Resistivity and Superconductors
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Resistance in a component
How difficult it is to get current to flow through it
Ohm’s Law
In an ohmic conductor at constant temperature:
V α I
What is resistance caused by?
Repeated collisions between charge carriers in the material and the fixed positive ions of the material
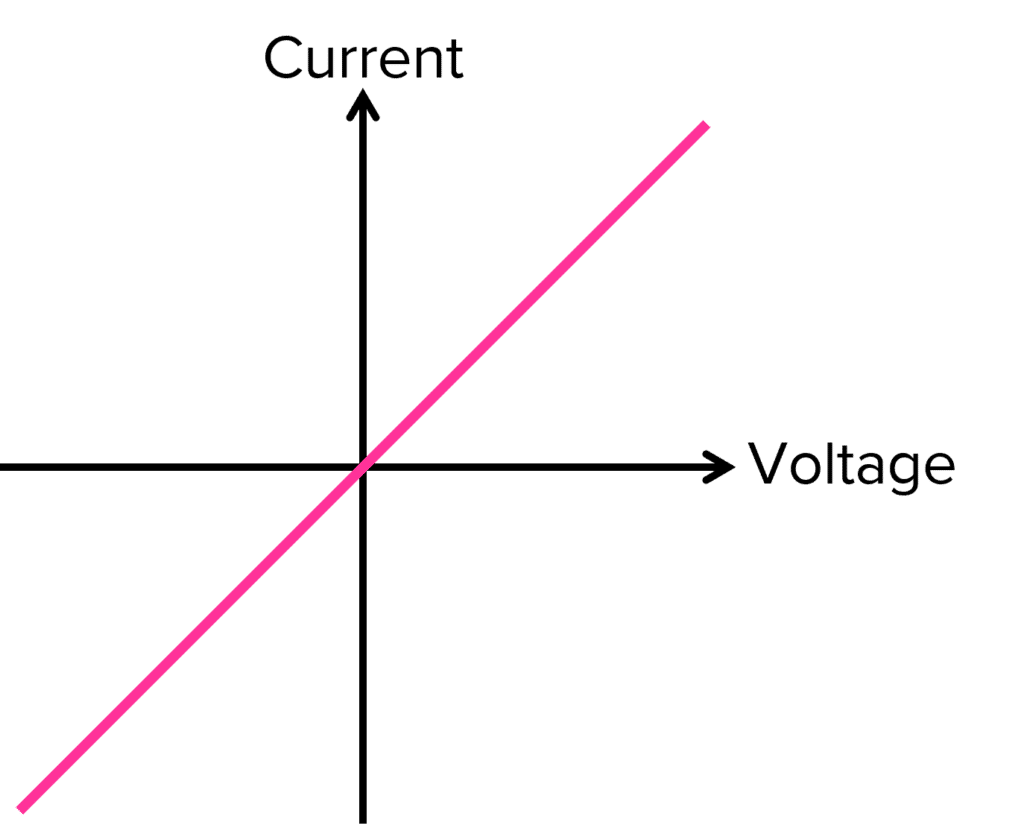
I-V characteristics graphs: resistor
I-V characteristics graphs: diode
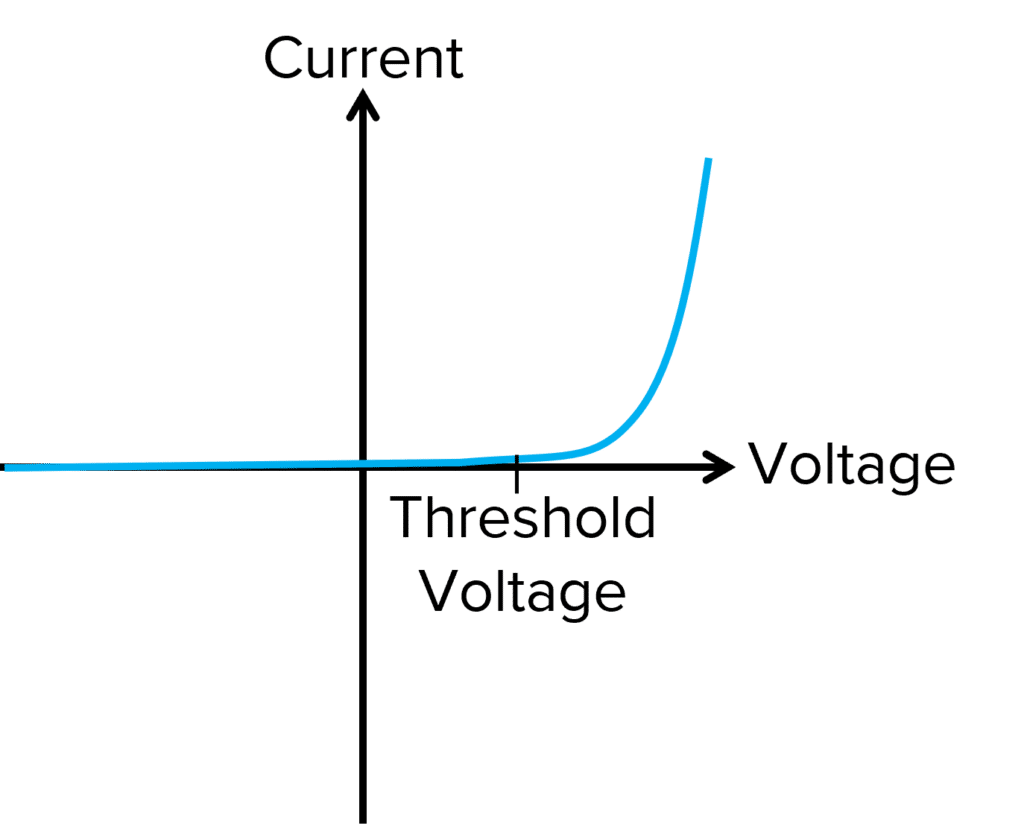
Forward bias
The current flows in the forward direction due to the voltage applied in the forward direction
What is the threshold voltage for a diode?
0.6V
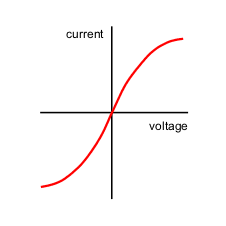
I-V characteristics graphs: filament lamp
Resistivity
The resistance of length 1m with a cross-sectional area of 1m2
What does resistivity tell you?
How difficult it is for current to flow through the material
What does resistance depend on?
Length
Area
Resistivity
Thermistor
A component with a resistance that depends on its temperature
What is a ‘Negative Temperature Coefficient’ (NTC) thermistor?
The resistance decreases as the temperature increases
Thermistor graph
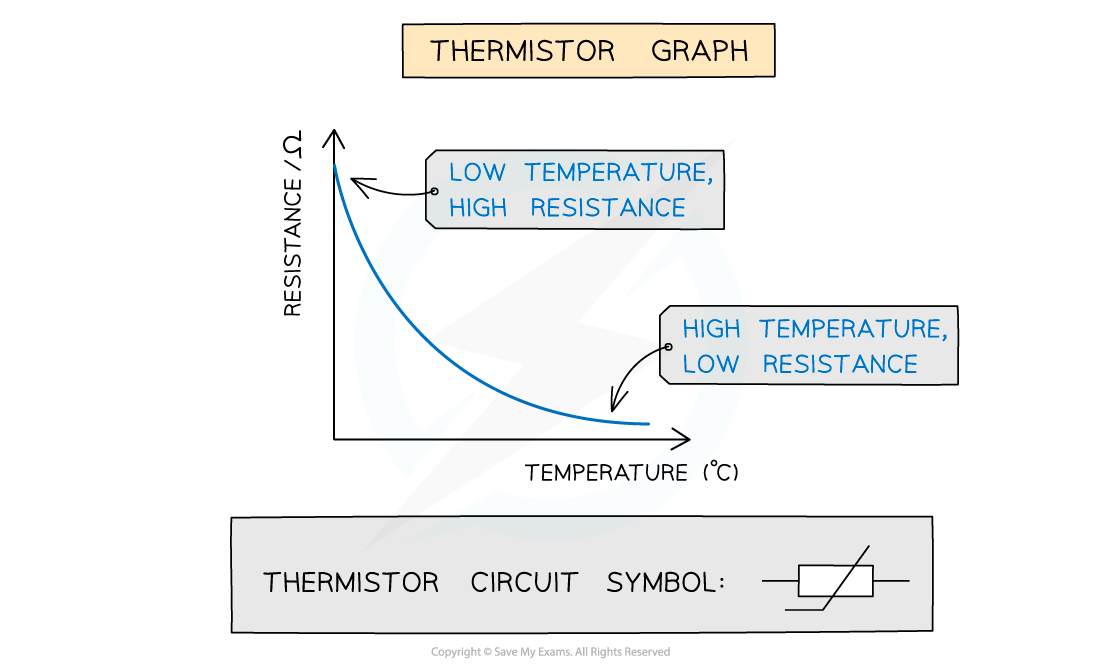
Explain the thermistor graph
Warming the thermistor gives more electrons enough energy to escape from their atoms. This means that there are more charge carriers available, so resistance is lower.
One use of thermistors
Temperature sensor
Superconductor
Carries electricity with 0 resistance
What is so good about superconductors?
No resistance, so none of the electrical energy is converted into heat, so none of it is wasted
How do you make something a supercondutor?
By cooling it down below its critical temperature
Uses of superconductors
Power cables that transmit electricity without any loss of power
Really strong electromagnets
Electronic circuits that work really fast with minimal energy loss
Discuss one advantage and one difficulty when using superconductors in electrical transmission over long distances
Advantage - no power will be lost
Difficulty - keeping the superconducting material below its critical temperature