Princeton Review AP Environmental Science Chapter 7
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
resource
any substance, capability (such as work performed by humans or animals), or other asset that is available in a supply that can be accessed and drawn on as needed
natural resources
resources that occur in nature
the Tragedy of the Commons
situation in which people acting individually and in their own interest use up commonly available but limited resources, creating disaster for the entire community (initially observed by William Foster Lynch, but later documented by Garrett Hardin in example of grazing land and cattle)
commons
a piece of open land for recreational use in an urban area
conservation
the management or regulation of a resource so that its use does not exceed the carrying capacity of the resource to regenerate itself
preservation
the maintenance of a species or ecosystem in order to ensure their perpetuation, with no concern as to their potential monetary value
ecosystem capital
sum of all the goods and
services provided by natural systems to
humans (natural capital)
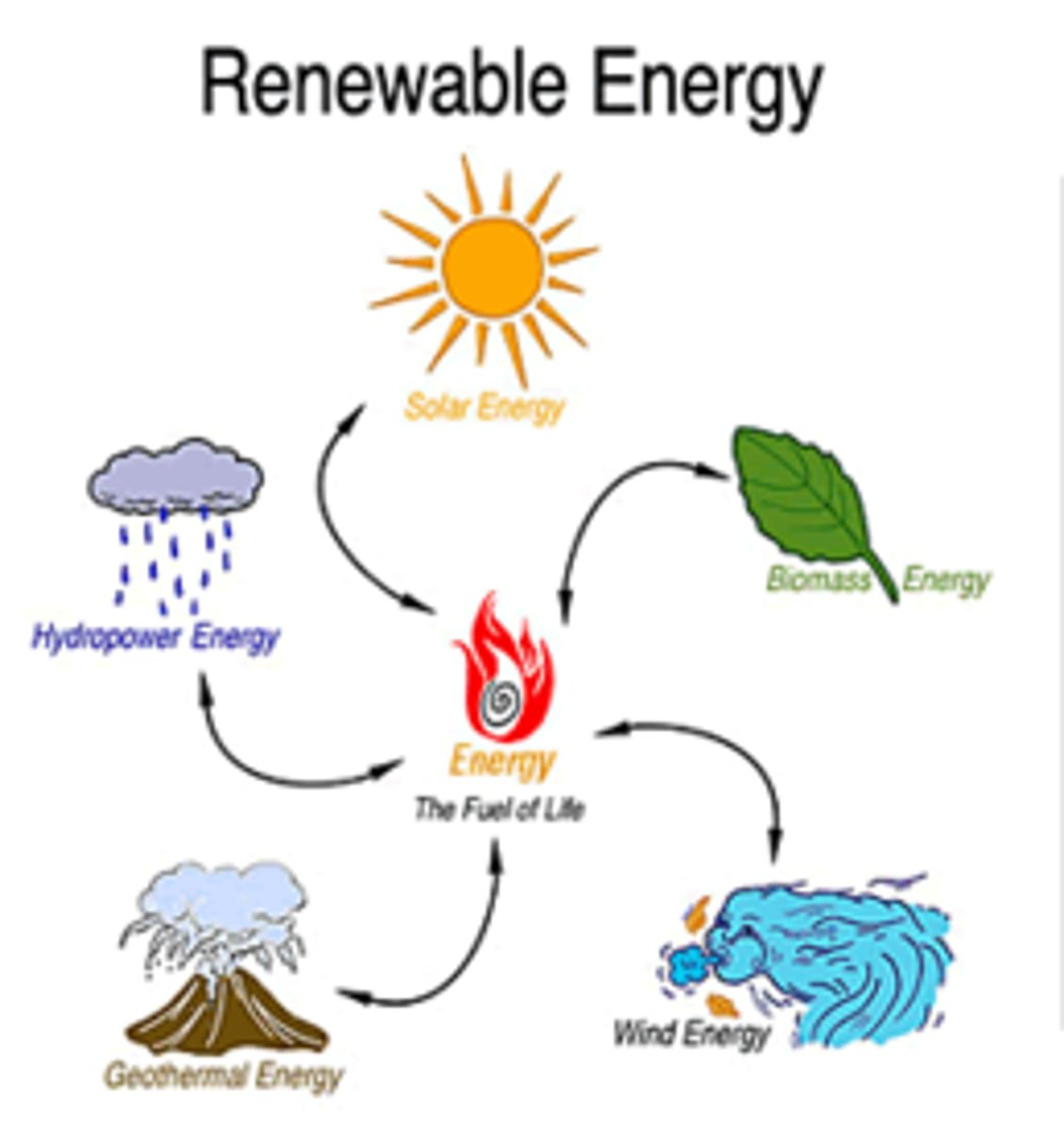
renewable resources
any natural resource that can replenish itself in a relatively short period of time, usually no longer than the length of a human life (ex. water, sun, wind, and the tides) (trees also if harvested in sustainable manner)
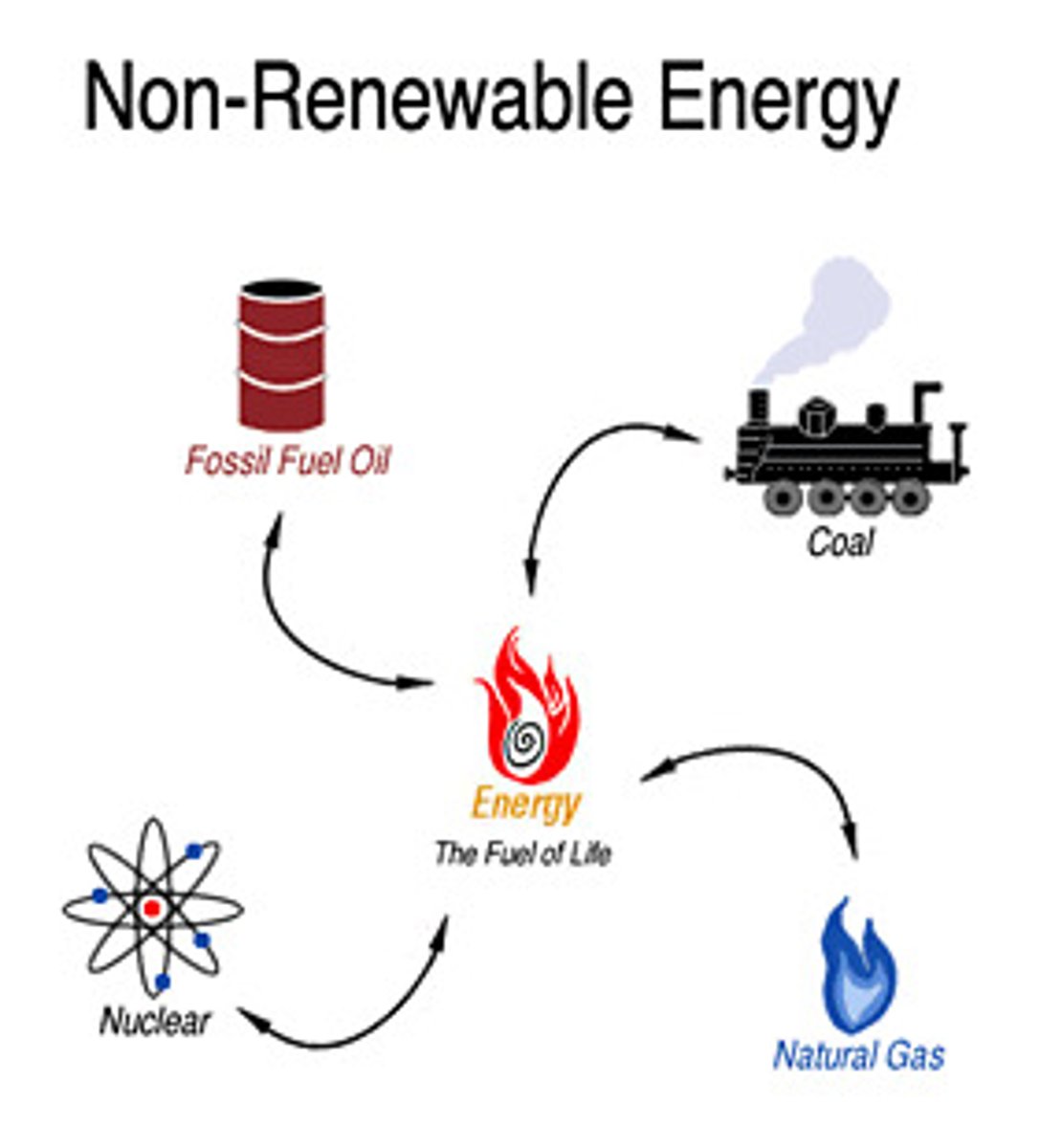
nonrenewable resources
a natural resource that is not replaced in a useful time frame (ex. minerals and fossil fuels)
consumption
refers to the day-to-day use of environmental resources such as food, clothing, and housing
production
refers to the use of environmental resources for profit
traditional subsistence agriculture
production of enough crops or livestock for a farm family's survival and, in good years, a surplus to sell or put aside for hard times; currently practiced by 42% of global population

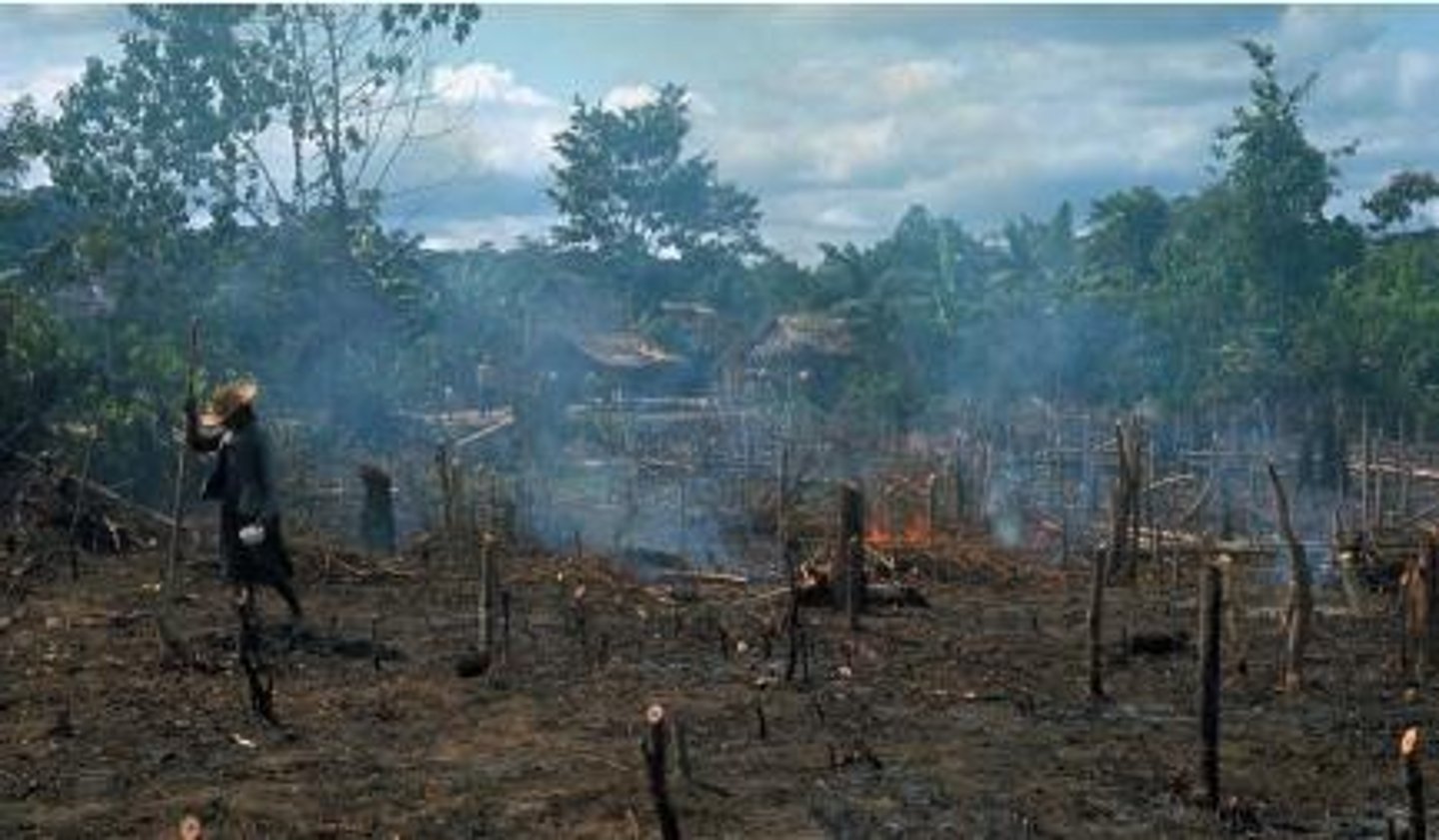
slash and burn
a farming method involving the cutting of trees, then burning them to provide ash-enriched soil for the planting of crops; common in the tropics

Green Revolution
rapid diffusion of new agricultural technology, especially new high-yield seeds and fertilizers
Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA)
law that requires the EPA to approve the use of all pesticides in the United States
salinization
accumulation of salts in soil that can eventually make the soil unable to support plant growth; caused by irrigation
integrated pest management (IPM)
an agricultural practice that uses a variety of techniques designed to minimize pesticide inputs; more environmentally sensitive approach than chemical pesticides that uses a combination of several methods to attack pests
genetically modified organisms (GMOs)
crops that carry new traits that have been inserted through advanced genetic engineering methods
GMO cons
discourage biodiversity, may harm beneficial insects and organisms, could pose new allergen risks, may increase antibiotic resistance, and could cause new pesticide-resistant pests
photosynthate
a sugar or other substance made by photosynthesis
monoculture
farming strategy in which large fields are planted with a single crop, year after year
plantation farming
a type of industrialized agriculture in which a monoculture cash crop is grown and then exported to developed nations (mainly in tropical developing nations)
Dust Bowl
region of the Great Plains that experienced a drought in 1930 lasting for a decade, leaving many farmers without work or substantial wages; caused by severe drought and unsustainable farming practices
Soil Conservation Act (1935)
districts were set up by the United States Soil and Conservation Service, of which these franchises provided education to farmers; established in light of the Dust Bowl
contour plowing
rows of crops are plowed across the hillside, thus preventing the erosion that can occur when rows are cut up and down on a slope

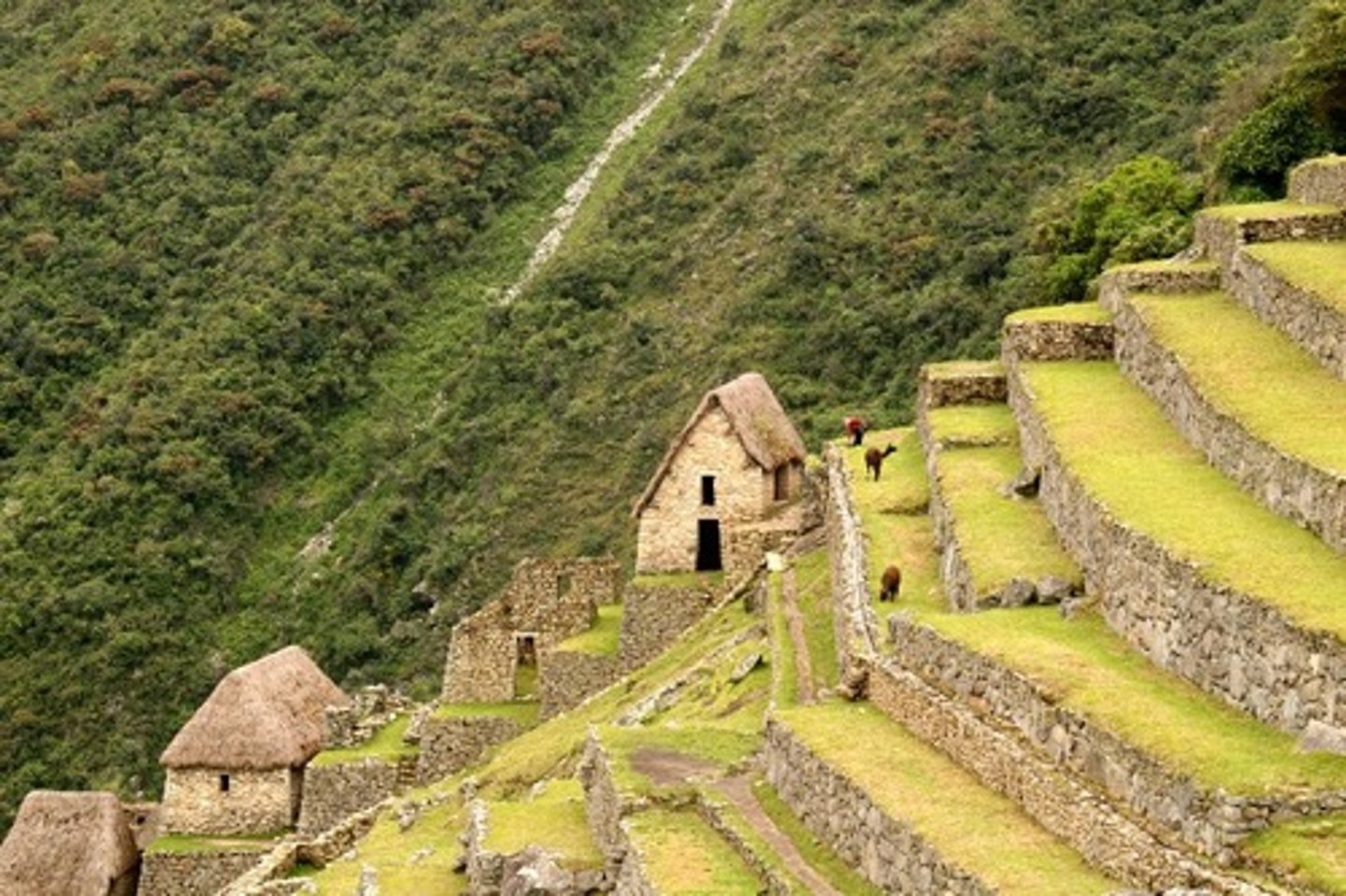
terracing
creating flat platforms in the hillside that provide a level planting surface, which reduces soil runoff from the slope
terrace
a raised, flat mound of earth (dirt) that looks like a platform with sloping sides

no-till methods
farmers plant seeds without using a plow to turn the soil
rice, wheat, and corn
3 main grains that provide more than half of the calories consumed worldwide
crop rotation
the system of growing a different crop in a field each year to preserve the fertility of the land; provides soils with nutrients when legumes are part of the cycle of crops in an area
intercropping (strip cropping)
the practice of planting bands of different crops in a field; can prevent soil erosion by creating an extensive network of roots
overgrazed
when grass is consumed by animals at a faster rate than it can regrow
the Bureau of Land Management
the federal bureau responsible for the managing of federal rangelands
deforestation
the removal of trees for agricultural purposes or purposes of exportation
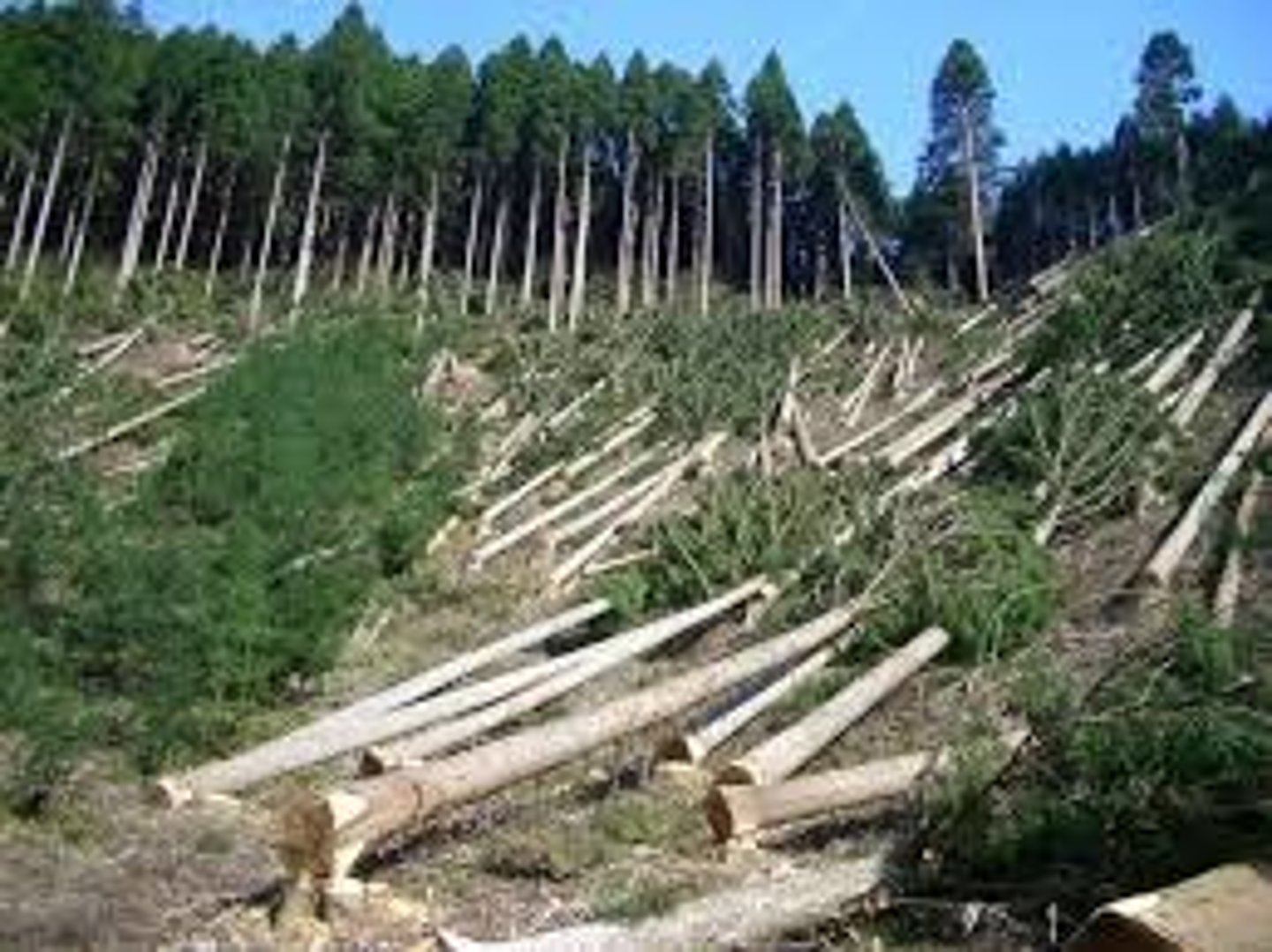

clear-cutting
the process of cutting down all the trees in an area at once

clear-cutting cons
great deal of runoff due to the loss of root structure- more erosion; soil is washed into streams and affects pH; higher stream temperatures; affects precipitation
deforestation of tropical rainforests cons
loss of biodiversity and erosion + depletion of soil's nutrients
Forest Stewardship Council
has developed certifying procedures based on standards that will encourage only the use of wood from sustainable forests
old growth forest
a forest that has never been cut; these forests have never been seriously disturbed for several hundred years; contain incredible biodiversity- myriad habitats and highly evolved, intricate niches for a multitude of organisms
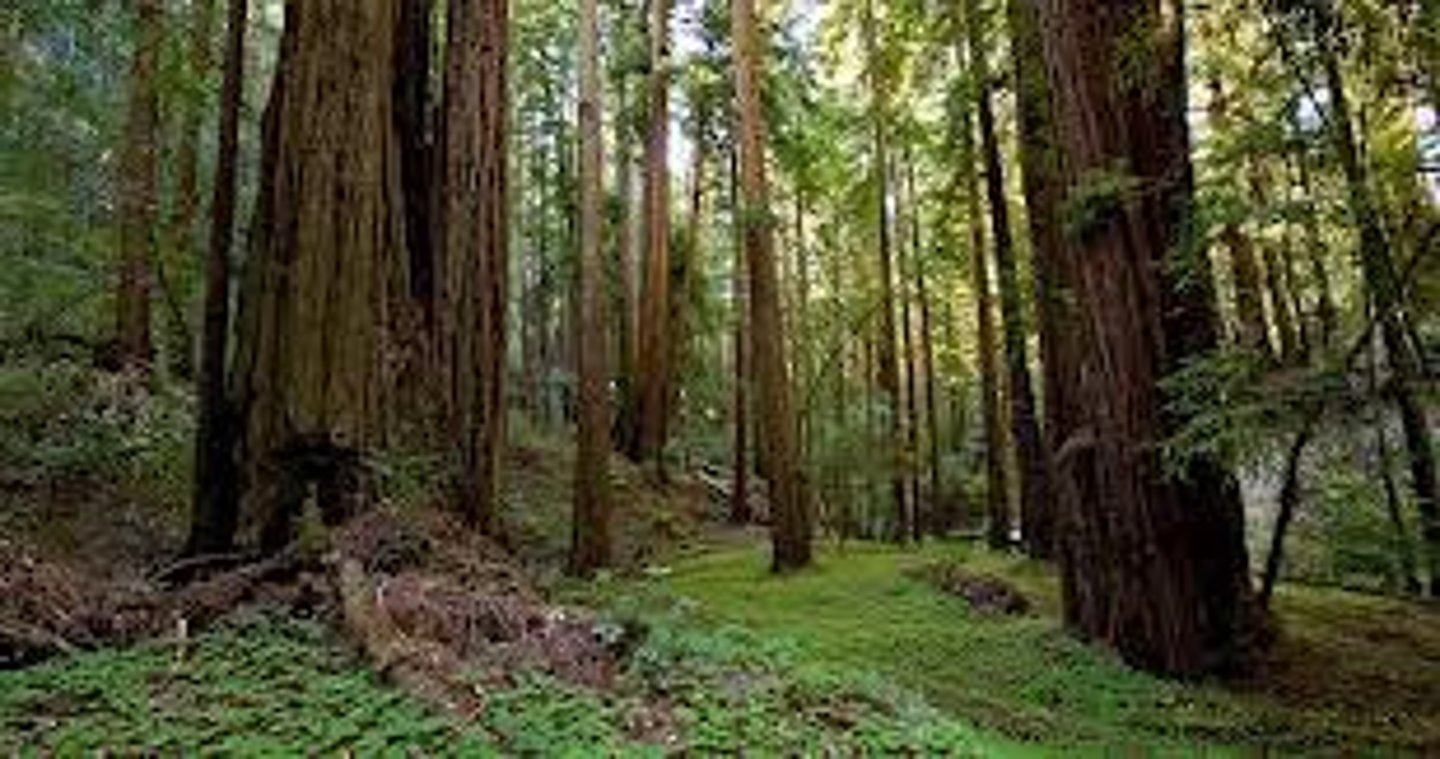

second growth forest
a forest where cutting has occurred, and a new, younger forest has arisen naturally
plantations (tree farms)
planted and managed tracts of trees of the same age that are harvested for commercial use

siviculture
the management of forest plantations for the purpose of harvesting timber; has a basic tenet to create a sustainable yield; to do this, humans must harvest only as many trees as they can replace through planting (clear-cutting and selective cutting)
selective cutting
the removal of select trees in an area; leaves the majority of the habitat in place and has less of an impact on the environment
uneven-aged management
method of forest management in which trees of different species in a given stand are maintained at many ages and sizes to permit continuous natural regeneration
shelter-wood cutting
when mature trees are cut over a period of time (usually 10-20 years); this leaves mature trees, which can reseed the forest, in place
agroforestry
an agricultural technique in which trees and crops are planted together; initiates a mutualistic symbiotic relationship: trees create habitats for animals that prey upon the pests that harm crops, and their roots stabilize and enrich the soil

28%
percentage of the United States' land that the federal government owns
Wilderness Act (1964)
established a review of road-free areas of 5,000 acres or more and islands within the National Wildlife Refuges or the National Park System for inclusion in the National Preservation System; restricted activities in these areas
Wild and Scenic Rivers Act (1968)
established a National Wild and Scenic Rivers System for the protection of rivers with important scenic, recreational, fish and wildlife, and other values
greenbelts
open or forested areas built at the outer edge of a city; increase the quality of life for people living nearby and put limits on urban growth

surface fires
fires that typically burn only the forest's underbrush and do little damage to mature trees; serve to protect the forest from more harmful fires by removing underbrush and dead materials that would burn quickly and at high temperatures if they accumulate, escalating more severe fires
crown fires
fires that may start on the ground or in the canopies of forests that have not experienced recent surface fires; spread quickly and are characterized by high temperatures because they consume underbrush and dead material on the forest floor; huge threat to wildlife, human life, and property
ground fires
smoldering fires that take place in bogs or swamps and can burn underground for days or weeks; originate from surface fires; difficult to detect and extinguish
prescribed burns
small fires are started when the conditions are just right and which lower the amounts of fuel
fishery
a commercially harvestable population of fish within a particular ecological region
capture fisheries
fish production in which fish are caught in the wild instead of being raised in captivity for consumption; most common practice
by-catch
species of fish, mammals, and birds that are caught during fishing operations but are not the target fish (highly used example: dolphins)
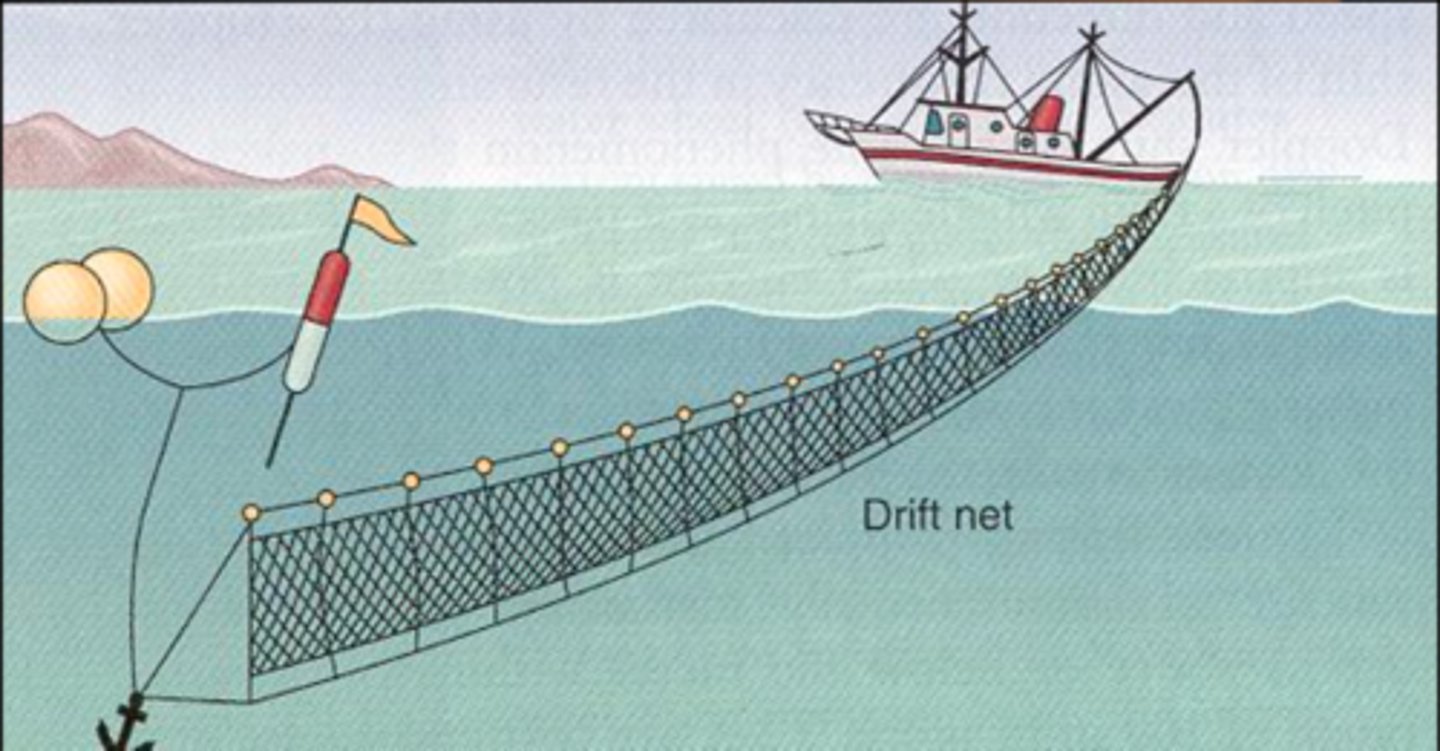
drift nets
nets that drift through the water and indiscriminately catch everything in their path
long lining
the use of long lines that have baited hooks and will be taken by numerous aquatic organisms
bottom trawling
the ocean floor is scraped by heavy nets that scrape away or smash everything in their path, including corals and other delicate marine life
seamounts
underwater sea mountains
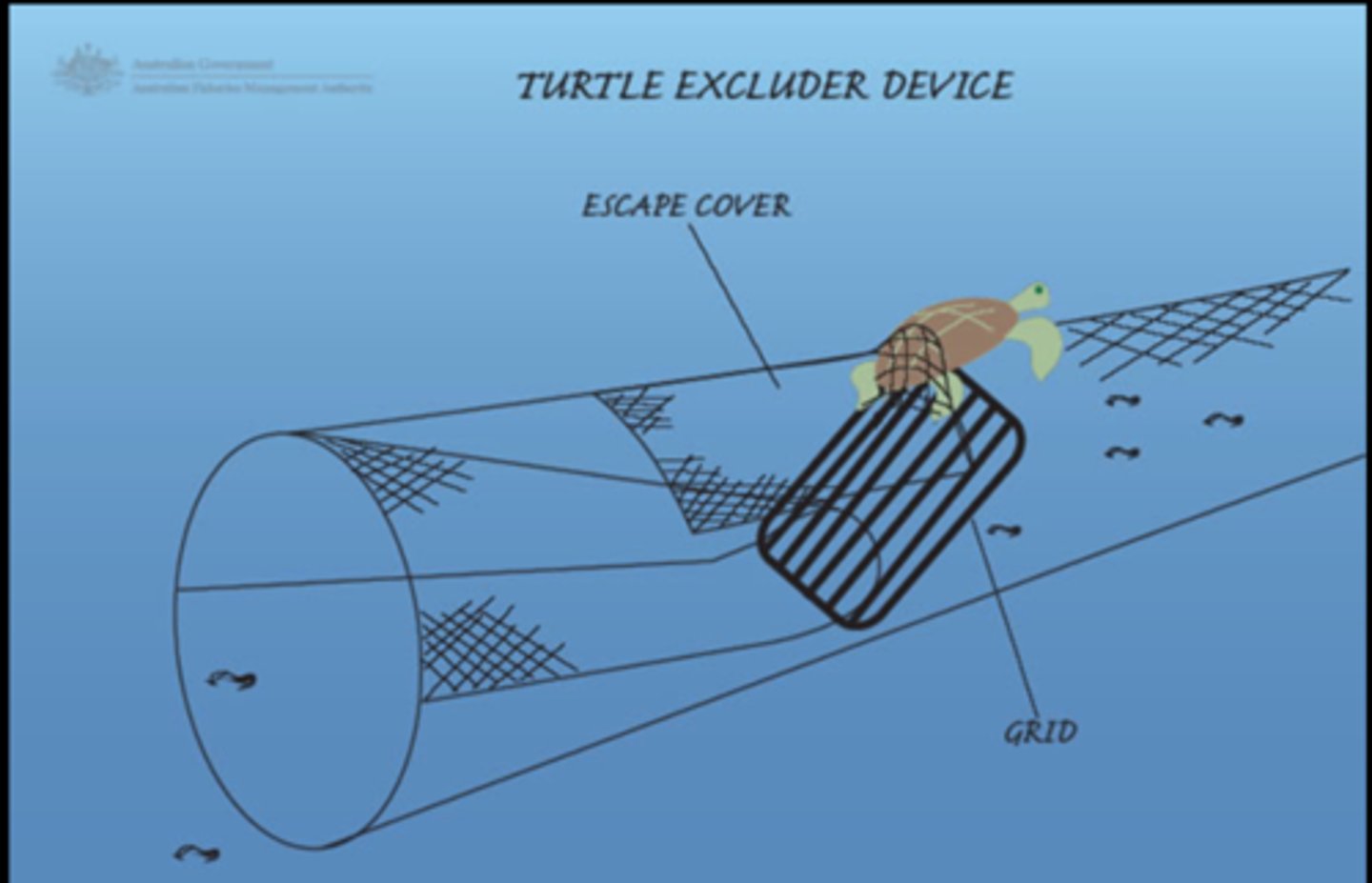
Turtle Excluder Device (TED)
device located at the end of the trawling net that will eject large organisms such as sea turtles and sharks from the net while keeping most of the shrimp
aquaculture (fish farming)
the raising of fish and other aquatic species in captivity for harvest
aquaculture cons
accidental release of fish may introduce new diseases to ocean fish and contaminate the native gene pool
International Whale Commission (1974)
a law that regulates whaling
cnidarians
small marine animals that create coral reefs; involved in mutualistic relationships with zooxanthellae
zooxanthellae
a yellowish-brown symbiotic dinoflagellate present in large numbers in the cytoplasm of many marine invertebrates
coral bleaching
higher-than-usual water temperatures cause the death of zooxanthellae, and this in turn causes the death of the coral reef
mangrove swamps
coastal wetlands- areas of land covered in freshwater, saltwater, or a combination of both- found in tropical and subtropical regions; characterized by trees, shrubs, and other plants that can grow in brackish waters and are often located in estuaries
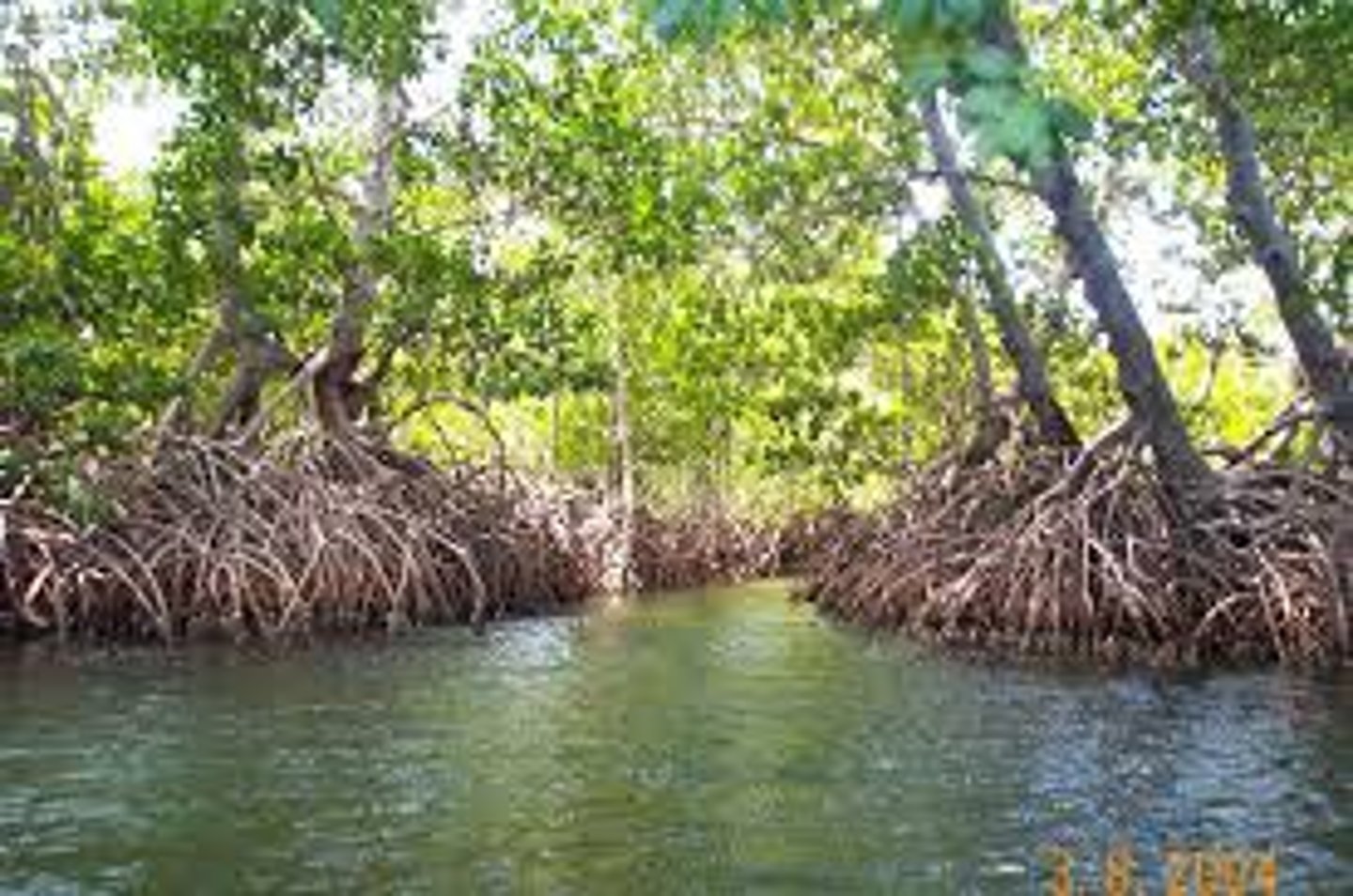

estuaries
areas where freshwater meets saltwater

Anadromous Fish Conservation Act (1965)
an act that protected fish that live in the sea but grow up and breed in freshwater (ex. salmon)
Magnuson Fishery Conservation and Management Act (1976)
an act that governed the conservation and management of ocean fishing
Marine Mammal Protection Act (1972)
an act that established a federal responsibility to conserve marine mammals
Endangered Species Act (1973)
an act that provided broad protection for species of fish, wildlife, and plants that are listed as threatened or endangered in the United States or elsewhere
the United Nations Agreement for the Implementation of the Provisions of the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (1982)
an act that set out the principles for the conservation and management of certain types of fish
the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) (1975)
an international agreement that ensured that international trade in species of wild animals and plants do not threaten their survival
mining
the excavation of earth for the purpose of extracting ore or minerals
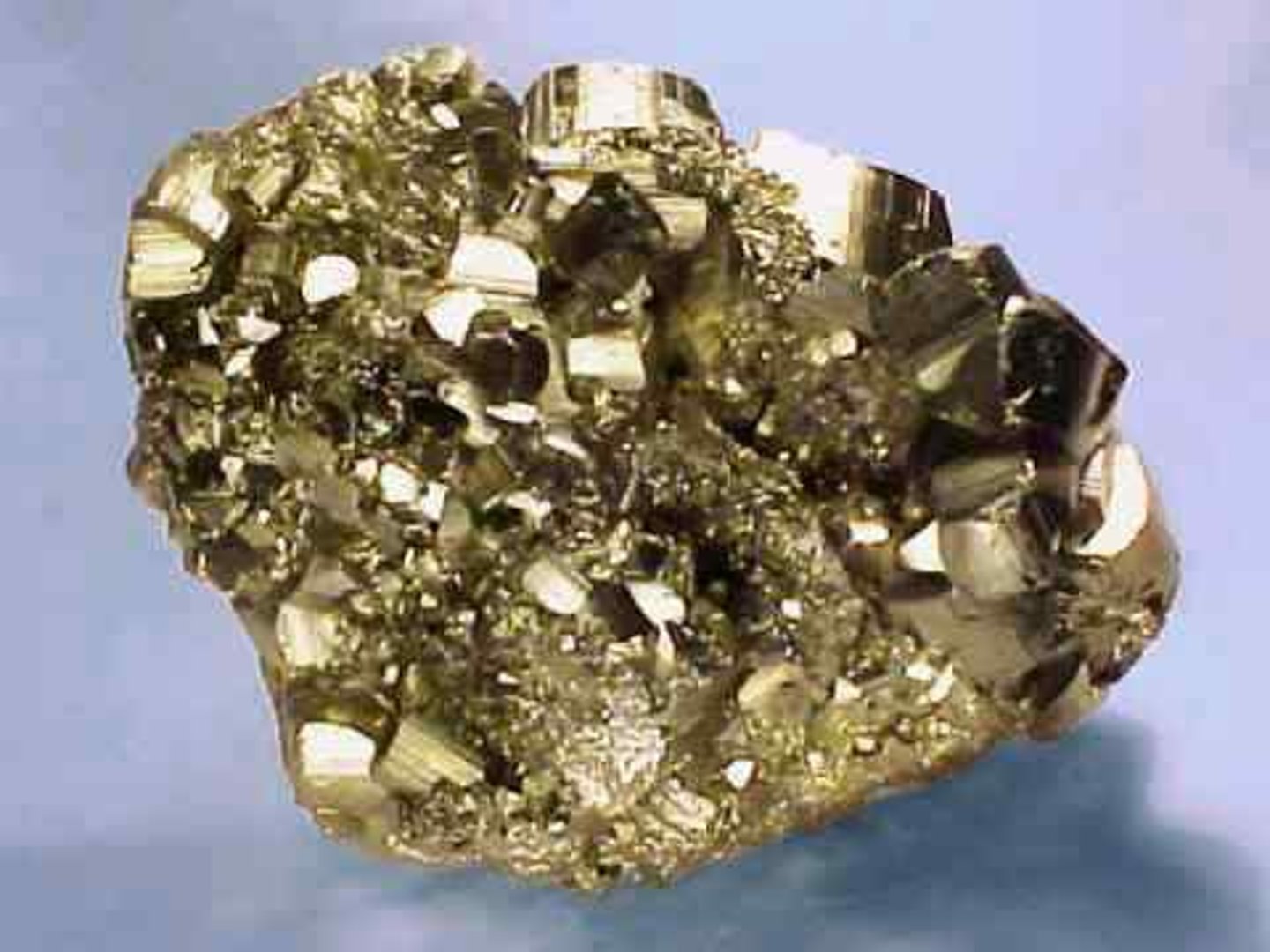
metallic minerals
have shiny surfaces, do not let light shine through them, and are good conductors of heat and electricity; mined for their metals that can be extracted via smelting (ex. zinc)

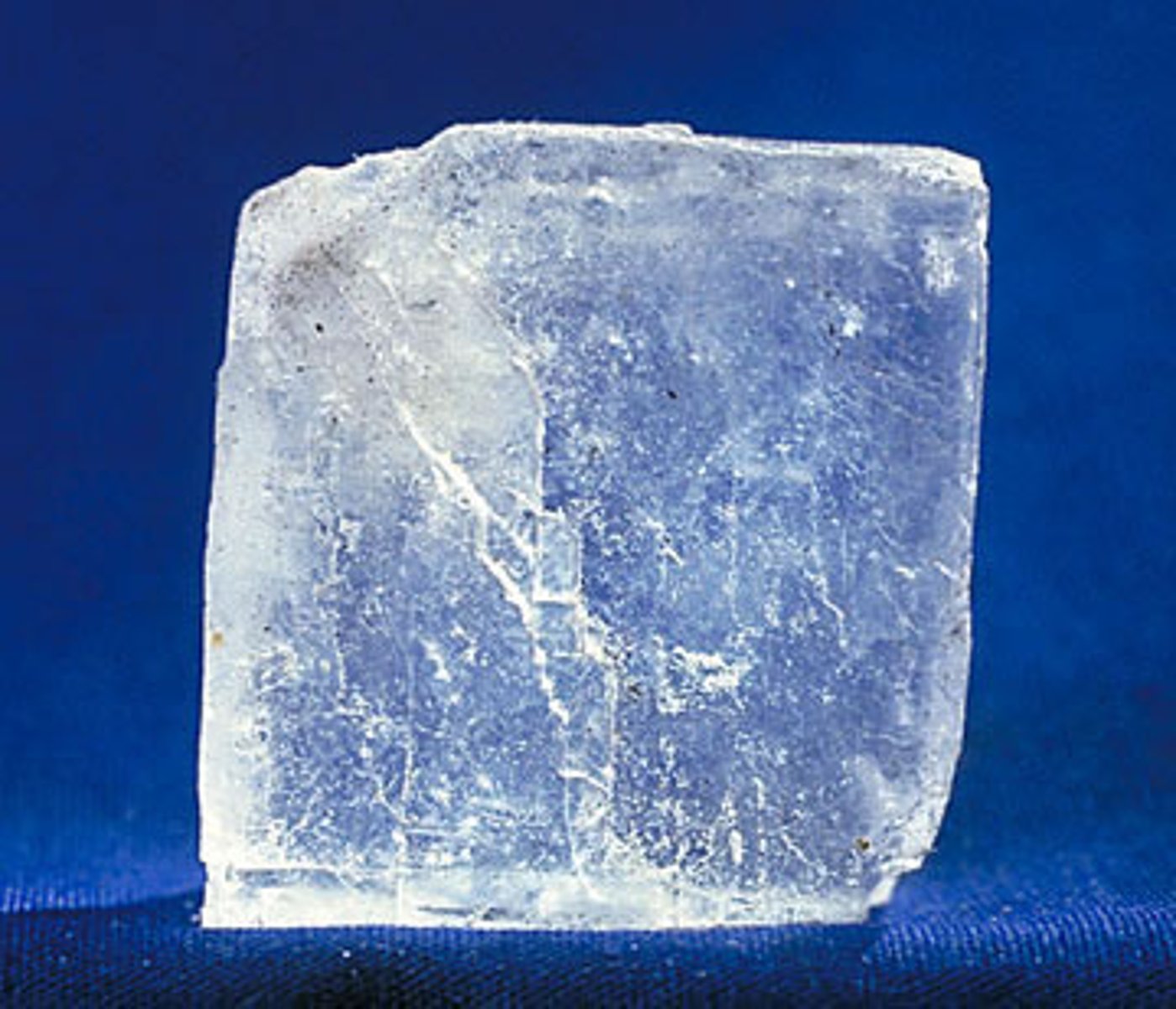
nonmetallic minerals
nonmetals that have a shiny (glassy) or dull surface, may let light pass through, and are insulators of heat and electricity; mined to be used in their natural state- nothing is extracted from them (ex. salt and precious gems)

smelting
the process by which ore is melted to separate the useful metal from other elements
mineral deposit
an area in which a particular mineral is concentrated
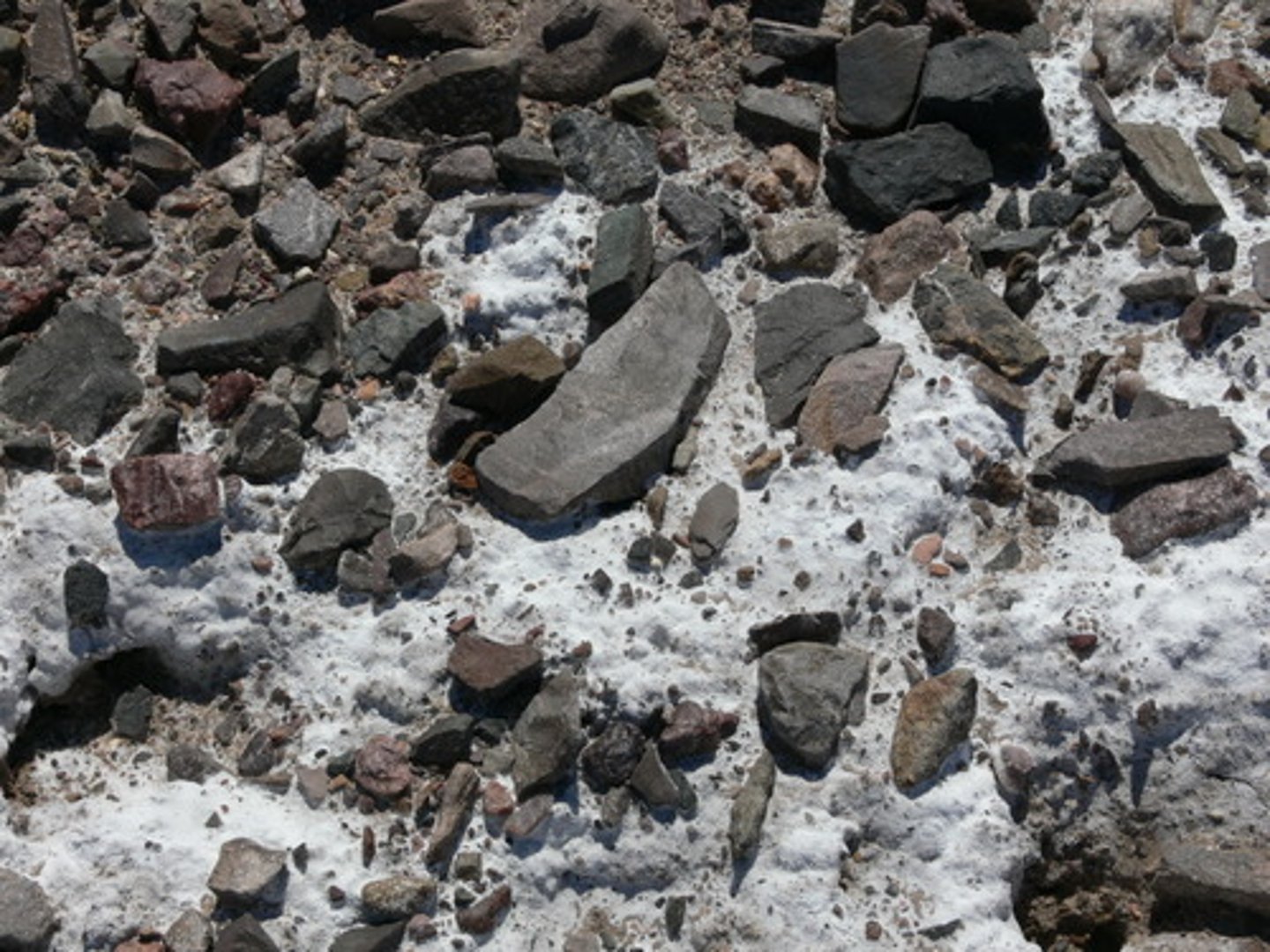

ore
a rock or mineral from which a valuable substance can be extracted at a profit

sulfuric acid
main acid released as a by-product of mining
gangue
waste material of mining processes
tailings
piles of gangues
strip mining
involves stripping the surface layer of soil and rock in order to expose a seam of mineral ore; mineral must be very close to surface; least expensive and least dangerous mining method; removes massive amounts of topsoil
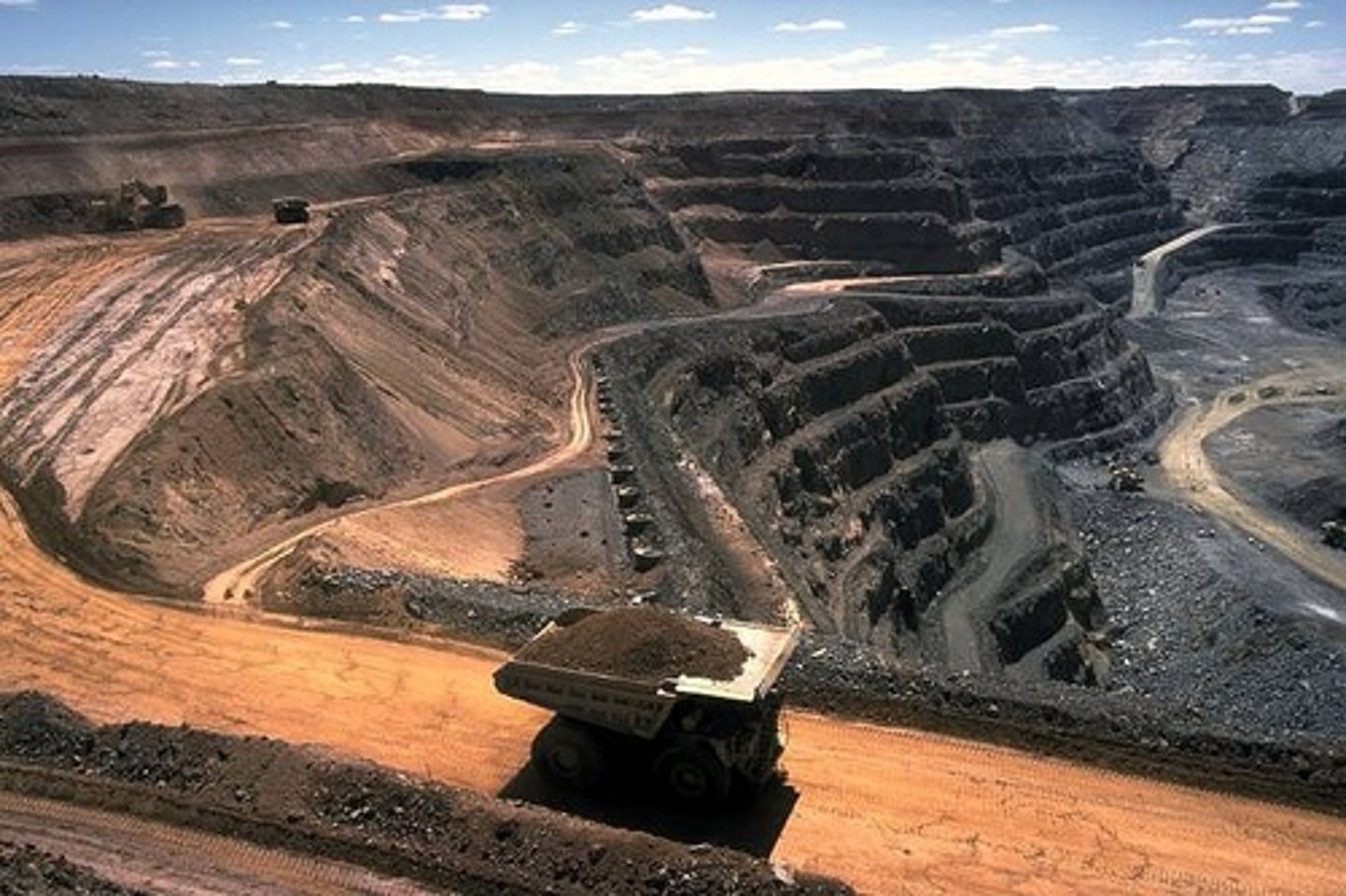

overburden
the surface layer of soil and rock of land
mountaintop removal
a mining technique in which the entire top of a mountain is removed with explosives

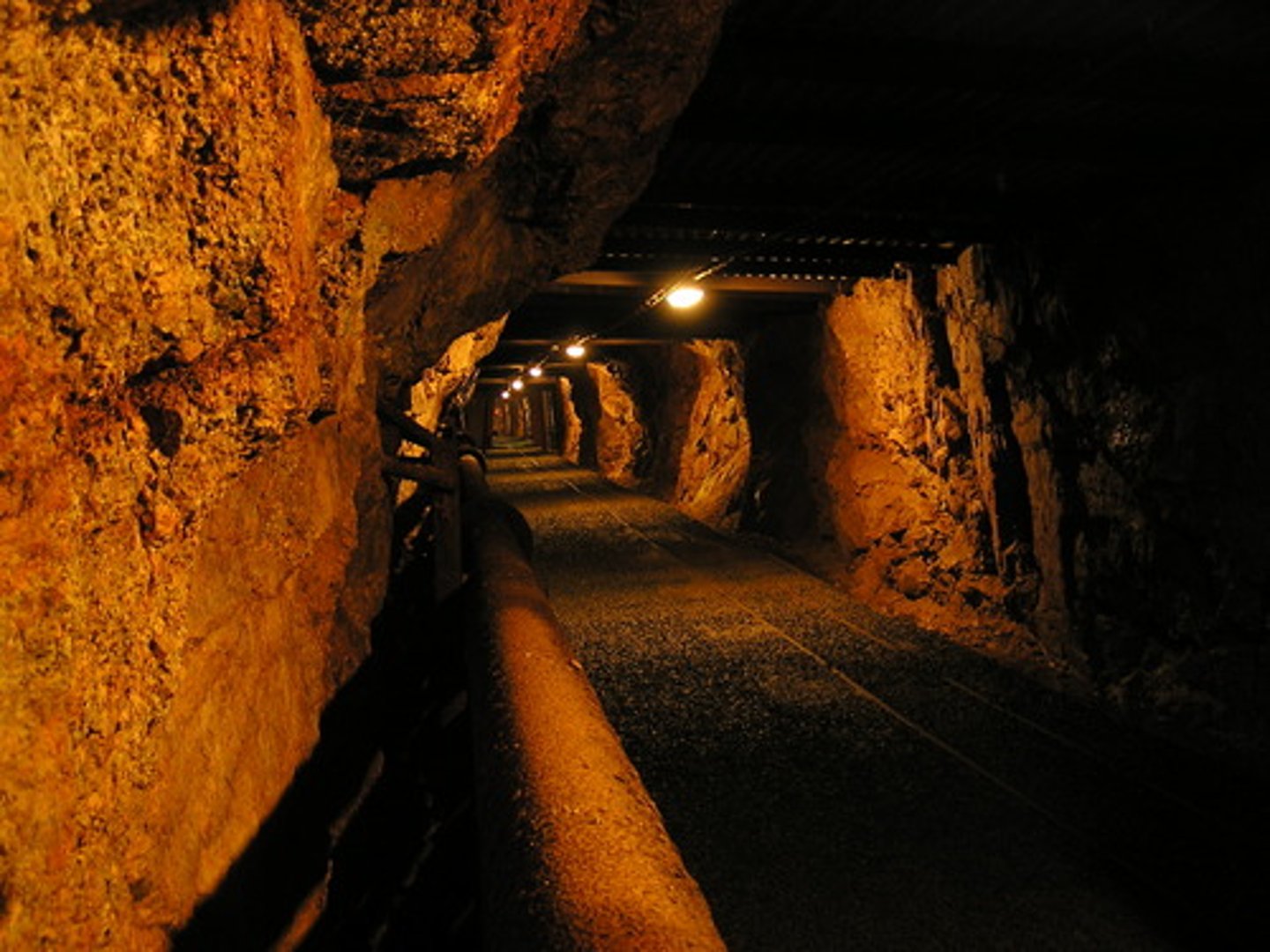
shaft mining
vertical tunnels are built to access and then excavate minerals that are underground and otherwise unreachable

Mining Act (1872)
governed prospecting and mining of minerals on publicly owned land
Mineral Leasing Act (1920)
permitted the Bureau of Land Management to grant leases for development of deposits of coal, phosphate, potash, sodium, sulphur, and other minerals on public domain lands
Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act (CERCLA) (1980)
(superfund); regulated damage done by mining
Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) (1976)
regulated some mineral processing wastes
Surface Mining Control and Reclamation Act (SMCRA) (1977)
established a program for regulating surface coal mining and reclamation activities; established mandatory standards for these activities on state and federal lands, including a requirement that adverse impacts in fish, wildlife, and related environmental values be minimized
tangible resources
assets that can be observed and quantified
intangible resources
organizational assets that are difficult to identify and account for and are typically embedded in unique routines and practices, including human resources, innovation resources, and reputation resources
cost-benefit analysis
a study that compares the costs and benefits to society of providing a public good; helps to make decisions on how to use resources
marginal costs
additional costs of adding one more unit
marginal benefits
added benefits of adding one more unit
externalities
often unwanted consequences of our using resources (can be positive or negative)