soft tissue neck test
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Which of the following body positions is preferable for a soft tissue neck examination?
upright sitting
Upright standing
True or false:
The patients shoulders should lie in the same parallel plane for both the AP and lateral soft tissue neck projections
True
On the AP projection, how much should the patients head be extended?
Just enough to prevent the mandible from obscuring the laryngeal area
Which of the following respiration techniques should be utilized for both the AP and lateral projections?
Expose during quiet nasal inspiration
If your patient can’t cooperate to follow breathing instructions, when should you make an he exposure?
When the chest is nearly expanded
Which plane is perpendicular with the IR for the AP projection?
Midsagittal
Which plane is perpendicular with the IR for the lateral projection?
Midsagittal
If you are concerned that the patients shoulders may superimpose the anterior neck on the lateral projection, what should you do?
clasp the hands posteriorly
Rotate the shoulders posteriorly
Where should the CR be on the AP projection (for upper airway)?
laryngeal prominence
C5
Thyroid cartilage
How much should the CR be angled for the AP projection?
There is no CR angle, it should be kept perpendicular to the IR
What anatomy should be demonstrated on the soft tissue neck (for upper airway), AP projection?
Air filled upper airway from the pharynx to the proximal trachea
What anatomy should be demonstrated on the soft tissue neck ( for upper airway), lateral projection?
Air filled upper airway from the pharynx to the proximal trachea
True or false:
The only portion of the pharynx you can see on the AP projection is the oropharynx
False
True or false:
The only portion of the pharynx you can see on the lateral projection is the nasopharynx
False
Which of the following are evaluation criteria for the AP soft tissue neck (for upper airway) projection?
evidence of proper collimation and presence of a side marker placed clear of anatomy of interest
Air filled upper airway, from pharynx to the proximal trachea
Radiographic density should be such to visualize the pharyngolaryngeal structures. Bony trabecular detail
No rotation, with spinous processes equidistant to the pedicles and aligned with the midline of the cervical bodies
Which of the following are evaluation criteria for the lateral soft tissue neck (upper airway) projection?
evidence of proper collimation and presence of a side marker placed clear of anatomy of interest
No rotation or tilt of the cervical spine
Radiographic density should be such to visualize the pharyngolaryngeal structures. Bony trabecular detail
Superimposed zygapophyseal joints and open intervertebral joints
Mandibular shadows (rami and angles) should be superimposed or nearly superimposed
On the lateral projection, how much should the head be extended?
Slightly
True or false:
On the lateral projection, the shoulders should be elevated to demonstrate proper breathing technique
False
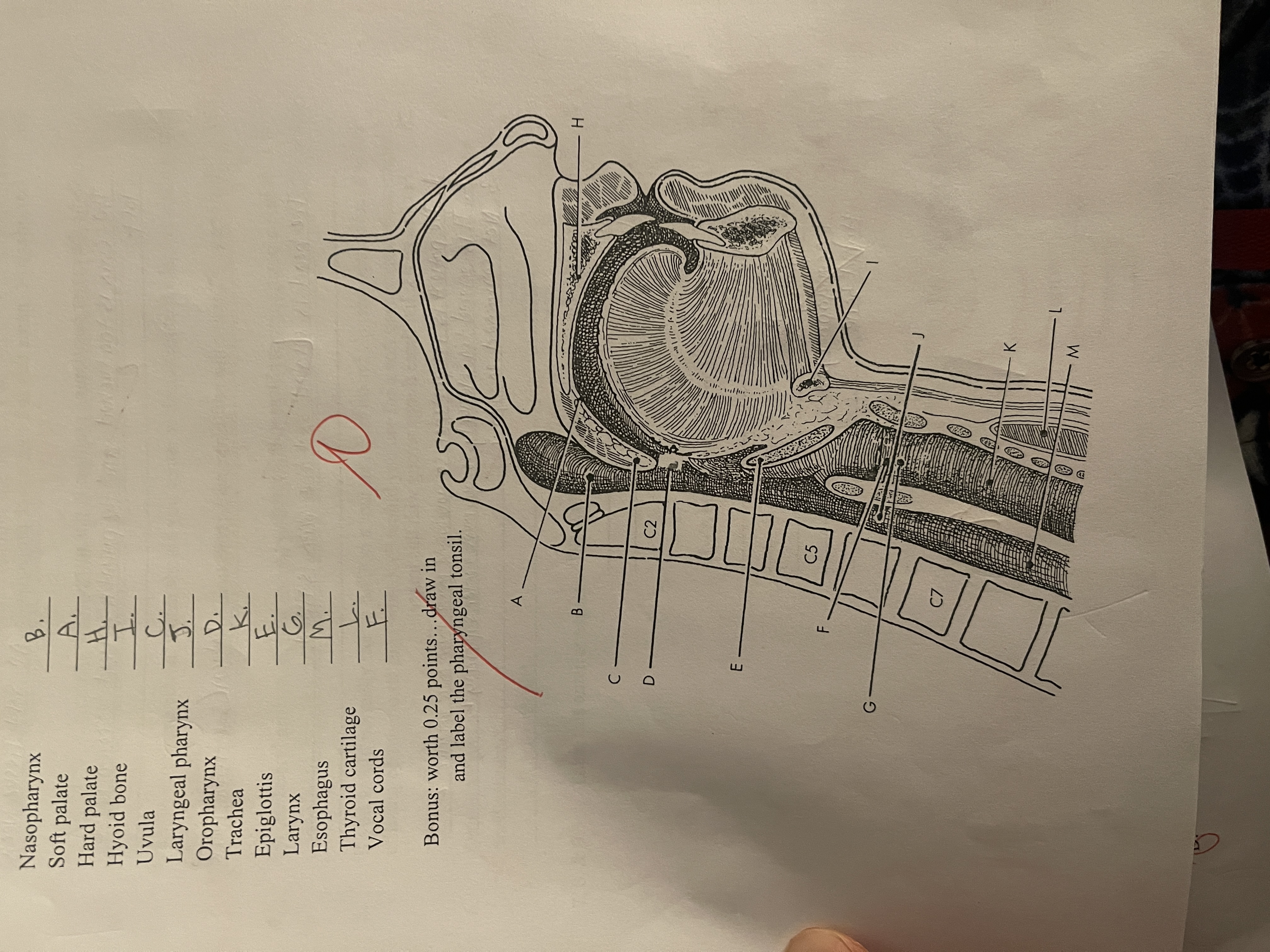
The nasopharynx is situated just posterior to the ______ and just superior to the _____
Nasal septum, soft and hard palates
The _____ extends from the soft palate to the level of the hyoid bone
Oropharynx
The _____ extends from the larynx inferiorly to become continuous with the _____
Laryngopharynx, esophagus
The act of swallowing is termed ______
Deglutition
In order to have air filling of the piriform recesses and the laryngopharynx, the _____ would be utilized
Modified valsalva maneuver
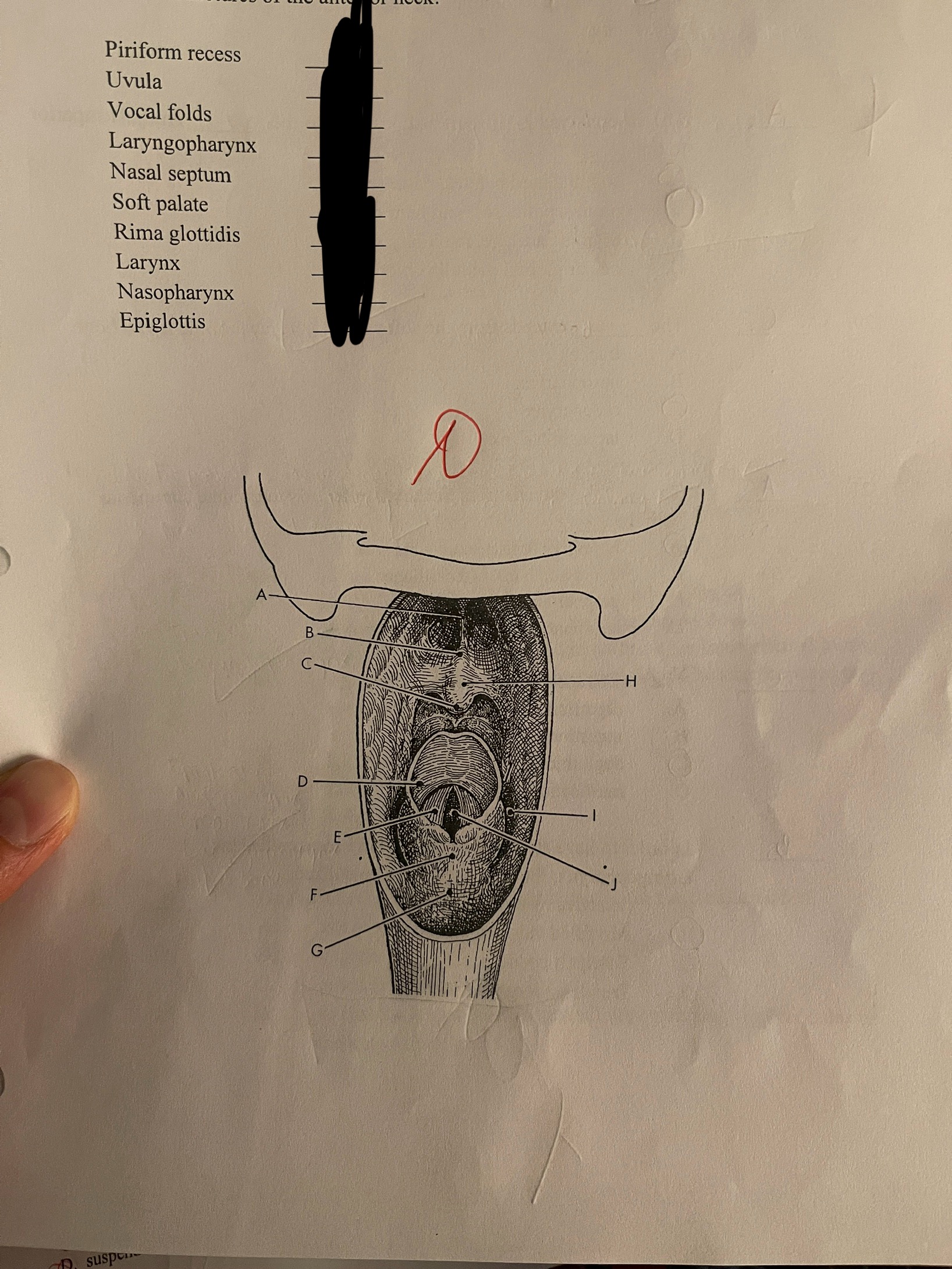
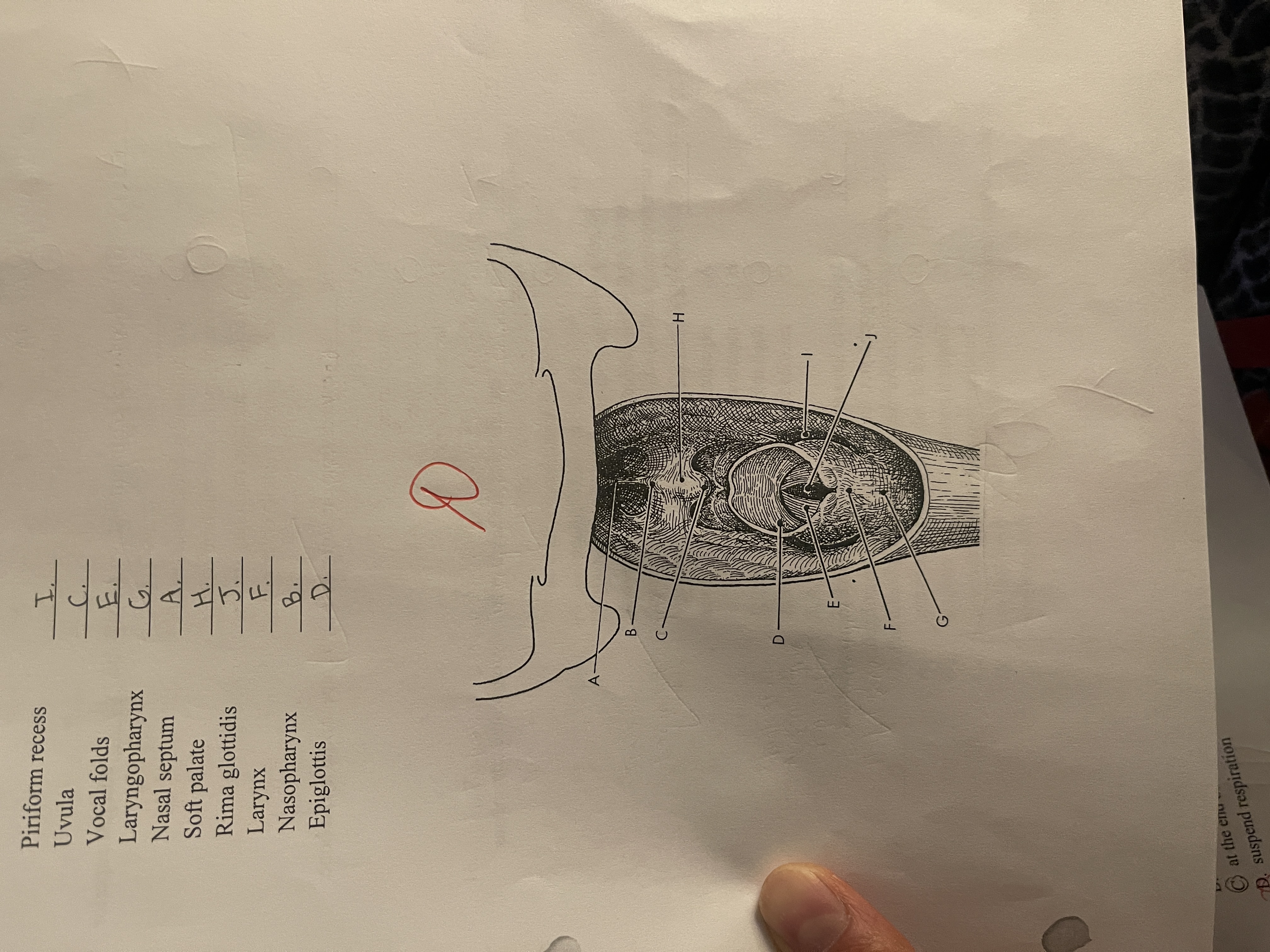
Match the following anatomy to its correct location on this posterior view of the soft tissue structures of the anterior neck
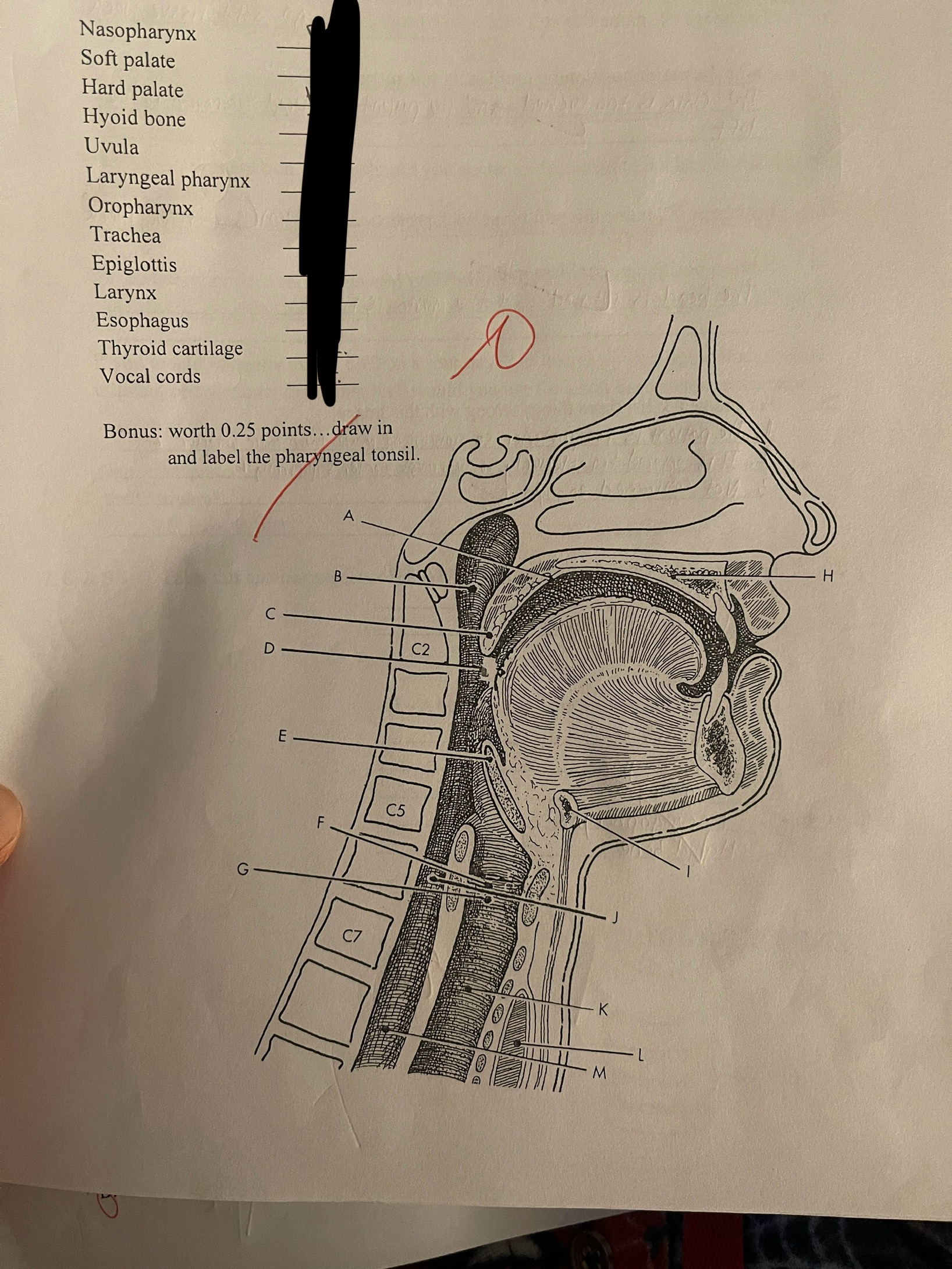
Match the following anatomy to its correct location on this lateral view of the soft tissue structures of the anterior neck