Chemistry - Organic Theory
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Organic Chemistry
the study of carbon-containing compounds
Aliphatic
compounds that contain straight (or branched) chains
Aromatic
compounds that contain a benzene ring
Functional Group
group of atoms on which the characteristic properties of a particular compound depend
Homologous Series
group of compounds that contain the same functional group, have a general formula, show a graduation in physical properties, have similar properties but as you go up the series the successive members differ by CH2
Alkane
functional group is C-C
Alkene
functional group is C=C
Alkyne
functional group is C≡C
Alcohol
functional group is -OH
Ketone
functional group is C=O
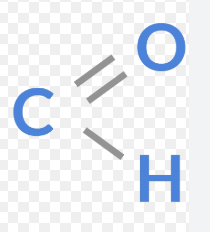
Aldehyde
functional group is
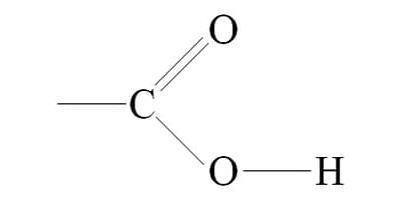
Ester
functional group is
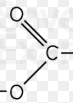
Carboxylic Acid
functional group is
Primary Alcohol
has one carbon attached to the carbon attached to the OH group
Secondary Alcohol
has two carbons attached to the carbon attached to the OH group
Tertiary Alcohol
has three carbons attached to the carbon attached to the OH group
Esters
are formed when a carboxylic acid reacts with an alcohol in the presence of dilute sulphuric acid
Sulphuric Acid
performs two tasks in esterification:
acts as a catalyst
soaks up the water formed
Condensation Reaction
where two molecules combine to form a larger molecule, with the loss of a small molecule, such as water
e.g. esterification
Making Soap
involves using fat (lard of vegetable oil) which contains naturally ocurring esters
Tetrahedral Carbons
are saturated
Planar Carbons
are unsaturated
Non Polar Solvents
ethyl benzene, benzene, and methyl benzene are examples
Benzene
a carcinogenic, aromatic compound
Benzaldehyde
found in almonds
Benzoic Acid
acts as a preservative
Benzene Bonds
are intermediate in length
Carbon in Benzene
is bonded to 2 other carbons and one hydrogen by sigma bonds
Sigma Bonds
bond carbons and hydrogen together in benzene
Electron in 2py Orbital
overlaps with neighbouring orbitals to form a ring above and below the main carbon ring in benzene
Delocalised Electrons
there are 6 in benzene, which give extra stability
Acidified Sodium Dichromate
used to oxidise alcohols, along with dilute sulphuric acid
Aldehydes
formed from the oxidation of primary alcohols
(same as carboxylic acids)
Carboxylic Acids
formed from the oxidation of primary alcohols
(same as aldehydes)
Ketones
formed by the oxidation of secondary alcohols
Aldehydes
are good reducing agents, ketones are not
Organic Compounds
burn to produce CO2 and H2O
Elimination Reaction
a double bond is formed and a small molecule is removed
Van der Waals
intermolecular force in alkanes, alkenes and alkynes
Dipole Dipole
intermolecular forces in aldehydes and ketones
Hydrogen
bonding in alcohols and carboxylic acids
Polymers
are made by joining smaller molecules into a long chain repeating structure
Polythene
use : plastic bags
Polypropene
use : lunch boxes
Polychloroethene
use : records
(aka PVC)
Polytetrafluoroethene
use : non stick coating on frying pans
(aka teflon)
Methanoic Acid
in ant and nettle stings
Carboxylic Acid
acts as an acid due to:
inductive effect, C=O group pulls electrons away from the -OH group, allows H+ to be released
stability of the carboxylate ions
Isomers
molecules with the same molecular formula but a different structural formula, due to different arrangement of atoms in space