Honors Biology - Unit 3
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
d. All of them
Which of the following types of cells has a cell membrane?
a. Plant
b. Animal
c. Bacteria
d. All of them
Eukaryotic
Which type of cells would you expect fungi to have?
Prokaryotic
Which type of cells would you expect bacteria to have?
Eukaryotic
Which type of cells would you expect protists to have?
Eukaryotic
Which type of cells would you expect plants and animals to have?
Prokaryote
This type of cell does NOT have a nucleus
Eukaryote
This type of cell is more complex
Prokaryote
This type of cell is small in size
Eukaryote
This type of cell has membrane-bound organelles
d. All cells are prokaryote at some stage
Which of the following is NOT part of the cell theory?
a. Cells come from other cells
b. All living things are made of cells
c. Cells are the basic units of structure and function
d. All cells are prokaryotic at some stage
True
True or false? At some point, all cells will contain DNA
False
True or false? You can use the coarse focus knob on any power.
c. Bacteria
Which of the following organisms are not eukaryotic?
a. Plant
b. Animal
c. Bacteria
d. Fungi
Robert Hooke
who discovered cells?
Anton van Leeuwenhoek
Who was the first to see living microorganisms in a sample of pond water?
A. Robert Hooke
Which of the following individuals did NOT contribute to the cell theory
a. Robert Hooke
b. Rudolf Virchow
c. Matthias Schleiden
d. Theodore Schwann
100x
Medium power = ______x (total magnification)
40x
Low power = _______x (total magnification)
400x
High power = ______x (total magnification)
10x
Ocular lens (eyepiece) = ________x
37,000um
You measure a specimen viewed under a microscope and determine it to be about 3.7cm in length. How long is it in um?
6.3cm
You measure a specimen viewed under a microscope and determine it to be about 63mm in length. How long is it in cm?
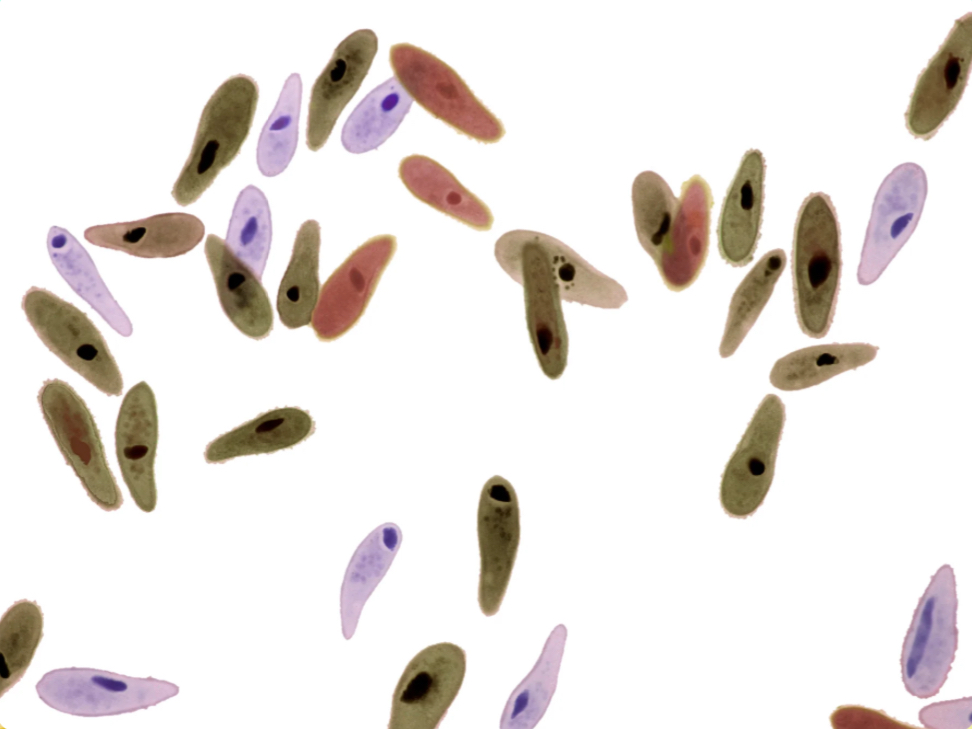
Protists
What types of cells are these?

Plant
What type of cell is this?
Animal cell
What type of cell is this?
Light microscope
A microscope where visible light is passed through a specimen and then through glass lenses
Scanning electron microscope
A microscope where an electron beam is used to study the surface details of a cell or other specimens
Transmission electron microscope
A microscope that uses an electron beam to study the internal structure of thinly sectioned specimens
Robert Hooke
The person who first identified cells in 1665 by using an early compound microscope by looking at a thin slice of cork (plant material)
Anton van Leeuwenhoek
A person who observed a sample of pond water using a single lens (simple) microscope
Matthias Schleiden
Came to the conclusion that plants are made of cells
Theodor Schwann
Came to the conclusion that animals are made of cells
Rudolf Virchow
Came to the conclusion that cells come from pre-existing cells
All living things are composed of cells
Cells are the basic units of structure and function
New cells are produced from existing cells
What are the three parts of the cell theory?
SA/V ratio
The ratio where cells need a surface area large enough to service volume of cell
Cell membrane
Contain DNA at some point
Cytoplasm
Ribosomes
What are 4 things all cells have
Prokaryote
A type of cell that has no nucleus present, no membrane-bound organelles, is smaller in size, has a simple form. Ex: bacteria
Eukaryote
A type of cell that has a nucleus, has membrane-bound organelles, is larger in size, is more complex. Ex: plants, animals, fungi, protists
Cell (plasma) membrane
The selectively permeable barrier that regulates the passage of substances into and out of the cell; composed of a phospholipid bilayer
Cell wall
A rigid outer layer of a plant cell, prokaryote, fungus, or protist that provides structural support and protection; located outside the plasma membrane.
Cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms; the smallest unit of life.
Chloroplast
An organelle found in plant cells and photosynthetic protists that is the site of photosynthesis.
Chromosome
A structure composed of a single, long DNA molecule coiled around associated proteins (histones); carries the genetic information (genes).
Coarse adjustment
The large, macro-control knob on a microscope used for initial, large-scale focusing when using low-power objective lenses.
Cytoplasm (cytosol)
all the cellular contents outside the nucleus, and the semi-fluid, aqueous component in it
Diaphragm
An adjustable mechanism (usually an iris) on a microscope that controls the amount and angle of light reaching the specimen.
Endomembrane System
A group of membranes and organelles in eukaryotic cells (ER, Golgi, lysosomes, vacuoles) that modify, package, and transport lipids and proteins.
Eyepiece (Ocular Lens)
The lens at the top of the microscope through which a user looks; typically provides a 10x magnification.
Field of View
The circular area visible when looking through the eyepiece of a microscope.
Fine adjustment
The small, micro-control knob on a microscope used for precise, sharp focusing, especially with high-power objective lenses.
Light Source
The built-in electric lamp or mirror at the base of the microscope that provides the illumination for viewing the specimen.
Magnification
The process of enlarging an object's apparent size. Calculated as: Eyepiece × Objective Lens.
Nucleoid
The non-membrane-bound region in a prokaryotic cell that contains the genetic material (DNA).
Nucleus
The membrane-bound organelle in a eukaryotic cell that contains the cell's genetic material (DNA) and controls cell activities.
Objective Lens
The set of adjustable lenses mounted on the nosepiece (e.g., 4x,10x,40x) that are positioned directly above the specimen.
Organelle
A specialized membrane-bound structure within a eukaryotic cell that performs a specific function.
Ratio
A comparison of two quantities by division, often used in biology (e.g., surface area to volume ratio).
Ribosome
A non-membrane-bound cellular structure that is the site of protein synthesis (translation).
Rotating Nosepiece
The turret on a microscope that holds the objective lenses and allows the user to switch between magnifications.
Stage
The flat platform on a microscope where the specimen slide is placed for viewing.
Stage Clips
Metal clips on the microscope stage used to hold the slide securely in place.
Surface Area
The total exposed area of an object's outer boundary (e.g., the plasma membrane of a cell).
Turgidity
The internal pressure exerted by water against the cell wall, which makes plant cells rigid and firm.
Vacuole
A large, membrane-bound sac in a plant cell that stores water, nutrients, and waste; helps maintain turgor pressure.
Volume
The amount of three-dimensional space occupied by an object (e.g., the inside space of a cell).
Wet-Mount Slide
A temporary slide preparation created by placing a specimen in a drop of water (or liquid) and covering it with a coverslip.
Cytoplasm
Liquid portion of the cell that surrounds the nucleus and supports all the organelles
Nucleus
Control center if the cell that contains a cell’s DNA
Vacuole
Storage center of a cell (much larger in plant cells).
Chloroplast
Organelle where photosynthesis occurs in a plant cell
Ribosome
Organelle responsible for making proteins
Plant cell and bacteria
Which type of cell from the list has a CELL WALL?
a. Animal cell
b. Plant cell
c. Bacteria
Animal cell
Which type of cell from the list is more irregular in shape? Animal cell or plant cell
Plant cell
Which type of cell from the list is more geometric in SHAPE? Plant cell or animal cell
Plant cell
Which type of cell has a single large vacuole? Animal cell or plant cell
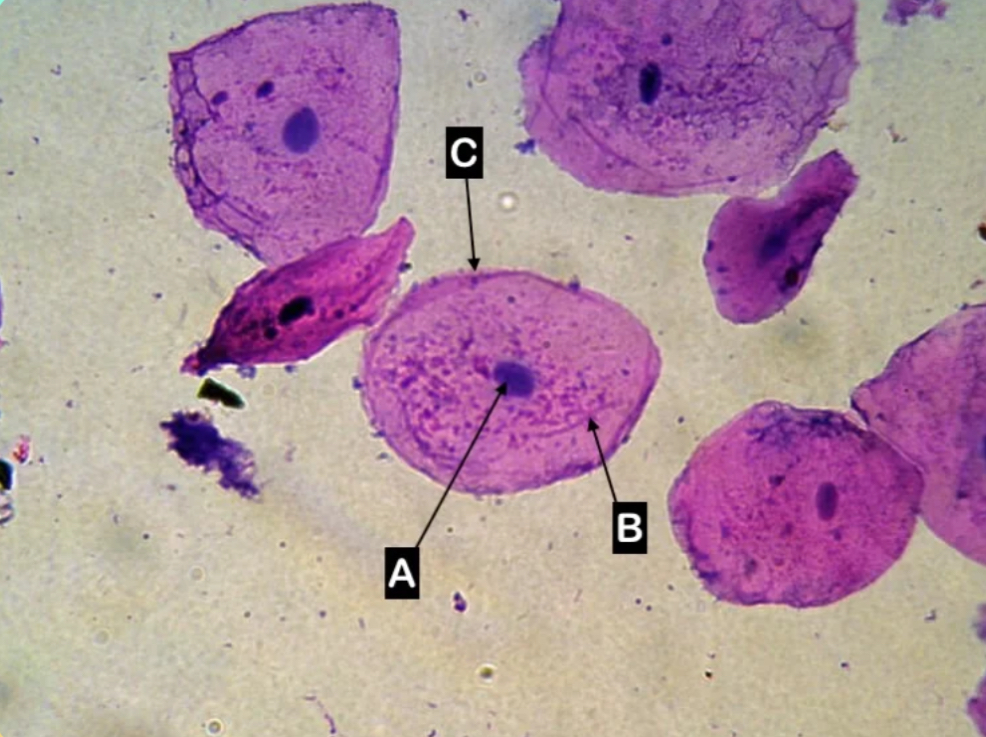
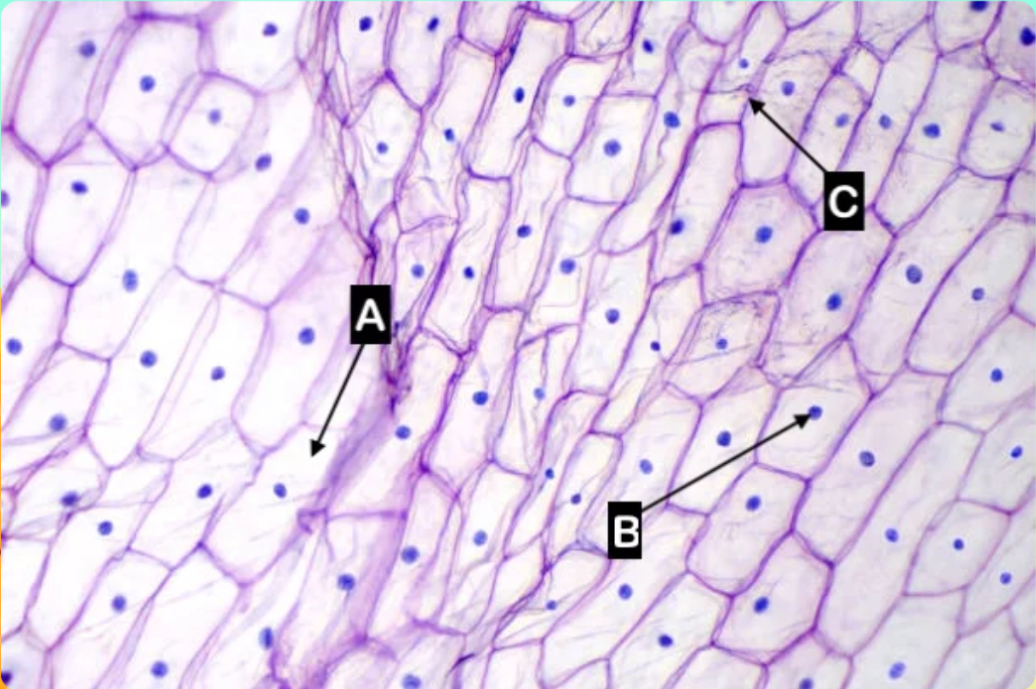
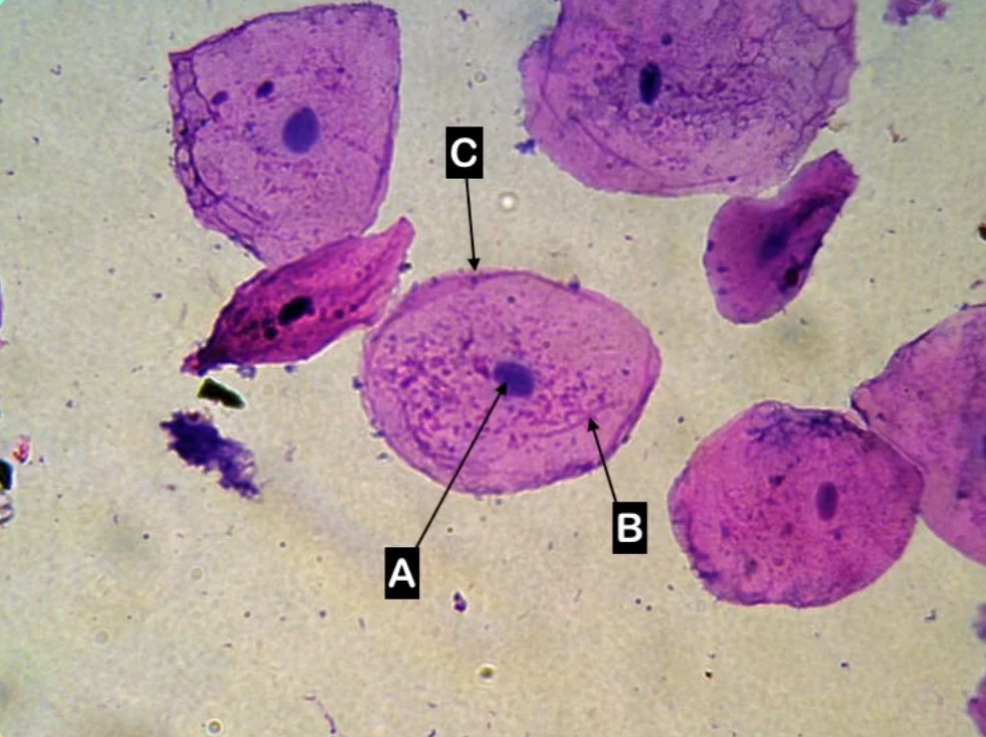
A
Which letter is pointing to the cytoplasm of the cell?
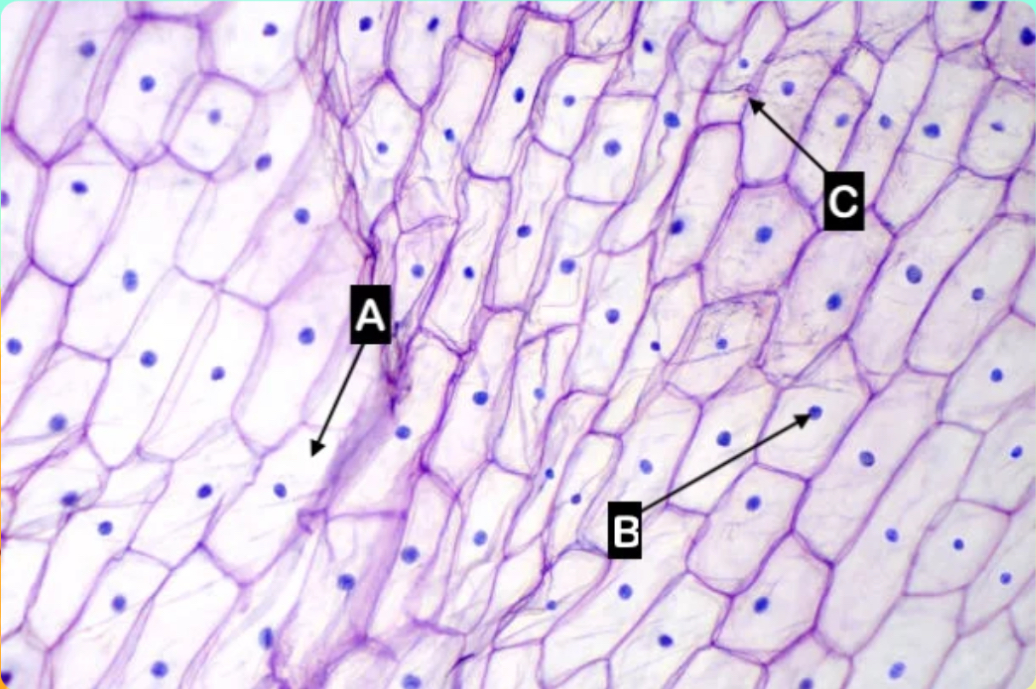
C
Which letter is pointing to the cell wall of the cell
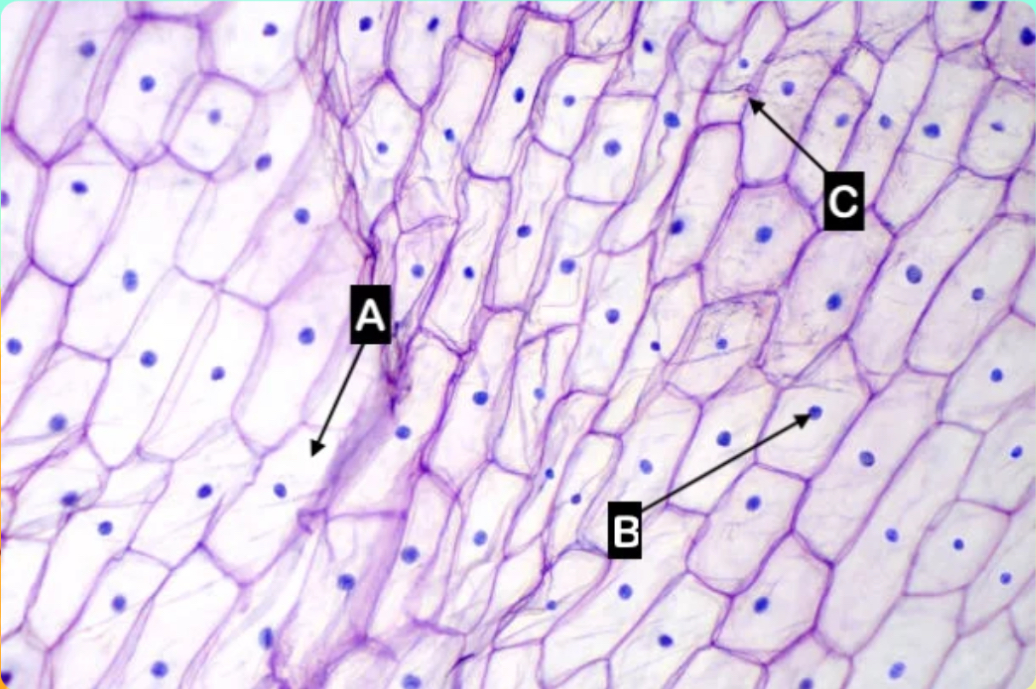
None of these
Which letter is pointing to the cell wall of the cell?
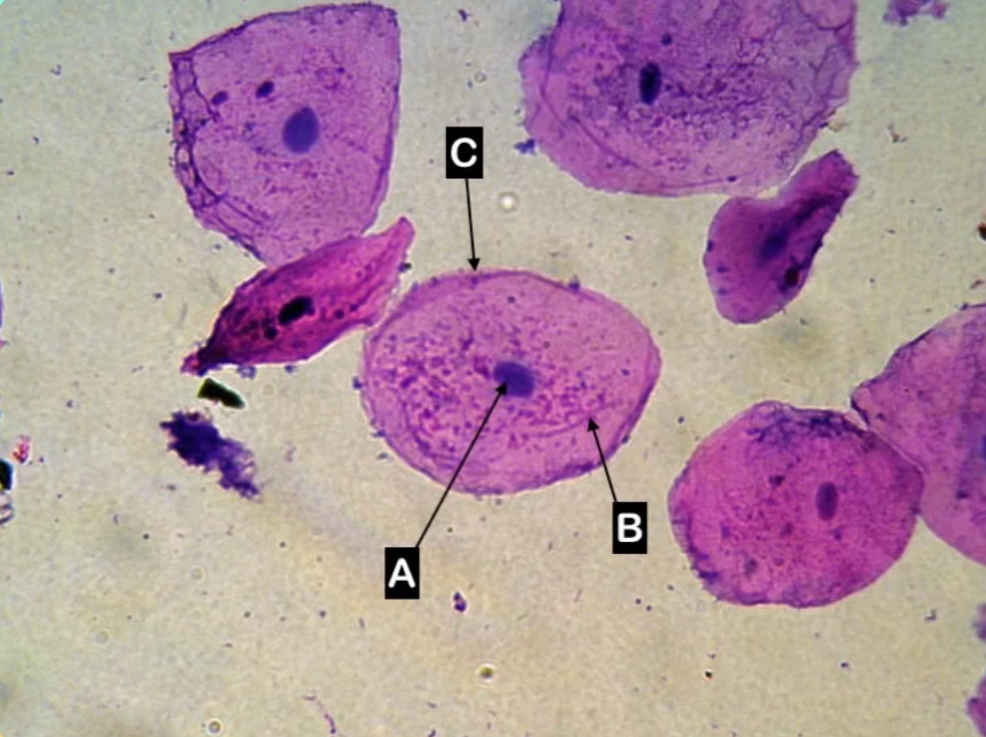
C
Which letter is pointing to the cell membrane of the cell?
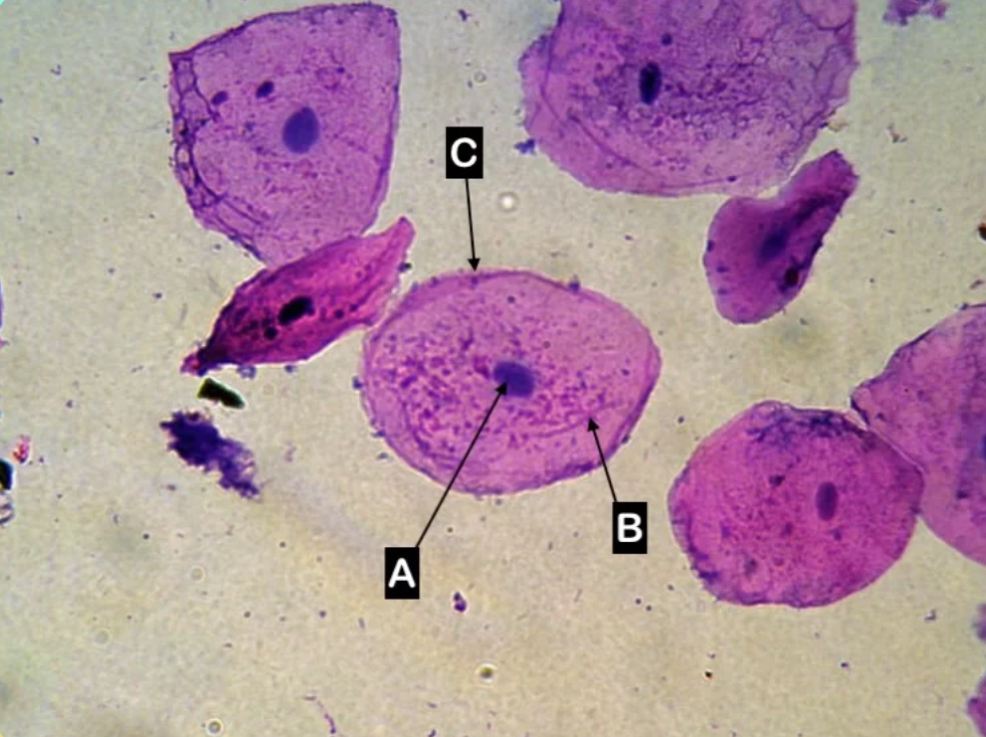
A
Which letter is pointing to the nucleus of the cell?
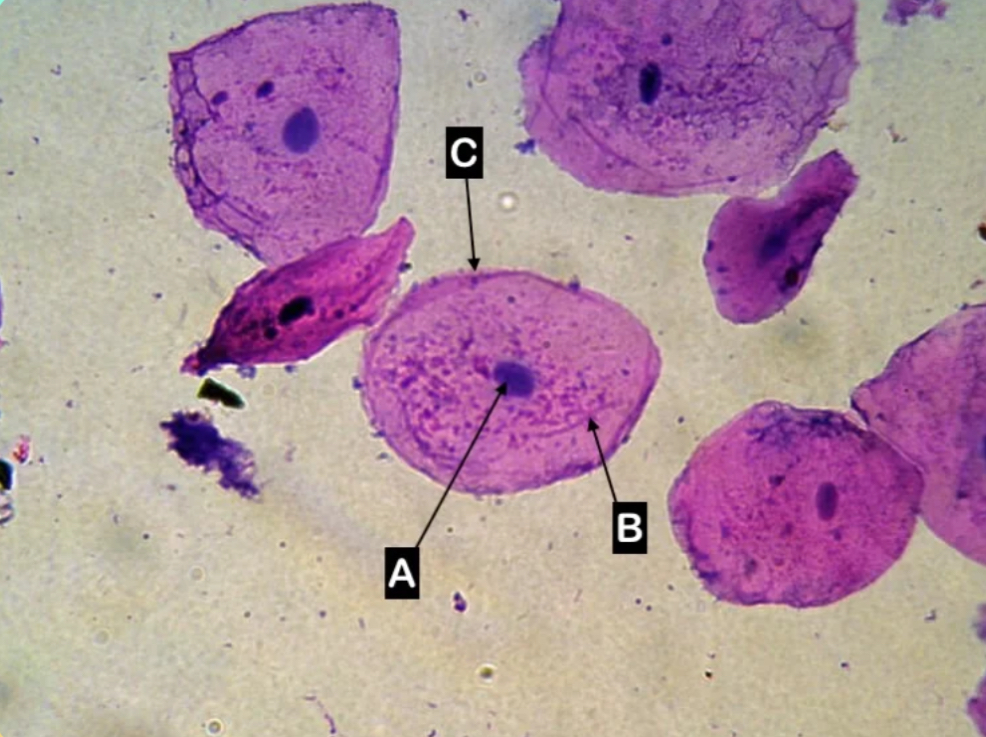
Animal cell
What type of cell is this?