L7: Hygiene, Bed Baths, Incontinence Care
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Bariatric equipment
devices that assist clients who are overweight

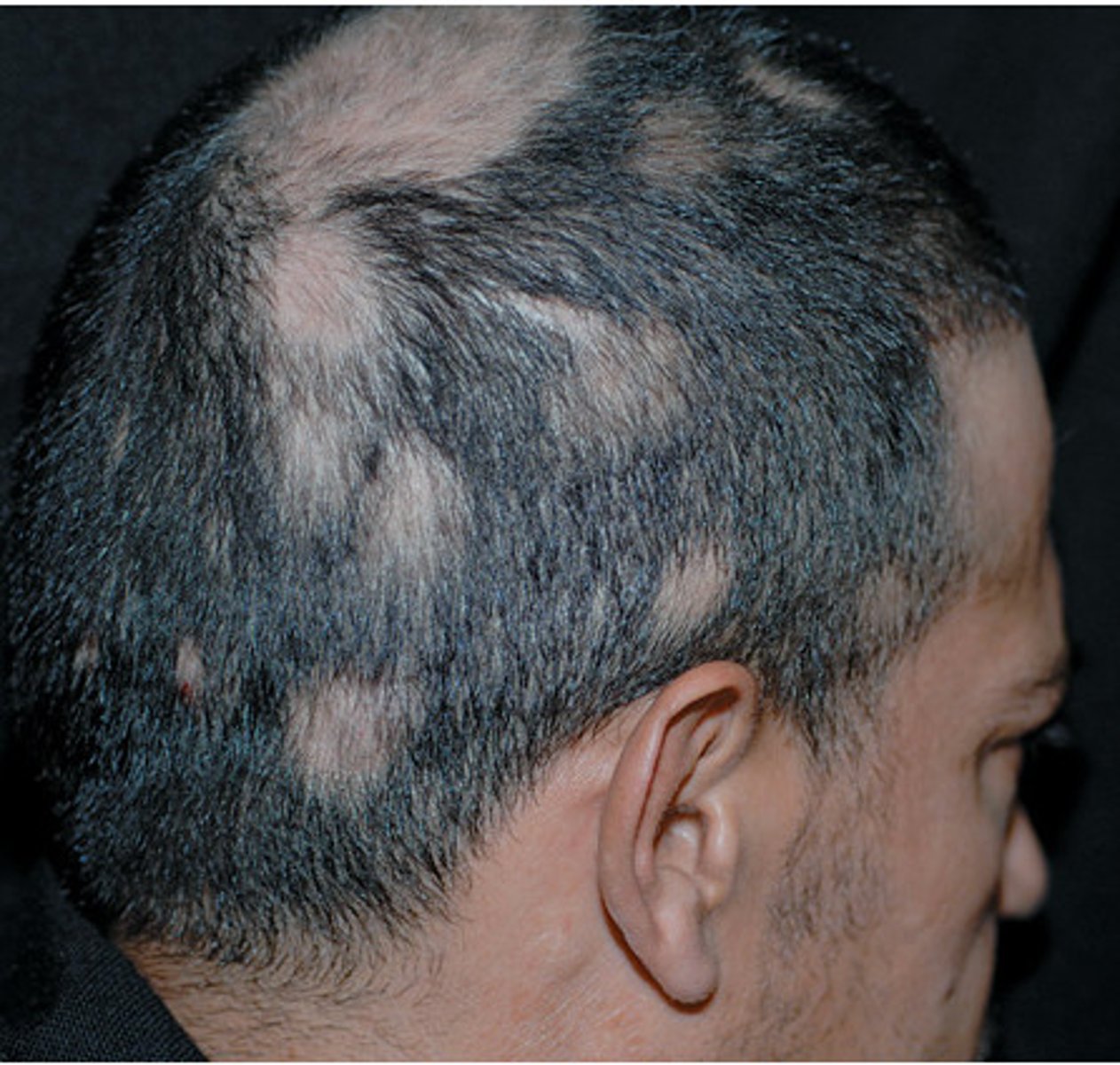
Alopecia
loss of hair from the head and/or body
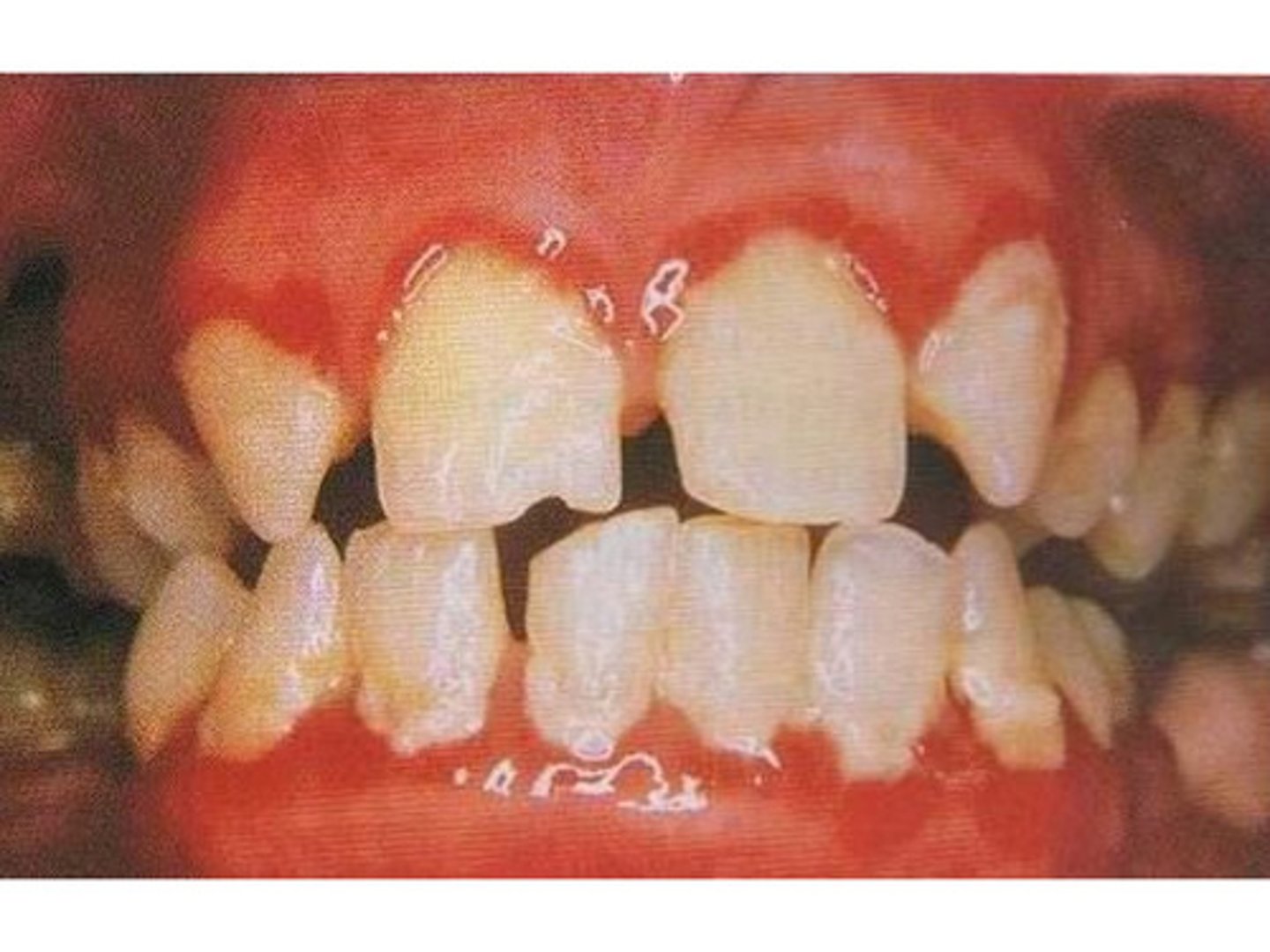
Hygiene
conditions or practices of cleanliness or care of the body that are conducive to health and wellness

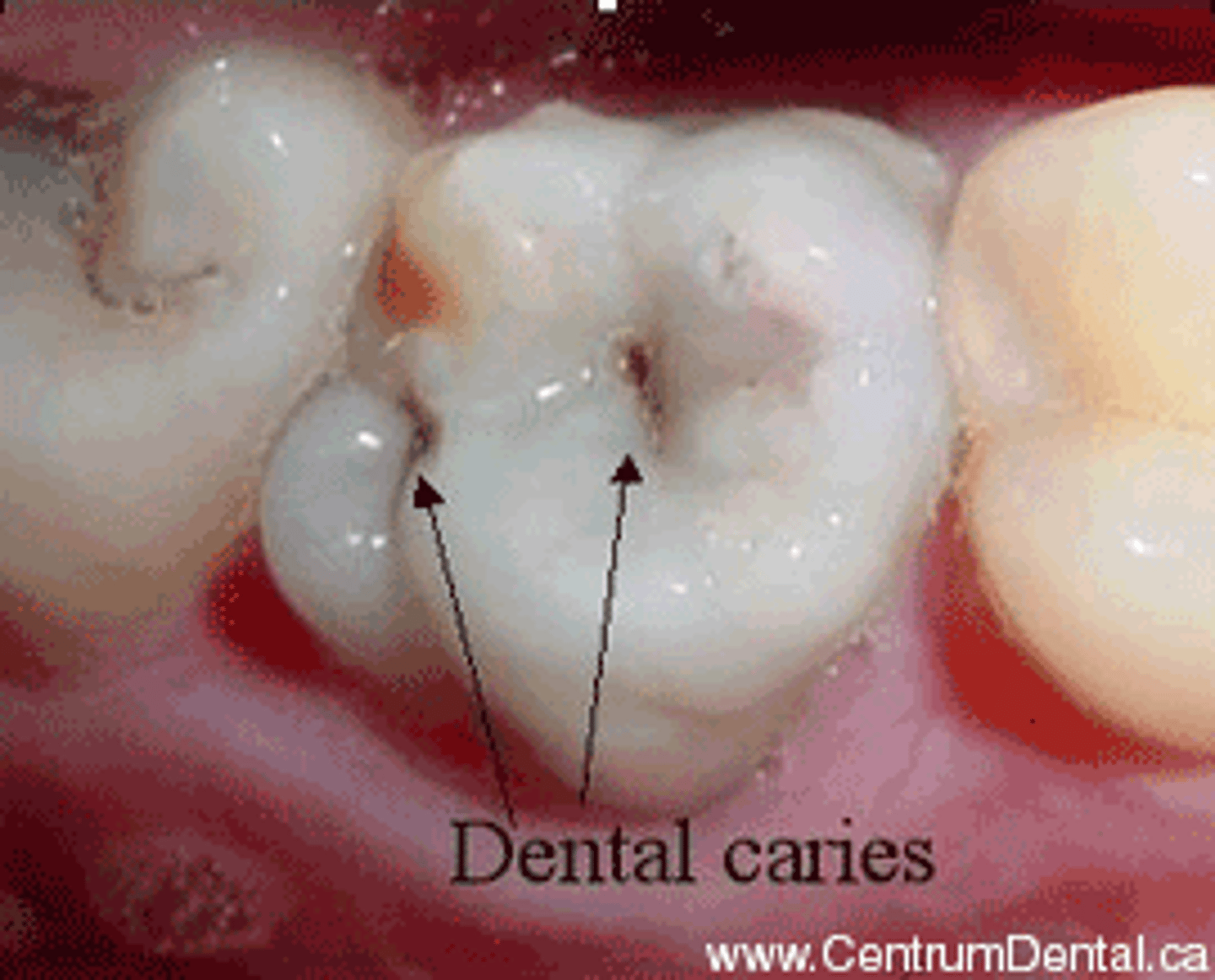
Caries
cavities due to decay of the enamel of teeth
Cerumen
earwax that forms inside the ear

Commode
a portable toilet, usually with wheels, that can be placed at the bedside of a client who has limited activity

Halitosis
mouth odour

Pannus
a large protuberant abdominal skinfold

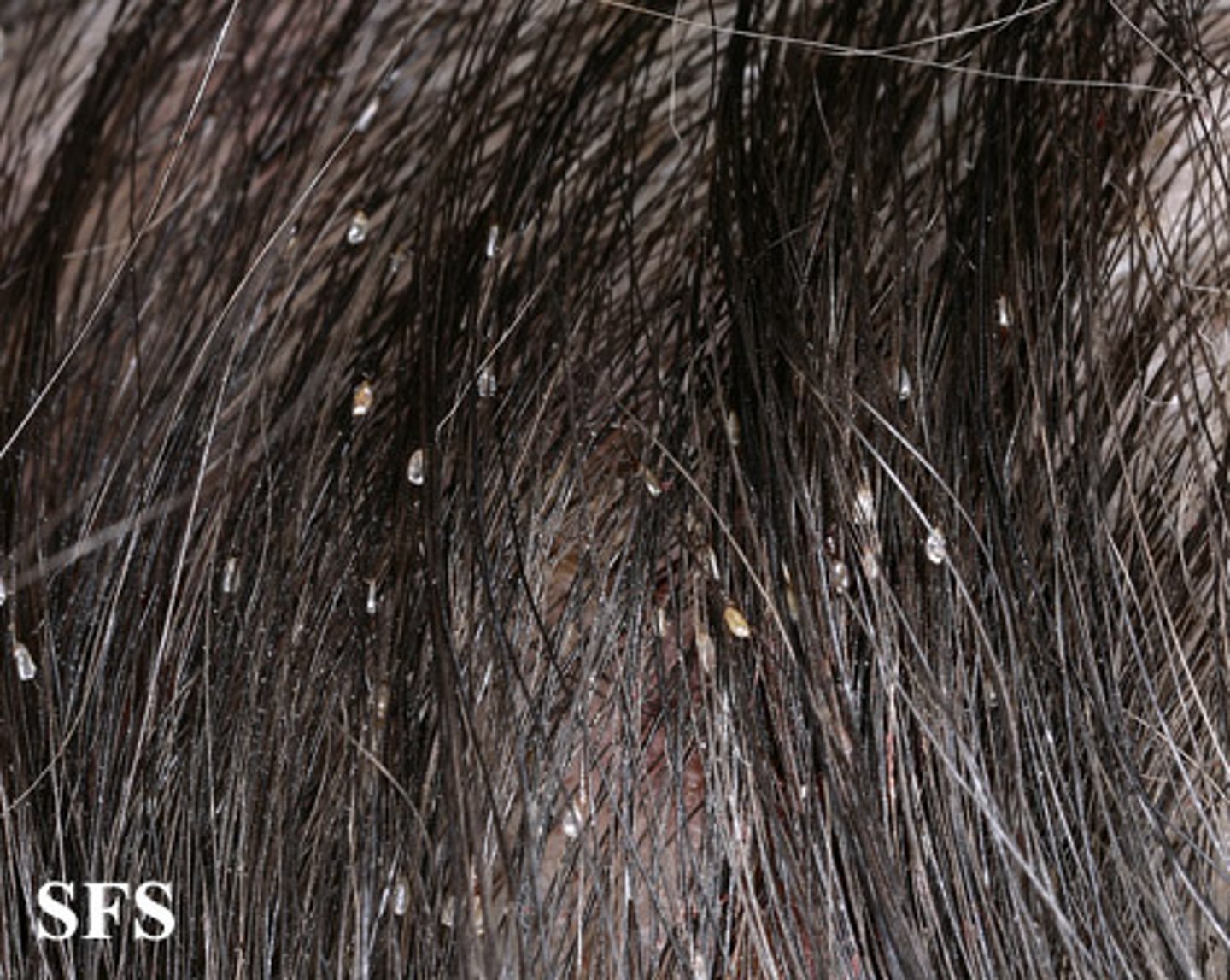
Pediculosis
an infection with lice
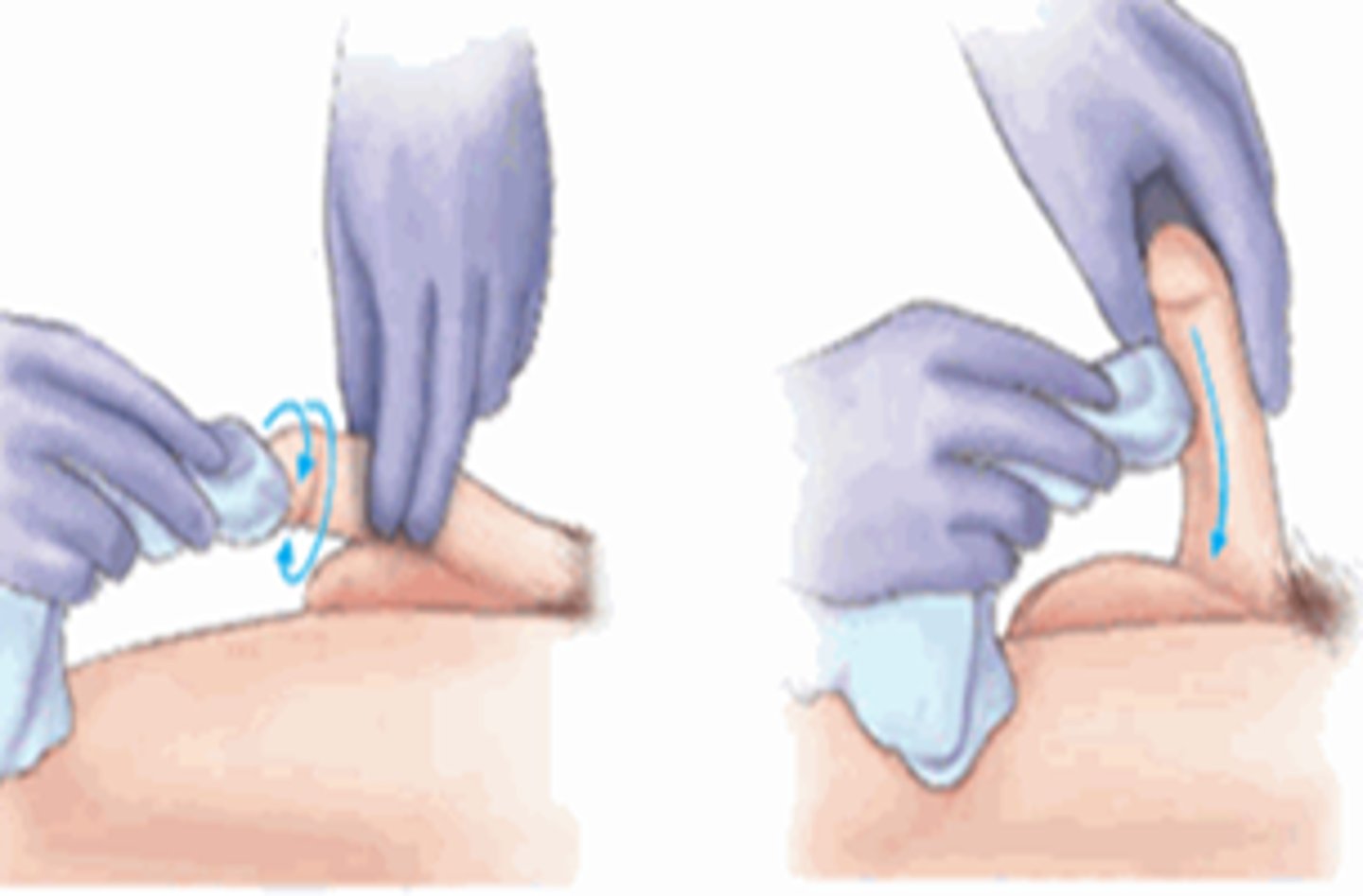
Perineal care
routine procedure to cleanse and perform hygiene on the perineum
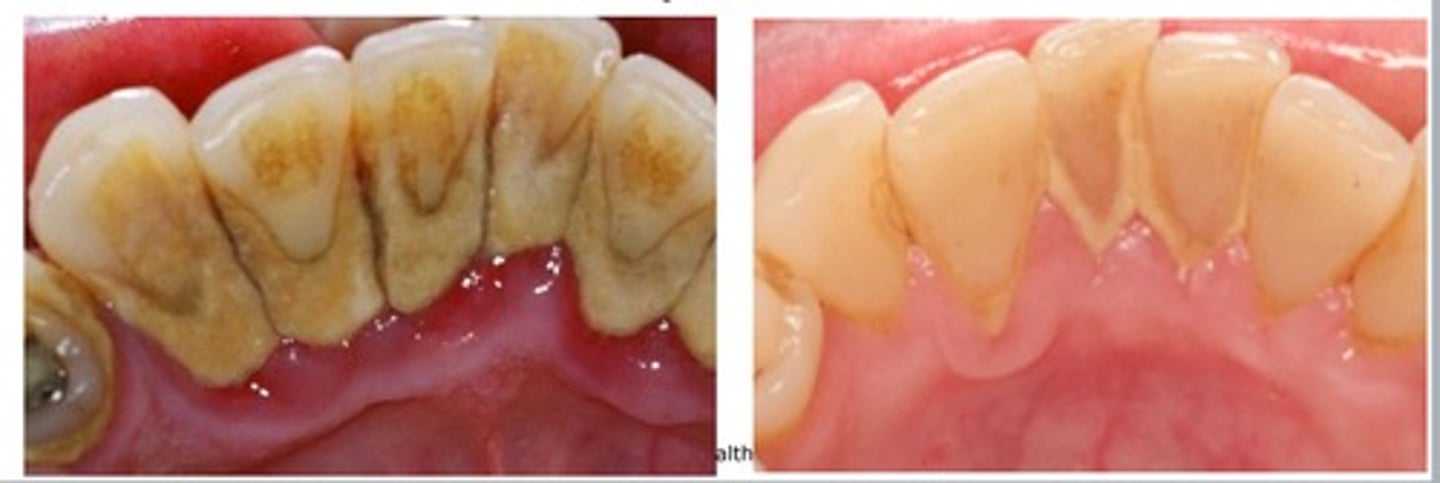
Plaque
a substance primarily composed of bacteria and saliva that forms on teeth
Self-care
refers to a person's ability to perform primary care functions in the following four areas: bathing, feeding, toileting, and dressing, without the help of others

Tartar
hardened plaque that remains on teeth
Urinal
an external plastic or metal receptacle for collecting urine

Xerostomia
dry mouth when the oral mucosa becomes drier as saliva production decreases (a common side effect of many medications)
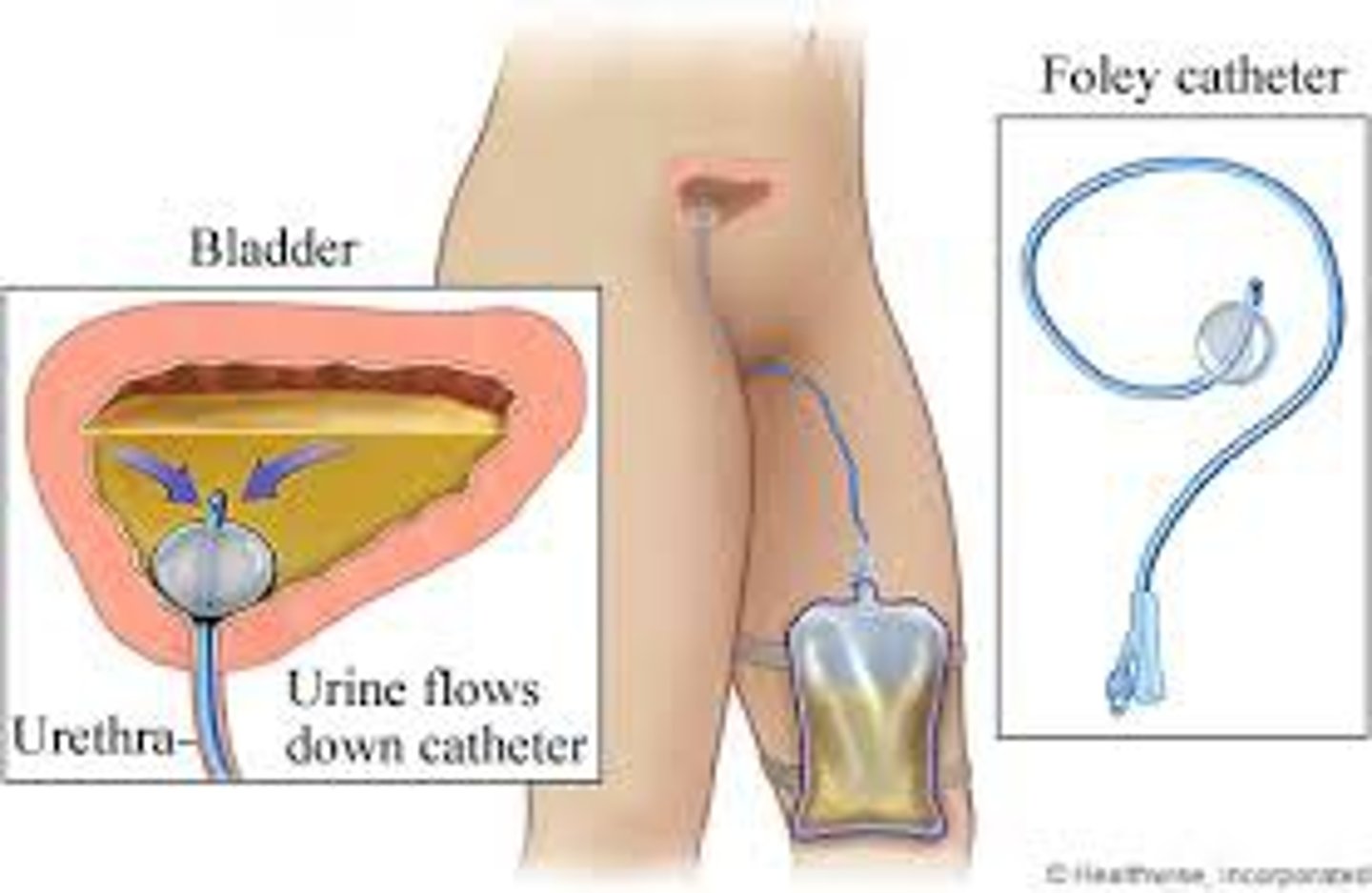
CAUTI
catheter-associated urinary tract infection
- a urinary tract infection that occurs in a person with an indwelling urinary catheter
- most common type of health care-associated infection
Constipation
bowel movements are irregular with feces that may be hard and painful to pass

Defecation
evacuation or removal of feces from the body through the anus

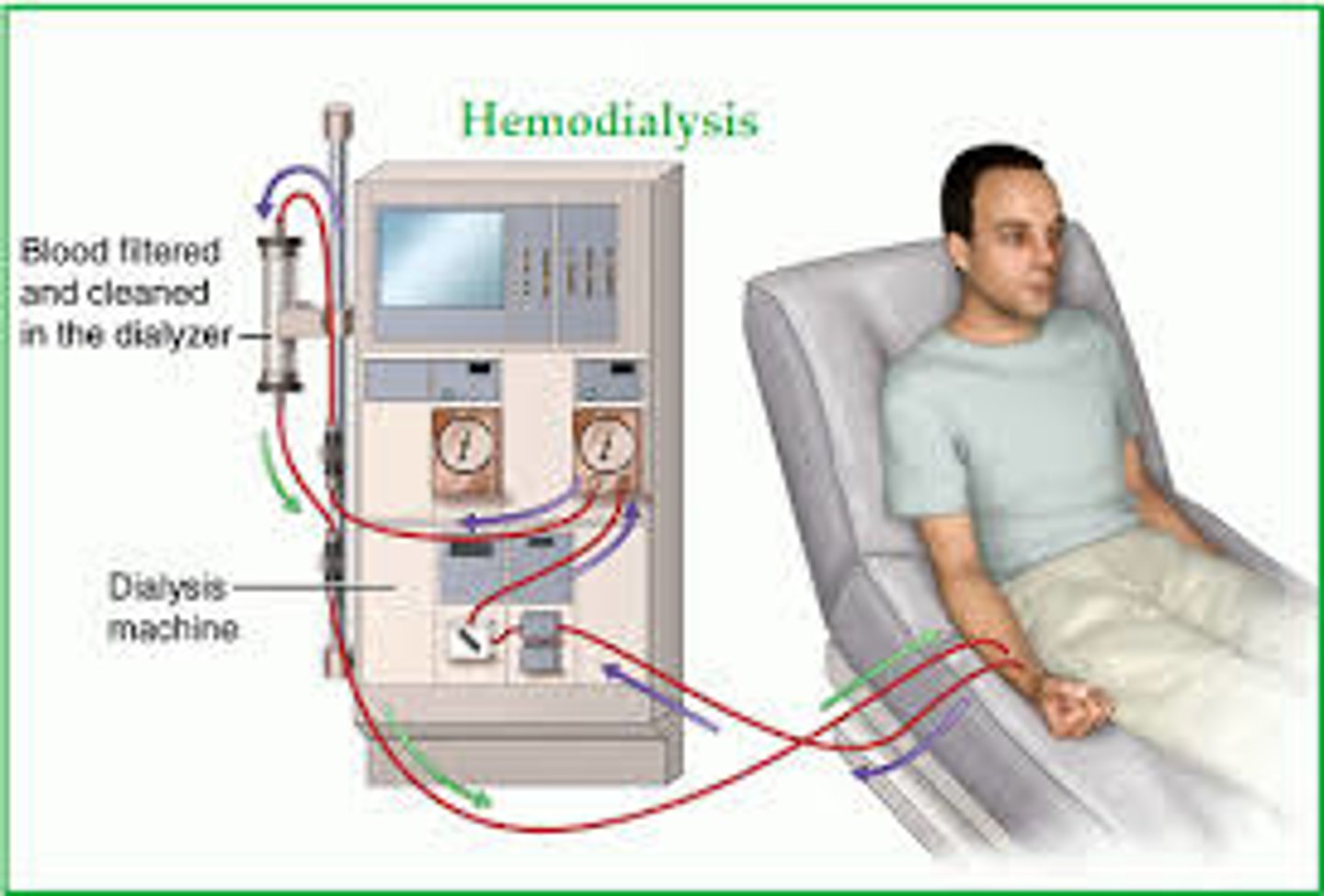
dialysis
a process that removes waste and excess fluid from the blood
- pts impaired kidney function (renal failure)
- two types: hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis
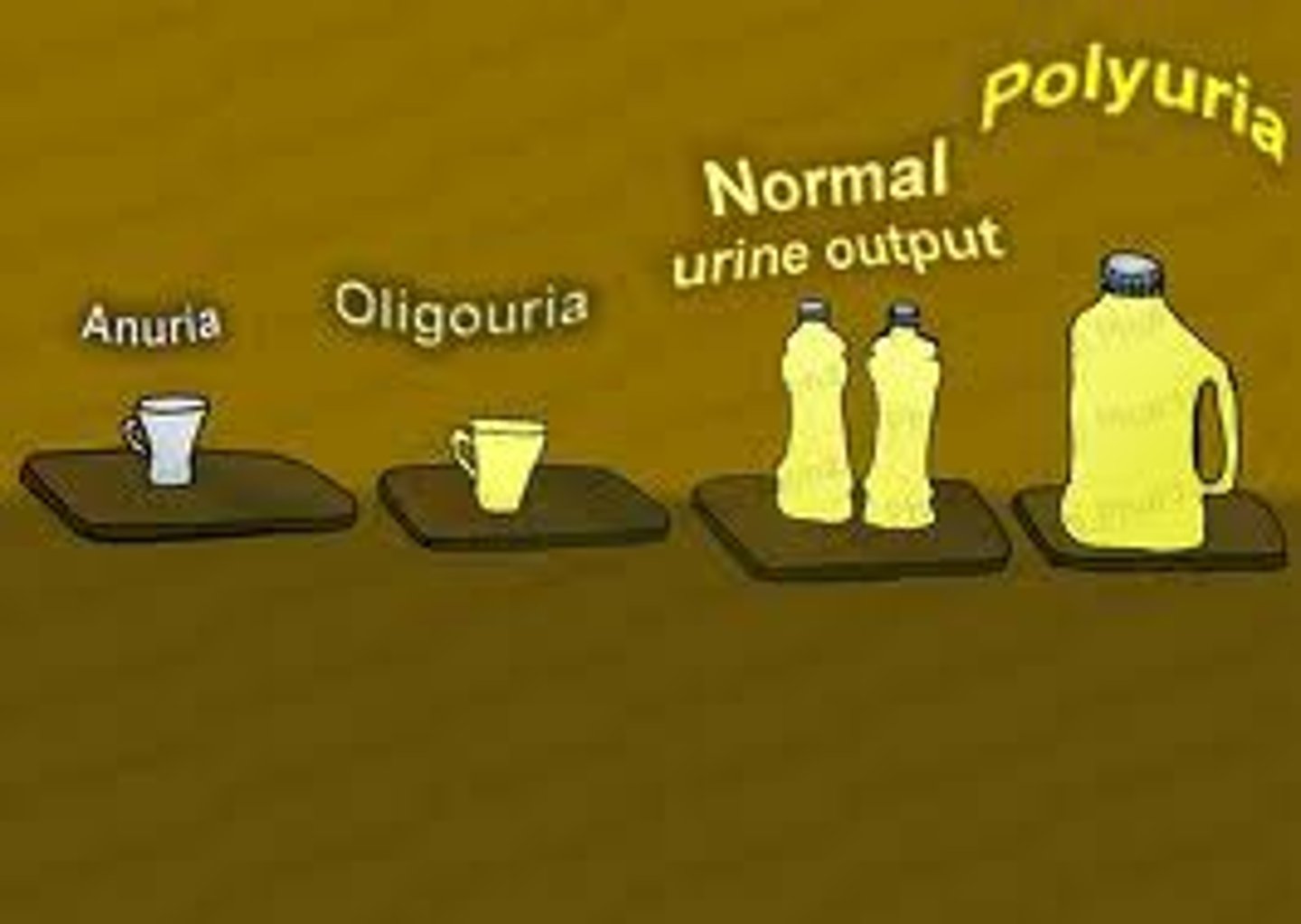
Diuresis
excessive urine production

Diuretic
refers to any substance that promotes the production of urine

Dysuria
Difficult urination

Enuresis
the passing of urine while sleeping (bed-wetting)

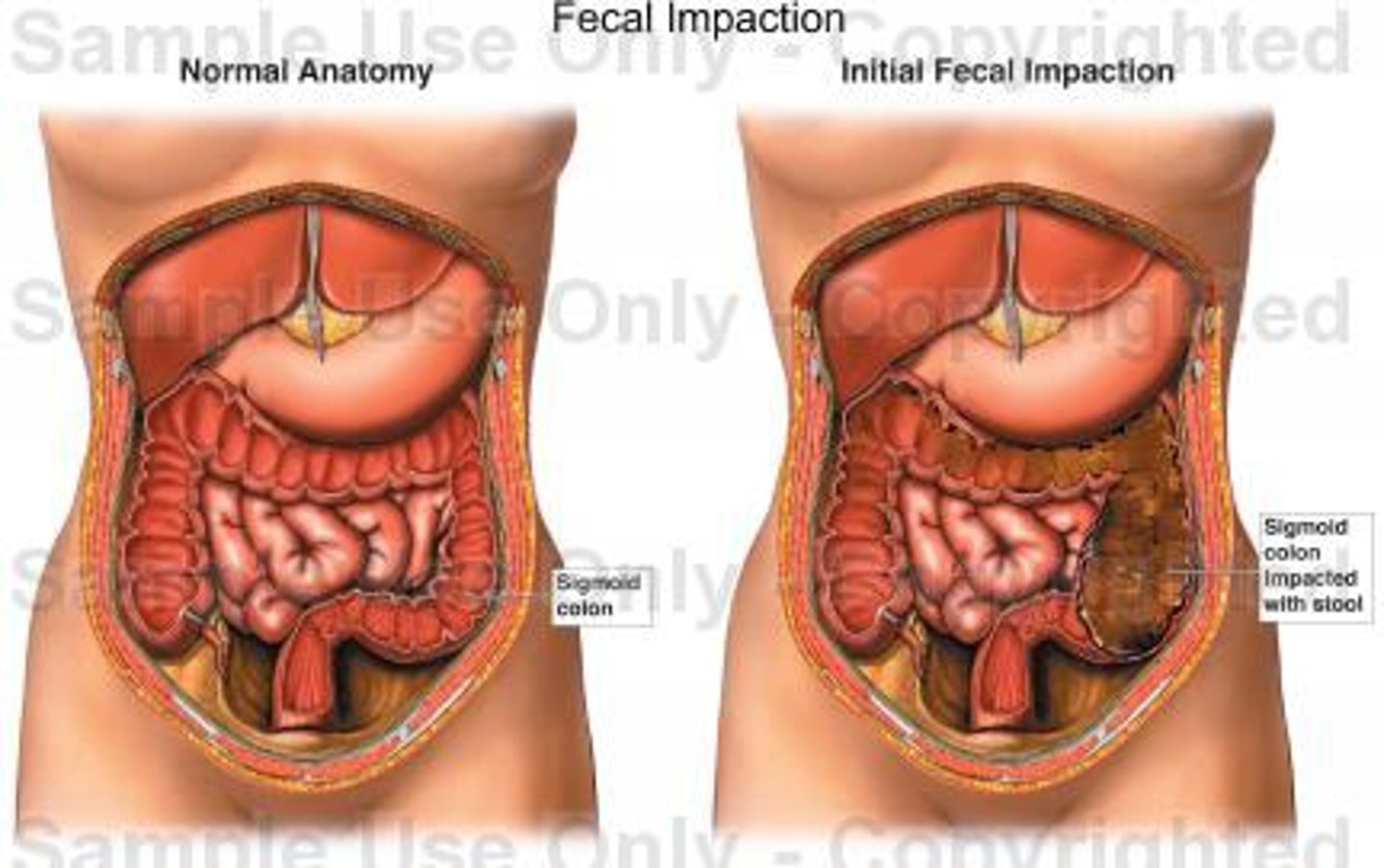
Fecal impaction
hardened and dry feces in the folds of the rectum, resulting from prolonged retention and accumulation of fecal material
Feces
waste products produced and eliminated from the digestive tract (stool)

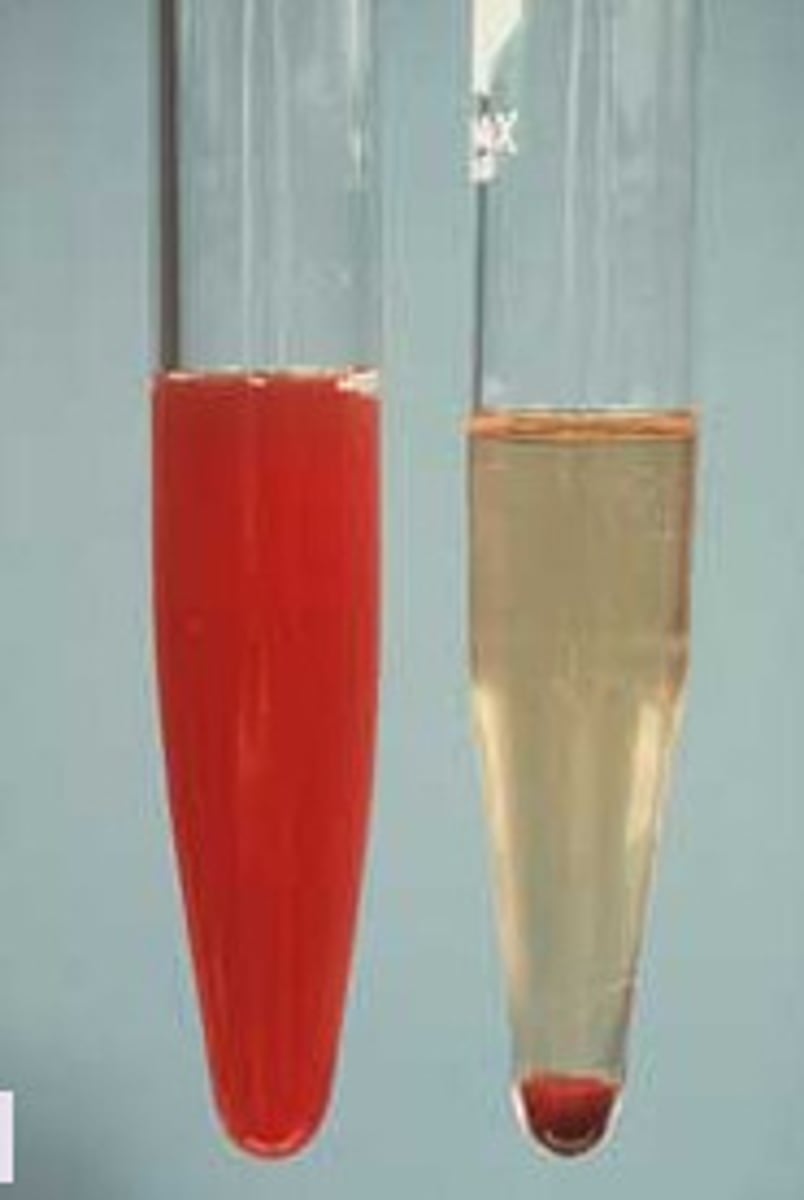
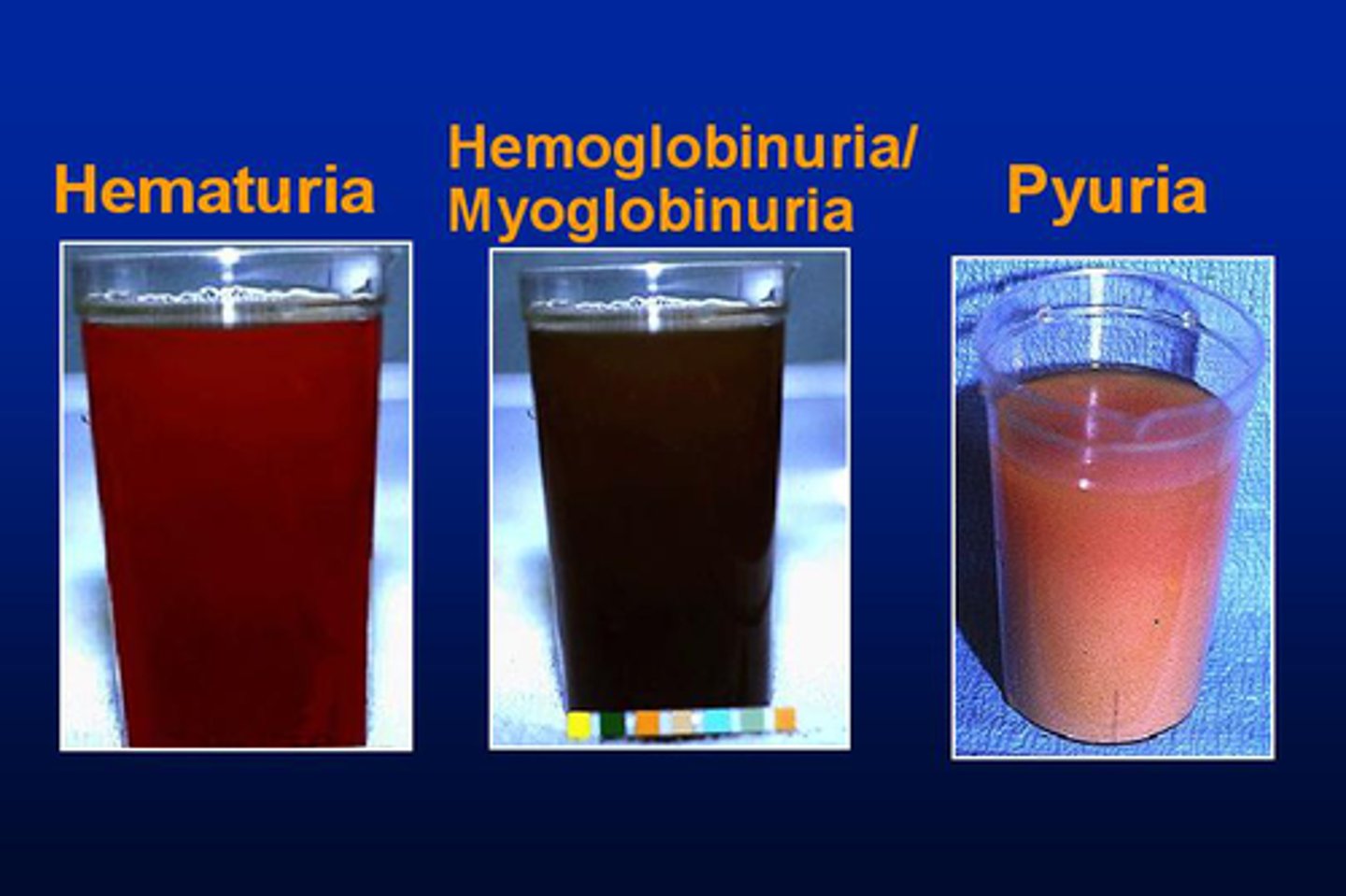
Hematuria
blood in the urine

Hemorrhoids
enlarged and distended veins in the rectum that can be internal or may protrude outside the anus

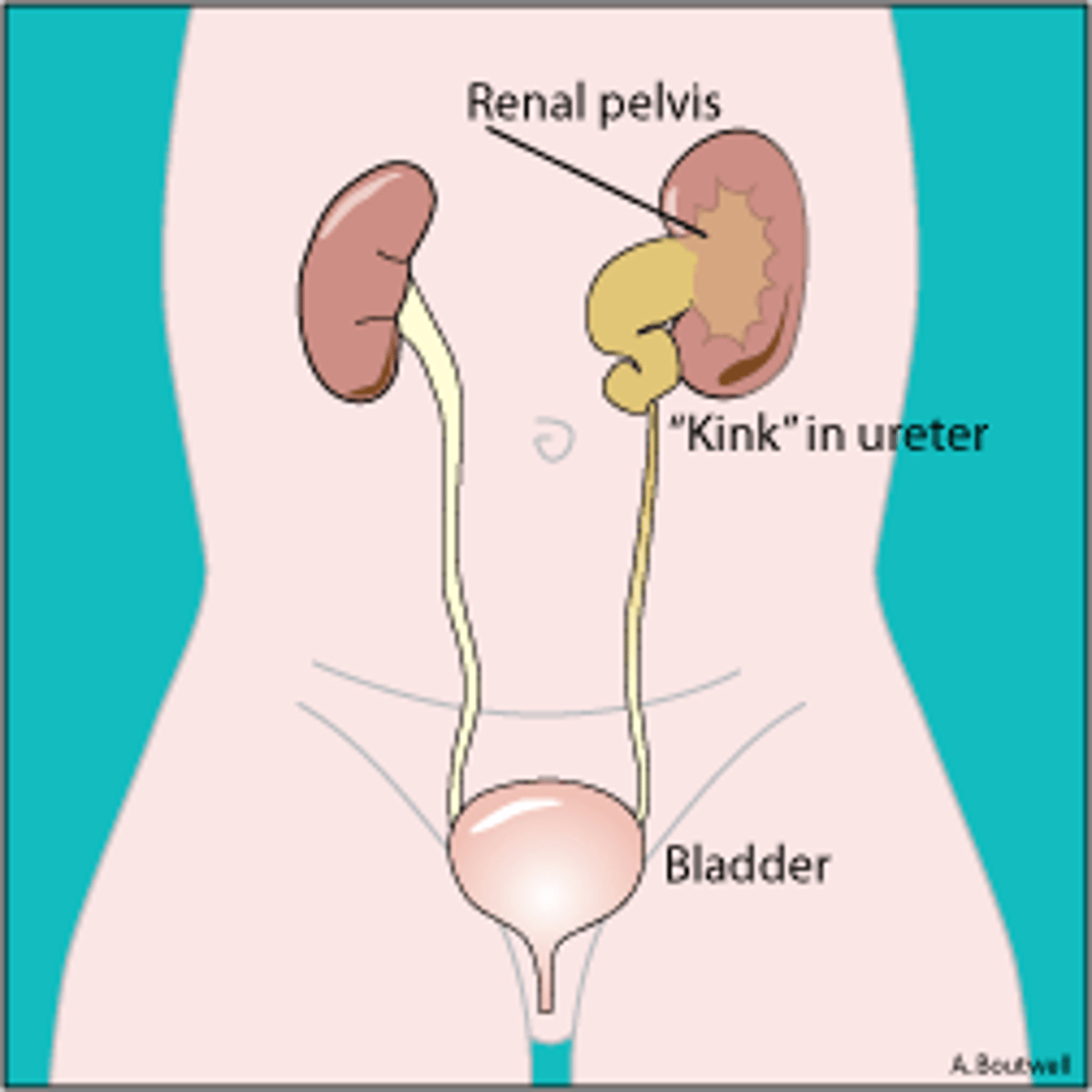
Hydronephrosis
water in the kidneys/distension of the kidney pelvis
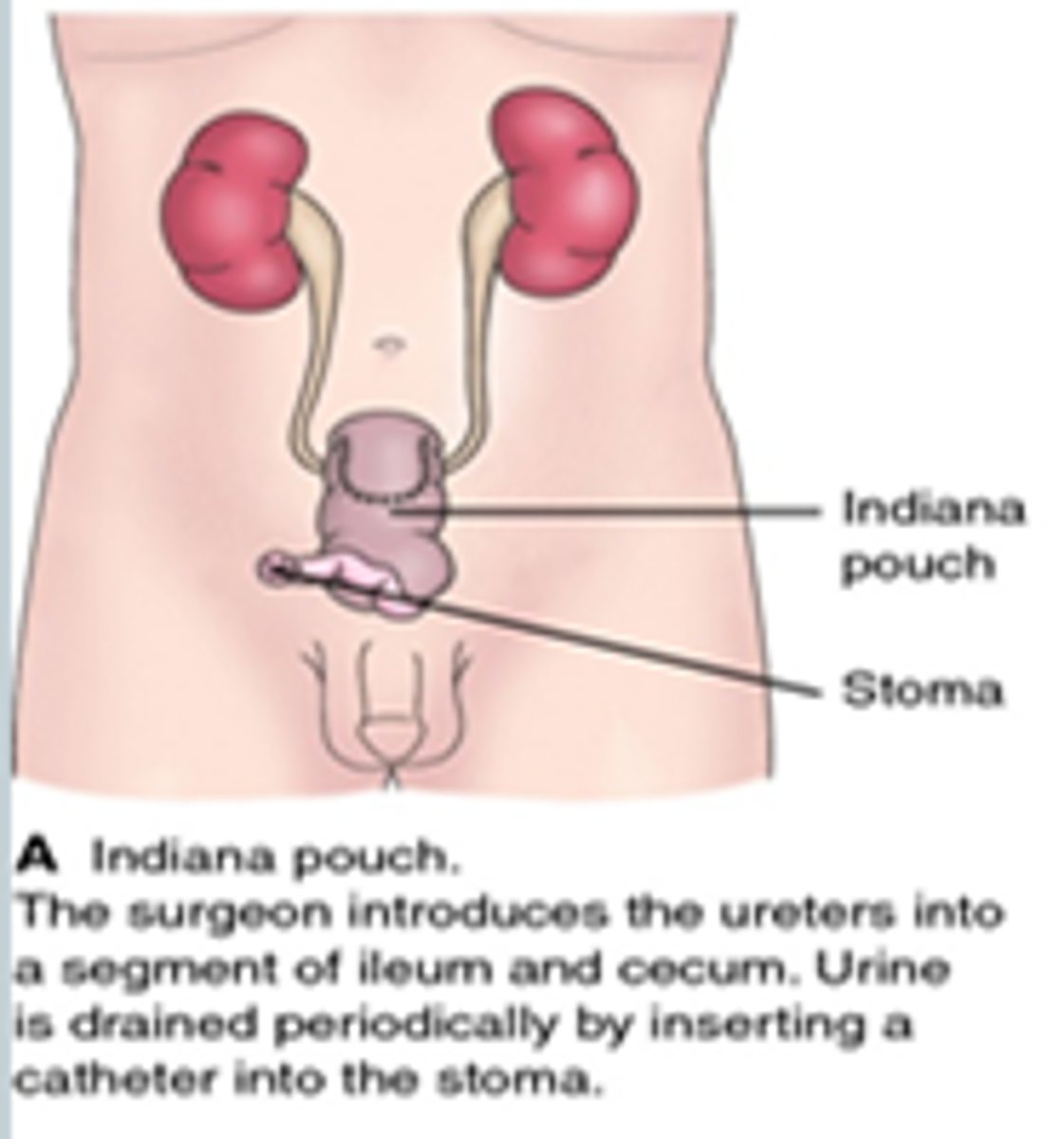
Indiana Pouch
continent cutaneous urinary reservoir
- portion of the large intestine and ileum used to form a urine pouch or reservoir
- clients can control the passage of urine using intermittent catheterization of this internal reservoir through a small stoma
Micturition
another term for urination
Meatus
a term used to describe an opening or a natural body passage
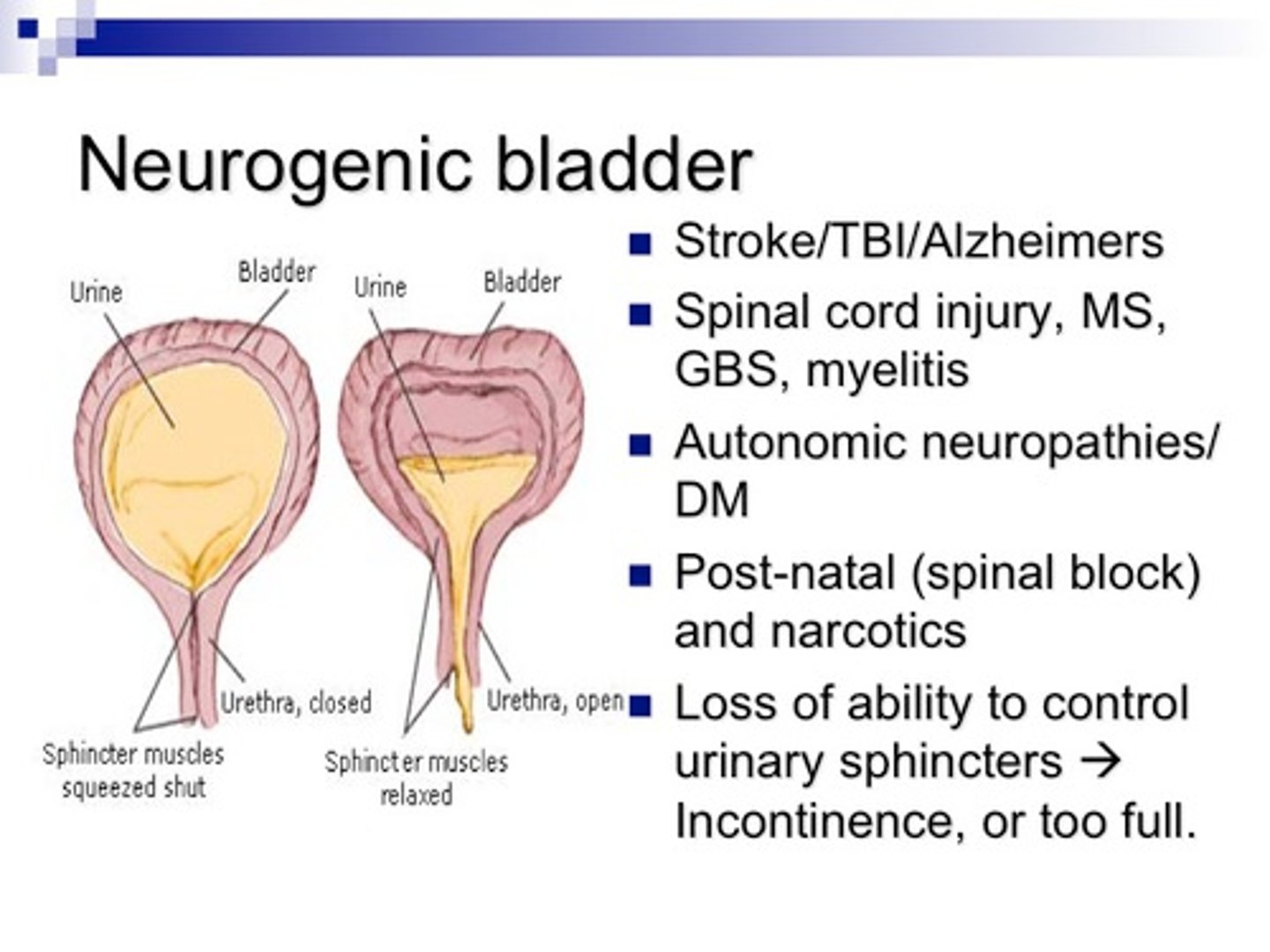
Neurogenic bladder
absence of bladder control due to a condition that may occur with the brain, the spinal cord, or a nerve condition
Nocturia
waking up to empty the bladder at night, interrupting sleep patterns

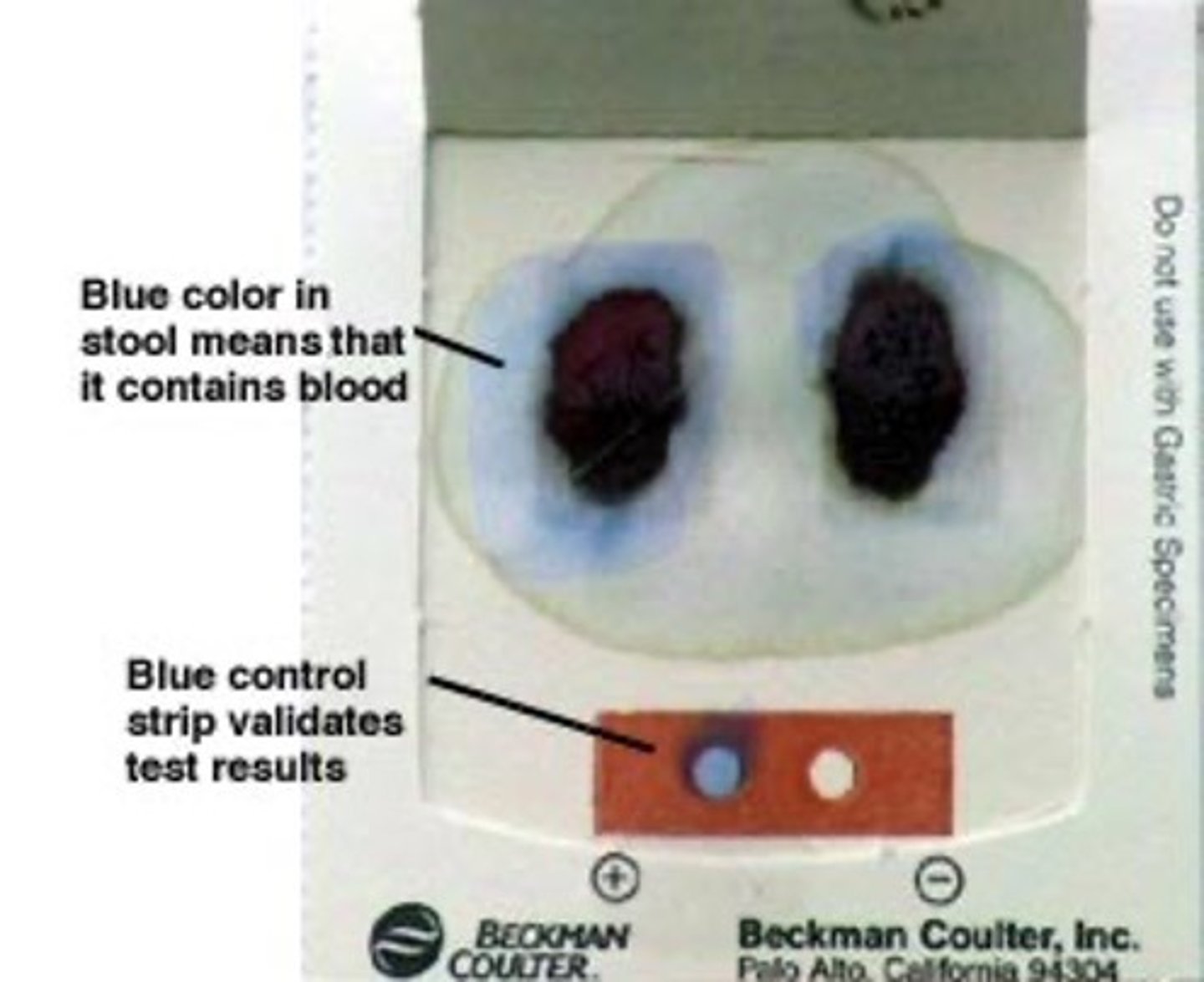
Occult (hidden) blood
- blood that is only detected by microscopic examination
- fecal occult blood test looks for blood in feces
Oliguria
decreased production and elimination of urine
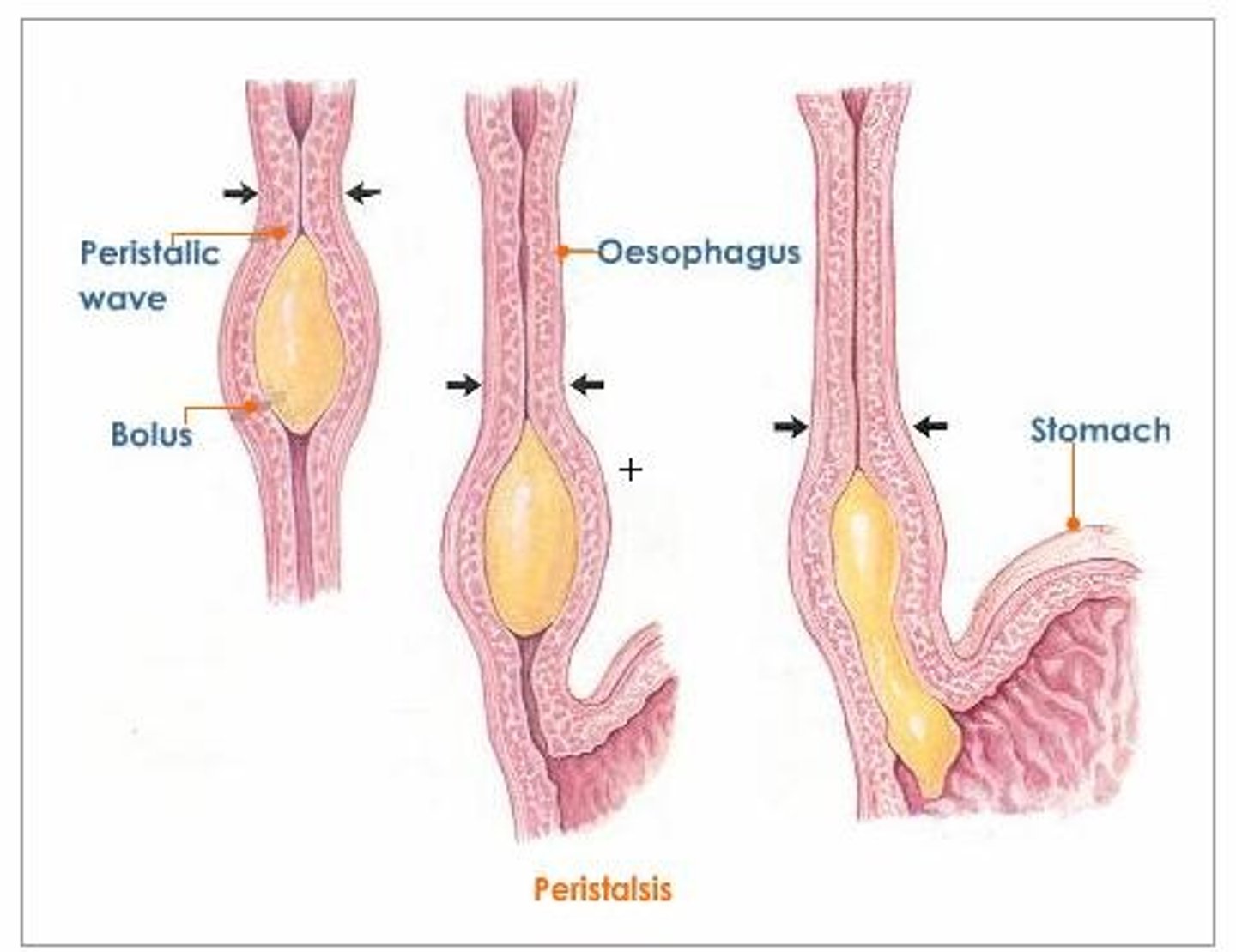
Peristalsis
muscle contractions in the digestive tract that move gastric contents through to elimination
- also move urine from the kidneys into the bladder
Pyuria
presence of pus in the urine
- pus is made up of white blood cells and most often indicates the presence of infection
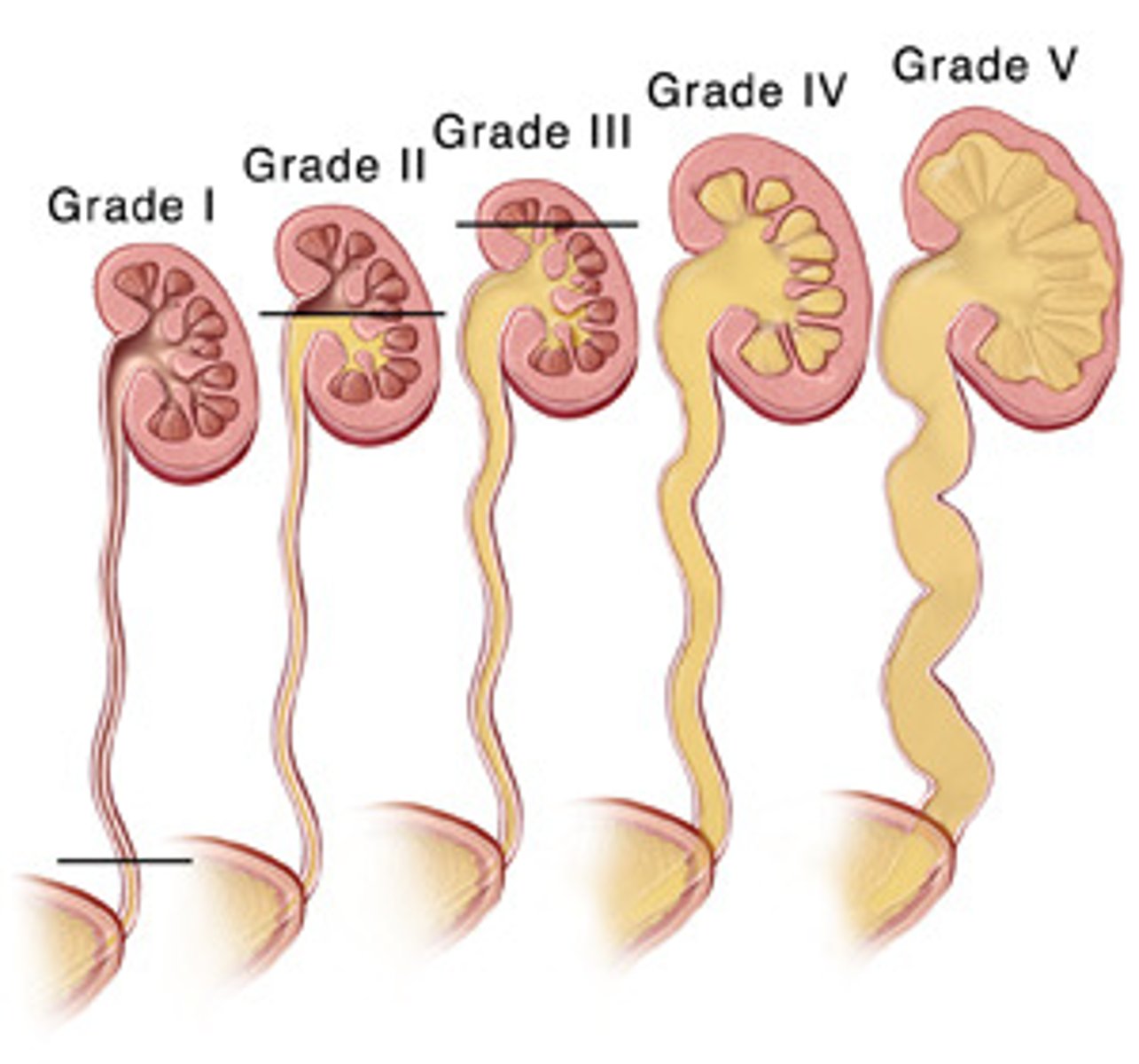
Reflux
backflow of urine
- urine moves up ureters toward kidney instead of down into the bladder
Stoma
a surgically created opening to reroute a body pathway to outside of the body
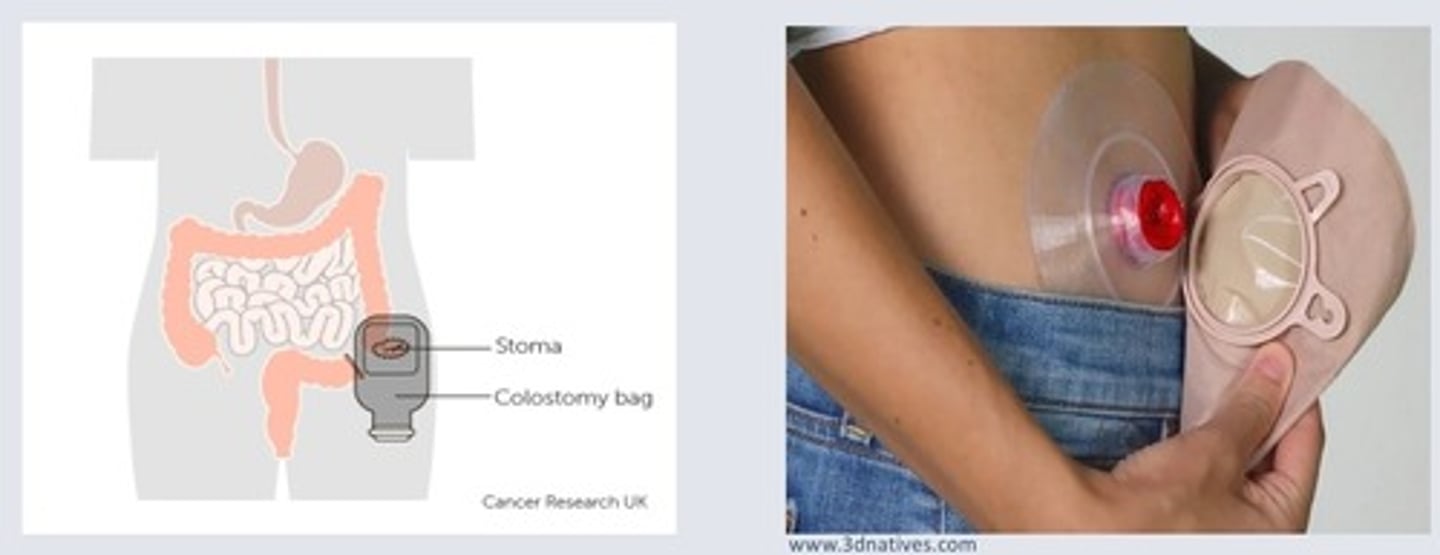
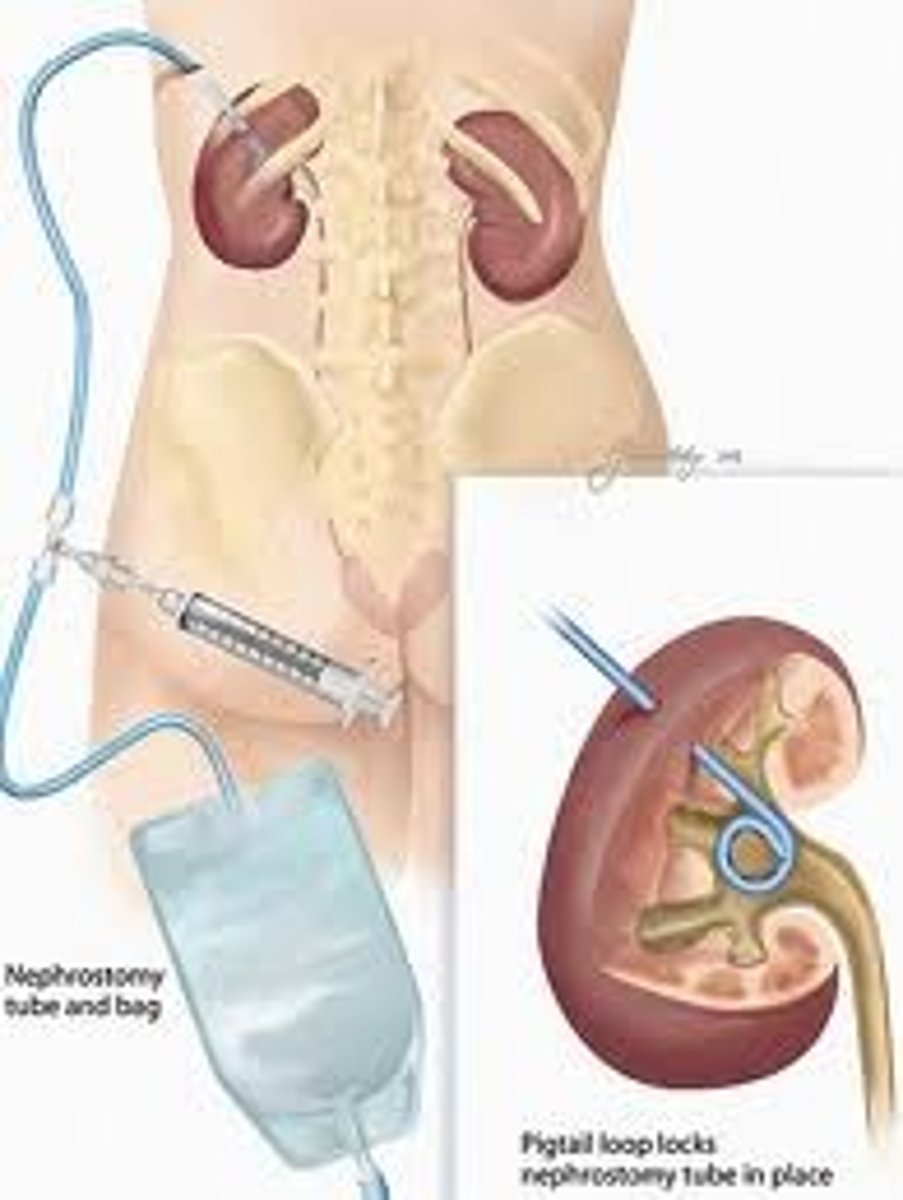
Urinary diversion
a surgically created alternate route for urine flow
- nephrostomy means urine is diverted from kidney to a stoma
urinary tract infection (UTI)
infection in any part of the urinary system (kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra)
- most infections involve the lower urinary tract—the bladder and the urethra
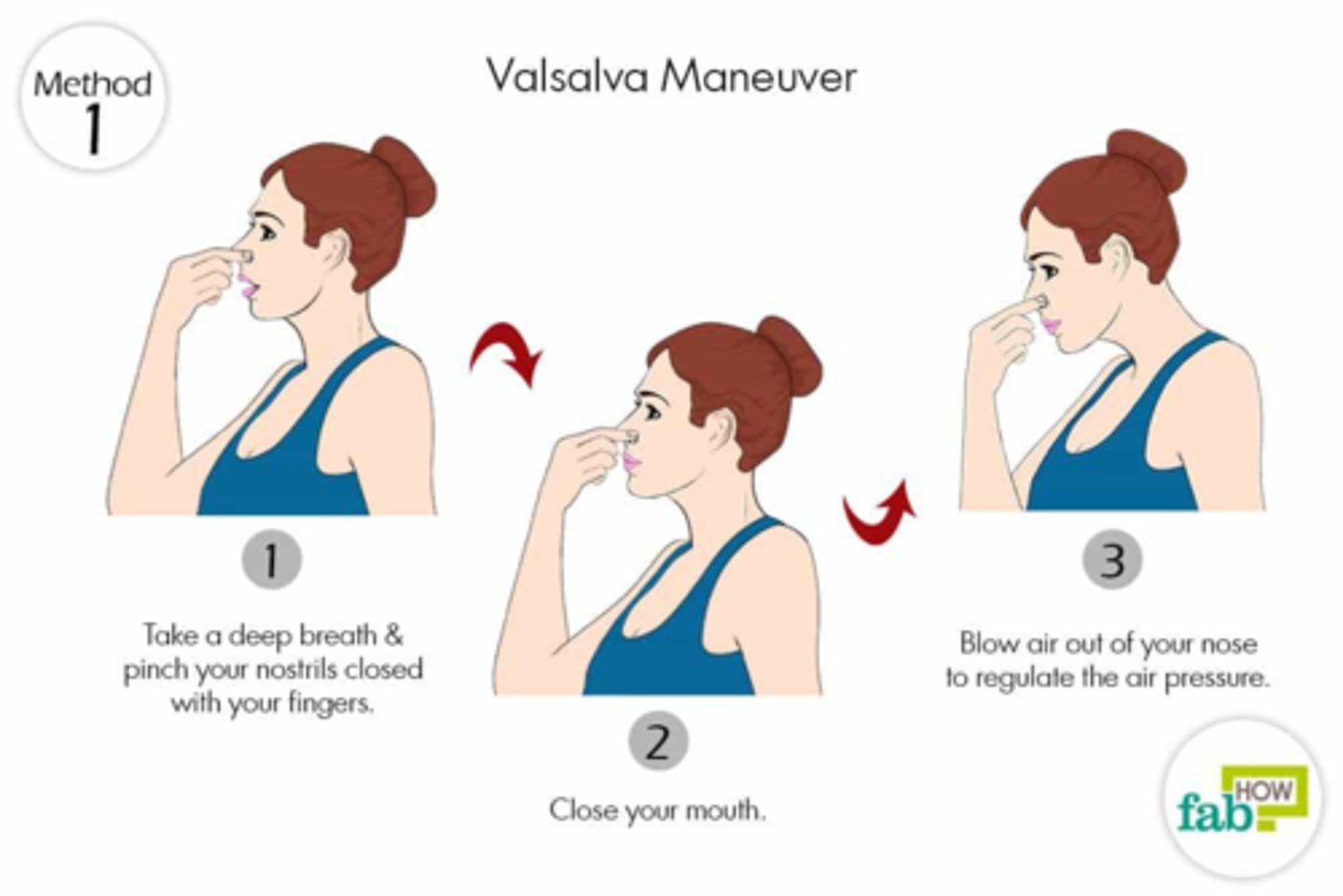
Valsalva maneuver
a voluntary contraction of abdominal muscles while holding one's breath, causing increased intraabdominal pressure
What is the safe water temperature range for assisted bathing for an adult?
38-43°C

What is the safe water temperature range for assisted bathing of infants?
warm to touch of an adult's elbow or the inner aspect of the bare wrist
How often should patients in a Continuing Care facility be given the opportunity to bathe?
- twice a week at minimum
- more frequent if in patient's care plan

How changes does aging cause to the skin?
- reduces its ability to act as a barrier, maintain homeostasis, and regulate temperature
- prone to drying due to co-morbidities, reduced fluid intake, and limited mobility
- epidermis and dermis layers thin, junctions flatten, and circulation decreases
- fibroblasts deteriorate, collagen production and connective tissue strength are reduced
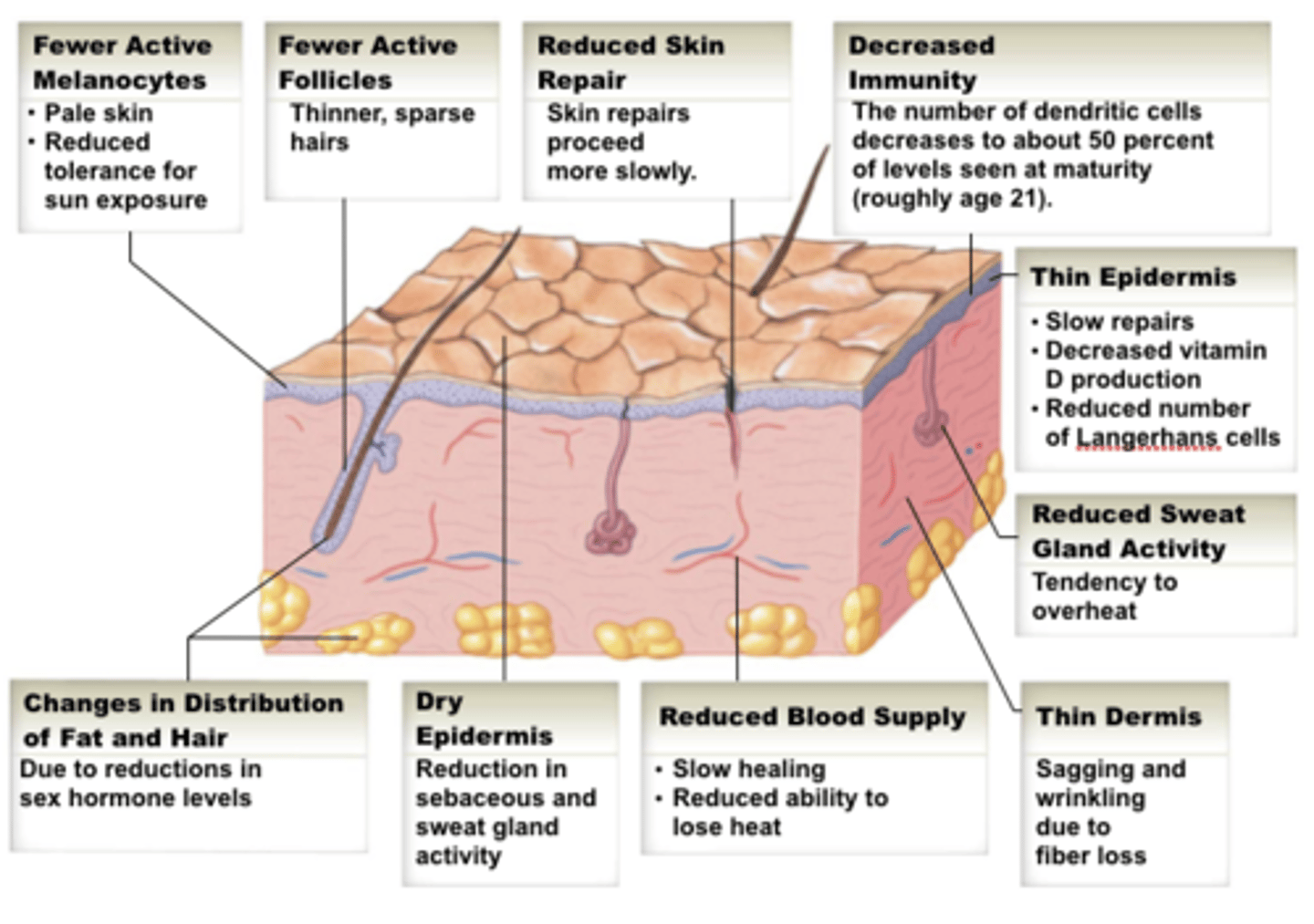
What are the risks to aging skin?
- increased vulnerability to infection, wounds, and trauma (e.g. pressure injuries, shear, friction)
- acute illnesses, fever, diaphoresis, and incontinence increase skin fragility
Skin Assessment
- should be done on admission and regularly (daily or per shift for high-risk patients)
- inspect for color, temperature, texture, moisture, integrity, and wounds
- document findings

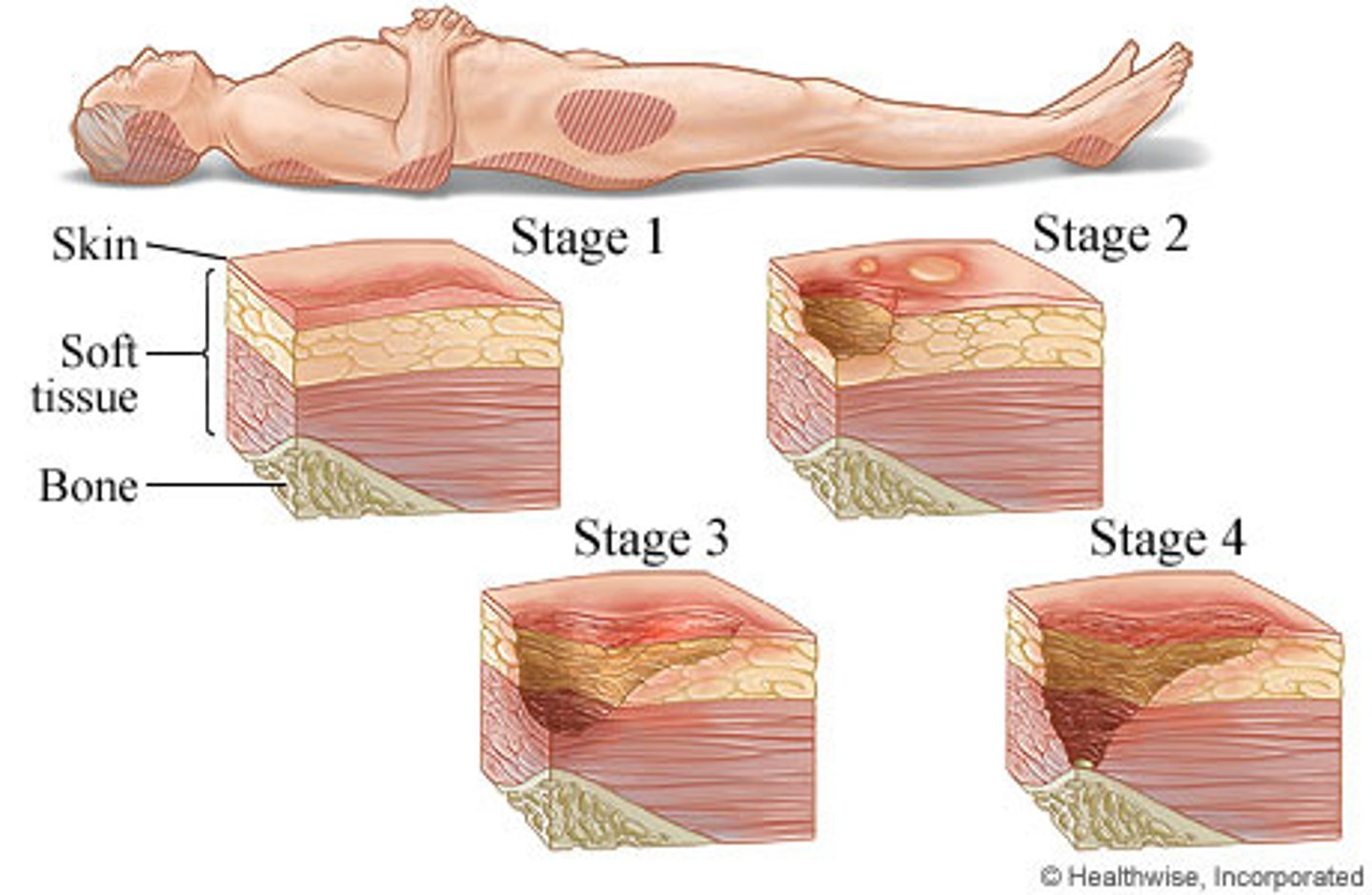
Who is at risk for inadequate skin care?
- older adults, acutely ill, or post-surgical patients with reduced mobility, nausea, or delirium are at high risk for skin failure
- poor skin management can lead to longer hospital stays, readmissions, or even mortality

What does early morning hygiene care consist of?
- bathroom, urinal, assistance in bathroom
- washing hands, face, oral care
- prep for breakfast
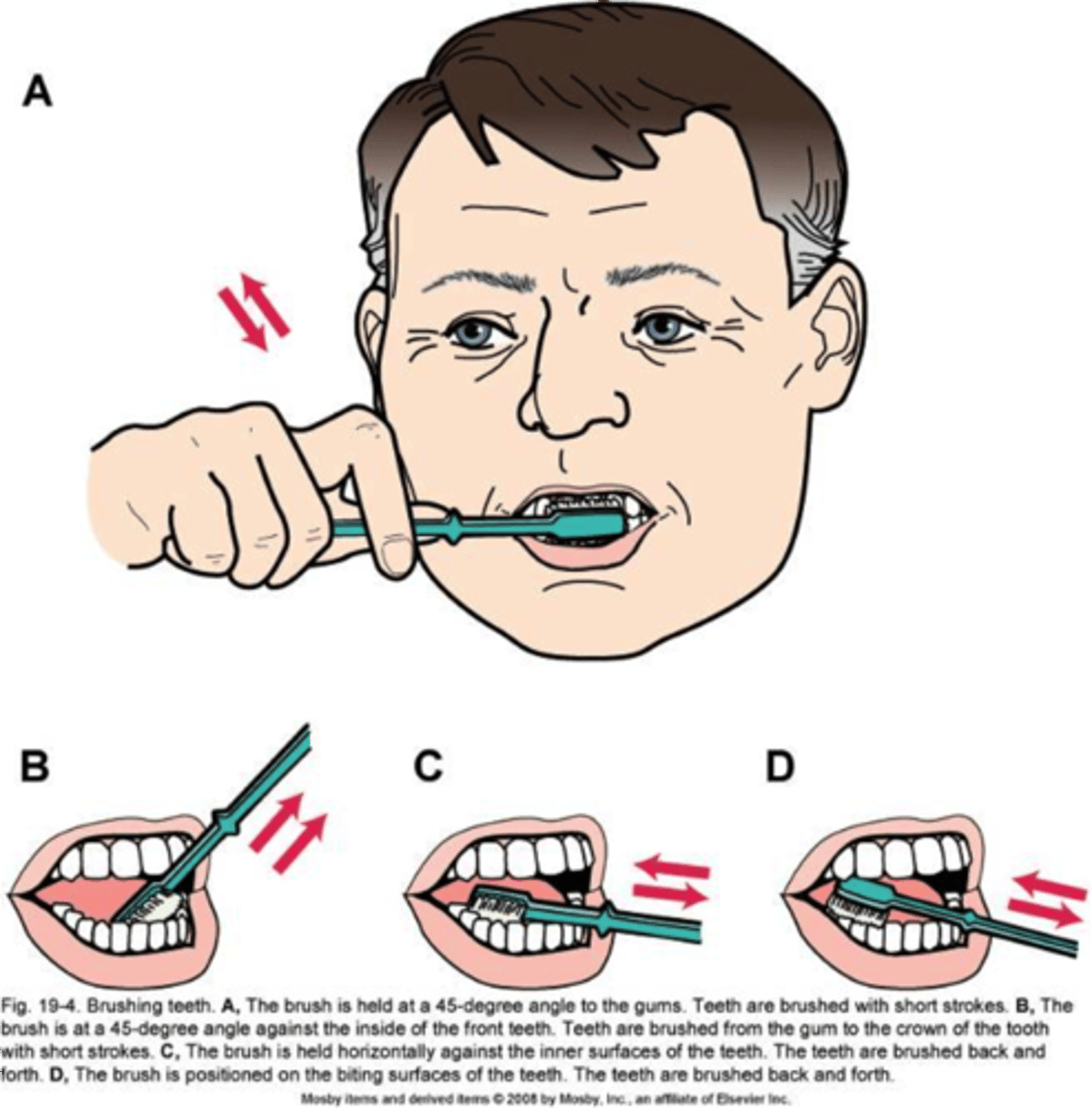
What does morning hygiene care (am care) consist of?
- bath, shower, or bed bath
- hair care, and shaving, oral care, foot/nail care
- dressing in clothes or changing gown, bed linen change
What does afternoon hygiene care consist of?
washing hands and face (to refresh), oral care, elimination needs, checking bed linens
What does HS or evening hygiene care consist of?
washing face and hands, oral care, elimination needs, changing into a new gown or bed clothes, back massage
- straightening up area-to reduce clutter

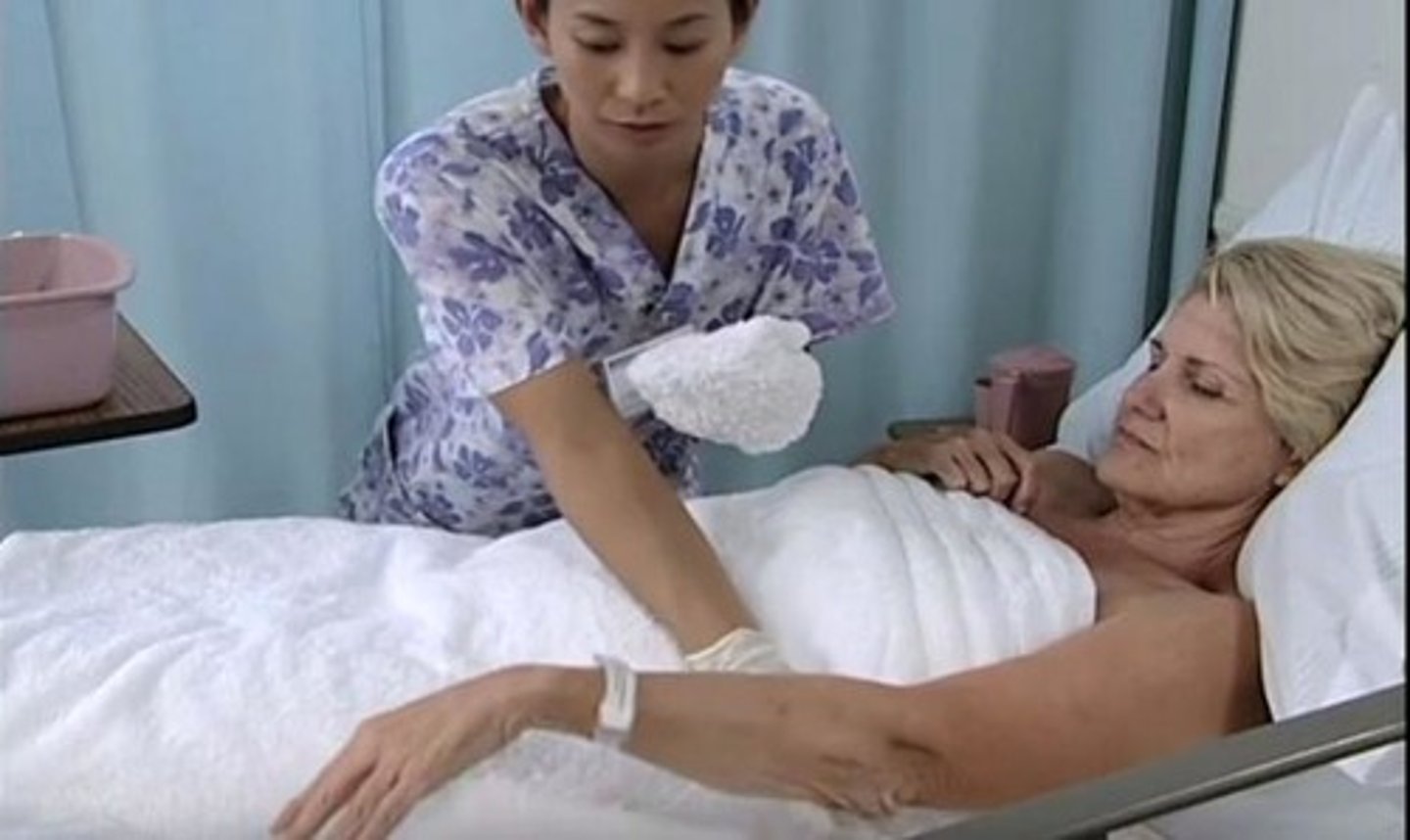
What is important to remember about bed baths?
- may be partial or complete depending on personal needs
- assess skin integrity and other systems
- safe temperature is 38-43celcius
What should you do when providing a bed bath?
- Provide privacy (curtains closed)
- Maintain safety (side rails up)
- Maintain warmth (only expose areas being washed)
- Promote independence (encourage and assist where needed)
- Anticipate needs (be organized and have supplies ready)
- Ensure you are working safely (IYM principles)
- Cleanse from clean to dirty areas (change cloth and water when needed)
- Use long strokes from distal to proximal
- Rinse and pat dry areas well
- Explain and communicate throughout
What is bath in a bag?
disposable, convenient, no drying needed, no cleaning of equipment, requires warming

What products are used for skin integrity and hygiene?
- moisturizers
- moisture barrier creams
- cleansers and wipes
- pharmaceutical creams and powders
- incontinence products

How do you conduct a urinary assessment?
- Health history: symptoms, bowel diary, habits, medication use, diet, fluid intake and output, exercise and mobility, med/surgical history, etc
- Physical assessment: flank pain, bladder position, skin and mucosa integrity, perineum
- Assessment of the urine: color, clarity, quantity, I/O, odor
- Lab tests: urine culture, urinalysis, BW
How do you conduct a bowel assessment?
- Health history: symptoms, bowel diary, habits, medications, diet, fluid intake and output, exercise and mobility, med/surgical history, etc
- Physical assessment: oral cavity, abdominal assessment, skin integrity, and rectal area
- Assessment of stool: Bristol stool chart, shape, color, odor, amount
- Lab tests: fecal specimen testing, BW, serum electrolytes, CBC

What interventions should be considered with hygiene, bed baths, and incontinence care?
- promote fluids
- monitor vital signs
- monitor for other symptoms/changes
- ensure safety when mobilizing
- utilize prescribed creams
- patient teaching
- enhance nutritional intake
- increase fiber in diet
- pain management
- increase mobility and exercise
