nclex study set
1/133
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
134 Terms
receptive aphasia
a language disorder that affects the ability to understand spoken language (wernicke’s aphasia)
aphasia
a communication disorder that affects a person's ability to speak, understand, read, and write
dysarthria
a motor speech disorder where the muscles involved in speaking are weak or don't work as they should, leading to slurred or difficult-to-understand speech
diplopia
double vision
dysphagia
difficulty swallowing
pronator drift
a clinical sign in neurology, indicating weakness of the upper motor neurons. It's characterized by the forearm turning in (pronating) and the arm dropping downwards when the patient tries to hold their arms extended with palms up. This sign is often observed in patients with neurological conditions like stroke
contraindications of TPA administration in stroke patients
>4.5 hrs from symptom onset
active bleeding
recent brain/spinal surgery
uncontrolled htn
low platelets/high PT/INR
hemineglect / unilateral neglect
a neurological disorder characterized by a reduced awareness or inability to attend to stimuli on one side of space, usually the left side
hemianopsia
vision loss in half of the visual field in both eyes. This means a person might only see the left or right half of their world
hypoparathyroidism causes what electrolyte imbalances
hyperphosphatemia and hypocalcemia
rule with phosphate binders medication (ex. calcium carbonate)
always dissolved, never chewed (drink 8oz water, take w/ meals or right after)
IV fluid for tx of hyponatremia
0.9% NaCl
tx for hyponatremia cx by excess fluid
fluid restriction, loop diuretics
potassium sparing diuretics
spironolactone, amiloride
electrolyte complication of thiazide and loop diuretics
hypokalemia
manifestations of hypokalemia
weakness, fatigue, muscle cramps; if severe: flaccid paralysis, hyporeflexia, cardiac dysrhythmias
foods high in potassium
fish, avocado, spinach, strawberries, tomato, bananas, cantelope, carrots, mushrooms, oranges, potatoes, pork, beef, raisins
dehydration causes high or low BUN levels
high
Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN)
Urea nitrogen is a waste product produced by the liver when it breaks down protein. Healthy kidneys filter urea nitrogen out of the blood and excrete it in urine
hematocrit
a blood test that measures the percentage of red blood cells in a person's blood
Urine specific gravity (USG)
a measure of the concentration of dissolved substances in urine, compared to the density of water. It reflects the kidneys' ability to concentrate or dilute urine, and can indicate hydration status and kidney function
dehydration causes lower or higher urine specific gravity levels
higher
s/s of dehydration
tachycardia, postural hypotension, dry mucous membranes, poor skin turgor, flat neck & hand veins, dec. urine output, weight loss, confusion and lethargy
albuterol type of med
short-acting beta agonist
salmeterol type of med
long-acting beta agonists
fluticasone type of med
inhaled corticosteroid
IV potassium chloride can cause what
extravasation
IM injection site for infants
vastus lateralis (top thigh)is the preferred site for administering intramuscular injections in infants, as it is well developed and away from major nerves and blood vessels.
rifampin side effects
orange secretions, interferes with contraceptives
isoniazid risks
hepatotoxicity (jaundice, anorexia)
common tx for acute otitis externa
ofloxacin, ciprofloxacin
for otic med admin in adults (>3 yo) the ear gets pulled:
up
for otic med admin in children (<3 yo) the ear gets pulled:
down
how long should nurse leave needle in place after administering IM injection?
10 seconds to allow for complete absorption.
isotonic crystalloid types
0.9% sodium chloride, Lactated ringers
what type of solution is administered to patients with inc ICP
hypertonic solutions like 3% sodium chloride
fluid tx for severe hyponatremia:
hypertonic solution like 3% sodium chloride
common cx of viral gastroenteritis
norovirus, rotavirus, enteric adenovirus, and astrovirus.
common cx for bacterial gastroenteritis
salmonella, shigella, E. coli
Tx for inc ICP
mannitol
recommended peripheral infusion rate for potassium chloride
5-10 mEq/hr
hypoaldosteronism
a condition marked by decreased synthesis or diminished release of aldosterone (ALD) from the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal glands, or resistance to its action on target tissues
can you crush potassium chloride tablets?
no
complication of mastectomy with axillary lymph node removal
lymphedema
measures for avoiding lymphedema
avoidance of injections, blood pressures, and venipuncture in affect arm
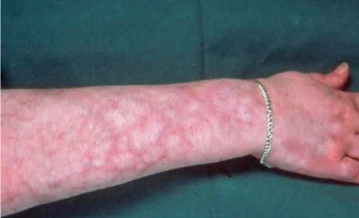
mottled skin
a skin condition characterized by a bluish-red, lace-like or web-like pattern on the skin, typically on the arms, legs, or trunk
hyperemesis gravidarum
a severe form of morning sickness during pregnancy characterized by persistent and excessive nausea and vomiting, potentially leading to dehydration, weight loss, and nutritional deficiencies
isotonic fluid function/use
expand only the extracellular fluid and are uses as a fluid replacement for clients with fluid volume deficit
types of medications contraindicated for NG administration
enteric coated, slow-, extended-, or sustained-release (should not be crushed of NG admin)
IV push medications should NEVER be given through a VAD that..
is infusing blood products or parental nutrition
covid-19 precautions
airborne and contact
RSV precautions
contact and droplet
common meds that can cx orthostatic hypotension
antihypertensives, antidepressants, opiods
standard dose for heparin flush of CVC
doses of 2-3 mL containing 10 units/mL - 100 units/mL are the standard
how often should occlusive dressing of CVC be changed?
every 7 days
examples of calcium channel blockers
nifedipine, amlodipine, felodipine
peripherally acting calcium channel blockers can cause:
vasodilation (clients may develop peripheral edema)
an expected side effect of nitroglycerin is:
headache
precautions varicella-zoster virus (chickenpox)
airborne and contact
precautions for herpes-zoster virus
airborne and contact
Romberg test
a physical exam used to assess balance and coordination, particularly related to the body's sense of position and movement (proprioception)
toxic megacolon
a serious condition where the colon (large intestine) swells significantly, potentially leading to severe complications and even death. complication of c. diff
status epilepticus
rapid succession of seizures without regaining conciousness
Negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT)
is a treatment that uses controlled suction to help wounds heal
immunization site for children <7 months
vastus lateralis (anterolateral thigh)
clients who are truly allergic to penicillins (anaphylaxis) have inc. risk of allergy to..
other beta-lactam antibiotics (cephalexin)
normal hydromorphone dose PRN
1.5 mg every 3-4 hr
type of isolation required for Ebola
airborne, droplet, contact
common infections that need airborne precautions
measles, tuberculosis, varicella, SARS
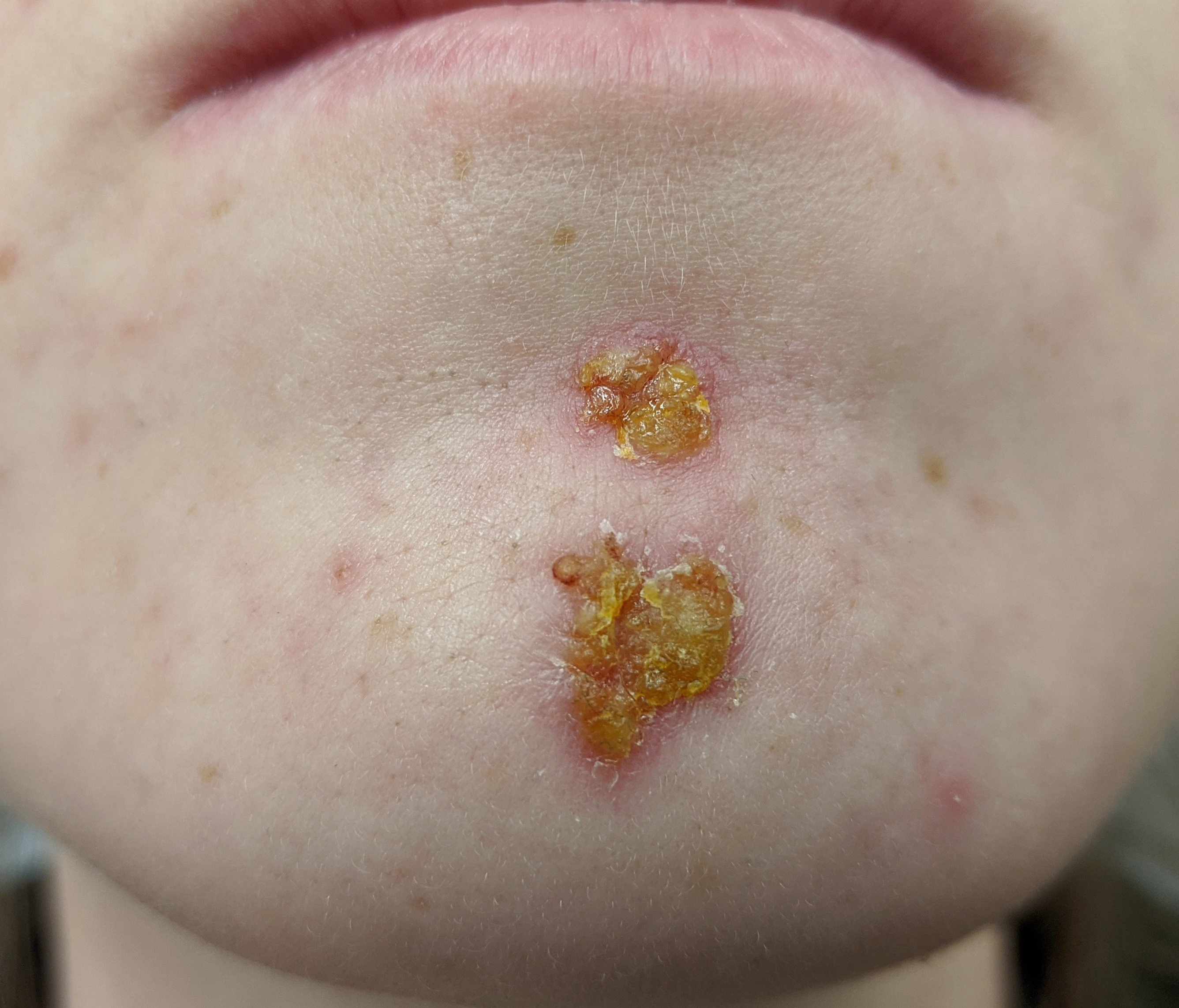
impetigo
a common and contagious bacterial skin infection, typically appearing as red, itchy sores that can blister and ooze
pertussis
respiratory infection caused by bacterium Bordetella pertussis
type of precautions for pertussis
droplet
povidone-iodine
betadinewhat
what common food allergies can be linked to latex allergy
bananas, avocados, tomatoes
morphine use in unstable angina
dec. preload and work on the heart
type A aortic dissection
involves ascending aorta,
type B aortic dissection
confined to aorta distal to subclavian artery
Marfan Syndrome
a genetic disorder that affects connective tissue, which provides support for the body and organs. This can lead to a variety of issues, particularly affecting the heart and blood vessels, eyes, and skeletal system
virchow’s triad
altered blood flow (venous stasis), endothelial damage, and hypercoagulable state
venous stasis
this refers to the slowing or stagnation of blood flow in the veins, which can be caused by prolonged immobility, surgery, or conditions like varicose veins. When blood flow is sluggish, it increases the likelihood of platelets and clotting factors coming into contact and forming a clot.
endothelial injury
The endothelium is the inner lining of blood vessels. Damage to this lining, whether from injury, inflammation, or disease, exposes the underlying tissue and triggers the body's clotting cascade. This can happen due to trauma, surgery, or even conditions like atherosclerosis.
hypercoagulability
This refers to an increased tendency of the blood to clot, either due to inherited conditions (like Factor V Leiden) or acquired factors (like certain medications, pregnancy, or cancer). Hypercoagulability can lead to an overactive clotting response, increasing the risk of clot formation.
d-dimer
protein released when a clot breaks up, high levels indicate that body is trying to break up a clot (diagnostic for DVT)
cardiac enzymes that inc. w/ MI
troponin, myoglobin, CK-MB
dressler syndrome
a type of pericarditis (inflammation of the sac surrounding the heart) that can occur after damage to the heart muscle, often following a heart attack or heart surgery.
manifestations of cardiac tamponade
narrowed pulse pressure, muffled heart sounds, distended neck veins, hypotension, pulsus paradoxus
intermittent claudication is a hallmark sign of what?
peripheral artery disease (PAD)
intermittent claudication
a condition characterized by muscle pain, cramping, or discomfort in the legs, typically the calf, that occurs during exercise and is relieved by rest
low ankle-brachial index indicates:
peripheral artery disease
components of vasodilation
inc. blood vessel diameter, inc. blood flow, dec. blood pressure
acute disseminated intravascular dissemination
inc. PT/PTT, dec. platelets & fibrinogen, fragmented RBCs, inc. d-dimer
clients using a cane should always hold it in which hand
hand of the stronger side
possible complication of PEEP
barotrauma
valsalva manuever
breath in, hold it, bear down (used when removing chest tubes)
when should chest x-ray be performed after removal of a chest tubes
within 2-24 hours after removal
intermediate-acting insulin names
NPH (cloudy suspension)
short-acting insulin names
regularr
rapid-acting insulin names
lispro, aspart
can intermediate-acting insulin be mixed with short- or rapid-acting insulins?
yes
proper order for mixing insulins
draw up regular (short-acting) insulin first, followed by NPH (intermediate-acting) insulin in the same syringe