Edexcel A Level Business Models and Theories
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
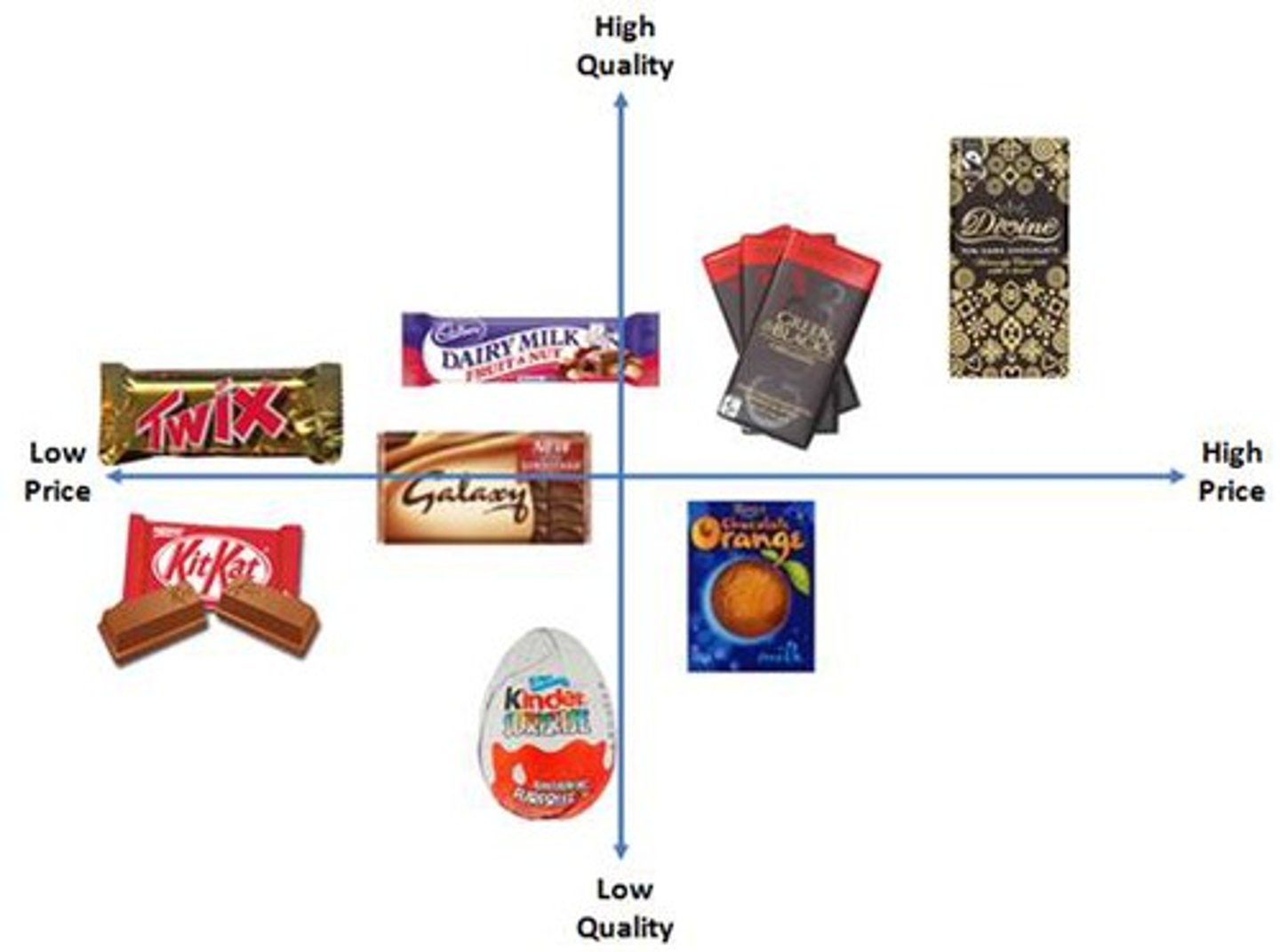
MARKET MAPPING
Compares two features of products or brands in a diagram e.g. quality and price. It is laid out as a matrix and is subjective. Gaps in the market based on the features can be spotted.
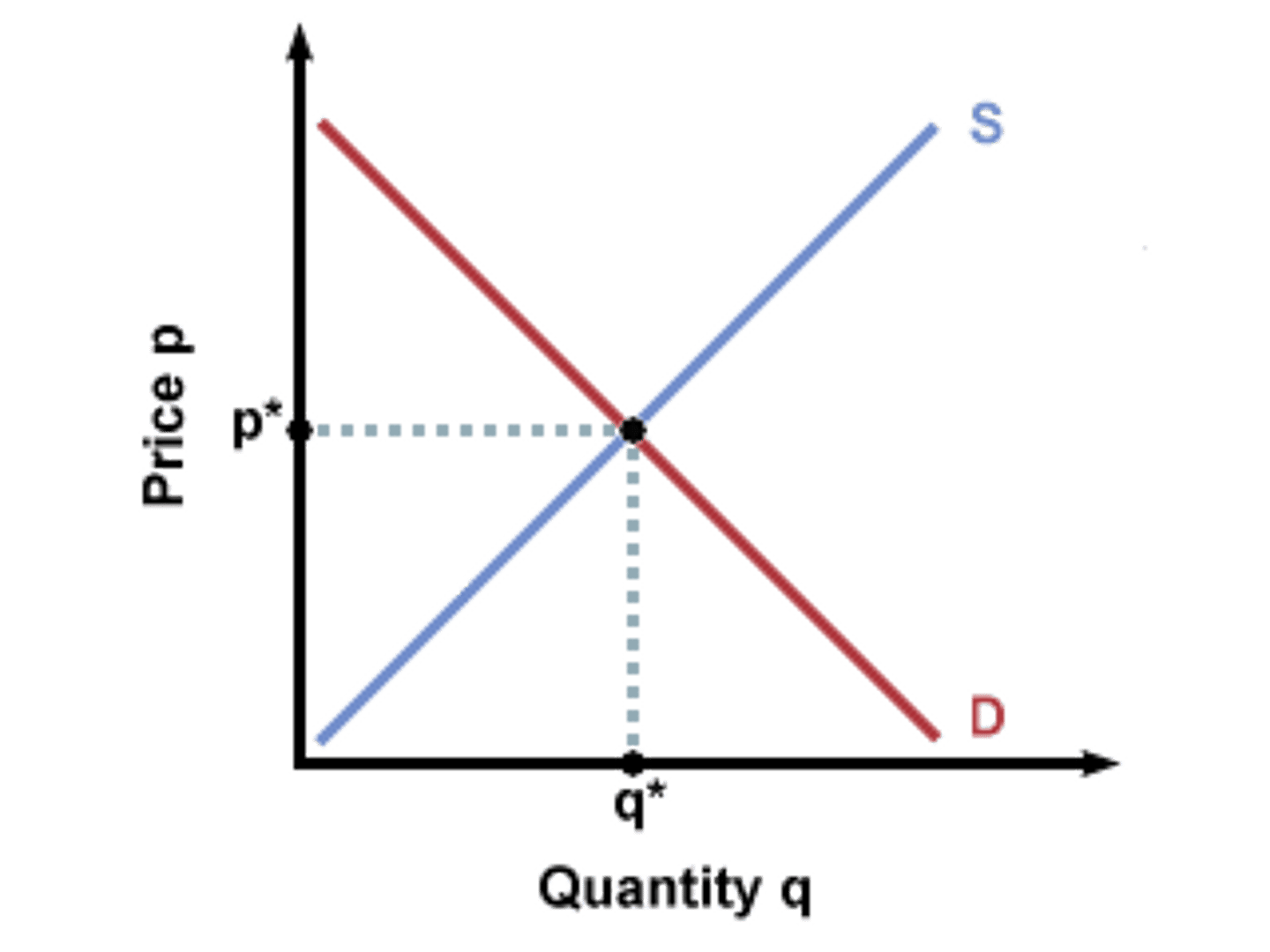
SUPPLY & DEMAND
relationship between the amount of product supplied and the desire for the product demanded
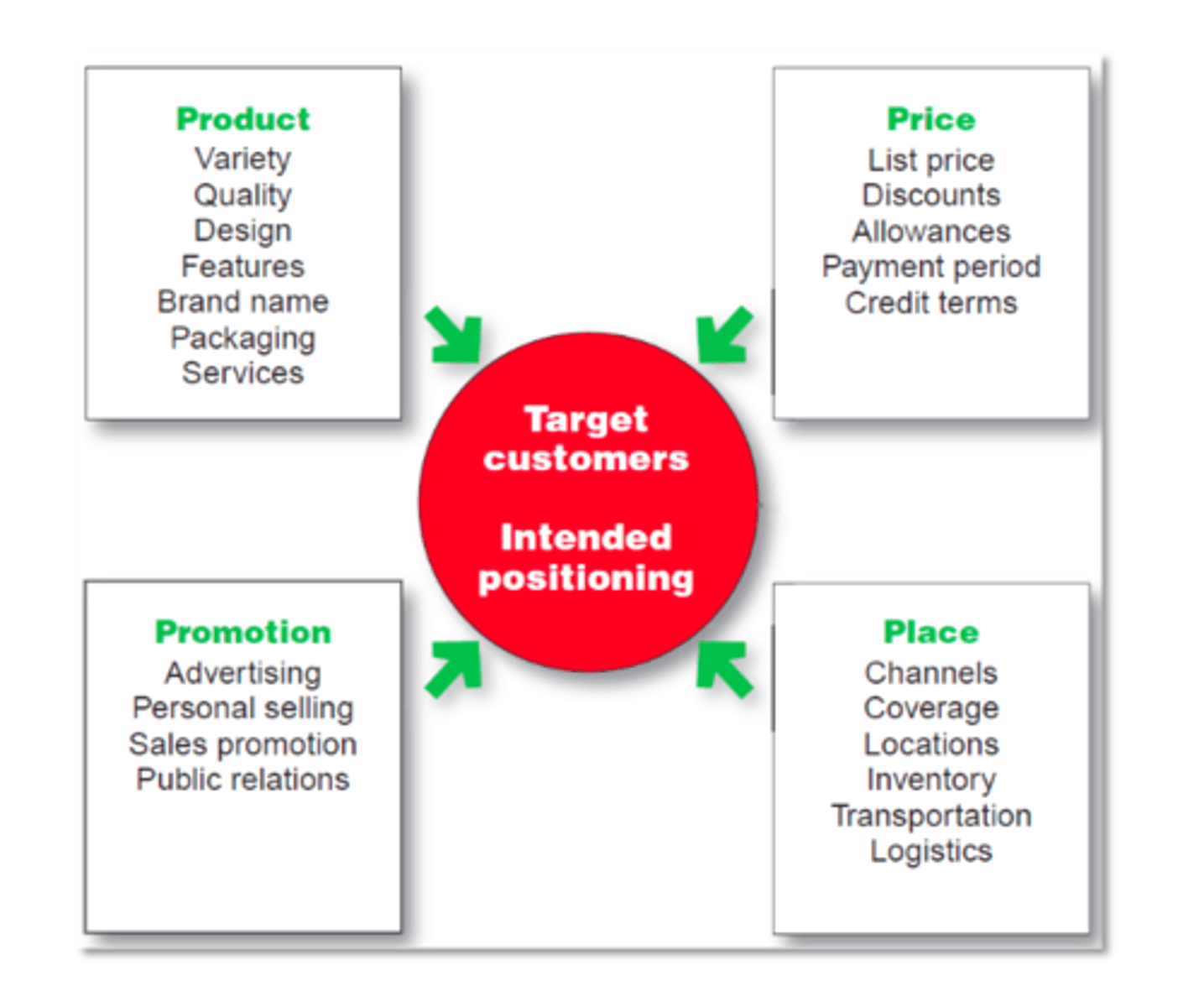
MARKETING MIX (4 P's)
Product, price, place, and promotion—the controllable set of activities that a firm uses to respond to the wants of its target markets.
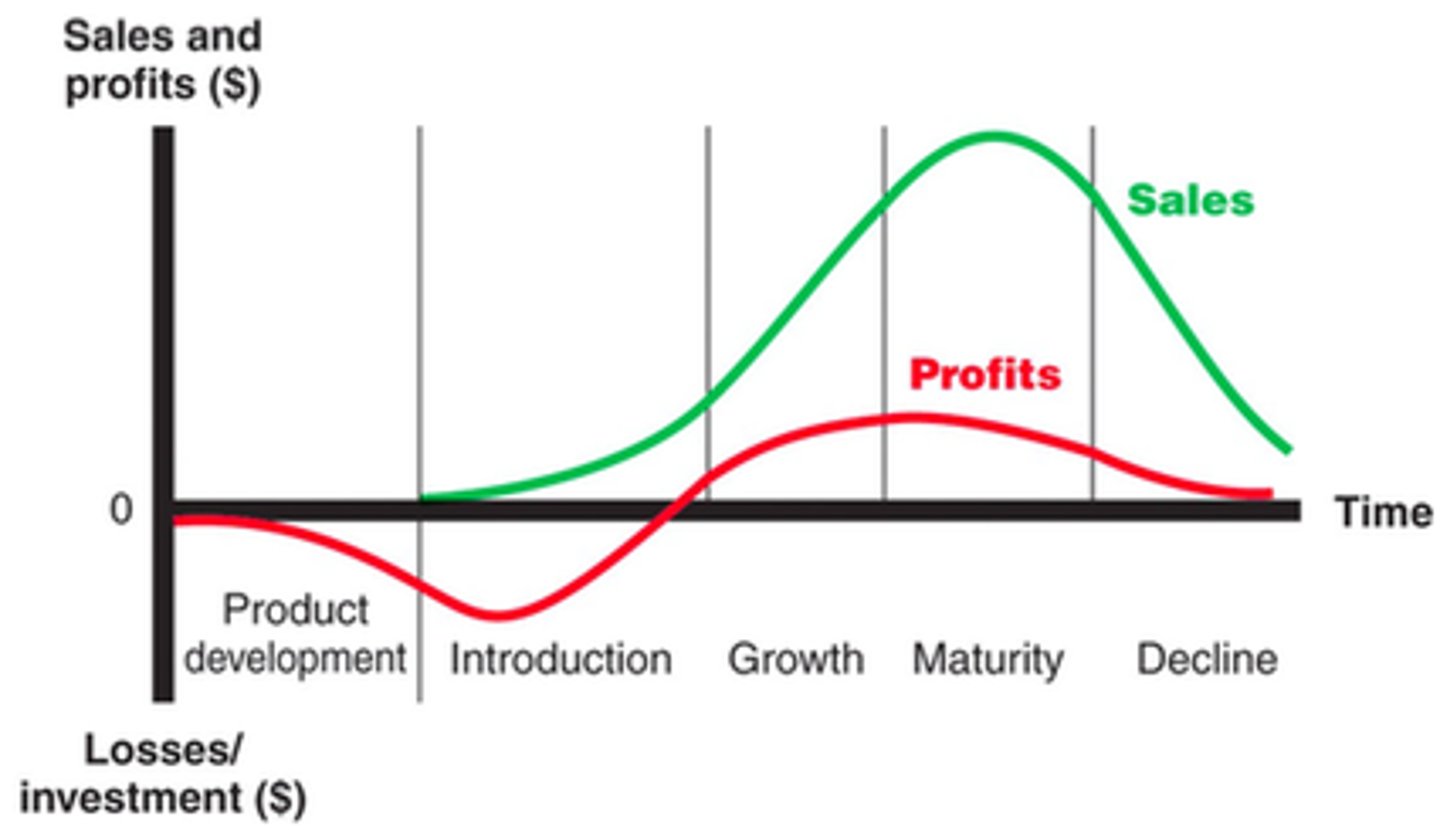
PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE
The stages through which goods and services move from the time they are developed and introduced on the market until they are taken off the market. This shows demands often shows sales levels and costs. Five stages: Development, Introduction, Growth, Maturity, Decline
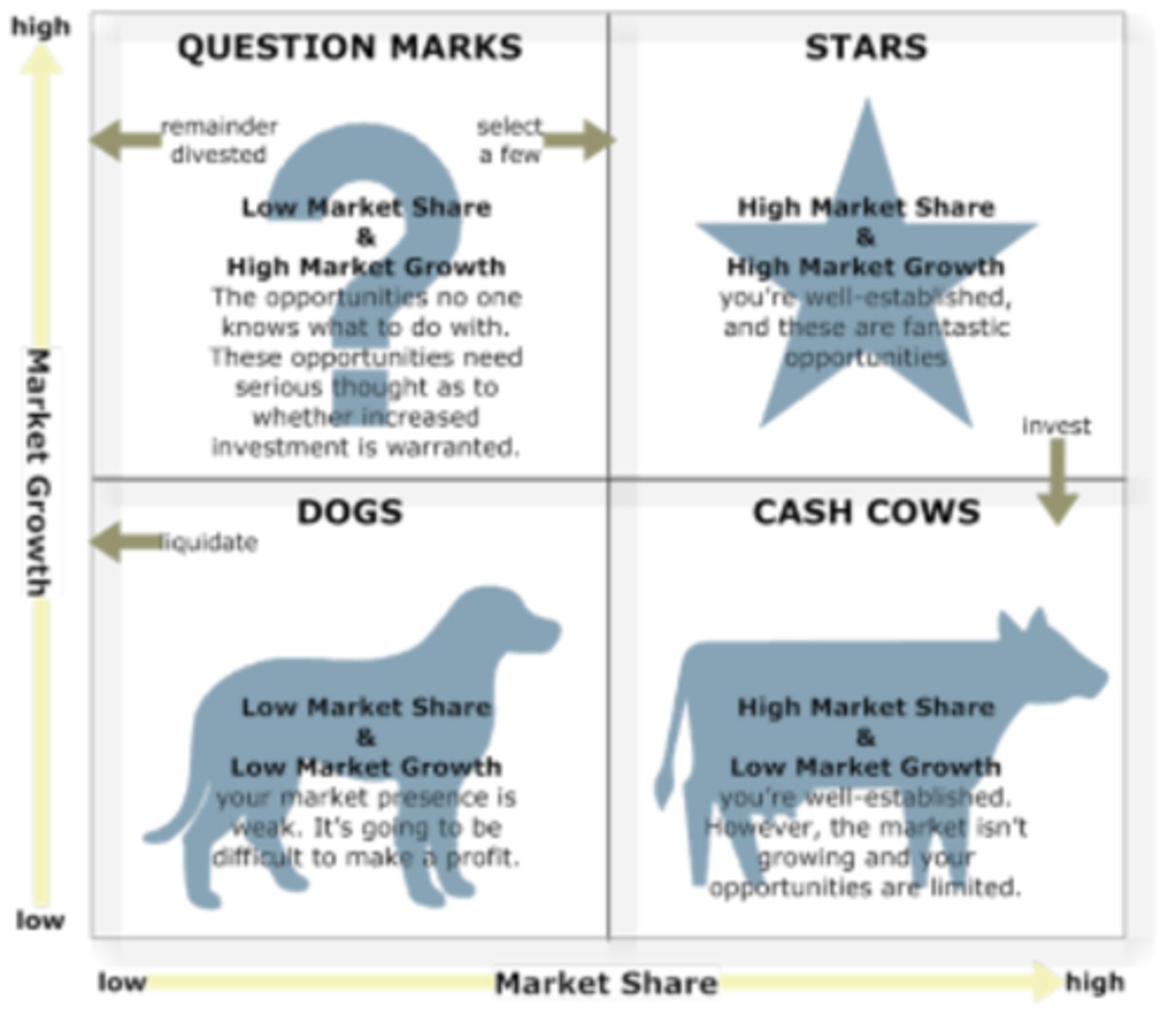
BOSTON MATRIX
Analyses all of the firm's products in terms of their market share and the growth of the market. Laid out as a matrix with four categories of product types e.g.s for Apple could be Stars e.g. iPhones; Question Marks (Problem Children) e.g. Apple TV; Cash Cows e.g. iPod; Dog products e.g. Apple pen
TAYLOR'S SCIENTIFIC MANAGEMENT
Created in 20th century. Believed workers were motivated by money. Time and motion studies done.
Favoured division of labour and piece-rate pay (paid for level of productivity)
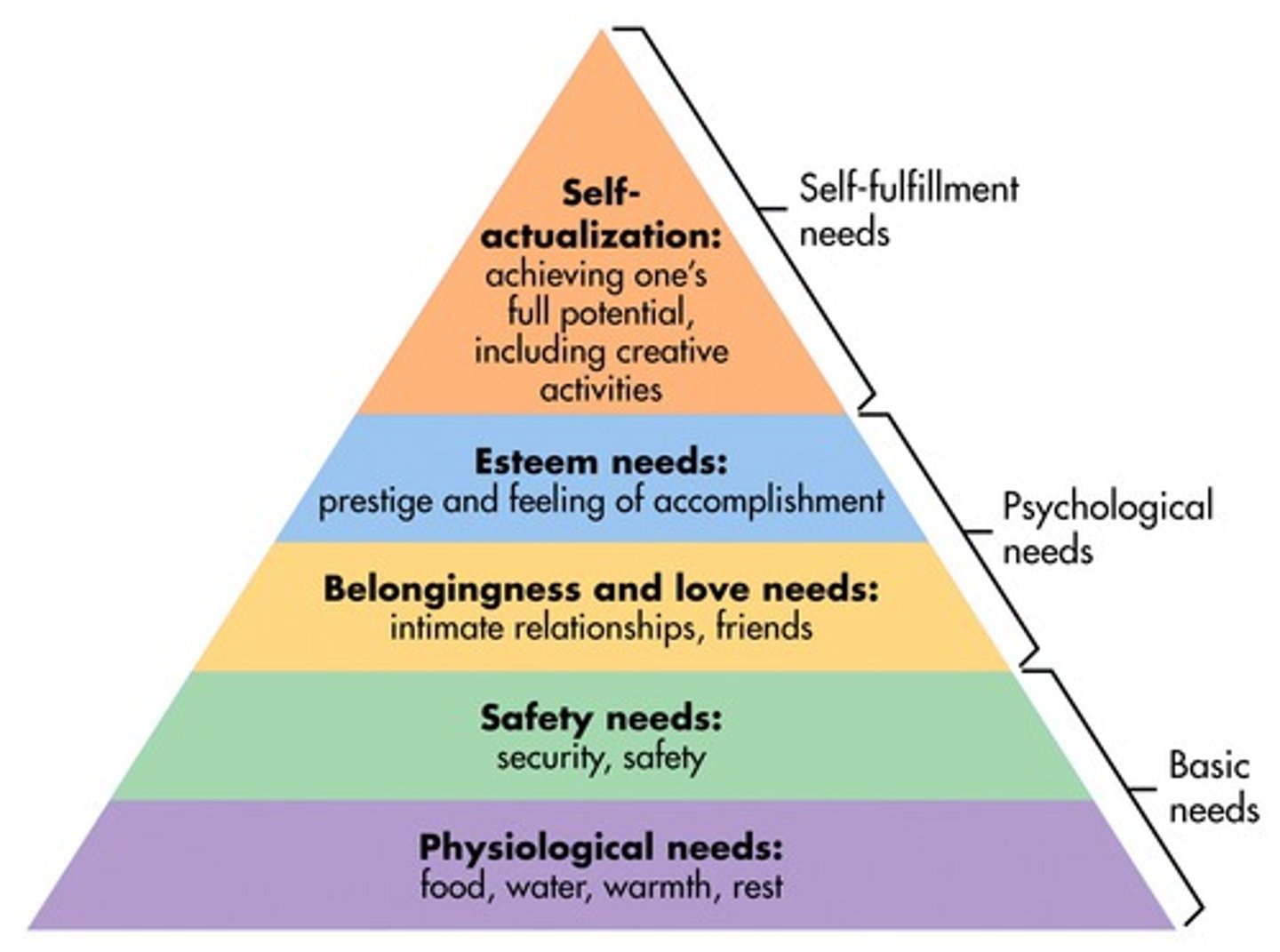
MASLOW'S HIERARCHY OF NEEDS
A Hierarchy of needs developed by Maslow showing hoe people can become their happiest. He insists you need to work through the levels. (level 1) Physiological Needs, (level 2) Safety and Security, (level 3) Relationships, Love and Affection, (level 4) Self Esteem, (level 5) Self Actualization
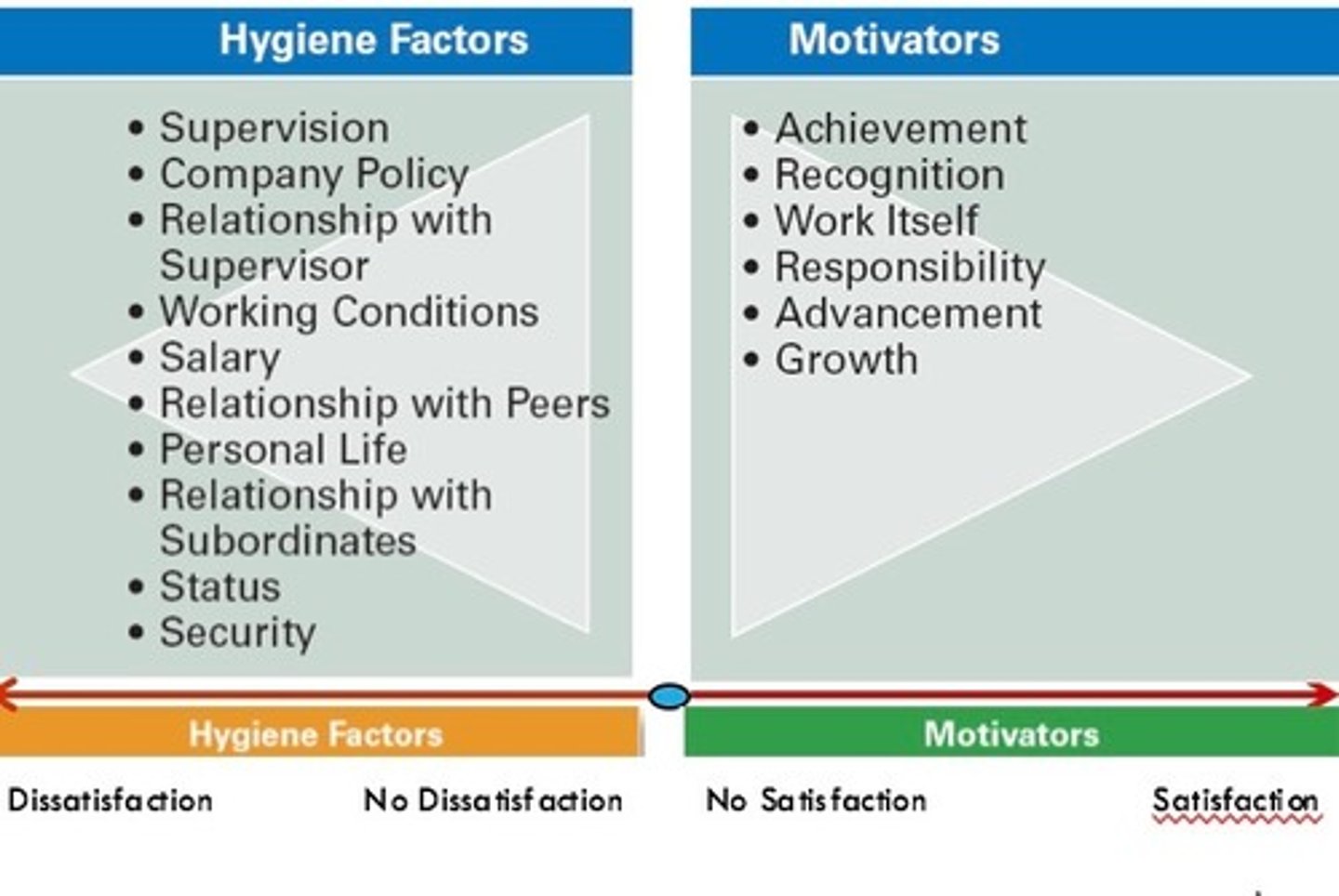
HERZBERG'S TWO FACTOR THEORY
A model that divides motivational forces into satisfiers ("motivators") and dissatisfiers ("hygiene factors"). Herzberg says that hygiene factors won't motivate by themselves but will cause dissatisfaction if they are not present. Only Motivating factors will motivate
MAYO'S HAWTHORNE EXPERIMENTS (HUMAN RELATIONS THEORY)
Experiments conducted in a workplace where one group of employees worked as normal and another group had their working conditions changed e.g. lighting, number of breaks etc. The group exposed to changes had an increase in productivity even if changes were worse. Mayo concluded it was the attention given to employees that made the improvements.
He suggested that managers improve communication with staff and listen to them, meet their social needs and give them feedback
PESTLE EXTERNAL FACTORS influencing Businesses
Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, Environmental (including competitors and ethics)
INTERNAL FACTORS influencing Businesses (LORBST)
Leadership, Objectives, Resources, Budgets, Staffing, Type of product
KAIZEN
Japanese term for continuous improvement e.g. to reduce waste or improve quality
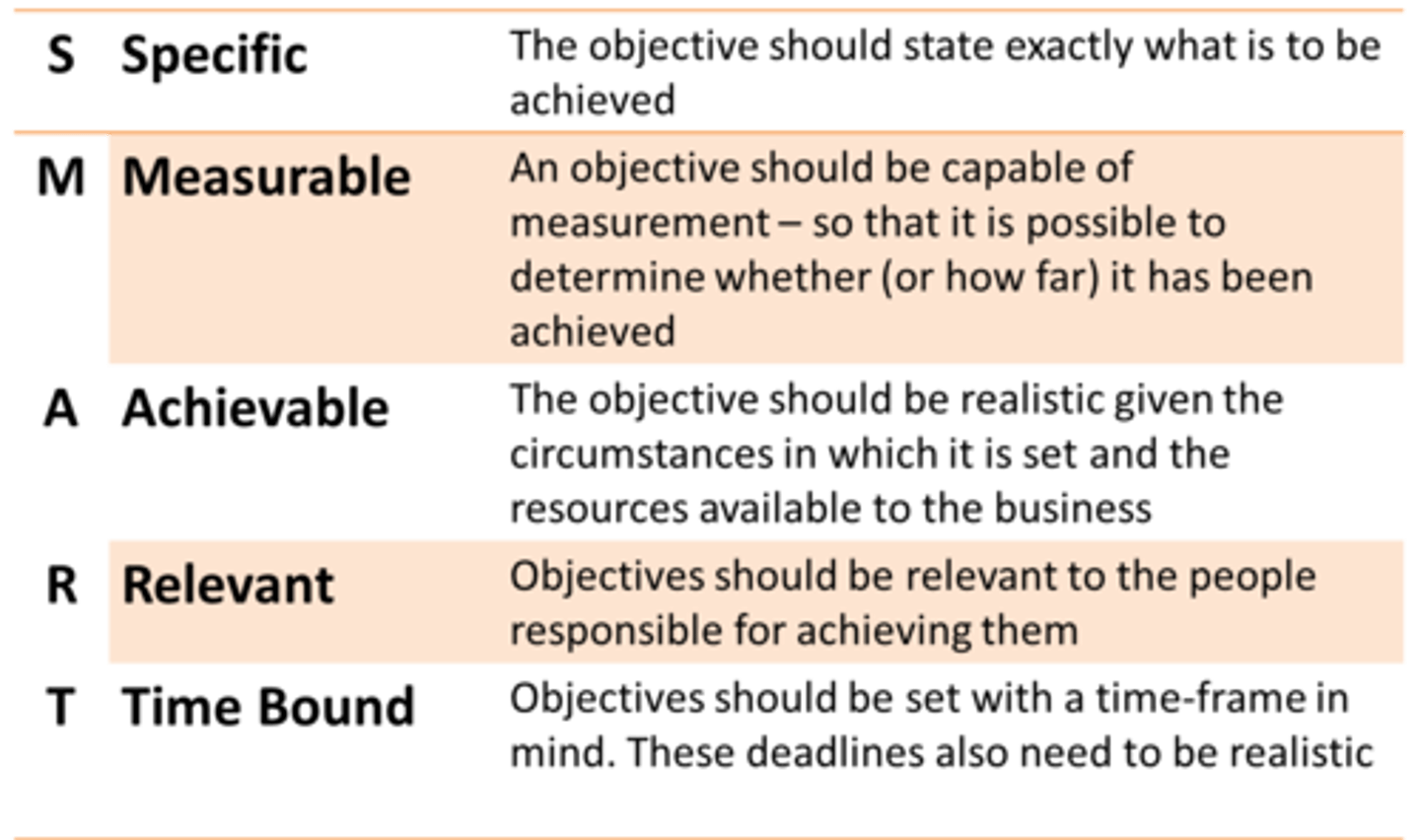
SMART OBJECTIVES
Specific
Measurable
Achievable
Relevant
Time-bound
ANSOFF'S MATRIX
a model used to show the degree of risk associated with the four growth strategies based on either selling a new or existing product in a new or existing market ... market penetration, market development, product development and diversification

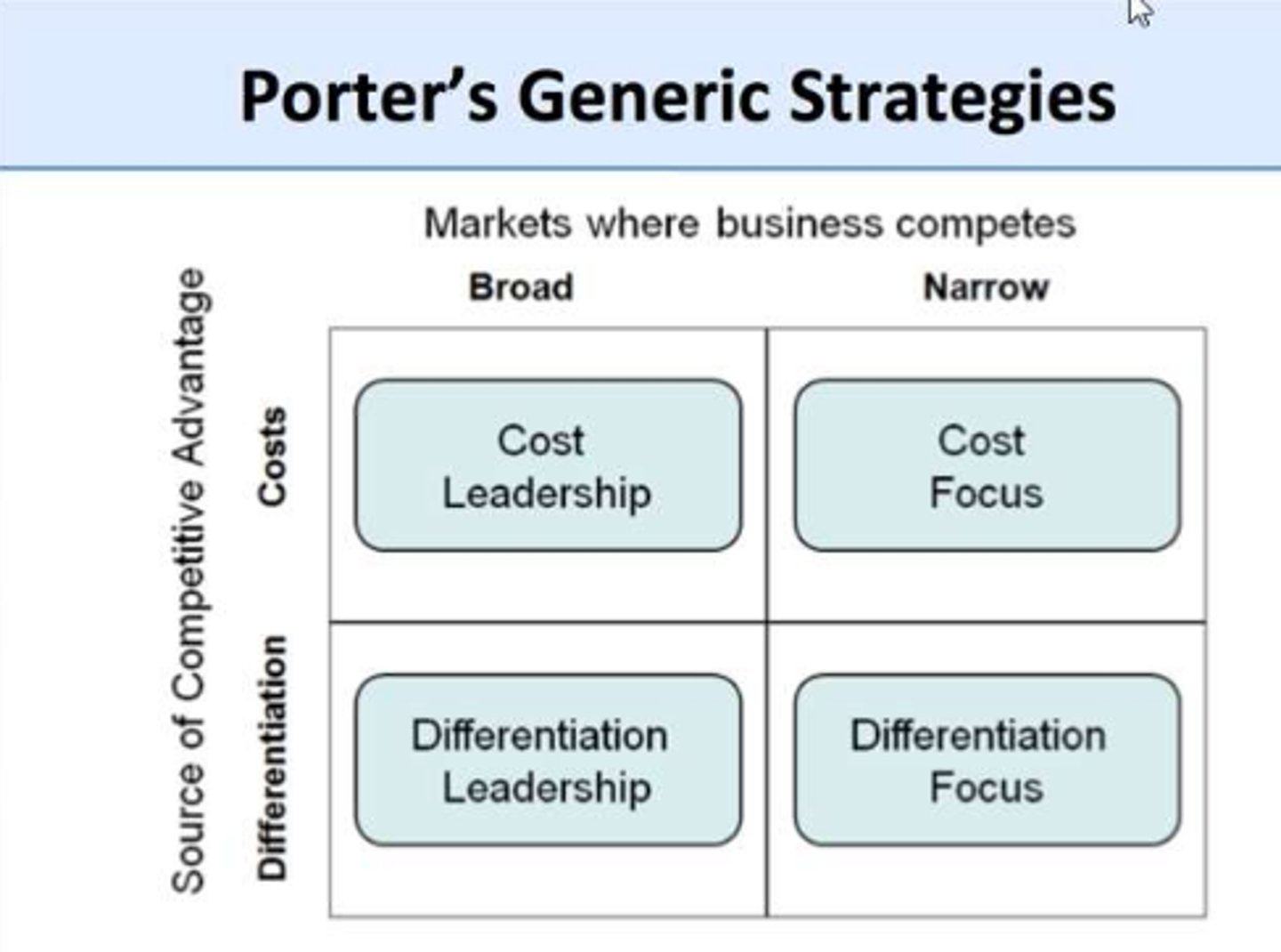
PORTER'S GENERIC STRATEGY
Differentiation and low cost are effective strategies for firms to gain competitive advantage. This is based on a leadership position if they target a broad market or a focussed position if they target a niche or narrow market.
Offering consumers greater value either by means of lower prices or by providing greater benefits and service that justifies higher prices.
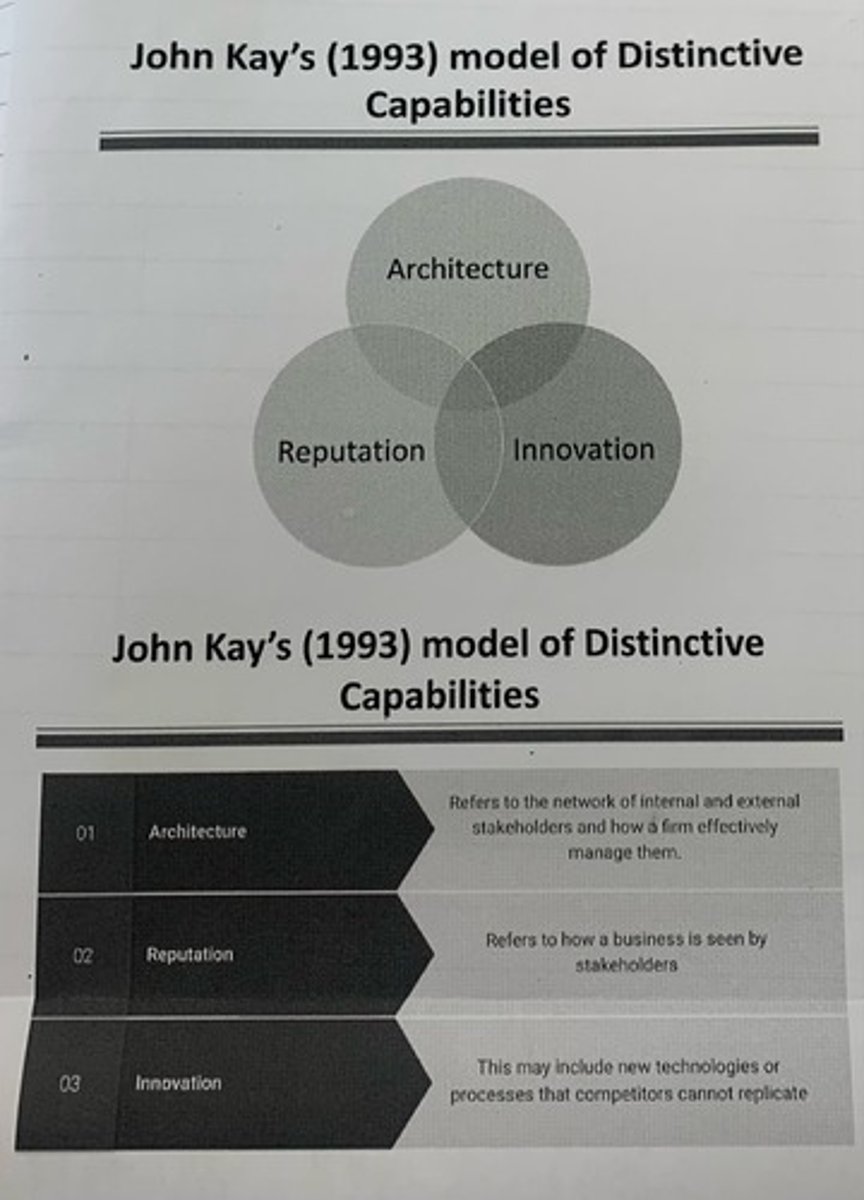
KAY'S MODEL OF DISTINCTIVE CAPABILITIES
Kay's model suggests that a businesses success depends on its ability to build on its distinctive capabilities (what it is good at.) three distinctive capabilities (architecture, reputation and innovation) that would give a business a competitive advantage if successfully exploited.
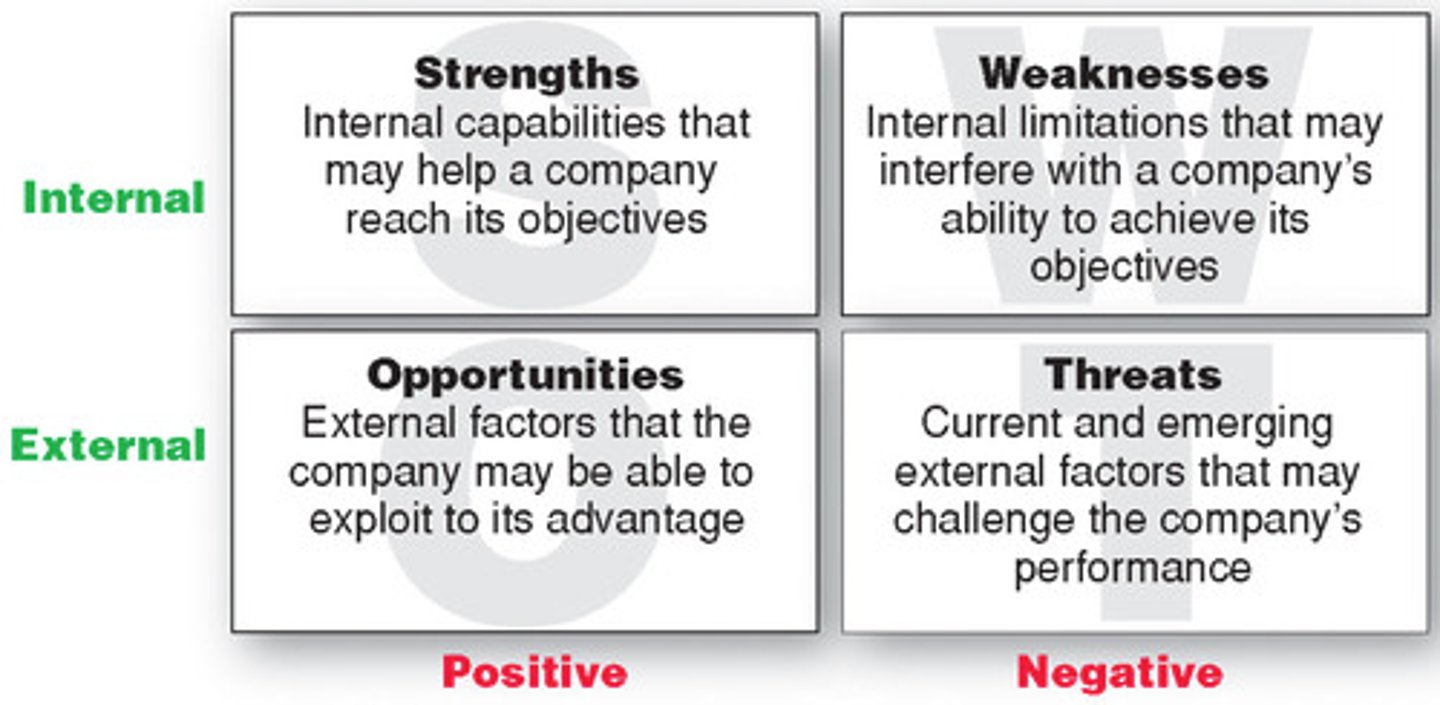
SWOT ANALYSIS
A planning tool used to analyze an organization's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats
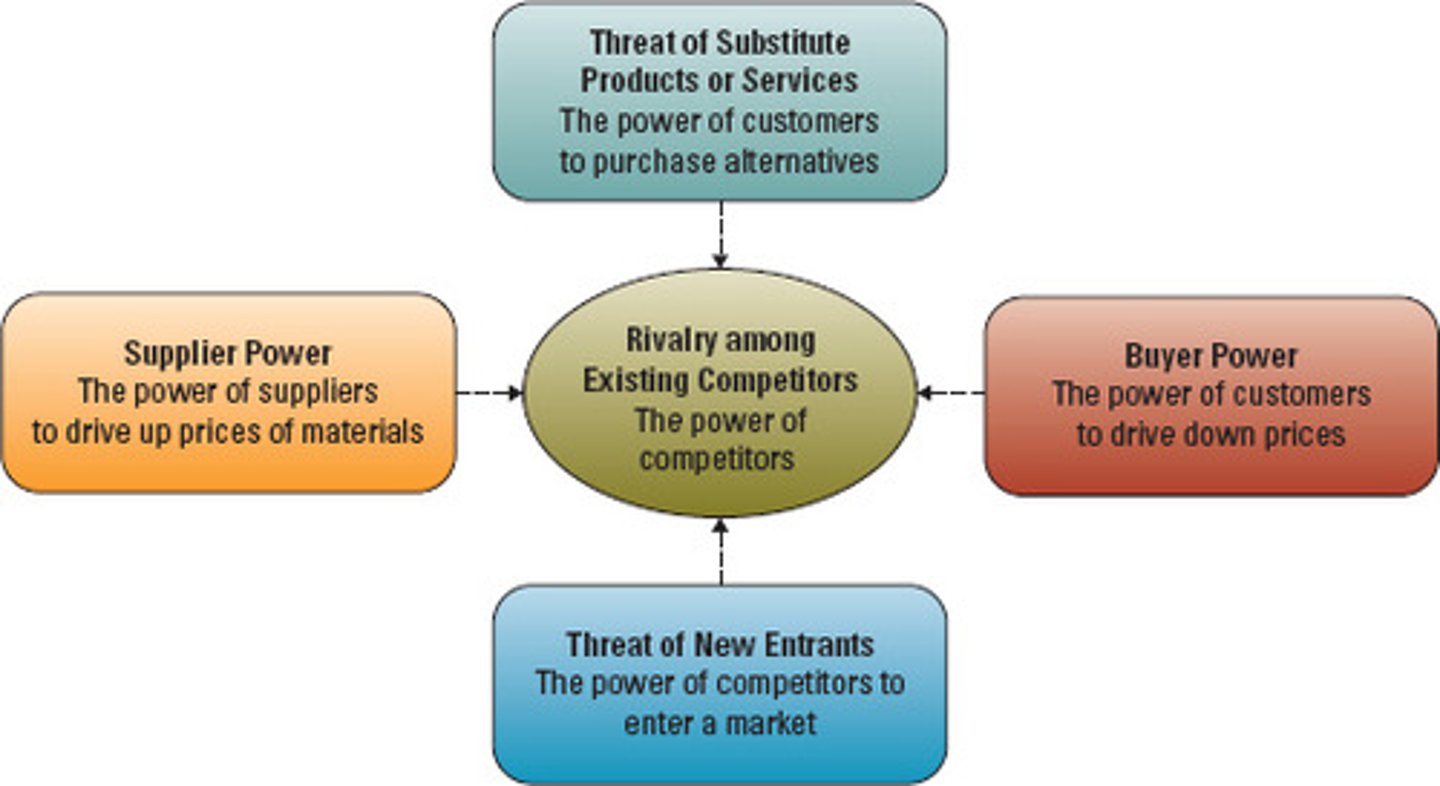
PORTER'S FIVE FORCES
Also known as Industry and Competitive Analysis. A framework considering the interplay between (1) the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors, (2) the threat of new entrants, (3) the threat of substitute goods or services, (4) the bargaining power of buyers, and (5) the bargaining power of suppliers. These forces will impact the ability of a business to compete and make a profit.
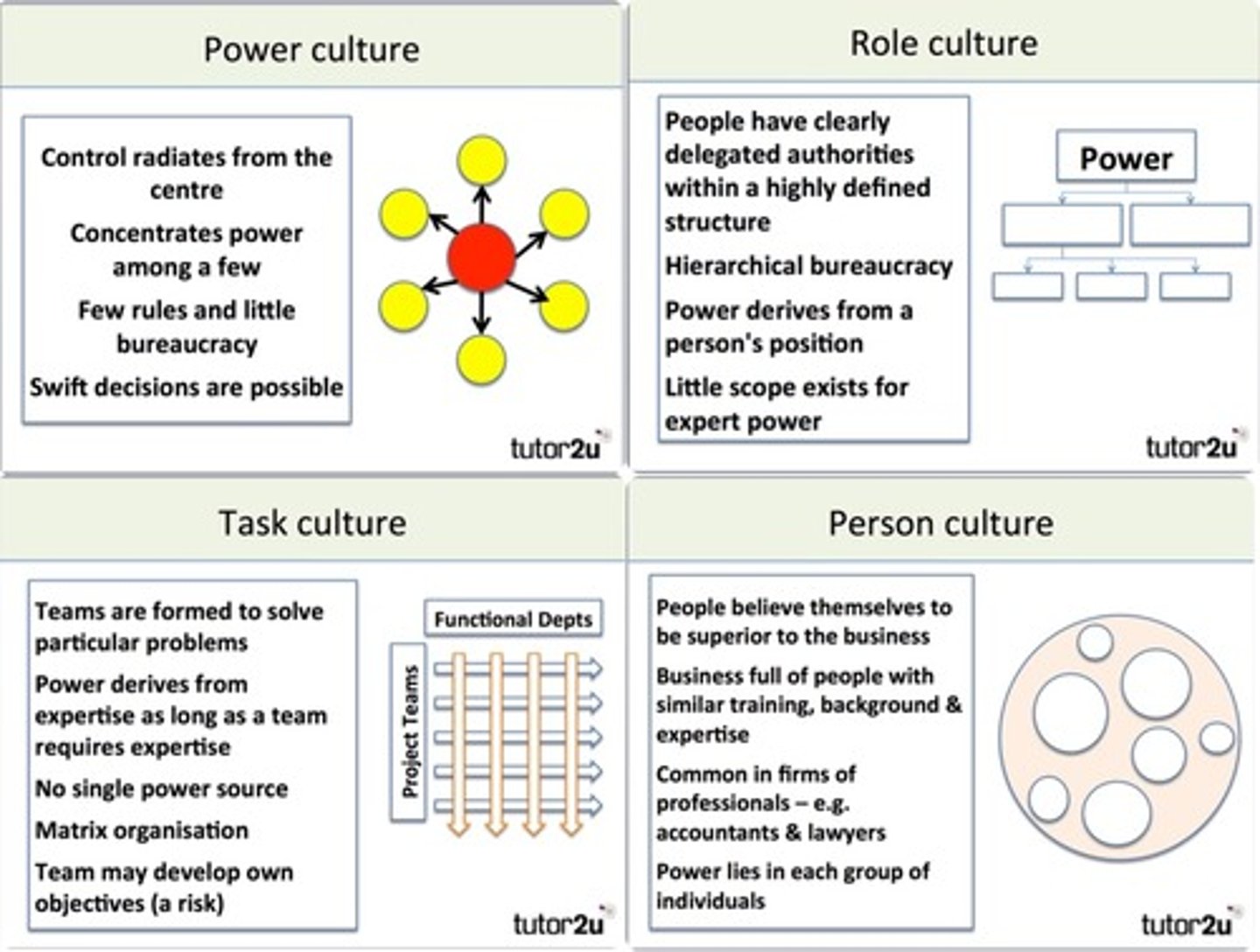
HANDY'S CULTURAL MODEL
Charles Handy, a leading authority on organisational culture, defined four different kinds of culture: Power, Role, Task and Person.
ETHNOCENTRIC MARKETING STRATEGY
Ethnocentric (or domestic) approach treats all markets as being similar and so doesn't change the way it markets abroad compared to domestic approaches.
POLYCENTRIC MARKETING STRATEGY
This uses a different approach in each country e.g. targeting the tastes and fashions of the individual country
GEOCENTRIC MARKETING STRATEGY
Geocentric or Mixed strategy uses a combination of Ethnocentric or Polycentric methods so central models used but with some tweaking for local markets e.g. Starbucks