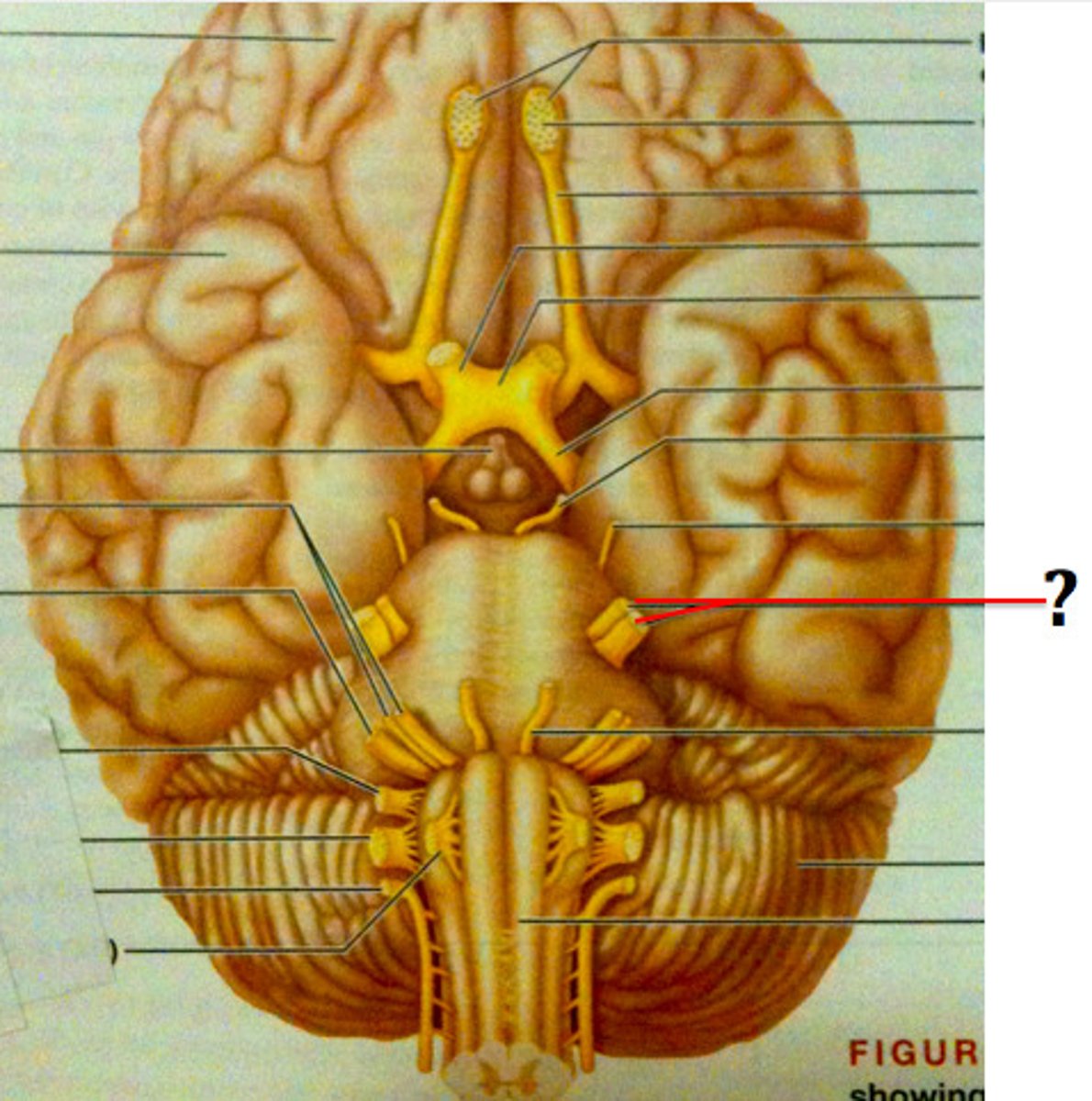
Abducens Nerve (VI)
Motor; controls the lateral rectus muscle, responsible for outward gaze.
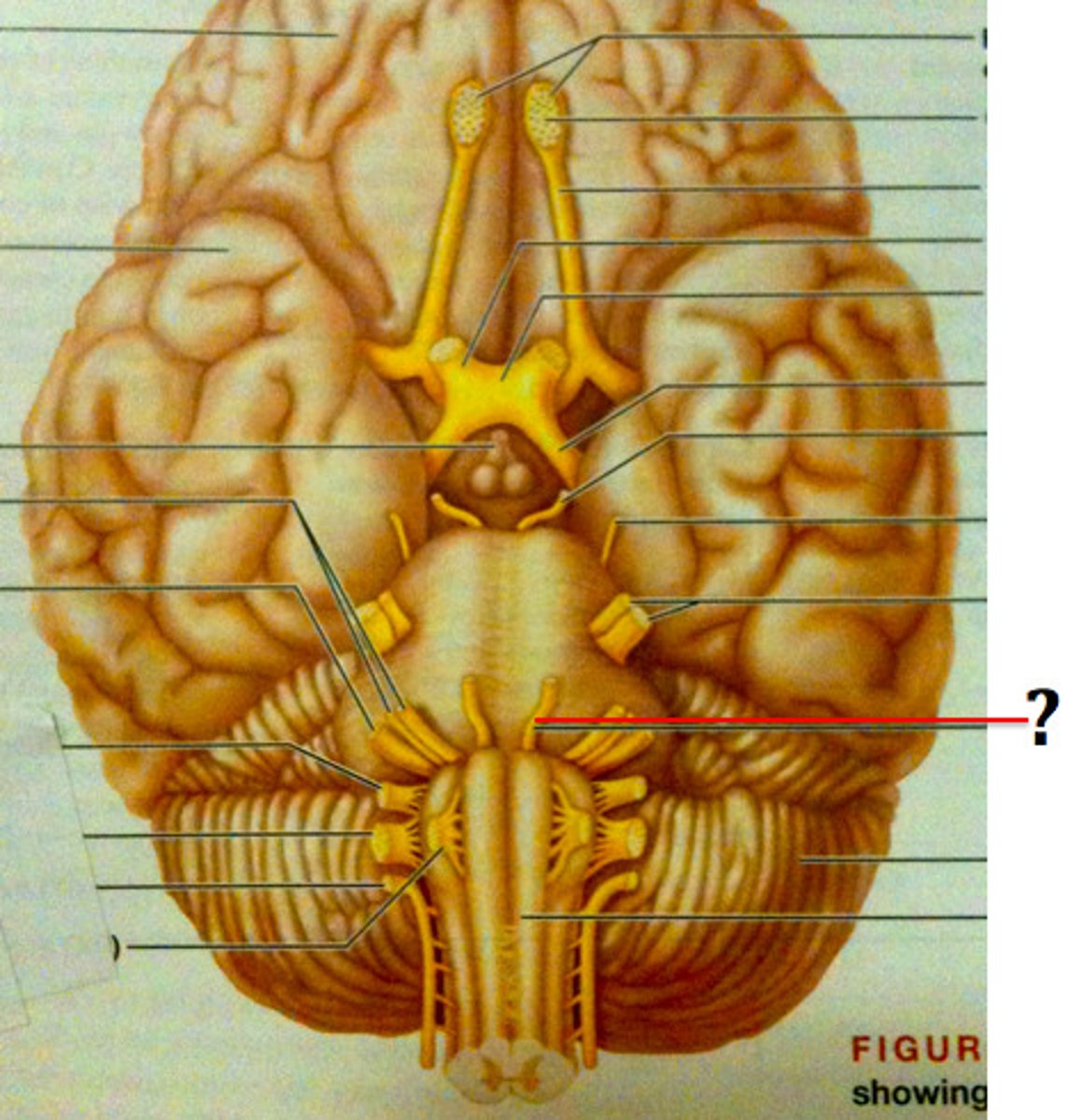
Facial Nerve (VII)
Sensory & Motor; controls facial expressions and contributes to taste perception.
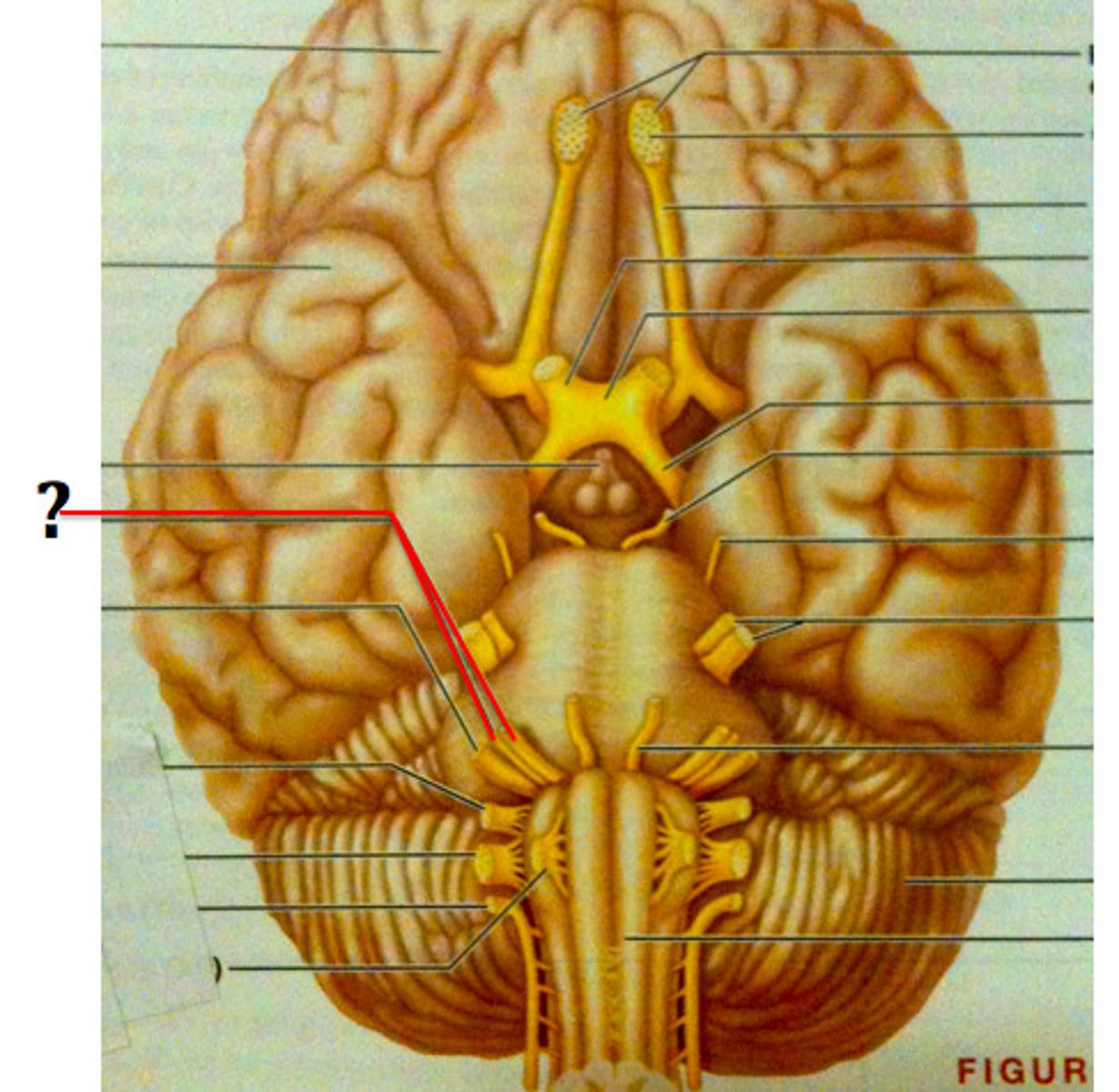
Vestibulocochlear Nerve (VIII)
Sensory; relays auditory information from the cochlea and balance information from the vestibular apparatus.
frontal lobe
: Located at the front of the brain. Responsible for reasoning, problem-solving, planning, decision-making, voluntary movement, and regulating emotions.
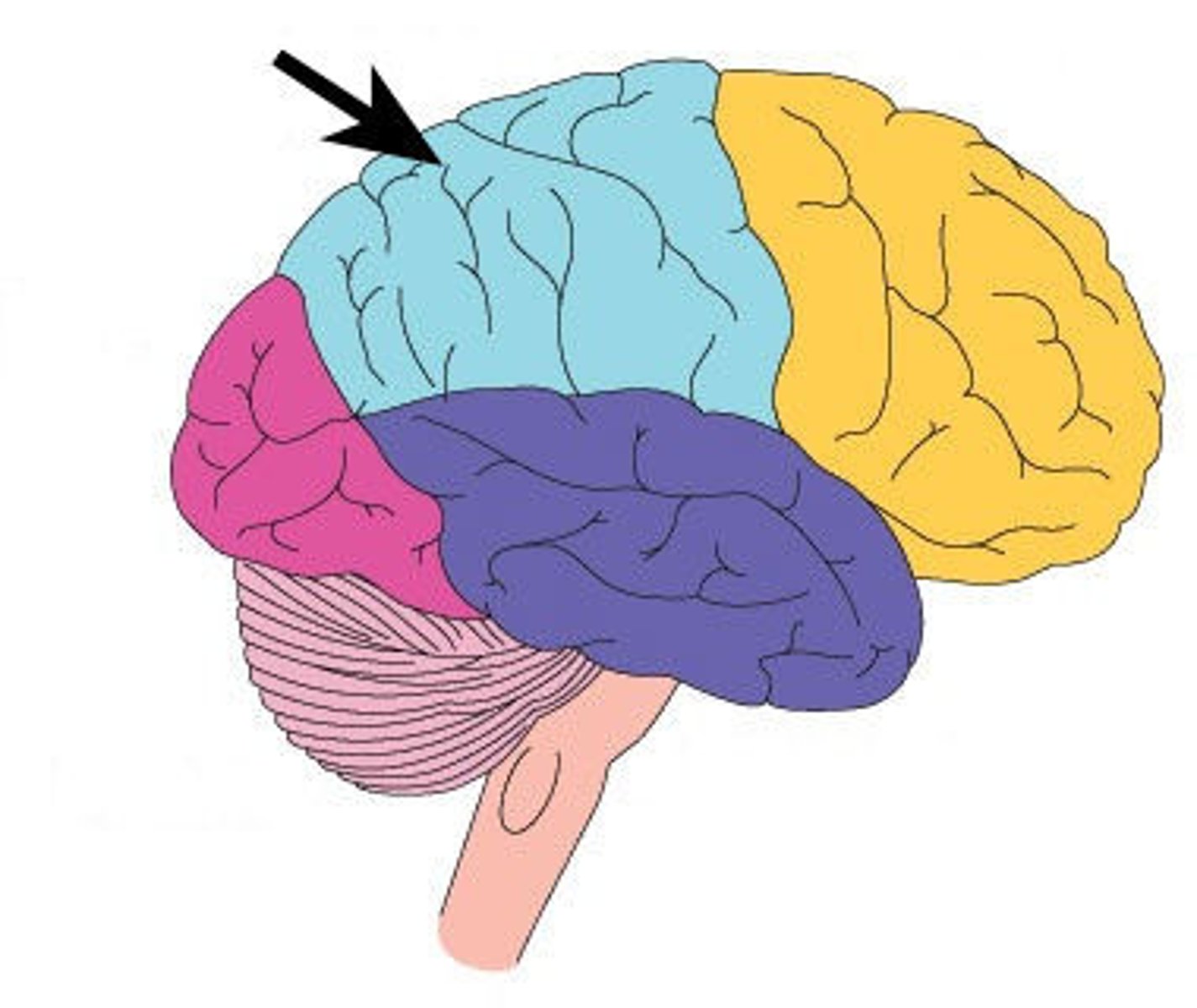
Parietal Lobe
Located at the top and back of the brain. Processes sensory information such as touch, temperature, and pain. Also involved in spatial awareness and coordination.
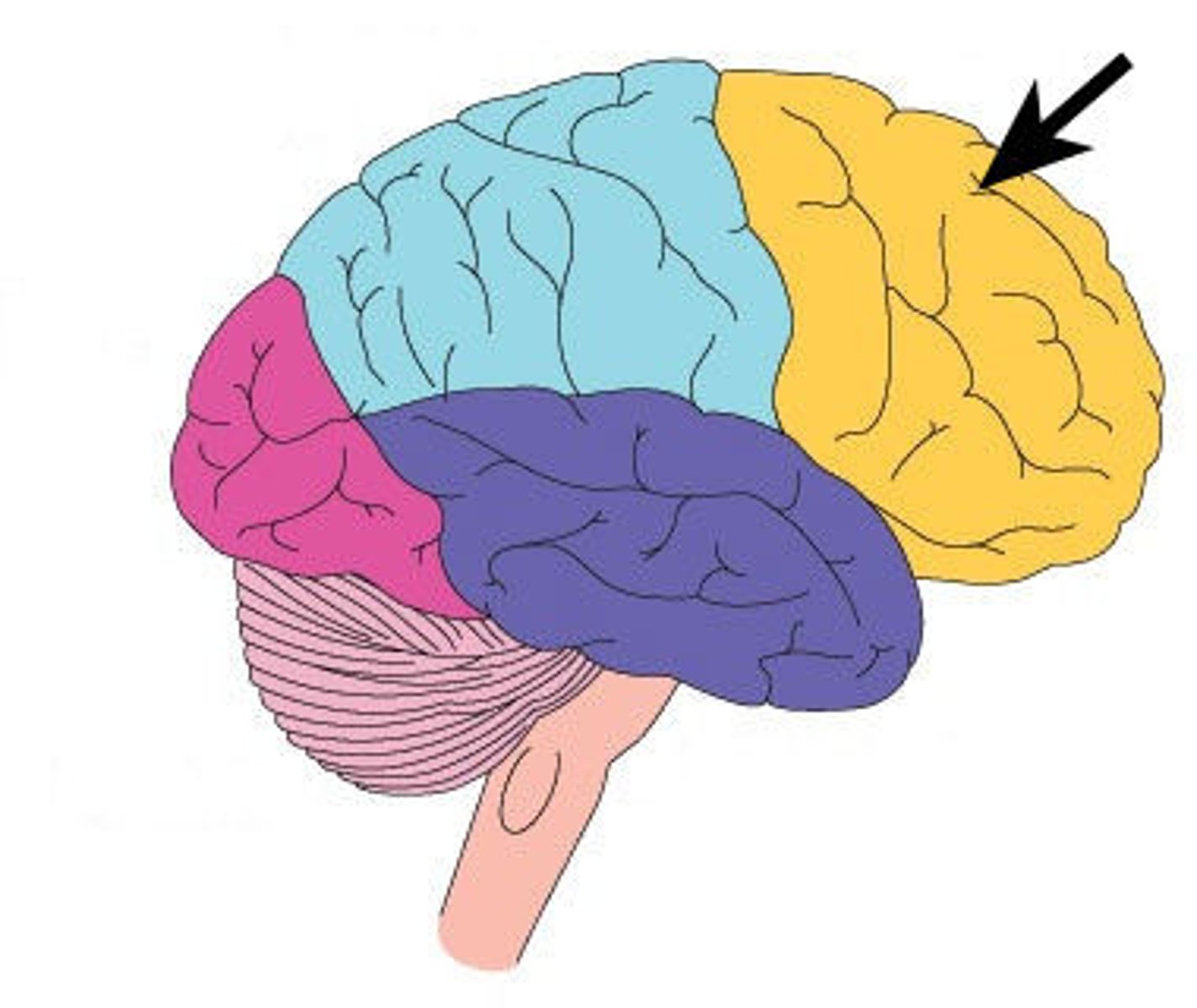
Occipital Lobe
Located at the back of the brain. Primary function is visual processing, including recognizing shapes, colors, and motion.
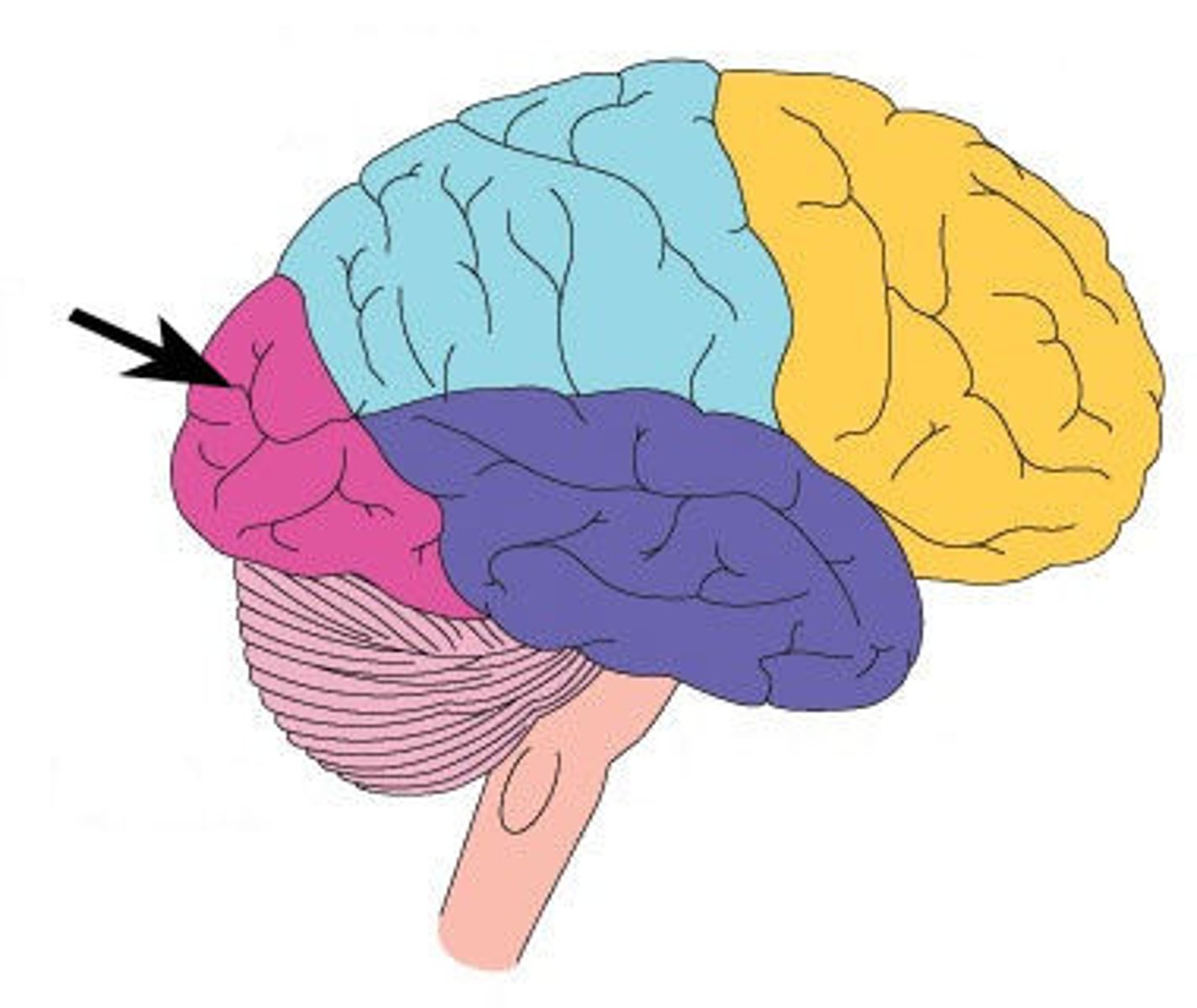
Temporal Lobe
Located on the sides of the brain, near the ears. Responsible for processing auditory information, language comprehension, and memory storage.
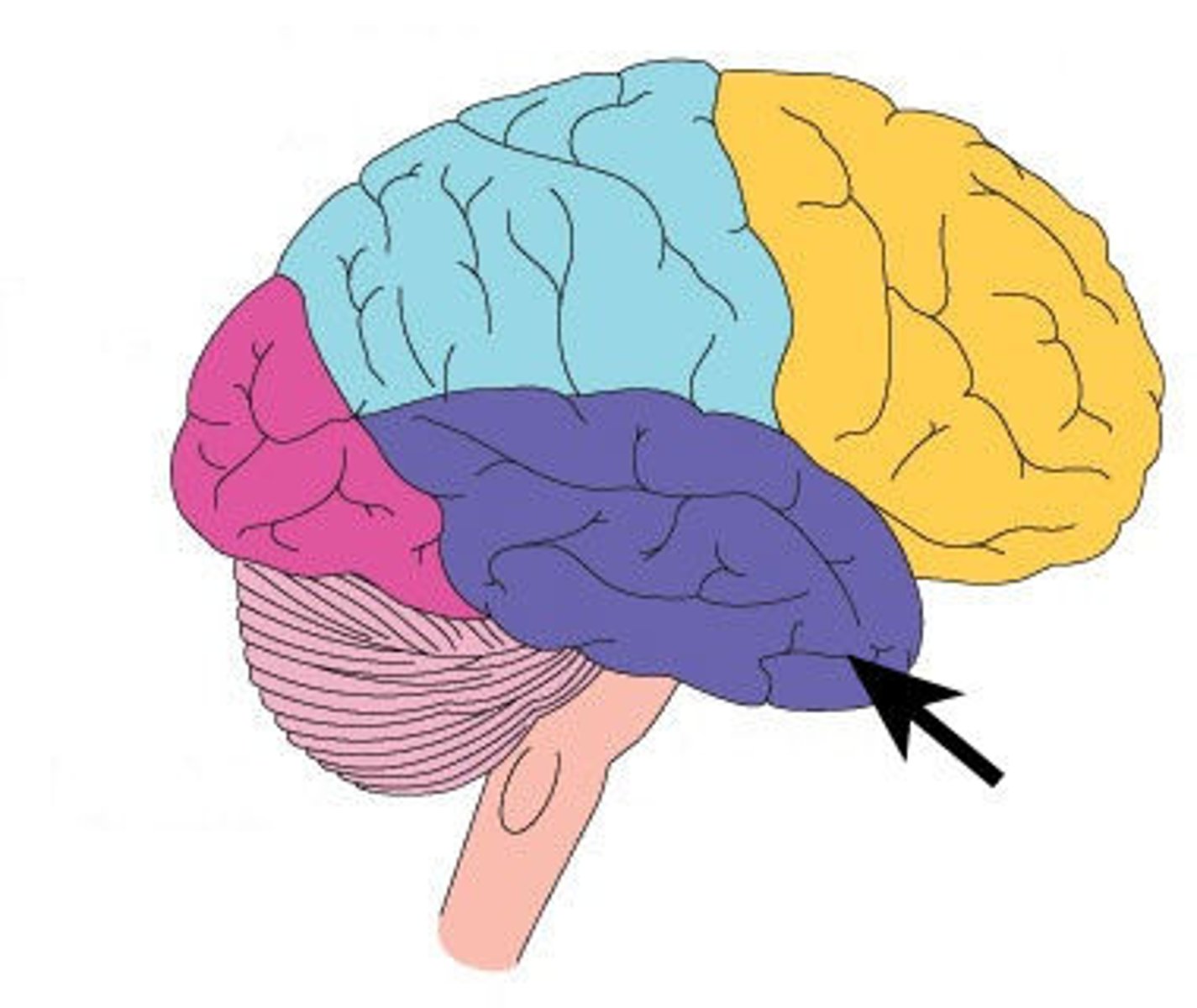
Cerebellum
Located at the back of the brain, below the occipital lobe. Controls coordination, balance, and fine motor movement
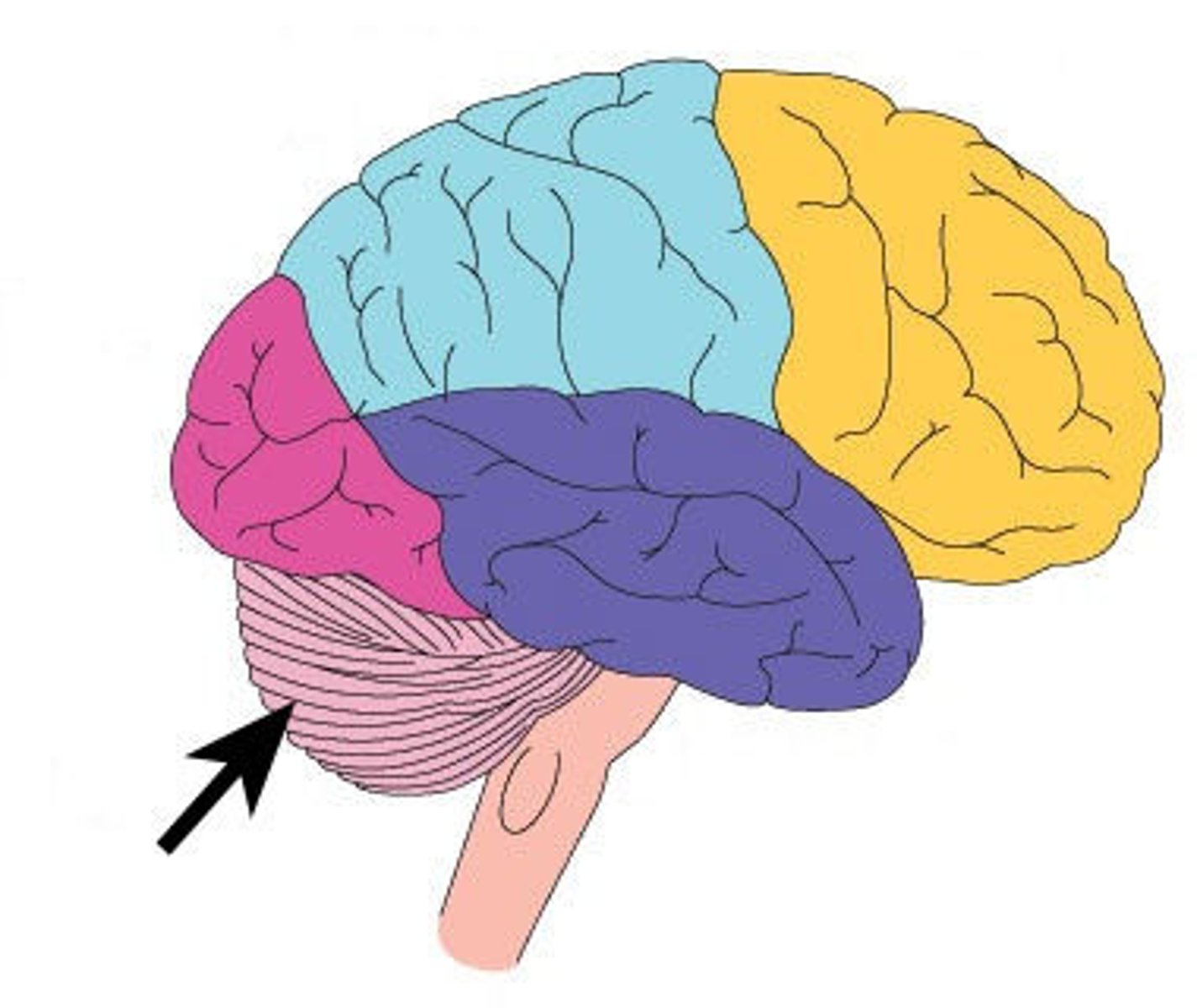
Medulla Oblongata
Located in the brainstem. Regulates involuntary functions such as breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure.
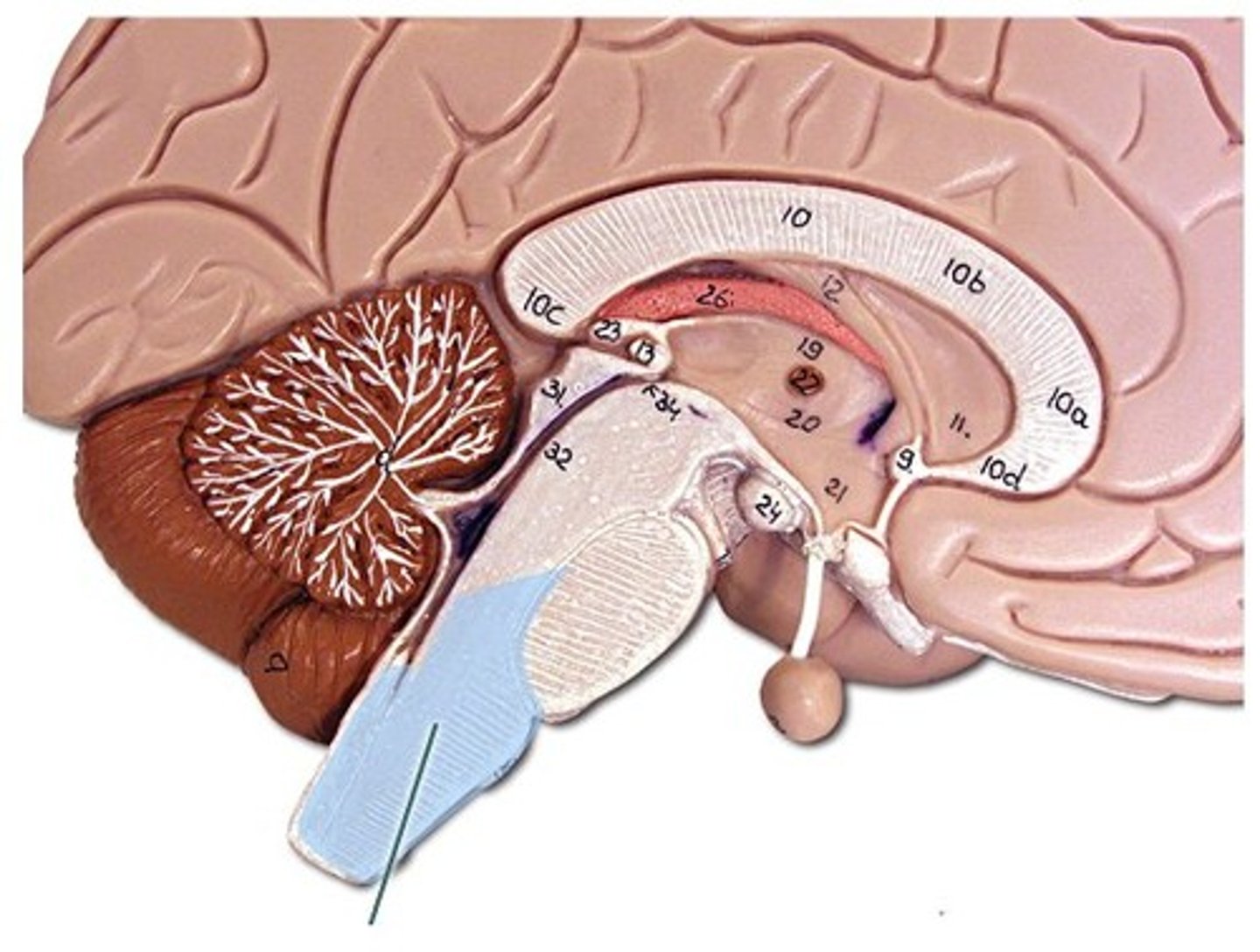
Pons
Located in the brainstem above the medulla. Acts as a relay between the cerebellum and other parts of the brain. Involved in sleep, respiration, and facial movements.
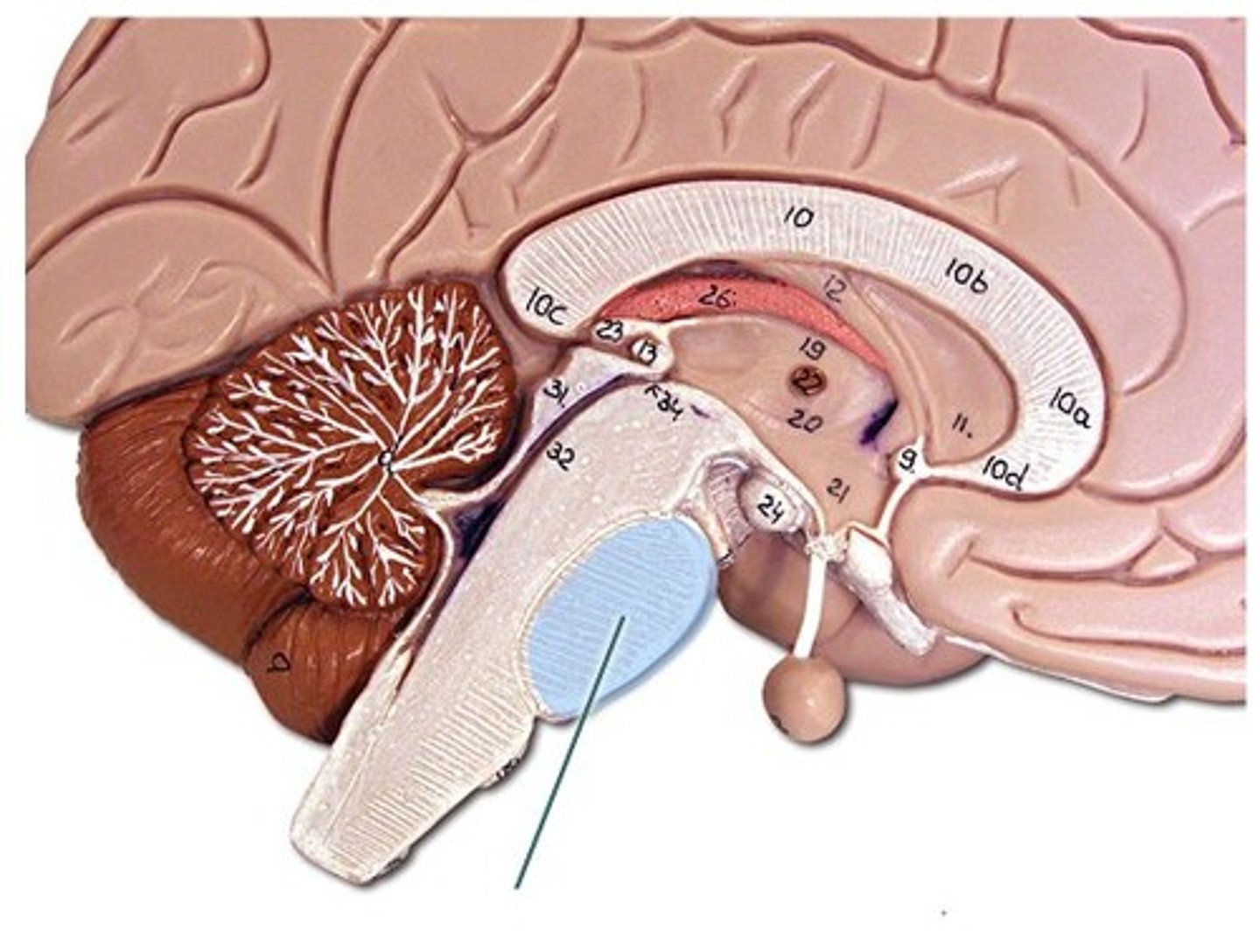
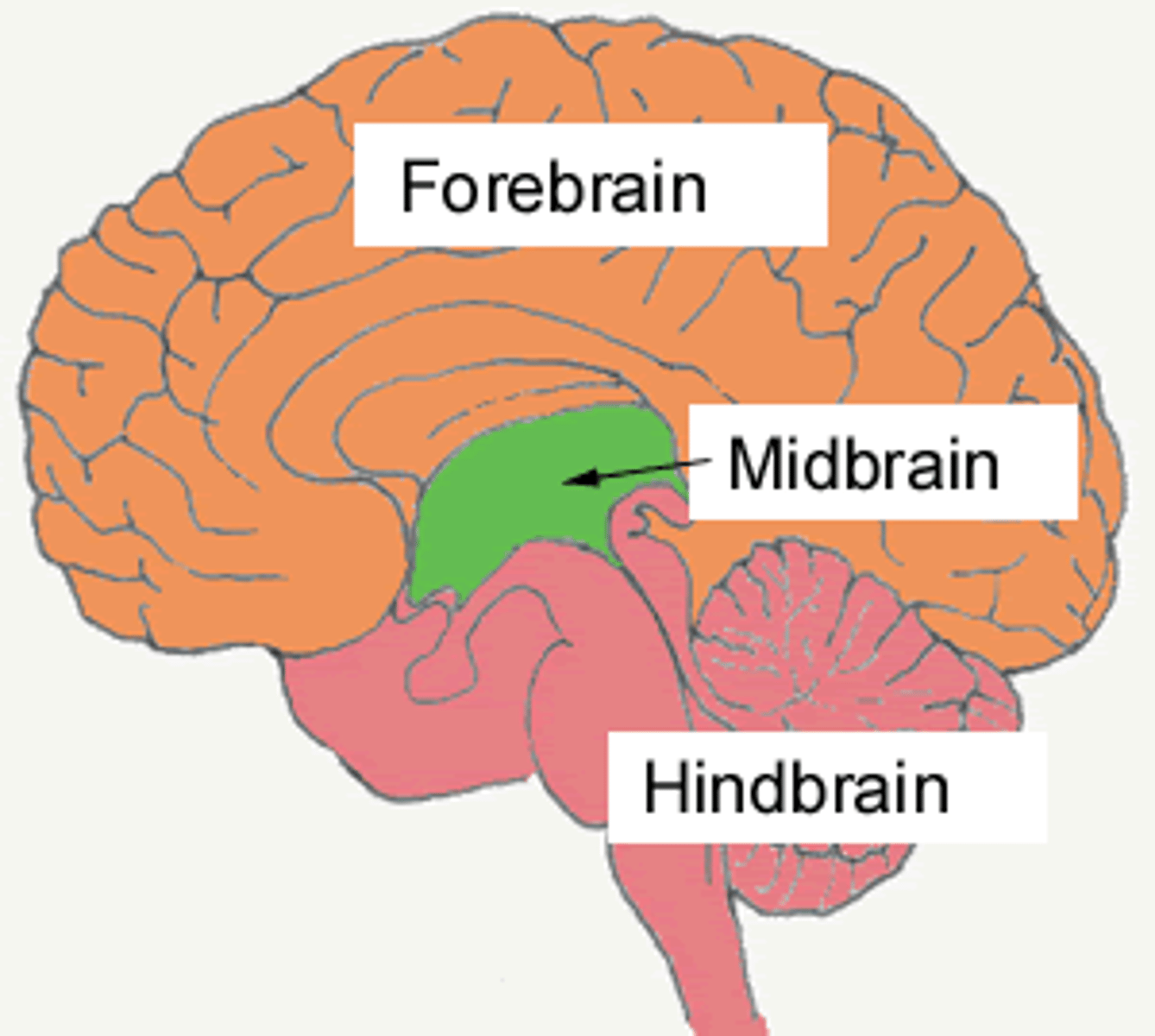
Midbrain
Located above the pons in the brainstem. Controls reflexive eye movements, auditory processing, and motor control.
Thalamus
Located in the center of the brain. Acts as a relay station for sensory and motor signals to the cerebral cortex.
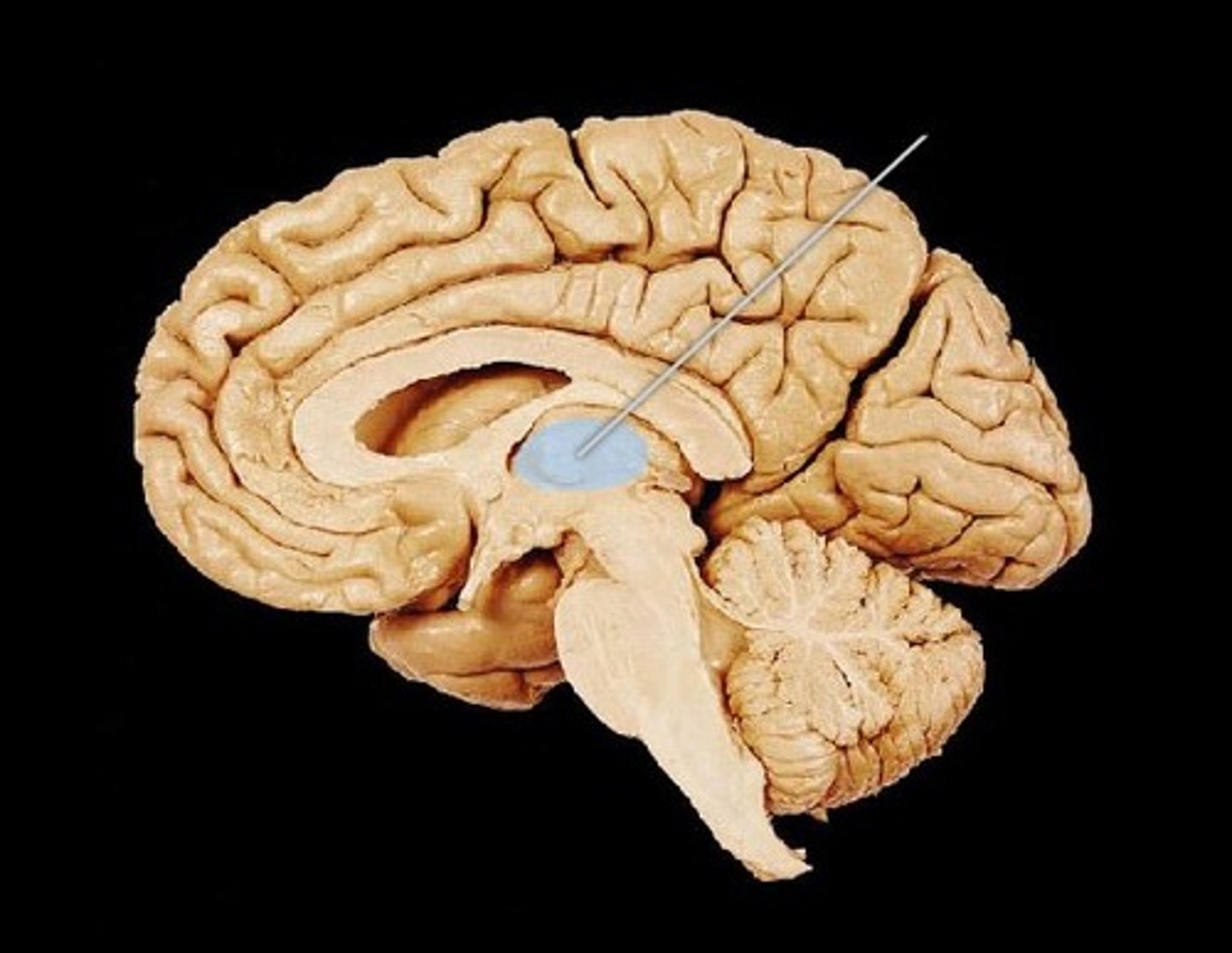
Hypothalamus
Located below the thalamus. Regulates body temperature, hunger, thirst, and controls the endocrine system via the pituitary gland.
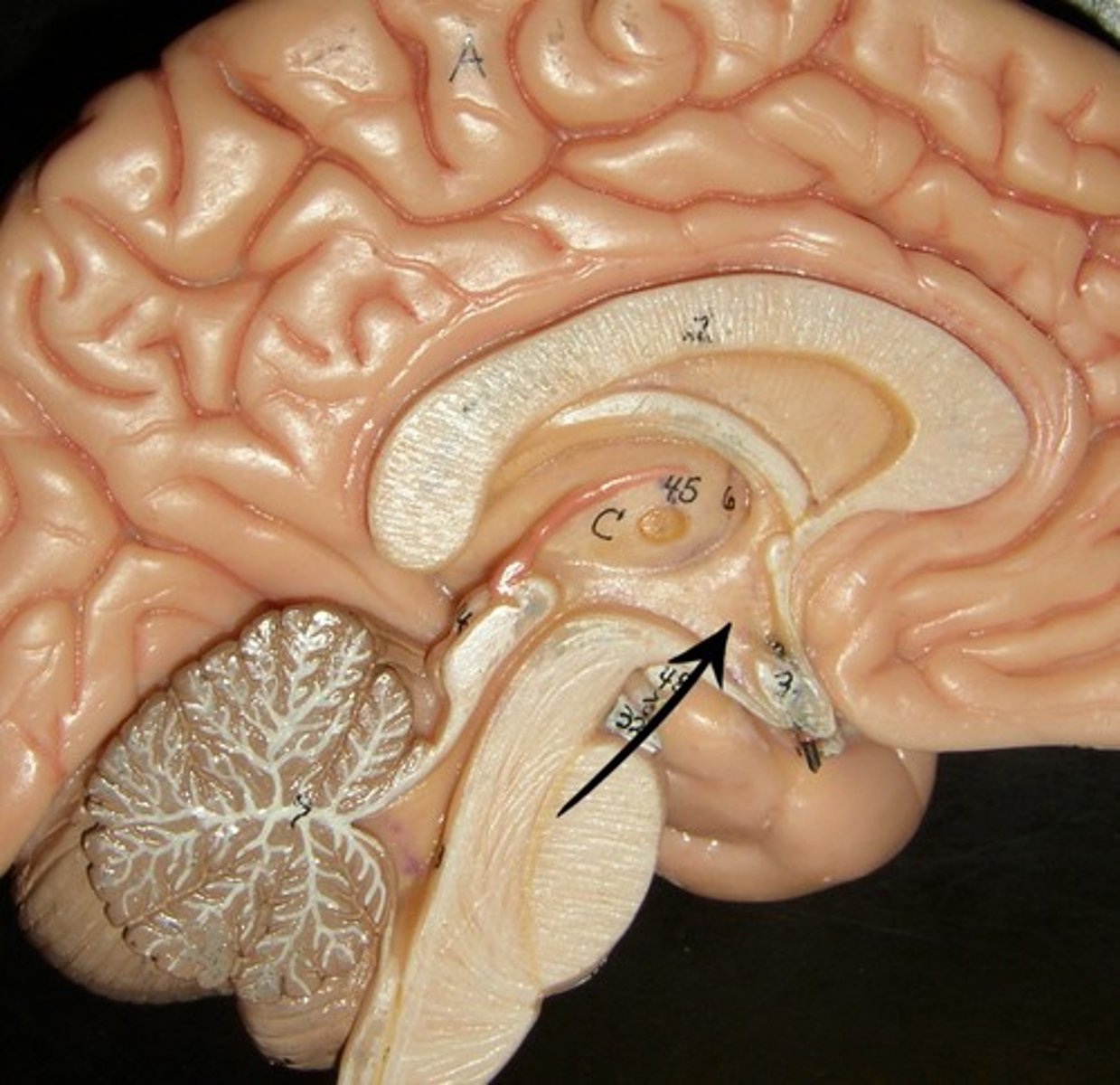
Hippocampus
Located deep in the temporal lobe. Critical for memory formation and spatial navigation.
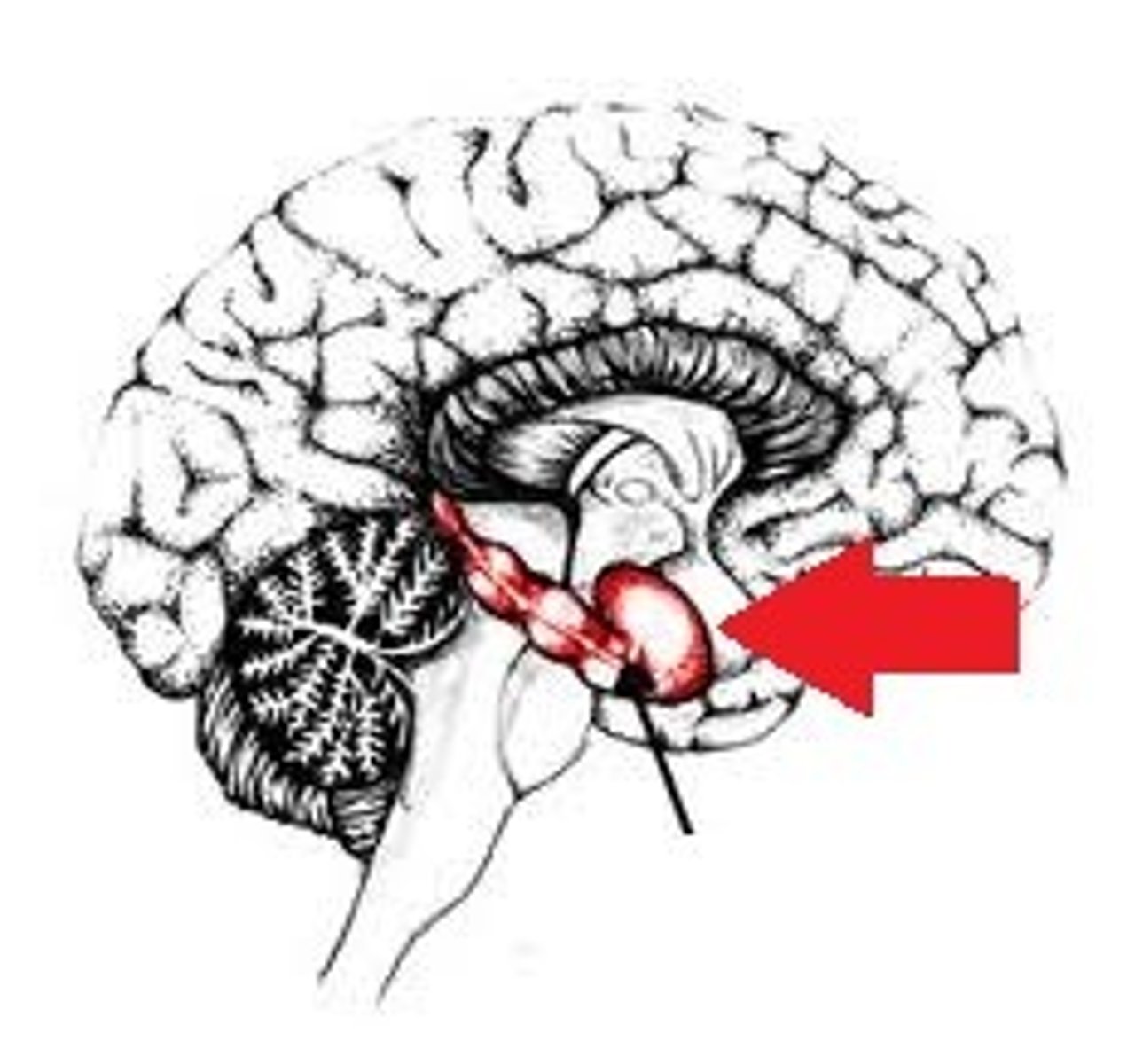
Amygdala
Located near the hippocampus. Involved in emotional processing, especially fear and aggression.
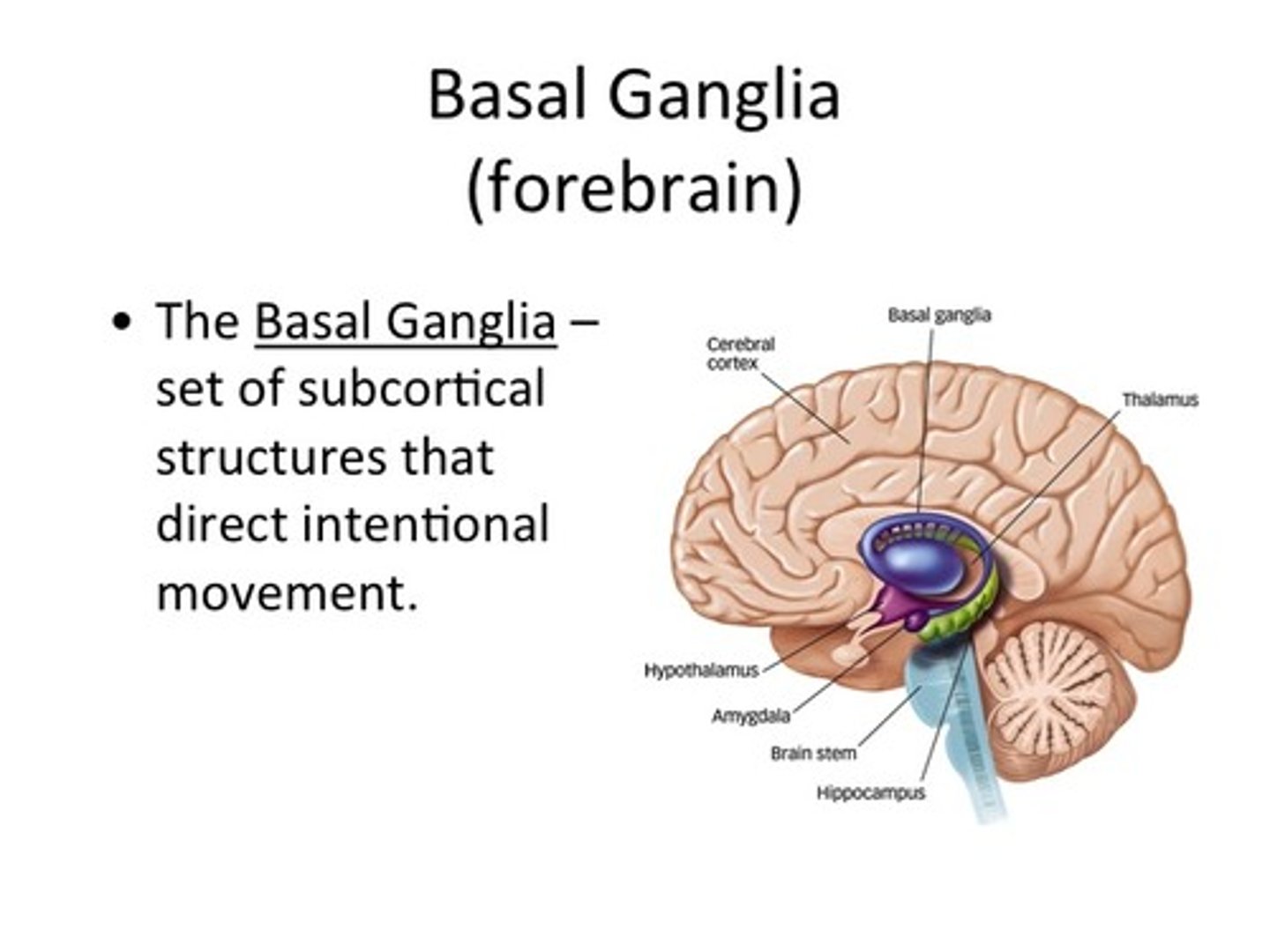
Basal Ganglia
Located deep within the cerebral hemispheres. Plays a role in movement regulation, habit formation, and reward processing.
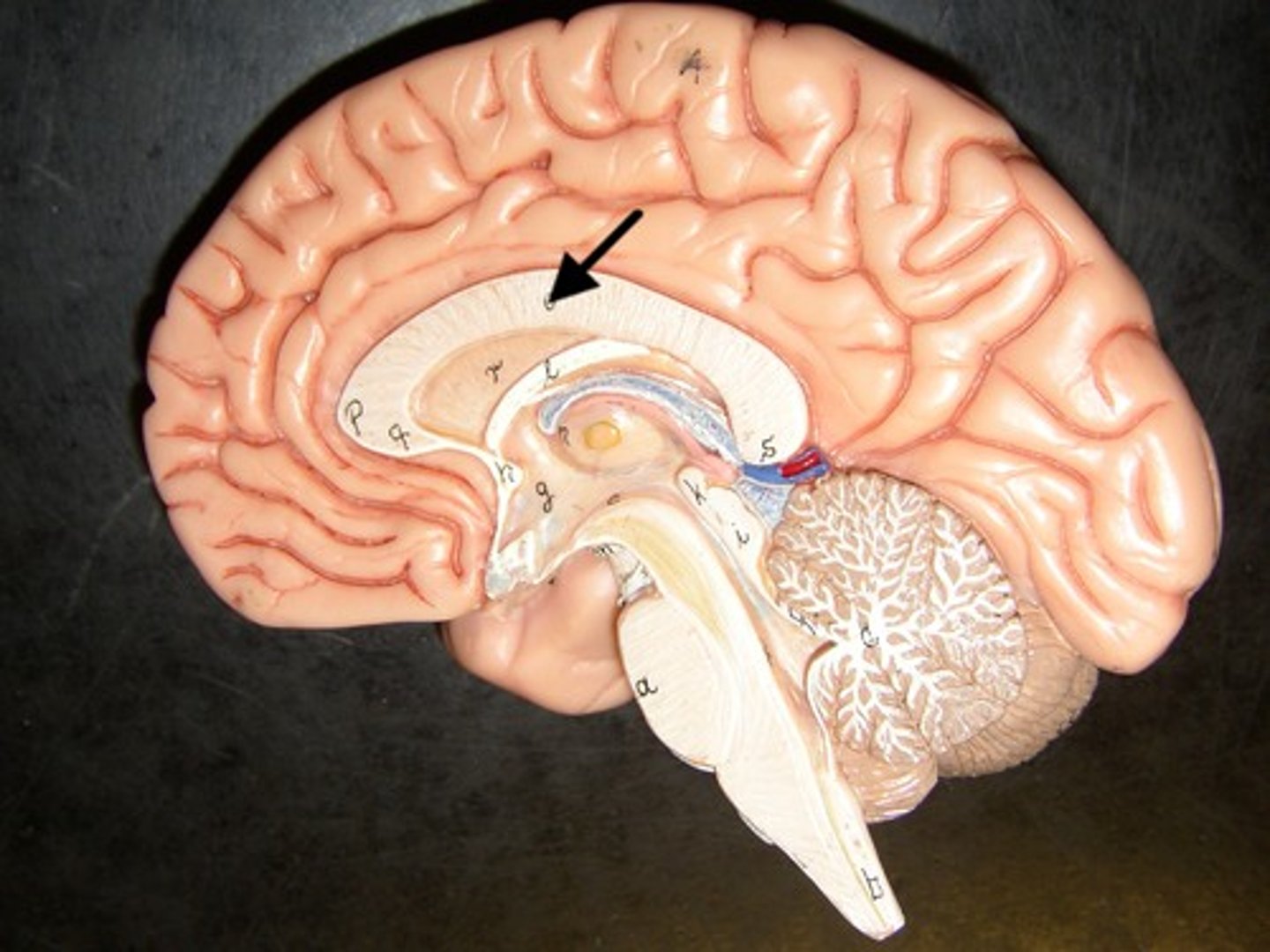
Corpus Callosum
Large bundle of nerve fibers connecting the two hemispheres of the brain, enabling communication between them.
psyche
The soul or mind

What is the mind-body problem and how did Decartes propose scientists test for it?
Mind and body are two separate entities that interact with each other. Proposed that pineal gland plugs into the mind and the heart is the soul and core of the psyche as the brain is a system of operating through and pulling on the body. What are the limitations of these tests? If separate, where do they interact
Explain how Descartes thought the brain guided movement and behavior
Pineal operates by pulling on the heart and muscles which pushes blood flow to cause things to act
What are four implications of materialism for studying the brain and behavior?
All animal species and their brains are related.
All species of animals are related, so their behavior must be related as well.
Brain and behaviors in complex animals such as humans evolved from simpler animals' brains and behavior.
Consciousness and other processes attributed to the mind must be the product of the nervous system.
Patricia Churchland 1986
Physical mechanisms can explain consciousness and other mental activities
Giulio Tononi: 2012
Integrated information theory ← we have memory "schema" that activate to allow us to perceive/process the world around us and in turn achieve "consciousness"-"Consciousness arises from integrated information within a network of brain structures"
White matter
Has long tracts of myelinated axons, and transports information across the different brain regions by facilitating rapid signal transmissions with those axons. Found in the deeper regions of the brain but on the outer surface of the spinal cord. Jelly-like substance due to /myelin on axons (white appearance when examined)
Gray matter
On the surface of the brain forming the cerebral cortex and is filled with cell bodies and glial cells. Plays a role in sensation processing, voluntary movement, learning, speech, cognition, perception. Concentrated cell bodies that gives "gray" appearance when examined
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
Clear liquid found throughout the CNS and cushions brain, fights diseases, removes metabolic waste, and aids in blood flow
Vomeronasal organ (VNO)
Location: Near the nasal bone at the base of the septum
Function: senses pheromones (help you decide who to date) and chemical messages, especially those related to sex.
Nucleus Accumbens
Location: Part of the basal ganglia located in the forebrain.
Function: plays a role in pleasure and reward, with a particular connection to addiction
Primary somatosensory cortex (postcentral gyrus)
Location: Parietal lobe. Between the postcentral sulcus and the central sulcus.
Function: Primary somatosensory cortex that receives and interprets sensory information such as? Including touch, temperature, pain, and proportion
Primary auditory cortex (superior temporal gyrus)
Location: Temporal lobe
Function: processes and interprets pitch, rhythm, volume, awareness of one's own voice
sensory nuerons
located in the spinal cord, sensory organs, and cranial nerves. Receive stimuli from the environment and transmit this information to the CNS for processing
Motor nuerons
located within the spinal cord and brain. Send commands from the brain to the muscles
Interneurons
found exclusively in the CNS. Connect motor and sensory neurons
Anaxonix nuerons
Found in the olfactory system. Axons and dendrites are difficult to differentiate
bipolar nuerons
:One branching axon and only one dendrite. See these in the retina of the eye and the olfactory system
What is a pseudounipolar neuron?
A neuron that starts as a unipolar neuron with one protuberance from the cell body.
How does a pseudounipolar neuron transmit information?
It contains an axon that is split into two branches, with one branch bringing information toward the cell body similar to a dendrite.
Where are pseudounipolar neurons found?
In the spinal cord.
What type of neurons do pseudounipolar neurons serve as?
They serve as sensory neurons.
What do pseudounipolar and bipolar neurons constitute in the human peripheral nervous system?
They constitute the entirety of the primary sensory neurons.
multipolar neuron
One axon leaving the cell body with several axon collaterals toward the terminal end and several dendrites branching
unipolar neuron
One nerve process extending from the cell body, an axon that extends into dendrites
What are the five types of Glial Cells?
Astrocytes,Oligodendrocytes,Microglia,Schwann Cells, Ependymal cells
Stephen Gray 1731
Proposed that electricity may be involved in NS
Galvani 18th century:
First to find electricity flowing along the nerve
Caton Early 19th century
First to measure electrical currents of the brain
Fritsch and Hitzig Mid 19th century
Found that electric stimulation to neocortex caused movement in arms and legs
Bartholow 1874
First to stimulate brain
Von Helmholtz Late 19th century
Reported that information in NS moved too slowly to be electric
Berstein 1886
Noted that the elective wave (not charge) travels along the axon
What discovery significantly changed how scientists, especially Hogdkin & Huxley, could study neuronal transmission?
Discovery of the squid giant axon This was a "big" deal because the neuron could be studied in detail for the first time given the technology available when it was discovered. It really launched the field of neuroscience.
What is the enteric nervous system commonly referred to as?
The brain in the gut
What does the enteric nervous system regulate?
Gastric acid secretion, GI blood flow, and gut hormone release
Why is the enteric nervous system referred to as the 'Second Brain'?
Because it has a high concentration of serotonin
How does the enteric nervous system interact with the body?
It interacts with the gut's immune system